 Semey State Medical University SIW Theme: “Endometriosis. Etiology. Classification.” Prepared by: 444 gr, GMF Tailybayeva U.K. Checked by: Antonova G.A. Semey,2013
Semey State Medical University SIW Theme: “Endometriosis. Etiology. Classification.” Prepared by: 444 gr, GMF Tailybayeva U.K. Checked by: Antonova G.A. Semey,2013
 Plan Introduction Etiology Classification Conclusion Literature
Plan Introduction Etiology Classification Conclusion Literature
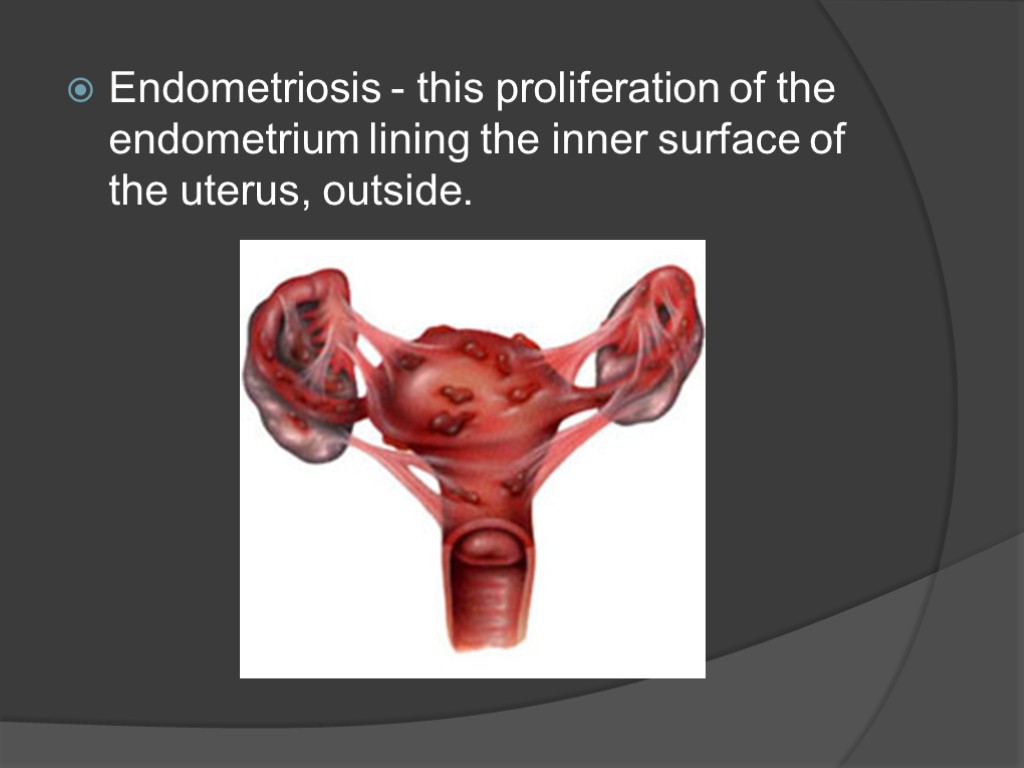 Endometriosis - this proliferation of the endometrium lining the inner surface of the uterus, outside.
Endometriosis - this proliferation of the endometrium lining the inner surface of the uterus, outside.
