bdbdefdd0c77e950659fcb976ebe7fdb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47

Semantic Web Services Lightweight SWS: WSMO-Lite, Micro. WSMO Lecture X – 4 th June 2009 Dieter Fensel slides from Jacek Kopecký ©www. sti-innsbruck. at INNSBRUCK www. sti-innsbruck. at Copyright 2008 STI 1
Where are we? # Date Title 1 5 th March Introduction 2 12 th March Web Science 3 19 th March Service Science 4 26 th March Web Services (WSDL, SOAP, UDDI, XML) 5 2 nd April Web 2. 0 and RESTful services 6 23 rd April WSMO 7 30 th April WSML 8 7 th May WSMX 9 14 th May OWL S and others 10 28 th May WSMO-Lite, Micro. WSMO 11 4 th June SWS Use Cases 12 18 th June seekda: the business point of view 13 25 th June Mobile services 14 2 nd July Exam Preparation www. sti-innsbruck. at 2

Overview • Motivation • Technical solutions – WSMO Lite Service semantics – SAWSDL, WSMO Lite – h. RESTS, Micro. WSMO www. sti-innsbruck. at 3

Motivation www. sti-innsbruck. at 4

Motivation • SAWSDL – New W 3 C standard – Building on SAWSDL, URIs – Assuming RDF, OWL • Lightweight approach – WSMO modularized – Key pieces of service semantics – Simple semantic representation www. sti-innsbruck. at 5
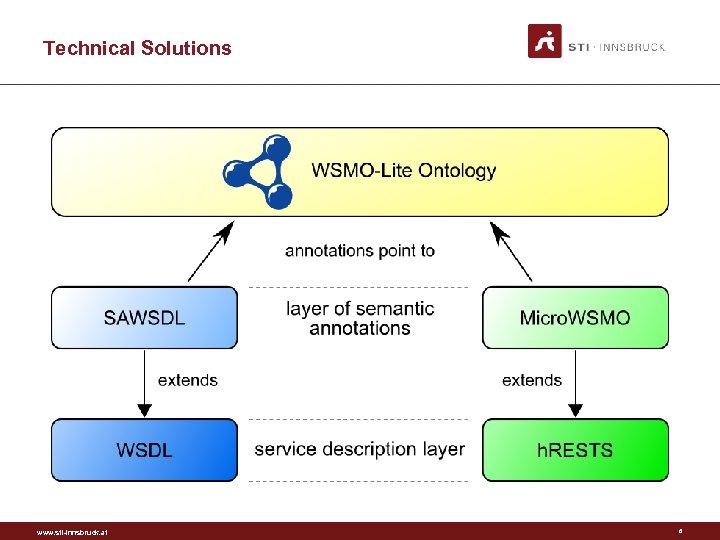
Technical Solutions www. sti-innsbruck. at 6

WSMO-Lite Ontology: Service Semantics www. sti-innsbruck. at 7

Overview • WSDL based service model • SAWSDL based annotations • Four types of semantics – Expressed in RDF(S) – Attached to the service model www. sti-innsbruck. at 8
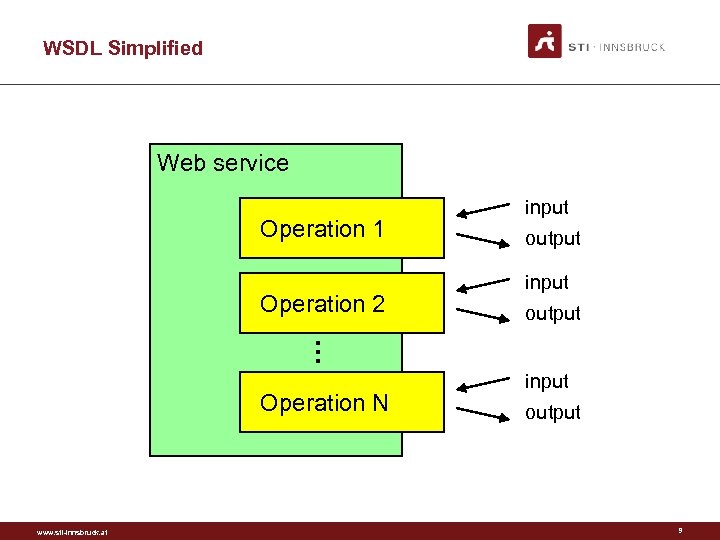
WSDL Simplified Web service Operation 1 Operation 2 . . . Operation N www. sti-innsbruck. at input output 9

