7c4a7e09b004ca47ff578fa8f8f779cf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Selection and Acquisition n Texts and Readings n Robson, W (1994) Strategic Management and Information Systems, Pitman, London, UK n n Lucas, H. (1997) Information technology for management, Mc. Graw-Hill, USA n n n Chapter 12 Chapter 14 and 17 Academic papers Lecture notes
Selection and Acquisition n Texts and Readings n Robson, W (1994) Strategic Management and Information Systems, Pitman, London, UK n n Lucas, H. (1997) Information technology for management, Mc. Graw-Hill, USA n n n Chapter 12 Chapter 14 and 17 Academic papers Lecture notes
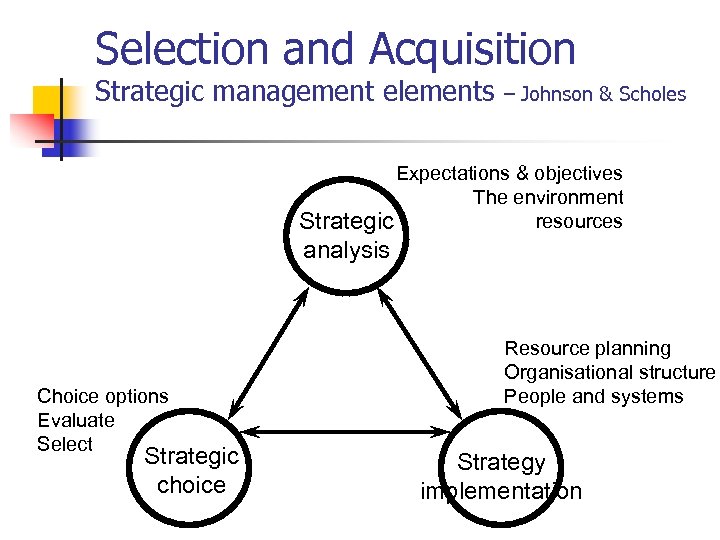 Selection and Acquisition Strategic management elements – Johnson & Scholes Expectations & objectives The environment resources Strategic analysis Choice options Evaluate Select Strategic choice Resource planning Organisational structure People and systems Strategy implementation
Selection and Acquisition Strategic management elements – Johnson & Scholes Expectations & objectives The environment resources Strategic analysis Choice options Evaluate Select Strategic choice Resource planning Organisational structure People and systems Strategy implementation
 Selection and Acquisition n n Software acquisition Hardware acquisition Communications acquisition Outsourcing
Selection and Acquisition n n Software acquisition Hardware acquisition Communications acquisition Outsourcing
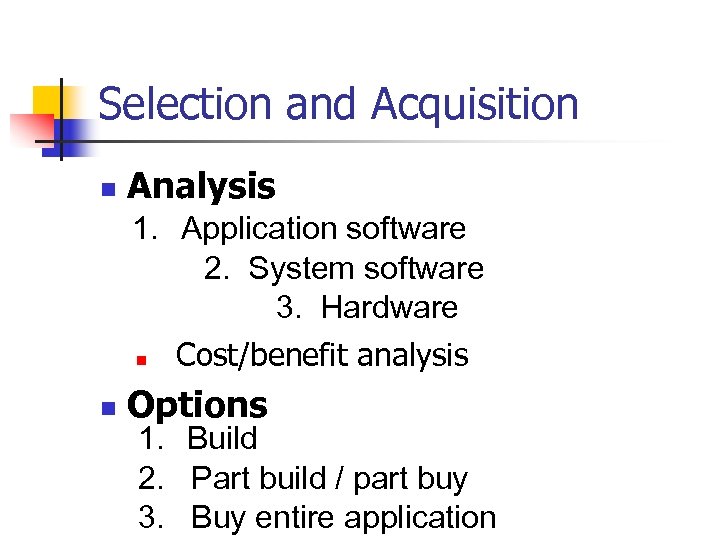 Selection and Acquisition n Analysis 1. Application software 2. System software 3. Hardware n n Cost/benefit analysis Options 1. Build 2. Part build / part buy 3. Buy entire application
Selection and Acquisition n Analysis 1. Application software 2. System software 3. Hardware n n Cost/benefit analysis Options 1. Build 2. Part build / part buy 3. Buy entire application
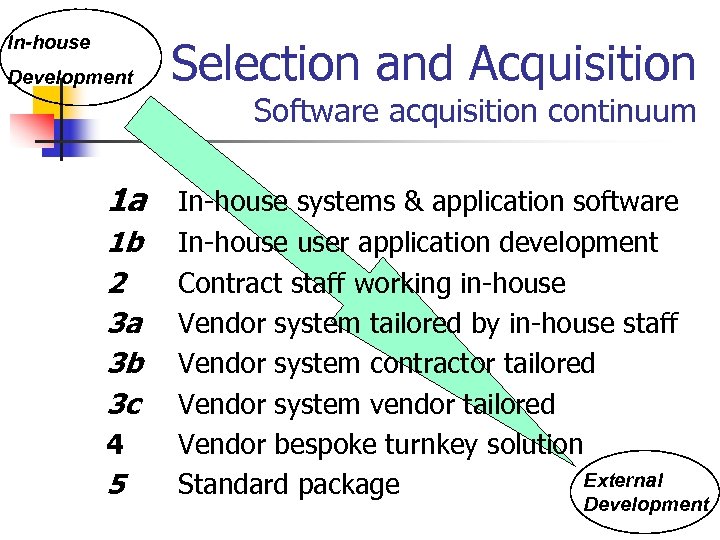 In-house Development Selection and Acquisition Software acquisition continuum 1 a In-house systems & application software 1 b 2 3 a 3 b 3 c 4 5 In-house user application development Contract staff working in-house Vendor system tailored by in-house staff Vendor system contractor tailored Vendor system vendor tailored Vendor bespoke turnkey solution External Standard package Development
