55fa021a1845c09160cca92a07c553ae.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Seed Dispersal
Seed Dispersal
 Thinking like a plant…. • Coast redwood – Live 2, 000 years – Make 1 -10 billion seeds (lifetime) • Replacement? • “Sweepstakes reproduction”
Thinking like a plant…. • Coast redwood – Live 2, 000 years – Make 1 -10 billion seeds (lifetime) • Replacement? • “Sweepstakes reproduction”
 Seed dispersal • Move to “safe site: ” suitable for germination & establishment • Recent importance: track “climate envelopes” during global climate change?
Seed dispersal • Move to “safe site: ” suitable for germination & establishment • Recent importance: track “climate envelopes” during global climate change?
 Why disperse?
Why disperse?
 Why disperse? • 1) Escape competition (parent/siblings) • 2) Escape predation/disease (if density -dependent)
Why disperse? • 1) Escape competition (parent/siblings) • 2) Escape predation/disease (if density -dependent)
 Why disperse? • 3) Discover new habitats • “Nothing lasts forever, even cold November rain” Axl!
Why disperse? • 3) Discover new habitats • “Nothing lasts forever, even cold November rain” Axl!
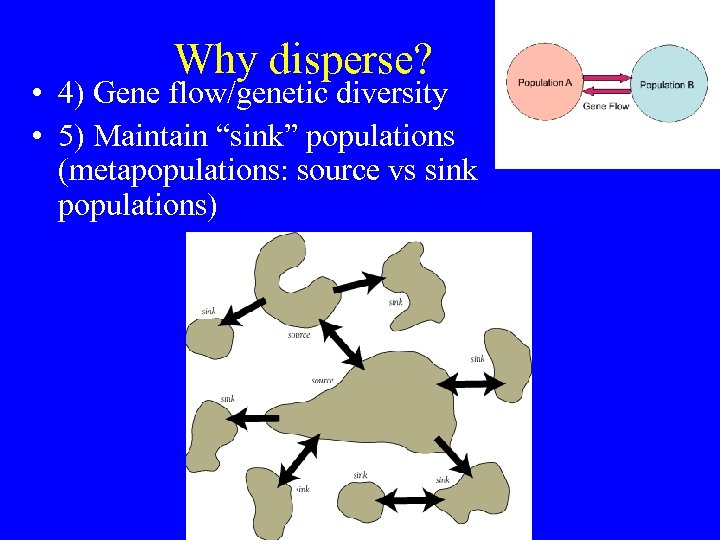 Why disperse? • 4) Gene flow/genetic diversity • 5) Maintain “sink” populations (metapopulations: source vs sink populations)
Why disperse? • 4) Gene flow/genetic diversity • 5) Maintain “sink” populations (metapopulations: source vs sink populations)
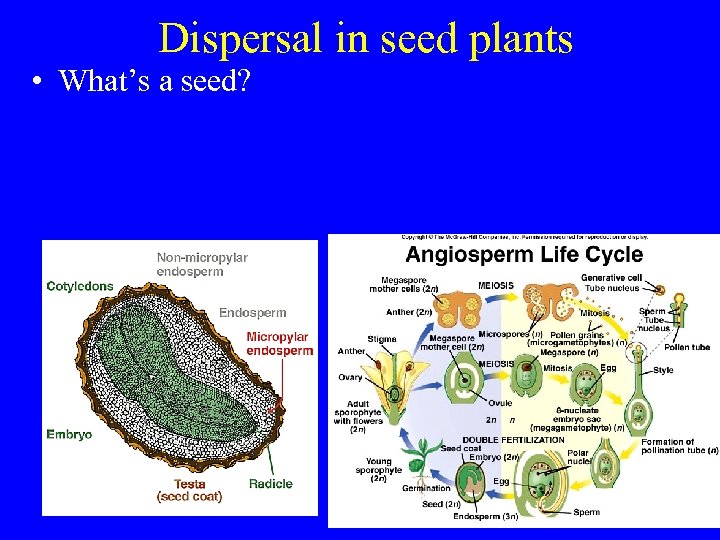 Dispersal in seed plants • What’s a seed?
Dispersal in seed plants • What’s a seed?
