5ff1935020e6515bdbece95b96d3ff76.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 82

Semantic Web Services John Domingue and David Martin

Acknowledgements • • Mary Rowlatt Leticia Gutierrez Michael Stollberg Liliana Cabral Vlad Tanasescu Alessio Gugliotta WSMO Working Group • DIP project • • • OWL-S Coalition Sheila Mc. Ilraith Terry Payne Task Computing project Ryusuke Masuoka Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

Web Services John Domingue

What’s a Web Service? • A programmatically accessible over standard internet protocols • Loosely coupled, reusable components • Encapsulate discrete functionality • Distributed • Add new level of functionality on top of the current web Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
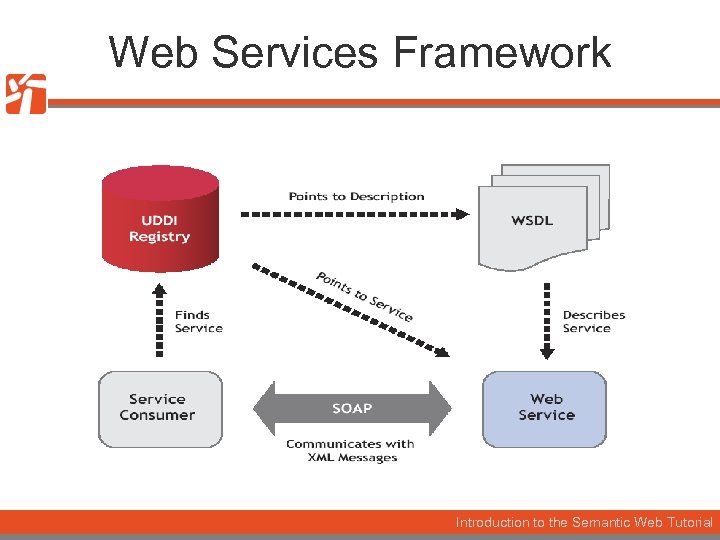
Web Services Framework Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

Problems with Web Services Today • Descriptions are syntactic • All tasks associated with web services application development have to be carried out by humans: – discovery, composition and invocation • Problems of scalability Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

Semantic Web Services John Domingue
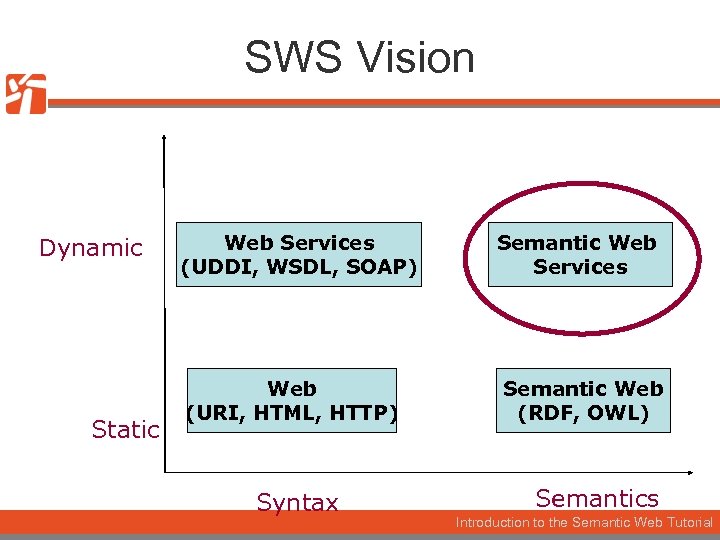
SWS Vision Dynamic Static Web Services (UDDI, WSDL, SOAP) Web (URI, HTML, HTTP) Syntax Semantic Web Services Semantic Web (RDF, OWL) Semantics Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
Semantic Web Services (is) • Semantic Web Technology – Machine readable data – Ontological basis Applied to • Web Services Technology – Reusable computational resources To automate all aspects of application development through reuse Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
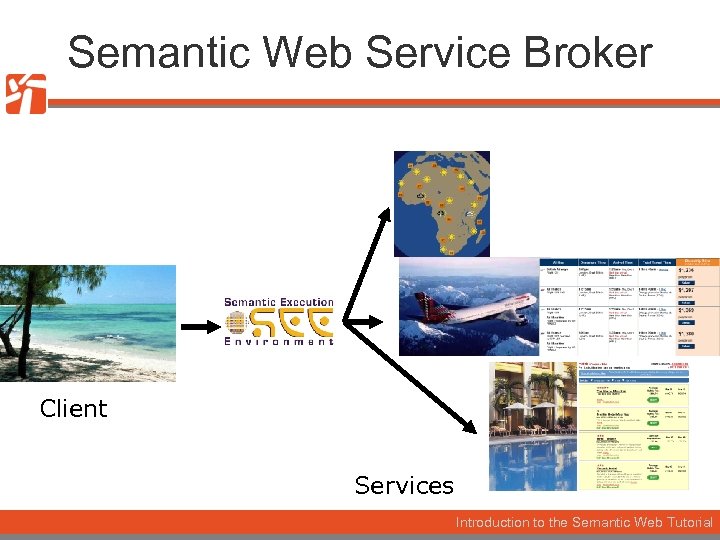
Semantic Web Service Broker Client Services Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

OWL-S David Martin

Some Active SWS Research Areas • Language, vocabulary & reasoning approaches for – – Preconditions & effects Policies Commitments Quality of Service • Discovery & selection (matchmaking) • Composition, workflow / choreography adaptation – Interoperability analysis • Resource & transaction management – Monitoring & recovery • Service use with mobile / ubiquitous devices – Context • Security • Tools & Environments – (Semi-)automatic annotation Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

What is OWL-S? • Ontology Web Language for Services • An OWL ontology/language for (formally) describing properties and capabilities of Web services • An approach that draws on many sources • Description logic • AI planning • Workflow • Formal process modeling • Agents • Web services http: //www. daml. org/services/owl-s Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
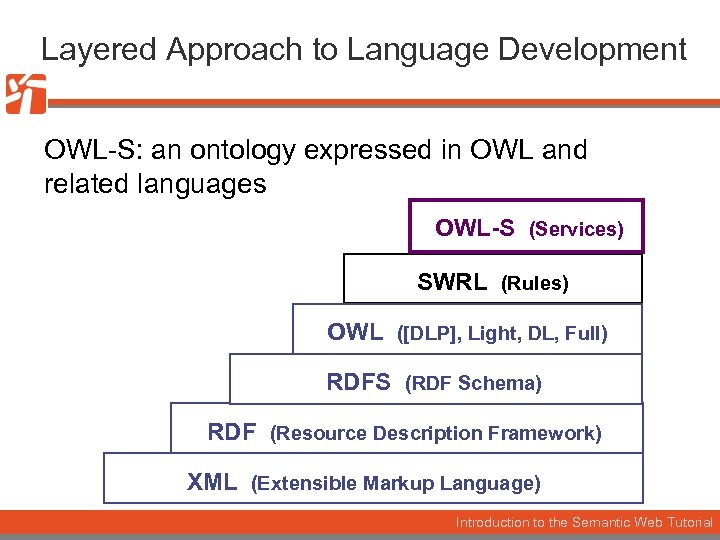
Layered Approach to Language Development OWL-S: an ontology expressed in OWL and related languages OWL-S (Services) SWRL (Rules) OWL ([DLP], Light, DL, Full) RDFS (RDF Schema) RDF (Resource Description Framework) XML (Extensible Markup Language) Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
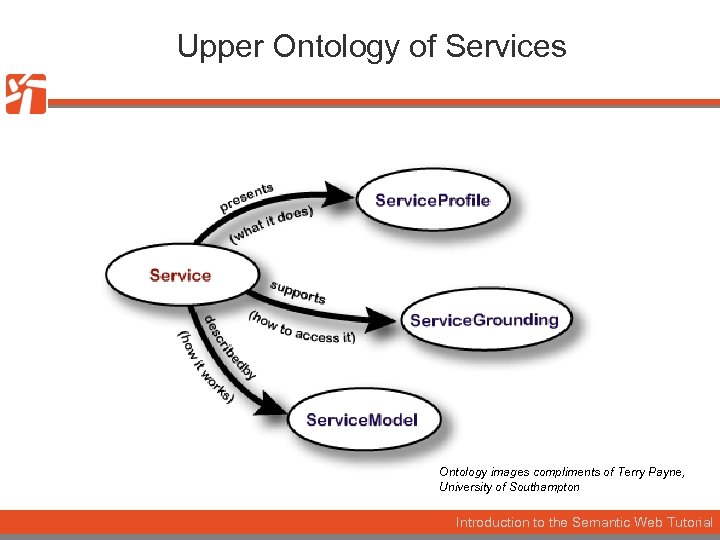
Upper Ontology of Services Ontology images compliments of Terry Payne, University of Southampton Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

