Semey State Medical University TOPIC: PLACENTA PREVIA Prepared by : Nessipkhan A.E. 548 gr Checked by: Antonova G.A.
Semey State Medical University TOPIC: PLACENTA PREVIA Prepared by : Nessipkhan A.E. 548 gr Checked by: Antonova G.A.
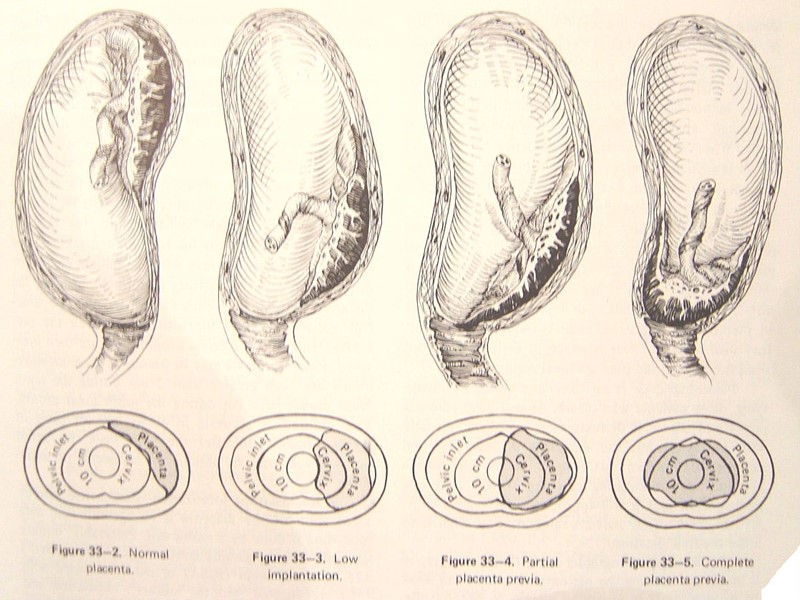
 Definition After 28 pregnant weeks placental implantation over the cervical os or in the lower uterine segment It constitutes an obstruction of descent of the presenting part Main cause of obstetrical hemorrhage(20%)
Definition After 28 pregnant weeks placental implantation over the cervical os or in the lower uterine segment It constitutes an obstruction of descent of the presenting part Main cause of obstetrical hemorrhage(20%)
 Predisposing factors: The scar on the uterus; Complicated obstetric and gynecological history Myoma of uterus.
Predisposing factors: The scar on the uterus; Complicated obstetric and gynecological history Myoma of uterus.
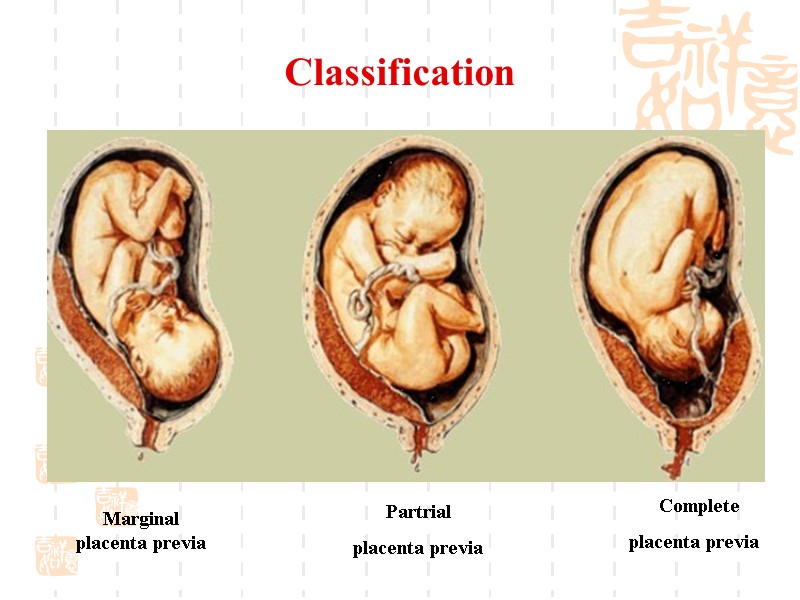 Classification Complete placenta previa Partrial placenta previa Marginal placenta previa
Classification Complete placenta previa Partrial placenta previa Marginal placenta previa
 Symptoms Painless vaginal bleeding (70%) Spontaneous,After coitus The most characteristic symptom late pregnancy (after the 28th week) and delivery Characteristics: sudden, painless and profuse Contractions No symptoms Routine ultrasound finding The mean gestational age of first bleed: 30 wks 1/3 before 30 weeks
Symptoms Painless vaginal bleeding (70%) Spontaneous,After coitus The most characteristic symptom late pregnancy (after the 28th week) and delivery Characteristics: sudden, painless and profuse Contractions No symptoms Routine ultrasound finding The mean gestational age of first bleed: 30 wks 1/3 before 30 weeks
 Anemia or shock repeated bleeding→ anemia heavy bleeding→ shock Abnormal fetal position a high presenting part breech presentation (often)
Anemia or shock repeated bleeding→ anemia heavy bleeding→ shock Abnormal fetal position a high presenting part breech presentation (often)
 Determining the severity of the general condition of the patient (heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, skin color). Algorithm diagnostics and tactics:
Determining the severity of the general condition of the patient (heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, skin color). Algorithm diagnostics and tactics:
 Figuring obstetric situation (gestational age, the presence or absence of regular labor)
Figuring obstetric situation (gestational age, the presence or absence of regular labor)
 Treatment Isotonic solution
Treatment Isotonic solution
 Identifying changes in the shape of the uterus, the definition of its tone, pain, nature of the presenting part by gentle external examination. Vaginal examination is possible only when deployed operating due to the risk of profuse uterine bleeding.
Identifying changes in the shape of the uterus, the definition of its tone, pain, nature of the presenting part by gentle external examination. Vaginal examination is possible only when deployed operating due to the risk of profuse uterine bleeding.