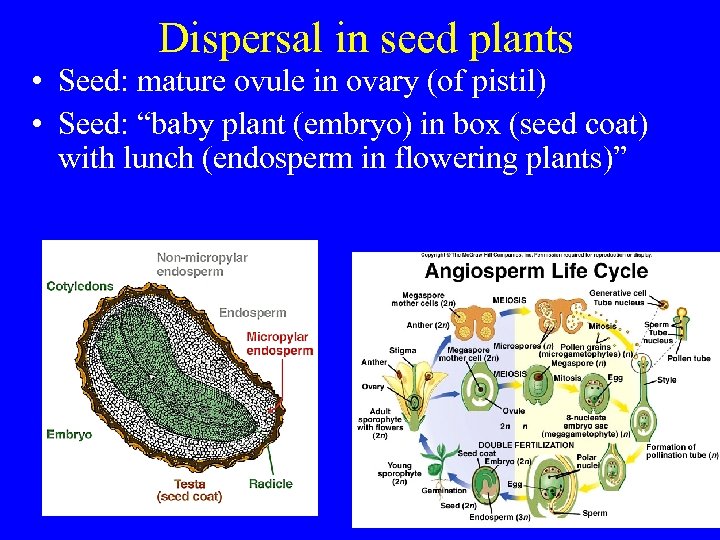 Dispersal in seed plants • Seed: mature ovule in ovary (of pistil) • Seed: “baby plant (embryo) in box (seed coat) with lunch (endosperm in flowering plants)”
Dispersal in seed plants • Seed: mature ovule in ovary (of pistil) • Seed: “baby plant (embryo) in box (seed coat) with lunch (endosperm in flowering plants)”
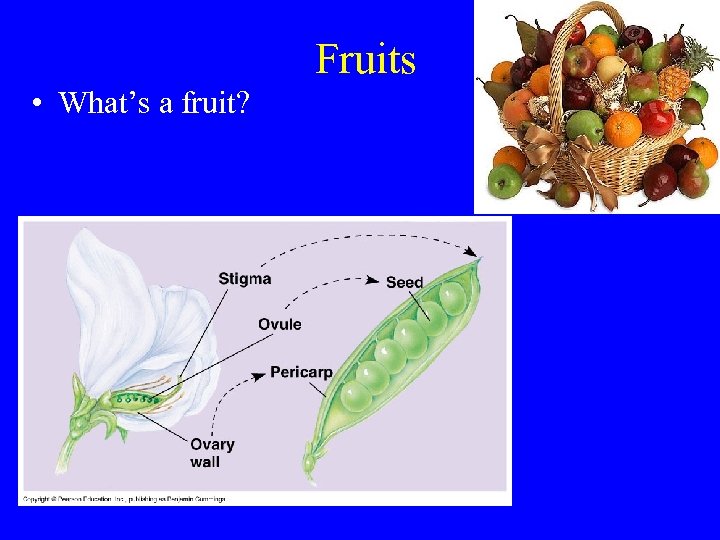 Fruits • What’s a fruit?
Fruits • What’s a fruit?
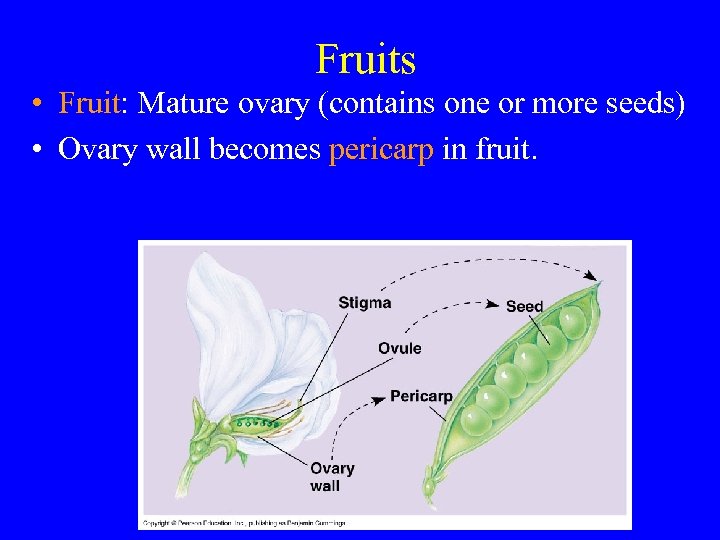 Fruits • Fruit: Mature ovary (contains one or more seeds) • Ovary wall becomes pericarp in fruit.
Fruits • Fruit: Mature ovary (contains one or more seeds) • Ovary wall becomes pericarp in fruit.
