022aff6e522a0f5647efe511b7fbc89c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

Semantic Web, Web Services and Museums: Mapping the Road to Implementation John Perkins “MESMUSES Workshop” Florence, June 16 -17, 2003

The Consortium for the Interchange of Museum Information • Solutions to digital information management, access, and use through standards and international collaboration • Training & education for professional capacity building

Outline • Strategic perspective – Useful for Semantic Web research but not limited to it • Illustrative examples – Open Archives Initiative (OAI-PMH) – ABC Ontology and Model
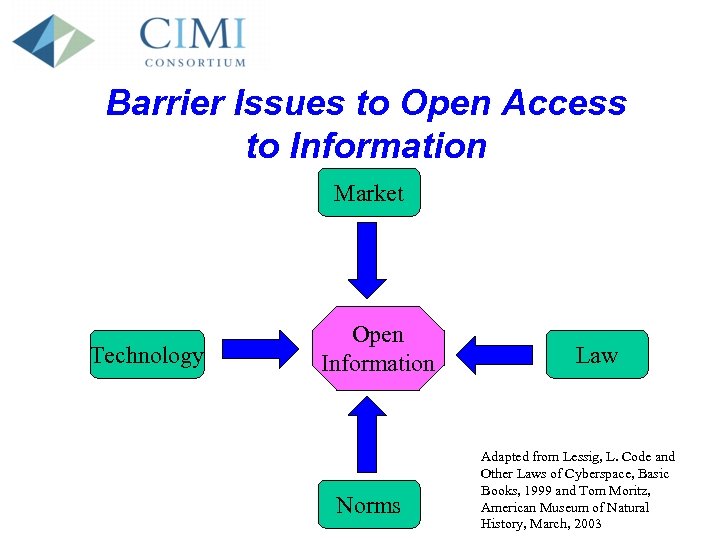
Barrier Issues to Open Access to Information Market Technology Open Information Norms Law Adapted from Lessig, L. Code and Other Laws of Cyberspace, Basic Books, 1999 and Tom Moritz, American Museum of Natural History, March, 2003
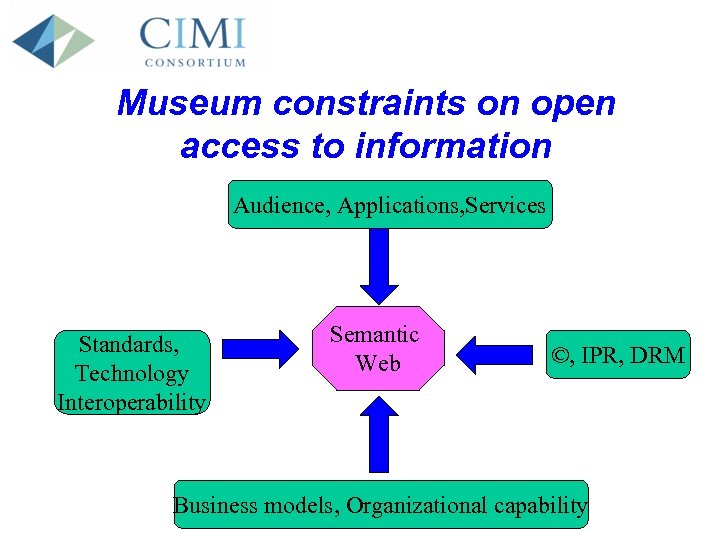
Museum constraints on open access to information Audience, Applications, Services Standards, Technology Interoperability Semantic Web ©, IPR, DRM Business models, Organizational capability

Some Strategic Responses

Audiences, Services, Applications • What do we need to know about public need for designing services to appeal to the widest possible audience? • What services are needed? • What’s needed to support services?

Audience • Collect& expose User Studies Needs and Evaluations • Develop frameworks, metrics and tools • Mine across studies • Non-Users “option values” • Cultural Content Forum & Handscape

Services • Mental models of services – Library, exhibition, exploration • Hybrid Spaces • Mediated Experience
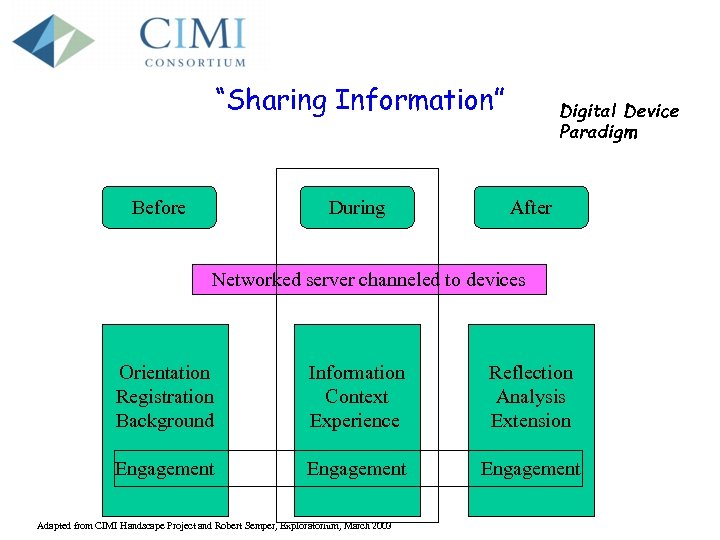
“Sharing Information” Before During Digital Device Paradigm After Networked server channeled to devices Orientation Registration Background Information Context Experience Reflection Analysis Extension Engagement Adapted from CIMI Handscape Project and Robert Semper, Exploratorium, March 2003