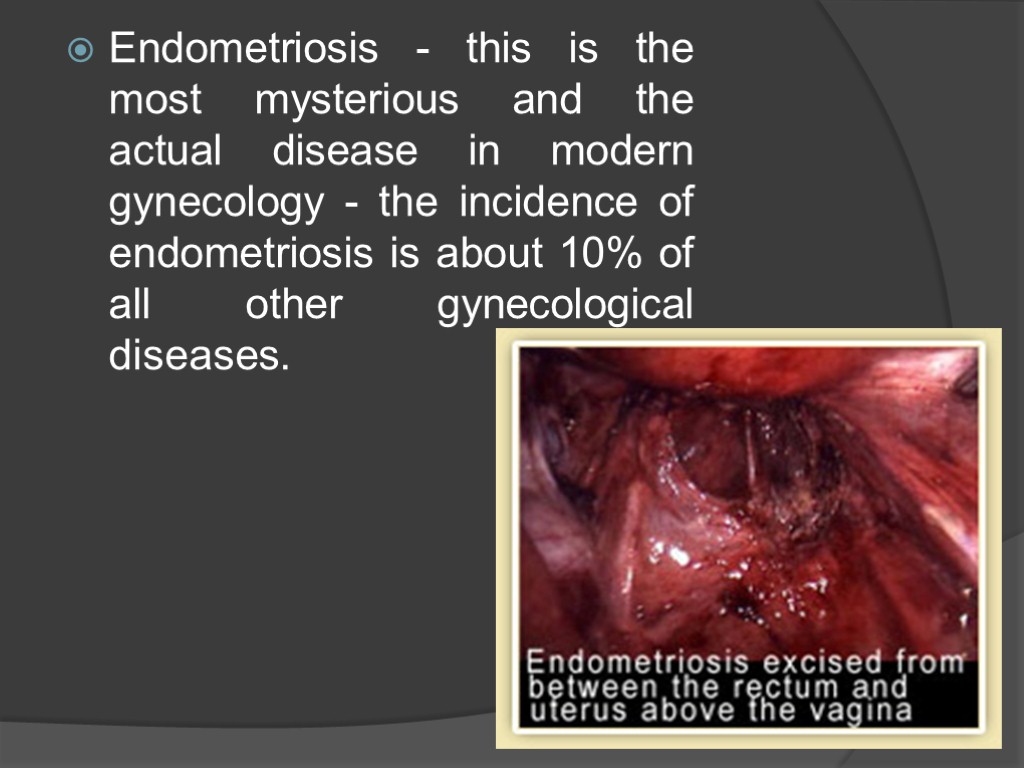 Endometriosis - this is the most mysterious and the actual disease in modern gynecology - the incidence of endometriosis is about 10% of all other gynecological diseases.
Endometriosis - this is the most mysterious and the actual disease in modern gynecology - the incidence of endometriosis is about 10% of all other gynecological diseases.
 Etiology Endometriosis - this is polyetiological disease. - Hormonal disorders. Is noted that almost at all patients with endometriosis there are changes in the ratio of steroid hormones has a high release of FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone). This reduces the levels of progesterone, prolactin increases and broken androgenic function of the adrenal cortex;
Etiology Endometriosis - this is polyetiological disease. - Hormonal disorders. Is noted that almost at all patients with endometriosis there are changes in the ratio of steroid hormones has a high release of FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone). This reduces the levels of progesterone, prolactin increases and broken androgenic function of the adrenal cortex;
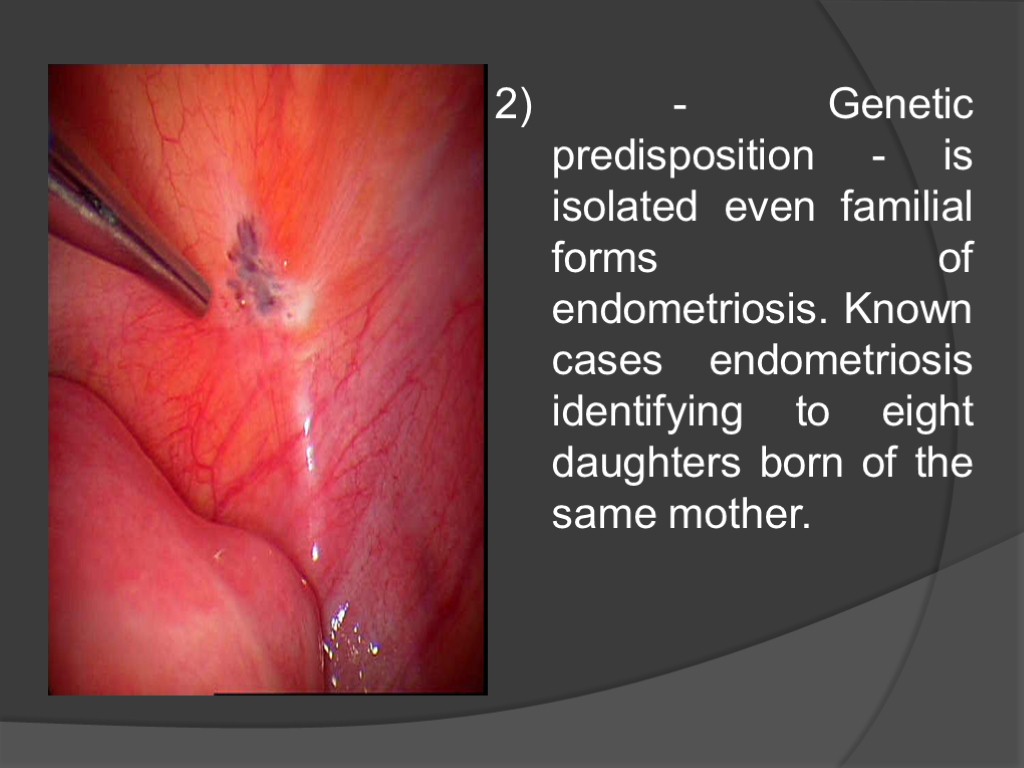 2) - Genetic predisposition - is isolated even familial forms of endometriosis. Known cases endometriosis identifying to eight daughters born of the same mother.
