Rakhimbekov 547 Coma.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Semey State Medical University SIW Topic: «Comatose states» Prepared by: Rakhimbekov R. T. 547 group GM Checked by: Akimzhanova A. K. Semey 2016
Semey State Medical University SIW Topic: «Comatose states» Prepared by: Rakhimbekov R. T. 547 group GM Checked by: Akimzhanova A. K. Semey 2016
 The forms of consciousness disturbance Ø • Stun Ø • somnolence Ø • Delirious syndrome Ø • Sopor Ø • Coma
The forms of consciousness disturbance Ø • Stun Ø • somnolence Ø • Delirious syndrome Ø • Sopor Ø • Coma
 Coma is a condition in which there is depression of consciousness, lack of mental activities and violation of the motor, sensitive and somatovegetatvie functions of organism. In fact, a coma manifestation of cerebral insufficiency, in which the broken coordinating role central nervous system.
Coma is a condition in which there is depression of consciousness, lack of mental activities and violation of the motor, sensitive and somatovegetatvie functions of organism. In fact, a coma manifestation of cerebral insufficiency, in which the broken coordinating role central nervous system.
 § When coma occurs in the separation of the body separate, independently functioning systems that lose their ability to autoregulation and maintenance of homeostasis. § Development of the coma - always a sign of the terrible, and if miss time, the changes in the patient's body may become irreversible and lead to death.
§ When coma occurs in the separation of the body separate, independently functioning systems that lose their ability to autoregulation and maintenance of homeostasis. § Development of the coma - always a sign of the terrible, and if miss time, the changes in the patient's body may become irreversible and lead to death.
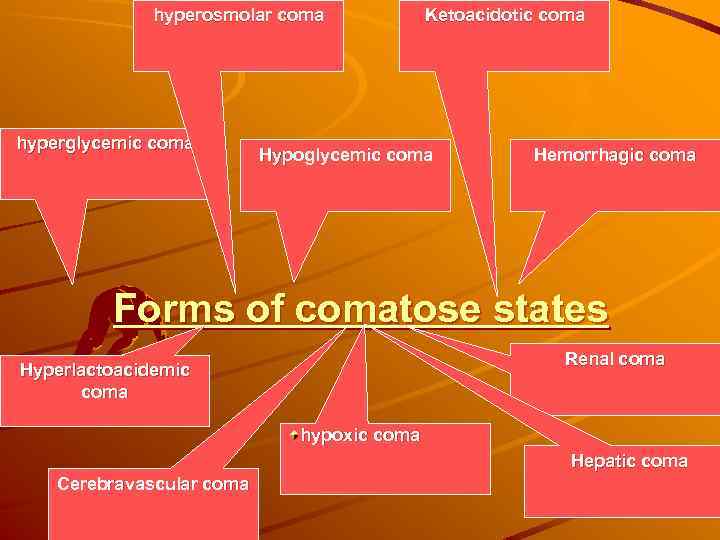 hyperosmolar coma hyperglycemic coma Ketoacidotic coma Hypoglycemic coma Hemorrhagic coma Forms of comatose states Renal coma Hyperlactoacidemic coma hypoxic coma Hepatic coma Cerebravascular coma
hyperosmolar coma hyperglycemic coma Ketoacidotic coma Hypoglycemic coma Hemorrhagic coma Forms of comatose states Renal coma Hyperlactoacidemic coma hypoxic coma Hepatic coma Cerebravascular coma
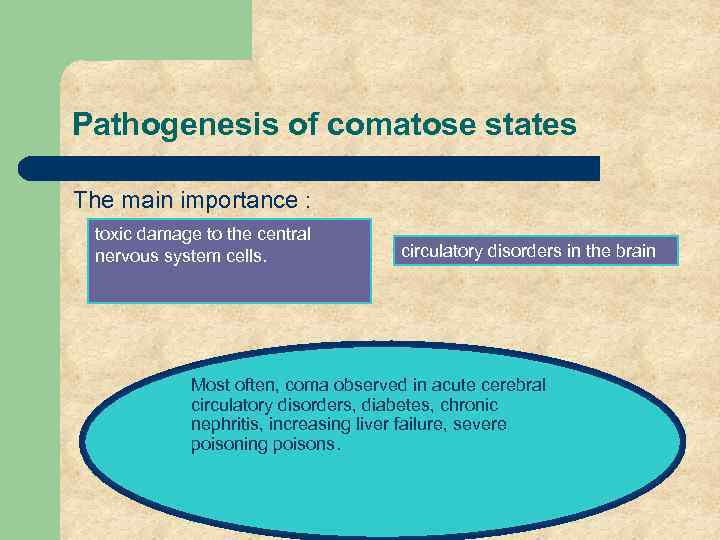 Pathogenesis of comatose states The main importance : toxic damage to the central nervous system cells. circulatory disorders in the brain Most often, coma observed in acute cerebral circulatory disorders, diabetes, chronic nephritis, increasing liver failure, severe poisoning poisons.
