100c4966d5e3c8ed646320312359e452.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Security Markets Objectives Primary market Secondary Market

Objectives U. S. Treasury Bonds q Stock Issue in the Primary Market q Ø Ø Ø q Why do companies issue stock? How are stocks placed? Where are the opportunities? Stock Trading in the Secondary Market Ø Ø Where are stocks traded? How are stocks traded? Investments 4 2

U. S. Treasury Bonds q Initially sold in an auction by the NY Fed Ø Auction participants: q Ø q Competitive vs. Non-competitive bids On-the-run vs. off-the-run treasuries Ø Ø q Primary dealers On-the-run - most recently issued bonds or notes of a particular maturity Off-the-run – treasuries issued before on-the-run treasuries On-the-run treasuries are more liquid and expensive compared to off-the-run treasuries Investments 4 3
Primary Market q Why do Companies Issue Stock? Ø To finance business expansion q Ø To retire existing debt q Ø A new factory costs $100 MM Payoff $10 MM high interest loan from the bank To buy-out venture capital q Venture capitalist exits in 1 -3 years after IPO *usually 7% of the issue Investments 4 4
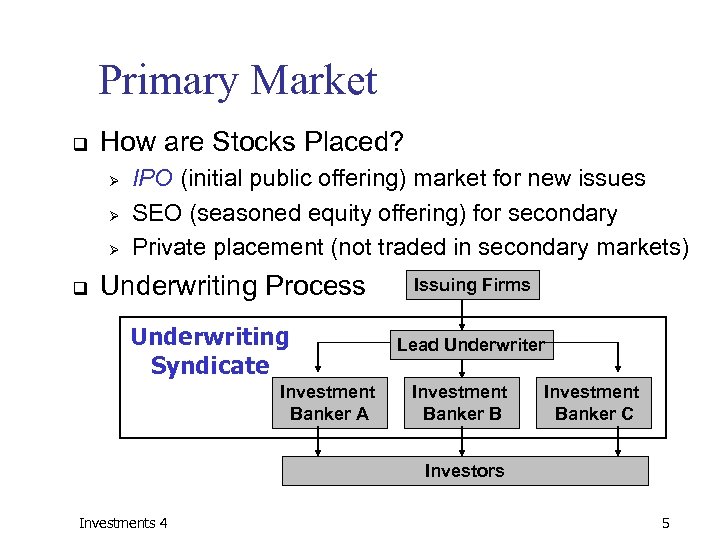
