lecture 11 self-regulation.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 12
 SELF-KNOWLEDGE AND ELFS REGULATION. LECTURE 11 Self-Regulation as Self’s Capacity 2. Ingredients of Self-Regulation 3. Self-regulation Motivation: Friends or Enemies. 4. Motivation after ego-depletion. 1.
SELF-KNOWLEDGE AND ELFS REGULATION. LECTURE 11 Self-Regulation as Self’s Capacity 2. Ingredients of Self-Regulation 3. Self-regulation Motivation: Friends or Enemies. 4. Motivation after ego-depletion. 1.
 Self-regulation Self’s Capacity for altering its behaviors Characteristics: 1) Greatly increases the flexibility and adaptability of human behavior. 2) Important basis for free will and socially desirable behavior 3) Constrains motivations.
Self-regulation Self’s Capacity for altering its behaviors Characteristics: 1) Greatly increases the flexibility and adaptability of human behavior. 2) Important basis for free will and socially desirable behavior 3) Constrains motivations.
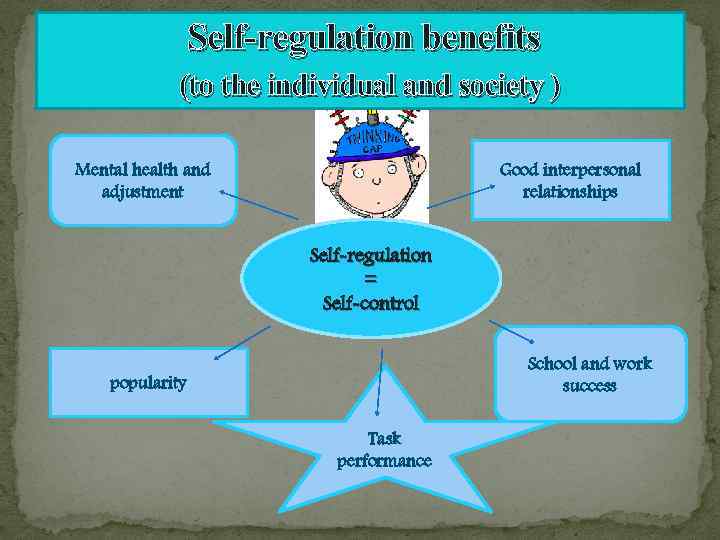 Self-regulation benefits (to the individual and society ) Good interpersonal relationships Mental health and adjustment Self-regulation = Self-control School and work success popularity Task performance
Self-regulation benefits (to the individual and society ) Good interpersonal relationships Mental health and adjustment Self-regulation = Self-control School and work success popularity Task performance
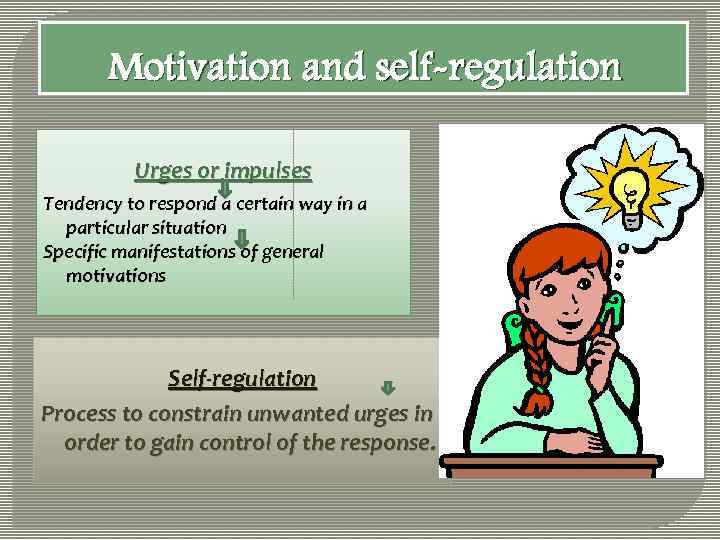 Motivation and self-regulation Urges or impulses Tendency to respond a certain way in a particular situation Specific manifestations of general motivations Self-regulation Process to constrain unwanted urges in order to gain control of the response.
Motivation and self-regulation Urges or impulses Tendency to respond a certain way in a particular situation Specific manifestations of general motivations Self-regulation Process to constrain unwanted urges in order to gain control of the response.