Service Profile: “What does it do? ” High-level characterization/summary of a service Used for • Populating service registries • A service can have many profiles • Possibly specialized for different communities • Automated service discovery • Service selection Used for both: • Service advertisements • Service requests Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
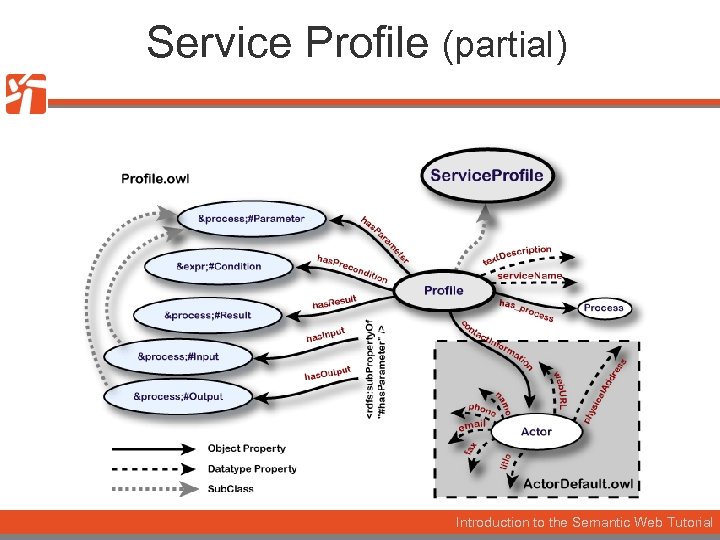
Service Profile (partial) Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
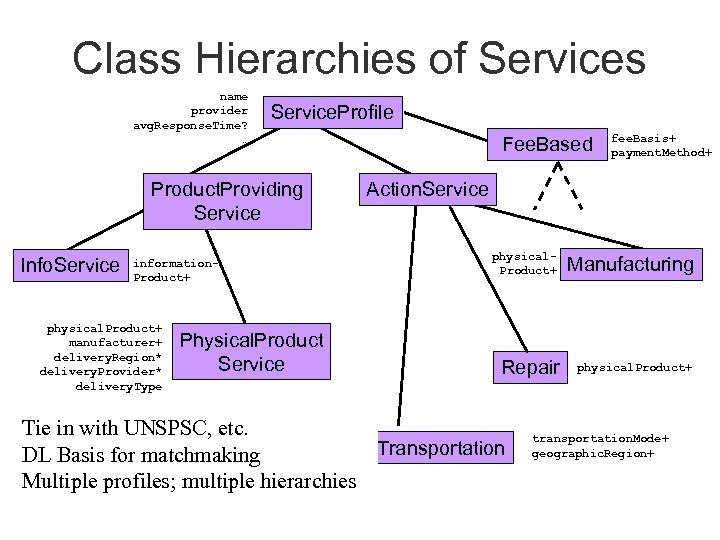
Class Hierarchies of Services name provider avg. Response. Time? … Service. Profile Product. Providing Service Info. Service information. Product+ physical. Product+ manufacturer+ delivery. Region* delivery. Provider* delivery. Type Physical. Product Service Fee. Based fee. Basis+ payment. Method+ Action. Service physical. Product+ Manufacturing Repair physical. Product+ Tie in with UNSPSC, etc. Transportation DL Basis for matchmaking Multiple profiles; multiple hierarchies transportation. Mode+ geographic. Region+

Service Profile: Styles of use • Class hierarchical yellow pages – – Implicit capability characterization Arrangement of attributes on class hierarchy Can use multiple inheritance Relies primarily on “non-functional” properties • Process summaries for planning purposes – – – More explicit Inputs, outputs, preconditions, effects Less reliance on formal hierarchical organization Summarizes process model specs Relies primarily on functional description Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
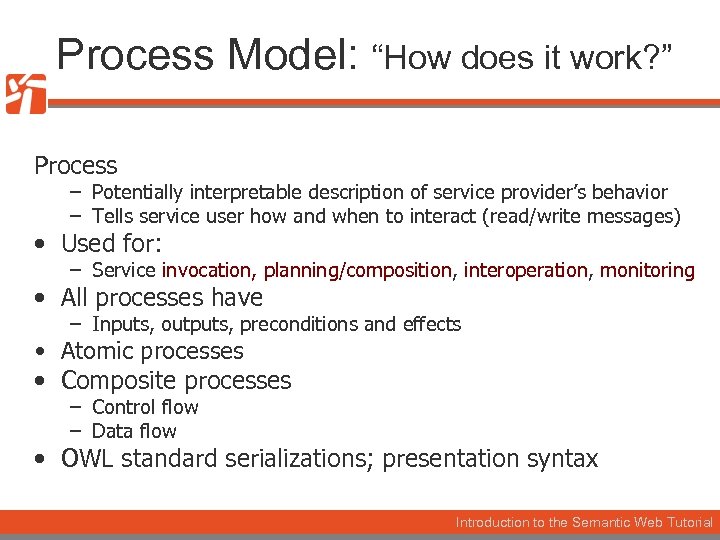
Process. Service Model it work? ” Model: “How does it work? ” Process – Potentially interpretable description of service provider’s behavior – Tells service user how and when to interact (read/write messages) • Used for: – Service invocation, planning/composition, interoperation, monitoring • All processes have – Inputs, outputs, preconditions and effects • Atomic processes • Composite processes – Control flow – Data flow • OWL standard serializations; presentation syntax Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
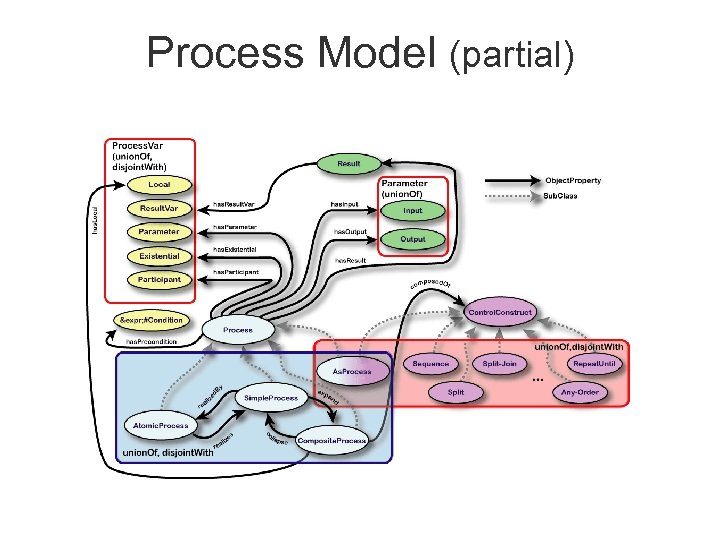
Process Model (partial)
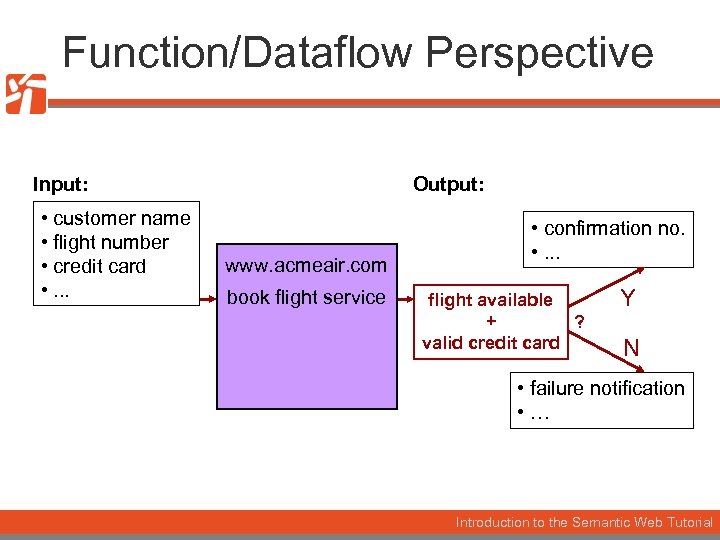
Function/Dataflow Perspective Input: • customer name • flight number • credit card • . . . Output: www. acmeair. com book flight service • confirmation no. • . . . flight available + ? valid credit card Y N • failure notification • … Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
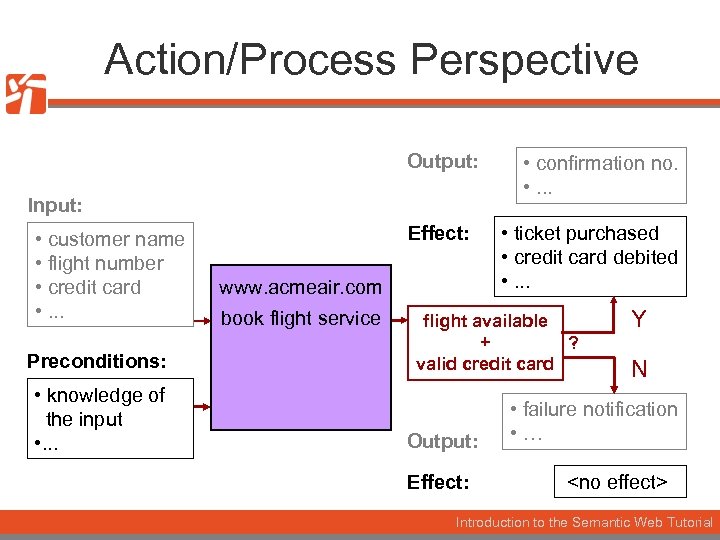
Action/Process Perspective Output: Input: • customer name • flight number • credit card • . . . Preconditions: • knowledge of the input • . . . Effect: www. acmeair. com book flight service • confirmation no. • . . . • ticket purchased • credit card debited • . . . flight available + ? valid credit card Output: Effect: Y N • failure notification • … <no effect> Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
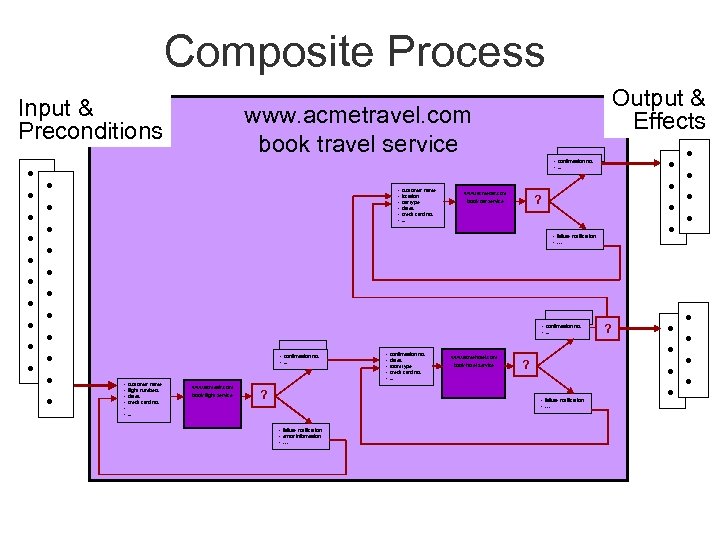
Composite Process Input & Preconditions • • • Output & Effects www. acmetravel. com book travel service • • • confirmation no. • . . . • • • customer name • location • car type • dates • credit card no. • . . . www. acmecar. com ? book car service • failure notification • … • confirmation no. • . . . • customer name • flight numbers • dates • credit card no. • • . . . www. acmeair. com book flight service ? • confirmation no. • dates • room type • credit card no. • . . . www. acmehotel. com book hotel service ? • failure notification • … • failure notification • errror information • … ? • •

