bbfb6e7769968b08aaf99eec3284a14d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Framing Our Discussions: Partnering to Harmonize Enrolment Management Susan Gottheil, Mount Royal College Clayton Smith, University of Windsor © Gottheil/Smith 1
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Framing Our Discussions: Partnering to Harmonize Enrolment Management Susan Gottheil, Mount Royal College Clayton Smith, University of Windsor © Gottheil/Smith 1
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Topics Ø Welcome Ø Introductions Ø Setting the tone Ø A bit about SEM Ø Importance of partnering © Gottheil/Smith 2
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Topics Ø Welcome Ø Introductions Ø Setting the tone Ø A bit about SEM Ø Importance of partnering © Gottheil/Smith 2
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Setting the Tone Ø Our unique discussion style • The discussion leader will take 10 -20 minutes or so to frame the issue • This will be followed by a facilitated discussion of the topic Ø Notes will be taken, with a summary placed to our web site (www. uwindsor. ca/sem) at the conclusion of the Summit © Gottheil/Smith 3
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Setting the Tone Ø Our unique discussion style • The discussion leader will take 10 -20 minutes or so to frame the issue • This will be followed by a facilitated discussion of the topic Ø Notes will be taken, with a summary placed to our web site (www. uwindsor. ca/sem) at the conclusion of the Summit © Gottheil/Smith 3
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Setting the Tone (Cont’d) Ø A written compilation of our thoughts will be developed, which will create a jumping off place for further Canadian SEM discussions Ø Lots of great discussion, opportunities for networking: The SEM Summit Way! © Gottheil/Smith 4
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Setting the Tone (Cont’d) Ø A written compilation of our thoughts will be developed, which will create a jumping off place for further Canadian SEM discussions Ø Lots of great discussion, opportunities for networking: The SEM Summit Way! © Gottheil/Smith 4
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 First, A bit About SEM… © Gottheil/Smith 5
SEM Summit ‘ 09 First, A bit About SEM… © Gottheil/Smith 5
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Definition of SEM Strategic enrollment management (SEM) is a concept and process that enables the fulfillment of institutional mission and students’ educational goals. -Bontrager, 2009 © Gottheil/Smith 6
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Definition of SEM Strategic enrollment management (SEM) is a concept and process that enables the fulfillment of institutional mission and students’ educational goals. -Bontrager, 2009 © Gottheil/Smith 6
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 The Purposes of SEM are Achieved by… Ø Establishing clear goals for the number and types of students needed to fulfill the institutional mission Ø Promoting students’ academic success by improving access, transition, persistence, and graduation Ø Promoting institutional success by enabling effective strategic and financial planning © Gottheil/Smith 7
