1b140871d6f5ac61ebe6a5247adad6b2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Semantic Web - an introduction By Daniel Wu (danielwujr)

Presentation Outline (Why) Problem Definition (Who and When) Semantic Web (SW) Proposal (What) SW Features & Services (How) SW KR* & Layers (Where) SW Current Status *knowledge representation

Presentation Outline (Why) Problem Definition (Who and When) Semantic Web (SW) Proposal (What) SW Features & Services (How) SW KR* & Layers (Where) SW Current Status *knowledge representation

Semantic? • Assalamu alaikum • Let’s give it semantic… – Assalamu alaikum is Arabian – Assalamu alaikum means “Hello” • sēmantikós (Greek) = having meaning

Problem Definition • Computer have no reliable way to process semantics on Web content. • (Most of the Web’s content today is designed for humans to read. )

Semantic Web (SW) Proposal • Tim Berners-Lee – inventor of the WWW • 1998 Solution 1. Achieving a set of connected applications for data on the Web in such a way as to form a consistent logical web of data. 2. Develops languages for expressing information in a machineprocessable form. - Semantic Web Road map, Tim Berners-Lee

Presentation Outline (Why) Problem Definition (Who and When) Semantic Web (SW) Proposal (What) SW Features & Services (How) SW KR* & Layers (Where) SW Current Status *knowledge representation

SW Features & Services • Semantic Web • The semantic web is an evolving extension of the World Wide Web in which web content can be expressed not only in natural language, but also in a form that can be understood, interpreted and used by software agents, thus permitting them to find, share and integrate information more easily. • Source: W 3 C Semantic Web FAQ

SW Features & Services (cont. ) • Benefits – data integration, • whereby data in various locations and various formats can be integrated in one, seamless application; – resource discovery and classification (vertical search) • provide better, domain specific search engine capabilities; – cataloging • describing the content and content relationships available at a particular Web site, page, or digital library; – intelligent software agents • facilitate knowledge sharing and exchange;

SW Features & Services (cont. ) • However… – You probably won’t “see” SW – And this is Weak AI

