455fbd088c2ea74589308d926a3e9ac9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Security
Security
 Security Needs Security policy is to ensure that n n Computers and data are used by the authorized persons Computers and their accessories, data, and information are available to the genuine users
Security Needs Security policy is to ensure that n n Computers and data are used by the authorized persons Computers and their accessories, data, and information are available to the genuine users
 Security Services n n n Authentication Access control Data confidentiality Data integrity Non-repudiation
Security Services n n n Authentication Access control Data confidentiality Data integrity Non-repudiation
 Security Services Authentication n n A user proves its identity to another party A data sender proves that the data is actually sent by him/her
Security Services Authentication n n A user proves its identity to another party A data sender proves that the data is actually sent by him/her
 Security Services Access control n Guard against unauthorized use of resources
Security Services Access control n Guard against unauthorized use of resources
 Security Services Data confidentially n n Data and its meanings are only available to those who are the genuine receivers For other parties, the data would appear to be “rubbish”
Security Services Data confidentially n n Data and its meanings are only available to those who are the genuine receivers For other parties, the data would appear to be “rubbish”
 Security Services Data integrity n n Guards against active attack – modification, insertion, deletion, replay If a piece of data is changed, such a change can be detected
Security Services Data integrity n n Guards against active attack – modification, insertion, deletion, replay If a piece of data is changed, such a change can be detected
 Security Services Non-repudiation n n When a party sends a piece of information, it can be proved that the sender is actually that party The sender cannot subsequently deny the act of having sent a piece of information
Security Services Non-repudiation n n When a party sends a piece of information, it can be proved that the sender is actually that party The sender cannot subsequently deny the act of having sent a piece of information
 Security Mechanisms To provide security services, some specific security mechanisms may be implemented: n Encipherment n Digital signature n Access control
Security Mechanisms To provide security services, some specific security mechanisms may be implemented: n Encipherment n Digital signature n Access control
 DES n n n The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a private key encryption system developed by the U. S. government in the 1970 s It was based on a previous IBM encryption system called “Lucifer” It was adopted as a U. S. federal standard in 1976, and then as an international standard
DES n n n The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a private key encryption system developed by the U. S. government in the 1970 s It was based on a previous IBM encryption system called “Lucifer” It was adopted as a U. S. federal standard in 1976, and then as an international standard
 DES Overview n n n Plaintext size : 64 bits Key size : 64 bits input, only 56 bits are used Ciphertext size : 64 bits 64 bit message Encryption 64 bit ciphertext 56 bit key
DES Overview n n n Plaintext size : 64 bits Key size : 64 bits input, only 56 bits are used Ciphertext size : 64 bits 64 bit message Encryption 64 bit ciphertext 56 bit key
 Strength of DES n n n DES has been cryptanalyzed for many years by many people, no serious flaws have been revealed up to now The 56 -bit key size : there are 256=7. 2 x 1016 different possible keys May not be sufficient to resist bruteforce key search attack
Strength of DES n n n DES has been cryptanalyzed for many years by many people, no serious flaws have been revealed up to now The 56 -bit key size : there are 256=7. 2 x 1016 different possible keys May not be sufficient to resist bruteforce key search attack
 Strength of DES n n n If it takes 1 sec to test 1 key then 228 million years are needed to test all keys If it takes 1 μsec to test 1 key then 2, 280 years to test all keys If there are 1 million machines working in parallel then the key can be found in a day!
Strength of DES n n n If it takes 1 sec to test 1 key then 228 million years are needed to test all keys If it takes 1 μsec to test 1 key then 2, 280 years to test all keys If there are 1 million machines working in parallel then the key can be found in a day!