SEM Summit ‘ 09 The Purposes of SEM are Achieved by… Ø Establishing clear goals for the number and types of students needed to fulfill the institutional mission Ø Promoting students’ academic success by improving access, transition, persistence, and graduation Ø Promoting institutional success by enabling effective strategic and financial planning © Gottheil/Smith 7
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 The Purposes of SEM are Achieved by… Ø Creating a data-rich environment to inform decisions and evaluate strategies Ø Improving process, organizational and financial efficiency and outcomes Ø Strengthening communications and marketing with internal and external stakeholders Ø Increasing collaboration among departments across the campus to support the enrolment program © Gottheil/Smith 8
SEM Summit ‘ 09 The Purposes of SEM are Achieved by… Ø Creating a data-rich environment to inform decisions and evaluate strategies Ø Improving process, organizational and financial efficiency and outcomes Ø Strengthening communications and marketing with internal and external stakeholders Ø Increasing collaboration among departments across the campus to support the enrolment program © Gottheil/Smith 8
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Some Core SEM Concepts… © Gottheil/Smith 9
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Some Core SEM Concepts… © Gottheil/Smith 9
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 The Concept of Optimum Enrolment Ethnicity Physical Capacity Undergrad/ Grad Majors Institutional Mission Academic Profiles International Special Skills Program Capacity © Gottheil/Smith 10
SEM Summit ‘ 09 The Concept of Optimum Enrolment Ethnicity Physical Capacity Undergrad/ Grad Majors Institutional Mission Academic Profiles International Special Skills Program Capacity © Gottheil/Smith 10
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 © Gottheil/Smith 11
SEM Summit ‘ 09 © Gottheil/Smith 11
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Institutional Mission & Enrolment Goals Are Determined By: Current competitive status Programs offered Range of influence Niche Weaknesses Historical status Aspirational status Strengths …with consideration to institutional differentiation! © Gottheil/Smith 12
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Institutional Mission & Enrolment Goals Are Determined By: Current competitive status Programs offered Range of influence Niche Weaknesses Historical status Aspirational status Strengths …with consideration to institutional differentiation! © Gottheil/Smith 12
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 The Student Success Continuum Ø Traditional Enrollment Perspective Recruitment/ Marketing Orientation Co-curricular Support Classroom Experience Attain Degree/Goal Student’s College Career Admission Financial Support Academic Support © Gottheil/Smith Retention 13