Service Grounding: “How to access it” • Implementation specific • Message formatting, transport mechanisms, protocols, serializations of types • Service Model + Grounding give everything needed for using the service • Builds upon WSDL Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
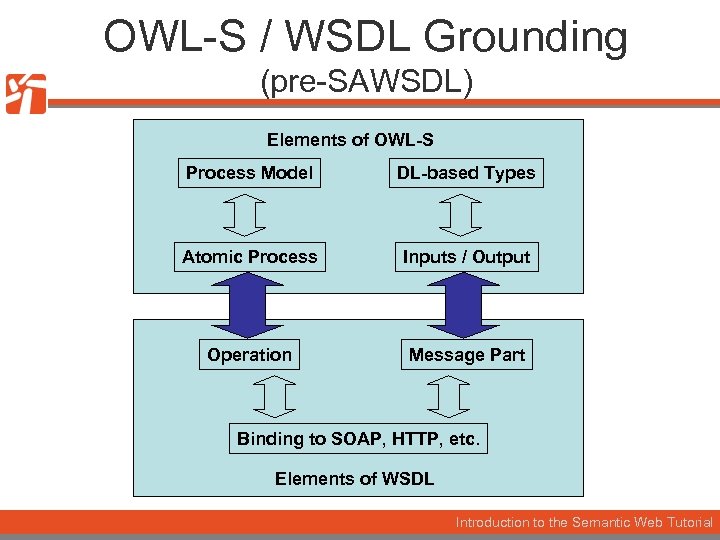
OWL-S / WSDL Grounding (pre-SAWSDL) Elements of OWL-S Process Model DL-based Types Atomic Process Inputs / Output Operation Message Part Binding to SOAP, HTTP, etc. Elements of WSDL Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
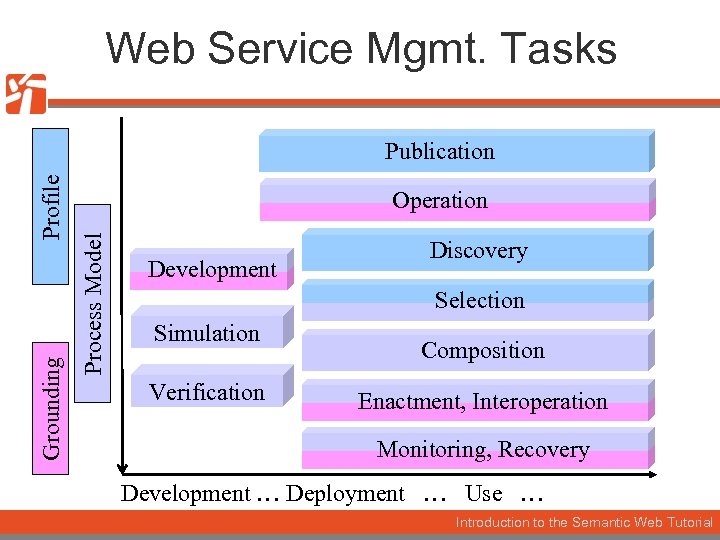
Web Service Mgmt. Tasks Operation Process Model Grounding Profile Publication Development Discovery Selection Simulation Verification Composition Enactment, Interoperation Monitoring, Recovery Development … Deployment … Use … Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

OWL-S: Summary & Status • Describes “what it does”, “how it works”, “how to access it” – Profile, Process, Grounding subontologies • Ties in naturally with WSDL, UDDI • Additional semantics supports – Automation of various Web service tasks – Varied applications (later slides) • W 3 C member submission – http: //www. w 3. org/Submission/2004/07/ – Corresponds to 1. 1 release on daml. org • 1. 2 release completed • Publications, tools, examples – See http; //www. daml. org/services/owl-s/ – See http: //www. semwebcentral. org Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

SWS at ISWC • Service Matchmaking & Resource Retrieval on the Semantic Web (SMR 2) – 2 nd workshop, tomorrow • Semantic Web Services Challenge – 7 th workshop, today • Semantic Web Enabled Software Engineering (SWESE) – 4 th workshop, today • Research track sessions – “Software and Service Engineering”, Tuesday – “Semantic Web Services”, Thursday • In Use track session – “Services and Infrastructure”, Tuesday • “Internet of Services” (Industry talk), Wednesday • Many workshops and tutorials at previous ISWCs (and other conferences such as WWW & ESWC) Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

Applications Using OWL-S • Many examples, including – Task Computing – Software Interoperability – e-Science – Geospatial Data / Query Integration – Autonomous Vehicles Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

Application: Task Computing Technology to enable easy orchestration of devices and e-services, and support users in executing complex tasks Fujitsu Laboratories of America, Inc. MINDLab of the University of Maryland http: //www. taskcomputing. org Thanks to Ryusuke Masuoka for use of this material Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

Goals of Task Computing • Minimize/facilitate user interaction – User interface: mouse clicks and voice • Focus on What (task) instead of How (means) • No preprogramming of devices for tasks User wants to do “Tasks” Filling the gap “Services” offered means Web services, UPn. P, etc. Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
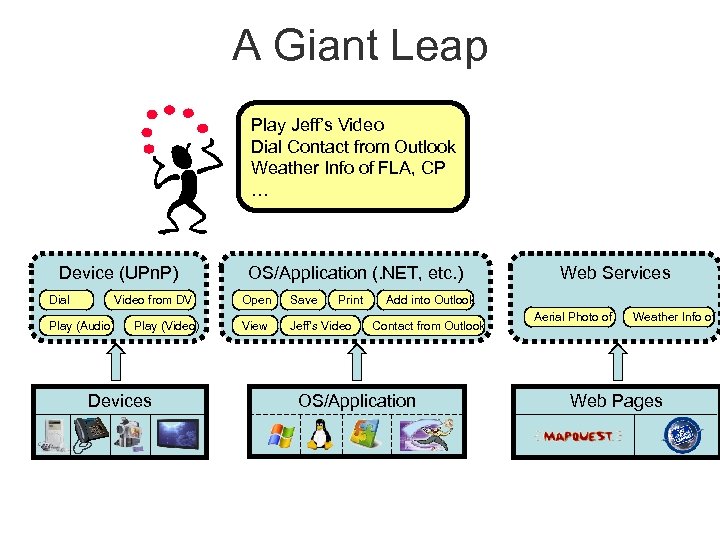
A Giant Leap Play Jeff’s Video Dial Contact from Outlook Weather Info of FLA, CP … Device (UPn. P) Dial Video from DV Play (Audio) Play (Video) Devices OS/Application (. NET, etc. ) Open Save Print View Jeff’s Video Web Services Add into Outlook Contact from Outlook OS/Application Aerial Photo of Weather Info of Web Pages
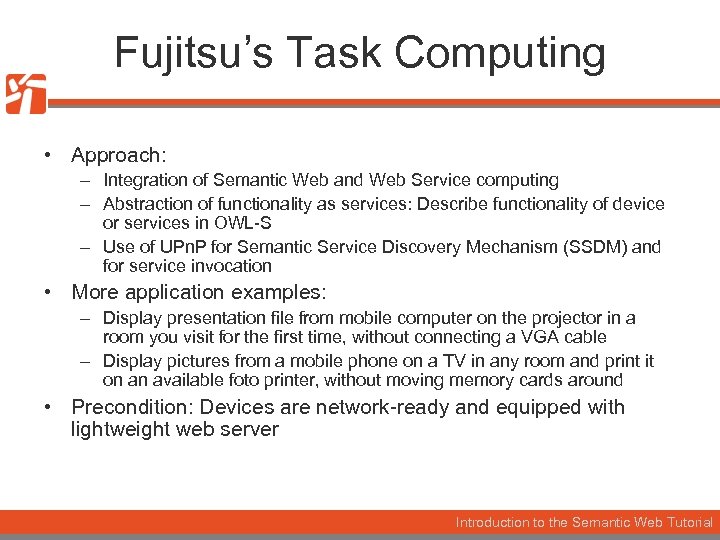
Fujitsu’s Task Computing • Approach: – Integration of Semantic Web and Web Service computing – Abstraction of functionality as services: Describe functionality of device or services in OWL-S – Use of UPn. P for Semantic Service Discovery Mechanism (SSDM) and for service invocation • More application examples: – Display presentation file from mobile computer on the projector in a room you visit for the first time, without connecting a VGA cable – Display pictures from a mobile phone on a TV in any room and print it on an available foto printer, without moving memory cards around • Precondition: Devices are network-ready and equipped with lightweight web server Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
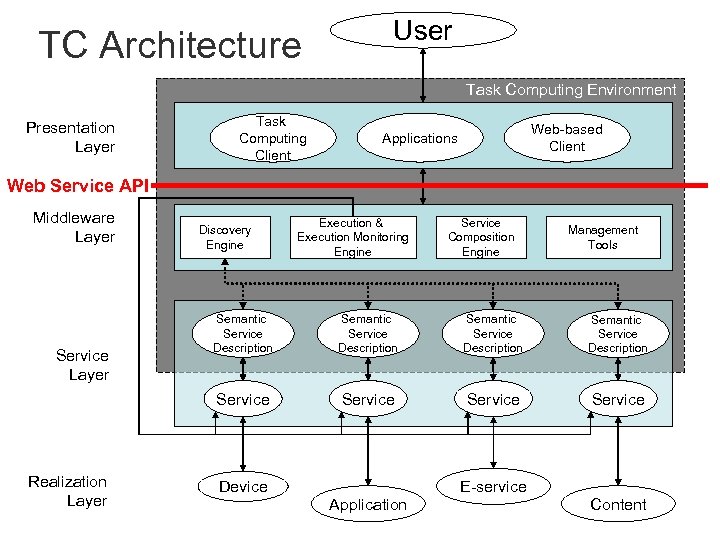
TC Architecture User Task Computing Environment Presentation Layer Task Computing Client Web-based Client Applications Web Service API Middleware Layer Discovery Engine Execution & Execution Monitoring Engine Service Composition Engine Management Tools Realization Layer Semantic Service Description Service Layer Semantic Service Description Service Device Application E-service Content
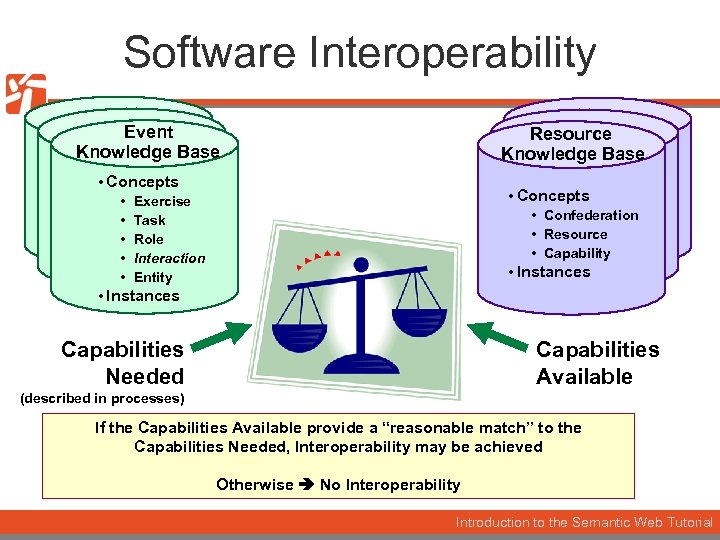
Software Interoperability Event Knowledge Base Resource Knowledge Base • Concepts • • • Concepts Exercise Task Role Interaction Entity • Confederation • Resource • Capability • Instances Capabilities Needed Capabilities Available (described in processes) If the Capabilities Available provide a “reasonable match” to the Capabilities Needed, Interoperability may be achieved Otherwise No Interoperability Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
E-Science 12181 acatttctac caacagtgga tgaggttgtt ggtctatgtt ctcaccaaat ttggtgttgt 12241 cagtctttta aattttaacc tttagagaag agtcatacag tcaatagcct tttttagctt 12301 gaccatccta atagatacac agtggtgtct cactgtgatt ttaatttgca ttttcctgct 12361 gactaattat gttgagcttg ttaccattta gacaacttca ttagagaagt gtctaatatt 12421 taggtgactt gcctgtttttaattgg Courtesy of Carol Goble Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
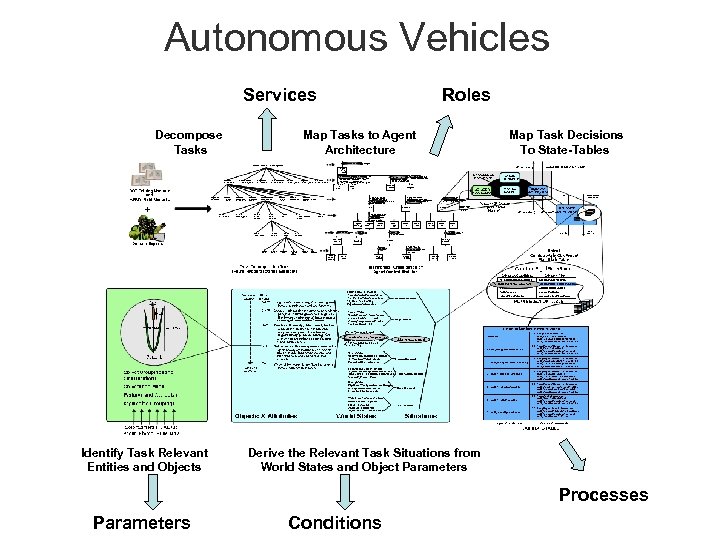
Autonomous Vehicles Services Decompose Tasks Identify Task Relevant Entities and Objects Roles Map Tasks to Agent Architecture Map Task Decisions To State-Tables Derive the Relevant Task Situations from World States and Object Parameters Processes Parameters Conditions