Presentation Outline (Why) Problem Definition (Who and When) Semantic Web (SW) Proposal (What) SW Features & Services (How) SW KR* & Layers (Where) SW Current Status *knowledge representation
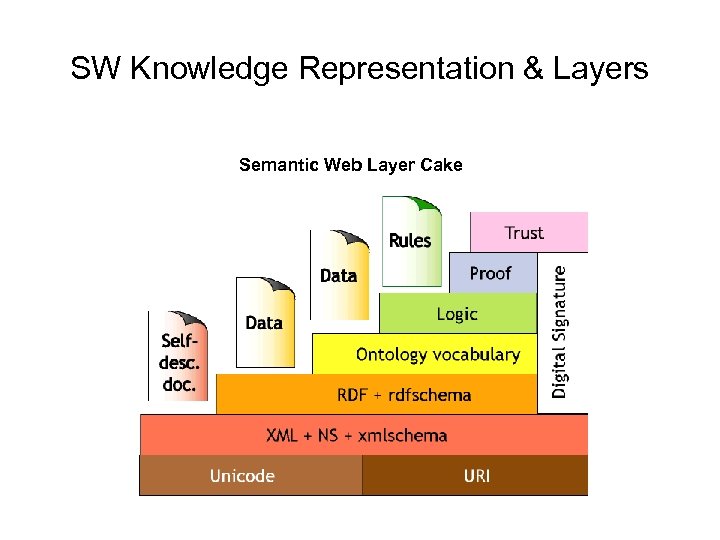
SW Knowledge Representation & Layers Semantic Web Layer Cake
• Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI) – URI is a name. (a pointer) – Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is one form of URI – URI does not need to be accessible over the Internet
• EXtensible Markup Language (XML) – XML provides a surface syntax for structured documents – XML imposes no semantic constraints on the meaning of documents
• Resource Description Framework (RDF) – RDF is a simple data model for referring to objects ("resources") and how they are related. – RDF enable anyone to say anything about anything – Triples: subject, predicate, object – RDF is composed of URIs – Ex. Daniel study CS
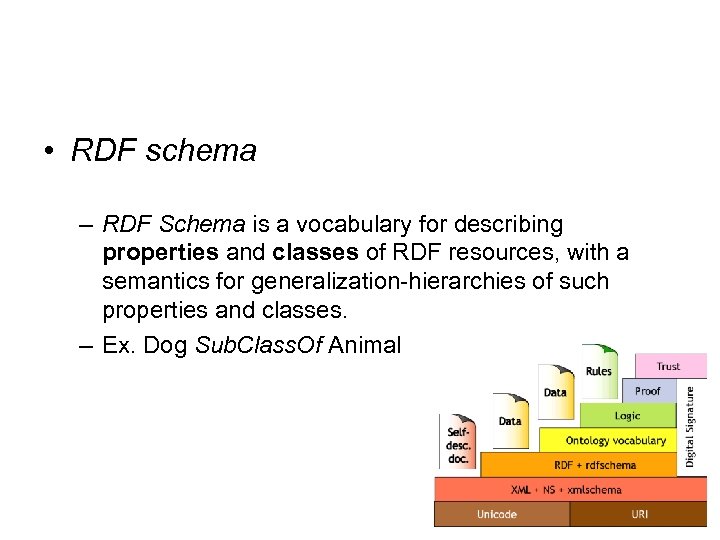
• RDF schema – RDF Schema is a vocabulary for describing properties and classes of RDF resources, with a semantics for generalization-hierarchies of such properties and classes. – Ex. Dog Sub. Class. Of Animal
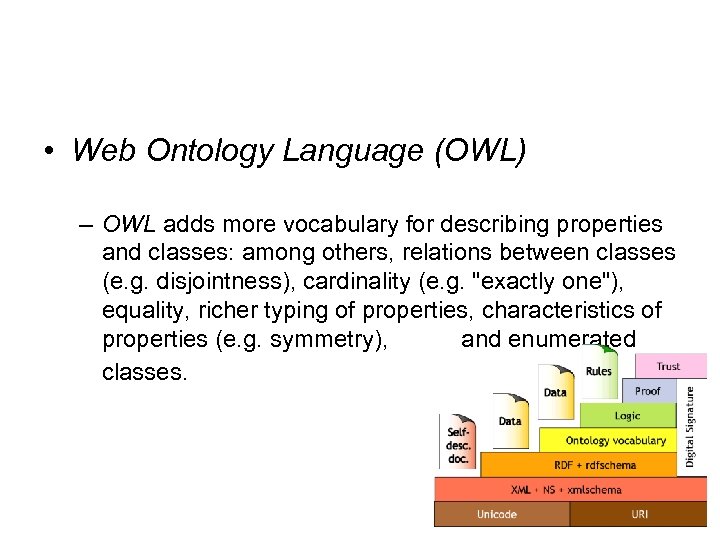
• Web Ontology Language (OWL) – OWL adds more vocabulary for describing properties and classes: among others, relations between classes (e. g. disjointness), cardinality (e. g. "exactly one"), equality, richer typing of properties, characteristics of properties (e. g. symmetry), and enumerated classes.

Ontology • • • Definition Example Ontology & Knowledge presentation Ontology & Building ontology Ontology & Folksonomy Ontology & Interoperability

Ontology - Definition • (short version) – Ontologies are systems of formally defined related concepts. • (long version) – Ontologies define the concepts and relationships used to describe and represent an area of knowledge. Ontologies are used to classify the terms used in a particular application, characterize possible relationships, and define possible constraints on using those relationships.

Ontology - Example • • • A company is a type organization. An organization may have a product or a service. An organization is a group of people. An employer may be a person or an organization. A person may be employed by an employer. A person may be in a marriage with only one other person at a time. A marriage is a kind of romantic relationship. A friendship is a kind of social relationship. A romantic relationship is a kind of friendship. A person may be socially related to another person. A person must have a gender.

Ontology & Knowledge presentation – Back to “Assalamu alaikum” – We need previous knowledge to fully understand the concept of “Assalamu alaikum” – previous knowledge = world view = ontology – Oh! “Assalamu alaikum” means “Hello”

Ontology & Building ontology • Cyc – Top down approach – Defines ontology on its own – Centralized • Semantic Web – Bottom up approach – Defines language to define ontology – Destributed • Everyone defines his/her own ontologies!