Primary Market q How are Stocks Placed? Ø Ø Ø q IPO (initial public offering) market for new issues SEO (seasoned equity offering) for secondary Private placement (not traded in secondary markets) Underwriting Process Underwriting Syndicate Investment Banker A Issuing Firms Lead Underwriter Investment Banker B Investment Banker C Investors Investments 4 5
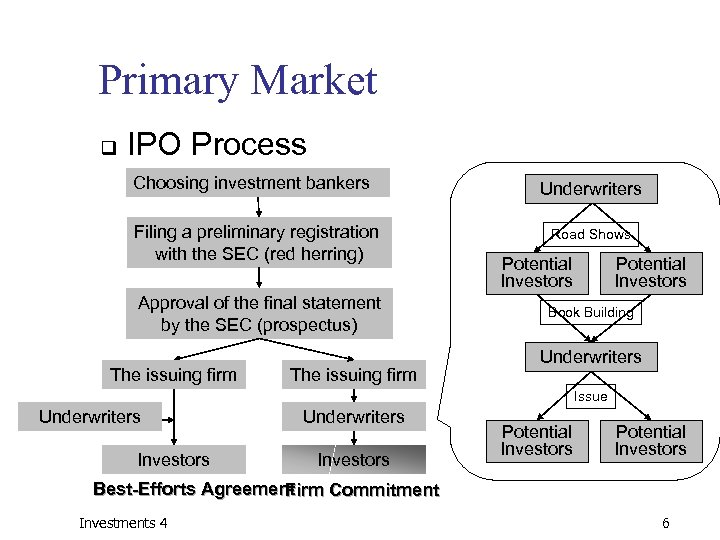
Primary Market q IPO Process Choosing investment bankers Filing a preliminary registration with the SEC (red herring) Approval of the final statement by the SEC (prospectus) The issuing firm Underwriters Road Shows Potential Investors Book Building Underwriters Issue Underwriters Investors Potential Investors Best-Efforts Agreement Firm Commitment Investments 4 6
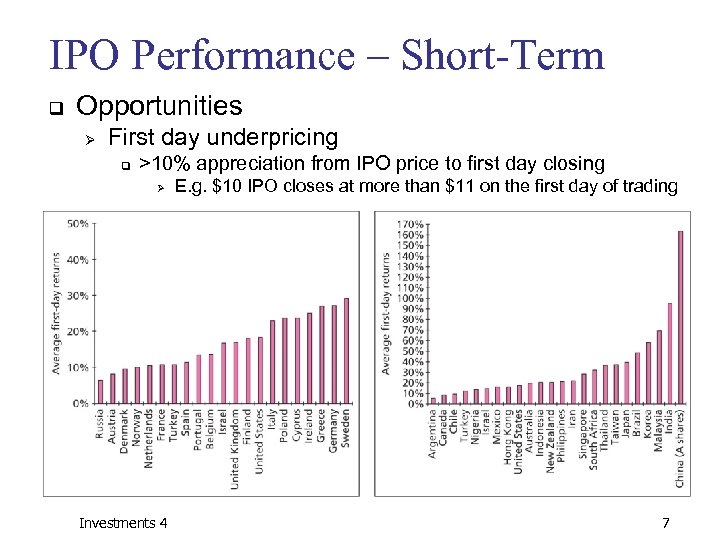
IPO Performance – Short-Term q Opportunities Ø First day underpricing q >10% appreciation from IPO price to first day closing Ø Investments 4 E. g. $10 IPO closes at more than $11 on the first day of trading 7
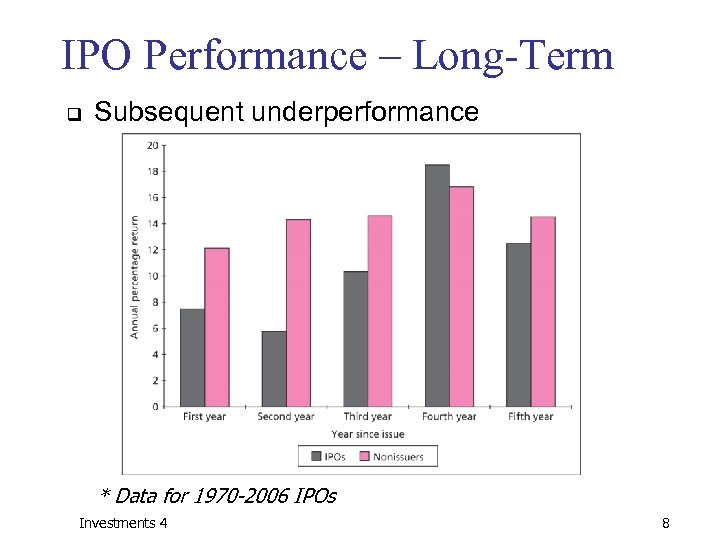
IPO Performance – Long-Term q Subsequent underperformance * Data for 1970 -2006 IPOs Investments 4 8