 Assessment of the fetus (stir, palpitations). Assessment of the extent and nature of bleeding from the birth canal. At birth at term blood loss 350-400 ml is considered the maximum allowable (Frontier), as it can be compensated for by the adaptive capabilities of the female organism, blood loss greater than 0.5% by weight or pregnant mothers considered pathological and requires therapeutic interventions.
Assessment of the fetus (stir, palpitations). Assessment of the extent and nature of bleeding from the birth canal. At birth at term blood loss 350-400 ml is considered the maximum allowable (Frontier), as it can be compensated for by the adaptive capabilities of the female organism, blood loss greater than 0.5% by weight or pregnant mothers considered pathological and requires therapeutic interventions.
 When spotting prehospital treatment is needed. With abundant spotting immediately begin infusion therapy, aimed at filling the BCC and stabilizing the women
When spotting prehospital treatment is needed. With abundant spotting immediately begin infusion therapy, aimed at filling the BCC and stabilizing the women
 To reduce uterine activity shown intramuscular antispasmodics (drotaverin, Nospanum, spazoverin, spakovin): 10 ml of 25% magnesium sulfate solution, 2 ml of a 2% solution of papaverine. In order to prevent intrauterine fetal hypoxia recommended 20 ml of 40% glucose and 2.3 mL of a 5% solution of ascorbic acid intravenously, inhalation air-oxygen mixture is 40-60%. Haemostatic therapy - ditsinon Ambene or 2-4 ml intravenously.
To reduce uterine activity shown intramuscular antispasmodics (drotaverin, Nospanum, spazoverin, spakovin): 10 ml of 25% magnesium sulfate solution, 2 ml of a 2% solution of papaverine. In order to prevent intrauterine fetal hypoxia recommended 20 ml of 40% glucose and 2.3 mL of a 5% solution of ascorbic acid intravenously, inhalation air-oxygen mixture is 40-60%. Haemostatic therapy - ditsinon Ambene or 2-4 ml intravenously.
 Transporting the patient should be in a horizontal position, with a full-term pregnancy - with a raised head part of the body to reduce respiratory failure.
Transporting the patient should be in a horizontal position, with a full-term pregnancy - with a raised head part of the body to reduce respiratory failure.
 Pregnant (new mother) with placenta previa should be delivered in a maternity hospital, which is resuscitation and operational offices. Obstetric hospital staff mandatory advance notify me when seriously ill. On arrival at the hospital the patient should be transferred directly to the doctor on duty.
Pregnant (new mother) with placenta previa should be delivered in a maternity hospital, which is resuscitation and operational offices. Obstetric hospital staff mandatory advance notify me when seriously ill. On arrival at the hospital the patient should be transferred directly to the doctor on duty.