SEM Summit ‘ 09 The Student Success Continuum Ø Traditional Enrollment Perspective Recruitment/ Marketing Orientation Co-curricular Support Classroom Experience Attain Degree/Goal Student’s College Career Admission Financial Support Academic Support © Gottheil/Smith Retention 13
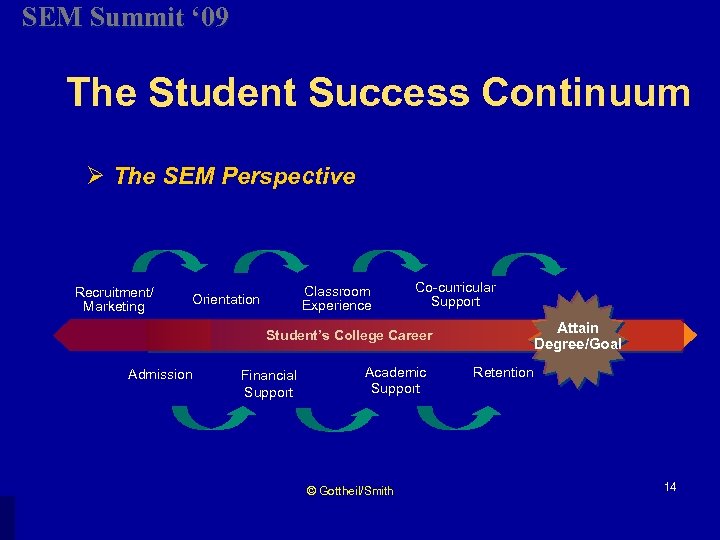 SEM Summit ‘ 09 The Student Success Continuum Ø The SEM Perspective Recruitment/ Marketing Classroom Experience Orientation Co-curricular Support Attain Degree/Goal Student’s College Career Admission Financial Support Academic Support © Gottheil/Smith Retention 14
SEM Summit ‘ 09 The Student Success Continuum Ø The SEM Perspective Recruitment/ Marketing Classroom Experience Orientation Co-curricular Support Attain Degree/Goal Student’s College Career Admission Financial Support Academic Support © Gottheil/Smith Retention 14
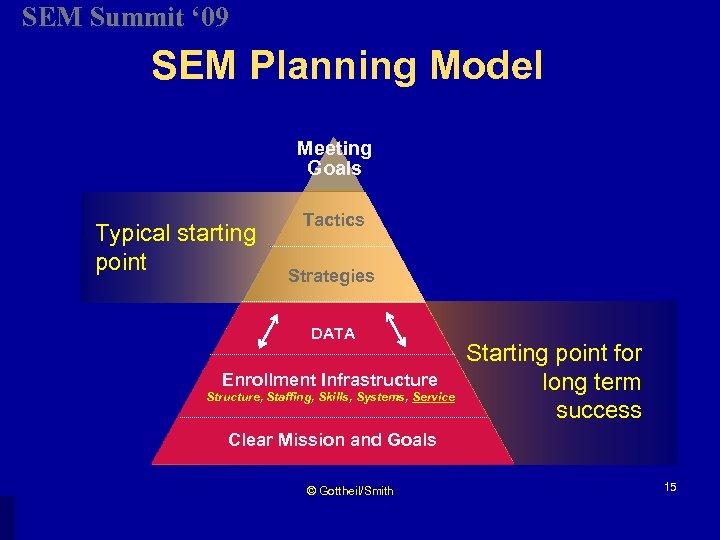 SEM Summit ‘ 09 SEM Planning Model Meeting Goals Typical starting point Tactics Strategies DATA Enrollment Infrastructure Structure, Staffing, Skills, Systems, Service Starting point for long term success Clear Mission and Goals © Gottheil/Smith 15
SEM Summit ‘ 09 SEM Planning Model Meeting Goals Typical starting point Tactics Strategies DATA Enrollment Infrastructure Structure, Staffing, Skills, Systems, Service Starting point for long term success Clear Mission and Goals © Gottheil/Smith 15
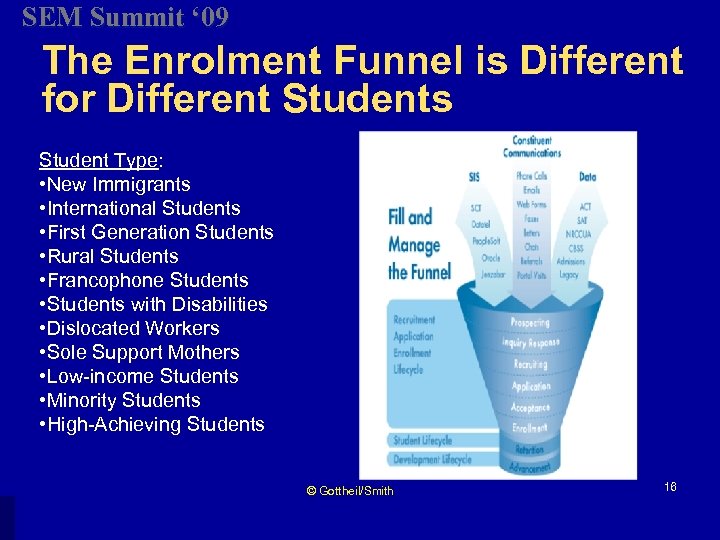 SEM Summit ‘ 09 The Enrolment Funnel is Different for Different Students Student Type: • New Immigrants • International Students • First Generation Students • Rural Students • Francophone Students • Students with Disabilities • Dislocated Workers • Sole Support Mothers • Low-income Students • Minority Students • High-Achieving Students © Gottheil/Smith 16
SEM Summit ‘ 09 The Enrolment Funnel is Different for Different Students Student Type: • New Immigrants • International Students • First Generation Students • Rural Students • Francophone Students • Students with Disabilities • Dislocated Workers • Sole Support Mothers • Low-income Students • Minority Students • High-Achieving Students © Gottheil/Smith 16
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 A Few Ways to Look at SEM © Gottheil/Smith 17
SEM Summit ‘ 09 A Few Ways to Look at SEM © Gottheil/Smith 17
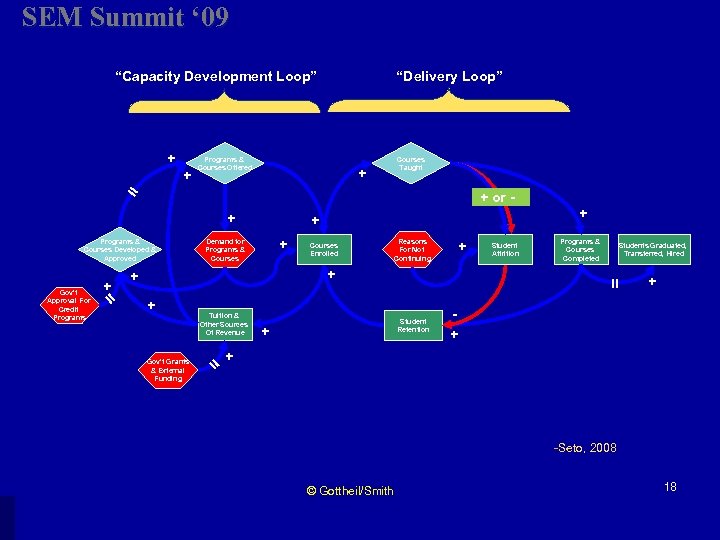 SEM Summit ‘ 09 “Capacity Development Loop” + + = Programs & Courses Offered + or - Programs & Courses Developed & Approved + + Demand for Programs & Courses Enrolled Reasons For Not Continuing + + Student Retention + Programs & Courses Completed Students Graduated, Transferred, Hired + + + = Gov’t Grants & External Funding Tuition & Other Sources Of Revenue Student Attrition + = = Gov’t Approval For Credit Programs Courses Taught + + + “Delivery Loop” -Seto, 2008 © Gottheil/Smith 18