Service Model in RDFS Service has. Operation has. Input. Message has. Output. Message has. Input. Fault has. Output. Fault Message www. sti-innsbruck. at a a a a rdfs: Class. rdf: Property. rdfs: Class. 10
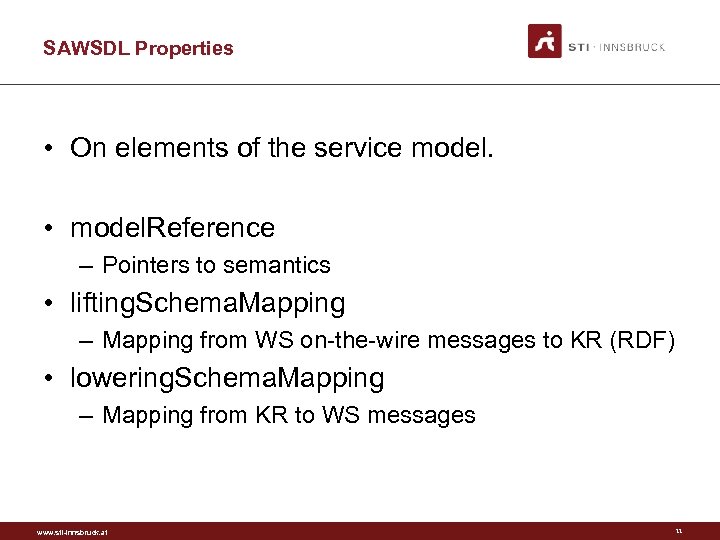
SAWSDL Properties • On elements of the service model. • model. Reference – Pointers to semantics • lifting. Schema. Mapping – Mapping from WS on the wire messages to KR (RDF) • lowering. Schema. Mapping – Mapping from KR to WS messages www. sti-innsbruck. at 11
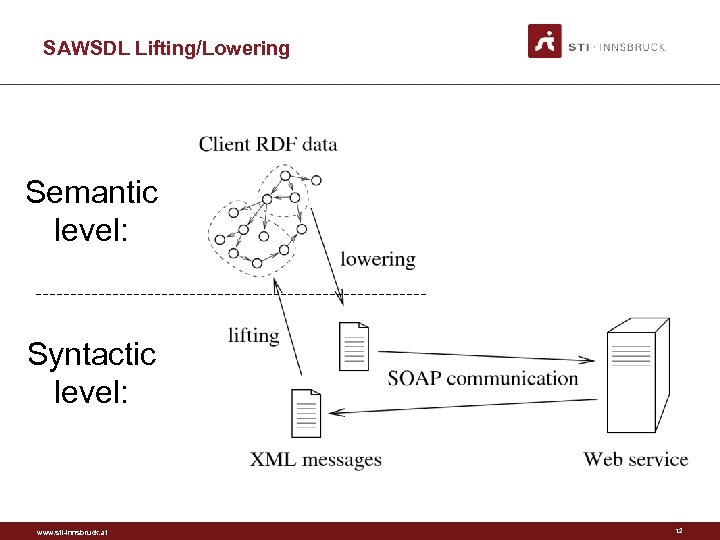
SAWSDL Lifting/Lowering Semantic level: Syntactic level: www. sti-innsbruck. at 12
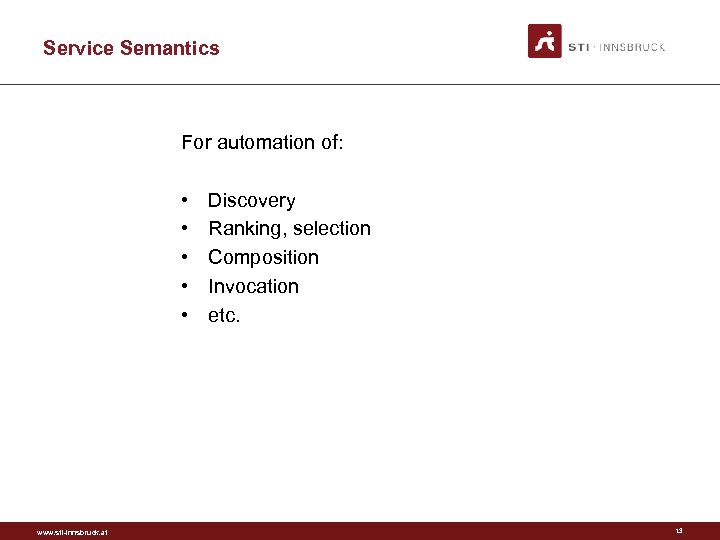
Service Semantics For automation of: • • • www. sti-innsbruck. at Discovery Ranking, selection Composition Invocation etc. 13
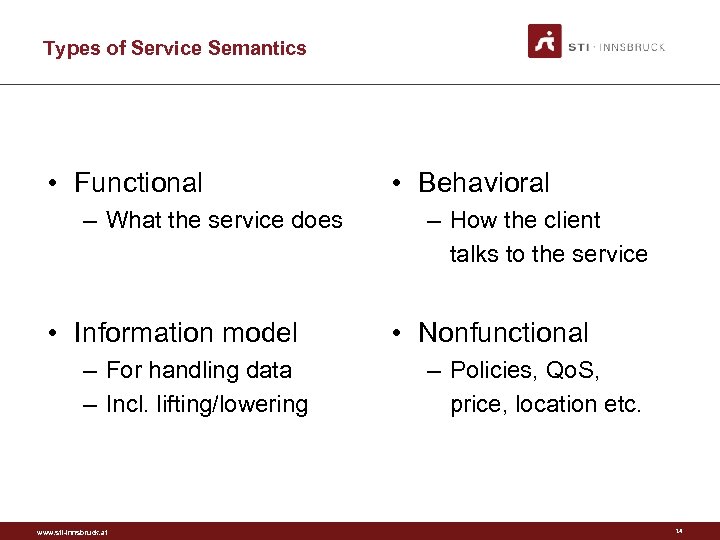
Types of Service Semantics • Functional – What the service does • Information model – For handling data – Incl. lifting/lowering www. sti-innsbruck. at • Behavioral – How the client talks to the service • Nonfunctional – Policies, Qo. S, price, location etc. 14
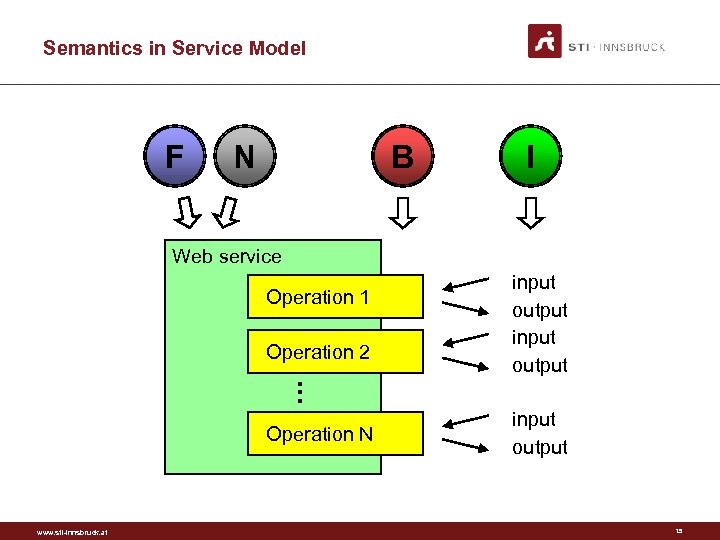
Semantics in Service Model F N B I Web service Operation 1 Operation 2 . . . Operation N www. sti-innsbruck. at input output 15