In-house Development Selection and Acquisition Software acquisition continuum 1 a In-house systems & application software 1 b 2 3 a 3 b 3 c 4 5 In-house user application development Contract staff working in-house Vendor system tailored by in-house staff Vendor system contractor tailored Vendor system vendor tailored Vendor bespoke turnkey solution External Standard package Development
 Selection and Acquisition n Build n Implemented in accordance with the Contract View and the Engineering View of ISO/IEC 12207 n n Acquisition process Supply process Development process Maintenance process
Selection and Acquisition n Build n Implemented in accordance with the Contract View and the Engineering View of ISO/IEC 12207 n n Acquisition process Supply process Development process Maintenance process
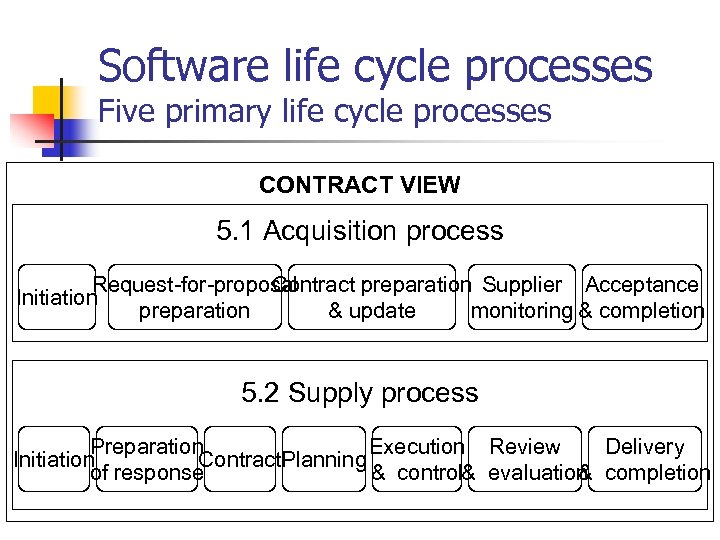 Software life cycle processes Five primary life cycle processes CONTRACT VIEW 5. 1 Acquisition process Request-for-proposal Contract preparation Supplier Acceptance Initiation preparation & update monitoring & completion 5. 2 Supply process Preparation Execution Review Delivery Initiation Contract. Planning of response & control& evaluation completion &
Software life cycle processes Five primary life cycle processes CONTRACT VIEW 5. 1 Acquisition process Request-for-proposal Contract preparation Supplier Acceptance Initiation preparation & update monitoring & completion 5. 2 Supply process Preparation Execution Review Delivery Initiation Contract. Planning of response & control& evaluation completion &
 Selection and Acquisition Request-for-proposal - Lucas n n n n n Present system (database, I/O, Volumes and Frequencies) Proposed system (needs items above) Vendor service Reliability data Backup Demonstration Evaluation arrangements Conversion and transition Descriptive material Price
Selection and Acquisition Request-for-proposal - Lucas n n n n n Present system (database, I/O, Volumes and Frequencies) Proposed system (needs items above) Vendor service Reliability data Backup Demonstration Evaluation arrangements Conversion and transition Descriptive material Price
 Selection and Acquisition Request-for-proposal n ISO/IEC 12207 n n n n System requirements Scope statement Instructions to bidders List of software products Terms and conditions Control of subcontracts Technical constraints NB
