2fe6f85f4b2ab5751a4d8e2bf65115b1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Semantic Web Approach in Designing a Collaborative E-Item Bank System Heung-Nam Kim With Ae-Ttie Ji, Soon-Geun Lee, and Geun-Sik Jo Ji Dept. of Computer Science & Information Engineering Inha University, Korea 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University

Outline ¥ ¥ ¥ Introduction Background and Related Works E-Item Bank System based on Semantic Web Experimental Evaluation Conclusion & Future Work 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University

Introduction ¥ Educational environment and the fundamental paradigm have been shifted ¤ E-Learning, Web-based online-assessment … ¥ Item banks is repositories of learning objects, particularly assessment questions ¤ Various factors are now coming together!! Organizing, Maintenance, Availability … ¤ Searching, Interoperability, Reusability … ¤ Quality assurance, Copyright … ¤ 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University

Introduction (Cont’) ¥ Goal of Designing Item banks Organizing item banks with well-defined semantics ¤ Clear definition of relationship between items and users (teachers or students) or between teachers and students ¤ Accurate searching not only item itself but also extra -information related to item and user ¤ Promoting item reusability and sharing ¤ Semantic Web technologies (Ontology, Domain rules, Knowledge inference …) 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
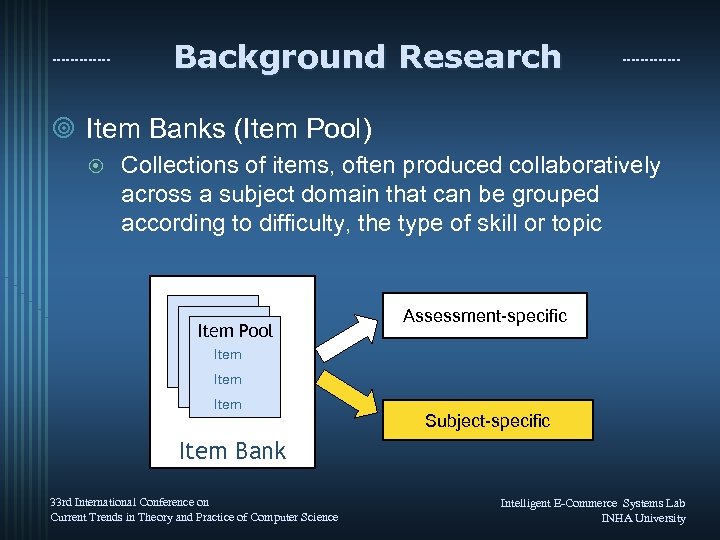
Background Research ¥ Item Banks (Item Pool) ¤ Collections of items, often produced collaboratively across a subject domain that can be grouped according to difficulty, the type of skill or topic Item Pool Assessment-specific Item Subject-specific Item Bank 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University

