 SEND Linux Implementation Report Jonathan Wood Do. Co. Mo USA Labs IETF 58 November 2003
SEND Linux Implementation Report Jonathan Wood Do. Co. Mo USA Labs IETF 58 November 2003
 Overview • Platform – – Linux 2. 5 / 2. 6 Open. SSL 0. 9. 7 (for crypto and ASN. 1) Radvd 0. 7. 2 (modified for secure RD) Iproute 2 2. 4. 7 (modified for CGAs) • Complete implementation of SEND, no major issues found – Implementing a robust timestamp cache is tricky, however.
Overview • Platform – – Linux 2. 5 / 2. 6 Open. SSL 0. 9. 7 (for crypto and ASN. 1) Radvd 0. 7. 2 (modified for secure RD) Iproute 2 2. 4. 7 (modified for CGAs) • Complete implementation of SEND, no major issues found – Implementing a robust timestamp cache is tricky, however.
 Design • SEND not performance critical, so keep as much as possible out of the kernel • Userspace: – – Public key crypto General ASN. 1 DCS/DCA Utilities and management • Userspace daemon handles crypto and RD operations for kernel
Design • SEND not performance critical, so keep as much as possible out of the kernel • Userspace: – – Public key crypto General ASN. 1 DCS/DCA Utilities and management • Userspace daemon handles crypto and RD operations for kernel
 Design • Kernel – CGA verification and generation – Specialized ASN. 1 parser for CGA parameters – Primary focus is to hand all other secure ND and RD tasks off to userspace daemon – Keeps secure ND and RD processing out of the interrupt context
Design • Kernel – CGA verification and generation – Specialized ASN. 1 parser for CGA parameters – Primary focus is to hand all other secure ND and RD tasks off to userspace daemon – Keeps secure ND and RD processing out of the interrupt context
 Complexity • RD Certificate profile is single most complex piece (~3800 lines of code) • CGA: ~2200 lines (kernel + user, including management tool) • User crypto: ~1200 lines (mostly Open. SSL glue) • Additional kernel code: ~2800 lines
Complexity • RD Certificate profile is single most complex piece (~3800 lines of code) • CGA: ~2200 lines (kernel + user, including management tool) • User crypto: ~1200 lines (mostly Open. SSL glue) • Additional kernel code: ~2800 lines
 Rough Performance Numbers • • • Two hosts, 1. 2 GHz Pentium IV 100 MBit Ethernet CGA Sec: 1 1024 bit RSA keys ND – – Flush neighbor cache Send a ping (Invoking secure ND) Ping reports RTT Instrumented code reports crypto timings
Rough Performance Numbers • • • Two hosts, 1. 2 GHz Pentium IV 100 MBit Ethernet CGA Sec: 1 1024 bit RSA keys ND – – Flush neighbor cache Send a ping (Invoking secure ND) Ping reports RTT Instrumented code reports crypto timings
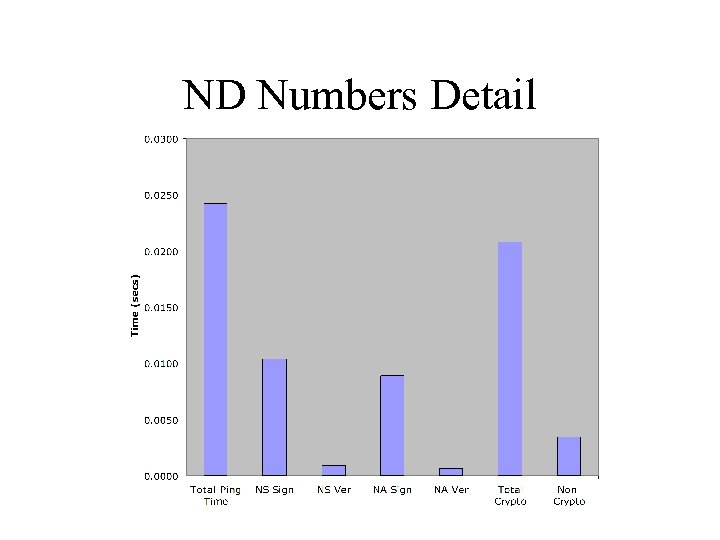
 ND Numbers • Average first ping RTT (requiring secure ND): 24 ms • Crypto took 21 ms on average – Signing is slow, verification is fast • For reference: – Average ping RTT (with insecure ND): 0. 46 ms – Average ping RTT (without ND): 0. 13 ms
ND Numbers • Average first ping RTT (requiring secure ND): 24 ms • Crypto took 21 ms on average – Signing is slow, verification is fast • For reference: – Average ping RTT (with insecure ND): 0. 46 ms – Average ping RTT (without ND): 0. 13 ms
 ND Numbers Detail
ND Numbers Detail
 RD Numbers • Certificate chain four deep, each certificate with PKIX IP Extensions • Two scenarios: – RA receiver does not have certificates cached, so it must use DCS/DCA exchange (slower) – RA receiver has all needed certificates cached • Measured time from sending RA until receipt of DAD NS.