Ontology & Folksonomy • Can ontology not be hierarchical? • Can ontology be built from folksonomy?

Interoperability between different ontologies • The OWL language can express mappings between concepts in different ontologies. But if there are many ontologies, and many of them partially overlap, it is a non-trivial task to actually make the mappings between their concepts.
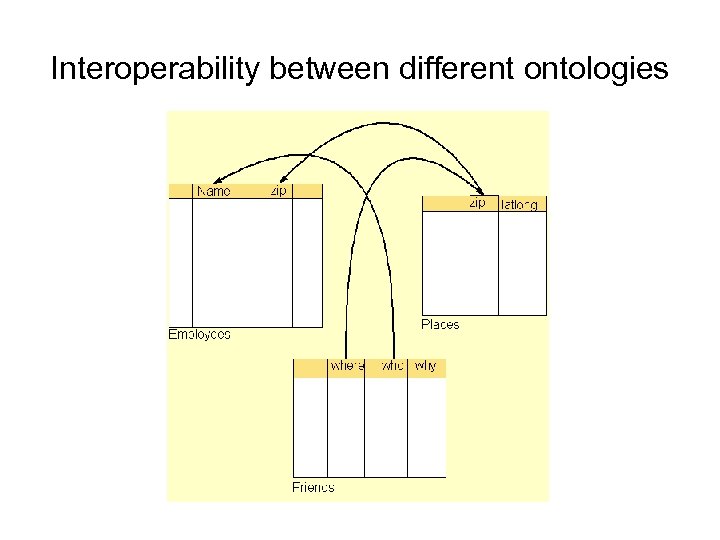
Interoperability between different ontologies