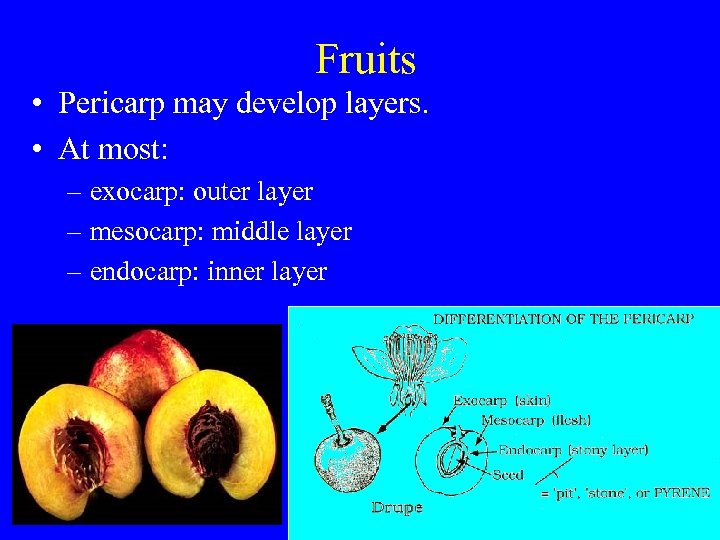 Fruits • Pericarp may develop layers. • At most: – exocarp: outer layer – mesocarp: middle layer – endocarp: inner layer
Fruits • Pericarp may develop layers. • At most: – exocarp: outer layer – mesocarp: middle layer – endocarp: inner layer
 Fruits vs seeds • Seed or fruit?
Fruits vs seeds • Seed or fruit?
 Fruits vs seeds • Dry indehiscent fruits – achene: one seed, fused to pericarp at one point – Ex, dandelion, sunflower.
Fruits vs seeds • Dry indehiscent fruits – achene: one seed, fused to pericarp at one point – Ex, dandelion, sunflower.
 Fruits vs seeds • Dry indehiscent fruits – grain (caryopsis): one seed, fused entirely to pericarp – Ex, corn, rice, wheat. rice
Fruits vs seeds • Dry indehiscent fruits – grain (caryopsis): one seed, fused entirely to pericarp – Ex, corn, rice, wheat. rice
 Resolution • What’s dispersed: fruit or seed? • Solution. Diaspore: Single dispersal unit (seed or fruit)
Resolution • What’s dispersed: fruit or seed? • Solution. Diaspore: Single dispersal unit (seed or fruit)
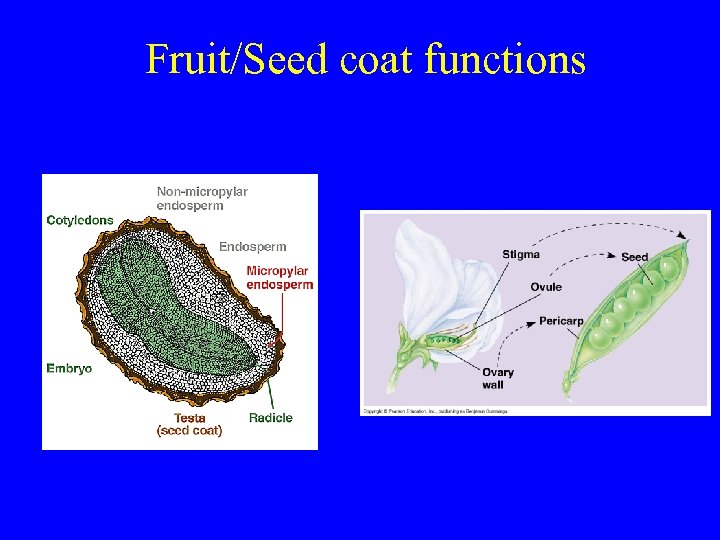 Fruit/Seed coat functions
Fruit/Seed coat functions
 Fruit/Seed coat functions • 1) Protect against: – Seed predators – Environmental conditions
Fruit/Seed coat functions • 1) Protect against: – Seed predators – Environmental conditions
 Fruit/Seed coat functions 2) Seed dormancy – Hard endocarp/coat seals out water/oxygen – Breaking layer: scarification – Fruit/seed coat can contain germination inhibitors
Fruit/Seed coat functions 2) Seed dormancy – Hard endocarp/coat seals out water/oxygen – Breaking layer: scarification – Fruit/seed coat can contain germination inhibitors
 Fruit/Seed coat functions • 3) Aid seed dispersal Maple samaras Milkweed
Fruit/Seed coat functions • 3) Aid seed dispersal Maple samaras Milkweed
 Seed Dispersal • May be mutualism Not!
Seed Dispersal • May be mutualism Not!
 Ballistic dispersal • NOT mutualism – Ballistic dispersal=Ballistochory: fruit throws or squirts seeds – Ex, touch-me-not (Impatiens, right), sorrel (Oxalis, left)
Ballistic dispersal • NOT mutualism – Ballistic dispersal=Ballistochory: fruit throws or squirts seeds – Ex, touch-me-not (Impatiens, right), sorrel (Oxalis, left)
 Wind/water dispersal • Other non-mutualist (physical forces) • Anemochory=Wind dispersal (dandelion) • Hydrochory=Water dispersal (coconut)* Dispersing dandelion fruits (achenes) *controversy!
