lecture 8 social identity.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Self-knowledge. Lecture 8. Social Component of the Self: Social Identity. 1) The nature of identity 2) Identity development 3) Identity Crisis: a. Identity deficit b. Identity conflict 4) Resolution of identity crises.
Self-knowledge. Lecture 8. Social Component of the Self: Social Identity. 1) The nature of identity 2) Identity development 3) Identity Crisis: a. Identity deficit b. Identity conflict 4) Resolution of identity crises.
 Identity Nature. Social Identity: Identity Elements that are socially observable Publicly available expressions of the self Let other people know who you are and what they can expect from you.
Identity Nature. Social Identity: Identity Elements that are socially observable Publicly available expressions of the self Let other people know who you are and what they can expect from you.
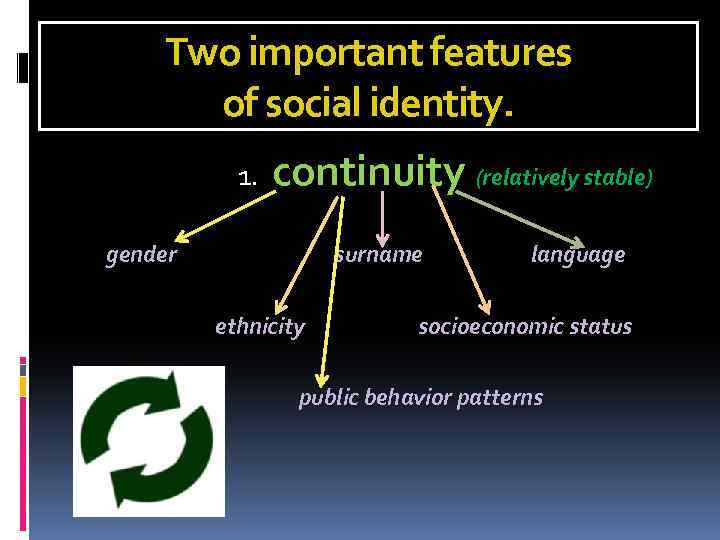 Two important features of social identity. 1. continuity (relatively stable) gender surname ethnicity language socioeconomic status public behavior patterns
Two important features of social identity. 1. continuity (relatively stable) gender surname ethnicity language socioeconomic status public behavior patterns
 2. contrast (unique in the eyes of others) Combination of characteristics that make up your identity differentiates you from everyone else. Example: among the students you are the only one who likes a particular type of music and has your ethnic background and color.
2. contrast (unique in the eyes of others) Combination of characteristics that make up your identity differentiates you from everyone else. Example: among the students you are the only one who likes a particular type of music and has your ethnic background and color.
 Identity development. Erikson (1968) believed: believed - Identity results from efforts to separate oneself from one’s parents in order to make decisions about what values to hold and goals to pursue in life. - There’s always a risk of role confusion (unachieved identity)
Identity development. Erikson (1968) believed: believed - Identity results from efforts to separate oneself from one’s parents in order to make decisions about what values to hold and goals to pursue in life. - There’s always a risk of role confusion (unachieved identity)
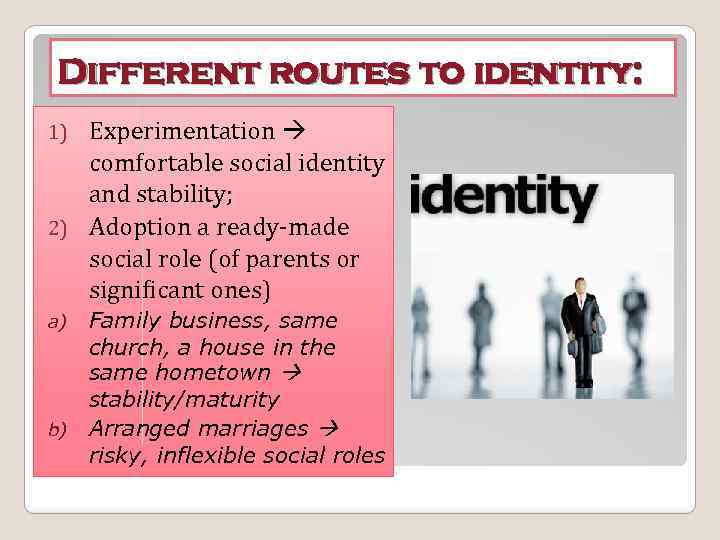 Different routes to identity: Experimentation comfortable social identity and stability; 2) Adoption a ready-made social role (of parents or significant ones) 1) Family business, same church, a house in the same hometown stability/maturity b) Arranged marriages risky, inflexible social roles a)
Different routes to identity: Experimentation comfortable social identity and stability; 2) Adoption a ready-made social role (of parents or significant ones) 1) Family business, same church, a house in the same hometown stability/maturity b) Arranged marriages risky, inflexible social roles a)
 Identity Crisis what? Feeling of anxiety that accompany efforts to define or redefine one’s own individuality when? Early in adolescence or later in midlife or multiple times which? Identity deficit or identity conflict
Identity Crisis what? Feeling of anxiety that accompany efforts to define or redefine one’s own individuality when? Early in adolescence or later in midlife or multiple times which? Identity deficit or identity conflict
 Identity Deficit. When a person has not formed an adequate identity and thus has trouble making major decisions. Example: ‘Should I go to college or not? If I go, what should I study for? Should I get married? ’ Trouble no inner foundation, or you have to doubt previous assumptions about yourself or the world.