Selection and Acquisition Request-for-proposal n ISO/IEC 12207 n n n n System requirements Scope statement Instructions to bidders List of software products Terms and conditions Control of subcontracts Technical constraints NB
 Selection and Acquisition Contract preparation & update n All happens before planning begins
Selection and Acquisition Contract preparation & update n All happens before planning begins
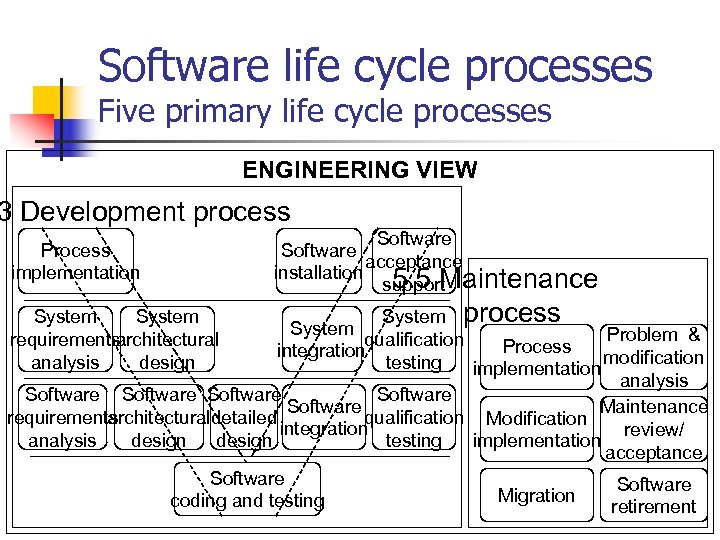 Software life cycle processes Five primary life cycle processes ENGINEERING VIEW 3 Development process Process implementation Software acceptance installation 5. 5 Maintenance support System process System Problem & qualification Process integration modification testing implementation analysis Software Software Maintenance requirements architecturaldetailed qualification Modification integration review/ analysis design testing implementation acceptance Software Migration coding and testing retirement System requirements architectural analysis design
Software life cycle processes Five primary life cycle processes ENGINEERING VIEW 3 Development process Process implementation Software acceptance installation 5. 5 Maintenance support System process System Problem & qualification Process integration modification testing implementation analysis Software Software Maintenance requirements architecturaldetailed qualification Modification integration review/ analysis design testing implementation acceptance Software Migration coding and testing retirement System requirements architectural analysis design
 Selection and Acquisition n Buy n n (Buy, lease or rent) Large and midrange computers/systems Personal computers/systems
Selection and Acquisition n Buy n n (Buy, lease or rent) Large and midrange computers/systems Personal computers/systems
 Selection and Acquisition Software acquisition 1 n Vendor position in the marketplace n n Size, experience, certification Quality considerations n n External usability Factors Context of use matters (Users, Tasks & Environment) Amount of Functionality Internal quality factors
Selection and Acquisition Software acquisition 1 n Vendor position in the marketplace n n Size, experience, certification Quality considerations n n External usability Factors Context of use matters (Users, Tasks & Environment) Amount of Functionality Internal quality factors