Pathogenesis of comatose states The main importance : toxic damage to the central nervous system cells. circulatory disorders in the brain Most often, coma observed in acute cerebral circulatory disorders, diabetes, chronic nephritis, increasing liver failure, severe poisoning poisons.
 Cerebravascular coma consequence of acute stroke is the most common. It is developing quite rapidly, or lightning at break of the vessel and bleeding into the brain or meninges (hemorrhagic stroke).
Cerebravascular coma consequence of acute stroke is the most common. It is developing quite rapidly, or lightning at break of the vessel and bleeding into the brain or meninges (hemorrhagic stroke).
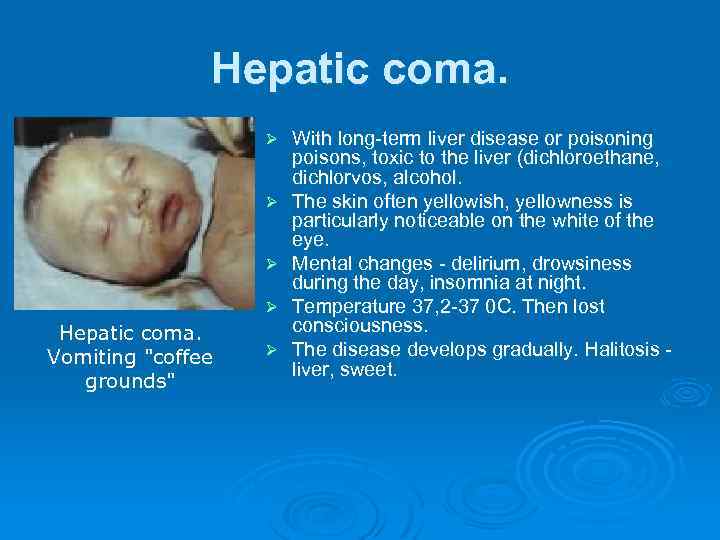 Hepatic coma. Ø Ø Hepatic coma. Vomiting "coffee grounds" Ø With long-term liver disease or poisoning poisons, toxic to the liver (dichloroethane, dichlorvos, alcohol. The skin often yellowish, yellowness is particularly noticeable on the white of the eye. Mental changes - delirium, drowsiness during the day, insomnia at night. Temperature 37, 2 -37 0 C. Then lost consciousness. The disease develops gradually. Halitosis - liver, sweet.
Hepatic coma. Ø Ø Hepatic coma. Vomiting "coffee grounds" Ø With long-term liver disease or poisoning poisons, toxic to the liver (dichloroethane, dichlorvos, alcohol. The skin often yellowish, yellowness is particularly noticeable on the white of the eye. Mental changes - delirium, drowsiness during the day, insomnia at night. Temperature 37, 2 -37 0 C. Then lost consciousness. The disease develops gradually. Halitosis - liver, sweet.
 Hypoxic coma ¡ may develop as a result of cardiac or cardiogenic shock, myocardial infarction, hypoxic state occurs due to lack of oxygen and nutrients. This condition occurs very quickly, because the brain cells do not have a supply of oxygen and nutrients, and their destruction, occurs within 5 minutes.
