ETP48200 V300R002C00 Training Slides.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 89
 Security Level: INTERNAL ETP 48200 V 300 R 002 C 00 Training Slides www. huawei. com Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved.
Security Level: INTERNAL ETP 48200 V 300 R 002 C 00 Training Slides www. huawei. com Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved.
 Preface This course describes the working principles, installation, routine maintenance, and troubleshooting of the ETP 48200. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 2
Preface This course describes the working principles, installation, routine maintenance, and troubleshooting of the ETP 48200. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 2
 Reference Documentation ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1&ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 User Manual ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 User Manual ETP 48200 -C 5 Technical Proposals Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 3
Reference Documentation ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1&ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 User Manual ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 User Manual ETP 48200 -C 5 Technical Proposals Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 3
 Course Objectives Upon completion of this course, you should be able to: [ Understand the features and working principles of ETP 48200 series products. [ Understand the installation, commissioning, and maintenance of ETP 48200 series products. [ Understand common faults for ETP 48200 series products and troubleshooting methods. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 4
Course Objectives Upon completion of this course, you should be able to: [ Understand the features and working principles of ETP 48200 series products. [ Understand the installation, commissioning, and maintenance of ETP 48200 series products. [ Understand common faults for ETP 48200 series products and troubleshooting methods. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 4
 Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 5
Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 5
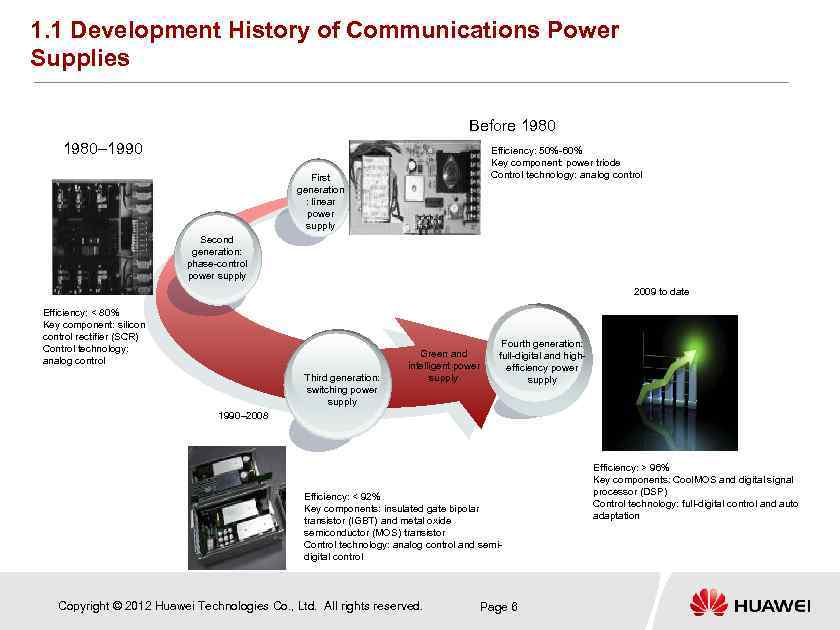 1. 1 Development History of Communications Power Supplies Before 1980– 1990 Efficiency: 50%-60% Key component: power triode Control technology: analog control First generation : linear power supply Second generation: phase-control power supply 2009 to date Efficiency: < 80% Key component: silicon control rectifier (SCR) Control technology: analog control Third generation: switching power supply Green and intelligent power supply Fourth generation: full-digital and highefficiency power supply 1990– 2008 Efficiency: < 92% Key components: insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) and metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistor Control technology: analog control and semidigital control Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 6 Efficiency: > 96% Key components: Cool. MOS and digital signal processor (DSP) Control technology: full-digital control and auto adaptation
1. 1 Development History of Communications Power Supplies Before 1980– 1990 Efficiency: 50%-60% Key component: power triode Control technology: analog control First generation : linear power supply Second generation: phase-control power supply 2009 to date Efficiency: < 80% Key component: silicon control rectifier (SCR) Control technology: analog control Third generation: switching power supply Green and intelligent power supply Fourth generation: full-digital and highefficiency power supply 1990– 2008 Efficiency: < 92% Key components: insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) and metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistor Control technology: analog control and semidigital control Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 6 Efficiency: > 96% Key components: Cool. MOS and digital signal processor (DSP) Control technology: full-digital control and auto adaptation
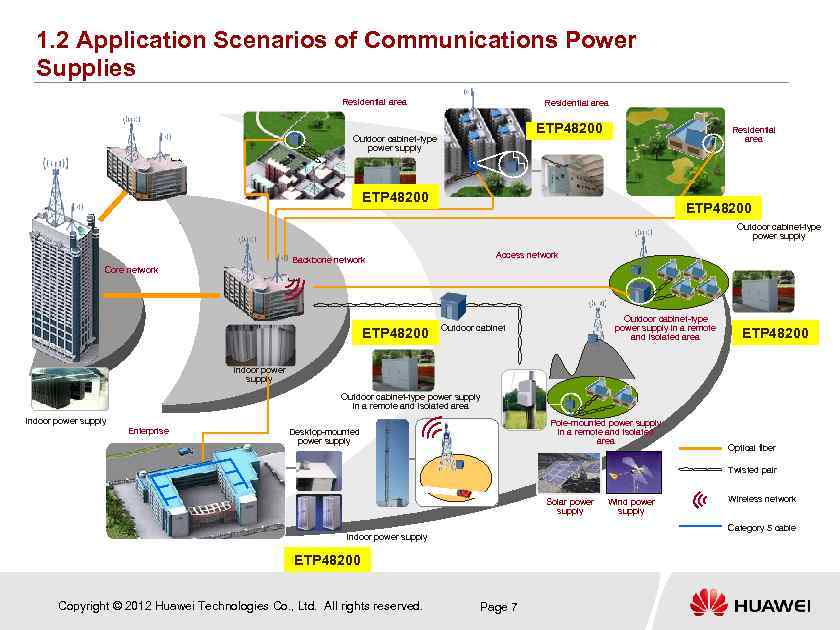 1. 2 Application Scenarios of Communications Power Supplies Residential area ETP 48200 Outdoor cabinet-type power supply Access network Backbone network Core network ETP 48200 Outdoor cabinet-type power supply in a remote and isolated area Outdoor cabinet ETP 48200 Indoor power supply Outdoor cabinet-type power supply in a remote and isolated area Indoor power supply Enterprise Pole-mounted power supply in a remote and isolated area Desktop-mounted power supply Optical fiber Twisted pair Solar power supply Wireless network Category 5 cable Indoor power supply ETP 48200 Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Wind power supply Page 7
1. 2 Application Scenarios of Communications Power Supplies Residential area ETP 48200 Outdoor cabinet-type power supply Access network Backbone network Core network ETP 48200 Outdoor cabinet-type power supply in a remote and isolated area Outdoor cabinet ETP 48200 Indoor power supply Outdoor cabinet-type power supply in a remote and isolated area Indoor power supply Enterprise Pole-mounted power supply in a remote and isolated area Desktop-mounted power supply Optical fiber Twisted pair Solar power supply Wireless network Category 5 cable Indoor power supply ETP 48200 Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Wind power supply Page 7
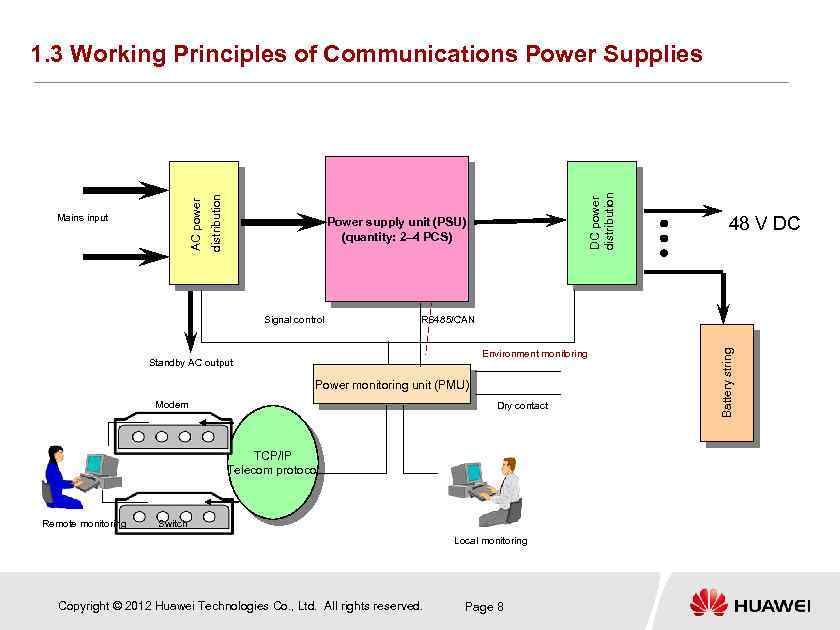 DC power distribution Power supply unit (PSU) (quantity: 2– 4 PCS) Signal control RS 485/CAN Environment monitoring Standby AC output Power monitoring unit (PMU) Modem Dry contact TCP/IP Telecom protocol Remote monitoring 48 V DC Switch Local monitoring Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 8 Battery string Mains input distribution AC power 1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies
DC power distribution Power supply unit (PSU) (quantity: 2– 4 PCS) Signal control RS 485/CAN Environment monitoring Standby AC output Power monitoring unit (PMU) Modem Dry contact TCP/IP Telecom protocol Remote monitoring 48 V DC Switch Local monitoring Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 8 Battery string Mains input distribution AC power 1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies
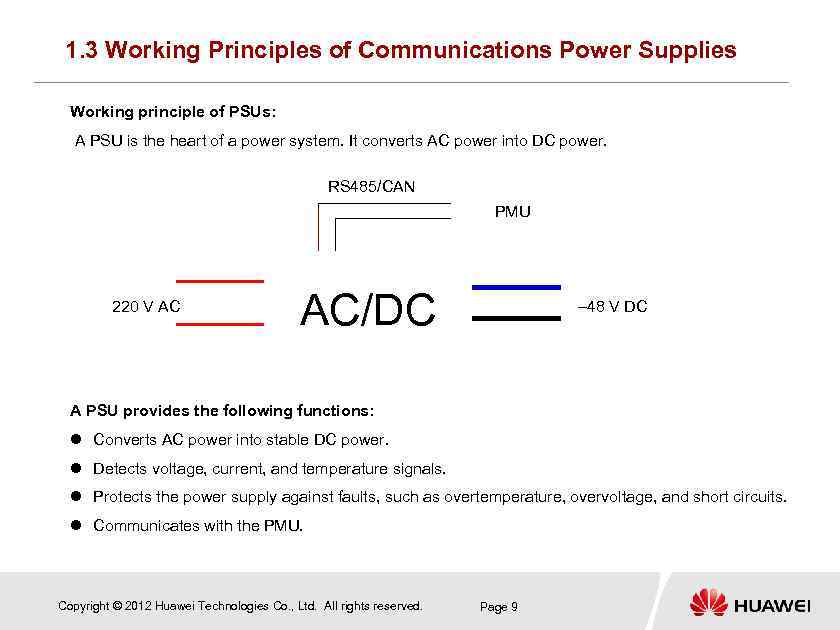 1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies Working principle of PSUs: A PSU is the heart of a power system. It converts AC power into DC power. RS 485/CAN PMU 220 V AC AC/DC – 48 V DC A PSU provides the following functions: Converts AC power into stable DC power. Detects voltage, current, and temperature signals. Protects the power supply against faults, such as overtemperature, overvoltage, and short circuits. Communicates with the PMU. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 9
1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies Working principle of PSUs: A PSU is the heart of a power system. It converts AC power into DC power. RS 485/CAN PMU 220 V AC AC/DC – 48 V DC A PSU provides the following functions: Converts AC power into stable DC power. Detects voltage, current, and temperature signals. Protects the power supply against faults, such as overtemperature, overvoltage, and short circuits. Communicates with the PMU. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 9
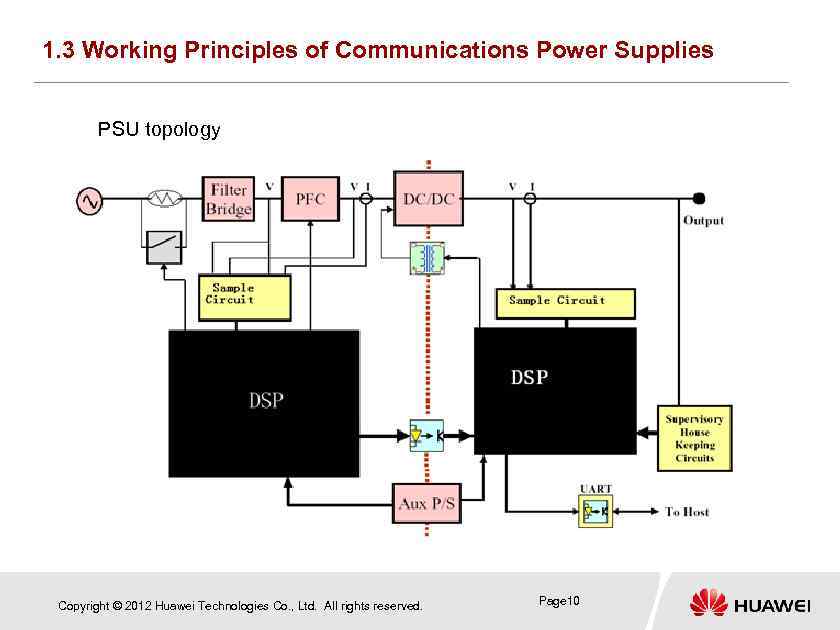 1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies PSU topology Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 10
1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies PSU topology Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 10
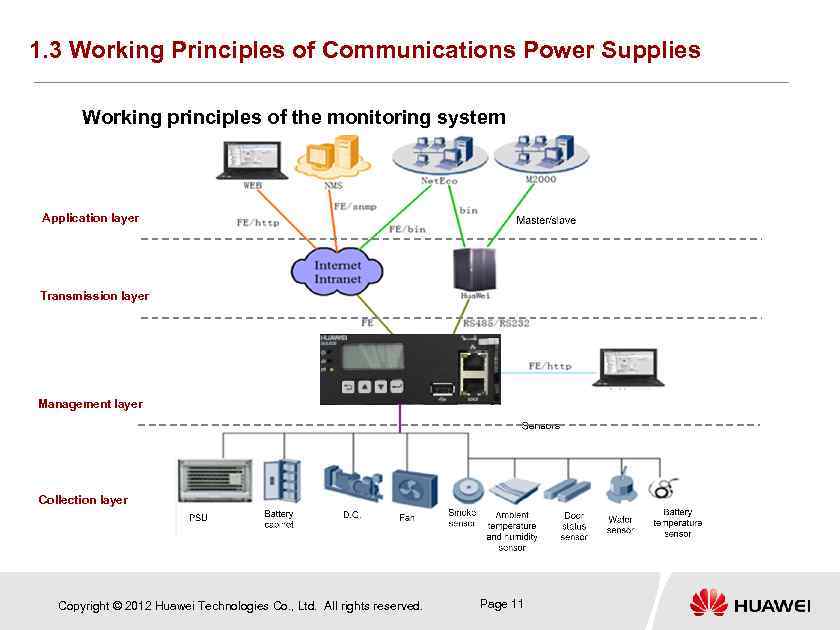 1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies Working principles of the monitoring system Application layer Transmission layer Management layer Collection layer Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 11
1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies Working principles of the monitoring system Application layer Transmission layer Management layer Collection layer Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 11
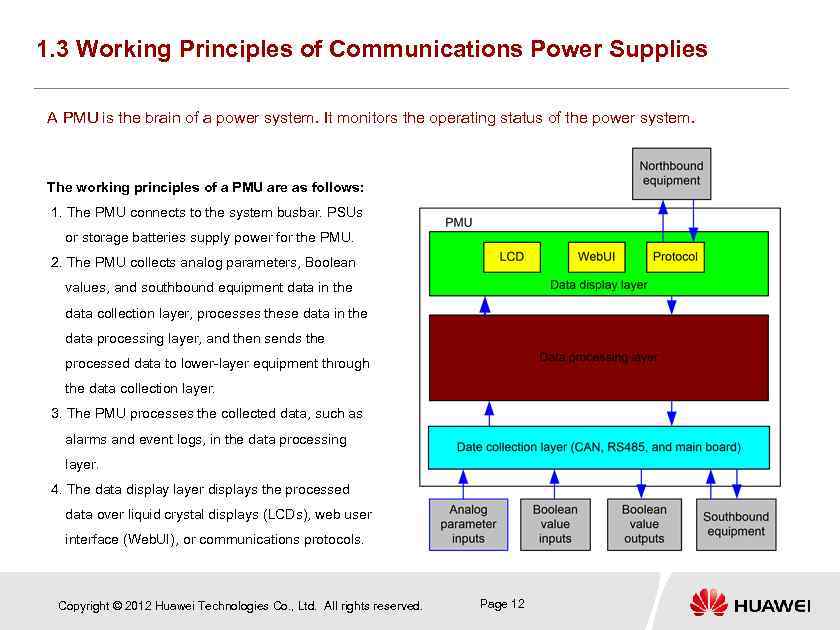 1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies A PMU is the brain of a power system. It monitors the operating status of the power system. The working principles of a PMU are as follows: 1. The PMU connects to the system busbar. PSUs or storage batteries supply power for the PMU. 2. The PMU collects analog parameters, Boolean values, and southbound equipment data in the data collection layer, processes these data in the data processing layer, and then sends the processed data to lower-layer equipment through the data collection layer. 3. The PMU processes the collected data, such as alarms and event logs, in the data processing layer. 4. The data display layer displays the processed data over liquid crystal displays (LCDs), web user interface (Web. UI), or communications protocols. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 12
1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies A PMU is the brain of a power system. It monitors the operating status of the power system. The working principles of a PMU are as follows: 1. The PMU connects to the system busbar. PSUs or storage batteries supply power for the PMU. 2. The PMU collects analog parameters, Boolean values, and southbound equipment data in the data collection layer, processes these data in the data processing layer, and then sends the processed data to lower-layer equipment through the data collection layer. 3. The PMU processes the collected data, such as alarms and event logs, in the data processing layer. 4. The data display layer displays the processed data over liquid crystal displays (LCDs), web user interface (Web. UI), or communications protocols. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 12
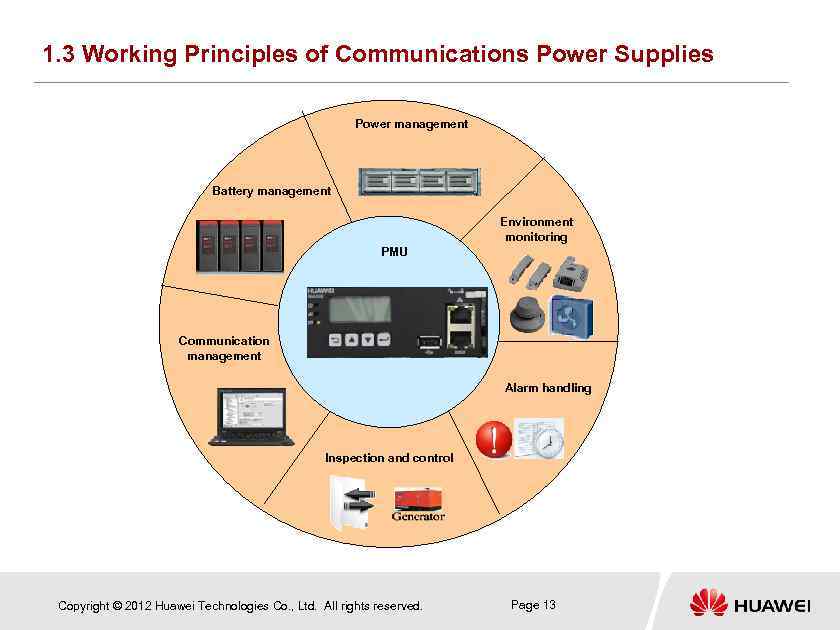 1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies Power management Battery management Environment monitoring PMU Communication management Alarm handling Inspection and control Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 13
1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies Power management Battery management Environment monitoring PMU Communication management Alarm handling Inspection and control Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 13
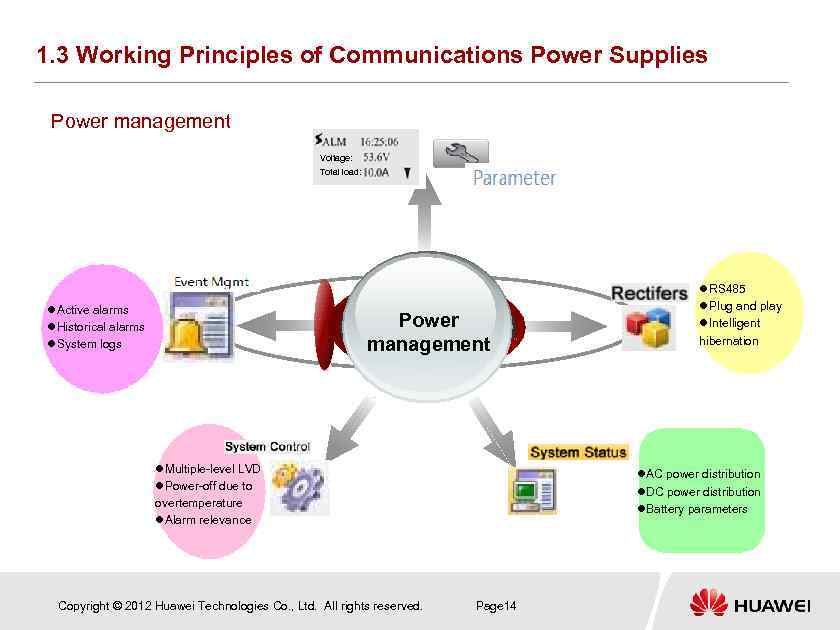 1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies Power management Voltage: Total load: Active alarms Historical alarms System logs Power management Multiple-level LVD Power-off due to overtemperature Alarm relevance Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. RS 485 Plug and play Intelligent hibernation AC power distribution DC power distribution Battery parameters Page 14
1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies Power management Voltage: Total load: Active alarms Historical alarms System logs Power management Multiple-level LVD Power-off due to overtemperature Alarm relevance Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. RS 485 Plug and play Intelligent hibernation AC power distribution DC power distribution Battery parameters Page 14
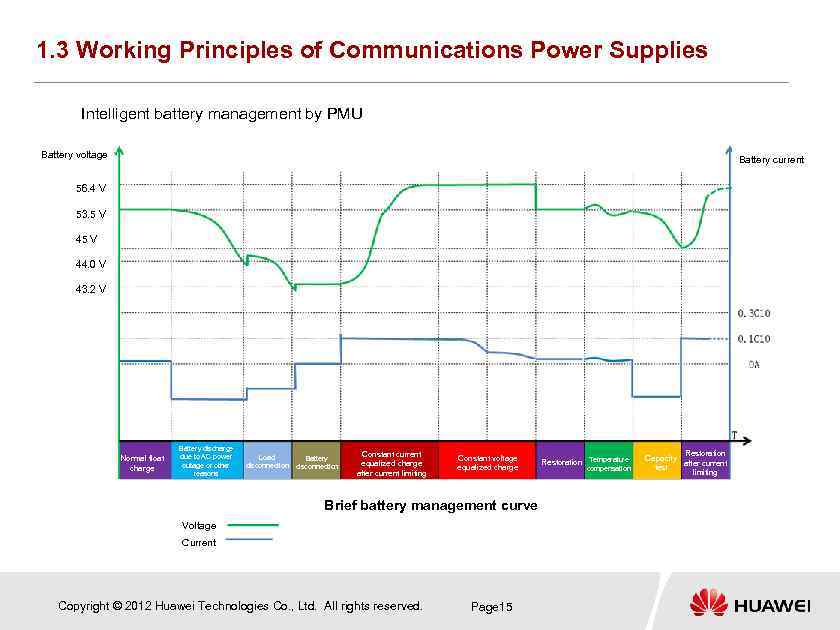 1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies Intelligent battery management by PMU Battery voltage Battery current 56. 4 V 53. 5 V 44. 0 V 43. 2 V Normal float charge Battery discharge due to AC power outage or other reasons Load disconnection Battery disconnection Constant current equalized charge after current limiting Constant voltage equalized charge Brief battery management curve Voltage Current Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 15 Restoration Temperature compensation Restoration Capacity after current test limiting
1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies Intelligent battery management by PMU Battery voltage Battery current 56. 4 V 53. 5 V 44. 0 V 43. 2 V Normal float charge Battery discharge due to AC power outage or other reasons Load disconnection Battery disconnection Constant current equalized charge after current limiting Constant voltage equalized charge Brief battery management curve Voltage Current Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 15 Restoration Temperature compensation Restoration Capacity after current test limiting
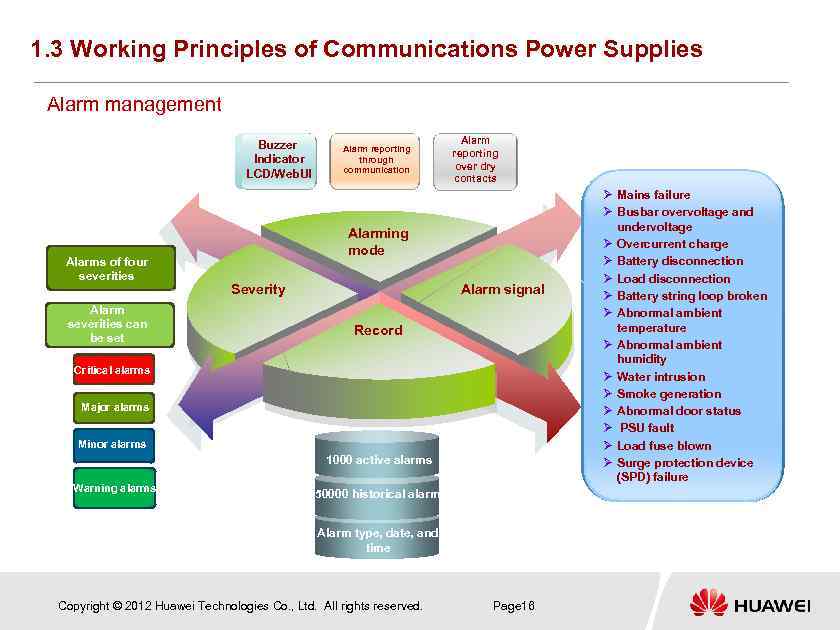 1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies Alarm management Buzzer Indicator LCD/Web. UI Alarms of four severities Alarm severities can be set Alarm reporting through communication Alarm reporting over dry contacts Alarming mode Severity Alarm signal Record Critical alarms Major alarms Minor alarms 1000 active alarms Warning alarms 50000 historical alarms Alarm type, date, and time Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 16 Ø Mains failure Ø Busbar overvoltage and undervoltage Ø Overcurrent charge Ø Battery disconnection Ø Load disconnection Ø Battery string loop broken Ø Abnormal ambient temperature Ø Abnormal ambient humidity Ø Water intrusion Ø Smoke generation Ø Abnormal door status Ø PSU fault Ø Load fuse blown Ø Surge protection device (SPD) failure
1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies Alarm management Buzzer Indicator LCD/Web. UI Alarms of four severities Alarm severities can be set Alarm reporting through communication Alarm reporting over dry contacts Alarming mode Severity Alarm signal Record Critical alarms Major alarms Minor alarms 1000 active alarms Warning alarms 50000 historical alarms Alarm type, date, and time Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 16 Ø Mains failure Ø Busbar overvoltage and undervoltage Ø Overcurrent charge Ø Battery disconnection Ø Load disconnection Ø Battery string loop broken Ø Abnormal ambient temperature Ø Abnormal ambient humidity Ø Water intrusion Ø Smoke generation Ø Abnormal door status Ø PSU fault Ø Load fuse blown Ø Surge protection device (SPD) failure
