6e1f60bd40bc666ce6f91bf556332561.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Seminar Presentation Multimedia Audio / Video Communication Standards Instructor: Dr. Imran Ahmad By: Ju Wang November 7, 2003 1
Seminar Presentation Multimedia Audio / Video Communication Standards Instructor: Dr. Imran Ahmad By: Ju Wang November 7, 2003 1
 In this presentation …… o o There are many standards in multimedia world MPEG’s standards are well-known and are used everywhere This organization – Moving Picture Experts Group, was established in 1988 MPEG family’s standards…… 2
In this presentation …… o o There are many standards in multimedia world MPEG’s standards are well-known and are used everywhere This organization – Moving Picture Experts Group, was established in 1988 MPEG family’s standards…… 2
 Outline o o o o MPEG – 1 MPEG – 2 MPEG – 4 MPEG – 7 MPEG – 21 A comparison of them Other standards 3
Outline o o o o MPEG – 1 MPEG – 2 MPEG – 4 MPEG – 7 MPEG – 21 A comparison of them Other standards 3
 MPEG-1 o o o Code of moving pictures and associated audio for digital media at up to 1, 5 Mbit/s Became an international standard in 1993 Remarkable achievement 4
MPEG-1 o o o Code of moving pictures and associated audio for digital media at up to 1, 5 Mbit/s Became an international standard in 1993 Remarkable achievement 4
 Why need MPEG-1 o o v CD-ROM enabled users to have hundreds of Megabyte storages Interactive video applications on CD 1. 5 Megabit/s was the transfer rate of CD at that time (single speed) 5
Why need MPEG-1 o o v CD-ROM enabled users to have hundreds of Megabyte storages Interactive video applications on CD 1. 5 Megabit/s was the transfer rate of CD at that time (single speed) 5
 MPEG-1 brought us o Video CD o MP 3 – MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 6
MPEG-1 brought us o Video CD o MP 3 – MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 6
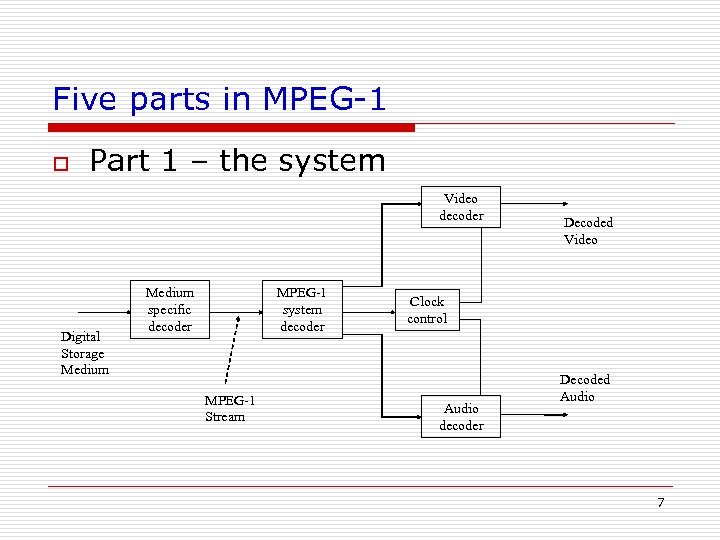 Five parts in MPEG-1 o Part 1 – the system Video decoder Digital Storage Medium specific decoder MPEG-1 system decoder MPEG-1 Stream Decoded Video Clock control Audio decoder Decoded Audio 7
Five parts in MPEG-1 o Part 1 – the system Video decoder Digital Storage Medium specific decoder MPEG-1 system decoder MPEG-1 Stream Decoded Video Clock control Audio decoder Decoded Audio 7
 Five parts in MPEG-1 o o Part 2, video Part 3, audio Part 4, testing Part 5, technique report for the implementation 8
Five parts in MPEG-1 o o Part 2, video Part 3, audio Part 4, testing Part 5, technique report for the implementation 8
 Outline o MPEG – 1 o MPEG – 2 o o o MPEG – 4 MPEG – 7 MPEG – 21 A comparison of them Other standards 9
Outline o MPEG – 1 o MPEG – 2 o o o MPEG – 4 MPEG – 7 MPEG – 21 A comparison of them Other standards 9
 MPEG-2 o o Generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information Started in 1990, became international standard in 1995 10
MPEG-2 o o Generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information Started in 1990, became international standard in 1995 10
 MPEG-2’s goal o Improve the audiovisual quality of MPEG-1 o Support digital TV o Compatible with MPEG-1 11