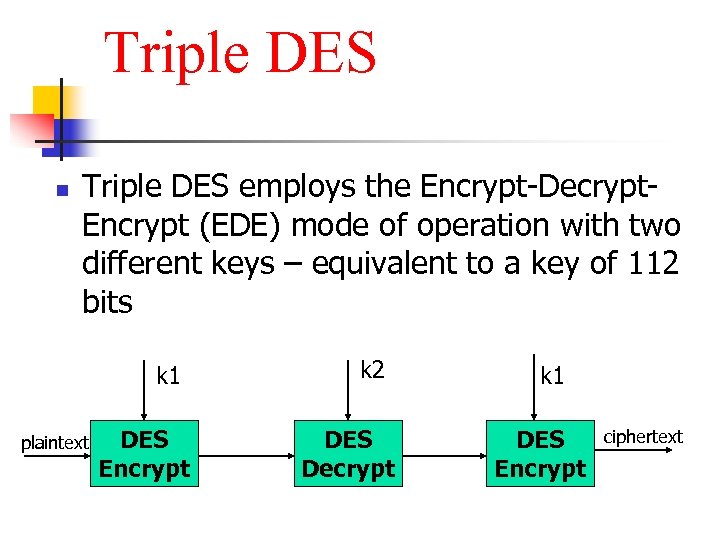 Triple DES n Triple DES employs the Encrypt-Decrypt. Encrypt (EDE) mode of operation with two different keys – equivalent to a key of 112 bits k 1 plaintext DES Encrypt k 2 DES Decrypt k 1 DES Encrypt ciphertext
Triple DES n Triple DES employs the Encrypt-Decrypt. Encrypt (EDE) mode of operation with two different keys – equivalent to a key of 112 bits k 1 plaintext DES Encrypt k 2 DES Decrypt k 1 DES Encrypt ciphertext
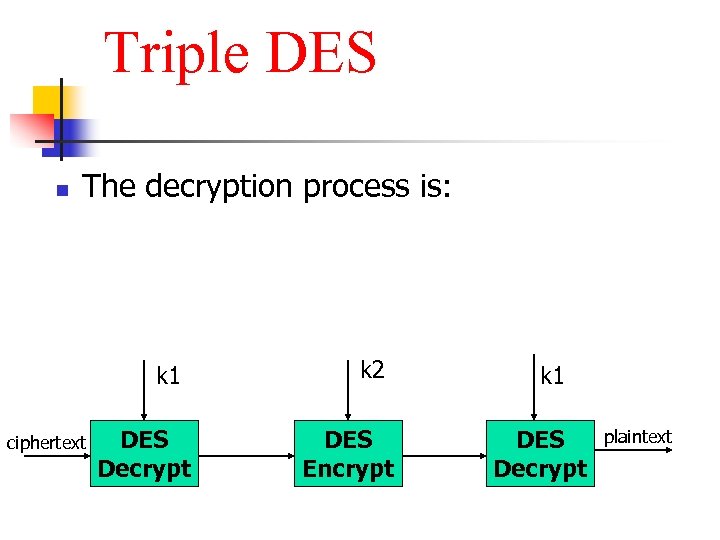 Triple DES n The decryption process is: k 1 ciphertext DES Decrypt k 2 DES Encrypt k 1 DES Decrypt plaintext
Triple DES n The decryption process is: k 1 ciphertext DES Decrypt k 2 DES Encrypt k 1 DES Decrypt plaintext
 Triple DES n n n Triple DES can use the existing DES block When K 2=K 1, the triple DES system “falls back” to the single DES system It is “backward compatible” with single key DES
Triple DES n n n Triple DES can use the existing DES block When K 2=K 1, the triple DES system “falls back” to the single DES system It is “backward compatible” with single key DES
 AES n n AES stands for “Advanced Encryption System” NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) of USA announced AES in 1997, and then called for algorithms from the public on 12 Sept 1997
AES n n AES stands for “Advanced Encryption System” NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) of USA announced AES in 1997, and then called for algorithms from the public on 12 Sept 1997
 AES n n n Researchers from 12 different countries submitted 15 algorithms for the AES As at Aug 1999, 5 algorithms have been chosen by NIST for further consideration On 3 -Oct-2000, the proposal by Rijdael [pro. Rhine doll] – Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen of Belgium was selected