Functional Semantics • For service discovery, composition F • Category – Functionality categorization – E. g. e. Cl@ss, UDDI – Or tagging, folksonomies • Capability – Precondition, Effect – Using WSML rule languages www. sti-innsbruck. at 16
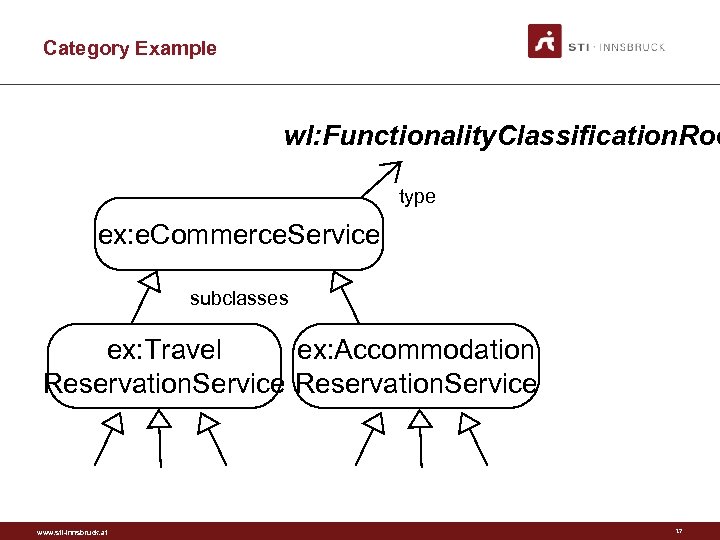
Category Example wl: Functionality. Classification. Roo type ex: e. Commerce. Service subclasses ex: Travel ex: Accommodation Reservation. Service www. sti-innsbruck. at 17