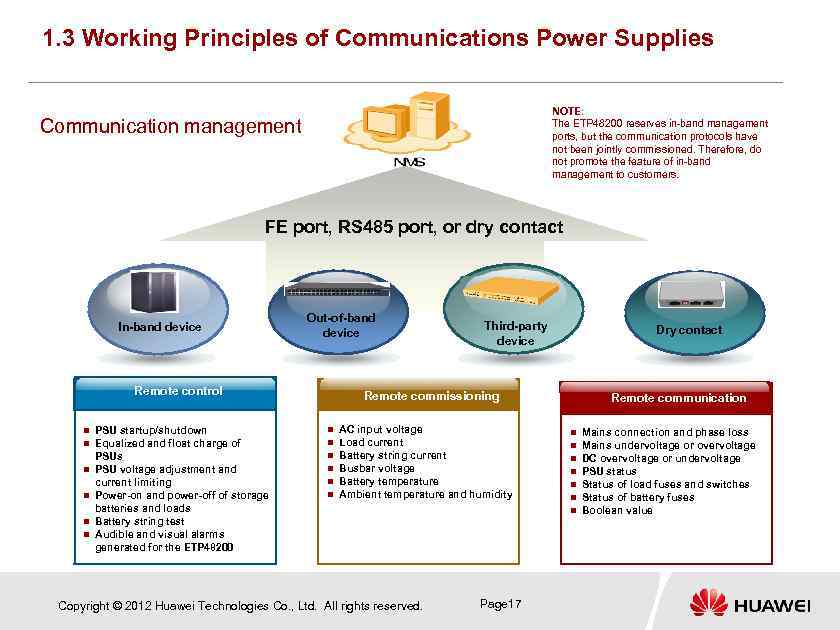 1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies NOTE: The ETP 48200 reserves in-band management ports, but the communication protocols have not been jointly commissioned. Therefore, do not promote the feature of in-band management to customers. Communication management FE port, RS 485 port, or dry contact In-band device Out-of-band device Remote control n n n PSU startup/shutdown Equalized and float charge of PSUs PSU voltage adjustment and current limiting Power-on and power-off of storage batteries and loads Battery string test Audible and visual alarms generated for the ETP 48200 Third-party device Dry contact Remote commissioning n n n AC input voltage Load current Battery string current Busbar voltage Battery temperature Ambient temperature and humidity Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Remote communication n n n Page 17 Mains connection and phase loss Mains undervoltage or overvoltage DC overvoltage or undervoltage PSU status Status of load fuses and switches Status of battery fuses Boolean value
1. 3 Working Principles of Communications Power Supplies NOTE: The ETP 48200 reserves in-band management ports, but the communication protocols have not been jointly commissioned. Therefore, do not promote the feature of in-band management to customers. Communication management FE port, RS 485 port, or dry contact In-band device Out-of-band device Remote control n n n PSU startup/shutdown Equalized and float charge of PSUs PSU voltage adjustment and current limiting Power-on and power-off of storage batteries and loads Battery string test Audible and visual alarms generated for the ETP 48200 Third-party device Dry contact Remote commissioning n n n AC input voltage Load current Battery string current Busbar voltage Battery temperature Ambient temperature and humidity Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Remote communication n n n Page 17 Mains connection and phase loss Mains undervoltage or overvoltage DC overvoltage or undervoltage PSU status Status of load fuses and switches Status of battery fuses Boolean value
 Questions What are the major components of a communications power supply? What functions do they perform? What are the main parameters and specifications of a communications power supply? What external ports do a PMU and a PSU provide? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 18
Questions What are the major components of a communications power supply? What functions do they perform? What are the main parameters and specifications of a communications power supply? What external ports do a PMU and a PSU provide? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 18
 Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 19
Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 19
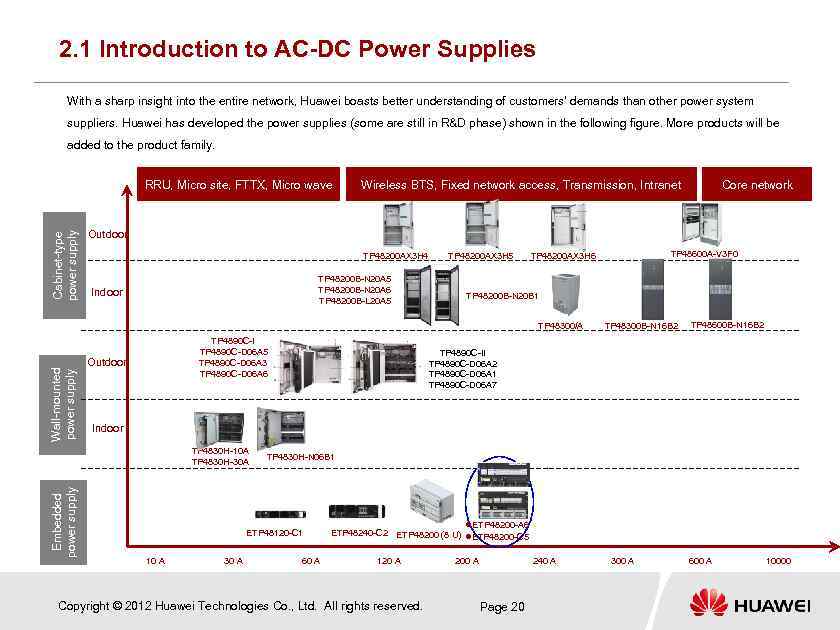 2. 1 Introduction to AC-DC Power Supplies With a sharp insight into the entire network, Huawei boasts better understanding of customers' demands than other power system suppliers. Huawei has developed the power supplies (some are still in R&D phase) shown in the following figure. More products will be added to the product family. Cabinet-type power supply RRU, Micro site, FTTX, Micro wave Wireless BTS, Fixed network access, Transmission, Intranet Outdoor TP 48200 AX 3 H 4 TP 48200 B-N 20 A 5 TP 48200 B-N 20 A 6 TP 48200 B-L 20 A 5 Indoor TP 48200 AX 3 H 5 Wall-mounted power supply TP 4890 C-I TP 4890 C-D 06 A 5 TP 4890 C-D 06 A 3 TP 4890 C-D 06 A 6 Outdoor TP 48600 A-V 3 F 0 TP 48200 AX 3 H 6 TP 48200 B-N 20 B 1 TP 48300/A TP 48300 B-N 16 B 2 TP 48600 B-N 16 B 2 TP 4890 C-II TP 4890 C-D 06 A 2 TP 4890 C-D 06 A 1 TP 4890 C-D 06 A 7 Indoor TP 4830 H-10 A TP 4830 H-30 A Embedded power supply Core network TP 4830 H-N 06 B 1 ETP 48120 -C 1 10 A 30 A 60 A ETP 48200 -A 6 ETP 48240 -C 2 ETP 48200 (8 U) ETP 48200 -C 5 120 A Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. 200 A 240 A Page 20 300 A 600 A 10000
2. 1 Introduction to AC-DC Power Supplies With a sharp insight into the entire network, Huawei boasts better understanding of customers' demands than other power system suppliers. Huawei has developed the power supplies (some are still in R&D phase) shown in the following figure. More products will be added to the product family. Cabinet-type power supply RRU, Micro site, FTTX, Micro wave Wireless BTS, Fixed network access, Transmission, Intranet Outdoor TP 48200 AX 3 H 4 TP 48200 B-N 20 A 5 TP 48200 B-N 20 A 6 TP 48200 B-L 20 A 5 Indoor TP 48200 AX 3 H 5 Wall-mounted power supply TP 4890 C-I TP 4890 C-D 06 A 5 TP 4890 C-D 06 A 3 TP 4890 C-D 06 A 6 Outdoor TP 48600 A-V 3 F 0 TP 48200 AX 3 H 6 TP 48200 B-N 20 B 1 TP 48300/A TP 48300 B-N 16 B 2 TP 48600 B-N 16 B 2 TP 4890 C-II TP 4890 C-D 06 A 2 TP 4890 C-D 06 A 1 TP 4890 C-D 06 A 7 Indoor TP 4830 H-10 A TP 4830 H-30 A Embedded power supply Core network TP 4830 H-N 06 B 1 ETP 48120 -C 1 10 A 30 A 60 A ETP 48200 -A 6 ETP 48240 -C 2 ETP 48200 (8 U) ETP 48200 -C 5 120 A Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. 200 A 240 A Page 20 300 A 600 A 10000
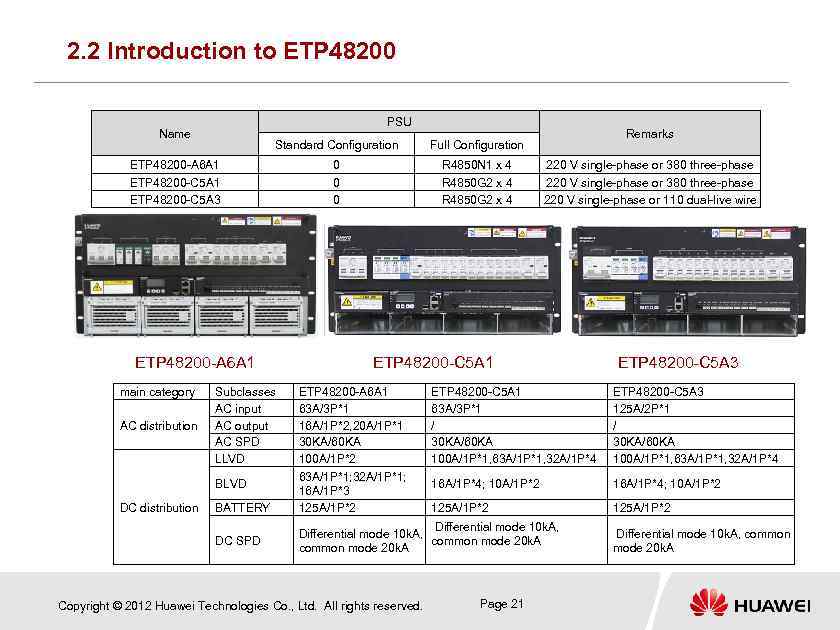 2. 2 Introduction to ETP 48200 PSU Name Standard Configuration 0 0 0 R 4850 N 1 x 4 R 4850 G 2 x 4 ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 main category AC distribution Subclasses AC input AC output AC SPD LLVD BLVD DC distribution BATTERY DC SPD Remarks Full Configuration 220 V single-phase or 380 three-phase 220 V single-phase or 110 dual-live wire ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 63 A/3 P*1 16 A/1 P*2, 20 A/1 P*1 30 KA/60 KA 100 A/1 P*2 63 A/1 P*1; 32 A/1 P*1; 16 A/1 P*3 125 A/1 P*2 ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 63 A/3 P*1 / 30 KA/60 KA 100 A/1 P*1, 63 A/1 P*1, 32 A/1 P*4 ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 125 A/2 P*1 / 30 KA/60 KA 100 A/1 P*1, 63 A/1 P*1, 32 A/1 P*4 16 A/1 P*4; 10 A/1 P*2 125 A/1 P*2 Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 21 Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A
2. 2 Introduction to ETP 48200 PSU Name Standard Configuration 0 0 0 R 4850 N 1 x 4 R 4850 G 2 x 4 ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 main category AC distribution Subclasses AC input AC output AC SPD LLVD BLVD DC distribution BATTERY DC SPD Remarks Full Configuration 220 V single-phase or 380 three-phase 220 V single-phase or 110 dual-live wire ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 63 A/3 P*1 16 A/1 P*2, 20 A/1 P*1 30 KA/60 KA 100 A/1 P*2 63 A/1 P*1; 32 A/1 P*1; 16 A/1 P*3 125 A/1 P*2 ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 63 A/3 P*1 / 30 KA/60 KA 100 A/1 P*1, 63 A/1 P*1, 32 A/1 P*4 ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 125 A/2 P*1 / 30 KA/60 KA 100 A/1 P*1, 63 A/1 P*1, 32 A/1 P*4 16 A/1 P*4; 10 A/1 P*2 125 A/1 P*2 Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 21 Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A
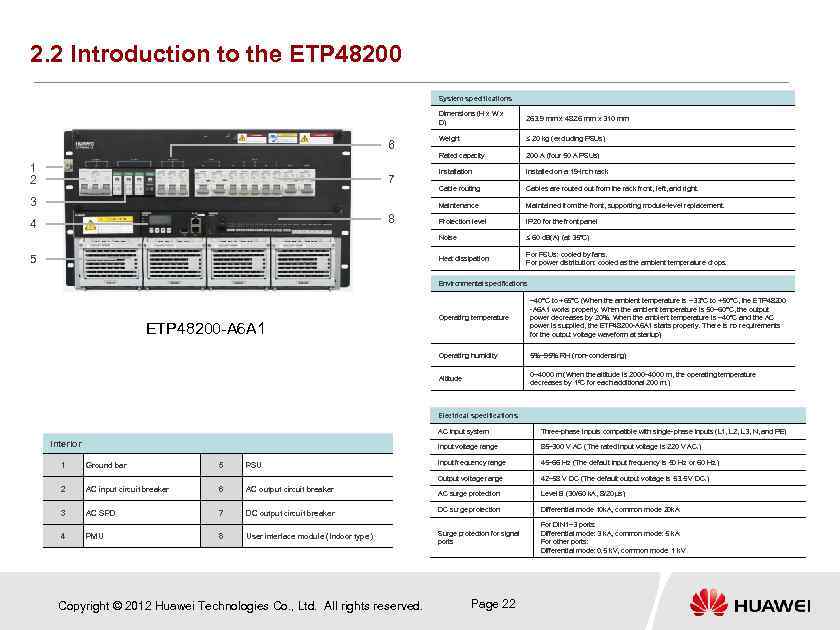 2. 2 Introduction to the ETP 48200 System specifications Dimensions (H x W x D) 8 4 5 Installation Installed on a 19 -inch rack Cable routing Cables are routed out from the rack front, left, and right. Maintained from the front, supporting module-level replacement. Protection level IP 20 for the front panel ≤ 60 d. B(A) (at 35°C) Heat dissipation 3 200 A (four 50 A PSUs) Noise 7 ≤ 20 kg (excluding PSUs) Maintenance 1 2 Weight Rated capacity 6 263. 9 mm x 482. 6 mm x 310 mm For PSUs: cooled by fans. For power distribution: cooled as the ambient temperature drops. Environmental specifications Operating temperature Operating humidity 5%– 95% RH (non-condensing) Altitude ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 – 40°C to +65°C (When the ambient temperature is – 33°C to +50°C, the ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 works properly. When the ambient temperature is 50– 60°C, the output power decreases by 20%. When the ambient temperature is – 40°C and the AC power is supplied, the ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 starts properly. There is no requirements for the output voltage waveform at startup) 0– 4000 m (When the altitude is 2000– 4000 m, the operating temperature decreases by 1ºC for each additional 200 m. ) Electrical specifications AC input system Ground bar 5 PSU 2 AC input circuit breaker 6 AC output circuit breaker 85– 300 V AC (The rated input voltage is 220 V AC. ) Input frequency range 45– 66 Hz (The default input frequency is 50 Hz or 60 Hz. ) Output voltage range 1 Three-phase inputs compatible with single-phase inputs (L 1, L 2, L 3, N, and PE) Input voltage range Interior 42– 58 V DC (The default output voltage is 53. 5 V DC. ) AC surge protection Level B (30/60 k. A, 8/20 µs) Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A For DIN 1– 3 ports: Differential mode: 3 k. A, common mode: 5 k. A For other ports: Differential mode: 0. 5 k. V, common mode: 1 k. V 3 AC SPD 7 DC output circuit breaker DC surge protection 4 PMU 8 User interface module (Indoor type) Surge protection for signal ports Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 22
2. 2 Introduction to the ETP 48200 System specifications Dimensions (H x W x D) 8 4 5 Installation Installed on a 19 -inch rack Cable routing Cables are routed out from the rack front, left, and right. Maintained from the front, supporting module-level replacement. Protection level IP 20 for the front panel ≤ 60 d. B(A) (at 35°C) Heat dissipation 3 200 A (four 50 A PSUs) Noise 7 ≤ 20 kg (excluding PSUs) Maintenance 1 2 Weight Rated capacity 6 263. 9 mm x 482. 6 mm x 310 mm For PSUs: cooled by fans. For power distribution: cooled as the ambient temperature drops. Environmental specifications Operating temperature Operating humidity 5%– 95% RH (non-condensing) Altitude ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 – 40°C to +65°C (When the ambient temperature is – 33°C to +50°C, the ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 works properly. When the ambient temperature is 50– 60°C, the output power decreases by 20%. When the ambient temperature is – 40°C and the AC power is supplied, the ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 starts properly. There is no requirements for the output voltage waveform at startup) 0– 4000 m (When the altitude is 2000– 4000 m, the operating temperature decreases by 1ºC for each additional 200 m. ) Electrical specifications AC input system Ground bar 5 PSU 2 AC input circuit breaker 6 AC output circuit breaker 85– 300 V AC (The rated input voltage is 220 V AC. ) Input frequency range 45– 66 Hz (The default input frequency is 50 Hz or 60 Hz. ) Output voltage range 1 Three-phase inputs compatible with single-phase inputs (L 1, L 2, L 3, N, and PE) Input voltage range Interior 42– 58 V DC (The default output voltage is 53. 5 V DC. ) AC surge protection Level B (30/60 k. A, 8/20 µs) Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A For DIN 1– 3 ports: Differential mode: 3 k. A, common mode: 5 k. A For other ports: Differential mode: 0. 5 k. V, common mode: 1 k. V 3 AC SPD 7 DC output circuit breaker DC surge protection 4 PMU 8 User interface module (Indoor type) Surge protection for signal ports Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 22
 2. 2 Introduction to the ETP 48200 System specifications Dimensions (H x W x D) Weight Installed on a 19 -inch rack Cables are routed out from the top. Maintained from the front, supporting module-level replacement. Protection level IP 20 for the front panel Noise 7 Installation Maintenance 3 4 200 A (four 50 A PSUs) Cable routing 1 2 ≤ 20 kg (excluding PSUs) Rated capacity 6 222. 25 mm x 482. 6 mm x 330 mm ≤ 60 d. B(A) (at 35°C) Heat dissipation For PSUs: cooled by fans. For power distribution: cooled as the ambient temperature drops. 5 Environmental specifications Operating temperature – 40°C to +65°C (When the ambient temperature is – 33°C to +55°C, the ETP 48200 C 5 A 1 works properly. When the ambient temperature is 55– 65°C, the output power decreases by 20%. When the ambient temperature is – 40°C and the AC power is supplied, the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 starts properly. There is no requirements for the output voltage waveform at startup) Operating humidity 5%– 95% RH (non-condensing) Altitude ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 0– 4000 m (When the altitude is 2000– 4000 m, the operating temperature decreases by 1ºC for each additional 200 m. ) Electrical specifications AC input system Input voltage range Interior Three-phase inputs compatible with single-phase inputs (L 1, L 2, L 3, N, and PE) 85– 300 V AC (The rated input voltage is 220 V AC. 2 3 4 Input frequency range Ground bar AC input circuit breaker AC SPD 5 6 7 PSU DC output circuit breaker 45– 66 Hz (The default input frequency is 50 Hz or 60 Hz. ) Output voltage range 42– 58 V DC (The default output voltage is 53. 5 V DC. ) AC surge protection Level B (30/60 k. A, 8/20 µs) DC surge protection 1 Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A Surge protection for signal ports For DIN 1– 4, ALM 1– 4 ports: Differential mode: 3 k. A, common mode: 5 k. A For other ports: Differential mode: 0. 5 k. V, common mode: 1 k. V UIM 02 C(Outdoor type) PMU Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 23