AES n n n Researchers from 12 different countries submitted 15 algorithms for the AES As at Aug 1999, 5 algorithms have been chosen by NIST for further consideration On 3 -Oct-2000, the proposal by Rijdael [pro. Rhine doll] – Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen of Belgium was selected
 Public Key Encryption
Public Key Encryption
 Public Key Encryption n n n Each user will have a pair of keys K 1 & K 2 Use keys K 1 to encrypt and K 2 to decrypt Keep K 1 private and top secret Gives out K 2 to anybody who needs it K 1 is called the private key K 2 is called the public key
Public Key Encryption n n n Each user will have a pair of keys K 1 & K 2 Use keys K 1 to encrypt and K 2 to decrypt Keep K 1 private and top secret Gives out K 2 to anybody who needs it K 1 is called the private key K 2 is called the public key
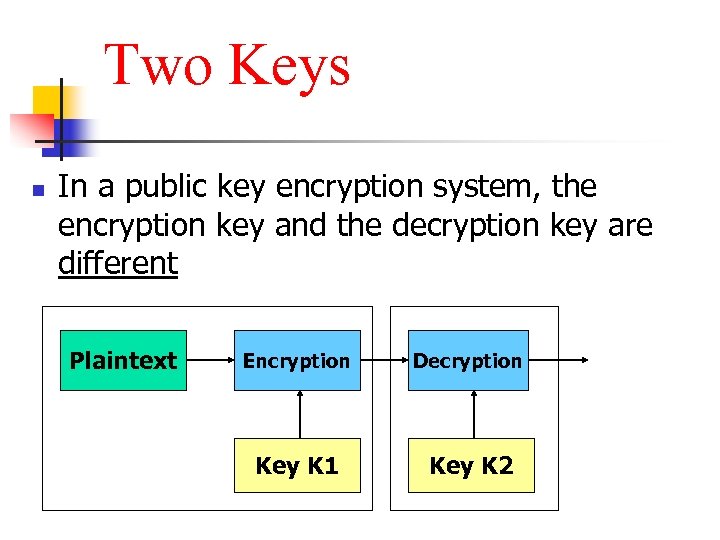 Two Keys n In a public key encryption system, the encryption key and the decryption key are different Plaintext Encryption Decryption Key K 1 Key K 2
Two Keys n In a public key encryption system, the encryption key and the decryption key are different Plaintext Encryption Decryption Key K 1 Key K 2
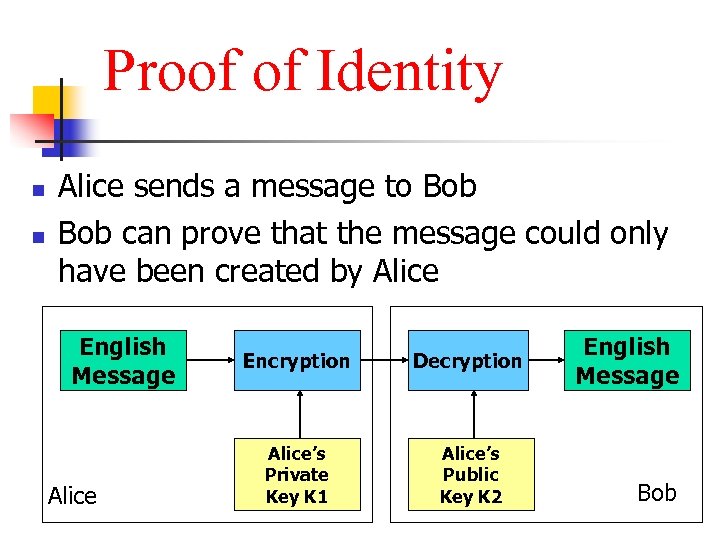 Proof of Identity n n Alice sends a message to Bob can prove that the message could only have been created by Alice English Message Alice Encryption Decryption Alice’s Private Key K 1 Alice’s Public Key K 2 English Message Bob
Proof of Identity n n Alice sends a message to Bob can prove that the message could only have been created by Alice English Message Alice Encryption Decryption Alice’s Private Key K 1 Alice’s Public Key K 2 English Message Bob
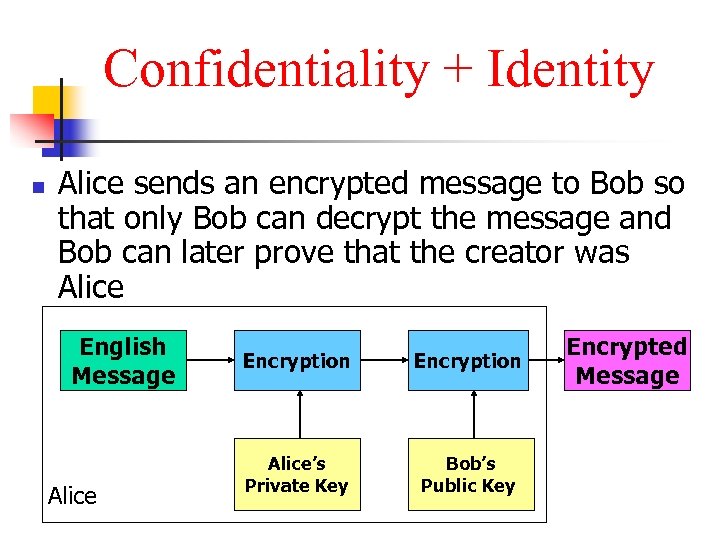 Confidentiality + Identity n Alice sends an encrypted message to Bob so that only Bob can decrypt the message and Bob can later prove that the creator was Alice English Message Alice Encryption Alice’s Private Key Bob’s Public Key Encrypted Message