 Selection and Acquisition Software acquisition 2 n Technology requirements n n Ownership n n Own or licence, copyright, escrow Cost and funding n n System software, hardware, communications requirements Number of quotations Documentation and manuals
Selection and Acquisition Software acquisition 2 n Technology requirements n n Ownership n n Own or licence, copyright, escrow Cost and funding n n System software, hardware, communications requirements Number of quotations Documentation and manuals
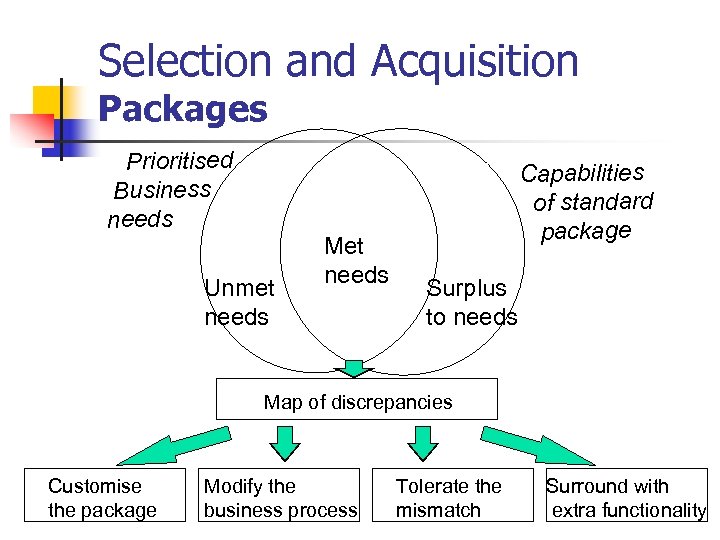 Selection and Acquisition Packages Prioritised Business needs Unmet needs Met needs Capabilities of standard package Surplus to needs Map of discrepancies Customise the package Modify the business process Tolerate the mismatch Surround with extra functionality
Selection and Acquisition Packages Prioritised Business needs Unmet needs Met needs Capabilities of standard package Surplus to needs Map of discrepancies Customise the package Modify the business process Tolerate the mismatch Surround with extra functionality
 Selection and Acquisition Software acquisition 3 n n n Demonstration copy. Maturity of the software product. User groups.
Selection and Acquisition Software acquisition 3 n n n Demonstration copy. Maturity of the software product. User groups.
 Selection and Acquisition Software acquisition 4
Selection and Acquisition Software acquisition 4
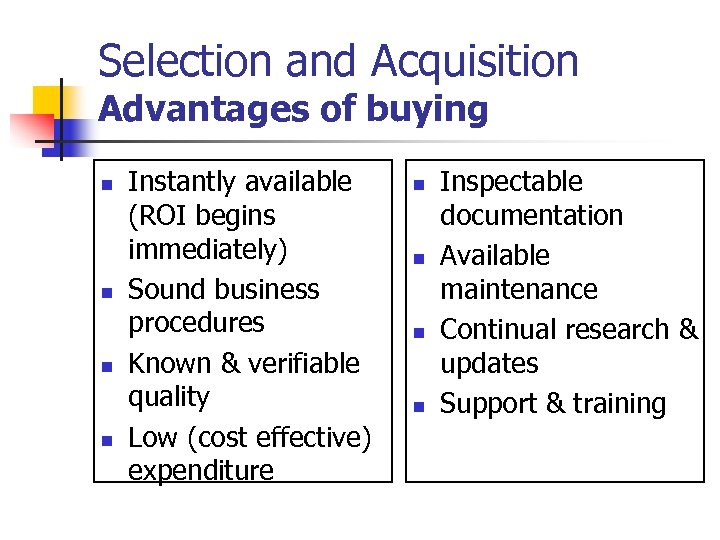 Selection and Acquisition Advantages of buying n n Instantly available (ROI begins immediately) Sound business procedures Known & verifiable quality Low (cost effective) expenditure n n Inspectable documentation Available maintenance Continual research & updates Support & training
Selection and Acquisition Advantages of buying n n Instantly available (ROI begins immediately) Sound business procedures Known & verifiable quality Low (cost effective) expenditure n n Inspectable documentation Available maintenance Continual research & updates Support & training
 Selection and Acquisition Disadvantages of buying n See page 471 n Too much functionality
Selection and Acquisition Disadvantages of buying n See page 471 n Too much functionality
 NB Selection and Acquisition Buying off-the-shelf n ISO/IEC 12207 n n The requirements for the software product are met. The documentation is available. Proprietary, usage, ownership, warranty and licensing rights are satisfied. Future support for the software product is planned.