Interoperability between different ontologies • However… It’s hard. • Having same name doesn’t guarantee having same meaning • A bad example… – 嘟嚕嘟嚕達達達 • Wrong conversion… • Same name doesn’t guarantee same meaning
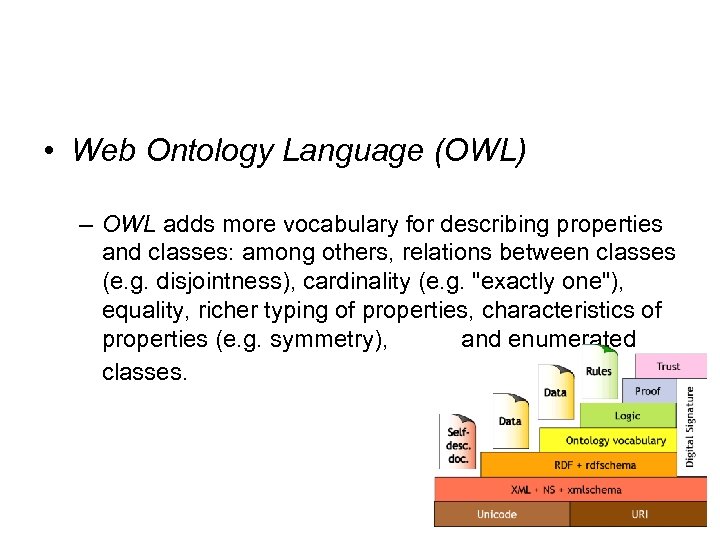
• Web Ontology Language (OWL) – OWL adds more vocabulary for describing properties and classes: among others, relations between classes (e. g. disjointness), cardinality (e. g. "exactly one"), equality, richer typing of properties, characteristics of properties (e. g. symmetry), and enumerated classes.
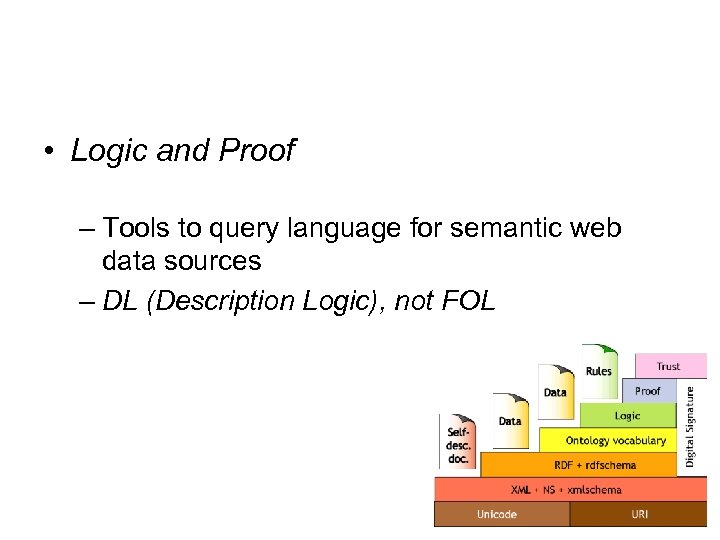
• Logic and Proof – Tools to query language for semantic web data sources – DL (Description Logic), not FOL
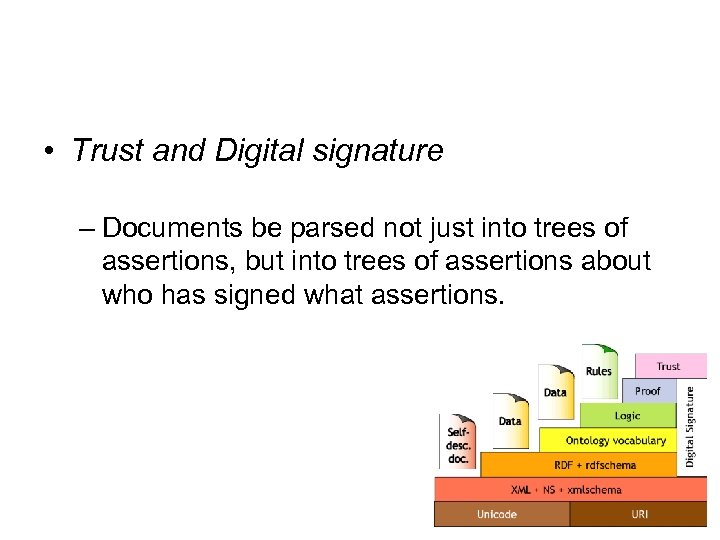
• Trust and Digital signature – Documents be parsed not just into trees of assertions, but into trees of assertions about who has signed what assertions.
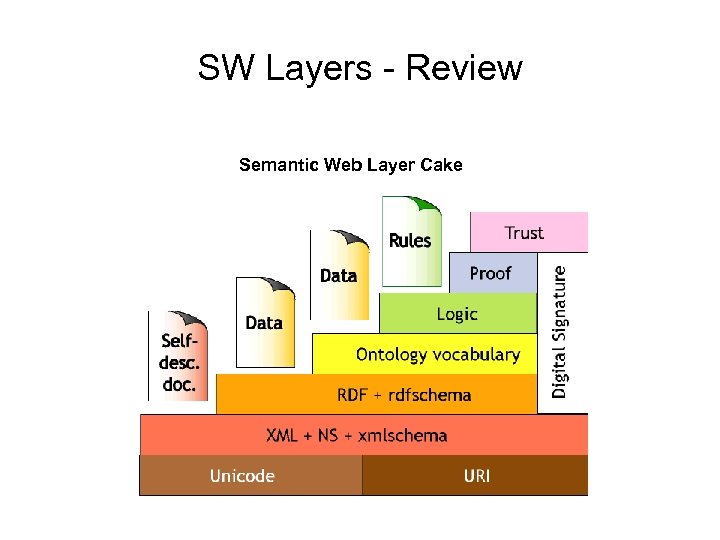
SW Layers - Review Semantic Web Layer Cake

Presentation Outline (Why) Problem Definition (Who and When) Semantic Web (SW) Proposal (What) SW Features & Services (How) SW KR* & Layers (Where) SW Current Status *knowledge representation
SW Current Status • Bump! – Tools problem – Ontology problem – Poor rule engine performance
SW Current Status • Important players - Google – Not taking actions – Ask question! • Incompetence • Competition • Deception

Presentation Outline (Why) Problem Definition (Who and When) Semantic Web (SW) Proposal (What) SW Features & Services (How) SW KR* & Layers (Where) SW Current Status *knowledge representation

Q&A • Welcome!
1b140871d6f5ac61ebe6a5247adad6b2.ppt