SEM Summit ‘ 09 “Capacity Development Loop” + + = Programs & Courses Offered + or - Programs & Courses Developed & Approved + + Demand for Programs & Courses Enrolled Reasons For Not Continuing + + Student Retention + Programs & Courses Completed Students Graduated, Transferred, Hired + + + = Gov’t Grants & External Funding Tuition & Other Sources Of Revenue Student Attrition + = = Gov’t Approval For Credit Programs Courses Taught + + + “Delivery Loop” -Seto, 2008 © Gottheil/Smith 18
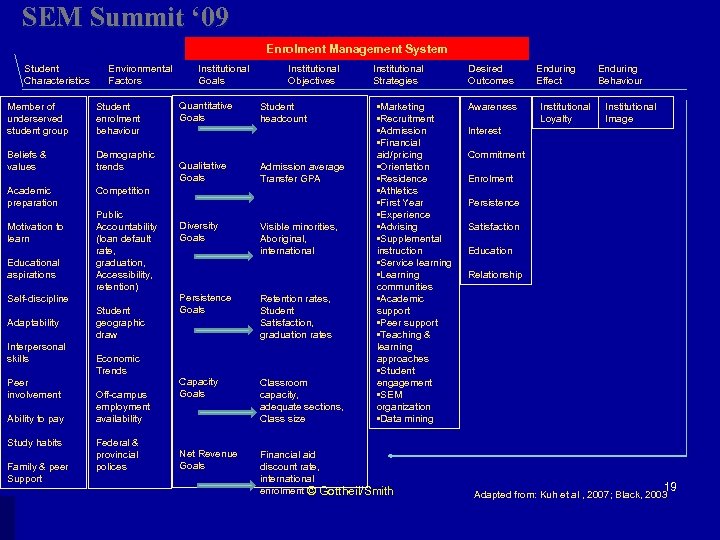 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Enrolment Management System Student Characteristics Environmental Factors Member of underserved student group Student enrolment behaviour Beliefs & values Demographic trends Academic preparation Institutional Goals Quantitative Goals Institutional Objectives Student headcount Competition Motivation to learn Educational aspirations Public Accountability (loan default rate, graduation, Accessibility, retention) Self-discipline Adaptability Interpersonal skills Peer involvement Ability to pay Study habits Family & peer Support Student geographic draw Economic Trends Off-campus employment availability Federal & provincial polices Qualitative Goals Diversity Goals Admission average Transfer GPA Visible minorities, Aboriginal, international Institutional Strategies • Marketing • Recruitment • Admission • Financial aid/pricing • Orientation • Residence • Athletics • First Year • Experience • Advising • Supplemental instruction • Service learning • Learning communities • Academic support • Peer support • Teaching & learning approaches • Student engagement • SEM organization • Data mining Persistence Goals Retention rates, Student Satisfaction, graduation rates Capacity Goals Classroom capacity, adequate sections, Class size Net Revenue Goals Financial aid discount rate, international enrolment © Gottheil/Smith Desired Outcomes Awareness Enduring Effect Institutional Loyalty Enduring Behaviour Institutional Image Interest Commitment Enrolment Persistence Satisfaction Education Relationship 19 Adapted from: Kuh et al , 2007; Black, 2003
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Enrolment Management System Student Characteristics Environmental Factors Member of underserved student group Student enrolment behaviour Beliefs & values Demographic trends Academic preparation Institutional Goals Quantitative Goals Institutional Objectives Student headcount Competition Motivation to learn Educational aspirations Public Accountability (loan default rate, graduation, Accessibility, retention) Self-discipline Adaptability Interpersonal skills Peer involvement Ability to pay Study habits Family & peer Support Student geographic draw Economic Trends Off-campus employment availability Federal & provincial polices Qualitative Goals Diversity Goals Admission average Transfer GPA Visible minorities, Aboriginal, international Institutional Strategies • Marketing • Recruitment • Admission • Financial aid/pricing • Orientation • Residence • Athletics • First Year • Experience • Advising • Supplemental instruction • Service learning • Learning communities • Academic support • Peer support • Teaching & learning approaches • Student