NB Selection and Acquisition Buying off-the-shelf n ISO/IEC 12207 n n The requirements for the software product are met. The documentation is available. Proprietary, usage, ownership, warranty and licensing rights are satisfied. Future support for the software product is planned.
 Selection and Acquisition Strategic considerations n n n Prioritise requirements. Cost benefits. End-user computing fit. n n Single vendor environment Best of breed for each businees situation
Selection and Acquisition Strategic considerations n n n Prioritise requirements. Cost benefits. End-user computing fit. n n Single vendor environment Best of breed for each businees situation
 Selection and Acquisition Hardware acquisition 1 n n n Vendor position in the marketplace. ISO/other standards compliant. Taxonomy issues. n n Mainframe, Minicomputer or Microcomputer. Technical maturity. Large computer, Midrange or PC • Number of users • Processing speed • Memory capacity • Cost
Selection and Acquisition Hardware acquisition 1 n n n Vendor position in the marketplace. ISO/other standards compliant. Taxonomy issues. n n Mainframe, Minicomputer or Microcomputer. Technical maturity. Large computer, Midrange or PC • Number of users • Processing speed • Memory capacity • Cost
 Selection and Acquisition Hardware acquisition 2 n n Cost and funding (Buy, lease or rent). Human-Computer Interaction considerations. Legal considerations - health & safety, EU directive. Service level agreements.
Selection and Acquisition Hardware acquisition 2 n n Cost and funding (Buy, lease or rent). Human-Computer Interaction considerations. Legal considerations - health & safety, EU directive. Service level agreements.
 Selection and Acquisition Communications acquisition n Software n Hardware
Selection and Acquisition Communications acquisition n Software n Hardware
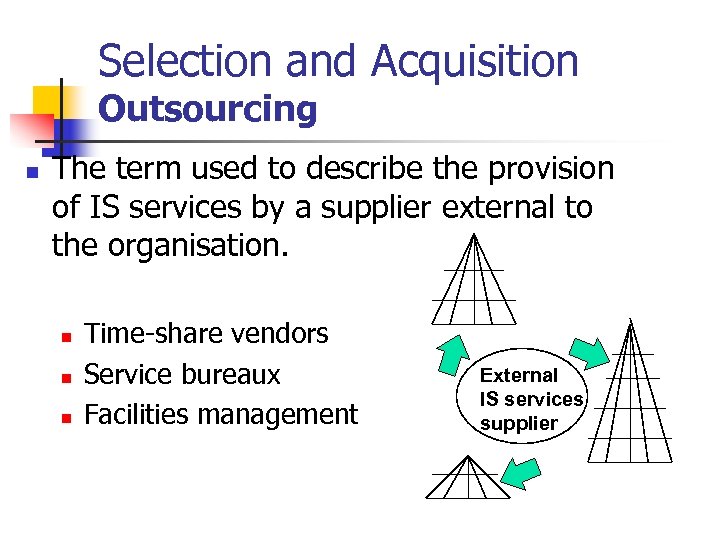 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing n The term used to describe the provision of IS services by a supplier external to the organisation. n n n Time-share vendors Service bureaux Facilities management External IS services supplier
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing n The term used to describe the provision of IS services by a supplier external to the organisation. n n n Time-share vendors Service bureaux Facilities management External IS services supplier
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Time-share vendors n n n In a time-share system processor time is divided into time-slices and these are shared between users. Processor time can be measured and sold to subscribing users. Interactive use of processor time.
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Time-share vendors n n n In a time-share system processor time is divided into time-slices and these are shared between users. Processor time can be measured and sold to subscribing users. Interactive use of processor time.