2) - Genetic predisposition - is isolated even familial forms of endometriosis. Known cases endometriosis identifying to eight daughters born of the same mother.
 Factors that trigger the occurrence of endometriosis: abortion in the anamnesis, influence of the environment, iron deficiency in an organism, surgical interventions on the pelvic organs (including cesarean delivery, cauterization of cervical erosion) obesity, inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs, wearing an intrauterine device, abnormal liver function
Factors that trigger the occurrence of endometriosis: abortion in the anamnesis, influence of the environment, iron deficiency in an organism, surgical interventions on the pelvic organs (including cesarean delivery, cauterization of cervical erosion) obesity, inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs, wearing an intrauterine device, abnormal liver function
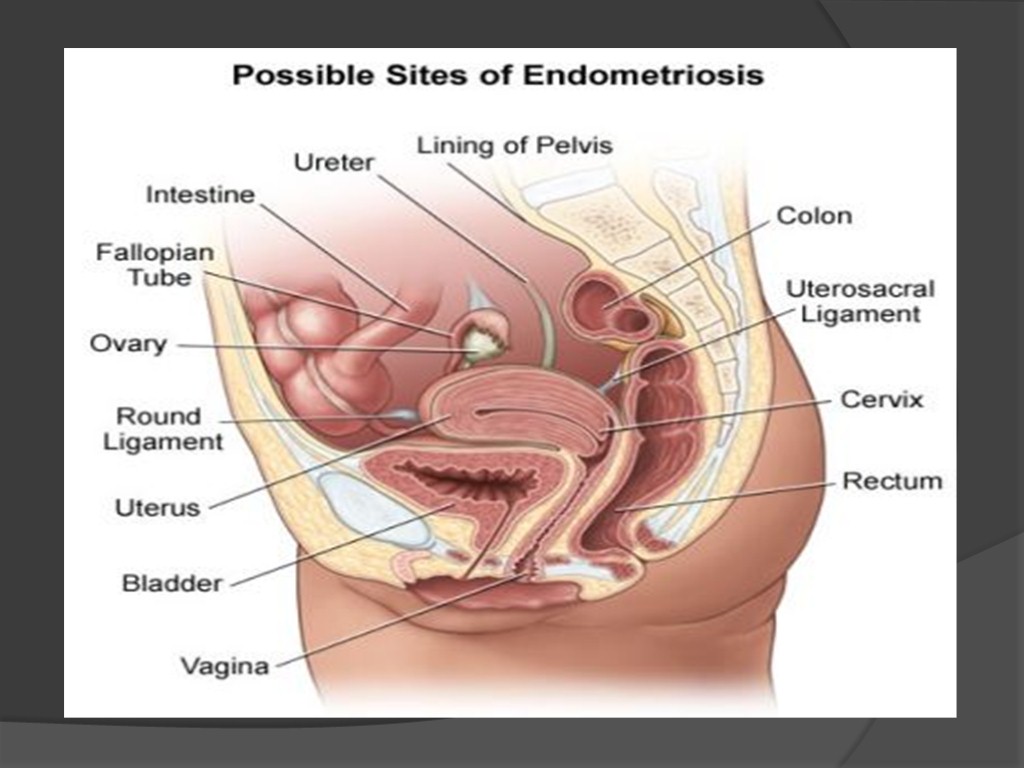
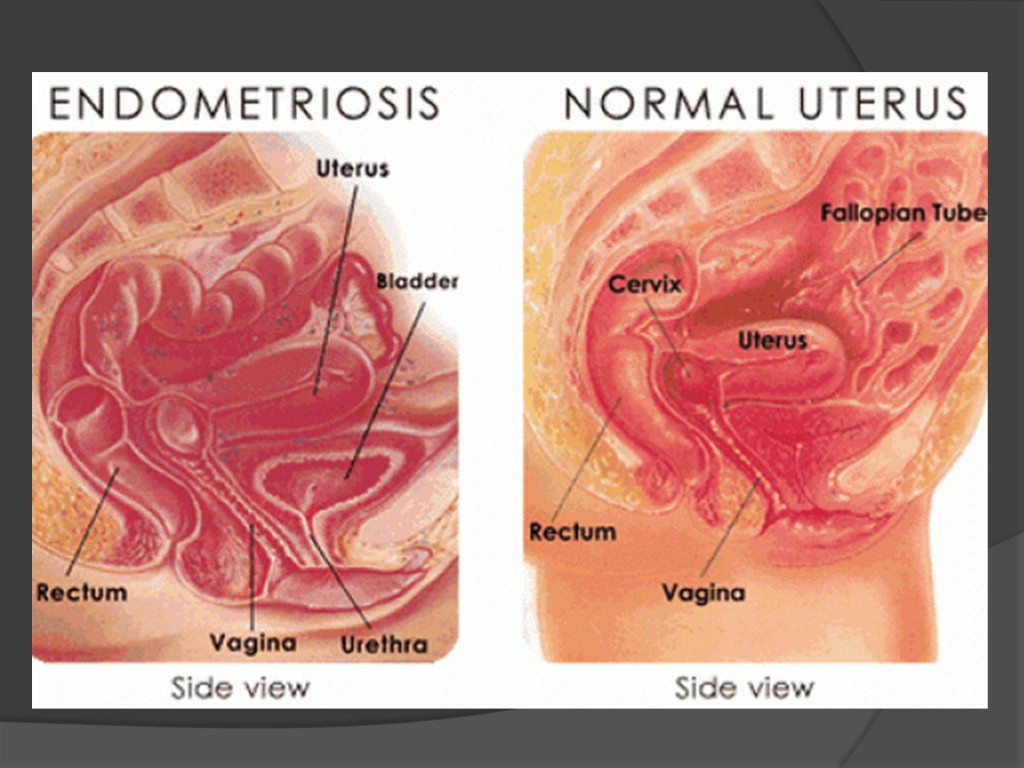
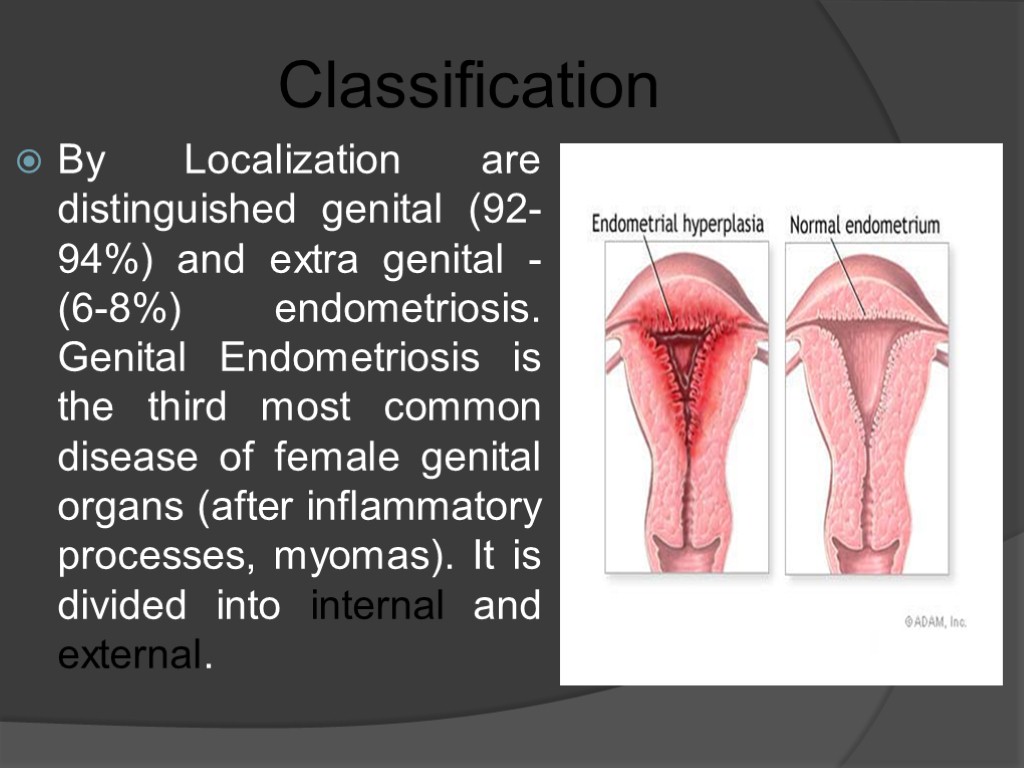 Classification By Localization are distinguished genital (92-94%) and extra genital -(6-8%) endometriosis. Genital Endometriosis is the third most common disease of female genital organs (after inflammatory processes, myomas). It is divided into internal and external.