Primary Market q Money on the Table Ø Q: FBN, Inc sold 100, 000 shares at offer price of $50/share in an IPO, underwriter charges a fee of $70, 000 and the share price jumps immediately to $53 after trading q q Ø What is the cost of equity issue to FBN? What is the profit for the underwriter? A: The stock is under priced at $50. The company could have got $53, so … q Total cost to the company Ø Ø Ø q Underwriter’s profit Ø q Investments 4 Money on the table = 100, 000× 3 = 300, 000, Fee = 70, 000, Total cost = 370, 000 Fee = 70, 000 Where did the $300, 000 go? 9

Primary Market q Exploiting the Opportunities Ø Buy at IPO price and flip after IPO date q Benefit: Ø q Concern: Ø Ø Ø >10% return on average for one day Smaller chance of getting into good IPOs Greater chance of getting into bad IPOs Sell short IPO stocks on the first day of trading q Benefit: Ø q Problem: Ø Investments 4 Profit from the long-run underperformance Cost of shorting IPO shares 10

Secondary Market q Definition Ø q Markets for investors to buy and sell stocks How are stocks traded? Ø Ø Q: How do I buy 100 shares of Microsoft? A: Depending on the type of order q Market order: buy immediately at current market price Ø Ø q Limit order: buy with a price specified Ø Ø Investments 4 Quick execution with unknown price E. g. , last transaction for MSFT is $26. 12, so you will be able to buy at a price around $26. 12 immediately. Slow execution with known price E. g. , you submit an order to buy MSFT at $26 (limit price), and wait until the price drops to $26. 11