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Service bureaux n An organisation that provides computing or data-processing services for other organisations or individuals Longley & Shain
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Service bureaux n An organisation that provides computing or data-processing services for other organisations or individuals Longley & Shain
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management n n n The use of an independent service organisation to manage and operate a computing installation - Longley & Shain Can also be described as using an outside firm who specialise in operating, developing and managing various aspects of IT. Provides management and technical skills
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management n n n The use of an independent service organisation to manage and operate a computing installation - Longley & Shain Can also be described as using an outside firm who specialise in operating, developing and managing various aspects of IT. Provides management and technical skills
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management n Driving factors 1 Business pressures n n Perceived to be of a lower cost. IS services are not part of the core business activity therefore not necessary to have in-house specialisation in IS.
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management n Driving factors 1 Business pressures n n Perceived to be of a lower cost. IS services are not part of the core business activity therefore not necessary to have in-house specialisation in IS.
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management n Driving factors 2 Technical/People pressures. n n n Non-availability of qualified technical staff required to provide a mature IS service. Non-availability of qualified technical staff required to provide a leading edge IS service. Need for staff to work on new initiatives.
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management n Driving factors 2 Technical/People pressures. n n n Non-availability of qualified technical staff required to provide a mature IS service. Non-availability of qualified technical staff required to provide a leading edge IS service. Need for staff to work on new initiatives.
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management n n n Examples Outsource legacy systems and concentrate on client/server architecture in house. Outsource network management. Outsource Internet requirements.
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management n n n Examples Outsource legacy systems and concentrate on client/server architecture in house. Outsource network management. Outsource Internet requirements.
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management Model for outsourcing n n Strategic statement Decide whether to outsource n n Define outsourcing requirements n n Identify and evaluate benefits, risks and options identify or develop functions to be outsourced, specification of requirements and potential suppliers. Invite tenders. Choose a contractor Negotiate a contract Implement & monitor
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management Model for outsourcing n n Strategic statement Decide whether to outsource n n Define outsourcing requirements n n Identify and evaluate benefits, risks and options identify or develop functions to be outsourced, specification of requirements and potential suppliers. Invite tenders. Choose a contractor Negotiate a contract Implement & monitor
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management Organisational Benefits (perceived) n n IS annual requirements are known so a fixed quotation (accountancy fit) can be got for IS service. Long term salary gains as staff transfer to the FM supplier. IS service can be guaranteed through Service Level Agreements. Cost effective access to the expertise of the FM supplier.
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management Organisational Benefits (perceived) n n IS annual requirements are known so a fixed quotation (accountancy fit) can be got for IS service. Long term salary gains as staff transfer to the FM supplier. IS service can be guaranteed through Service Level Agreements. Cost effective access to the expertise of the FM supplier.
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management Organisational Risks n n n n Loss of in-house expertise in technology and applications. Loss of control. Supplier’s lack of business knowledge. True costs are never fully appreciated. People problems. Dependant on supplier reinvesting in new technology. Difficult to bring back in-house
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management Organisational Risks n n n n Loss of in-house expertise in technology and applications. Loss of control. Supplier’s lack of business knowledge. True costs are never fully appreciated. People problems. Dependant on supplier reinvesting in new technology. Difficult to bring back in-house
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management Employee Benefits n n n Opportunities for career advancement in the FM company. Exposure to alternative and leading edge technology. Opportunity to bring specialised skill to FM company.
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management Employee Benefits n n n Opportunities for career advancement in the FM company. Exposure to alternative and leading edge technology. Opportunity to bring specialised skill to FM company.
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management Employee Risks n Lost opportunities for career advancement.
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management Employee Risks n Lost opportunities for career advancement.
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management n See handout page 354
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing - Facilities management n See handout page 354
 Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing Review question n In some countries, the outsourcing process in governed by Law. n BCS, 1996, option 1 E, Q 6 Why would this be so?
Selection and Acquisition Outsourcing Review question n In some countries, the outsourcing process in governed by Law. n BCS, 1996, option 1 E, Q 6 Why would this be so?
 Selection and Acquisition Contracting practice n n Professional team. Importance of tender documents. n n Importance of records Contracting procedures. n Variation charges
Selection and Acquisition Contracting practice n n Professional team. Importance of tender documents. n n Importance of records Contracting procedures. n Variation charges