Hypoxic coma ¡ may develop as a result of cardiac or cardiogenic shock, myocardial infarction, hypoxic state occurs due to lack of oxygen and nutrients. This condition occurs very quickly, because the brain cells do not have a supply of oxygen and nutrients, and their destruction, occurs within 5 minutes.
 Renal coma It occurs after prolonged kidney disease (renal stone disease, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis), followed by chronic renal failure (CRF). Ø the brain is poisoned decay products of protein (urea, uric acid, etc. ). Ø Coma develops gradually, first appear weakness, bleeding gums, noise in the head and ears, severe pallor (anemia). At some point in time the patient begins to rave, and then completely loses consciousness. Ø Mouth appears smell of urine or ammonia, the skin is covered with a white coating (salt crystals). Ø
Renal coma It occurs after prolonged kidney disease (renal stone disease, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis), followed by chronic renal failure (CRF). Ø the brain is poisoned decay products of protein (urea, uric acid, etc. ). Ø Coma develops gradually, first appear weakness, bleeding gums, noise in the head and ears, severe pallor (anemia). At some point in time the patient begins to rave, and then completely loses consciousness. Ø Mouth appears smell of urine or ammonia, the skin is covered with a white coating (salt crystals). Ø
 Hemorrhagic coma. Coma in blood loss develops gradually In this patient, very rapid pulse, very low blood pressure. l If the blood loss is gradual (often with internal bleeding), the consciousness remains unchanged for a long time, but when it becomes a critical blood loss, lost consciousness, and this is a very dangerous sign because the consequences of a lack of oxygen in the brain and body tissues may become irreversible. l l
Hemorrhagic coma. Coma in blood loss develops gradually In this patient, very rapid pulse, very low blood pressure. l If the blood loss is gradual (often with internal bleeding), the consciousness remains unchanged for a long time, but when it becomes a critical blood loss, lost consciousness, and this is a very dangerous sign because the consequences of a lack of oxygen in the brain and body tissues may become irreversible. l l
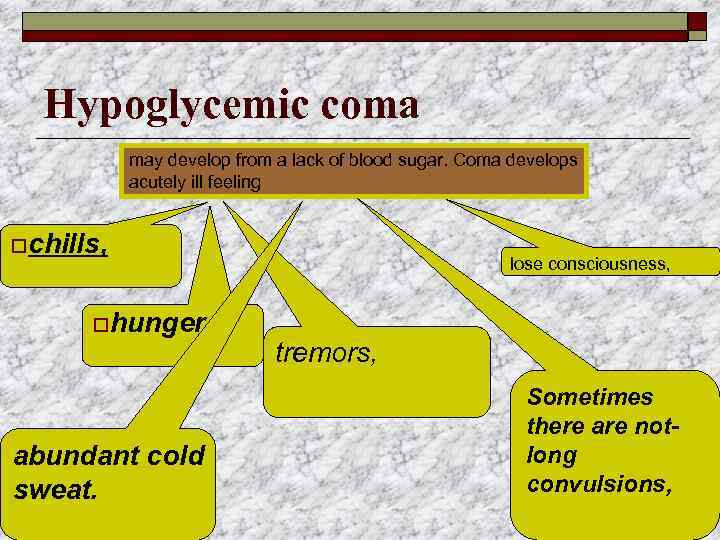 Hypoglycemic coma may develop from a lack of blood sugar. Coma develops acutely ill feeling ochills, ohunger, abundant cold sweat. lose consciousness, tremors, Sometimes there are notlong convulsions,
Hypoglycemic coma may develop from a lack of blood sugar. Coma develops acutely ill feeling ochills, ohunger, abundant cold sweat. lose consciousness, tremors, Sometimes there are notlong convulsions,
 Hyperglycemic coma • develops gradually • accompanied by dry mouth, • the patient drinks a lot, if at this point to take a blood sugar analysis, the indicators increased. • Coma usually develops in patients with diabetes. • A distinctive feature of the coma is that in addition to a complete loss of consciousness, the skin is dry, warm to the touch, breath odor of apples or acetone.