Category Example (RDF) ex: e. Commerce. Service rdf: type wl: Functionality. Classification. Root. ex: Travel. Reservation. Service rdfs: sub. Class. Of ex: e. Commerce. Service. ex: Accommodation. Reservation. Service rdfs: sub. Class. Of ex: e. Commerce. Service. … www. sti-innsbruck. at 18

Capability Example ex: Roma. Hotel. Reservation. Precondition rdf: type wl: Precondition ; rdf: value """ ? request [ number. Of. Guests has. Value ? guests and city has. Value ? city ] member. Of Reservation. Data and ? guests <= 10 and ? city = 'Roma' """^^wsml: Axiom. Literal. www. sti-innsbruck. at 19
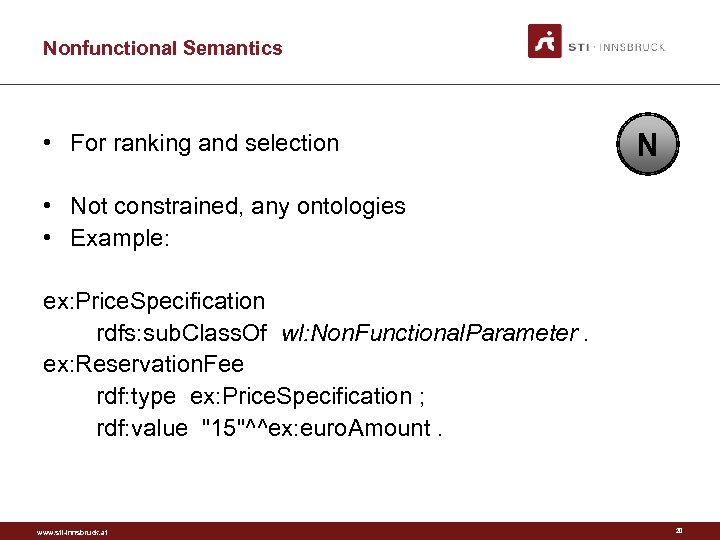
Nonfunctional Semantics • For ranking and selection N • Not constrained, any ontologies • Example: ex: Price. Specification rdfs: sub. Class. Of wl: Non. Functional. Parameter. ex: Reservation. Fee rdf: type ex: Price. Specification ; rdf: value "15"^^ex: euro. Amount. www. sti-innsbruck. at 20