Wind/water dispersal • Other non-mutualist (physical forces) • Anemochory=Wind dispersal (dandelion) • Hydrochory=Water dispersal (coconut)* Dispersing dandelion fruits (achenes) *controversy!
 Ectozoochory • NOT mutualism – Most ectozoochory (or epizoochory): seed/fruit carried by animal outside body (hooks, barbs, glue) Fruits of sandspur (Cenchrus)
Ectozoochory • NOT mutualism – Most ectozoochory (or epizoochory): seed/fruit carried by animal outside body (hooks, barbs, glue) Fruits of sandspur (Cenchrus)
 Ectozoochory – Many plant species – 17 top “hitchhiker plants”: ranked by SRDUs (Sock Removal Difficulty Units) Uncarina #1!!
Ectozoochory – Many plant species – 17 top “hitchhiker plants”: ranked by SRDUs (Sock Removal Difficulty Units) Uncarina #1!!
 Dispersal Mutualisms • Ectozoochory mutualisms: • Ex, scatter hoarding animals (squirrels, nutcrackers)
Dispersal Mutualisms • Ectozoochory mutualisms: • Ex, scatter hoarding animals (squirrels, nutcrackers)
 Dispersal Mutualisms – Pinus albicaulis (white bark pine) and Clark’s nutcracker – 1 bird can hide 90, 000 seeds in 1 season
Dispersal Mutualisms – Pinus albicaulis (white bark pine) and Clark’s nutcracker – 1 bird can hide 90, 000 seeds in 1 season
 Dispersal Mutualisms • Endozoochory: fruit eaten & seeds thru gut – Fleshy fruits (soft, sweet fruits) – Fruit pulp nutritive reward
Dispersal Mutualisms • Endozoochory: fruit eaten & seeds thru gut – Fleshy fruits (soft, sweet fruits) – Fruit pulp nutritive reward
 Dispersal Mutualisms • Endozoochory: sometimes seed scarified – Ex. , dodo & Calvaria tree
Dispersal Mutualisms • Endozoochory: sometimes seed scarified – Ex. , dodo & Calvaria tree
 Myrmecochory • Seed dispersal by ants (ectozoochory mutualism) – Elaiosome: food body on outside seed coat/fruit – Only major mode using insect! Stylophorum seeds Fremontodendron seeds
Myrmecochory • Seed dispersal by ants (ectozoochory mutualism) – Elaiosome: food body on outside seed coat/fruit – Only major mode using insect! Stylophorum seeds Fremontodendron seeds
 Myrmecochory • Common Eastern forest spring flowering plants. Trillium Bloodroot Hexastylis Trout lily Viola
Myrmecochory • Common Eastern forest spring flowering plants. Trillium Bloodroot Hexastylis Trout lily Viola
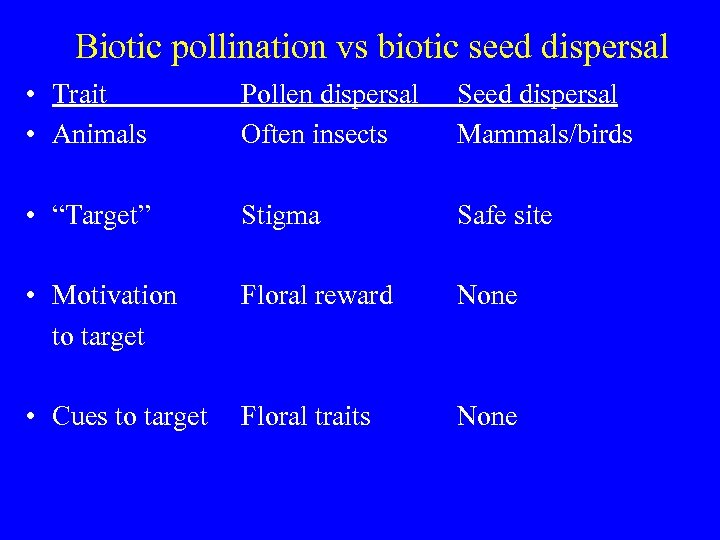 Biotic pollination vs biotic seed dispersal • Trait • Animals Pollen dispersal Often insects Seed dispersal Mammals/birds • “Target” Stigma Safe site • Motivation to target Floral reward None • Cues to target Floral traits None
Biotic pollination vs biotic seed dispersal • Trait • Animals Pollen dispersal Often insects Seed dispersal Mammals/birds • “Target” Stigma Safe site • Motivation to target Floral reward None • Cues to target Floral traits None
 Biotic pollination vs biotic seed dispersal • Seed “directed dispersal” (concept: seed carried directly to safe site) unlikely Syndromes?