Hyperglycemic coma • develops gradually • accompanied by dry mouth, • the patient drinks a lot, if at this point to take a blood sugar analysis, the indicators increased. • Coma usually develops in patients with diabetes. • A distinctive feature of the coma is that in addition to a complete loss of consciousness, the skin is dry, warm to the touch, breath odor of apples or acetone.
 Glasgow Coma Scale (Teasdale G. , Bennett B. , 1974) Researched EVALUATION CRITERIA 1. OPENING EYES: (SCORE) spontaneous 4 to voice command 3 pain 2 no answer 1
Glasgow Coma Scale (Teasdale G. , Bennett B. , 1974) Researched EVALUATION CRITERIA 1. OPENING EYES: (SCORE) spontaneous 4 to voice command 3 pain 2 no answer 1
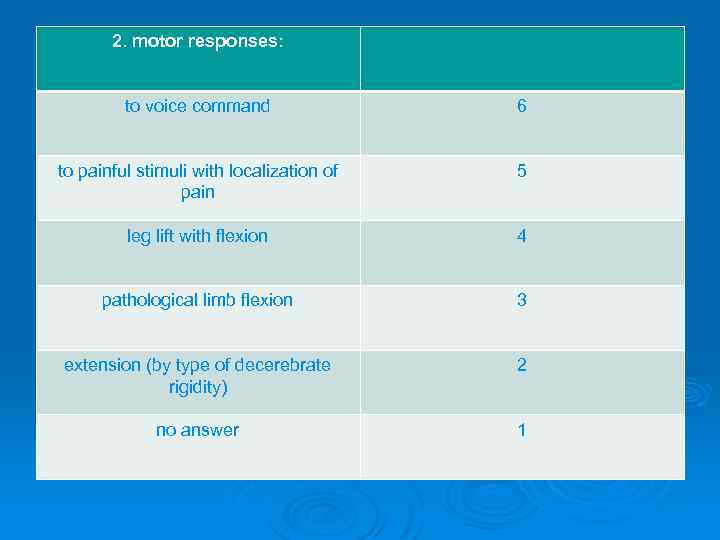 2. motor responses: to voice command 6 to painful stimuli with localization of pain 5 leg lift with flexion 4 pathological limb flexion 3 extension (by type of decerebrate rigidity) 2 no answer 1
2. motor responses: to voice command 6 to painful stimuli with localization of pain 5 leg lift with flexion 4 pathological limb flexion 3 extension (by type of decerebrate rigidity) 2 no answer 1
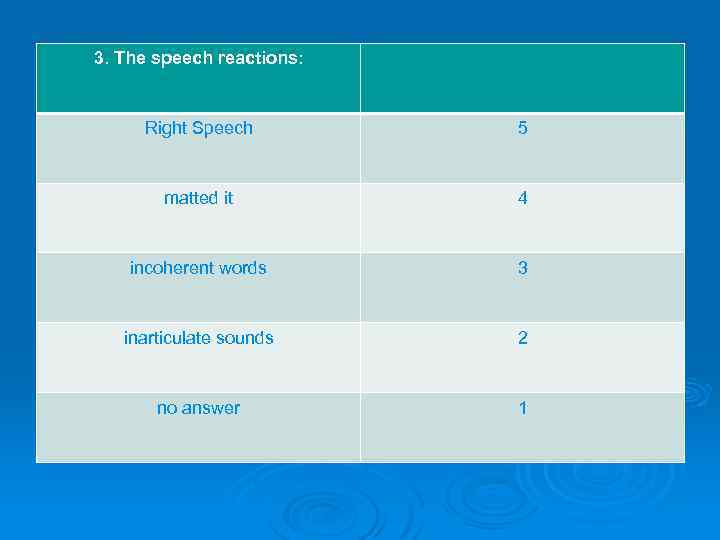 3. The speech reactions: Right Speech 5 matted it 4 incoherent words 3 inarticulate sounds 2 no answer 1
3. The speech reactions: Right Speech 5 matted it 4 incoherent words 3 inarticulate sounds 2 no answer 1
 Interpretation of the results: Ø • 15 points - normal, Ø • 14 -13 - stunning, Ø • 12 -9 - sopor, Ø • 8 -4 - coma, Ø • 3 - brain death
Interpretation of the results: Ø • 15 points - normal, Ø • 14 -13 - stunning, Ø • 12 -9 - sopor, Ø • 8 -4 - coma, Ø • 3 - brain death
 Coma has 4 degrees of severity n 1 n 2 degree n 3 degree n 4 degree
Coma has 4 degrees of severity n 1 n 2 degree n 3 degree n 4 degree
 Coma 1 degree (mild) Consciousness is absent ØSwallowing difficult, sluggish pupil photoreaction, corneal reflexes saved. ØThere are no voluntary movements Øthere are no disturbances in the cardiovascular system and respiratory ØIt does not react to light and response, but the response is stored in the pain and ammonia Ømuscle tone and tendon reflexes are reduced
Coma 1 degree (mild) Consciousness is absent ØSwallowing difficult, sluggish pupil photoreaction, corneal reflexes saved. ØThere are no voluntary movements Øthere are no disturbances in the cardiovascular system and respiratory ØIt does not react to light and response, but the response is stored in the pain and ammonia Ømuscle tone and tendon reflexes are reduced
 Coma grade 2 (medium) Ø - Consciousness and the response to external stimuli have been lost completely, Ø photoreaction sluggish pupils, and narrowed Ø corneal and tendon reflexes were sharply reduced, Ø swallowing disorder, Ø disorder of the pelvic organs, pathological breathing, a disorder of CVS activities.