Web Service Modelling Ontology (WSMO) John Domingue
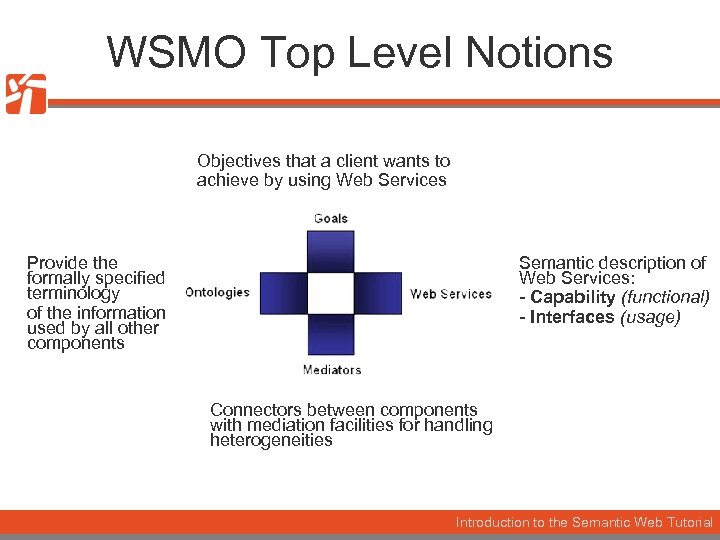
WSMO Top Level Notions Objectives that a client wants to achieve by using Web Services Provide the formally specified terminology of the information used by all other components Semantic description of Web Services: - Capability (functional) - Interfaces (usage) Connectors between components with mediation facilities for handling heterogeneities Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
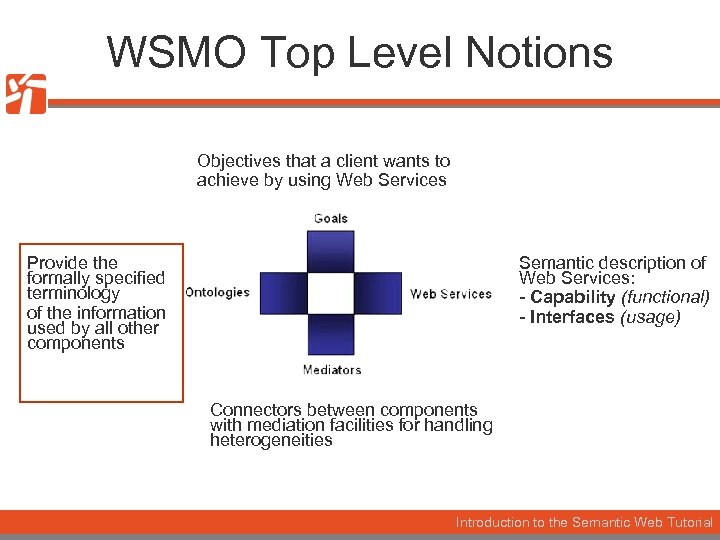
WSMO Top Level Notions Objectives that a client wants to achieve by using Web Services Provide the formally specified terminology of the information used by all other components Semantic description of Web Services: - Capability (functional) - Interfaces (usage) Connectors between components with mediation facilities for handling heterogeneities Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
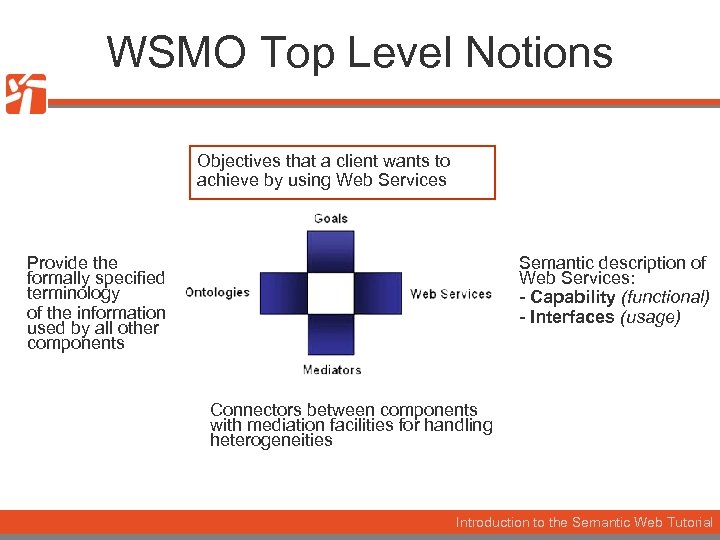
WSMO Top Level Notions Objectives that a client wants to achieve by using Web Services Provide the formally specified terminology of the information used by all other components Semantic description of Web Services: - Capability (functional) - Interfaces (usage) Connectors between components with mediation facilities for handling heterogeneities Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