engagement • SEM organization • Data mining Persistence Goals Retention rates, Student Satisfaction, graduation rates Capacity Goals Classroom capacity, adequate sections, Class size Net Revenue Goals Financial aid discount rate, international enrolment © Gottheil/Smith Desired Outcomes Awareness Enduring Effect Institutional Loyalty Enduring Behaviour Institutional Image Interest Commitment Enrolment Persistence Satisfaction Education Relationship 19 Adapted from: Kuh et al , 2007; Black, 2003
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 © Gottheil/Smith 20
SEM Summit ‘ 09 © Gottheil/Smith 20
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Major SEM Components Ø Accessibility Ø Enrolment Marketing Ø Accountability Ø Organization Ø Admission Policies Ø Financial Aid Ø Planning Ø Recruitment Ø Geographic Draw © Gottheil/Smith Ø Retention 21
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Major SEM Components Ø Accessibility Ø Enrolment Marketing Ø Accountability Ø Organization Ø Admission Policies Ø Financial Aid Ø Planning Ø Recruitment Ø Geographic Draw © Gottheil/Smith Ø Retention 21
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 SEM Started in the U. S. Ø Started in the late 1970’s at Boston College • As a result of declining traditional student enrolments Ø Early focus on attracting new students (e. g. , returning adults, women, minorities, lowincome) Ø Expanded to all types of PSE institutions (e. g. , public, private, 2 -year, 4 -year, grad) © Gottheil/Smith 22
SEM Summit ‘ 09 SEM Started in the U. S. Ø Started in the late 1970’s at Boston College • As a result of declining traditional student enrolments Ø Early focus on attracting new students (e. g. , returning adults, women, minorities, lowincome) Ø Expanded to all types of PSE institutions (e. g. , public, private, 2 -year, 4 -year, grad) © Gottheil/Smith 22
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 SEM Started in the U. S. (Cont’d) Ø Grew to include student success • First-Year Experience programs • Increased levels of student engagement Ø Increasing emphasis on connecting with institutional financial management Ø Now the concern of the senior leadership team – presidents, provost, deans © Gottheil/Smith 23
SEM Summit ‘ 09 SEM Started in the U. S. (Cont’d) Ø Grew to include student success • First-Year Experience programs • Increased levels of student engagement Ø Increasing emphasis on connecting with institutional financial management Ø Now the concern of the senior leadership team – presidents, provost, deans © Gottheil/Smith 23
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Emergence of SEM in Canada Ø Slower emergence of SEM in Canada Ø Driven by funding cuts, lack of revenue, heavier reliance on tuition, changing demographics Ø Many Canadian institutions have now adopted SEM in name, practice or both • We’re attending webinars, workshops & conferences • Some of us are working with consultants © Gottheil/Smith 24