Classification By Localization are distinguished genital (92-94%) and extra genital -(6-8%) endometriosis. Genital Endometriosis is the third most common disease of female genital organs (after inflammatory processes, myomas). It is divided into internal and external.
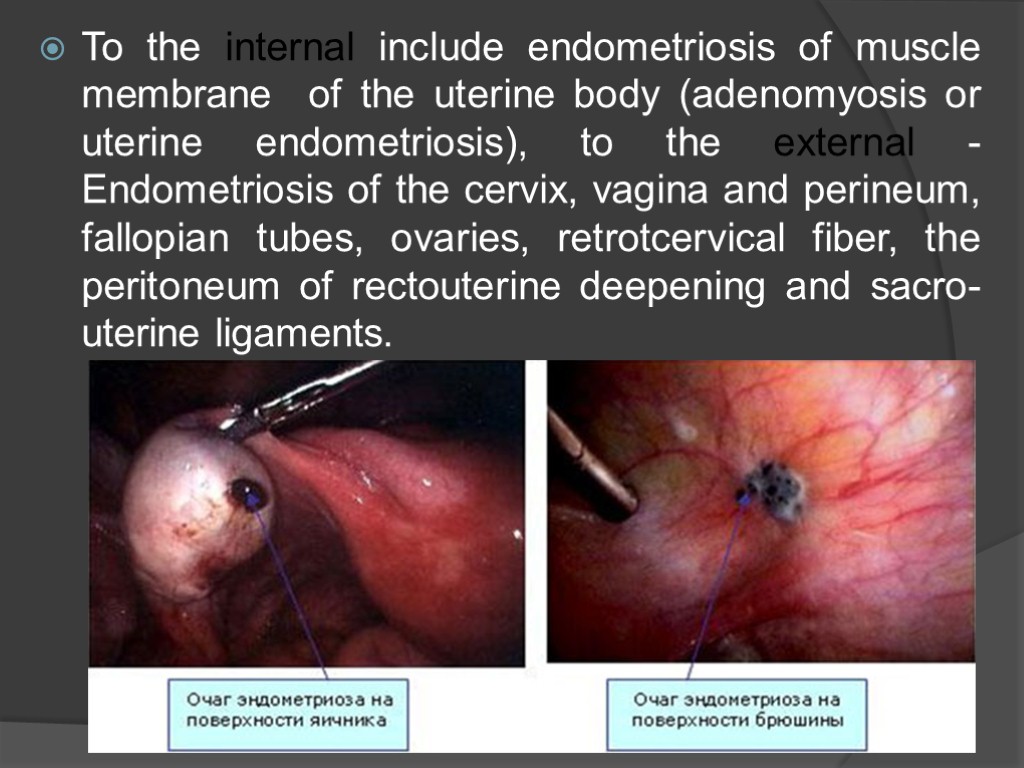 To the internal include endometriosis of muscle membrane of the uterine body (adenomyosis or uterine endometriosis), to the external - Endometriosis of the cervix, vagina and perineum, fallopian tubes, ovaries, retrotcervical fiber, the peritoneum of rectouterine deepening and sacro-uterine ligaments.