Biotic pollination vs biotic seed dispersal • Seed “directed dispersal” (concept: seed carried directly to safe site) unlikely Syndromes?
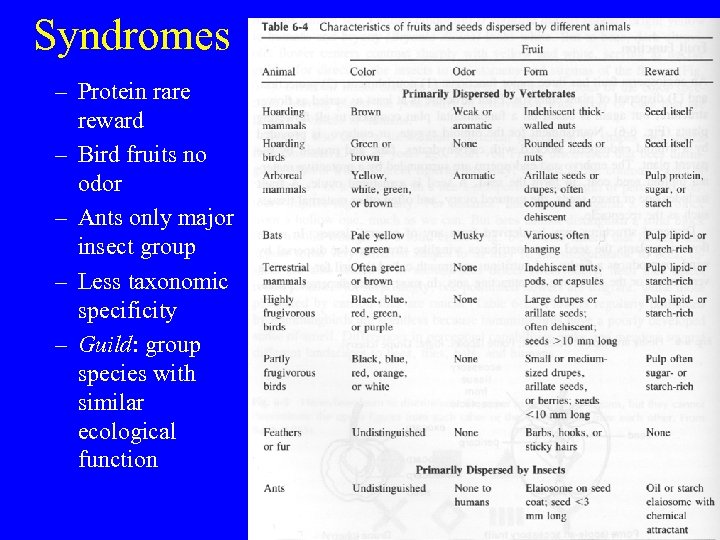 Syndromes – Protein rare reward – Bird fruits no odor – Ants only major insect group – Less taxonomic specificity – Guild: group species with similar ecological function
Syndromes – Protein rare reward – Bird fruits no odor – Ants only major insect group – Less taxonomic specificity – Guild: group species with similar ecological function
 The (Plant) View • How measure dispersal? Metric? • 1) Single species study: absolute distance
The (Plant) View • How measure dispersal? Metric? • 1) Single species study: absolute distance
 The Plant View • • • How measure dispersal? Metric? 1) Single species study: absolute distance 2) Comparative study: canopy diameters Ex, grasses vs oaks 3) Self-incompatible clonal plants: genetic neighborhood
The Plant View • • • How measure dispersal? Metric? 1) Single species study: absolute distance 2) Comparative study: canopy diameters Ex, grasses vs oaks 3) Self-incompatible clonal plants: genetic neighborhood
 Plant “choices” • As seed size increases: – dispersal ______ – chance establishment ______
Plant “choices” • As seed size increases: – dispersal ______ – chance establishment ______
 Plant “choices” • Seeds yummy! High protein, high lipid • How protect?
Plant “choices” • Seeds yummy! High protein, high lipid • How protect?
 Plant “choices” • Bribery! • Large number seeds (scatter hoarders)
Plant “choices” • Bribery! • Large number seeds (scatter hoarders)
 Plant “choices” • Bribery! • Non-seed food reward. Fruit pulp, etc Aril on nutmeg seed: aril is spice “mace” Aril: outgrowth attachment ovule to ovary (funiculus) Mace Windu…. .
Plant “choices” • Bribery! • Non-seed food reward. Fruit pulp, etc Aril on nutmeg seed: aril is spice “mace” Aril: outgrowth attachment ovule to ovary (funiculus) Mace Windu…. .
 Plant “choices” • Poison! – Defend seeds with toxins – Ex, castor beans (ricin) – Lethal dose: 1/5000 gram (twice as deadly as cobra venom!) Castor beans
Plant “choices” • Poison! – Defend seeds with toxins – Ex, castor beans (ricin) – Lethal dose: 1/5000 gram (twice as deadly as cobra venom!) Castor beans
 Plant “choices” • Armor! Mechanical protection (stony seed coat, endocarp)
Plant “choices” • Armor! Mechanical protection (stony seed coat, endocarp)
 Plant “choices” • Advertise: disperser gets message before seed predators – Ripeness cues (color, smell, etc) – Pre-ripening flags: ripening begun – Foliar flags: leaf color indicates fruits ripening (ex, poison ivy)
Plant “choices” • Advertise: disperser gets message before seed predators – Ripeness cues (color, smell, etc) – Pre-ripening flags: ripening begun – Foliar flags: leaf color indicates fruits ripening (ex, poison ivy)