Background Research ¥ Semantic Web ¤ Extension of the current web in which information is given well-defined meaning, better enabling computers and people to work in cooperation (Tim Berners-Lee, 2001) ¥ Knowledge representation in SW Ontology - OWL, RDF ¤ Rules – Rule. ML, SWRL, ORL ¤ ¥ Reasoning or Inferencing in SW ¤ Jena, OWLJess. KB, JESS, F-OWL 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
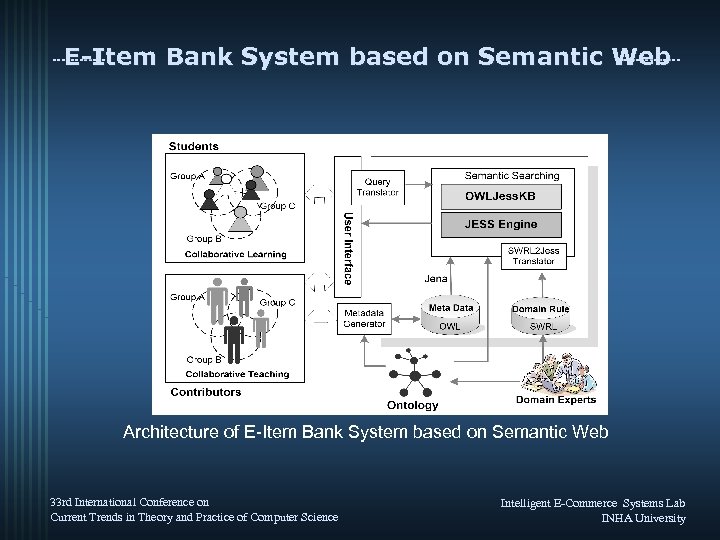
E-Item Bank System based on Semantic Web Architecture of E-Item Bank System based on Semantic Web 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
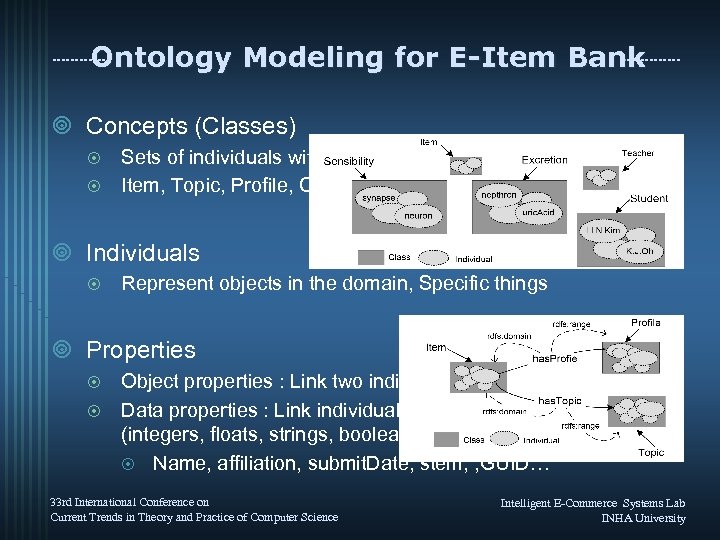
Ontology Modeling for E-Item Bank ¥ Concepts (Classes) Sets of individuals with common characteristics ¤ Item, Topic, Profile, Curriculum, Answer ¤ ¥ Individuals ¤ Represent objects in the domain, Specific things ¥ Properties Object properties : Link two individuals together ¤ Data properties : Link individuals to primitive values (integers, floats, strings, booleans etc) ¤ Name, affiliation, submit. Date, stem, , GUID… ¤ 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
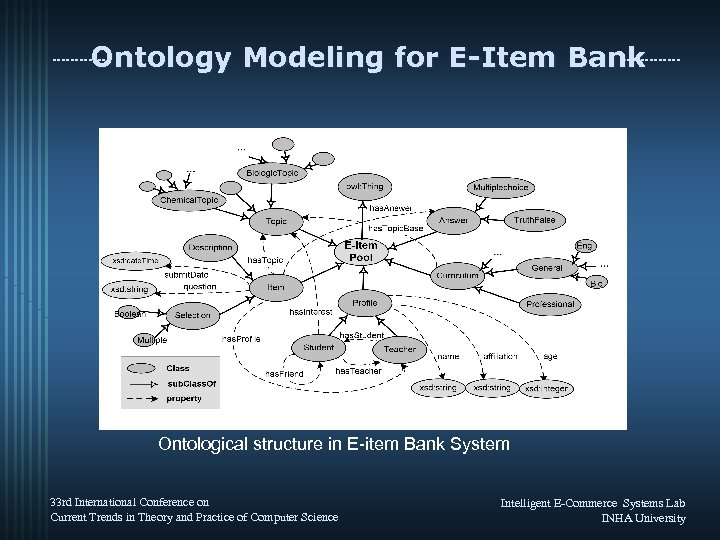
Ontology Modeling for E-Item Bank Ontological structure in E-item Bank System 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
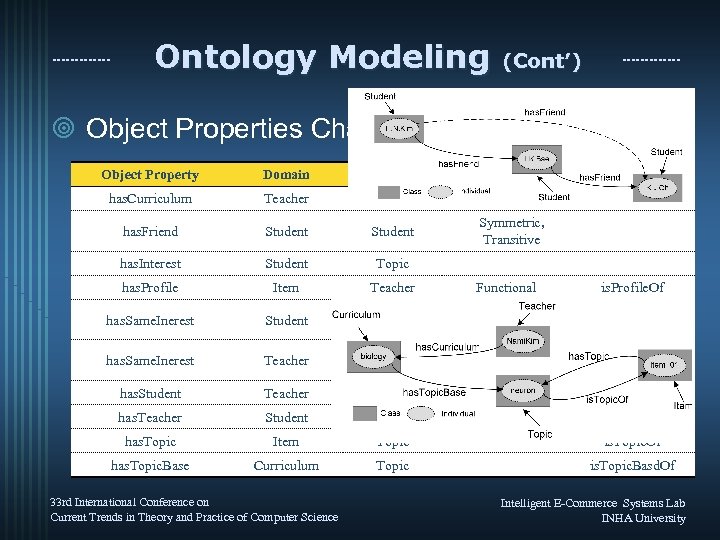
Ontology Modeling (Cont’) ¥ Object Properties Characiteristics Object Property Domain Range has. Curriculum Teacher Curriculum has. Friend Student has. Interest Student Topic has. Profile Item Teacher Functional has. Same. Inerest Student Symmetric, Transitive has. Same. Inerest Teacher