Goals • Ontological De-coupling of Requester and Provider • Derived from task / problem solving methods/domain model • Structure and reuse of requests – – – Search Diagnose Classify Personalise Book a holiday • Requests may in principle not be satisfiable • Ontological relationships & mediators used to link goals to web services Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
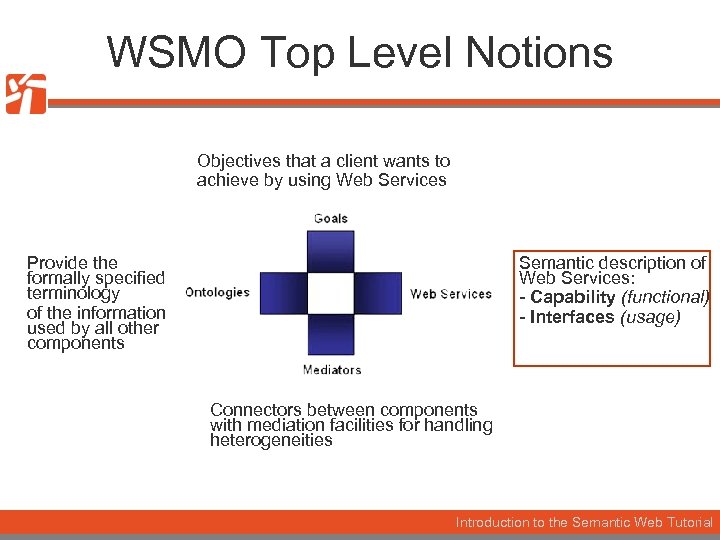
WSMO Top Level Notions Objectives that a client wants to achieve by using Web Services Provide the formally specified terminology of the information used by all other components Semantic description of Web Services: - Capability (functional) - Interfaces (usage) Connectors between components with mediation facilities for handling heterogeneities Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
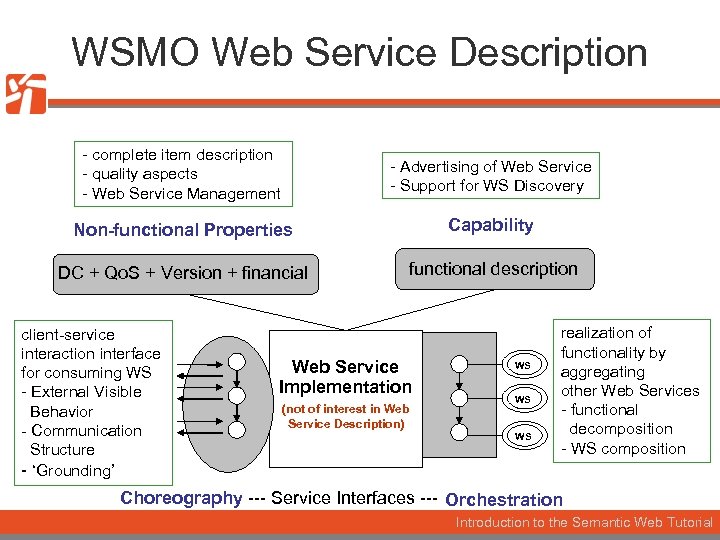
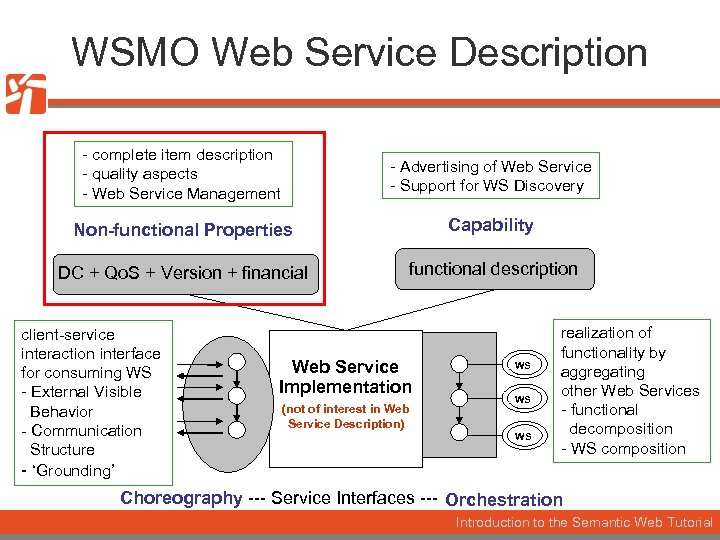
WSMO Web Service Description - complete item description - quality aspects - Web Service Management - Advertising of Web Service - Support for WS Discovery Non-functional Properties Capability DC + Qo. S + Version + financial functional description client-service interaction interface for consuming WS - External Visible Behavior - Communication Structure - ‘Grounding’ Web Service Implementation (not of interest in Web Service Description) WS WS WS realization of functionality by aggregating other Web Services - functional decomposition - WS composition Choreography --- Service Interfaces --- Orchestration Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
WSMO Web Service Description - complete item description - quality aspects - Web Service Management - Advertising of Web Service - Support for WS Discovery Non-functional Properties Capability DC + Qo. S + Version + financial functional description client-service interaction interface for consuming WS - External Visible Behavior - Communication Structure - ‘Grounding’ Web Service Implementation (not of interest in Web Service Description) WS WS WS realization of functionality by aggregating other Web Services - functional decomposition - WS composition Choreography --- Service Interfaces --- Orchestration Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
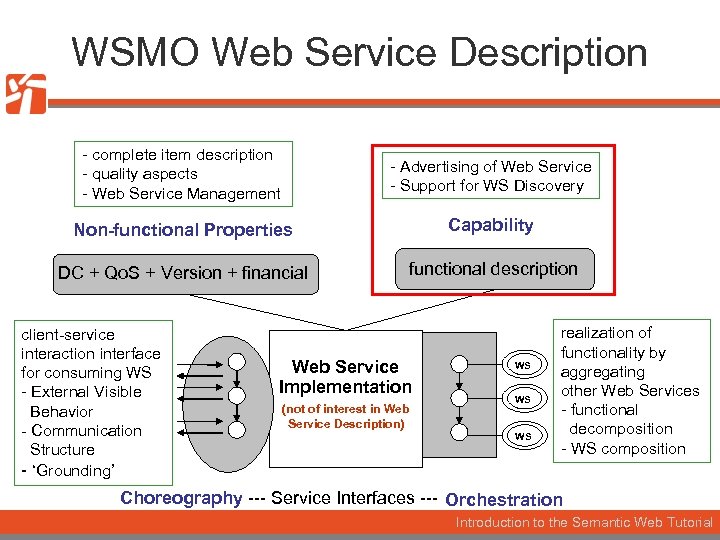
WSMO Web Service Description - complete item description - quality aspects - Web Service Management - Advertising of Web Service - Support for WS Discovery Non-functional Properties Capability DC + Qo. S + Version + financial functional description client-service interaction interface for consuming WS - External Visible Behavior - Communication Structure - ‘Grounding’ Web Service Implementation (not of interest in Web Service Description) WS WS WS realization of functionality by aggregating other Web Services - functional decomposition - WS composition Choreography --- Service Interfaces --- Orchestration Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
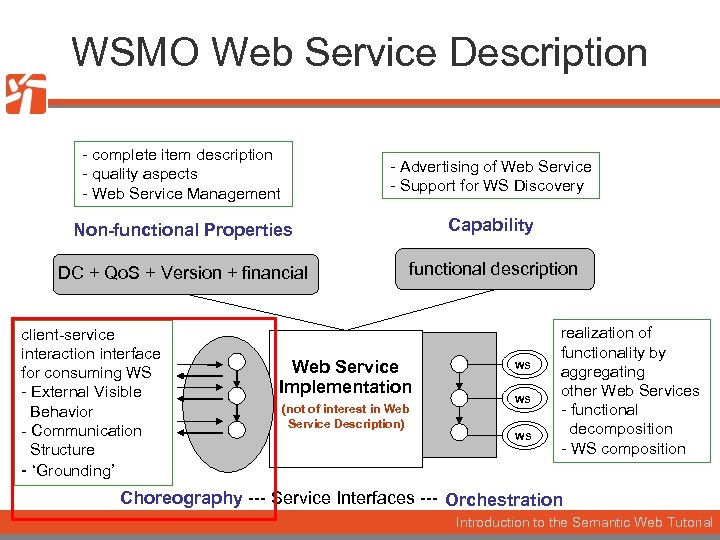
WSMO Web Service Description - complete item description - quality aspects - Web Service Management - Advertising of Web Service - Support for WS Discovery Non-functional Properties Capability DC + Qo. S + Version + financial functional description client-service interaction interface for consuming WS - External Visible Behavior - Communication Structure - ‘Grounding’ Web Service Implementation (not of interest in Web Service Description) WS WS WS realization of functionality by aggregating other Web Services - functional decomposition - WS composition Choreography --- Service Interfaces --- Orchestration Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
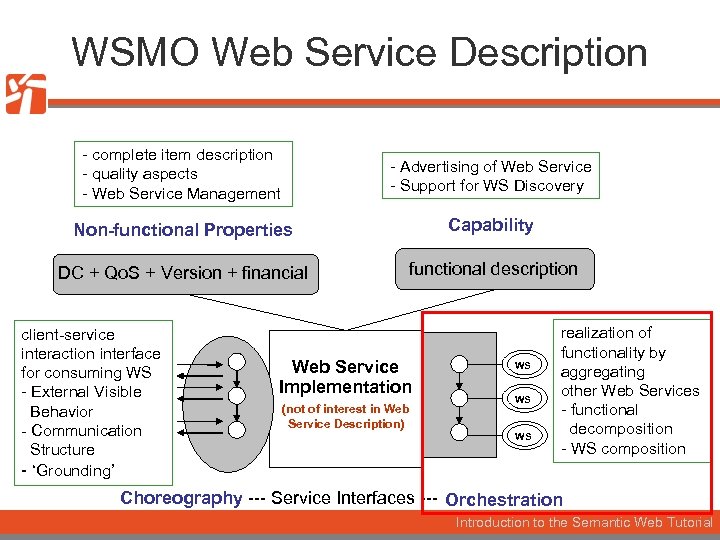
WSMO Web Service Description - complete item description - quality aspects - Web Service Management - Advertising of Web Service - Support for WS Discovery Non-functional Properties Capability DC + Qo. S + Version + financial functional description client-service interaction interface for consuming WS - External Visible Behavior - Communication Structure - ‘Grounding’ Web Service Implementation (not of interest in Web Service Description) WS WS WS realization of functionality by aggregating other Web Services - functional decomposition - WS composition Choreography --- Service Interfaces --- Orchestration Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
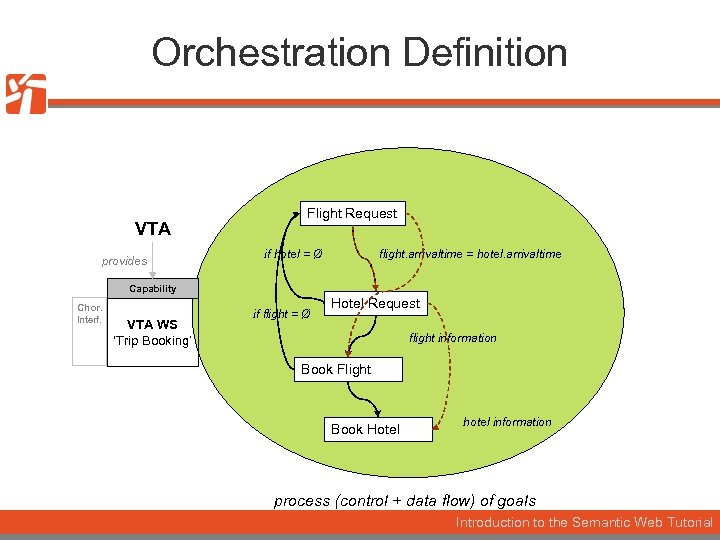
Orchestration Definition VTA provides Flight Request if hotel = Ø flight. arrivaltime = hotel. arrivaltime Capability Chor. Interf. VTA WS ‘Trip Booking’ if flight = Ø Hotel Request flight information Book Flight Book Hotel hotel information process (control + data flow) of goals Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
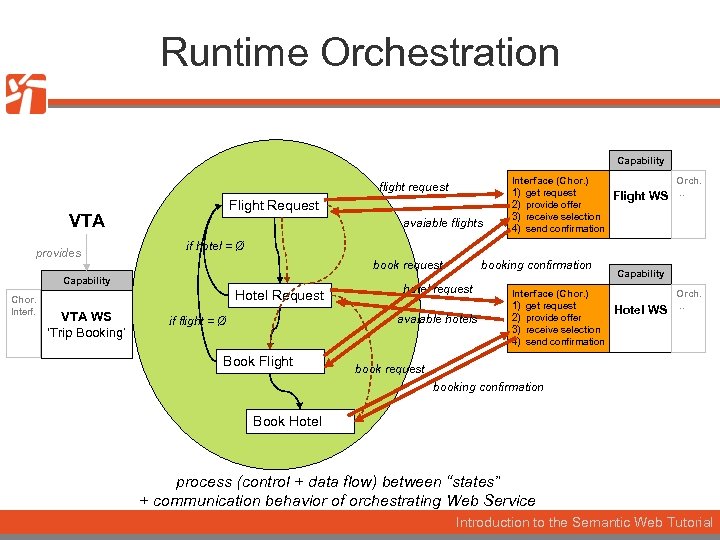
Runtime Orchestration Capability flight request Flight Request VTA provides avaiable flights book request Hotel Request VTA WS ‘Trip Booking’ Flight WS Orch. . . if hotel = Ø Capability Chor. Interface (Chor. ) 1) get request 2) provide offer 3) receive selection 4) send confirmation booking confirmation hotel request avaiable hotels if flight = Ø Book Flight Interface (Chor. ) 1) get request 2) provide offer 3) receive selection 4) send confirmation Capability Hotel WS Orch. . . book request booking confirmation Book Hotel process (control + data flow) between “states” + communication behavior of orchestrating Web Service Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
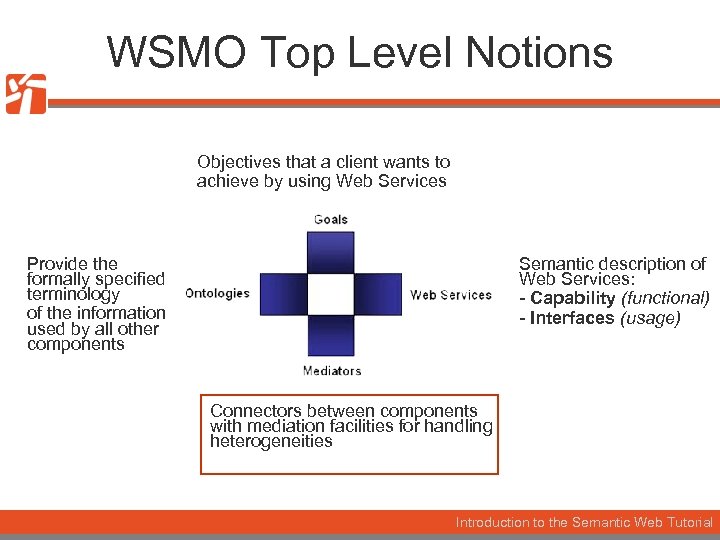
WSMO Top Level Notions Objectives that a client wants to achieve by using Web Services Provide the formally specified terminology of the information used by all other components Semantic description of Web Services: - Capability (functional) - Interfaces (usage) Connectors between components with mediation facilities for handling heterogeneities Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
Mediation • • For 1$ on programming, $5 - $9 on integration © IBM, Nelson Mattos Mismatches on structural / semantic / conceptual / level Assume (nearly) always necessary Description of role Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
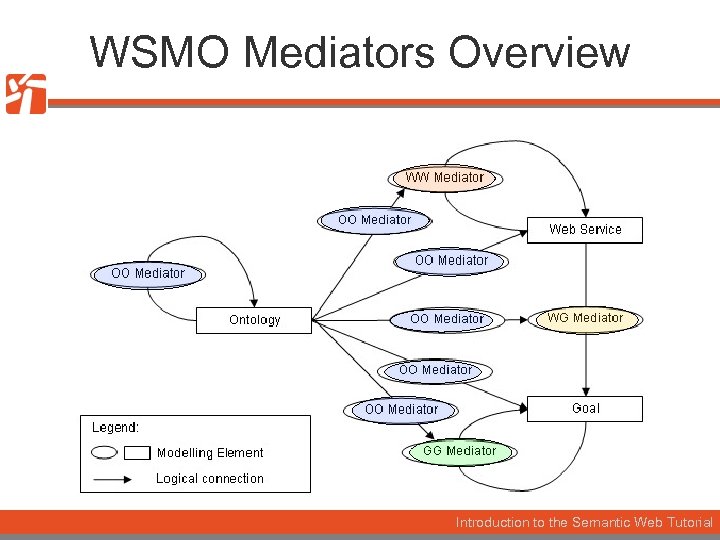
WSMO Mediators Overview Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
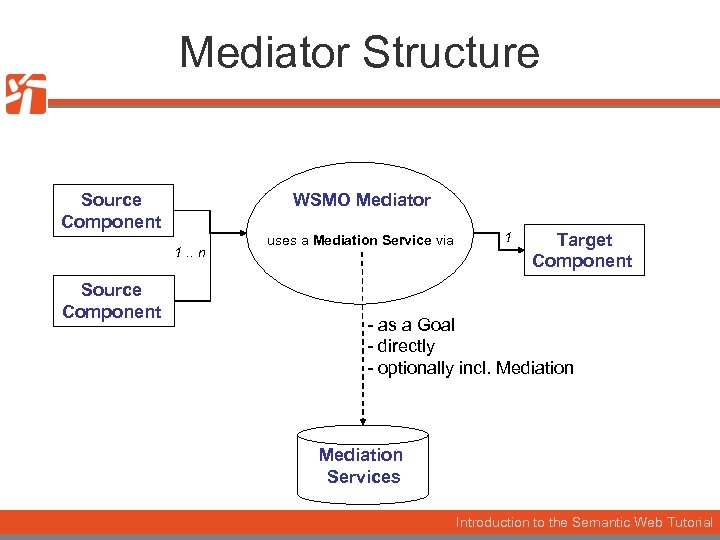
Mediator Structure Source Component WSMO Mediator 1. . n Source Component uses a Mediation Service via 1 Target Component - as a Goal - directly - optionally incl. Mediation Services Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