Behavioral Semantics • For invocation, composition, process mediation B • Functionalities on operations – Capabilities, categories • Client selects operation to invoke next – Instead of being strictly guided by an explicit process • Example functional category for operations: Web. Arch interaction safety www. sti-innsbruck. at 21
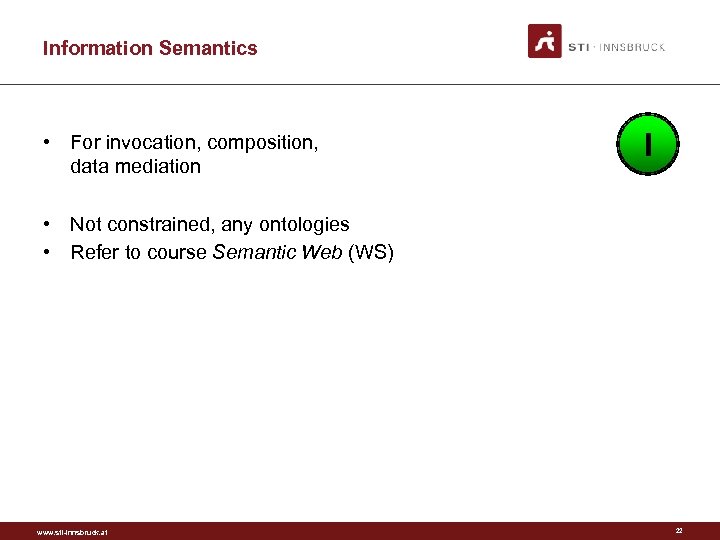
Information Semantics • For invocation, composition, data mediation I • Not constrained, any ontologies • Refer to course Semantic Web (WS) www. sti-innsbruck. at 22
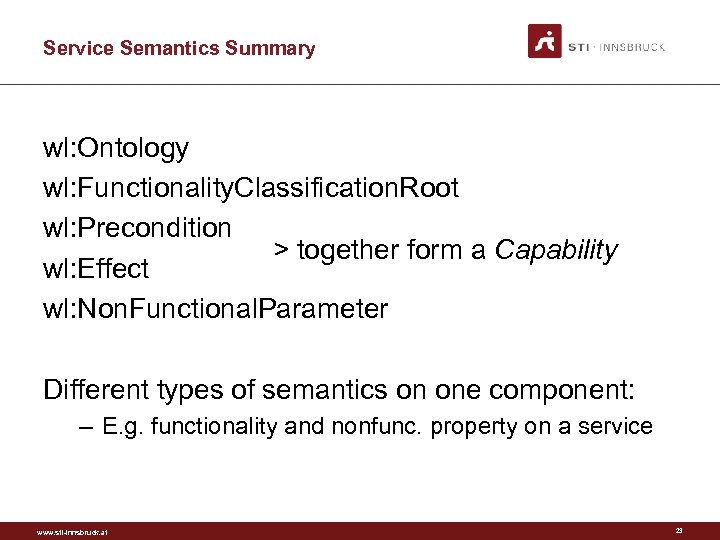
Service Semantics Summary wl: Ontology wl: Functionality. Classification. Root wl: Precondition > together form a Capability wl: Effect wl: Non. Functional. Parameter Different types of semantics on one component: – E. g. functionality and nonfunc. property on a service www. sti-innsbruck. at 23

WSMO-Lite in SAWSDL www. sti-innsbruck. at 24
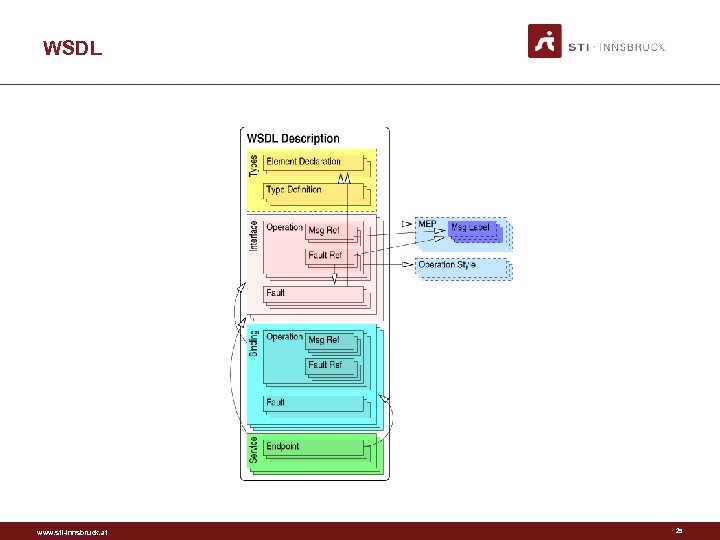
WSDL www. sti-innsbruck. at 25
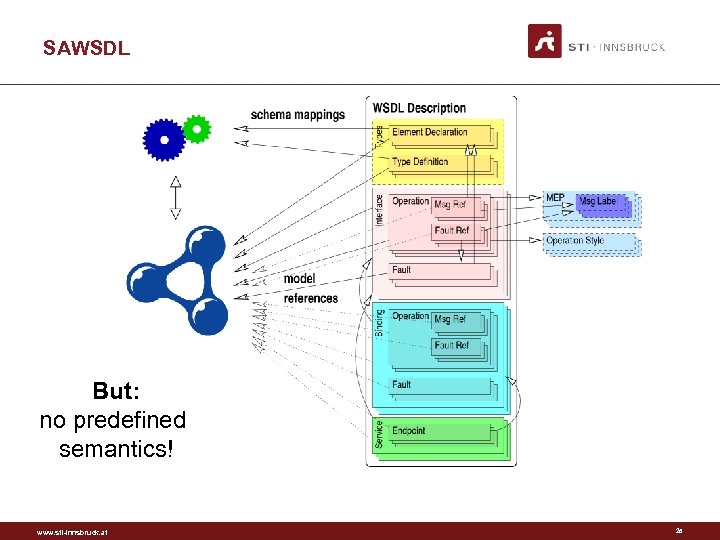
SAWSDL But: no predefined semantics! www. sti-innsbruck. at 26
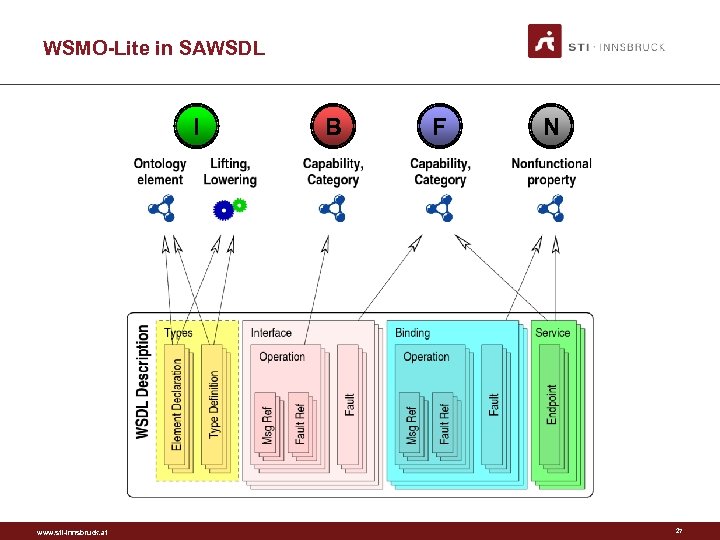
WSMO-Lite in SAWSDL I www. sti-innsbruck. at B F N 27