MPEG-2’s goal o Improve the audiovisual quality of MPEG-1 o Support digital TV o Compatible with MPEG-1 11
 MPEG-2 brought us o o v DVD HDTV Because MPEG-2’s performance, the MPEG-3, whose goal was enabling HDTV, was abandoned 12
MPEG-2 brought us o o v DVD HDTV Because MPEG-2’s performance, the MPEG-3, whose goal was enabling HDTV, was abandoned 12
 Ten parts in MPEG-2 o o o 1. System 2. Video 3. Audio 4, 5. correspond to those in MPEG-1 6. Digital Storage Media Command control 7. Advanced audio 13
Ten parts in MPEG-2 o o o 1. System 2. Video 3. Audio 4, 5. correspond to those in MPEG-1 6. Digital Storage Media Command control 7. Advanced audio 13
 10 Parts in MPEG-2 o o o 9. Real time interface for system decoder 10. Conformance test 11. IPMP in MPEG-2 14
10 Parts in MPEG-2 o o o 9. Real time interface for system decoder 10. Conformance test 11. IPMP in MPEG-2 14
 MPEG-2 vs. MPEG-1 o Video quality n n o Audio quality n n o MPEG-1: VCD MPEG-2: DVD / DTV MPEG-1: two (stereo) MPEG-2: multichannel Bitrates n n MPEG-1: 0. 8 – 2 M MPEG-2: 2 – 8 M 15
MPEG-2 vs. MPEG-1 o Video quality n n o Audio quality n n o MPEG-1: VCD MPEG-2: DVD / DTV MPEG-1: two (stereo) MPEG-2: multichannel Bitrates n n MPEG-1: 0. 8 – 2 M MPEG-2: 2 – 8 M 15
 Outline o MPEG – 1 MPEG – 2 o MPEG – 4 o o o MPEG – 7 MPEG – 21 A comparison of them Other standards 16
Outline o MPEG – 1 MPEG – 2 o MPEG – 4 o o o MPEG – 7 MPEG – 21 A comparison of them Other standards 16
 MPEG-4 o o Coding of audiovisual object Became international standard in 1998 (version 1) 17
MPEG-4 o o Coding of audiovisual object Became international standard in 1998 (version 1) 17
 MPEG-4’s goal o o Provide high quality audiovisual over a large range of bitrates Enable higher level of interaction with media content 18
MPEG-4’s goal o o Provide high quality audiovisual over a large range of bitrates Enable higher level of interaction with media content 18
 MPEG-4’s scope o Satisfy the needs of n n n content authors service providers end users 19
MPEG-4’s scope o Satisfy the needs of n n n content authors service providers end users 19
 MPEG-4’s feature o o Use “media object” to represent audiovisual content Facilitate content-based interaction Improve the video compression efficiency Work in a wide range of bitrate 64 kbps – 4 mbps 20
MPEG-4’s feature o o Use “media object” to represent audiovisual content Facilitate content-based interaction Improve the video compression efficiency Work in a wide range of bitrate 64 kbps – 4 mbps 20
 MPEG-4’s features o Provide robustness to information errors and loss, resolution scalability, and object scalability 21
MPEG-4’s features o Provide robustness to information errors and loss, resolution scalability, and object scalability 21
 MPEG-4’s applications o o o o Internet multimedia Interactive video game Interpersonal communication Interactive storage media Wireless multimedia Broadcasting applications And more… 22
MPEG-4’s applications o o o o Internet multimedia Interactive video game Interpersonal communication Interactive storage media Wireless multimedia Broadcasting applications And more… 22
 Outline o MPEG – 1 MPEG – 2 MPEG – 4 o MPEG – 7 o o o MPEG – 21 A comparison of them Other standards 23