Symmetric, Transitive has. Student Teacher Student has. Teacher Student Teacher has. Topic Item Topic is. Topic. Of has. Topic. Base Curriculum Topic is. Topic. Basd. Of 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Characteristics Inverse is. Curriculum. Of Symmetric, Transitive is. Profile. Of Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
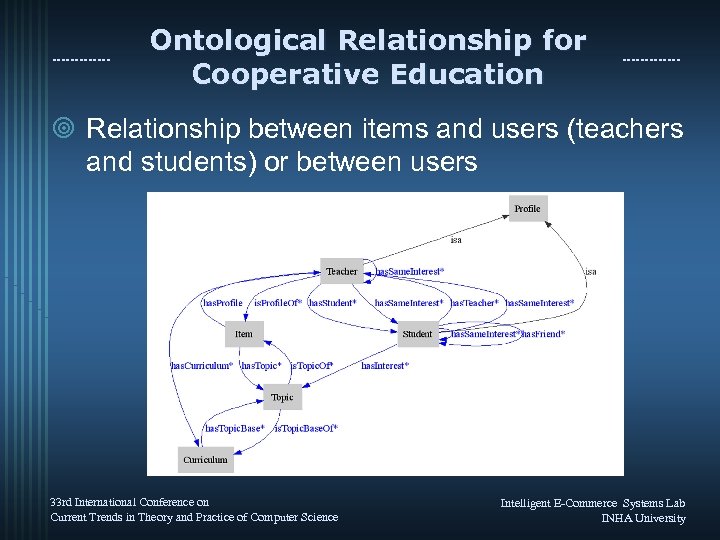
Ontological Relationship for Cooperative Education ¥ Relationship between items and users (teachers and students) or between users 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
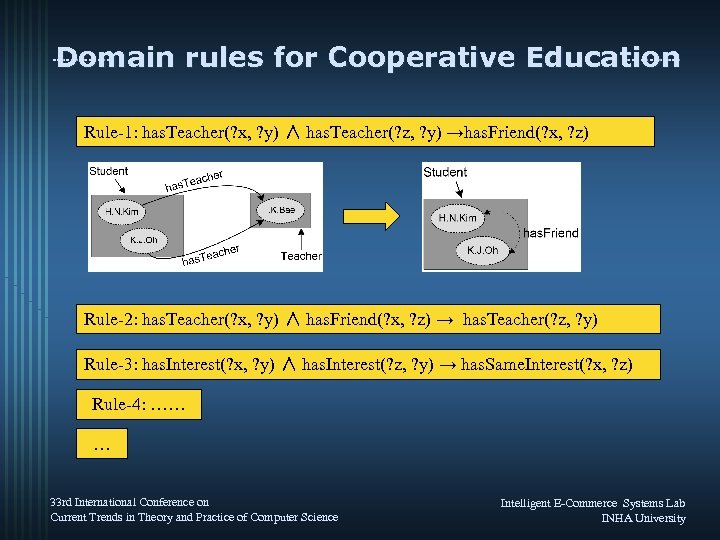
Domain rules for Cooperative Education Rule-1: has. Teacher(? x, ? y) ∧ has. Teacher(? z, ? y) →has. Friend(? x, ? z) Rule-2: has. Teacher(? x, ? y) ∧ has. Friend(? x, ? z) → has. Teacher(? z, ? y) Rule-3: has. Interest(? x, ? y) ∧ has. Interest(? z, ? y) → has. Same. Interest(? x, ? z) Rule-4: …… … 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
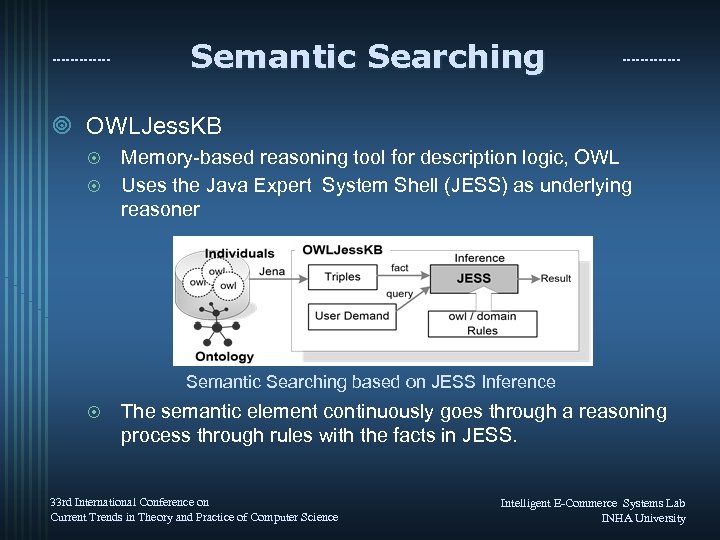
Semantic Searching ¥ OWLJess. KB Memory-based reasoning tool for description logic, OWL ¤ Uses the Java Expert System Shell (JESS) as underlying reasoner ¤ Semantic Searching based on JESS Inference ¤ The semantic element continuously goes through a reasoning process through rules with the facts in JESS. 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University

Semantic Searching (Cont’) ¥ OWL rules ¤ provides the meaning of ontology composed of OWL to JESS as a rule. (defrule OWL_inverse. Of (triple (predicate "http: //www. w 3. org/2002/07/owl#inverse. Of") (subject ? x) (object ? y)) (triple (predicate ? x) (subject ? u) (object ? v)) => (assert (triple (predicate ? y) (subject ? v) (object ? u))) ) The property characteristic inverse. Of for JESS triple 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