To the internal include endometriosis of muscle membrane of the uterine body (adenomyosis or uterine endometriosis), to the external - Endometriosis of the cervix, vagina and perineum, fallopian tubes, ovaries, retrotcervical fiber, the peritoneum of rectouterine deepening and sacro-uterine ligaments.
 At internal endometriosis may experience the local or widespread damage of myometrium - diffuse and focal forms; growth endometrial tissue as a node called nodular form of internal endometriosis. Depending on the depth of penetration of endometrial tissue in the myometrium are three degrees of diffuse forms of internal endometriosis: I - to a depth of no more than 1 cm, II - until mid-thickness of the myometrium, Ill - to the serous membrane of the uterus.
At internal endometriosis may experience the local or widespread damage of myometrium - diffuse and focal forms; growth endometrial tissue as a node called nodular form of internal endometriosis. Depending on the depth of penetration of endometrial tissue in the myometrium are three degrees of diffuse forms of internal endometriosis: I - to a depth of no more than 1 cm, II - until mid-thickness of the myometrium, Ill - to the serous membrane of the uterus.
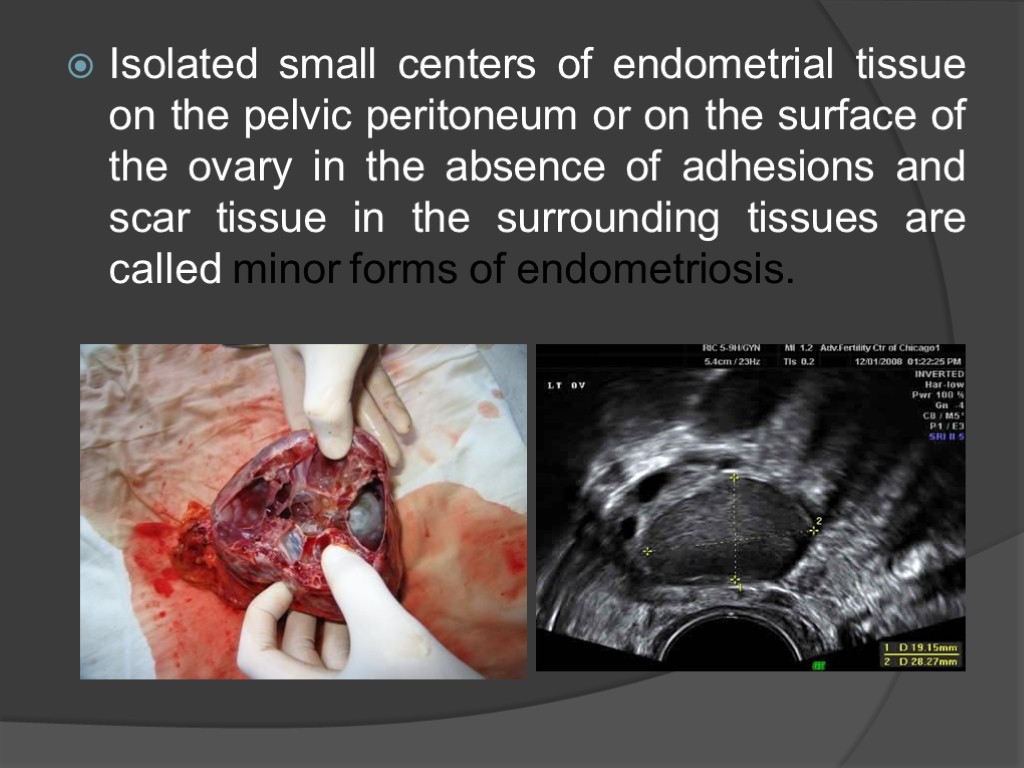 Isolated small centers of endometrial tissue on the pelvic peritoneum or on the surface of the ovary in the absence of adhesions and scar tissue in the surrounding tissues are called minor forms of endometriosis.