2. 2 Introduction to the ETP 48200 System specifications Dimensions (H x W x D) Weight Installed on a 19 -inch rack Cables are routed out from the top. Maintained from the front, supporting module-level replacement. Protection level IP 20 for the front panel Noise 7 Installation Maintenance 3 4 200 A (four 50 A PSUs) Cable routing 1 2 ≤ 20 kg (excluding PSUs) Rated capacity 6 222. 25 mm x 482. 6 mm x 330 mm ≤ 60 d. B(A) (at 35°C) Heat dissipation For PSUs: cooled by fans. For power distribution: cooled as the ambient temperature drops. 5 Environmental specifications Operating temperature – 40°C to +65°C (When the ambient temperature is – 33°C to +55°C, the ETP 48200 C 5 A 1 works properly. When the ambient temperature is 55– 65°C, the output power decreases by 20%. When the ambient temperature is – 40°C and the AC power is supplied, the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 starts properly. There is no requirements for the output voltage waveform at startup) Operating humidity 5%– 95% RH (non-condensing) Altitude ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 0– 4000 m (When the altitude is 2000– 4000 m, the operating temperature decreases by 1ºC for each additional 200 m. ) Electrical specifications AC input system Input voltage range Interior Three-phase inputs compatible with single-phase inputs (L 1, L 2, L 3, N, and PE) 85– 300 V AC (The rated input voltage is 220 V AC. 2 3 4 Input frequency range Ground bar AC input circuit breaker AC SPD 5 6 7 PSU DC output circuit breaker 45– 66 Hz (The default input frequency is 50 Hz or 60 Hz. ) Output voltage range 42– 58 V DC (The default output voltage is 53. 5 V DC. ) AC surge protection Level B (30/60 k. A, 8/20 µs) DC surge protection 1 Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A Surge protection for signal ports For DIN 1– 4, ALM 1– 4 ports: Differential mode: 3 k. A, common mode: 5 k. A For other ports: Differential mode: 0. 5 k. V, common mode: 1 k. V UIM 02 C(Outdoor type) PMU Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 23
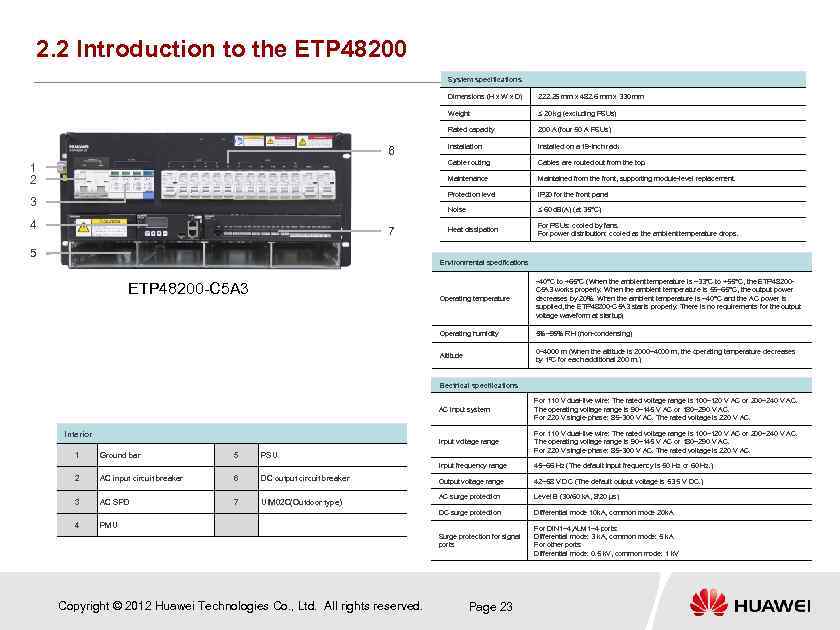 2. 2 Introduction to the ETP 48200 System specifications Dimensions (H x W x D) Weight 5 Cables are routed out from the top. Maintained from the front, supporting module-level replacement. IP 20 for the front panel Noise 7 Installed on a 19 -inch rack Protection level 4 Installation Maintenance 3 200 A (four 50 A PSUs) Cable routing 1 2 ≤ 20 kg (excluding PSUs) Rated capacity 6 222. 25 mm x 482. 6 mm x 330 mm ≤ 60 d. B(A) (at 35°C) Heat dissipation For PSUs: cooled by fans. For power distribution: cooled as the ambient temperature drops. Environmental specifications Operating temperature – 40°C to +65°C (When the ambient temperature is – 33°C to +55°C, the ETP 48200 C 5 A 3 works properly. When the ambient temperature is 55– 65°C, the output power decreases by 20%. When the ambient temperature is – 40°C and the AC power is supplied, the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 starts properly. There is no requirements for the output voltage waveform at startup) Operating humidity 5%– 95% RH (non-condensing) Altitude ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 0– 4000 m (When the altitude is 2000– 4000 m, the operating temperature decreases by 1ºC for each additional 200 m. ) Electrical specifications AC input system Input voltage range 5 AC input circuit breaker 6 DC output circuit breaker 3 AC SPD 7 UIM 02 C(Outdoor type) 4 42– 58 V DC (The default output voltage is 53. 5 V DC. ) AC surge protection Level B (30/60 k. A, 8/20 µs) Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A For DIN 1– 4, ALM 1– 4 ports: Differential mode: 3 k. A, common mode: 5 k. A For other ports: Differential mode: 0. 5 k. V, common mode: 1 k. V PSU 2 45– 66 Hz (The default input frequency is 50 Hz or 60 Hz. ) Surge protection for signal ports Ground bar Output voltage range DC surge protection 1 For 110 V dual-live wire: The rated voltage range is 100– 120 V AC or 200– 240 V AC. The operating voltage range is 90– 145 V AC or 180– 290 V AC. For 220 V single-phase: 85– 300 V AC. The rated voltage is 220 V AC. Input frequency range Interior For 110 V dual-live wire: The rated voltage range is 100– 120 V AC or 200– 240 V AC. The operating voltage range is 90– 145 V AC or 180– 290 V AC. For 220 V single-phase: 85– 300 V AC. The rated voltage is 220 V AC. PMU Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 23
2. 2 Introduction to the ETP 48200 System specifications Dimensions (H x W x D) Weight 5 Cables are routed out from the top. Maintained from the front, supporting module-level replacement. IP 20 for the front panel Noise 7 Installed on a 19 -inch rack Protection level 4 Installation Maintenance 3 200 A (four 50 A PSUs) Cable routing 1 2 ≤ 20 kg (excluding PSUs) Rated capacity 6 222. 25 mm x 482. 6 mm x 330 mm ≤ 60 d. B(A) (at 35°C) Heat dissipation For PSUs: cooled by fans. For power distribution: cooled as the ambient temperature drops. Environmental specifications Operating temperature – 40°C to +65°C (When the ambient temperature is – 33°C to +55°C, the ETP 48200 C 5 A 3 works properly. When the ambient temperature is 55– 65°C, the output power decreases by 20%. When the ambient temperature is – 40°C and the AC power is supplied, the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 starts properly. There is no requirements for the output voltage waveform at startup) Operating humidity 5%– 95% RH (non-condensing) Altitude ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 0– 4000 m (When the altitude is 2000– 4000 m, the operating temperature decreases by 1ºC for each additional 200 m. ) Electrical specifications AC input system Input voltage range 5 AC input circuit breaker 6 DC output circuit breaker 3 AC SPD 7 UIM 02 C(Outdoor type) 4 42– 58 V DC (The default output voltage is 53. 5 V DC. ) AC surge protection Level B (30/60 k. A, 8/20 µs) Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A For DIN 1– 4, ALM 1– 4 ports: Differential mode: 3 k. A, common mode: 5 k. A For other ports: Differential mode: 0. 5 k. V, common mode: 1 k. V PSU 2 45– 66 Hz (The default input frequency is 50 Hz or 60 Hz. ) Surge protection for signal ports Ground bar Output voltage range DC surge protection 1 For 110 V dual-live wire: The rated voltage range is 100– 120 V AC or 200– 240 V AC. The operating voltage range is 90– 145 V AC or 180– 290 V AC. For 220 V single-phase: 85– 300 V AC. The rated voltage is 220 V AC. Input frequency range Interior For 110 V dual-live wire: The rated voltage range is 100– 120 V AC or 200– 240 V AC. The operating voltage range is 90– 145 V AC or 180– 290 V AC. For 220 V single-phase: 85– 300 V AC. The rated voltage is 220 V AC. PMU Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 23
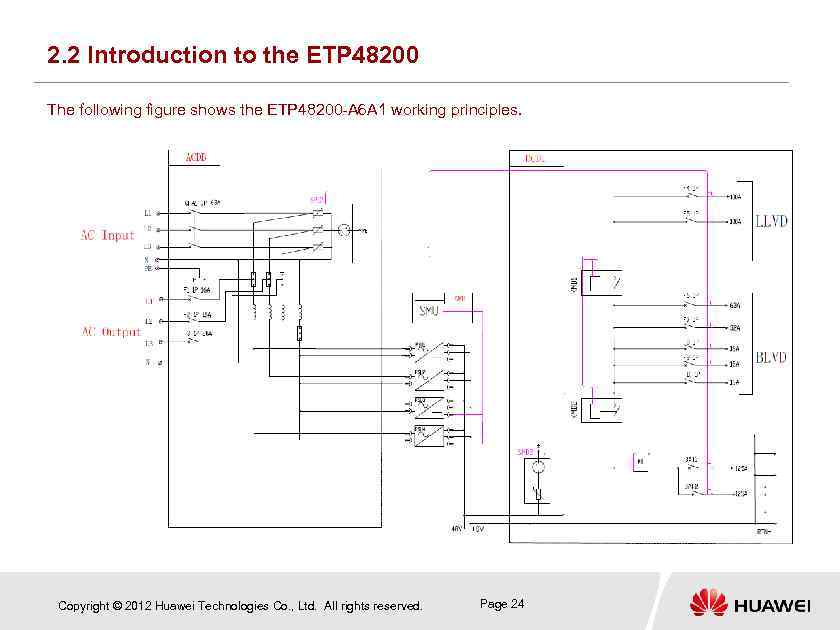 2. 2 Introduction to the ETP 48200 The following figure shows the ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 working principles. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 24
2. 2 Introduction to the ETP 48200 The following figure shows the ETP 48200 -A 6 A 1 working principles. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 24
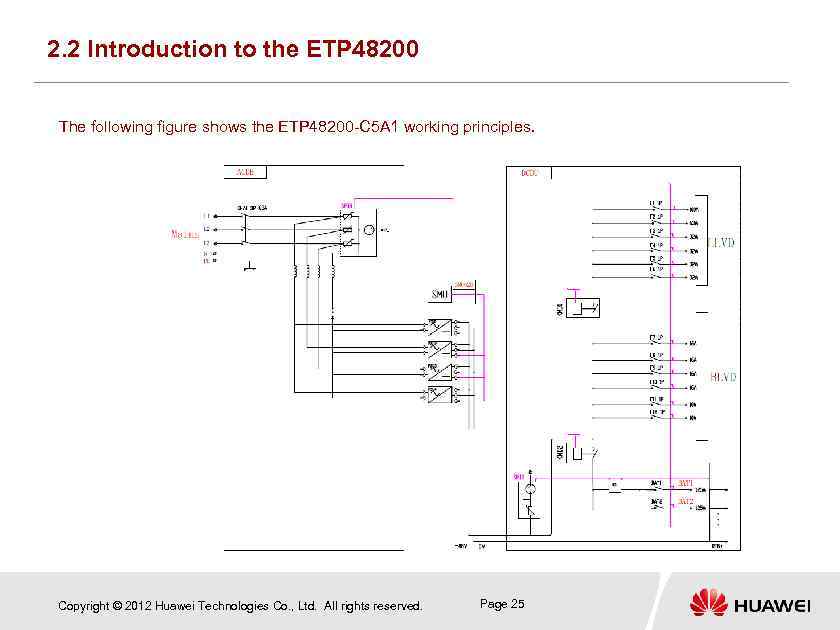 2. 2 Introduction to the ETP 48200 The following figure shows the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 working principles. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 25
2. 2 Introduction to the ETP 48200 The following figure shows the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 working principles. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 25
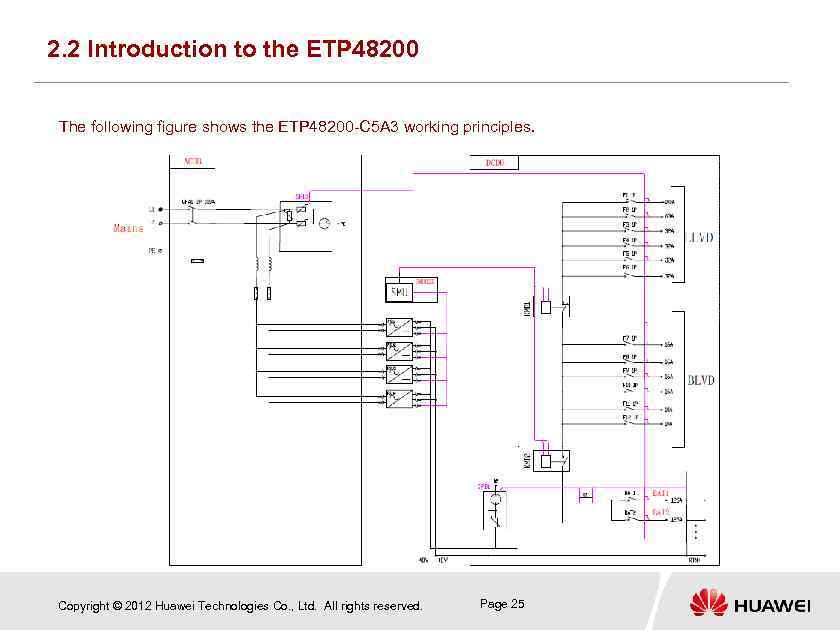 2. 2 Introduction to the ETP 48200 The following figure shows the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 working principles. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 25
2. 2 Introduction to the ETP 48200 The following figure shows the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 working principles. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 25
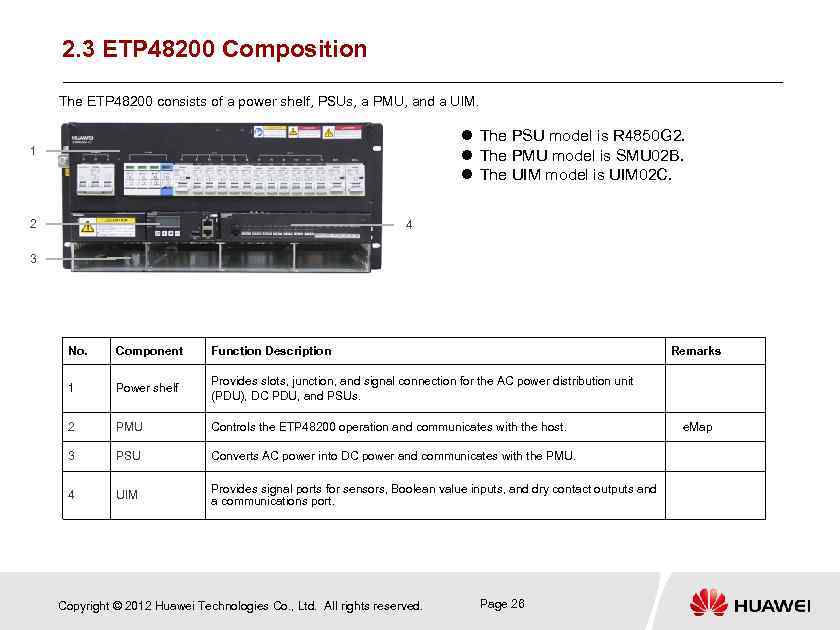 2. 3 ETP 48200 Composition The ETP 48200 consists of a power shelf, PSUs, a PMU, and a UIM. The PSU model is R 4850 G 2. The PMU model is SMU 02 B. The UIM model is UIM 02 C. 1 2 4 3 No. Component Function Description 1 Power shelf Provides slots, junction, and signal connection for the AC power distribution unit (PDU), DC PDU, and PSUs. 2 PMU Controls the ETP 48200 operation and communicates with the host. e. Map 3 PSU Converts AC power into DC power and communicates with the PMU. 4 UIM Provides signal ports for sensors, Boolean value inputs, and dry contact outputs and a communications port. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Remarks Page 26
2. 3 ETP 48200 Composition The ETP 48200 consists of a power shelf, PSUs, a PMU, and a UIM. The PSU model is R 4850 G 2. The PMU model is SMU 02 B. The UIM model is UIM 02 C. 1 2 4 3 No. Component Function Description 1 Power shelf Provides slots, junction, and signal connection for the AC power distribution unit (PDU), DC PDU, and PSUs. 2 PMU Controls the ETP 48200 operation and communicates with the host. e. Map 3 PSU Converts AC power into DC power and communicates with the PMU. 4 UIM Provides signal ports for sensors, Boolean value inputs, and dry contact outputs and a communications port. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Remarks Page 26
 2. 4 Introduction to ETP 48200 Components PSU (1) Run indicator (2) Protection indicator (3) Fault indicator Standard configuration: 50 A PSUs of high efficiency; PSU efficiency: the peak point is ≥ 96%; ≥ 95%(230 V AC, 30%– 100% load Power grid voltage: 85– 300 V AC Operating temperature: – 40°C to +70°C. Supports hot swap. Communicates over CAN. Indicator displaying alarms Supports voltage adjustment and current limiting. Complies with restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances (Ro. HS) requirements Passes the TUV, CE, FCC,UL certifications and obtains the CB certificate. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 27
2. 4 Introduction to ETP 48200 Components PSU (1) Run indicator (2) Protection indicator (3) Fault indicator Standard configuration: 50 A PSUs of high efficiency; PSU efficiency: the peak point is ≥ 96%; ≥ 95%(230 V AC, 30%– 100% load Power grid voltage: 85– 300 V AC Operating temperature: – 40°C to +70°C. Supports hot swap. Communicates over CAN. Indicator displaying alarms Supports voltage adjustment and current limiting. Complies with restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances (Ro. HS) requirements Passes the TUV, CE, FCC,UL certifications and obtains the CB certificate. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 27
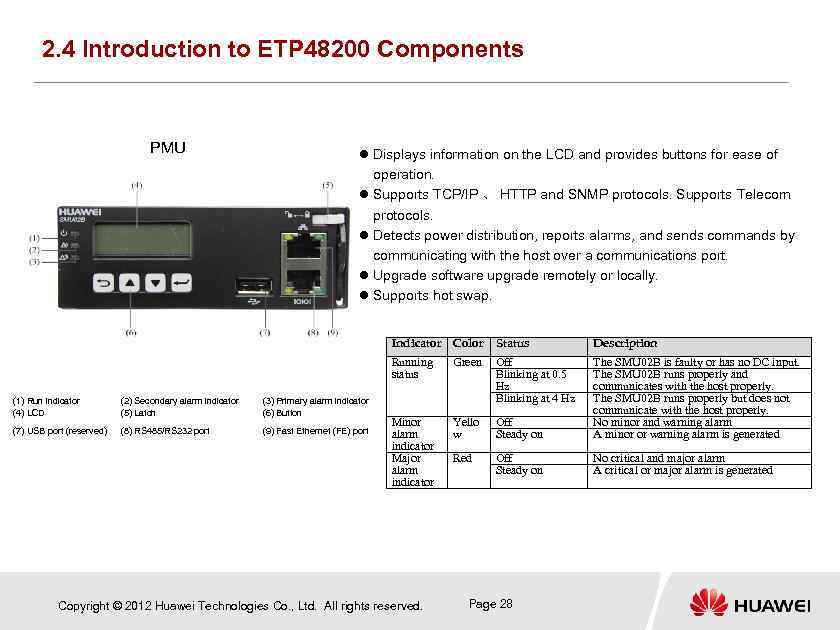 2. 4 Introduction to ETP 48200 Components PMU Displays information on the LCD and provides buttons for ease of operation. Supports TCP/IP 、 HTTP and SNMP protocols. Supports Telecom protocols. Detects power distribution, reports alarms, and sends commands by communicating with the host over a communications port. Upgrade software upgrade remotely or locally. Supports hot swap. Indicator Color (2) Secondary alarm indicator (5) Latch (3) Primary alarm indicator (6) Button (7) USB port (reserved) (8) RS 485/RS 232 port (9) Fast Ethernet (FE) port Description Running status (1) Run indicator (4) LCD Status Green Off Blinking at 0. 5 Hz Blinking at 4 Hz Minor alarm indicator Major alarm indicator Yello w Off Steady on The SMU 02 B is faulty or has no DC input. The SMU 02 B runs properly and communicates with the host properly. The SMU 02 B runs properly but does not communicate with the host properly. No minor and warning alarm A minor or warning alarm is generated Red Off Steady on No critical and major alarm A critical or major alarm is generated Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 28
2. 4 Introduction to ETP 48200 Components PMU Displays information on the LCD and provides buttons for ease of operation. Supports TCP/IP 、 HTTP and SNMP protocols. Supports Telecom protocols. Detects power distribution, reports alarms, and sends commands by communicating with the host over a communications port. Upgrade software upgrade remotely or locally. Supports hot swap. Indicator Color (2) Secondary alarm indicator (5) Latch (3) Primary alarm indicator (6) Button (7) USB port (reserved) (8) RS 485/RS 232 port (9) Fast Ethernet (FE) port Description Running status (1) Run indicator (4) LCD Status Green Off Blinking at 0. 5 Hz Blinking at 4 Hz Minor alarm indicator Major alarm indicator Yello w Off Steady on The SMU 02 B is faulty or has no DC input. The SMU 02 B runs properly and communicates with the host properly. The SMU 02 B runs properly but does not communicate with the host properly. No minor and warning alarm A minor or warning alarm is generated Red Off Steady on No critical and major alarm A critical or major alarm is generated Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 28
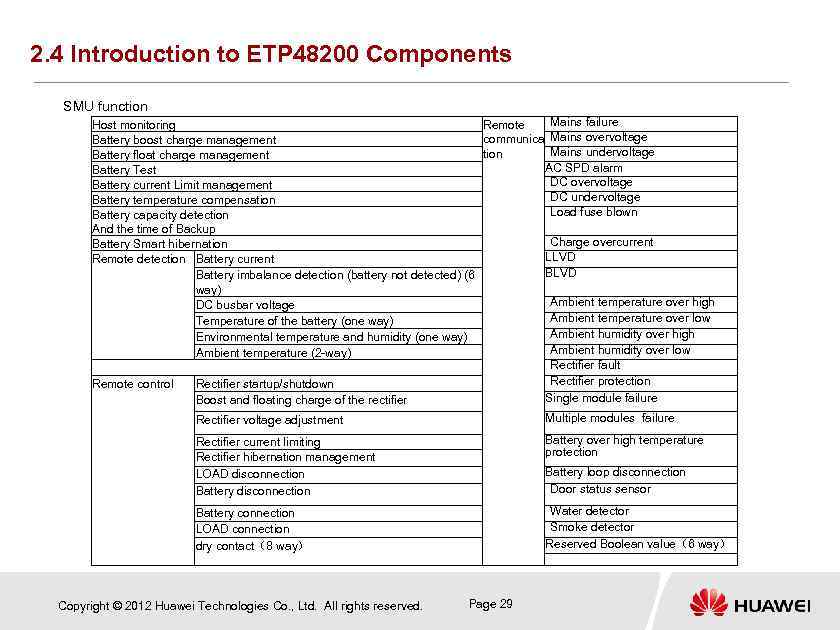 2. 4 Introduction to ETP 48200 Components SMU function Mains failure Host monitoring Remote communica Mains overvoltage Battery boost charge management Mains undervoltage tion Battery float charge management AC SPD alarm Battery Test DC overvoltage Battery current Limit management DC undervoltage Battery temperature compensation Load fuse blown Battery capacity detection And the time of Backup Charge overcurrent Battery Smart hibernation LLVD Remote detection Battery current BLVD Battery imbalance detection (battery not detected) (6 way) Ambient temperature over high DC busbar voltage Ambient temperature over low Temperature of the battery (one way) Ambient humidity over high Environmental temperature and humidity (one way) Ambient humidity over low Ambient temperature (2 -way) Rectifier fault Rectifier protection Remote control Rectifier startup/shutdown Single module failure Boost and floating charge of the rectifier Multiple modules failure Rectifier voltage adjustment Rectifier current limiting Rectifier hibernation management LOAD disconnection Battery over high temperature protection Battery connection LOAD connection dry contact(8 way) Water detector Smoke detector Reserved Boolean value(6 way) Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Battery loop disconnection Door status sensor Page 29