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Emergence of SEM in Canada Ø Slower emergence of SEM in Canada Ø Driven by funding cuts, lack of revenue, heavier reliance on tuition, changing demographics Ø Many Canadian institutions have now adopted SEM in name, practice or both • We’re attending webinars, workshops & conferences • Some of us are working with consultants © Gottheil/Smith 24
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Importance of Partnering… 25
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Importance of Partnering… 25
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 What SEM factors are most associated with institutions successfully reaching their enrolment goals? © Gottheil/Smith 26
SEM Summit ‘ 09 What SEM factors are most associated with institutions successfully reaching their enrolment goals? © Gottheil/Smith 26
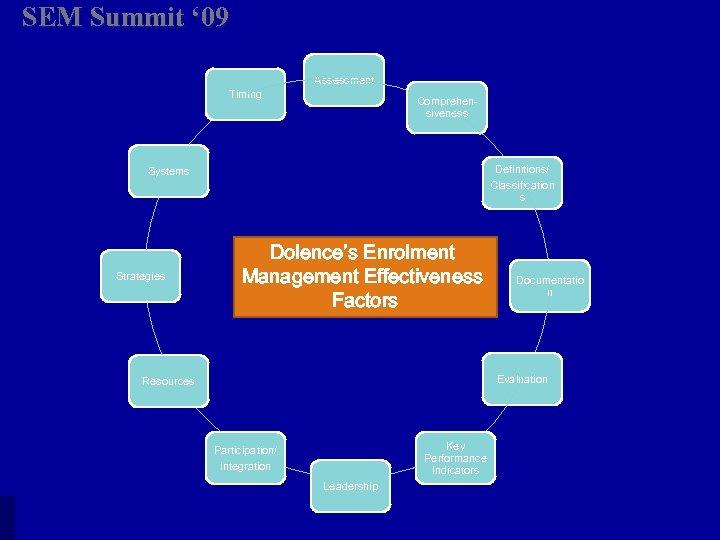 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Assessment Timing Comprehensiveness Definitions/ Classification s Systems Strategies Dolence’s Enrolment Management Effectiveness Factors Documentatio n Evaluation Resources Key Performance Indicators Participation/ Integration Leadership
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Assessment Timing Comprehensiveness Definitions/ Classification s Systems Strategies Dolence’s Enrolment Management Effectiveness Factors Documentatio n Evaluation Resources Key Performance Indicators Participation/ Integration Leadership
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Methodology Ø Mail survey sent to enrolment managers at 500 two- and four-year (public and private) undergraduate institutions, with the following response rates: • 4 -year public: 53% • 4 -year private: 53% • 2 -year public: 55% • 2 -year private: 49% Ø Multiple regression techniques were used to determine the relationship between the 12 individual enrolment management factors (identified by Dolence) and enrolment manager perceptions of enrolment performance (recruitment/retention) Ø An analysis was conducted for each of the 4 institutional stratifications © Gottheil/Smith 28
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Methodology Ø Mail survey sent to enrolment managers at 500 two- and four-year (public and private) undergraduate institutions, with the following response rates: • 4 -year public: 53% • 4 -year private: 53% • 2 -year public: 55% • 2 -year private: 49% Ø Multiple regression techniques were used to determine the relationship between the 12 individual enrolment management factors (identified by Dolence) and enrolment manager perceptions of enrolment performance (recruitment/retention) Ø An analysis was conducted for each of the 4 institutional stratifications © Gottheil/Smith 28
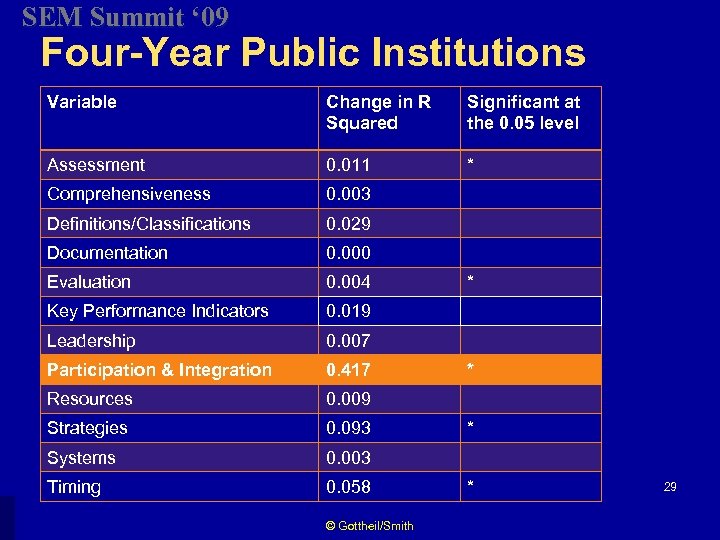 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Four-Year Public Institutions Variable Change in R Squared Significant at the 0. 05 level Assessment 0. 011 * Comprehensiveness 0. 003 Definitions/Classifications 0. 029 Documentation 0. 000 Evaluation 0. 004 Key Performance Indicators 0. 019 Leadership 0. 007 Participation & Integration 0. 417 Resources 0. 009 Strategies 0. 093 Systems 0. 003 Timing 0. 058 © Gottheil/Smith * * 29