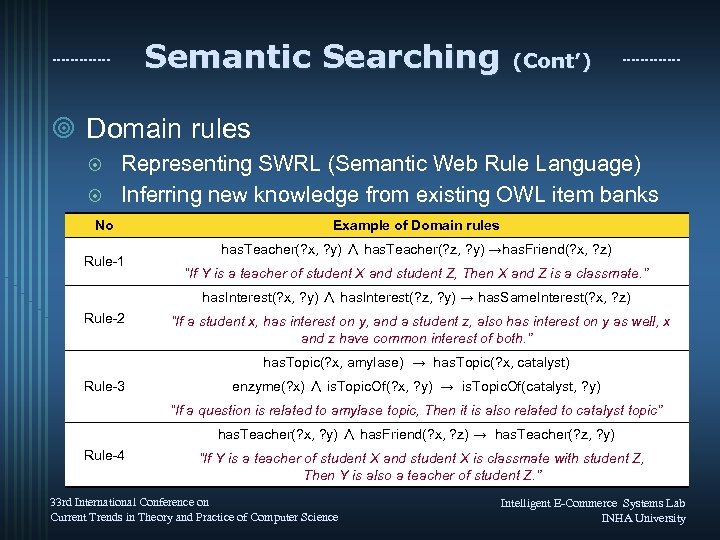
Semantic Searching (Cont’) ¥ Domain rules Representing SWRL (Semantic Web Rule Language) ¤ Inferring new knowledge from existing OWL item banks ¤ No Rule-1 Example of Domain rules has. Teacher(? x, ? y) ∧ has. Teacher(? z, ? y) →has. Friend(? x, ? z) “If Y is a teacher of student X and student Z, Then X and Z is a classmate. ” has. Interest(? x, ? y) ∧ has. Interest(? z, ? y) → has. Same. Interest(? x, ? z) Rule-2 “If a student x, has interest on y, and a student z, also has interest on y as well, x and z have common interest of both. ” has. Topic(? x, amylase) → has. Topic(? x, catalyst) Rule-3 enzyme(? x) ∧ is. Topic. Of(? x, ? y) → is. Topic. Of(catalyst, ? y) “If a question is related to amylase topic, Then it is also related to catalyst topic” has. Teacher(? x, ? y) ∧ has. Friend(? x, ? z) → has. Teacher(? z, ? y) Rule-4 “If Y is a teacher of student X and student X is classmate with student Z, Then Y is also a teacher of student Z. ” 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
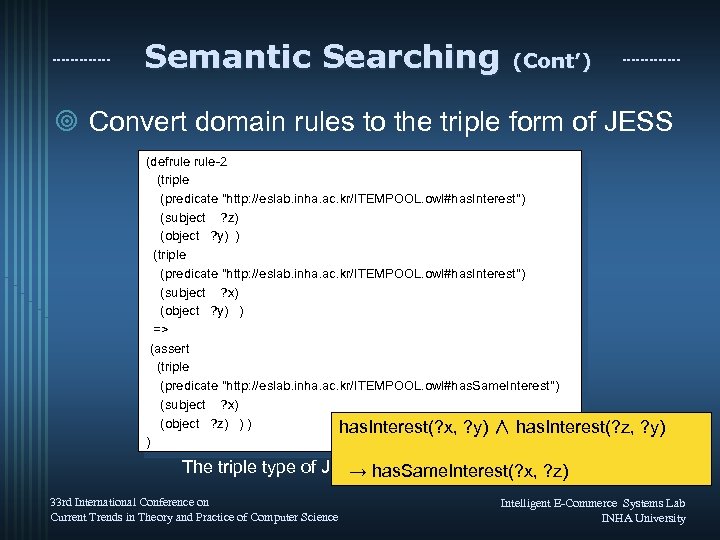
Semantic Searching (Cont’) ¥ Convert domain rules to the triple form of JESS (defrule-2 (triple (predicate "http: //eslab. inha. ac. kr/ITEMPOOL. owl#has. Interest") (subject ? z) (object ? y) ) (triple (predicate "http: //eslab. inha. ac. kr/ITEMPOOL. owl#has. Interest") (subject ? x) (object ? y) ) => (assert (triple (predicate "http: //eslab. inha. ac. kr/ITEMPOOL. owl#has. Same. Interest") (subject ? x) (object ? z) ) ) has. Interest(? x, ? y) ∧ has. Interest(? z, ? y) ) The triple type of JESS for Rule-2 → has. Same. Interest(? x, ? z) 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