Confidentiality + Identity n Alice sends an encrypted message to Bob so that only Bob can decrypt the message and Bob can later prove that the creator was Alice English Message Alice Encryption Alice’s Private Key Bob’s Public Key Encrypted Message
 RSA Algorithm n n n The most widely used public key algorithm Proposed by Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman Security is based on the difficulty in factorizing a large integer that is the product of two large prime numbers E. g. 437 = ? x ? 437 = 19 x 23 Reference web page: http: //www. rsa. com http: //www. orst. edu/dept/honors/makmur/
RSA Algorithm n n n The most widely used public key algorithm Proposed by Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman Security is based on the difficulty in factorizing a large integer that is the product of two large prime numbers E. g. 437 = ? x ? 437 = 19 x 23 Reference web page: http: //www. rsa. com http: //www. orst. edu/dept/honors/makmur/
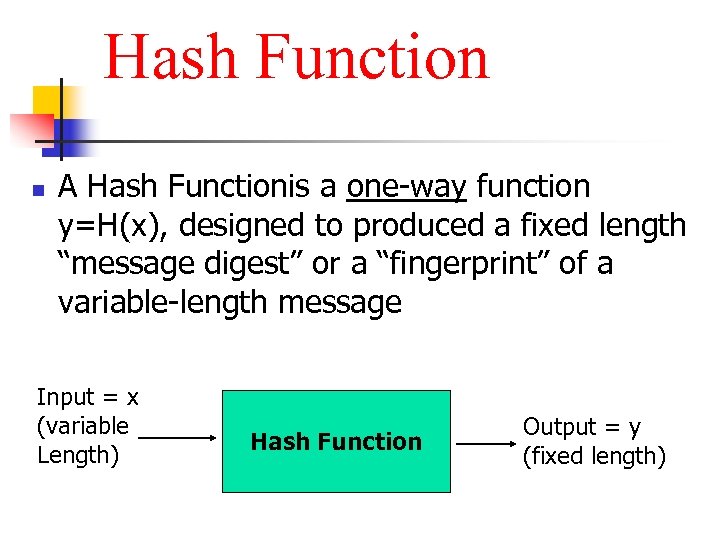 Hash Function n A Hash Functionis a one-way function y=H(x), designed to produced a fixed length “message digest” or a “fingerprint” of a variable-length message Input = x (variable Length) Hash Function Output = y (fixed length)
Hash Function n A Hash Functionis a one-way function y=H(x), designed to produced a fixed length “message digest” or a “fingerprint” of a variable-length message Input = x (variable Length) Hash Function Output = y (fixed length)
 MD 5 n n n MD 5 – Message Digest 5 Designed by Prof. R. Rivest of MIT Internet standard – RFC 1321 Thought to be a strong hash function The message digest is 128 bits Message is processed in 512 -bit blocks
MD 5 n n n MD 5 – Message Digest 5 Designed by Prof. R. Rivest of MIT Internet standard – RFC 1321 Thought to be a strong hash function The message digest is 128 bits Message is processed in 512 -bit blocks
 Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) n n SHA was FIPS PUB 180 -1, designed by the U. S. National Security Agency (NSA) To be used in the Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) – part of the Digital Signature Standard (DSS) Input data length is less than 264 bits Message digest is 160 bits
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) n n SHA was FIPS PUB 180 -1, designed by the U. S. National Security Agency (NSA) To be used in the Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) – part of the Digital Signature Standard (DSS) Input data length is less than 264 bits Message digest is 160 bits
 Digital Signature n n A digital signature has functions similar to those of conventional signature Support authentic messages: n n Signer of document can be confirmed Contents of a signed document can be verified
Digital Signature n n A digital signature has functions similar to those of conventional signature Support authentic messages: n n Signer of document can be confirmed Contents of a signed document can be verified
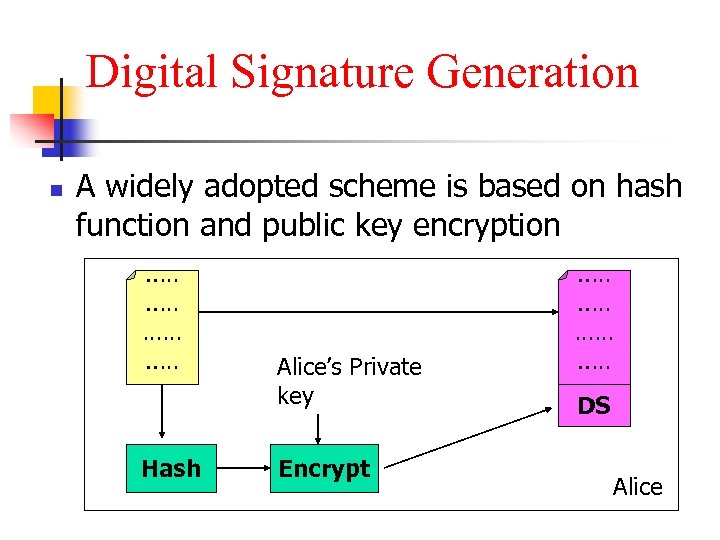 Digital Signature Generation A widely adopted scheme is based on hash function and public key encryption …. . …… …. . Hash Alice’s Private key Encrypt …. . …… …. . n DS Alice
Digital Signature Generation A widely adopted scheme is based on hash function and public key encryption …. . …… …. . Hash Alice’s Private key Encrypt …. . …… …. . n DS Alice
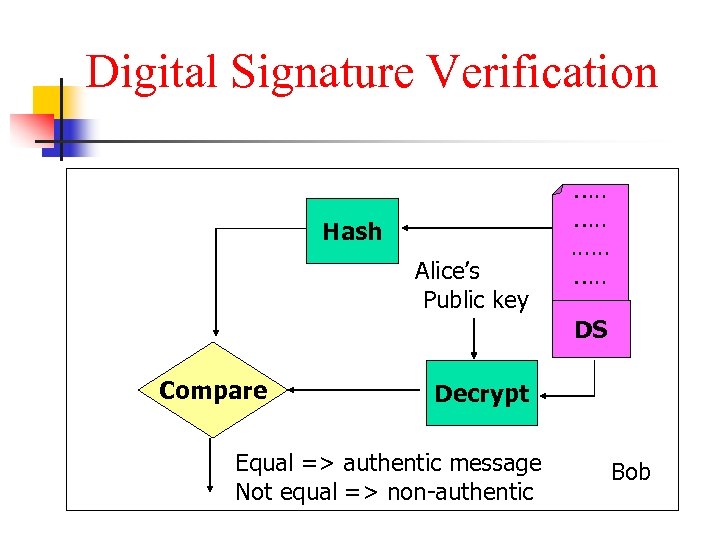 Digital Signature Verification Alice’s Public key …. . …… …. . Hash DS Compare Decrypt Equal => authentic message Not equal => non-authentic Bob
Digital Signature Verification Alice’s Public key …. . …… …. . Hash DS Compare Decrypt Equal => authentic message Not equal => non-authentic Bob
 Public Key Infrastructure n n n How to give your public key to your friend? How can you be sure that the public key you obtain is indeed your friend’s public key? For a small number of mutually trusted users, a “web of trust” system is O. K.