WSMO based Application using IRS-III John Domingue
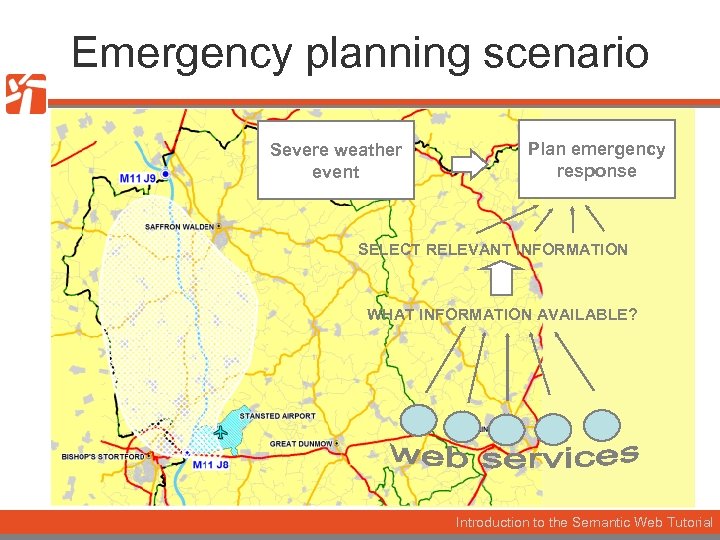
Emergency planning scenario Severe weather event Plan emergency response SELECT RELEVANT INFORMATION WHAT INFORMATION AVAILABLE? Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
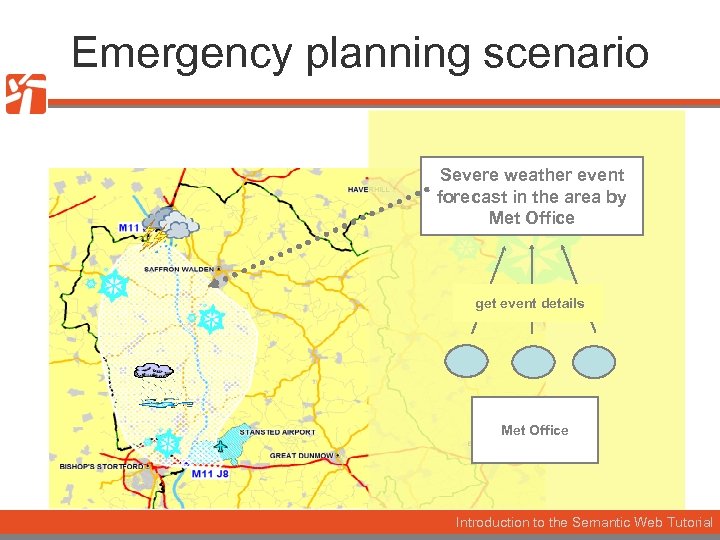
Emergency planning scenario Severe weather event forecast in the area by Met Office get event details Met Office Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
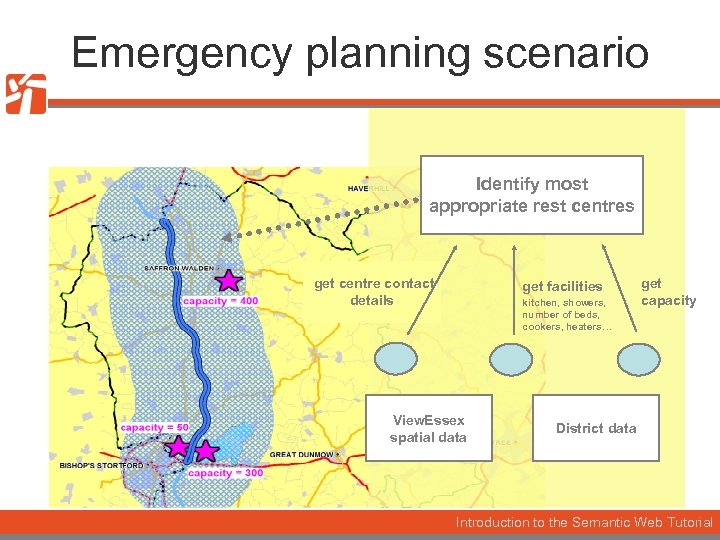
Emergency planning scenario Identify most appropriate rest centres get centre contact details get facilities kitchen, showers, number of beds, cookers, heaters… View. Essex spatial data get capacity District data Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
e. Merges Ontologies Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
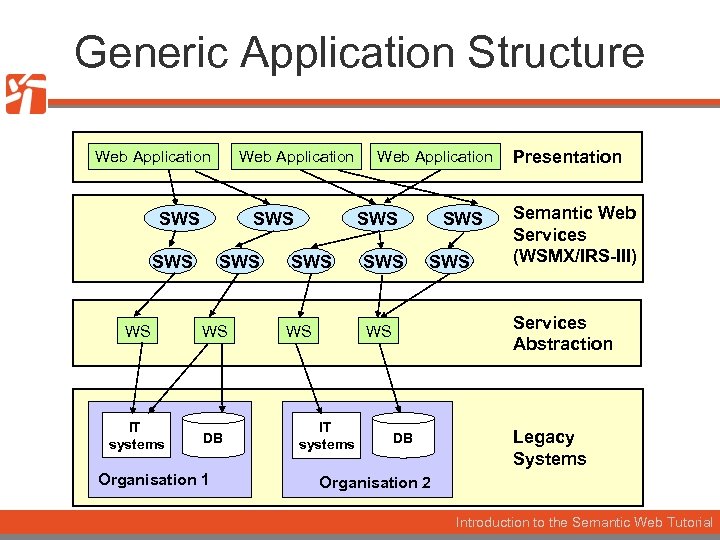
Generic Application Structure Web Application SWS SWS WS WS IT systems DB Organisation 1 Web Application SWS WS SWS Semantic Web Services (WSMX/IRS-III) Services Abstraction WS IT systems Presentation DB Legacy Systems Organisation 2 Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
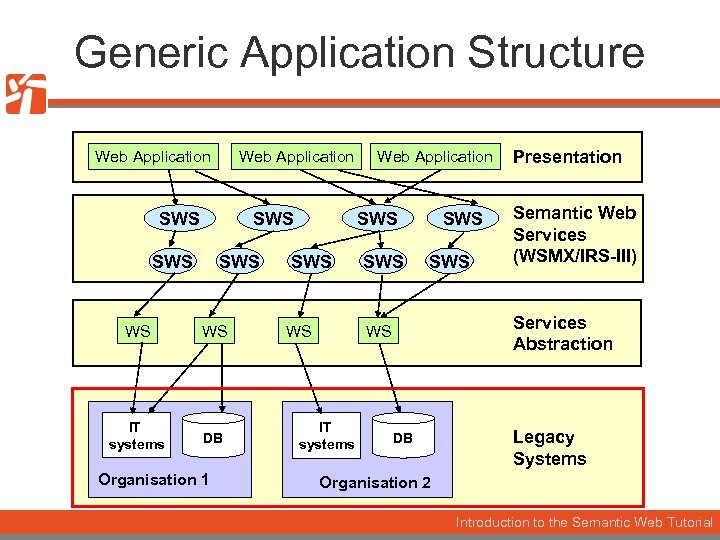
Generic Application Structure Web Application SWS SWS WS WS IT systems DB Organisation 1 Web Application SWS WS SWS Semantic Web Services (WSMX/IRS-III) Services Abstraction WS IT systems Presentation DB Legacy Systems Organisation 2 Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
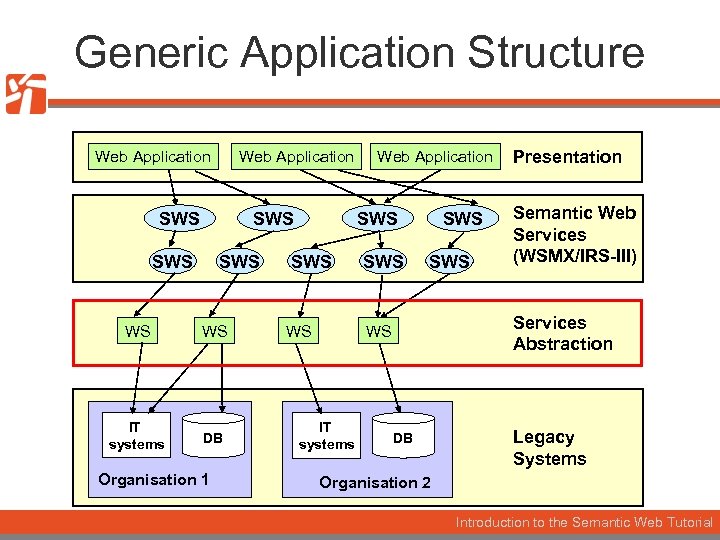
Generic Application Structure Web Application SWS SWS WS WS IT systems DB Organisation 1 Web Application SWS WS SWS Semantic Web Services (WSMX/IRS-III) Services Abstraction WS IT systems Presentation DB Legacy Systems Organisation 2 Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