WSMO-Lite Example <wsdl: description> <wsdl: types> <xs: schema> <xs: element name="Reservation. Request" sawsdl: model. Reference="&ex; Reservation" sawsdl: lowering. Schema. Mapping="&ex; Res. Mapping. xsparql" … /> </xs: schema> </wsdl: types> <wsdl: interface name="Hotel. Reservations" sawsdl: model. Reference= "&ex; Accommodation. Reservation. Service"> <wsdl: operation name="search. For. Rooms" sawsdl: model. Reference="&wsdlx; Safe. Interaction"> … </wsdl: operation> … </wsdl: interface> <wsdl: service name="Roma. Hotels" interface="Hotel. Reservations" sawsdl: model. Reference="&ex; Roma. Hotel. Reservation. Precondition &ex; Reservation. Fee" … /> </wsdl: description> www. sti-innsbruck. at I I F B F N 28

h. RESTS & Micro. WSMO www. sti-innsbruck. at 29

Recap: RESTful WS • A RESTful Web service is: – A set of Web resources – Interlinked – Data centric, not functionality centric – Machine oriented www. sti-innsbruck. at 30
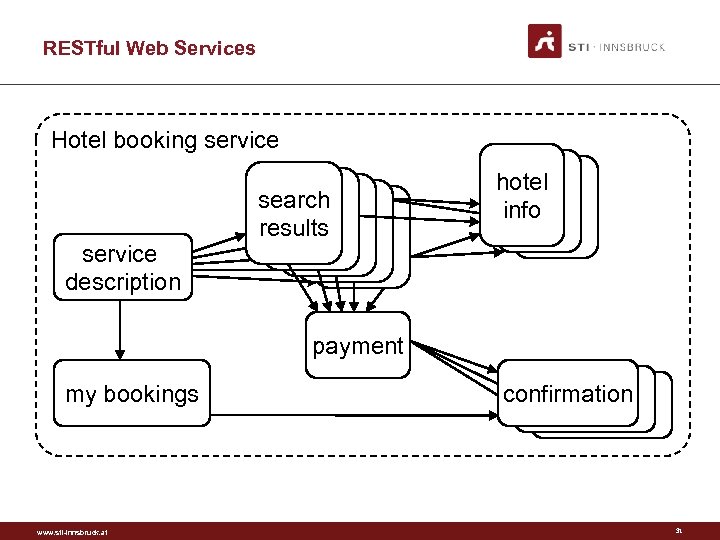
RESTful Web Services Hotel booking service description search results hotel info payment my bookings www. sti-innsbruck. at confirmation 31
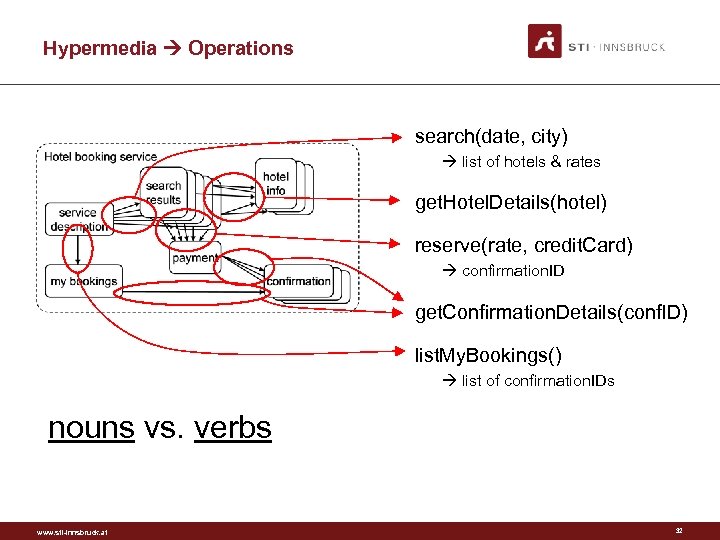
Hypermedia Operations search(date, city) list of hotels & rates get. Hotel. Details(hotel) reserve(rate, credit. Card) confirmation. ID get. Confirmation. Details(conf. ID) list. My. Bookings() list of confirmation. IDs nouns vs. verbs www. sti-innsbruck. at 32