Public Key Infrastructure n n n How to give your public key to your friend? How can you be sure that the public key you obtain is indeed your friend’s public key? For a small number of mutually trusted users, a “web of trust” system is O. K.
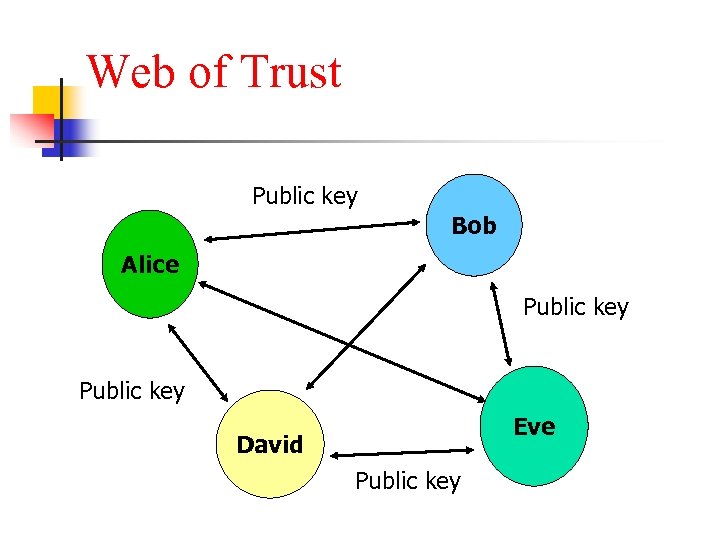 Web of Trust Public key Bob Alice Public key Eve David Public key
Web of Trust Public key Bob Alice Public key Eve David Public key
 Certification Authority n n n For a large population of users, a central trusted party can act as a Certification Authority (CA) Users may deposit their public keys in a CA who they trust The CA may pass out the public keys to any user who need them in certificates
Certification Authority n n n For a large population of users, a central trusted party can act as a Certification Authority (CA) Users may deposit their public keys in a CA who they trust The CA may pass out the public keys to any user who need them in certificates
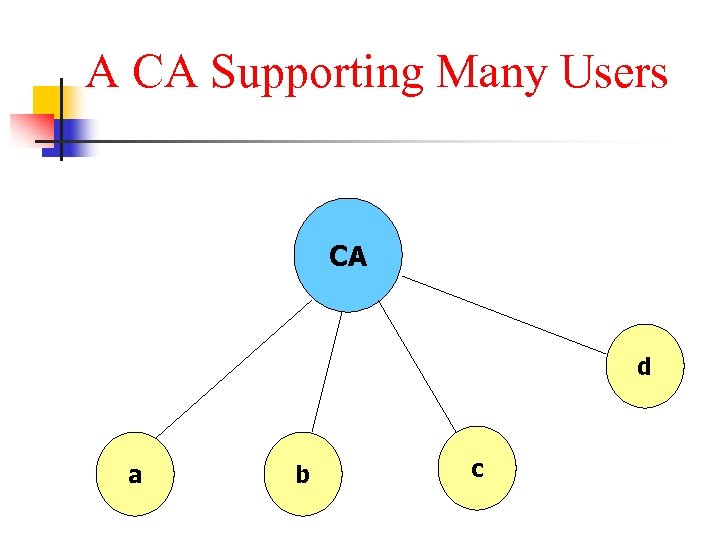 A CA Supporting Many Users CA d a b c
A CA Supporting Many Users CA d a b c
 Certificate n n A certificate for a user (also called a subscriber) contains the user’s particulars and the user’s public key The certificate is an electronic document signed by the CA who issue it
Certificate n n A certificate for a user (also called a subscriber) contains the user’s particulars and the user’s public key The certificate is an electronic document signed by the CA who issue it