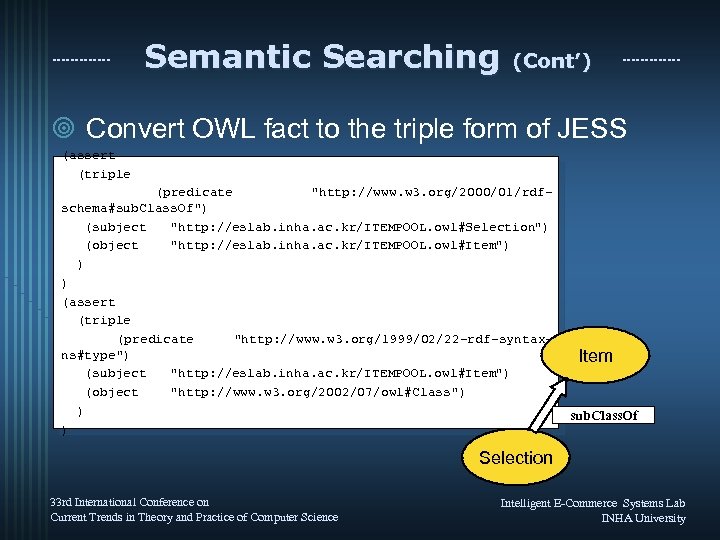
Semantic Searching (Cont’) ¥ Convert OWL fact to the triple form of JESS (assert (triple (predicate "http: //www. w 3. org/2000/01/rdfschema#sub. Class. Of") (subject "http: //eslab. inha. ac. kr/ITEMPOOL. owl#Selection") (object "http: //eslab. inha. ac. kr/ITEMPOOL. owl#Item") ) ) (assert (triple (predicate "http: //www. w 3. org/1999/02/22 -rdf-syntaxns#type") (subject "http: //eslab. inha. ac. kr/ITEMPOOL. owl#Item") (object "http: //www. w 3. org/2002/07/owl#Class") ) ) Item sub. Class. Of Selection 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
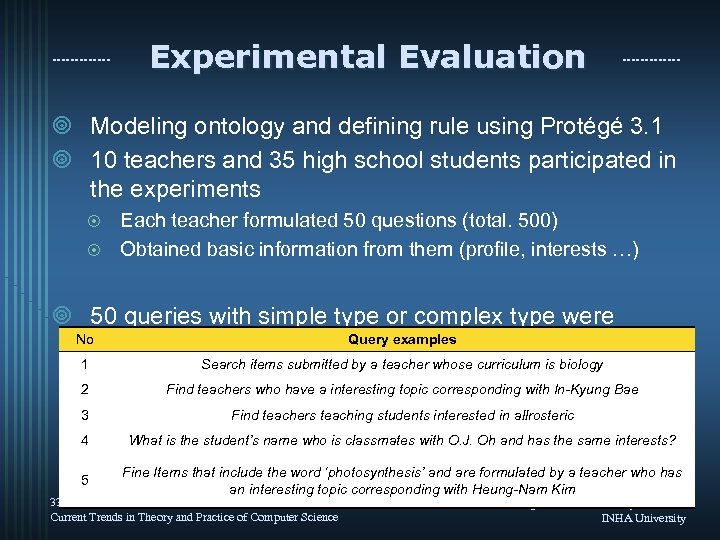
Experimental Evaluation ¥ Modeling ontology and defining rule using Protégé 3. 1 ¥ 10 teachers and 35 high school students participated in the experiments Each teacher formulated 50 questions (total. 500) ¤ Obtained basic information from them (profile, interests …) ¤ ¥ 50 queries with simple type or complex type were No generated and tested Query examples 1 Search items submitted by a teacher whose curriculum is biology 2 Find teachers who have a interesting topic corresponding with In-Kyung Bae 3 Find teachers teaching students interested in allrosteric 4 What is the student’s name who is classmates with O. J. Oh and has the same interests? 5 Fine Items that include the word ‘photosynthesis’ and are formulated by a teacher who has an interesting topic corresponding with Heung-Nam Kim 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
Experimental Evaluation ¥ Comparison of three type of E-item bank system RDBIB: RDB-based E-item bank ¤ SWEIB: Semantic web-based E-item bank without domain rules ¤ SWEIB+SWRL: Semantic web-based E-item bank with domain rules ¤ ¥ Evaluation Metrics 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