Outline o MPEG – 1 MPEG – 2 MPEG – 4 o MPEG – 7 o o o MPEG – 21 A comparison of them Other standards 23
 MPEG-7 o o Multimedia Content Description Interface Initiated in 1996, and became an international standard in 2002 24
MPEG-7 o o Multimedia Content Description Interface Initiated in 1996, and became an international standard in 2002 24
 MPEG-7’s goal o Search, access, filter, retrieve, and manage audiovisual information n n o o Digital multimedia spreads Transmission speeds increase and storage costs fall Allow higher interoperability Support a broad range of applications 25
MPEG-7’s goal o Search, access, filter, retrieve, and manage audiovisual information n n o o Digital multimedia spreads Transmission speeds increase and storage costs fall Allow higher interoperability Support a broad range of applications 25
 MPEG-7’s Feature o Provide a set of audiovisual description tools n n n describe the “meaning” of the multimedia content The descriptions do not relay on the way the content is coded or stored This description can be passed to, or accessed by other tools or applications 26
MPEG-7’s Feature o Provide a set of audiovisual description tools n n n describe the “meaning” of the multimedia content The descriptions do not relay on the way the content is coded or stored This description can be passed to, or accessed by other tools or applications 26
 MPEG-7’s feature o Allow different granularity in the description n n n Creation: author, title Usage: copyright Low level feature: color, texture Conceptual: event Collection of object Interaction: user preference 27
MPEG-7’s feature o Allow different granularity in the description n n n Creation: author, title Usage: copyright Low level feature: color, texture Conceptual: event Collection of object Interaction: user preference 27
 MPEG-7’s feature o The description can be extracted n n Automatically – only for some low level features, like color, textual Manually – for most high level features e. g. there are three persons in the scene 28
MPEG-7’s feature o The description can be extracted n n Automatically – only for some low level features, like color, textual Manually – for most high level features e. g. there are three persons in the scene 28
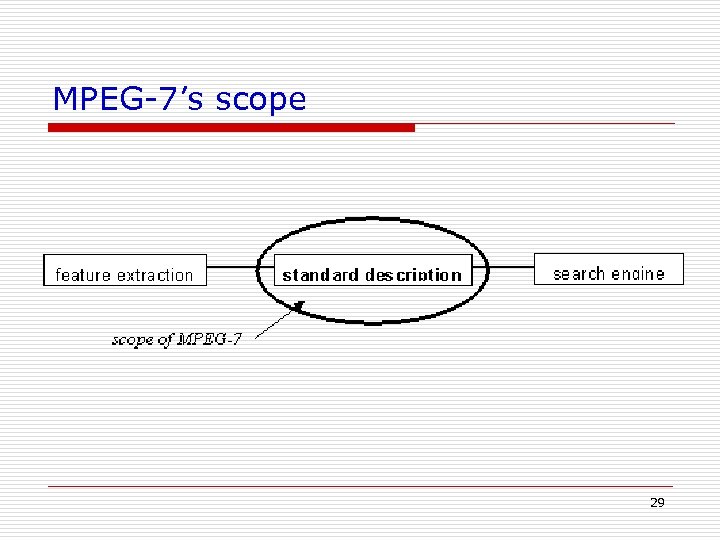 MPEG-7’s scope 29
MPEG-7’s scope 29
 MPEG-7’s main elements o Descriptive tools n n o o Descriptors Description schema Description definition language System tools 30
MPEG-7’s main elements o Descriptive tools n n o o Descriptors Description schema Description definition language System tools 30
 MPEG-7’s applications o o o Broadcast media selection Multimedia editing Home entertainments Multimedia searching, filter Much more… 31
MPEG-7’s applications o o o Broadcast media selection Multimedia editing Home entertainments Multimedia searching, filter Much more… 31
 Outline o MPEG o MPEG – 21 o o o – – 1 2 4 7 A comparison of them Other standards 32
Outline o MPEG o MPEG – 21 o o o – – 1 2 4 7 A comparison of them Other standards 32
 MPEG-21 o o o Multimedia Framework Part 2 & 3 became international standard this year The rest of other parts are under developing 33