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Four-Year Public Institutions Variable Change in R Squared Significant at the 0. 05 level Assessment 0. 011 * Comprehensiveness 0. 003 Definitions/Classifications 0. 029 Documentation 0. 000 Evaluation 0. 004 Key Performance Indicators 0. 019 Leadership 0. 007 Participation & Integration 0. 417 Resources 0. 009 Strategies 0. 093 Systems 0. 003 Timing 0. 058 © Gottheil/Smith * * 29
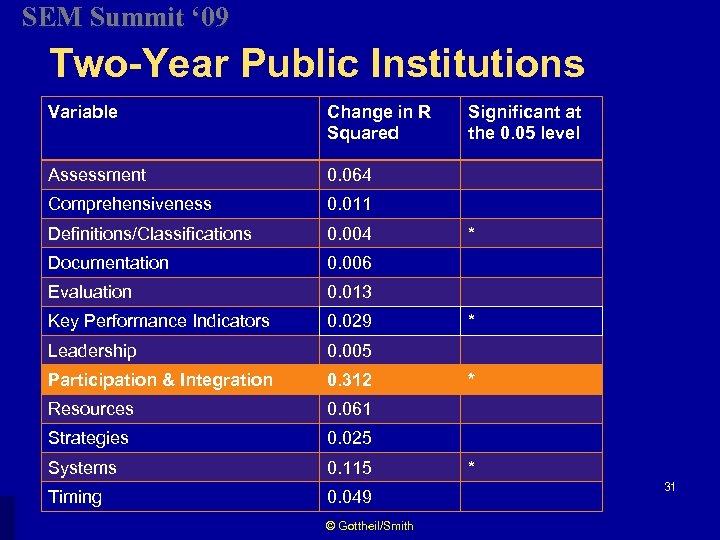 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Two-Year Public Institutions Variable Change in R Squared Assessment 0. 064 Comprehensiveness 0. 011 Definitions/Classifications 0. 004 Documentation 0. 006 Evaluation 0. 013 Key Performance Indicators 0. 029 Leadership 0. 005 Participation & Integration 0. 312 Resources 0. 061 Strategies 0. 025 Systems 0. 115 Timing 0. 049 © Gottheil/Smith Significant at the 0. 05 level * * 31
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Two-Year Public Institutions Variable Change in R Squared Assessment 0. 064 Comprehensiveness 0. 011 Definitions/Classifications 0. 004 Documentation 0. 006 Evaluation 0. 013 Key Performance Indicators 0. 029 Leadership 0. 005 Participation & Integration 0. 312 Resources 0. 061 Strategies 0. 025 Systems 0. 115 Timing 0. 049 © Gottheil/Smith Significant at the 0. 05 level * * 31
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Participation & integration is the most important factor at both 4 -year and 2 -year public institutions in sustaining long-term SEM success. -Smith, 1997 © Gottheil/Smith 33
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Participation & integration is the most important factor at both 4 -year and 2 -year public institutions in sustaining long-term SEM success. -Smith, 1997 © Gottheil/Smith 33
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 What is Participation & Integration? Ø Participation of senior administration, academic governance, academic administration, faculty and the persons responsible for strategy and tactic implementation Ø In short, both vertical and horizontal involvement in SEM © Gottheil/Smith 34
SEM Summit ‘ 09 What is Participation & Integration? Ø Participation of senior administration, academic governance, academic administration, faculty and the persons responsible for strategy and tactic implementation Ø In short, both vertical and horizontal involvement in SEM © Gottheil/Smith 34
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Some Collaboration is Common Ø High levels of collaboration generally exist between academic and student affairs activities related to counselling, first-year experience programs, orientation and recruitment -Kezaar, Hirsh & Burak (2002) © Gottheil/Smith 41
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Some Collaboration is Common Ø High levels of collaboration generally exist between academic and student affairs activities related to counselling, first-year experience programs, orientation and recruitment -Kezaar, Hirsh & Burak (2002) © Gottheil/Smith 41