2. 4 Introduction to ETP 48200 Components SMU function Mains failure Host monitoring Remote communica Mains overvoltage Battery boost charge management Mains undervoltage tion Battery float charge management AC SPD alarm Battery Test DC overvoltage Battery current Limit management DC undervoltage Battery temperature compensation Load fuse blown Battery capacity detection And the time of Backup Charge overcurrent Battery Smart hibernation LLVD Remote detection Battery current BLVD Battery imbalance detection (battery not detected) (6 way) Ambient temperature over high DC busbar voltage Ambient temperature over low Temperature of the battery (one way) Ambient humidity over high Environmental temperature and humidity (one way) Ambient humidity over low Ambient temperature (2 -way) Rectifier fault Rectifier protection Remote control Rectifier startup/shutdown Single module failure Boost and floating charge of the rectifier Multiple modules failure Rectifier voltage adjustment Rectifier current limiting Rectifier hibernation management LOAD disconnection Battery over high temperature protection Battery connection LOAD connection dry contact(8 way) Water detector Smoke detector Reserved Boolean value(6 way) Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Battery loop disconnection Door status sensor Page 29
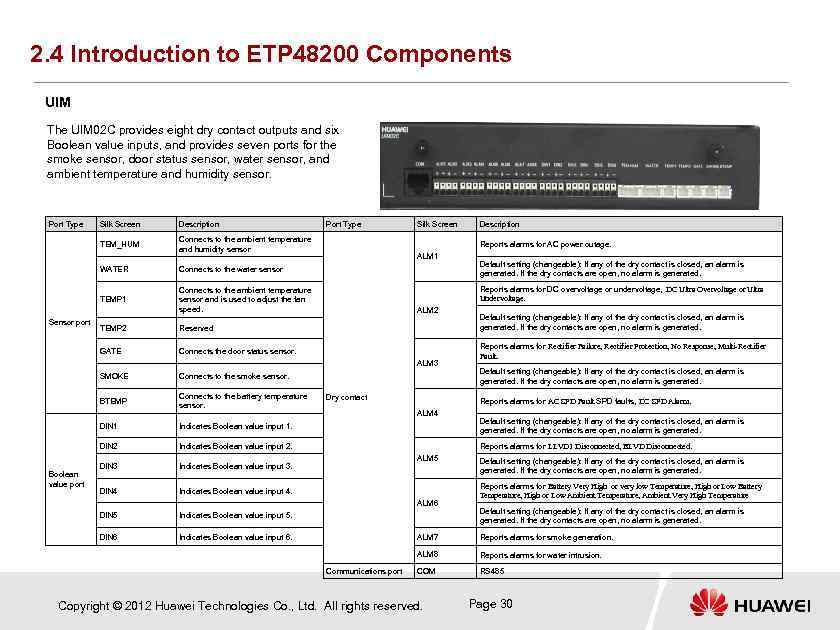 2. 4 Introduction to ETP 48200 Components UIM The UIM 02 C provides eight dry contact outputs and six Boolean value inputs, and provides seven ports for the smoke sensor, door status sensor, water sensor, and ambient temperature and humidity sensor. Port Type Silk Screen Description TEM_HUM Connects to the ambient temperature and humidity sensor WATER Sensor port Silk Screen Connects to the ambient temperature sensor and is used to adjust the fan speed. TEMP 2 Connects to the smoke sensor. BTEMP Connects to the battery temperature sensor. DIN 1 Indicates Boolean value input 1. DIN 2 ALM 2 Connects the door status sensor. SMOKE Indicates Boolean value input 2. ALM 3 DIN 4 Default setting (changeable): If any of the dry contact is closed, an alarm is generated. If the dry contacts are open, no alarm is generated. Reports alarms for Rectifier Failure, Rectifier Protection, No Response, Multi-Rectifier Fault. Default setting (changeable): If any of the dry contact is closed, an alarm is generated. If the dry contacts are open, no alarm is generated. Reports alarms for AC SPD Fault SPD faults, DC SPD Alarm. ALM 4 Default setting (changeable): If any of the dry contact is closed, an alarm is generated. If the dry contacts are open, no alarm is generated. Reports alarms for LLVD 1 Disconnected, BLVD Disconnected. ALM 5 Indicates Boolean value input 4. Indicates Boolean value input 5. DIN 6 Dry contact Indicates Boolean value input 3. DIN 5 Boolean value port DIN 3 Default setting (changeable): If any of the dry contact is closed, an alarm is generated. If the dry contacts are open, no alarm is generated. Reports alarms for DC overvoltage or undervoltage, DC Ultra Overvoltage or Ultra Undervoltage. Reserved GATE Description Reports alarms for AC power outage. ALM 1 Connects to the water sensor TEMP 1 Port Type Indicates Boolean value input 6. ALM 6 Default setting (changeable): If any of the dry contact is closed, an alarm is generated. If the dry contacts are open, no alarm is generated. Reports alarms for Battery Very High or very low Temperature, High or Low Battery Temperature, High or Low Ambient Temperature, Ambient Very High Temperature Default setting (changeable): If any of the dry contact is closed, an alarm is generated. If the dry contacts are open, no alarm is generated. ALM 7 ALM 8 Communications port Reports alarms for smoke generation. Reports alarms for water intrusion. COM RS 485 Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 30
2. 4 Introduction to ETP 48200 Components UIM The UIM 02 C provides eight dry contact outputs and six Boolean value inputs, and provides seven ports for the smoke sensor, door status sensor, water sensor, and ambient temperature and humidity sensor. Port Type Silk Screen Description TEM_HUM Connects to the ambient temperature and humidity sensor WATER Sensor port Silk Screen Connects to the ambient temperature sensor and is used to adjust the fan speed. TEMP 2 Connects to the smoke sensor. BTEMP Connects to the battery temperature sensor. DIN 1 Indicates Boolean value input 1. DIN 2 ALM 2 Connects the door status sensor. SMOKE Indicates Boolean value input 2. ALM 3 DIN 4 Default setting (changeable): If any of the dry contact is closed, an alarm is generated. If the dry contacts are open, no alarm is generated. Reports alarms for Rectifier Failure, Rectifier Protection, No Response, Multi-Rectifier Fault. Default setting (changeable): If any of the dry contact is closed, an alarm is generated. If the dry contacts are open, no alarm is generated. Reports alarms for AC SPD Fault SPD faults, DC SPD Alarm. ALM 4 Default setting (changeable): If any of the dry contact is closed, an alarm is generated. If the dry contacts are open, no alarm is generated. Reports alarms for LLVD 1 Disconnected, BLVD Disconnected. ALM 5 Indicates Boolean value input 4. Indicates Boolean value input 5. DIN 6 Dry contact Indicates Boolean value input 3. DIN 5 Boolean value port DIN 3 Default setting (changeable): If any of the dry contact is closed, an alarm is generated. If the dry contacts are open, no alarm is generated. Reports alarms for DC overvoltage or undervoltage, DC Ultra Overvoltage or Ultra Undervoltage. Reserved GATE Description Reports alarms for AC power outage. ALM 1 Connects to the water sensor TEMP 1 Port Type Indicates Boolean value input 6. ALM 6 Default setting (changeable): If any of the dry contact is closed, an alarm is generated. If the dry contacts are open, no alarm is generated. Reports alarms for Battery Very High or very low Temperature, High or Low Battery Temperature, High or Low Ambient Temperature, Ambient Very High Temperature Default setting (changeable): If any of the dry contact is closed, an alarm is generated. If the dry contacts are open, no alarm is generated. ALM 7 ALM 8 Communications port Reports alarms for smoke generation. Reports alarms for water intrusion. COM RS 485 Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 30
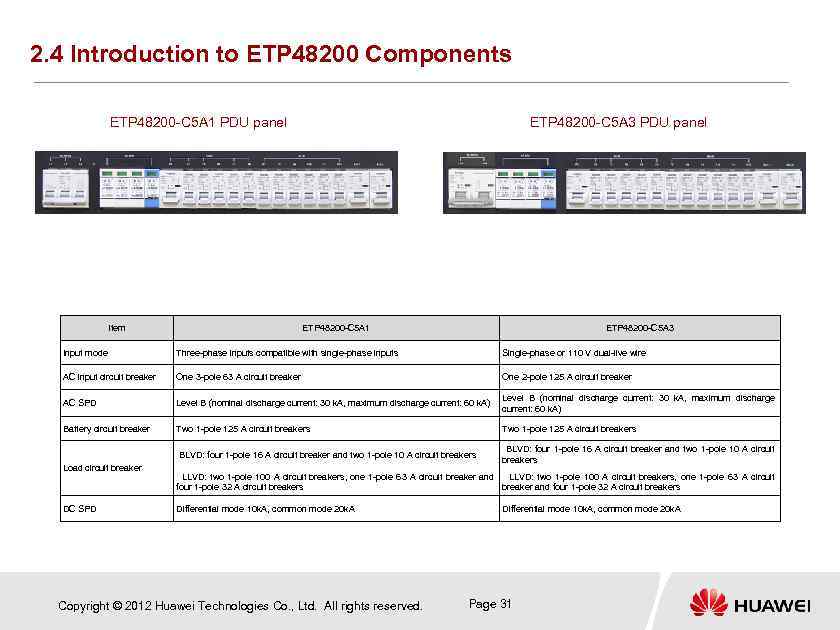 2. 4 Introduction to ETP 48200 Components ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 PDU panel Item ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 PDU panel ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 Input mode Three-phase inputs compatible with single-phase inputs Single-phase or 110 V dual-live wire AC input circuit breaker One 3 -pole 63 A circuit breaker One 2 -pole 125 A circuit breaker AC SPD Level B (nominal discharge current: 30 k. A, maximum discharge current: 60 k. A) Level B (nominal discharge current: 30 k. A, maximum discharge current: 60 k. A) Battery circuit breaker Two 1 -pole 125 A circuit breakers BLVD: four 1 -pole 16 A circuit breaker and two 1 -pole 10 A circuit breakers Load circuit breaker DC SPD LLVD: two 1 -pole 100 A circuit breakers, one 1 -pole 63 A circuit breaker and LLVD: two 1 -pole 100 A circuit breakers, one 1 -pole 63 A circuit four 1 -pole 32 A circuit breakers breaker and four 1 -pole 32 A circuit breakers Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A Page 31
2. 4 Introduction to ETP 48200 Components ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 PDU panel Item ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 PDU panel ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 Input mode Three-phase inputs compatible with single-phase inputs Single-phase or 110 V dual-live wire AC input circuit breaker One 3 -pole 63 A circuit breaker One 2 -pole 125 A circuit breaker AC SPD Level B (nominal discharge current: 30 k. A, maximum discharge current: 60 k. A) Level B (nominal discharge current: 30 k. A, maximum discharge current: 60 k. A) Battery circuit breaker Two 1 -pole 125 A circuit breakers BLVD: four 1 -pole 16 A circuit breaker and two 1 -pole 10 A circuit breakers Load circuit breaker DC SPD LLVD: two 1 -pole 100 A circuit breakers, one 1 -pole 63 A circuit breaker and LLVD: two 1 -pole 100 A circuit breakers, one 1 -pole 63 A circuit four 1 -pole 32 A circuit breakers breaker and four 1 -pole 32 A circuit breakers Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Differential mode 10 k. A, common mode 20 k. A Page 31
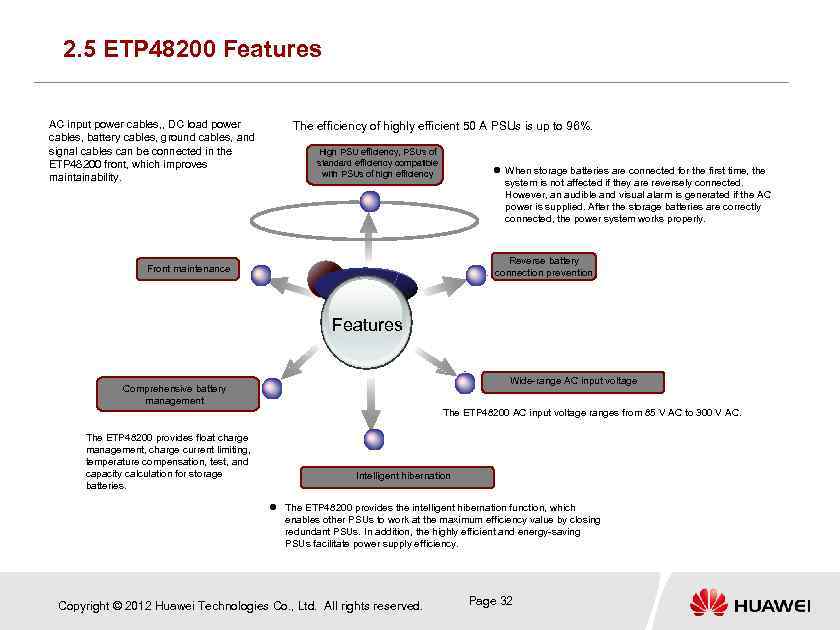 2. 5 ETP 48200 Features AC input power cables, , DC load power cables, battery cables, ground cables, and signal cables can be connected in the ETP 48200 front, which improves maintainability. The efficiency of highly efficient 50 A PSUs is up to 96%. High PSU efficiency, PSUs of standard efficiency compatible with PSUs of high efficiency When storage batteries are connected for the first time, the system is not affected if they are reversely connected. However, an audible and visual alarm is generated if the AC power is supplied. After the storage batteries are correctly connected, the power system works properly. Reverse battery connection prevention Front maintenance Features Wide-range AC input voltage Comprehensive battery management The ETP 48200 AC input voltage ranges from 85 V AC to 300 V AC. The ETP 48200 provides float charge management, charge current limiting, temperature compensation, test, and capacity calculation for storage batteries. Intelligent hibernation The ETP 48200 provides the intelligent hibernation function, which enables other PSUs to work at the maximum efficiency value by closing redundant PSUs. In addition, the highly efficient and energy-saving PSUs facilitate power supply efficiency. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 32
2. 5 ETP 48200 Features AC input power cables, , DC load power cables, battery cables, ground cables, and signal cables can be connected in the ETP 48200 front, which improves maintainability. The efficiency of highly efficient 50 A PSUs is up to 96%. High PSU efficiency, PSUs of standard efficiency compatible with PSUs of high efficiency When storage batteries are connected for the first time, the system is not affected if they are reversely connected. However, an audible and visual alarm is generated if the AC power is supplied. After the storage batteries are correctly connected, the power system works properly. Reverse battery connection prevention Front maintenance Features Wide-range AC input voltage Comprehensive battery management The ETP 48200 AC input voltage ranges from 85 V AC to 300 V AC. The ETP 48200 provides float charge management, charge current limiting, temperature compensation, test, and capacity calculation for storage batteries. Intelligent hibernation The ETP 48200 provides the intelligent hibernation function, which enables other PSUs to work at the maximum efficiency value by closing redundant PSUs. In addition, the highly efficient and energy-saving PSUs facilitate power supply efficiency. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 32
 2. 6 ETP 48200 Installation Scenarios The ETP 48200 applies to indoor Class B environments. The following shows typical ETP 48200 application scenarios. F ron ETP 48200 embedded in a Mini-shelter t ETP 48200 embedded in a 19 -inch rack NOTE: Application scope: The ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 and ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 can be also used outdoors. However, you must embed the ETP 48200 C 5 A 1 and ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 in natural-ventilation cabinets of outdoor Class B environments with caution. Do not apply the ETP 48200 C 5 A 1 and ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 to natural-ventilation cabinets of outdoor Class C environments. Class B environments refer to rooms with uncontrollable temperatures and humidity or outdoor environments (with simple shielding measures, such as awnings, and uncontrollable humidity which may rise to 100% RH). Class C environments refer to sea environments or the outdoor land environments (with simple shielding measures) near pollution sources. If a site is near a pollution source, it is at most 3. 7 km away from salt water such as the sea and salt lakes, 3 km away from heavy pollution sources such as smelteries, coal mines, and thermal power plants, 2 km away from medium pollution sources such as chemical, rubber, and galvanization industries, and 1 km away from light pollution sources such as packinghouses, tanneries, and boiler rooms. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 33
2. 6 ETP 48200 Installation Scenarios The ETP 48200 applies to indoor Class B environments. The following shows typical ETP 48200 application scenarios. F ron ETP 48200 embedded in a Mini-shelter t ETP 48200 embedded in a 19 -inch rack NOTE: Application scope: The ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 and ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 can be also used outdoors. However, you must embed the ETP 48200 C 5 A 1 and ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 in natural-ventilation cabinets of outdoor Class B environments with caution. Do not apply the ETP 48200 C 5 A 1 and ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 to natural-ventilation cabinets of outdoor Class C environments. Class B environments refer to rooms with uncontrollable temperatures and humidity or outdoor environments (with simple shielding measures, such as awnings, and uncontrollable humidity which may rise to 100% RH). Class C environments refer to sea environments or the outdoor land environments (with simple shielding measures) near pollution sources. If a site is near a pollution source, it is at most 3. 7 km away from salt water such as the sea and salt lakes, 3 km away from heavy pollution sources such as smelteries, coal mines, and thermal power plants, 2 km away from medium pollution sources such as chemical, rubber, and galvanization industries, and 1 km away from light pollution sources such as packinghouses, tanneries, and boiler rooms. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 33