MPEG-21 o o o Multimedia Framework Part 2 & 3 became international standard this year The rest of other parts are under developing 33
 MPEG-21’s vision & goal o o Enable transparent and augmented use of multimedia resources across a wide range of network and devices to meet the needs for all users. Its goal is to describe a big picture of how different elements to build an infrastructure for delivery and consumption of multimedia content relate to each other. 34
MPEG-21’s vision & goal o o Enable transparent and augmented use of multimedia resources across a wide range of network and devices to meet the needs for all users. Its goal is to describe a big picture of how different elements to build an infrastructure for delivery and consumption of multimedia content relate to each other. 34
 MPEG-21’s framework o o o For all electronic creation, production, delivery and trade of content Seek existing standards where appropriate Based on two essential concepts: n n Digital items Users 35
MPEG-21’s framework o o o For all electronic creation, production, delivery and trade of content Seek existing standards where appropriate Based on two essential concepts: n n Digital items Users 35
 MPEG-21’s digital items & Users o Digital Items n o Can be anything from an element piece content (a single picture), to a complete collection of audiovisual work Users n n Can be anyone, from authors, to vendors to end users Users are equal, in the sense that they all have their rights and interests in digital items 36
MPEG-21’s digital items & Users o Digital Items n o Can be anything from an element piece content (a single picture), to a complete collection of audiovisual work Users n n Can be anyone, from authors, to vendors to end users Users are equal, in the sense that they all have their rights and interests in digital items 36
 MPEG-21’s applications o o o Digital library Broadcast usage Multimedia publishing & release Trade transactions Much more… 37
MPEG-21’s applications o o o Digital library Broadcast usage Multimedia publishing & release Trade transactions Much more… 37
 Outline o MPEG MPEG o A comparison of them o Other standards o o – – – 1 2 4 7 21 38
Outline o MPEG MPEG o A comparison of them o Other standards o o – – – 1 2 4 7 21 38
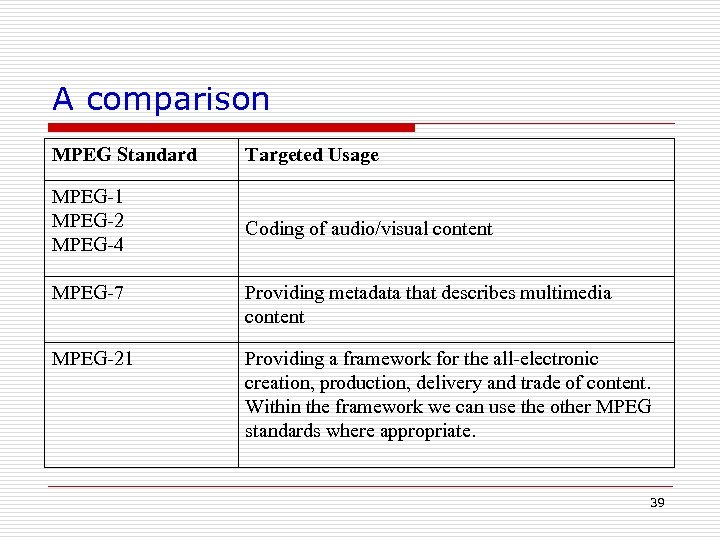 A comparison MPEG Standard Targeted Usage MPEG-1 MPEG-2 MPEG-4 Coding of audio/visual content MPEG-7 Providing metadata that describes multimedia content MPEG-21 Providing a framework for the all-electronic creation, production, delivery and trade of content. Within the framework we can use the other MPEG standards where appropriate. 39
A comparison MPEG Standard Targeted Usage MPEG-1 MPEG-2 MPEG-4 Coding of audio/visual content MPEG-7 Providing metadata that describes multimedia content MPEG-21 Providing a framework for the all-electronic creation, production, delivery and trade of content. Within the framework we can use the other MPEG standards where appropriate. 39
 A comparison o o o MPEG-1/2/4 all aim at coding of audiovisual content MPEG-1/2 are frame-based, and MPEG-2 compatible with MPEG-1 MPEG-4 is media object-based 40
A comparison o o o MPEG-1/2/4 all aim at coding of audiovisual content MPEG-1/2 are frame-based, and MPEG-2 compatible with MPEG-1 MPEG-4 is media object-based 40