h. RESTS • "There's usually an HTML page" – There's no WSDL for Web apps – APIs described mostly in text • Identifying machine readable parts – Service, its operations – Resource address, HTTP method – Input/output data format • h. RESTS microformat www. sti-innsbruck. at 33

Example Description of the ACME Hotels service: The operation get. Hotel. Details is invoked using the method GET at http: //example. com/h/{id}, with the ID of the particular hotel replacing the parameter id. It returns the hotel details in an ex: hotel. Information document. www. sti-innsbruck. at 34

Example HTML <p>Description of the ACME Hotels service: </p> <p> The operation <code>get. Hotel. Details</code> is invoked using the method <span>GET</span> at <code>http: //example. com/h/{id}</code>, with the ID of the particular hotel replacing the parameter <code>id</code>. It returns the hotel details in an <code>ex: hotel. Information</code> document. </p> www. sti-innsbruck. at 35

Example h. RESTS <div class="service" id="svc"> <p>Description of the <span class="label">ACME Hotels</span> service: </p> <div class="operation" id="op 1"> <p> The operation <code class="label">get. Hotel. Details</code> is invoked using the method <span class="method">GET</span> at <code class="address">http: //example. com/h/{id}</code>, with <span class="input">the ID of the particular hotel replacing the parameter <code>id</code>. </span> It returns <span class="output">the hotel details in an <code>ex: hotel. Information</code> document. </span> </p></div> www. sti-innsbruck. at 36
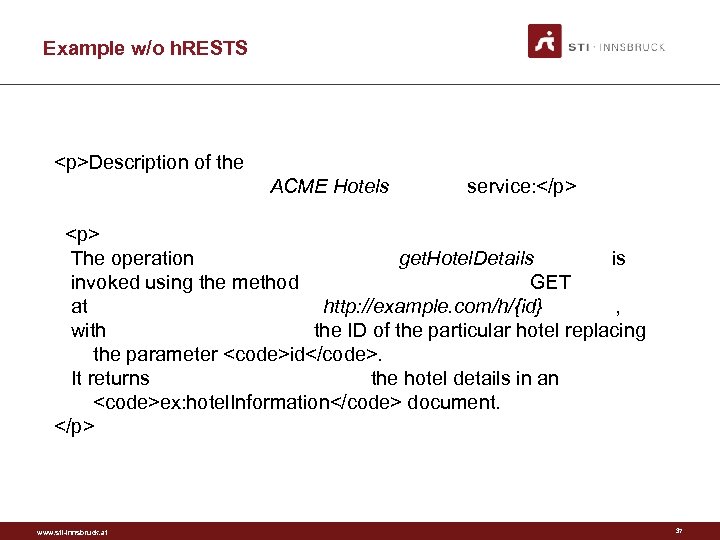
Example w/o h. RESTS <div class="service" id="svc"> <p>Description of the <span class="label">ACME Hotels</span> service: </p> <div class="operation" id="op 1"> <p> The operation <code class="label">get. Hotel. Details</code> is invoked using the method <span class="method">GET</span> at <code class="address">http: //example. com/h/{id}</code>, with <span class="input">the ID of the particular hotel replacing the parameter <code>id</code>. </span> It returns <span class="output">the hotel details in an <code>ex: hotel. Information</code> document. </span> </p></div> www. sti-innsbruck. at 37
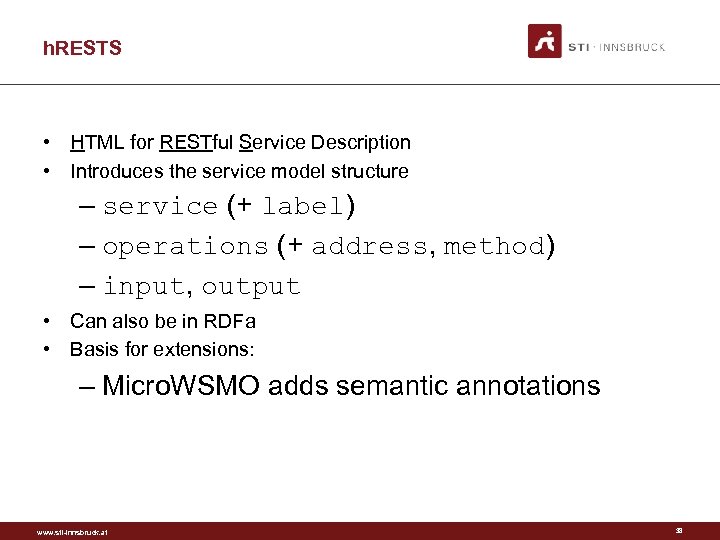
h. RESTS • HTML for RESTful Service Description • Introduces the service model structure – service (+ label) – operations (+ address, method) – input, output • Can also be in RDFa • Basis for extensions: – Micro. WSMO adds semantic annotations www. sti-innsbruck. at 38