Secondary Market q How are stocks traded? Ø Sell order q q q Ø Buy order q q q Ø Limit the gain Stop Order q q Market (23. 74? ) Limit (below 23. 723? ) Stop-buy (above 23. 74? ) Limit Order q Ø Market (23. 723? ) Limit (above 23. 74? ) Stop-loss (below 23. 723? ) Stop the loss Where is the price going? Investments 4 12
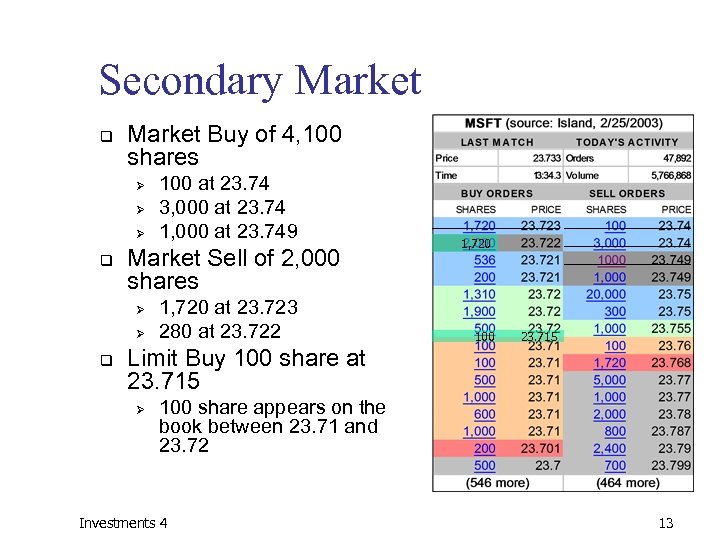
Secondary Market q Market Buy of 4, 100 shares Ø Ø Ø q Market Sell of 2, 000 shares Ø Ø q 100 at 23. 74 3, 000 at 23. 74 1, 000 at 23. 749 1, 720 at 23. 723 280 at 23. 722 1, 720 100 23. 715 Limit Buy 100 share at 23. 715 Ø 100 share appears on the book between 23. 71 and 23. 72 Investments 4 13
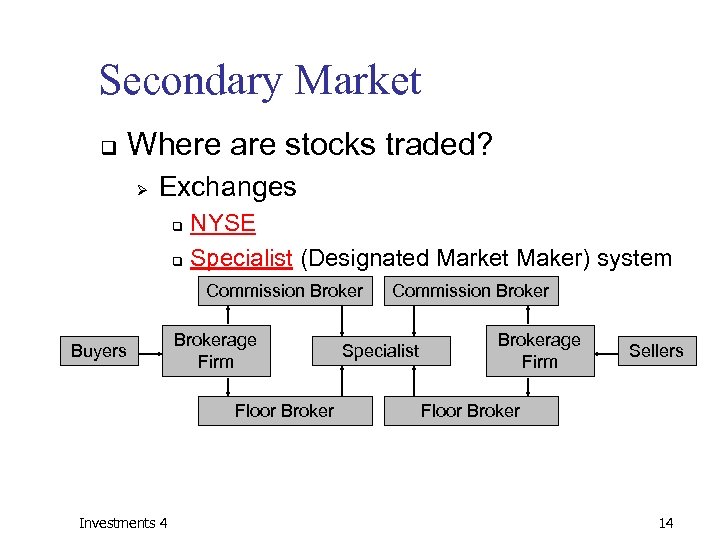
Secondary Market q Where are stocks traded? Ø Exchanges NYSE q Specialist (Designated Market Maker) system q Commission Broker Buyers Brokerage Firm Floor Broker Investments 4 Commission Broker Specialist Brokerage Firm Sellers Floor Broker 14
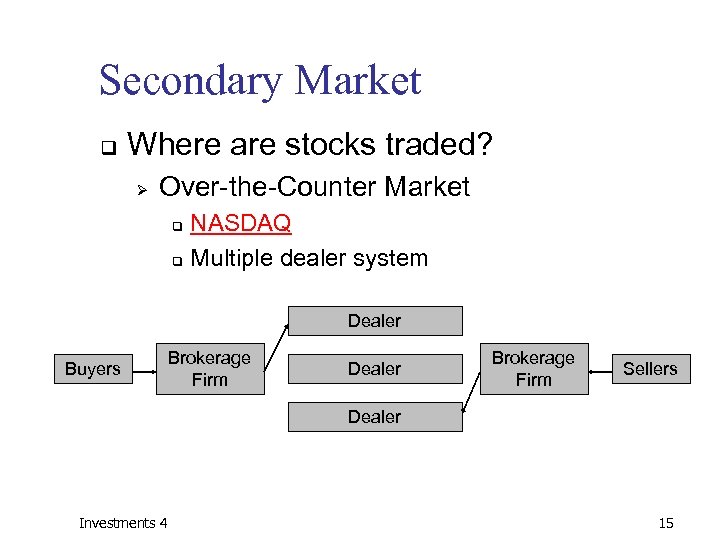
Secondary Market q Where are stocks traded? Ø Over-the-Counter Market NASDAQ q Multiple dealer system q Dealer Buyers Brokerage Firm Dealer Brokerage Firm Sellers Dealer Investments 4 15
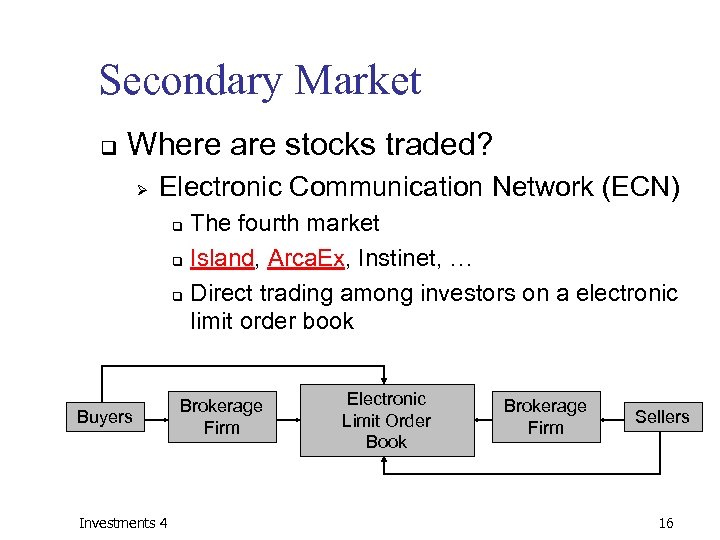
Secondary Market q Where are stocks traded? Ø Electronic Communication Network (ECN) The fourth market q Island, Arca. Ex, Instinet, … q Direct trading among investors on a electronic limit order book q Buyers Investments 4 Brokerage Firm Electronic Limit Order Book Brokerage Firm Sellers 16

To Think About… NYSE, NASDAQ, ECNs – are they all linked together? q Current trends in security trading: q Ø Ø Ø q Computers that run the stock market Flash Boys Dark Pools Price Discovery Ø Ø Investments 4 What is it? Where does it take place? 17
100c4966d5e3c8ed646320312359e452.ppt