 A comparison o o MPEG-7 will not replace the first three, it gives the contents ‘meaning’ by describing them MPEG-21 is much broader, dealing with units that consist of multiple resources 41
A comparison o o MPEG-7 will not replace the first three, it gives the contents ‘meaning’ by describing them MPEG-21 is much broader, dealing with units that consist of multiple resources 41
 Outline o MPEG – 1 MPEG – 2 MPEG – 4 MPEG – 7 MPEG – 21 A comparison of them o Other standards o o o 42
Outline o MPEG – 1 MPEG – 2 MPEG – 4 MPEG – 7 MPEG – 21 A comparison of them o Other standards o o o 42
 Other standards o o o H. 242, by CCITT. H. 320, by CCITT Quick. Time, by Apple computer, Inc. RIFF, by Microsoft and IBM RTP Much more… 43
Other standards o o o H. 242, by CCITT. H. 320, by CCITT Quick. Time, by Apple computer, Inc. RIFF, by Microsoft and IBM RTP Much more… 43
 References o MPEG home page: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/ o MPEG-1: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/standards/mpeg-1. htm o MPEG-2: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/standards/mpeg-2. htm o MPEG-4: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/standards/mpeg-4. htm o MPEG-7: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/standards/mpeg-7. htm o MPEG-21: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/standards/mpeg-21. htm o From MPEG-1 to MPEG-21: Creating an Interoperable Multimedia Infrastructure: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/from_mpeg-1_to_mpeg-21. htm o Riding the Media Bits: http: //www. chiariglione. org/ride/ o ISO/IEC JTC 29 Programme of Work: http: //www. itscj. ipsj. or. jp/sc 29/29 w 42911. htm o Standards in multimedia: http: //cui. unige. ch/OSG/info/Multimedia. Info/mmsurvey/standards. html o MPEG-2 FAQ at Berkeley Multimedia Research Center: http: //bmrc. berkeley. edu/frame/research/mpeg 2 faq. html 44
References o MPEG home page: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/ o MPEG-1: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/standards/mpeg-1. htm o MPEG-2: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/standards/mpeg-2. htm o MPEG-4: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/standards/mpeg-4. htm o MPEG-7: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/standards/mpeg-7. htm o MPEG-21: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/standards/mpeg-21. htm o From MPEG-1 to MPEG-21: Creating an Interoperable Multimedia Infrastructure: http: //www. chiariglione. org/mpeg/from_mpeg-1_to_mpeg-21. htm o Riding the Media Bits: http: //www. chiariglione. org/ride/ o ISO/IEC JTC 29 Programme of Work: http: //www. itscj. ipsj. or. jp/sc 29/29 w 42911. htm o Standards in multimedia: http: //cui. unige. ch/OSG/info/Multimedia. Info/mmsurvey/standards. html o MPEG-2 FAQ at Berkeley Multimedia Research Center: http: //bmrc. berkeley. edu/frame/research/mpeg 2 faq. html 44
 The end o Thanks n n o To the organizations like MPEG To everyone here today Questions 45
The end o Thanks n n o To the organizations like MPEG To everyone here today Questions 45