Applications • Applications & interfaces for both the production and delivery of services • Personalization • Communications • Sense-making

Law • • Copyright, Fair use, public access, first sale Privacy Digital Rights Management

Digital Rights Management • Digital solutions are driven by commercial purveyors of multimedia content • Middleware for authentication, authorization, tracking

Technology • High-level frameworks • Interoperability • Persistent, Recombinant Digital Repositories
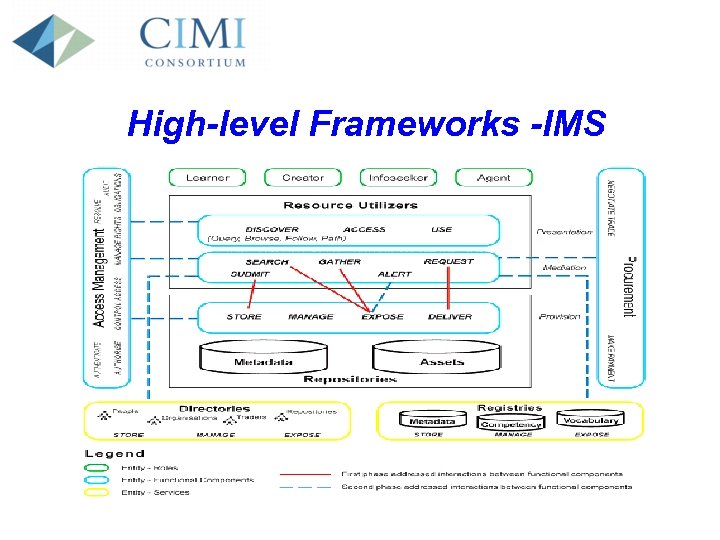
High-level Frameworks -IMS

Interoperability • Is about providing services people want • Based on “recombinant potential” – Bringing together and combining – Deconstructing resources

Recombinant Potential • Can I… – – – – Add to a repository Extract from a repository Fuse metadata from different sources Embed an interactive service in an exhibition Navigate various databases cite a resource and link to it Assemble resources into a new package …etc
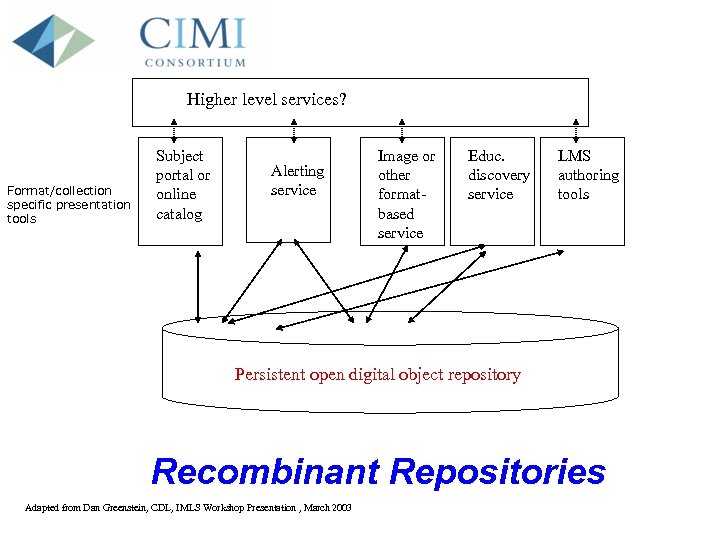
Higher level services? Format/collection specific presentation tools Subject portal or online catalog Alerting service Image or other formatbased service Educ. discovery service LMS authoring tools Persistent open digital object repository Recombinant Repositories Adapted from Dan Greenstein, CDL, IMLS Workshop Presentation , March 2003

Persistent Open Digital Repositories Need. . • • • Service models Metadata models Content package models Ontologies Tools/Infrastructure

Business Models & Organizational Capability • Organizational capability • Paying for it • Management support

Capability Needs • Standards & Good Practice • Content Management • Resources

Drawing it all together • Multiplicity of effort • Community efforts to lead & serve – Horizon scanning – Research – Capacity Building • Prototype critical path components

Semantic Web Building Blocks after W 3 C • • • HTTP XML/HTML RDF Ontologies Communities of Trust

Tactical Examples • Open Archives Initiative (OAI) • ABC Ontology & Model • “Dot” Museum - Top Level Domain

Open Archives Initiative (OAI) • Harvesting of Metadata • Generic protocol enables a service • Bindable to multiple protocols • Currently HTTP • SOAP enabled • SOAP specification in development – http: //www. cs. odu. edu/~rl/OAI_SOAP/gatewa y. html

ABC Ontology & Model • Harmony, CIMI, CIDOC • Goals – Conceptual basis for analyzing ontologies – Guidance in developing ontologies – Conceptual basis for mapping ontologies • Has basic entities common to many ontologies – IFLA’s FRBR, INDECS, DC, CIDOC/CRM

ABC Ontology & Model • Core intention is to model the creation, evolution and transition of objects over time • Development of a Query model • RDF for concrete syntax • SQUISH search engine

ABC Ontology & Model • Document at: – http: //jodi. ecs. soton. ac. uk/Articles/v 02/i 02/L agoze/

Dot Museum • Internet Top Level Domain • Forum for community of trust

CIMI Consortium • Http: //www. cimi. org • Jperkins@cimi. org
022aff6e522a0f5647efe511b7fbc89c.ppt