 Ego depletion A state in which the self does not have all the resources it has normally You are less able and less willing to function optimally why? Self’s executive function = self-regulation = effortful choice and active initiative Resources are consumed during such activities
Ego depletion A state in which the self does not have all the resources it has normally You are less able and less willing to function optimally why? Self’s executive function = self-regulation = effortful choice and active initiative Resources are consumed during such activities
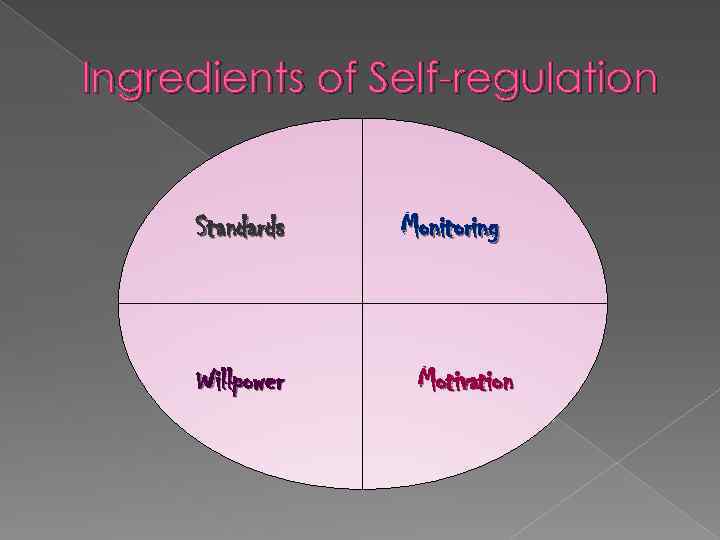 Ingredients of Self-regulation Standards Willpower Monitoring Motivation
Ingredients of Self-regulation Standards Willpower Monitoring Motivation
 Standards and Monitoring 1) Effective self-regulation requires a clear and well-defined standard. Ambiguous, uncertain, inconsistent, or conflicting standards make self-regulation difficult. 2) It is difficult if not impossible to regulate a behavior without keeping track of it. If the self falls short, then self-regulation requires initiating some operation to change the self in order to bring it up to what it should be.
Standards and Monitoring 1) Effective self-regulation requires a clear and well-defined standard. Ambiguous, uncertain, inconsistent, or conflicting standards make self-regulation difficult. 2) It is difficult if not impossible to regulate a behavior without keeping track of it. If the self falls short, then self-regulation requires initiating some operation to change the self in order to bring it up to what it should be.
 willpower Willpower is self-regulatory strength. Operations aimed at changing the self are difficult and require some power. Regulating the self depends on a limited resource that operates like a strength or energy and becomes temporary depleted. (acts of self-control consume substantial quantities of glucose, resulting in lower levels of it in
willpower Willpower is self-regulatory strength. Operations aimed at changing the self are difficult and require some power. Regulating the self depends on a limited resource that operates like a strength or energy and becomes temporary depleted. (acts of self-control consume substantial quantities of glucose, resulting in lower levels of it in
 Motivation To achieve the goal or meet the standard, which in practice amounts to motivation to regulate the self. 1. If the standards are clear, monitoring is fully effective, and the person’s resources are abundant, he may still fail to selfregulate and reach the goal 2. If motivation is high, this may compensate you lower level of willpower or a greater difficulty of monitoring.
Motivation To achieve the goal or meet the standard, which in practice amounts to motivation to regulate the self. 1. If the standards are clear, monitoring is fully effective, and the person’s resources are abundant, he may still fail to selfregulate and reach the goal 2. If motivation is high, this may compensate you lower level of willpower or a greater difficulty of monitoring.
 Self-regulation and motivation: friends or enemies? Friends 1. Self-stopping (restraining Enemies Motivational conflict: from overeating, smoking, Clashes between natural alcohol drinking, etc) impulses and cultural desire to be healthy. demands (desire for social 2. Meeting principal biological strategies of acceptance but demonstrating selfishness. human beings. (success at So, people learn that interpersonal and group restraining selfishness is life). helpful in order to gain social acceptance)
Self-regulation and motivation: friends or enemies? Friends 1. Self-stopping (restraining Enemies Motivational conflict: from overeating, smoking, Clashes between natural alcohol drinking, etc) impulses and cultural desire to be healthy. demands (desire for social 2. Meeting principal biological strategies of acceptance but demonstrating selfishness. human beings. (success at So, people learn that interpersonal and group restraining selfishness is life). helpful in order to gain social acceptance)
 Motivation and Ego depletion Research findings: Depleted participants can effectively self-regulate if they are offered an incentive to do so. Thus, the motivational incentive completely erased the effect of ego depletion. Fact 1: The fact that high motivation can overcome the effect of tiredness does not mean that tiredness is nothing more than a lack of motivation. Fact 2: Getting people to believe that they can do it seems to help them keep up with controlled response, but it doesn’t mean that ego-depletion is a lack of selfconfidence.
Motivation and Ego depletion Research findings: Depleted participants can effectively self-regulate if they are offered an incentive to do so. Thus, the motivational incentive completely erased the effect of ego depletion. Fact 1: The fact that high motivation can overcome the effect of tiredness does not mean that tiredness is nothing more than a lack of motivation. Fact 2: Getting people to believe that they can do it seems to help them keep up with controlled response, but it doesn’t mean that ego-depletion is a lack of selfconfidence.
 Effective self-regulation seems to involve using the glucose in the bloodstream to achieve what is a psychologically and biologically difficult. When the source of fuel for all brain processes (glucose) has been depleted the person is temporarily less able to function at optimal levels. The power of motivation to overcome depletion may lie in the
Effective self-regulation seems to involve using the glucose in the bloodstream to achieve what is a psychologically and biologically difficult. When the source of fuel for all brain processes (glucose) has been depleted the person is temporarily less able to function at optimal levels. The power of motivation to overcome depletion may lie in the