Generic Application Structure Web Application SWS SWS WS WS IT systems DB Organisation 1 Web Application SWS WS SWS Semantic Web Services (WSMX/IRS-III) Services Abstraction WS IT systems Presentation DB Legacy Systems Organisation 2 Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
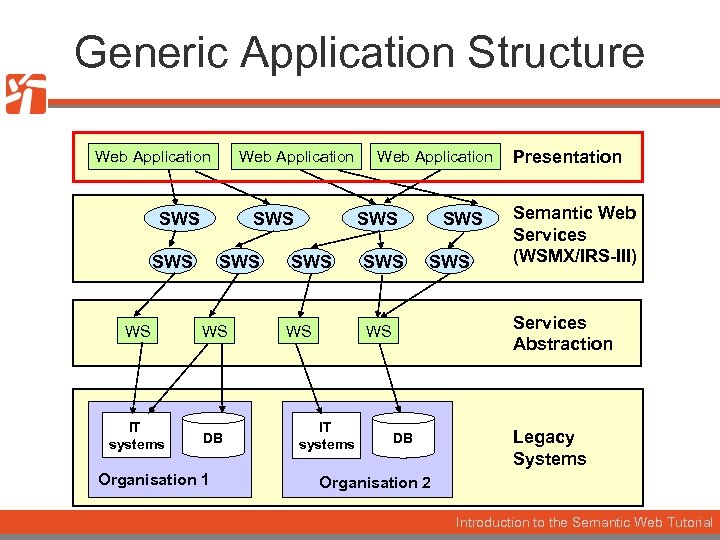
Generic Application Structure Web Application SWS SWS WS WS IT systems DB Organisation 1 Web Application SWS WS SWS Semantic Web Services (WSMX/IRS-III) Services Abstraction WS IT systems Presentation DB Legacy Systems Organisation 2 Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

Video of Emergency Planning (GIS) Prototype V 1
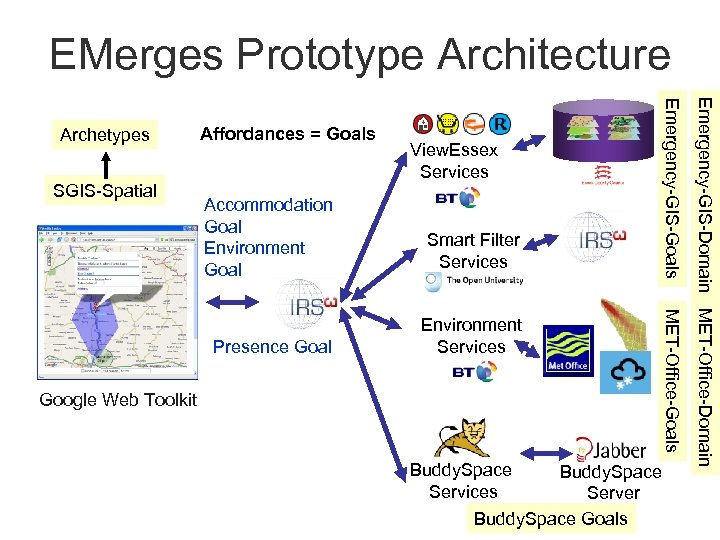
EMerges Prototype Architecture View. Essex Services Smart Filter Services Presence Goal Environment Services Google Web Toolkit Buddy. Space Services Server Buddy. Space Goals MET-Office-Goals Accommodation Goal Environment Goal Emergency-GIS-Domain MET-Office-Domain SGIS-Spatial Affordances = Goals Emergency-GIS-Goals Archetypes