 Questions What are ETP 48200 components? What are main ETP 48200 features? What should be noted for ETP 48200 application environments? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 34
Questions What are ETP 48200 components? What are main ETP 48200 features? What should be noted for ETP 48200 application environments? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 34
 Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Key Delivery Points Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 35
Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Key Delivery Points Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 35
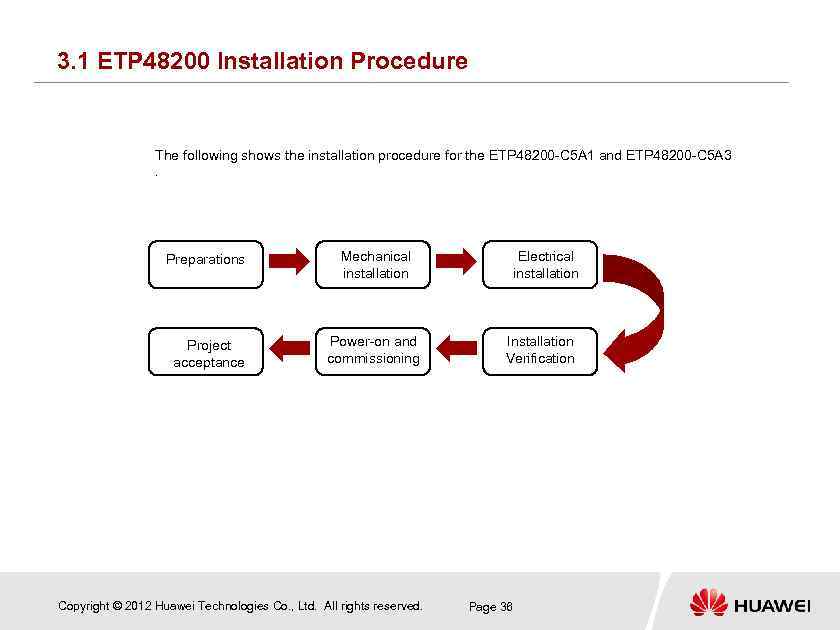 3. 1 ETP 48200 Installation Procedure The following shows the installation procedure for the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 and ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 . Preparations Mechanical installation Project acceptance Power-on and commissioning Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Electrical installation Installation Verification Page 36
3. 1 ETP 48200 Installation Procedure The following shows the installation procedure for the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 and ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 . Preparations Mechanical installation Project acceptance Power-on and commissioning Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Electrical installation Installation Verification Page 36
 3. 2 Safety Precautions High Voltage The personnel who install the AC facility must be qualified to perform high voltage and AC operations. You must abide by the local rules and regulations when bridging and wiring AC cables. During the installation of the AC power supply facility, follow the local safety regulations. Dedicated tools must be used during high voltage and AC operations. Avoid using ordinary tools. When the operation is performed in a damp environment, ensure that the device is dry. When water is found in the rack or the rack is damp, switch off the power supply immediately. Power Cable Do not install or remove power cables when the device is on. Transient contact between the core of the power cable and the conductor may generate electric arcs or sparks, which may cause fire or hurt human eyes. Before installing or removing the power cable, turn off the power switch. Before connecting a power cable, check that the label on the power cable is correct. Short circuit During operation, you must notice the following issues: Never wear conductive objects during operation. Use insulated tools. Check the polarity of the cable and connection terminal when performing DC live operations. As the operation space in the DC distribution unit is very tight, please carefully select the operation space. In live operation, keep the arm, wrist and hand tense, so that when the tool in operation slips, the movement of the human body and tool is reduced to a minimum. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 37
3. 2 Safety Precautions High Voltage The personnel who install the AC facility must be qualified to perform high voltage and AC operations. You must abide by the local rules and regulations when bridging and wiring AC cables. During the installation of the AC power supply facility, follow the local safety regulations. Dedicated tools must be used during high voltage and AC operations. Avoid using ordinary tools. When the operation is performed in a damp environment, ensure that the device is dry. When water is found in the rack or the rack is damp, switch off the power supply immediately. Power Cable Do not install or remove power cables when the device is on. Transient contact between the core of the power cable and the conductor may generate electric arcs or sparks, which may cause fire or hurt human eyes. Before installing or removing the power cable, turn off the power switch. Before connecting a power cable, check that the label on the power cable is correct. Short circuit During operation, you must notice the following issues: Never wear conductive objects during operation. Use insulated tools. Check the polarity of the cable and connection terminal when performing DC live operations. As the operation space in the DC distribution unit is very tight, please carefully select the operation space. In live operation, keep the arm, wrist and hand tense, so that when the tool in operation slips, the movement of the human body and tool is reduced to a minimum. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 37
 3. 3 Preparations Prepare tools and cables required for installing the ETP 48200. Choose cables that comply with electrical specifications and ensure that cable colors meet local power cable standards. Tools Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 38
3. 3 Preparations Prepare tools and cables required for installing the ETP 48200. Choose cables that comply with electrical specifications and ensure that cable colors meet local power cable standards. Tools Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 38
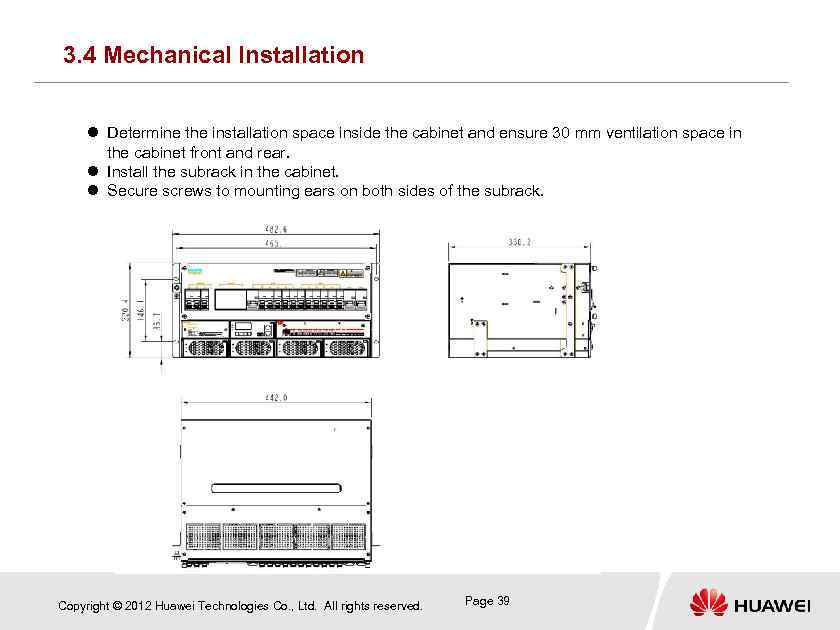 3. 4 Mechanical Installation Determine the installation space inside the cabinet and ensure 30 mm ventilation space in the cabinet front and rear. Install the subrack in the cabinet. Secure screws to mounting ears on both sides of the subrack. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 39
3. 4 Mechanical Installation Determine the installation space inside the cabinet and ensure 30 mm ventilation space in the cabinet front and rear. Install the subrack in the cabinet. Secure screws to mounting ears on both sides of the subrack. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 39
 3. 4 Mechanical Installation - Component Installation Installing PSUs Slots for installing PSUs Push the locking latch towards the left. Draw the handle downwards. Gently push a rectifier into its slot along the guide rail. Push the handle upwards and lock it. Push the locking latch towards the right to secure the handle. . Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 40
3. 4 Mechanical Installation - Component Installation Installing PSUs Slots for installing PSUs Push the locking latch towards the left. Draw the handle downwards. Gently push a rectifier into its slot along the guide rail. Push the handle upwards and lock it. Push the locking latch towards the right to secure the handle. . Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 40
 3. 5 Electrical Installation - Cable Installation Connect cables in the following sequence: ground cables, signal cables, communications cables, load cables, battery cables, and AC input cables. CAUTION: Disconnect the AC power before connecting cables and do not mix load ports with battery ports. 1. Connecting a ground cable 1 4. Connecting DC load cables RTN+ Site ground bar 2. Connecting signal cables 2 -48 V 3. Connecting communications cables BLVD FE RS 485/RS 232 Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 41 LLVD
3. 5 Electrical Installation - Cable Installation Connect cables in the following sequence: ground cables, signal cables, communications cables, load cables, battery cables, and AC input cables. CAUTION: Disconnect the AC power before connecting cables and do not mix load ports with battery ports. 1. Connecting a ground cable 1 4. Connecting DC load cables RTN+ Site ground bar 2. Connecting signal cables 2 -48 V 3. Connecting communications cables BLVD FE RS 485/RS 232 Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 41 LLVD
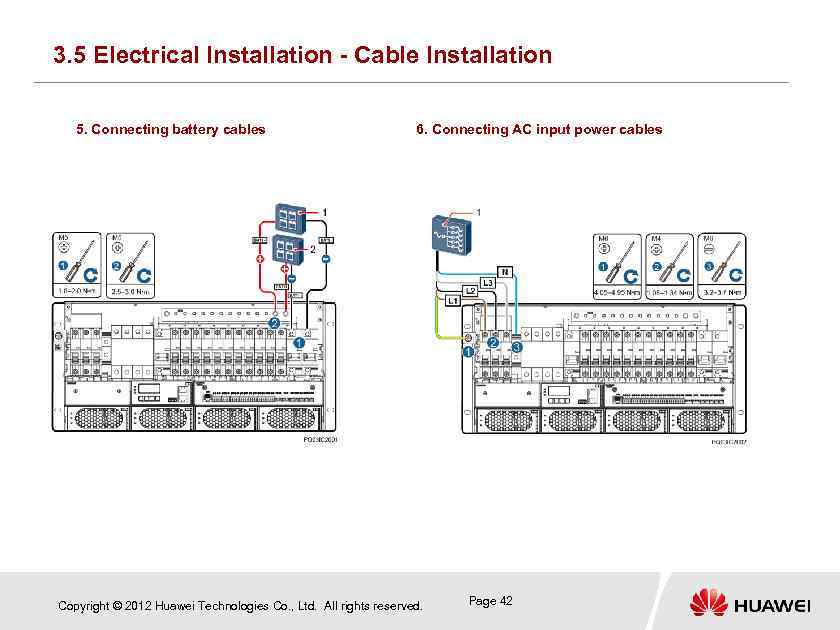 3. 5 Electrical Installation - Cable Installation 5. Connecting battery cables 6. Connecting AC input power cables Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 42
3. 5 Electrical Installation - Cable Installation 5. Connecting battery cables 6. Connecting AC input power cables Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 42
 3. 6 Installation Verification After ETP 48200 electrical installation is complete, check the following items: The ETP 48200 is grounded properly. All cables are reliably connected. The AC input circuit breaker, load circuit breakers, and battery circuit breakers are OFF. Load cables and battery cables are correctly connected. No short circuits occur between live wires, neutral wires, and ground cables, between load terminals, and between battery terminals. Serial Check items 1 The ETP 48200 is grounded properly 2 All cables are reliably connected Connecting signal cables Connecting communications cables Connecting DC load cables Connecting AC load cables Connecting battery cables Connecting AC input power cables 3 The AC input circuit breaker are OFF 4 Load circuit breakers are OFF 5 Battery circuit breakers are OFF 6 Load cables are correctly connected. 7 Battery cables are correctly connected. 8 No short circuits occur between live wires to neutral wires 9 No short circuits occur between live wires to ground cables 10 No short circuits occur between load terminals 11 No short circuits occur between battery terminals Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 43 Result
3. 6 Installation Verification After ETP 48200 electrical installation is complete, check the following items: The ETP 48200 is grounded properly. All cables are reliably connected. The AC input circuit breaker, load circuit breakers, and battery circuit breakers are OFF. Load cables and battery cables are correctly connected. No short circuits occur between live wires, neutral wires, and ground cables, between load terminals, and between battery terminals. Serial Check items 1 The ETP 48200 is grounded properly 2 All cables are reliably connected Connecting signal cables Connecting communications cables Connecting DC load cables Connecting AC load cables Connecting battery cables Connecting AC input power cables 3 The AC input circuit breaker are OFF 4 Load circuit breakers are OFF 5 Battery circuit breakers are OFF 6 Load cables are correctly connected. 7 Battery cables are correctly connected. 8 No short circuits occur between live wires to neutral wires 9 No short circuits occur between live wires to ground cables 10 No short circuits occur between load terminals 11 No short circuits occur between battery terminals Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 43 Result
 3. 7 Power-On and Commissioning To power on and commission the ETP 48200, perform the following steps: Step 1: Measure the input terminal phase voltage of the AC input circuit breaker. The normal voltage ranges from 200 V AC to 240 V AC and the rated voltage is 220 V AC. If the measured voltage is beyond the normal range, contact professionals to rectify the faulty. Switch on the AC input circuit breaker. If the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 is used, measure voltages between the L 1, L 2, or L 3 and the N wiring terminals. If the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 is used, measure the voltage between L 1 and L 2 wiring terminals or between L and N wiring terminals. The normal voltage ranges from 200 V AC to 240 V AC and the rated voltage is 220 V AC. If the PSU indicator (green) is on and other indicators are off, the PSU is ON successfully powered on. If the Run indicator (green) on the PMU panel is blinking and the LCD is on, the PMU is successfully powered on. Step 2: Set parameters on the PMU. Set the Net. Eco Main IP , Net. Eco Bak IP, Net. Eco Port, LUI Language and Set Time Zone according to actual conditions. Set the Qty of Battery, Rated Capacity, Set Date and Set Time according to actual conditions. (Always set Qty of Battery to 1 and set Rated Capacity to the total capacity of allbattery strings. ) Set the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway according to actual conditions. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 44
3. 7 Power-On and Commissioning To power on and commission the ETP 48200, perform the following steps: Step 1: Measure the input terminal phase voltage of the AC input circuit breaker. The normal voltage ranges from 200 V AC to 240 V AC and the rated voltage is 220 V AC. If the measured voltage is beyond the normal range, contact professionals to rectify the faulty. Switch on the AC input circuit breaker. If the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1 is used, measure voltages between the L 1, L 2, or L 3 and the N wiring terminals. If the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 is used, measure the voltage between L 1 and L 2 wiring terminals or between L and N wiring terminals. The normal voltage ranges from 200 V AC to 240 V AC and the rated voltage is 220 V AC. If the PSU indicator (green) is on and other indicators are off, the PSU is ON successfully powered on. If the Run indicator (green) on the PMU panel is blinking and the LCD is on, the PMU is successfully powered on. Step 2: Set parameters on the PMU. Set the Net. Eco Main IP , Net. Eco Bak IP, Net. Eco Port, LUI Language and Set Time Zone according to actual conditions. Set the Qty of Battery, Rated Capacity, Set Date and Set Time according to actual conditions. (Always set Qty of Battery to 1 and set Rated Capacity to the total capacity of allbattery strings. ) Set the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway according to actual conditions. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 44