Identity Deficit. When a person has not formed an adequate identity and thus has trouble making major decisions. Example: ‘Should I go to college or not? If I go, what should I study for? Should I get married? ’ Trouble no inner foundation, or you have to doubt previous assumptions about yourself or the world.
 Vulnerability of people with identity deficit: 1) Very curious about other belief systems and can be easily influenced 2) Feelings of emptiness and their search for new values make them very persuadable 3) Depressed and confused at one time point, but then euphoric about new possibilities.
Vulnerability of people with identity deficit: 1) Very curious about other belief systems and can be easily influenced 2) Feelings of emptiness and their search for new values make them very persuadable 3) Depressed and confused at one time point, but then euphoric about new possibilities.
 Identity Conflict what? Incompatibility between two or more aspects of identity when? A person is forced to make an important and difficult life decision example? a) Immigrant to the USA has a conflict between wanting to assimilate into the American culture or maintain his ethnicity b) A career woman or dedicated mother?
Identity Conflict what? Incompatibility between two or more aspects of identity when? A person is forced to make an important and difficult life decision example? a) Immigrant to the USA has a conflict between wanting to assimilate into the American culture or maintain his ethnicity b) A career woman or dedicated mother?
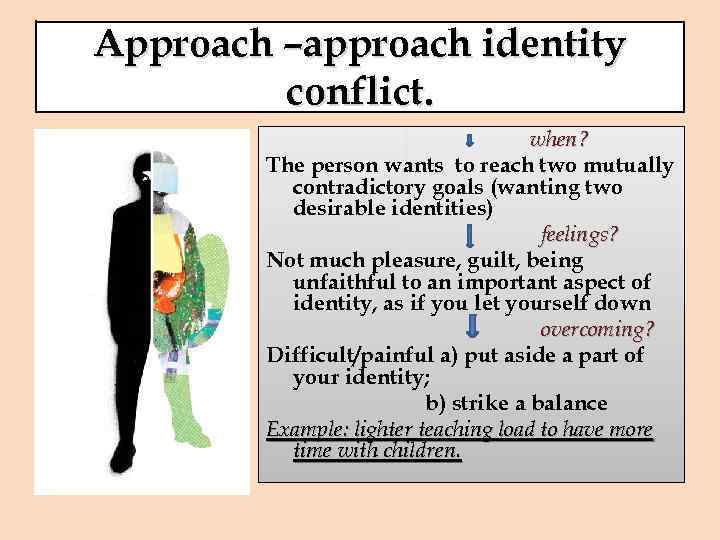 Approach –approach identity conflict. when? The person wants to reach two mutually contradictory goals (wanting two desirable identities) feelings? Not much pleasure, guilt, being unfaithful to an important aspect of identity, as if you let yourself down overcoming? Difficult/painful a) put aside a part of your identity; b) strike a balance Example: lighter teaching load to have more time with children.
Approach –approach identity conflict. when? The person wants to reach two mutually contradictory goals (wanting two desirable identities) feelings? Not much pleasure, guilt, being unfaithful to an important aspect of identity, as if you let yourself down overcoming? Difficult/painful a) put aside a part of your identity; b) strike a balance Example: lighter teaching load to have more time with children.
 Resolution of Identity Crisis Two steps: 1) Decide which values are most important to you 2) Transform these abstract values into desires and actual behaviors Example: value is a family (early find a spouse adulthood) work hard on relationship marry and have children
Resolution of Identity Crisis Two steps: 1) Decide which values are most important to you 2) Transform these abstract values into desires and actual behaviors Example: value is a family (early find a spouse adulthood) work hard on relationship marry and have children
 Midlife Crisis Characteristics: 1) Dissatisfaction with existing identities (at work or in a marriage) 2) A period of regret over time spent (if only I had done…) 3) Behaving like adolescents: experiments with alternative lifestyles, forming new relationships, giving up precious ambitions and responsibilities 4) Changing careers, spouses, religions, priorities.
Midlife Crisis Characteristics: 1) Dissatisfaction with existing identities (at work or in a marriage) 2) A period of regret over time spent (if only I had done…) 3) Behaving like adolescents: experiments with alternative lifestyles, forming new relationships, giving up precious ambitions and responsibilities 4) Changing careers, spouses, religions, priorities.