Coma grade 2 (medium) Ø - Consciousness and the response to external stimuli have been lost completely, Ø photoreaction sluggish pupils, and narrowed Ø corneal and tendon reflexes were sharply reduced, Ø swallowing disorder, Ø disorder of the pelvic organs, pathological breathing, a disorder of CVS activities.
 Coma 3 degrees (atonic coma) Ø - Complete loss of consciousness, Ø reflections on a background of disorders of the cardiovascular system to get angry, Ø pathological breathing. Ø pupils are dileted
Coma 3 degrees (atonic coma) Ø - Complete loss of consciousness, Ø reflections on a background of disorders of the cardiovascular system to get angry, Ø pathological breathing. Ø pupils are dileted
 Coma 4 degrees (otherwordly coma) Ø - The absence of spontaneous breathing, Ø gross violations of angry activity of the circulatory system in the background and complete areflexia absence of brain activity. Ø Pupils dilated
Coma 4 degrees (otherwordly coma) Ø - The absence of spontaneous breathing, Ø gross violations of angry activity of the circulatory system in the background and complete areflexia absence of brain activity. Ø Pupils dilated
 Features of a condition of the skin of the patient at different etiology of coma The pink color of the skin is characteristic of the coma in cases of poisoning by carbon monoxide When alcoholic coma, bleeding in the brain, the face is usually hyperemic. Wet covered then the skin is typical for hypoglycemic coma Traces of the old scratching the skin can be observed in patients with diabetes, hepatic and uremic coma icteritiousness of the skin is usually observed in hepatic coma In diabetic coma skin is always dry. for anemia, cerebral vascular thrombosis, anemia, pale skin.
Features of a condition of the skin of the patient at different etiology of coma The pink color of the skin is characteristic of the coma in cases of poisoning by carbon monoxide When alcoholic coma, bleeding in the brain, the face is usually hyperemic. Wet covered then the skin is typical for hypoglycemic coma Traces of the old scratching the skin can be observed in patients with diabetes, hepatic and uremic coma icteritiousness of the skin is usually observed in hepatic coma In diabetic coma skin is always dry. for anemia, cerebral vascular thrombosis, anemia, pale skin.
 Turgor Ø A certain importance is the study of skin turgor. In some diseases, accompanied by dehydration and lead to the development of coma, there was a significant decrease in skin turgor. This symptom is especially pronounced in diabetic coma. A similar decrease in turgor eyeballs in diabetic coma makes them soft, which is good is determined by palpation.