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 However… Ø Many institutions mistake a series of joint events for true collaboration Ø To truly be competitive and to meet the rigors of accountability, institutions must go beyond activities and embrace collaborative dialogue © Gottheil/Smith 42
SEM Summit ‘ 09 However… Ø Many institutions mistake a series of joint events for true collaboration Ø To truly be competitive and to meet the rigors of accountability, institutions must go beyond activities and embrace collaborative dialogue © Gottheil/Smith 42
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 It is time for academic and student affairs professionals alike to realize that it is only through the breaking down of current barriers— real and perceived—that institutions will achieve the outcomes they seek. Through strategic collaboration, both segments…can develop and implement programs and processes that add value and benefit students -Newton & Smith, 2009 © Gottheil/Smith 43
SEM Summit ‘ 09 It is time for academic and student affairs professionals alike to realize that it is only through the breaking down of current barriers— real and perceived—that institutions will achieve the outcomes they seek. Through strategic collaboration, both segments…can develop and implement programs and processes that add value and benefit students -Newton & Smith, 2009 © Gottheil/Smith 43
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Collaborative Dialogue Requires Partnerships with… Ø Senior Management Ø Deans, Associate Deans, Dept Heads Ø Student Affairs Ø Institutional Research/Analysis Ø Finance/Budget Ø Marketing/PR/Communication © Gottheil/Smith 44
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Collaborative Dialogue Requires Partnerships with… Ø Senior Management Ø Deans, Associate Deans, Dept Heads Ø Student Affairs Ø Institutional Research/Analysis Ø Finance/Budget Ø Marketing/PR/Communication © Gottheil/Smith 44
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 “What is needed is an adjustment in the lens with which enrollment professionals view (S)EM as a quintessentially academic enterprise. ” -Henderson, 2005 © Gottheil/Smith 45
SEM Summit ‘ 09 “What is needed is an adjustment in the lens with which enrollment professionals view (S)EM as a quintessentially academic enterprise. ” -Henderson, 2005 © Gottheil/Smith 45
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Guiding Principles – SEM Ethos Ø A shared responsibility Ø Integrated institutional planning Ø A focus on service Ø Accountability Ø Research & evaluation Ø For the long haul © Gottheil/Smith 46
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Guiding Principles – SEM Ethos Ø A shared responsibility Ø Integrated institutional planning Ø A focus on service Ø Accountability Ø Research & evaluation Ø For the long haul © Gottheil/Smith 46
 SEM Summit ‘ 09 Questions & Comments 47
SEM Summit ‘ 09 Questions & Comments 47