 3. 7 Power-On and Commissioning Step 3: Switch off the AC input circuit breaker, switch on the battery circuit breakers, and then switch on the AC input circuit breaker. Check whether the voltage between the RTN+ busbar and battery MCB output terminal are the same as the storage battery voltage and the voltage displayed on the monitoring unit. If not, ask professionals to rectify the fault. Switch on the BLVD and LLVD circuit breakers and measure the output voltage. The normal voltage ranges from 42 V to 58 V and the rated voltage is 53. 5 V. If loads do not work properly, refer to associated user manuals. Switch on or off the AC input circuit breaker, battery circuit breakers, BLVD circuit breakers, and LLVD circuit breakers based on site requirements. Check whether the element management system (EMS) can receive the information from the power system. If not, check whether the IP address is set correctly. Observe the operation of the power system for 15 minutes. If no alarms (except for door alarm) are generated, and current/voltage parameters of the storage battery and loads are set properly, then re-install the cover of the distribution unit, lock the door to the cabinet, give the key of the cabinet door to the customer, and clean the site before leaving. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 45
3. 7 Power-On and Commissioning Step 3: Switch off the AC input circuit breaker, switch on the battery circuit breakers, and then switch on the AC input circuit breaker. Check whether the voltage between the RTN+ busbar and battery MCB output terminal are the same as the storage battery voltage and the voltage displayed on the monitoring unit. If not, ask professionals to rectify the fault. Switch on the BLVD and LLVD circuit breakers and measure the output voltage. The normal voltage ranges from 42 V to 58 V and the rated voltage is 53. 5 V. If loads do not work properly, refer to associated user manuals. Switch on or off the AC input circuit breaker, battery circuit breakers, BLVD circuit breakers, and LLVD circuit breakers based on site requirements. Check whether the element management system (EMS) can receive the information from the power system. If not, check whether the IP address is set correctly. Observe the operation of the power system for 15 minutes. If no alarms (except for door alarm) are generated, and current/voltage parameters of the storage battery and loads are set properly, then re-install the cover of the distribution unit, lock the door to the cabinet, give the key of the cabinet door to the customer, and clean the site before leaving. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 45
 Questions How is the ETP 48200 installed? What are the steps for installing the ETP 48200? What is the installation sequence? What should be noted before powering on the ETP 48200? What parameters prove that the ETP 48200 is properly installed and you can exit the site if they are normal? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 46
Questions How is the ETP 48200 installed? What are the steps for installing the ETP 48200? What is the installation sequence? What should be noted before powering on the ETP 48200? What parameters prove that the ETP 48200 is properly installed and you can exit the site if they are normal? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 46
 Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 47
Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 47
 4. 1 Preparations for Acceptance objectives [ Acceptance is performed after installation and is to check that customer delivery standards are meet. It is an important operation before delivery. Typically, customers or customer-authorized personnel join the process. The ETP 48200 can be delivered to customers after it passes the acceptance. Acceptance document preparations [ The acceptance manual generated by research and development (R&D) personnel is the basis for acceptance. [ Acceptance items and criteria, such as parameter settings, are determined based on actual project requirements. Acceptance tools [ A multimeter which can be used to measure high currents and a Fluke 337 clamp meter are required. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 48
4. 1 Preparations for Acceptance objectives [ Acceptance is performed after installation and is to check that customer delivery standards are meet. It is an important operation before delivery. Typically, customers or customer-authorized personnel join the process. The ETP 48200 can be delivered to customers after it passes the acceptance. Acceptance document preparations [ The acceptance manual generated by research and development (R&D) personnel is the basis for acceptance. [ Acceptance items and criteria, such as parameter settings, are determined based on actual project requirements. Acceptance tools [ A multimeter which can be used to measure high currents and a Fluke 337 clamp meter are required. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 48
 4. 2 Acceptance Methods Acceptance procedure [ Perform acceptance in the following sequence: entire system installation acceptance > acceptance before system power-on -> PSU installation acceptance -> PMU installation acceptance -> PDU installation acceptance -> parameter setting acceptance -> system functions and performance acceptance. [ Typically, acceptance is performed by following the procedure described above. After acceptance is complete, customers should confirm the acceptance results. Acceptance method [ For projects such as entire PSU installation, perform the acceptance with customer representatives. The customer representatives should sign on the acceptance document after the project passes the acceptance. [ Use tools such as a multimeter during acceptance for parameter settings and system performance. Record related data and submit it to customer representatives for signature. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 49
4. 2 Acceptance Methods Acceptance procedure [ Perform acceptance in the following sequence: entire system installation acceptance > acceptance before system power-on -> PSU installation acceptance -> PMU installation acceptance -> PDU installation acceptance -> parameter setting acceptance -> system functions and performance acceptance. [ Typically, acceptance is performed by following the procedure described above. After acceptance is complete, customers should confirm the acceptance results. Acceptance method [ For projects such as entire PSU installation, perform the acceptance with customer representatives. The customer representatives should sign on the acceptance document after the project passes the acceptance. [ Use tools such as a multimeter during acceptance for parameter settings and system performance. Record related data and submit it to customer representatives for signature. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 49
 4. 3 Acceptance Criteria Project and customer requirements [ Generally, a project has specific requirements for the equalized charging voltage, float voltage, battery capacity, and power-off parameters. Write these parameters in the acceptance manual and take them as acceptance criteria. [ For such projects as appearance and power cable management, perform the acceptance with customers. Customers should sign on the acceptance manual after the project passes the acceptance. Content that is not specified in the project [ As for content that is not specified in the project, perform the acceptance according to product acceptance criteria. For details, see the acceptance manual. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 50
4. 3 Acceptance Criteria Project and customer requirements [ Generally, a project has specific requirements for the equalized charging voltage, float voltage, battery capacity, and power-off parameters. Write these parameters in the acceptance manual and take them as acceptance criteria. [ For such projects as appearance and power cable management, perform the acceptance with customers. Customers should sign on the acceptance manual after the project passes the acceptance. Content that is not specified in the project [ As for content that is not specified in the project, perform the acceptance according to product acceptance criteria. For details, see the acceptance manual. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 50
 Questions What are the objectives of system acceptance? What preparations should be made before system acceptance? What is the procedure for ETP 48200 acceptance? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 51
Questions What are the objectives of system acceptance? What preparations should be made before system acceptance? What is the procedure for ETP 48200 acceptance? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 51
 Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 52
Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 52
 Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance This chapter includes the following items: Maintenance objectives and principles Requirements for maintenance personnel Maintenance items and intervals Maintenance content and methods Replacement of key and vulnerable components Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 53
Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance This chapter includes the following items: Maintenance objectives and principles Requirements for maintenance personnel Maintenance items and intervals Maintenance content and methods Replacement of key and vulnerable components Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 53
 5. 1 Maintenance Objectives and Principles After long-term operation, ETP 48200 functions may deteriorate or fail due to aging components, bad weather (such as thunder and lightning), environment conditions, and human misoperations. To eliminate potential faults which may cause ETP 48200 failures, perform a regular maintenance on the existing power system. Maintenance principles [ Ensure human safety and equipment security during the maintenance. For details, see related user manuals. [ During the maintenance, take appropriate measures to control or rectify the fault. [ The maintenance purpose is to eliminate potential risks and rectify ETP 48200 faults. [ Confirm customers' requirements, for example, whether power outage is allowed. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 54
5. 1 Maintenance Objectives and Principles After long-term operation, ETP 48200 functions may deteriorate or fail due to aging components, bad weather (such as thunder and lightning), environment conditions, and human misoperations. To eliminate potential faults which may cause ETP 48200 failures, perform a regular maintenance on the existing power system. Maintenance principles [ Ensure human safety and equipment security during the maintenance. For details, see related user manuals. [ During the maintenance, take appropriate measures to control or rectify the fault. [ The maintenance purpose is to eliminate potential risks and rectify ETP 48200 faults. [ Confirm customers' requirements, for example, whether power outage is allowed. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 54
 5. 2 Requirements for Maintenance Personnel ETP 48200 maintenance personnel should master basic electrical operation technique, understand basic electrical safety precautions, and obtain related certificates issued by the local government or organization and the low voltage technician certificate. Maintenance personnel should understand basic ETP 48200 composition and working principles, faults that may cause component failures, and maintenance methods. The ETP 48200 components include the AC power input, PSUs, DC contactor, PMU, and circuit breakers. Maintenance personnel should understand the common operation mode, misoperations, and results for the ETP 48200 and prevent power failures due to misoperations. Maintenance personnel should understand how to use tools and instruments, such as the multimeter and oscilloscope. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 55
5. 2 Requirements for Maintenance Personnel ETP 48200 maintenance personnel should master basic electrical operation technique, understand basic electrical safety precautions, and obtain related certificates issued by the local government or organization and the low voltage technician certificate. Maintenance personnel should understand basic ETP 48200 composition and working principles, faults that may cause component failures, and maintenance methods. The ETP 48200 components include the AC power input, PSUs, DC contactor, PMU, and circuit breakers. Maintenance personnel should understand the common operation mode, misoperations, and results for the ETP 48200 and prevent power failures due to misoperations. Maintenance personnel should understand how to use tools and instruments, such as the multimeter and oscilloscope. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 55
 Routine Maintenance Activities Perform preventive maintenance on the ETP 48200 every six months. If a fault occurs (for example in dusty environments), rectify it immediately and shorten the maintenance interval. Routine maintenance checklist Maintenance Item Electricity Maintenance Task Check That Check Method Repair When The voltage output is normal. Multimeter Troubleshooting Measures The BLVD voltage or LLVD voltage exceeds the threshold. For details, see section 7. 2 "Rectifying Common Faults" in the ETP 48200 C 5 A 1&ETP 48200 C 5 A 3 User Manual. Fault preventive maintenance inspection (PMI) Indicators are normal. Visual observation An alarm is generated. Appearance The paint and electroplated coating on the cabinet are intact and free from scratches. Visual observation The cabinet exterior is damaged Repaint and repair the or distorted. cabinet exterior. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 56
Routine Maintenance Activities Perform preventive maintenance on the ETP 48200 every six months. If a fault occurs (for example in dusty environments), rectify it immediately and shorten the maintenance interval. Routine maintenance checklist Maintenance Item Electricity Maintenance Task Check That Check Method Repair When The voltage output is normal. Multimeter Troubleshooting Measures The BLVD voltage or LLVD voltage exceeds the threshold. For details, see section 7. 2 "Rectifying Common Faults" in the ETP 48200 C 5 A 1&ETP 48200 C 5 A 3 User Manual. Fault preventive maintenance inspection (PMI) Indicators are normal. Visual observation An alarm is generated. Appearance The paint and electroplated coating on the cabinet are intact and free from scratches. Visual observation The cabinet exterior is damaged Repaint and repair the or distorted. cabinet exterior. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 56