SAWSDL David Martin
SAWSDL • Semantic Annotations for WSDL and XML Schema • W 3 C Recommendation, August, 2007 • Largely based on WSDL-S – Some SAWSDL ideas also appeared earlier in OWL-S • A simple, incremental approach – Builds naturally on the WSDL-centric view of Web services Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
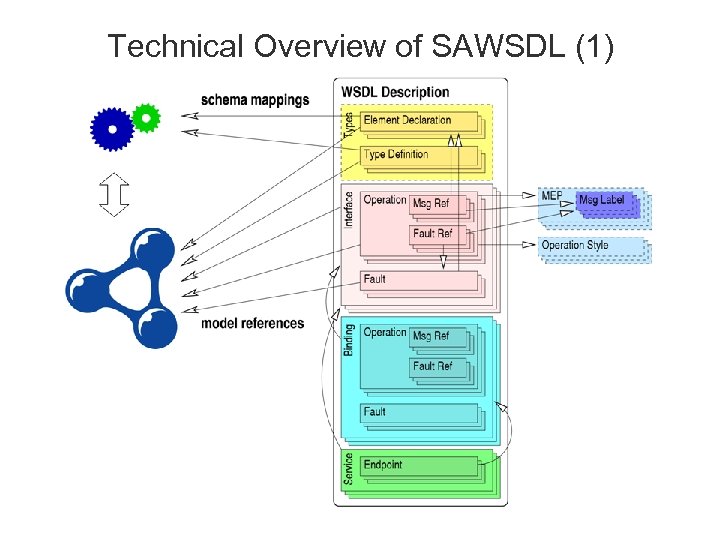
Technical Overview of SAWSDL (1)
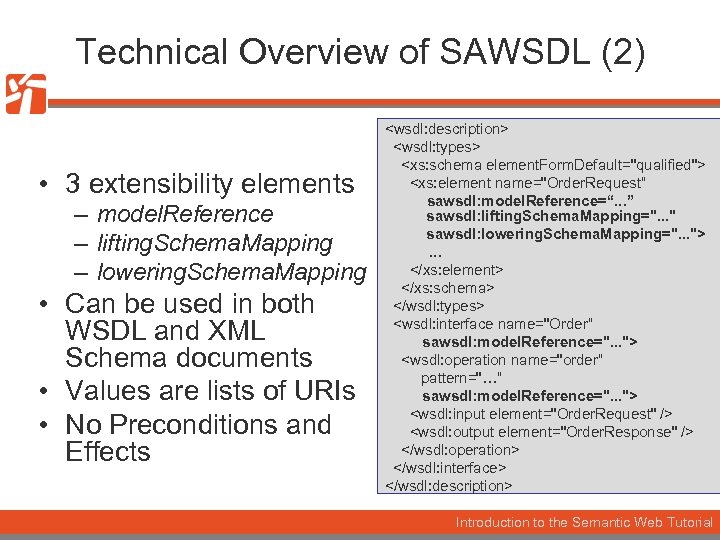
Technical Overview of SAWSDL (2) • 3 extensibility elements – model. Reference – lifting. Schema. Mapping – lowering. Schema. Mapping • Can be used in both WSDL and XML Schema documents • Values are lists of URIs • No Preconditions and Effects <wsdl: description> <wsdl: types> <xs: schema element. Form. Default="qualified"> <xs: element name="Order. Request“ sawsdl: model. Reference=“. . . ” sawsdl: lifting. Schema. Mapping=". . . " sawsdl: lowering. Schema. Mapping=". . . ">. . . </xs: element> </xs: schema> </wsdl: types> <wsdl: interface name="Order“ sawsdl: model. Reference=". . . "> <wsdl: operation name="order“ pattern="…“ sawsdl: model. Reference=". . . "> <wsdl: input element="Order. Request" /> <wsdl: output element="Order. Response" /> </wsdl: operation> </wsdl: interface> </wsdl: description> Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
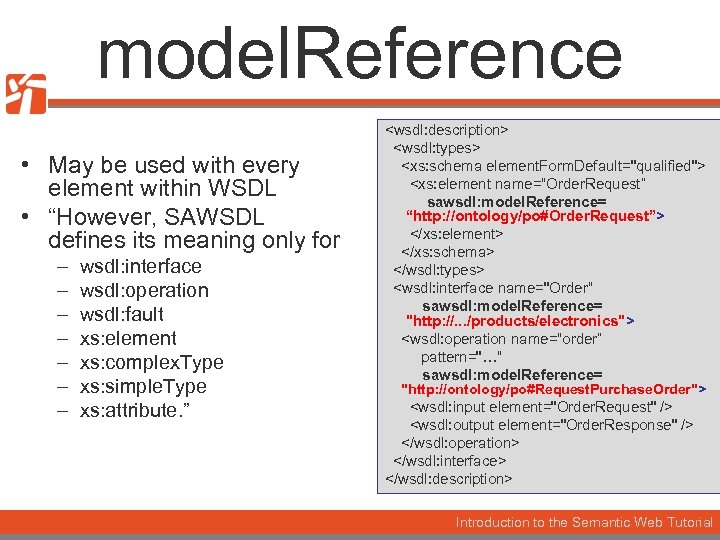
model. Reference • May be used with every element within WSDL • “However, SAWSDL defines its meaning only for – – – – wsdl: interface wsdl: operation wsdl: fault xs: element xs: complex. Type xs: simple. Type xs: attribute. ” <wsdl: description> <wsdl: types> <xs: schema element. Form. Default="qualified"> <xs: element name=“Order. Request” sawsdl: model. Reference= “http: //ontology/po#Order. Request”> </xs: element> </xs: schema> </wsdl: types> <wsdl: interface name="Order“ sawsdl: model. Reference= "http: //. . . /products/electronics"> <wsdl: operation name=“order” pattern="…“ sawsdl: model. Reference= "http: //ontology/po#Request. Purchase. Order"> <wsdl: input element="Order. Request" /> <wsdl: output element="Order. Response" /> </wsdl: operation> </wsdl: interface> </wsdl: description> Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
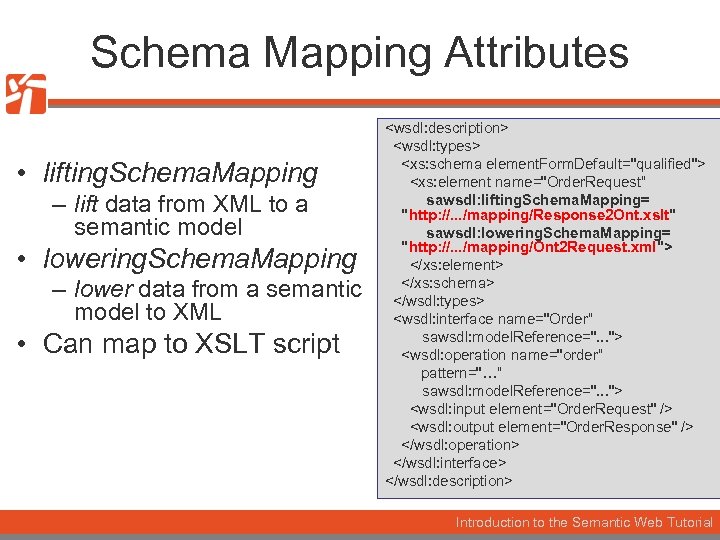
Schema Mapping Attributes • lifting. Schema. Mapping – lift data from XML to a semantic model • lowering. Schema. Mapping – lower data from a semantic model to XML • Can map to XSLT script <wsdl: description> <wsdl: types> <xs: schema element. Form. Default="qualified"> <xs: element name="Order. Request“ sawsdl: lifting. Schema. Mapping= "http: //. . . /mapping/Response 2 Ont. xslt" sawsdl: lowering. Schema. Mapping= "http: //. . . /mapping/Ont 2 Request. xml"> </xs: element> </xs: schema> </wsdl: types> <wsdl: interface name="Order“ sawsdl: model. Reference=". . . "> <wsdl: operation name="order“ pattern="…“ sawsdl: model. Reference=". . . "> <wsdl: input element="Order. Request" /> <wsdl: output element="Order. Response" /> </wsdl: operation> </wsdl: interface> </wsdl: description> Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
SAWSDL References • The Standard – http: //www. w 3. org/TR/sawsdl/ • Implementation Report – http: //www. w 3. org/2002/ws/sawsdl/CR/ • Initial Specs for Use with OWL-S – “Bringing Semantic Annotations to Web Services: OWL-S from the SAWSDL Perspective” • ISWC 2007 – “Grounding OWL-S in SAWSDL” • ICSOC 2007 • Initial Specs for Use with WSMO – WSMO Grounding • http: //www. wsmo. org/TR/d 24. 2/v 0. 1/20070427/ – WSMO Lite • http: //wsmo. org/TR/d 11/v 0. 2/20070622/d 11 v 02_20070622. pdf Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

Relevant URLs • DIP – http: //dip. semanticweb. org/ • IRS-III – http: //kmi. open. ac. uk/projects/irs/ • OWL-S, SAWSDL – See earlier slide • WSMO Working Group – http: //www. wsmo. org/ • Conceptual Models of Services WG – http: //cms-wg. sti 2. org • SOA 4 All – http: //www. soa 4 all. eu/ • Service Web 3. 0 – http: //www. serviceweb 30. eu Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial

Conclusion • • The service paradigm has become an important and integral part of the Web (including intranets) SWS aims to provide an expressive, comprehensive framework for handling activities on the Web – – Enabling greater automation of discovery, selection, invocation, composition, monitoring, and other service management tasks Should enable use of agents on the Web • • • Many tools & applications exist today; mostly prototype Many challenges remain – • SWS is a vigorous research area Strong interest and many paths to adoption exist – • Simplicity and widespread adoption of WS building blocks are enablers E. g. , the standards path Stay tuned – it will be interesting to see how far (and how fast) the service/process/agent-oriented Web will evolve! Introduction to the Semantic Web Tutorial
5ff1935020e6515bdbece95b96d3ff76.ppt