Micro. WSMO • Extends h. RESTS – model for model references – lifting, lowering • Applies WSMO Lite semantics www. sti-innsbruck. at 39

Micro. WSMO <div class="service" id="svc"> <p><span class="label">ACME Hotels</span> is a <a rel="model" href="…/ecommerce/hotel. Reservation"> hotel reservation</a> service. </p> … <div class="operation" id="op 1"><p> … <span class="input">A particular hotel ID replaces the param <a rel="model" href="…/onto. owl#Hotel"><code>id</code></a> (<a rel="lowering" href="…/hotel. ID. xslt">lowering</a>). </span>. … </p></div> www. sti-innsbruck. at 40

Semantics Implied in Web • Hypermedia behavioral semantics – Links become available through interaction • Uniform interface functional semantics – GET, PUT, DELETE have known effects – GET is safe, PUT and DELETE idempotent • Self description information model – Operation output data can specify what it is • GRDDL, other semantic annotations www. sti-innsbruck. at 41

Conclusions www. sti-innsbruck. at 42

Conclusions • Building on SAWSDL – Both for WS-* and RESTful services • Bottom-up annotations – Based on tech already known by WS people • Modular descriptions – Only use what you need www. sti-innsbruck. at 43

Further Developments • Adding WSMO Lite and Micro. WSMO support to WSMX • Tool support for service annotation • Standardization of WSMO Lite www. sti-innsbruck. at 44

References • SAWSDL: http: //w 3. org/TR/sawsdl • WSMO Lite: http: //cms wg. sti 2. org/TR/d 11 • h. RESTS & Micro. WSMO: http: //cms wg. sti 2. org/TR/d 12 • RDF: http: //w 3. org/TR/rdf primer • RDFS: http: //w 3. org/TR/rdf schema • REST: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/REST – Includes RESTful Web services • e. Cl@ss: http: //www. eclass online. com www. sti-innsbruck. at 45
Next Lecture # Date Title 1 5 th March Introduction 2 12 th March Web Science 3 19 th March Service Science 4 26 th March Web Services (WSDL, SOAP, UDDI, XML) 5 2 nd April Web 2. 0 and RESTful services 6 23 rd April WSMO 7 30 th April WSML 8 7 th May WSMX 9 14 th May OWL S and others 10 28 th May WSMO Lite, Micro. WSMO 11 4 th June SWS Use Cases 12 18 th June seekda: the business point of view 13 25 th June Mobile services 14 2 nd July Exam Preparation www. sti-innsbruck. at 46

Questions? www. sti-innsbruck. at 47
bdbdefdd0c77e950659fcb976ebe7fdb.ppt