 5. 3 Routine Maintenance Activities Electrical check [ Check whether the output voltage is within the specified range over the LCD, Web. UI, or host. Use a multimeter to check whether the difference between the value displayed on the LCD, Web. UI, or host and the actual value is within 0. 5. If the voltage is abnormal. troubleshoot the ETP 48200. [ Check the load and battery currents over the LCD, Web. UI, or host and measure the currents by using a clamp meter. Check whether the difference between the value on the LCD, Web. UI, or host and the actual value is within 1 A. If the current is abnormal, rectify the fault by take troubleshooting measures. [ Observe electrical devices (such as the contactor, circuit breaker, and power cables) for deterioration or failures. If a device deteriorates or fails, record and reserve a time to maintain it. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 57
5. 3 Routine Maintenance Activities Electrical check [ Check whether the output voltage is within the specified range over the LCD, Web. UI, or host. Use a multimeter to check whether the difference between the value displayed on the LCD, Web. UI, or host and the actual value is within 0. 5. If the voltage is abnormal. troubleshoot the ETP 48200. [ Check the load and battery currents over the LCD, Web. UI, or host and measure the currents by using a clamp meter. Check whether the difference between the value on the LCD, Web. UI, or host and the actual value is within 1 A. If the current is abnormal, rectify the fault by take troubleshooting measures. [ Observe electrical devices (such as the contactor, circuit breaker, and power cables) for deterioration or failures. If a device deteriorates or fails, record and reserve a time to maintain it. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 57
 5. 3 Routine Maintenance Activities Fault PMI [ Check the PMU for exceptions. If an exception alarm is generated, rectify the fault. [ Check that PMU and PSU indicators are normal. If a PMU works properly, the green indicator blinks and the red indicator is off. If a PSU works properly, the green indicator is steady on and the yellow and red indicators are off. [ For the indicator status is abnormal, rectify the fault by referring to the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1&ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 User Manual. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 58
5. 3 Routine Maintenance Activities Fault PMI [ Check the PMU for exceptions. If an exception alarm is generated, rectify the fault. [ Check that PMU and PSU indicators are normal. If a PMU works properly, the green indicator blinks and the red indicator is off. If a PSU works properly, the green indicator is steady on and the yellow and red indicators are off. [ For the indicator status is abnormal, rectify the fault by referring to the ETP 48200 -C 5 A 1&ETP 48200 -C 5 A 3 User Manual. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 58
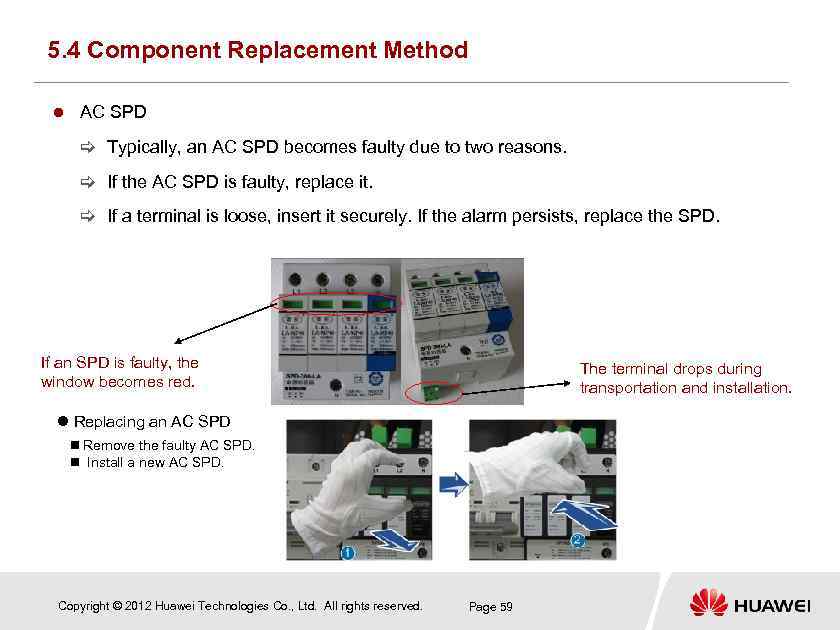 5. 4 Component Replacement Method AC SPD [ Typically, an AC SPD becomes faulty due to two reasons. [ If the AC SPD is faulty, replace it. [ If a terminal is loose, insert it securely. If the alarm persists, replace the SPD. If an SPD is faulty, the window becomes red. The terminal drops during transportation and installation. Replacing an AC SPD n Remove the faulty AC SPD. n Install a new AC SPD. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 59
5. 4 Component Replacement Method AC SPD [ Typically, an AC SPD becomes faulty due to two reasons. [ If the AC SPD is faulty, replace it. [ If a terminal is loose, insert it securely. If the alarm persists, replace the SPD. If an SPD is faulty, the window becomes red. The terminal drops during transportation and installation. Replacing an AC SPD n Remove the faulty AC SPD. n Install a new AC SPD. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 59
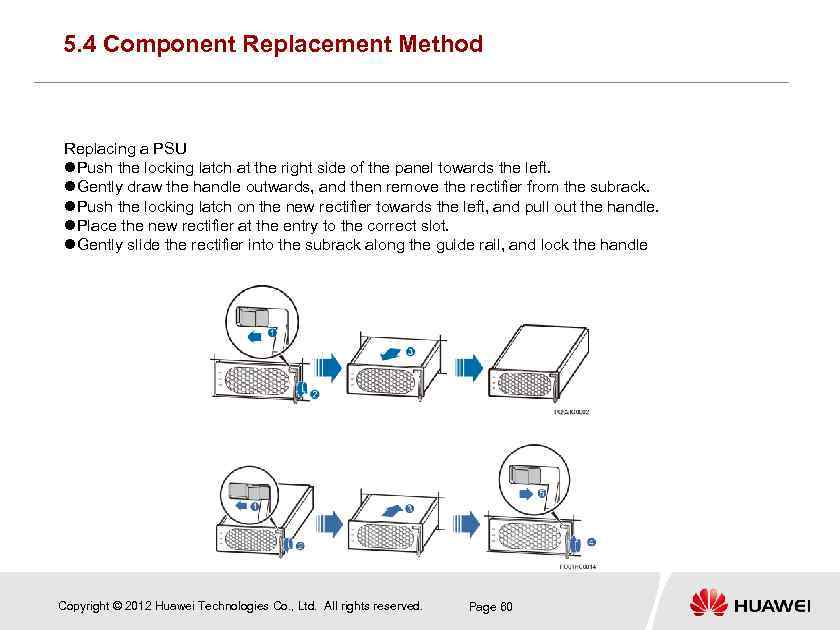 5. 4 Component Replacement Method Replacing a PSU Push the locking latch at the right side of the panel towards the left. Gently draw the handle outwards, and then remove the rectifier from the subrack. Push the locking latch on the new rectifier towards the left, and pull out the handle. Place the new rectifier at the entry to the correct slot. Gently slide the rectifier into the subrack along the guide rail, and lock the handle Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 60
5. 4 Component Replacement Method Replacing a PSU Push the locking latch at the right side of the panel towards the left. Gently draw the handle outwards, and then remove the rectifier from the subrack. Push the locking latch on the new rectifier towards the left, and pull out the handle. Place the new rectifier at the entry to the correct slot. Gently slide the rectifier into the subrack along the guide rail, and lock the handle Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 60
 5. 4 Component Replacement Method Replacing the PMU Push the locking latch on the front panel to the left. Pull the PMU handle outwards to remove the PSU from the subrack, as shown in the following figure. Put a new PMU in the corresponding slot, push the locking latch to the left, and put out its handle. Slide the PMU slowly into the subrack along the guide rails and push the locking latch to the right. Reset parameters on the PMU. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 61
5. 4 Component Replacement Method Replacing the PMU Push the locking latch on the front panel to the left. Pull the PMU handle outwards to remove the PSU from the subrack, as shown in the following figure. Put a new PMU in the corresponding slot, push the locking latch to the left, and put out its handle. Slide the PMU slowly into the subrack along the guide rails and push the locking latch to the right. Reset parameters on the PMU. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 61
 5. 4 Component Replacement Method Replacing a circuit breaker Disconnect the power to a faulty circuit breaker. For example, if an AC input circuit breaker is to be replaced, disconnect the power to the AC input circuit breaker and switch it off. Remove the power cables or copper bars from the circuit breaker using an insulated Phillips screwdriver, and then wrap the power cables or copper bars by using insulation tapes to avoid hazards. Press the contact plate at the bottom of the circuit breaker using an insulated flat-head screwdriver and then remove the circuit breaker, as shown in the following figure. Press the contact plate at the bottom of the circuit breaker using an insulated flat-head screwdriver to install a new circuit breaker in the correct position. Then push the contact plate upwards using the screwdriver. Reinstall the cables or copper bars using an insulated Phillips screwdriver. Switch on the circuit breaker and connect the power supply to the circuit breaker, as shown in the following figure. CAUTION: Do not wear conductive objects when replacing the circuit breaker. Replace the circuit breaker by using insulated tools. Connect cables to correct terminals. Reserve enough space before performing any operation. When the ETP 48200 is on, ensure that your hands, wrists, and arms are stable to prevent hazardous accidents. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 62
5. 4 Component Replacement Method Replacing a circuit breaker Disconnect the power to a faulty circuit breaker. For example, if an AC input circuit breaker is to be replaced, disconnect the power to the AC input circuit breaker and switch it off. Remove the power cables or copper bars from the circuit breaker using an insulated Phillips screwdriver, and then wrap the power cables or copper bars by using insulation tapes to avoid hazards. Press the contact plate at the bottom of the circuit breaker using an insulated flat-head screwdriver and then remove the circuit breaker, as shown in the following figure. Press the contact plate at the bottom of the circuit breaker using an insulated flat-head screwdriver to install a new circuit breaker in the correct position. Then push the contact plate upwards using the screwdriver. Reinstall the cables or copper bars using an insulated Phillips screwdriver. Switch on the circuit breaker and connect the power supply to the circuit breaker, as shown in the following figure. CAUTION: Do not wear conductive objects when replacing the circuit breaker. Replace the circuit breaker by using insulated tools. Connect cables to correct terminals. Reserve enough space before performing any operation. When the ETP 48200 is on, ensure that your hands, wrists, and arms are stable to prevent hazardous accidents. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 62
 Questions What is included in routine ETP 48200 maintenance? How to identify a faulty component? How to replace ETP 48200 components? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 62
Questions What is included in routine ETP 48200 maintenance? How to identify a faulty component? How to replace ETP 48200 components? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 62
 Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 64
Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 64
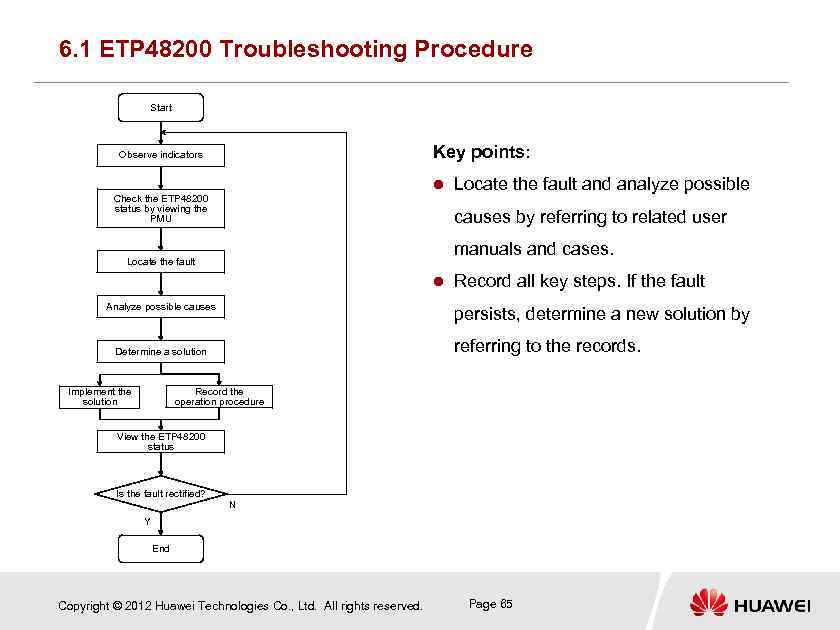 6. 1 ETP 48200 Troubleshooting Procedure Start Key points: Observe indicators Check the ETP 48200 status by viewing the PMU Locate the fault and analyze possible causes by referring to related user manuals and cases. Locate the fault Analyze possible causes Record all key steps. If the fault persists, determine a new solution by referring to the records. Determine a solution Record the operation procedure Implement the solution View the ETP 48200 status Is the fault rectified? N Y End Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 65
6. 1 ETP 48200 Troubleshooting Procedure Start Key points: Observe indicators Check the ETP 48200 status by viewing the PMU Locate the fault and analyze possible causes by referring to related user manuals and cases. Locate the fault Analyze possible causes Record all key steps. If the fault persists, determine a new solution by referring to the records. Determine a solution Record the operation procedure Implement the solution View the ETP 48200 status Is the fault rectified? N Y End Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 65
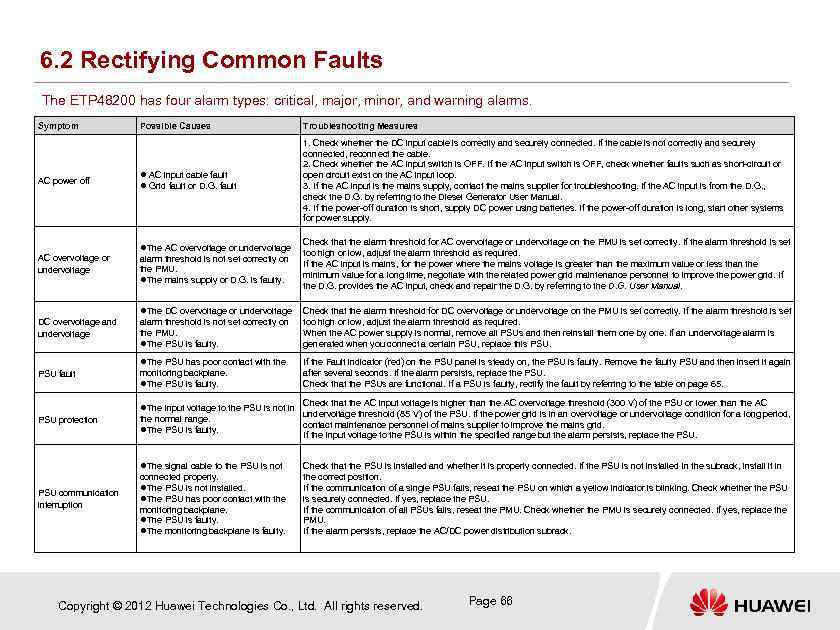 6. 2 Rectifying Common Faults The ETP 48200 has four alarm types: critical, major, minor, and warning alarms. Symptom AC power off Possible Causes Troubleshooting Measures AC input cable fault Grid fault or D. G. fault 1. Check whether the DC input cable is correctly and securely connected. If the cable is not correctly and securely connected, reconnect the cable. 2. Check whether the AC input switch is OFF. If the AC input switch is OFF, check whether faults such as short-circuit or open circuit exist on the AC input loop. 3. If the AC input is the mains supply, contact the mains supplier for troubleshooting. If the AC input is from the D. G. , check the D. G. by referring to the Diesel Generator User Manual. 4. If the power-off duration is short, supply DC power using batteries. If the power-off duration is long, start other systems for power supply. The AC overvoltage or undervoltage alarm threshold is not set correctly on the PMU. The mains supply or D. G. is faulty. Check that the alarm threshold for AC overvoltage or undervoltage on the PMU is set correctly. If the alarm threshold is set too high or low, adjust the alarm threshold as required. If the AC input is mains, for the power where the mains voltage is greater than the maximum value or less than the minimum value for a long time, negotiate with the related power grid maintenance personnel to improve the power grid. If the D. G. provides the AC input, check and repair the D. G. by referring to the D. G. User Manual. The DC overvoltage or undervoltage Check that the alarm threshold for DC overvoltage or undervoltage on the PMU is set correctly. If the alarm threshold is set DC overvoltage and undervoltage too high or low, adjust the alarm threshold as required. When the AC power supply is normal, remove all PSUs and then reinstall them one by one. If an undervoltage alarm is generated when you connect a certain PSU, replace this PSU. The PSU has poor contact with the PSU fault alarm threshold is not set correctly on the PMU. The PSU is faulty. If the Fault indicator (red) on the PSU panel is steady on, the PSU is faulty. Remove the faulty PSU and then insert it again after several seconds. If the alarm persists, replace the PSU. Check that the PSUs are functional. If a PSU is faulty, rectify the fault by referring to the table on page 65. monitoring backplane. The PSU is faulty. The input voltage to the PSU is not in PSU protection the normal range. The PSU is faulty. The signal cable to the PSU is not PSU communication interruption connected properly. The PSU is not installed. The PSU has poor contact with the monitoring backplane. The PSU is faulty. The monitoring backplane is faulty. Check that the AC input voltage is higher than the AC overvoltage threshold (300 V) of the PSU or lower than the AC undervoltage threshold (85 V) of the PSU. If the power grid is in an overvoltage or undervoltage condition for a long period, contact maintenance personnel of mains supplier to improve the mains grid. If the input voltage to the PSU is within the specified range but the alarm persists, replace the PSU. Check that the PSU is installed and whether it is properly connected. If the PSU is not installed in the subrack, install it in the correct position. If the communication of a single PSU fails, reseat the PSU on which a yellow indicator is blinking. Check whether the PSU is securely connected. If yes, replace the PSU. If the communication of all PSUs fails, reseat the PMU. Check whether the PMU is securely connected. If yes, replace the PMU. If the alarm persists, replace the AC/DC power distribution subrack. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 66