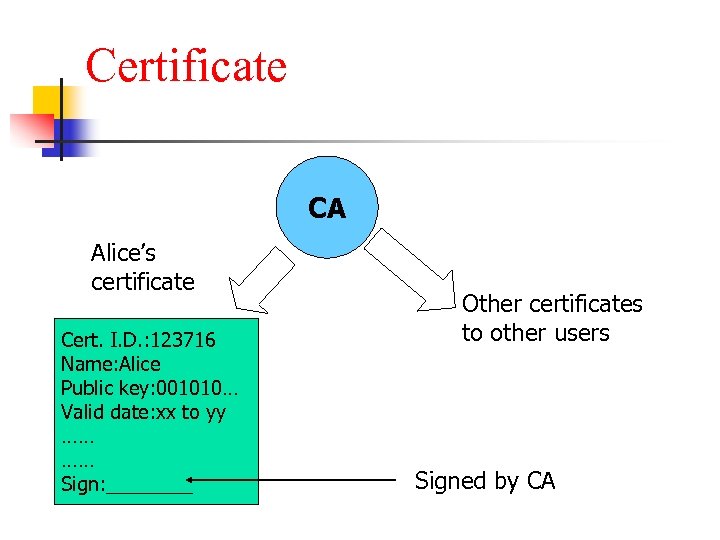 Certificate CA Alice’s certificate Cert. I. D. : 123716 Name: Alice Public key: 001010… Valid date: xx to yy …… …… Sign: ____ Other certificates to other users Signed by CA
Certificate CA Alice’s certificate Cert. I. D. : 123716 Name: Alice Public key: 001010… Valid date: xx to yy …… …… Sign: ____ Other certificates to other users Signed by CA
 Revocation n n A user may revoke the validity of his/her certificate before the actual expiry date Revocation information about a CA’s subscribers are published in a Certificate Revocation List (CRL)
Revocation n n A user may revoke the validity of his/her certificate before the actual expiry date Revocation information about a CA’s subscribers are published in a Certificate Revocation List (CRL)
 Public Key Infrastructure n n n When there are many CA’s and many subscribers, a hierarchy can be formed linking all the CA’s and the subscribers This form a public key infrastructure The subscribers can communicate securely by using digital signature techniques
Public Key Infrastructure n n n When there are many CA’s and many subscribers, a hierarchy can be formed linking all the CA’s and the subscribers This form a public key infrastructure The subscribers can communicate securely by using digital signature techniques
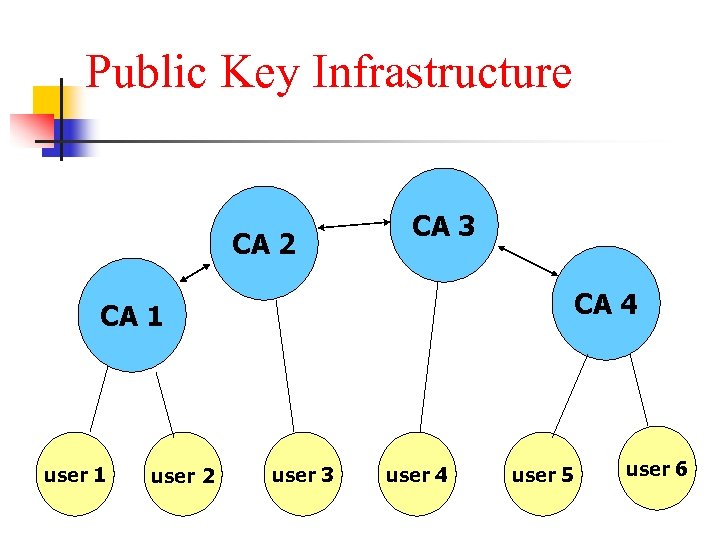 Public Key Infrastructure CA 2 CA 3 CA 4 CA 1 user 2 user 3 user 4 user 5 user 6
Public Key Infrastructure CA 2 CA 3 CA 4 CA 1 user 2 user 3 user 4 user 5 user 6