Turgor Ø A certain importance is the study of skin turgor. In some diseases, accompanied by dehydration and lead to the development of coma, there was a significant decrease in skin turgor. This symptom is especially pronounced in diabetic coma. A similar decrease in turgor eyeballs in diabetic coma makes them soft, which is good is determined by palpation.
 Distinctive features of the mucous membranes in coma of different etiology Pronounced swelling of subcutaneous tissue can be detected in patients with hepatic and uremic komah icteritiousness of of the sclera is usually detected in hepatic coma For uremic coma is characterized by an unusual dryness language presence of fresh bites and scars from old bites should be direct at the thought of epilepsy
Distinctive features of the mucous membranes in coma of different etiology Pronounced swelling of subcutaneous tissue can be detected in patients with hepatic and uremic komah icteritiousness of of the sclera is usually detected in hepatic coma For uremic coma is characterized by an unusual dryness language presence of fresh bites and scars from old bites should be direct at the thought of epilepsy
 Features of breathing of the patient in different types of coma §Big noisy breathing Kussmaul often observed in diabetic or hepatic coma. When brain coma usually appears rattling breath §Often, patients in a coma says Chane -Stokes breathing gradually increased, and then the depth of the weakening of respiratory movements until the appearance of a pause in breathing movements (apnea period).
Features of breathing of the patient in different types of coma §Big noisy breathing Kussmaul often observed in diabetic or hepatic coma. When brain coma usually appears rattling breath §Often, patients in a coma says Chane -Stokes breathing gradually increased, and then the depth of the weakening of respiratory movements until the appearance of a pause in breathing movements (apnea period).
 Features of the cardiovascular system in comas of various etiology o o Bradycardia with a voltage pulse and high blood pressure seen with eclampsia, in the initial stages of cerebral coma. High arterial hypertension is usually detected in patients with uremic coma. In diabetic coma determined by low blood pressure and tachycardia. Identification of gross neurological symptoms in the form of hemiplegia or hemiparesis evidence of acute ischemic stroke as the cause of coma.
Features of the cardiovascular system in comas of various etiology o o Bradycardia with a voltage pulse and high blood pressure seen with eclampsia, in the initial stages of cerebral coma. High arterial hypertension is usually detected in patients with uremic coma. In diabetic coma determined by low blood pressure and tachycardia. Identification of gross neurological symptoms in the form of hemiplegia or hemiparesis evidence of acute ischemic stroke as the cause of coma.
 Helping to patient with diabetic (hyperglycemic) coma n Coma treatment depends on the nature of the underlying disease. When administered to diabetic coma intended patient physician insulin subcutaneously and intravenously, sodium bicarbonate, saline.
Helping to patient with diabetic (hyperglycemic) coma n Coma treatment depends on the nature of the underlying disease. When administered to diabetic coma intended patient physician insulin subcutaneously and intravenously, sodium bicarbonate, saline.
 Helping to a patient in hypoglycemic coma l Hypoglycemic coma preceded by a feeling of hunger, weakness and tremors throughout the body. Before arrival of the doctor patient give sugar or sweet tea. In the vein injected 20 -40 ml of 40% glucose solution.
Helping to a patient in hypoglycemic coma l Hypoglycemic coma preceded by a feeling of hunger, weakness and tremors throughout the body. Before arrival of the doctor patient give sugar or sweet tea. In the vein injected 20 -40 ml of 40% glucose solution.
 Emergency aid to the patient with uremic coma l In uremic coma therapeutic measures aimed at reducing toxicity. For this purpose, washed stomach, put a cleansing enema, ka-Pelny administered isotonic sodium chloride solution and 5% glucose solution.
Emergency aid to the patient with uremic coma l In uremic coma therapeutic measures aimed at reducing toxicity. For this purpose, washed stomach, put a cleansing enema, ka-Pelny administered isotonic sodium chloride solution and 5% glucose solution.
 Emergency aid to the patient with hepatic coma Ø In hepatic coma on prescription drippings administered glucose solutions, steroid hormones, vitamins.
Emergency aid to the patient with hepatic coma Ø In hepatic coma on prescription drippings administered glucose solutions, steroid hormones, vitamins.
 END! Thank’s for attention
END! Thank’s for attention