RD Numbers • Certificate chain four deep, each certificate with PKIX IP Extensions • Two scenarios: – RA receiver does not have certificates cached, so it must use DCS/DCA exchange (slower) – RA receiver has all needed certificates cached • Measured time from sending RA until receipt of DAD NS.
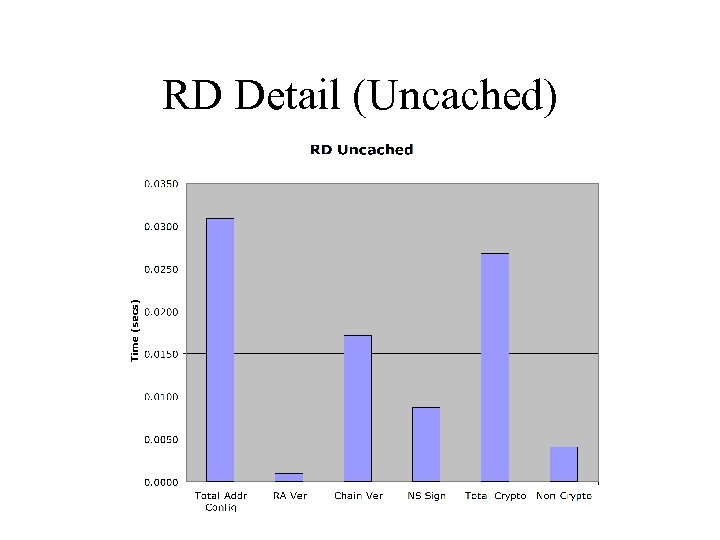
 RD Without Cached Certificates • Average total time: 31 ms • Crypto took 27 ms on average • Procedure: – Delete autoconfigured address on host, if necessary – Flush host’s certificate cache – Send RA – Sniffer and instrumented code reports timings
RD Without Cached Certificates • Average total time: 31 ms • Crypto took 27 ms on average • Procedure: – Delete autoconfigured address on host, if necessary – Flush host’s certificate cache – Send RA – Sniffer and instrumented code reports timings
 RD Detail (Uncached)
RD Detail (Uncached)
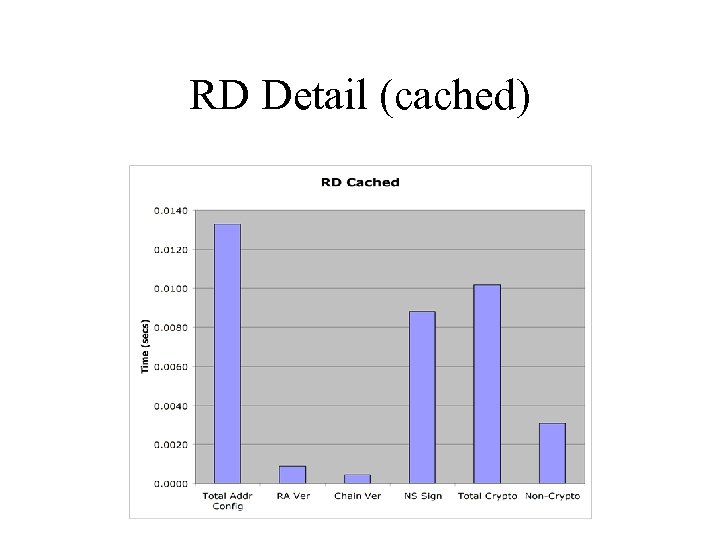
 RD with Cached Certificates • • No DCS/DCA exchange needed Average total time: 13 ms Average crypto time: 10 ms Proceedure: – Delete autoconfigured address on host, if necessary – Send RA – Sniffer and instrumented code reports timings
RD with Cached Certificates • • No DCS/DCA exchange needed Average total time: 13 ms Average crypto time: 10 ms Proceedure: – Delete autoconfigured address on host, if necessary – Send RA – Sniffer and instrumented code reports timings
 RD Detail (cached)
RD Detail (cached)
 Conclusion • Implementing SEND is straightforward. – No major problems. • Performance is about 2 orders of magnitude slower than without SEND. – Public key crypto is performance intensive. • But ND and RD are not typically critical path items. – Mobility may need attention.
Conclusion • Implementing SEND is straightforward. – No major problems. • Performance is about 2 orders of magnitude slower than without SEND. – Public key crypto is performance intensive. • But ND and RD are not typically critical path items. – Mobility may need attention.