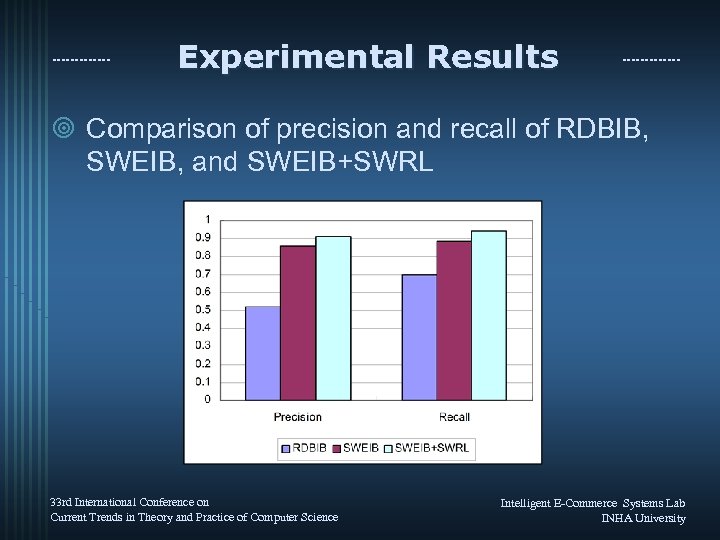
Experimental Results ¥ Comparison of precision and recall of RDBIB, SWEIB, and SWEIB+SWRL 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
Analysis of experimental Results ¥ Synonymic or ambiguous vocabulary Find items related to ‘assimilation’ ¤ In SWEIB, SWEIB+SWRL, item related to ‘photosynthesis’ was also searched. (same. As) ¥ Reasoning new facts by ontology Search the classmates of Mr. Kim is classmate with Miss. Ji ¤ Miss. Ji is classmate with Mr. Lee ¤ RDBIB did not find Mr. Lee, SWEIB & SWEIB+SWRL did (Transitivity property) ¤ ¥ Inference new facts by ontology & domain rules ¤ Mr. Kim and Mr. Lee is interested in ‘nephron’ Find the classmates who has common interest with a student Mr. Kim SWEIB+SWRL found the result ‘Mr. Lee’, but the others didn’t ¤ Inference new fact: Mr. Kim and Mr. Lee have the common interest (has. Same. Interest) ¤ 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
Conclusion ¥ Designing item banks with semantic web technologies induce users to cooperative education ¤ provide semantic searching not only item itself but also extra-information related to item and user ¤ promote item reusability and sharing ¤ ¥ Future study: Semantic Web Service Integration of distributed item banks ¤ Automated item selection for a personalized assessment ¤ 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University

nami@eslab. inha. ac. kr http: //eslab. inha. ac. kr Thank you !!! 33 rd International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science Intelligent E-Commerce Systems Lab INHA University
2fe6f85f4b2ab5751a4d8e2bf65115b1.ppt