Isolated small centers of endometrial tissue on the pelvic peritoneum or on the surface of the ovary in the absence of adhesions and scar tissue in the surrounding tissues are called minor forms of endometriosis.
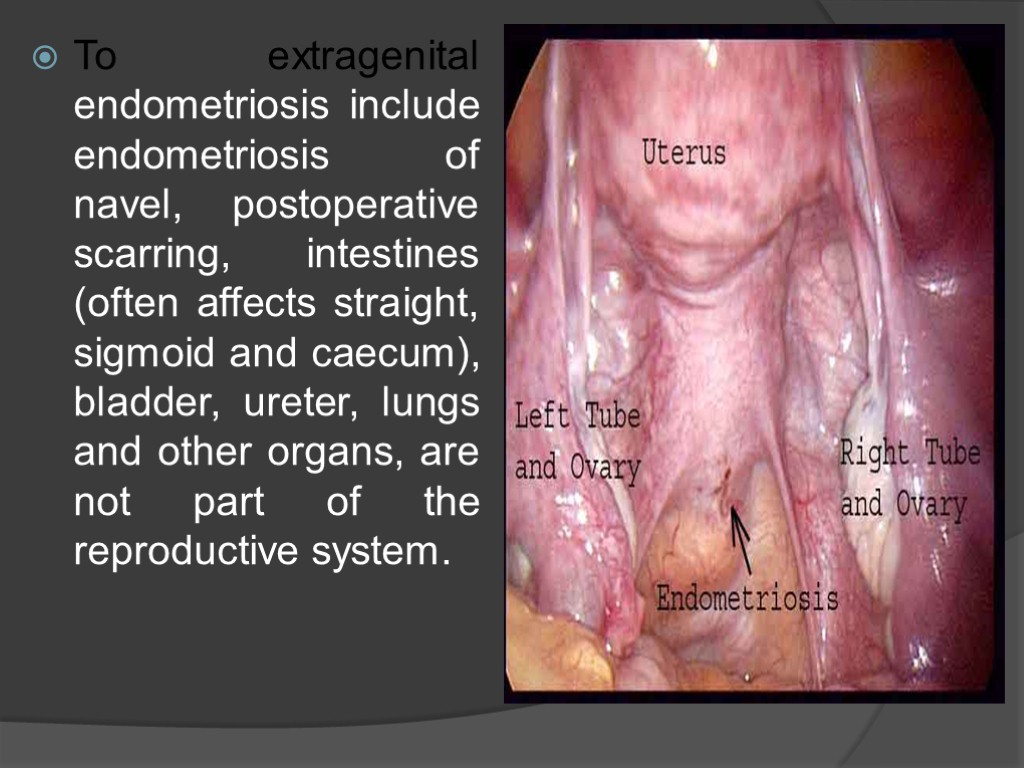 To extragenital endometriosis include endometriosis of navel, postoperative scarring, intestines (often affects straight, sigmoid and caecum), bladder, ureter, lungs and other organs, are not part of the reproductive system.
To extragenital endometriosis include endometriosis of navel, postoperative scarring, intestines (often affects straight, sigmoid and caecum), bladder, ureter, lungs and other organs, are not part of the reproductive system.
 Conclusion Endometriosis is one of the most common diseases of the reproductive system in women 20-40 years. Endometriosis occurs in 6-44 % of women with infertility and underwent laparoscopy and laparotomy . Genital endometriosis ( 92-94 %) , significantly less common extragenital endometriosis (6-8 %). Insufficient efficacy of treatment, disability and neuroticism patients, as well as infertility make possibility to consider the endometriosis as a social and state problems.
Conclusion Endometriosis is one of the most common diseases of the reproductive system in women 20-40 years. Endometriosis occurs in 6-44 % of women with infertility and underwent laparoscopy and laparotomy . Genital endometriosis ( 92-94 %) , significantly less common extragenital endometriosis (6-8 %). Insufficient efficacy of treatment, disability and neuroticism patients, as well as infertility make possibility to consider the endometriosis as a social and state problems.
 Literature www.medj.ru http://www.medichelp.ru http/allaboutgynecology.com Solovev, 2001 Razinskiy,2000
Literature www.medj.ru http://www.medichelp.ru http/allaboutgynecology.com Solovev, 2001 Razinskiy,2000