6. 2 Rectifying Common Faults The ETP 48200 has four alarm types: critical, major, minor, and warning alarms. Symptom AC power off Possible Causes Troubleshooting Measures AC input cable fault Grid fault or D. G. fault 1. Check whether the DC input cable is correctly and securely connected. If the cable is not correctly and securely connected, reconnect the cable. 2. Check whether the AC input switch is OFF. If the AC input switch is OFF, check whether faults such as short-circuit or open circuit exist on the AC input loop. 3. If the AC input is the mains supply, contact the mains supplier for troubleshooting. If the AC input is from the D. G. , check the D. G. by referring to the Diesel Generator User Manual. 4. If the power-off duration is short, supply DC power using batteries. If the power-off duration is long, start other systems for power supply. The AC overvoltage or undervoltage alarm threshold is not set correctly on the PMU. The mains supply or D. G. is faulty. Check that the alarm threshold for AC overvoltage or undervoltage on the PMU is set correctly. If the alarm threshold is set too high or low, adjust the alarm threshold as required. If the AC input is mains, for the power where the mains voltage is greater than the maximum value or less than the minimum value for a long time, negotiate with the related power grid maintenance personnel to improve the power grid. If the D. G. provides the AC input, check and repair the D. G. by referring to the D. G. User Manual. The DC overvoltage or undervoltage Check that the alarm threshold for DC overvoltage or undervoltage on the PMU is set correctly. If the alarm threshold is set DC overvoltage and undervoltage too high or low, adjust the alarm threshold as required. When the AC power supply is normal, remove all PSUs and then reinstall them one by one. If an undervoltage alarm is generated when you connect a certain PSU, replace this PSU. The PSU has poor contact with the PSU fault alarm threshold is not set correctly on the PMU. The PSU is faulty. If the Fault indicator (red) on the PSU panel is steady on, the PSU is faulty. Remove the faulty PSU and then insert it again after several seconds. If the alarm persists, replace the PSU. Check that the PSUs are functional. If a PSU is faulty, rectify the fault by referring to the table on page 65. monitoring backplane. The PSU is faulty. The input voltage to the PSU is not in PSU protection the normal range. The PSU is faulty. The signal cable to the PSU is not PSU communication interruption connected properly. The PSU is not installed. The PSU has poor contact with the monitoring backplane. The PSU is faulty. The monitoring backplane is faulty. Check that the AC input voltage is higher than the AC overvoltage threshold (300 V) of the PSU or lower than the AC undervoltage threshold (85 V) of the PSU. If the power grid is in an overvoltage or undervoltage condition for a long period, contact maintenance personnel of mains supplier to improve the mains grid. If the input voltage to the PSU is within the specified range but the alarm persists, replace the PSU. Check that the PSU is installed and whether it is properly connected. If the PSU is not installed in the subrack, install it in the correct position. If the communication of a single PSU fails, reseat the PSU on which a yellow indicator is blinking. Check whether the PSU is securely connected. If yes, replace the PSU. If the communication of all PSUs fails, reseat the PMU. Check whether the PMU is securely connected. If yes, replace the PMU. If the alarm persists, replace the AC/DC power distribution subrack. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 66
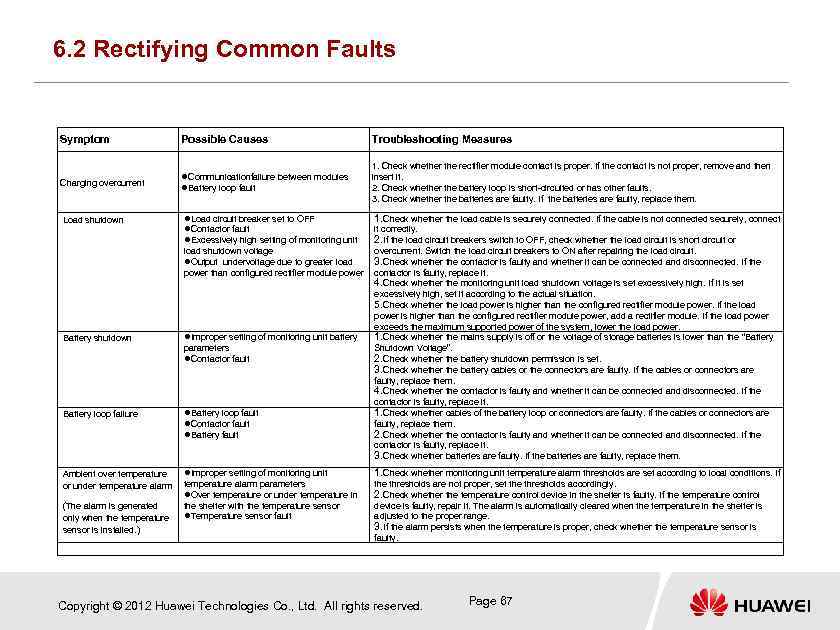 6. 2 Rectifying Common Faults Symptom Possible Causes Troubleshooting Measures Charging overcurrent Communicationfailure between modules Battery loop fault 1. Check whether the rectifier module contact is proper. If the contact is not proper, remove and then insert it. 2. Check whether the battery loop is short-circuited or has other faults. 3. Check whether the batteries are faulty. If the batteries are faulty, replace them. Load shutdown Load circuit breaker set to OFF Contactor fault Excessively high setting of monitoring unit load shutdown voltage Output undervoltage due to greater load power than configured rectifier module power 1. Check whether the load cable is securely connected. If the cable is not connected securely, connect it correctly. 2. If the load circuit breakers switch to OFF, check whether the load circuit is short circuit or overcurrent. Switch the load circuit breakers to ON after repairing the load circuit. 3. Check whether the contactor is faulty and whether it can be connected and disconnected. If the contactor is faulty, replace it. 4. Check whether the monitoring unit load shutdown voltage is set excessively high. If it is set excessively high, set it according to the actual situation. 5. Check whether the load power is higher than the configured rectifier module power. If the load power is higher than the configured rectifier module power, add a rectifier module. If the load power exceeds the maximum supported power of the system, lower the load power. 1. Check whether the mains supply is off or the voltage of storage batteries is lower than the “Battery Shutdown Voltage”. 2. Check whether the battery shutdown permission is set. 3. Check whether the battery cables or the connectors are faulty. If the cables or connectors are faulty, replace them. 4. Check whether the contactor is faulty and whether it can be connected and disconnected. If the contactor is faulty, replace it. 1. Check whether cables of the battery loop or connectors are faulty. If the cables or connectors are faulty, replace them. 2. Check whether the contactor is faulty and whether it can be connected and disconnected. If the contactor is faulty, replace it. 3. Check whether batteries are faulty. If the batteries are faulty, replace them. Battery shutdown Improper setting of monitoring unit battery Battery loop failure Battery loop fault Contactor fault Battery fault Ambient over temperature or under temperature alarm Improper setting of monitoring unit 1. Check whether monitoring unit temperature alarm thresholds are set according to local conditions. If temperature alarm parameters Over temperature or under temperature in the shelter with the temperature sensor Temperature sensor fault the thresholds are not proper, set the thresholds accordingly. 2. Check whether the temperature control device in the shelter is faulty. If the temperature control device is faulty, repair it. The alarm is automatically cleared when the temperature in the shelter is adjusted to the proper range. 3. If the alarm persists when the temperature is proper, check whether the temperature sensor is faulty. (The alarm is generated only when the temperature sensor is installed. ) parameters Contactor fault Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 67
6. 2 Rectifying Common Faults Symptom Possible Causes Troubleshooting Measures Charging overcurrent Communicationfailure between modules Battery loop fault 1. Check whether the rectifier module contact is proper. If the contact is not proper, remove and then insert it. 2. Check whether the battery loop is short-circuited or has other faults. 3. Check whether the batteries are faulty. If the batteries are faulty, replace them. Load shutdown Load circuit breaker set to OFF Contactor fault Excessively high setting of monitoring unit load shutdown voltage Output undervoltage due to greater load power than configured rectifier module power 1. Check whether the load cable is securely connected. If the cable is not connected securely, connect it correctly. 2. If the load circuit breakers switch to OFF, check whether the load circuit is short circuit or overcurrent. Switch the load circuit breakers to ON after repairing the load circuit. 3. Check whether the contactor is faulty and whether it can be connected and disconnected. If the contactor is faulty, replace it. 4. Check whether the monitoring unit load shutdown voltage is set excessively high. If it is set excessively high, set it according to the actual situation. 5. Check whether the load power is higher than the configured rectifier module power. If the load power is higher than the configured rectifier module power, add a rectifier module. If the load power exceeds the maximum supported power of the system, lower the load power. 1. Check whether the mains supply is off or the voltage of storage batteries is lower than the “Battery Shutdown Voltage”. 2. Check whether the battery shutdown permission is set. 3. Check whether the battery cables or the connectors are faulty. If the cables or connectors are faulty, replace them. 4. Check whether the contactor is faulty and whether it can be connected and disconnected. If the contactor is faulty, replace it. 1. Check whether cables of the battery loop or connectors are faulty. If the cables or connectors are faulty, replace them. 2. Check whether the contactor is faulty and whether it can be connected and disconnected. If the contactor is faulty, replace it. 3. Check whether batteries are faulty. If the batteries are faulty, replace them. Battery shutdown Improper setting of monitoring unit battery Battery loop failure Battery loop fault Contactor fault Battery fault Ambient over temperature or under temperature alarm Improper setting of monitoring unit 1. Check whether monitoring unit temperature alarm thresholds are set according to local conditions. If temperature alarm parameters Over temperature or under temperature in the shelter with the temperature sensor Temperature sensor fault the thresholds are not proper, set the thresholds accordingly. 2. Check whether the temperature control device in the shelter is faulty. If the temperature control device is faulty, repair it. The alarm is automatically cleared when the temperature in the shelter is adjusted to the proper range. 3. If the alarm persists when the temperature is proper, check whether the temperature sensor is faulty. (The alarm is generated only when the temperature sensor is installed. ) parameters Contactor fault Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 67
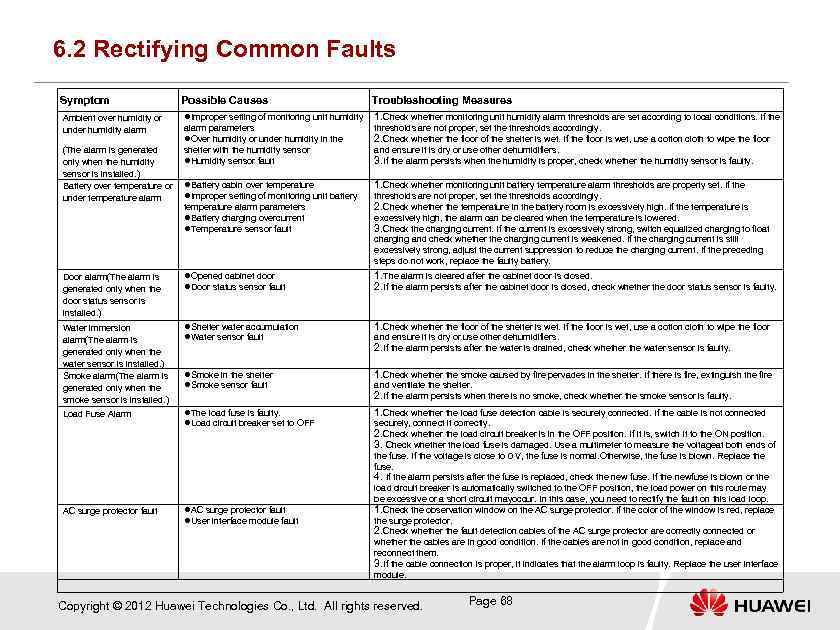 6. 2 Rectifying Common Faults Symptom Possible Causes Ambient over humidity or under humidity alarm Improper setting of monitoring unit humidity 1. Check whether monitoring unit humidity alarm thresholds are set according to local conditions. If the alarm parameters Over humidity or under humidity in the shelter with the humidity sensor Humidity sensor fault (The alarm is generated only when the humidity sensor is installed. ) Battery over temperature or Battery cabin over temperature Improper setting of monitoring unit battery under temperature alarm parameters Battery charging overcurrent Temperature sensor fault Troubleshooting Measures thresholds are not proper, set the thresholds accordingly. 2. Check whether the floor of the shelter is wet. If the floor is wet, use a cotton cloth to wipe the floor and ensure it is dry or use other dehumidifiers. 3. If the alarm persists when the humidity is proper, check whether the humidity sensor is faulty. 1. Check whether monitoring unit battery temperature alarm thresholds are properly set. If the thresholds are not proper, set the thresholds accordingly. 2. Check whether the temperature in the battery room is excessively high. If the temperature is excessively high, the alarm can be cleared when the temperature is lowered. 3. Check the charging current. If the current is excessively strong, switch equalized charging to float charging and check whether the charging current is weakened. If the charging current is still excessively strong, adjust the current suppression to reduce the charging current. If the preceding steps do not work, replace the faulty battery. Door alarm(The alarm is generated only when the door status sensor is installed. ) Opened cabinet door Door status sensor fault 1. The alarm is cleared after the cabinet door is closed. 2. If the alarm persists after the cabinet door is closed, check whether the door status sensor is faulty. Water immersion alarm(The alarm is generated only when the water sensor is installed. ) Smoke alarm(The alarm is generated only when the smoke sensor is installed. ) Shelter water accumulation Water sensor fault 1. Check whether the floor of the shelter is wet. If the floor is wet, use a cotton cloth to wipe the floor Smoke in the shelter Smoke sensor fault 1. Check whether the smoke caused by fire pervades in the shelter. If there is fire, extinguish the fire Load Fuse Alarm The load fuse is faulty. Load circuit breaker set to OFF 1. Check whether the load fuse detection cable is securely connected. If the cable is not connected AC surge protector fault User interface module fault and ensure it is dry or use other dehumidifiers. 2. If the alarm persists after the water is drained, check whether the water sensor is faulty. and ventilate the shelter. 2. If the alarm persists when there is no smoke, check whether the smoke sensor is faulty. securely, connect it correctly. 2. Check whether the load circuit breaker is in the OFF position. If it is, switch it to the ON position. 3. Check whether the load fuse is damaged. Use a multimeter to measure the voltageat both ends of the fuse. If the voltage is close to 0 V, the fuse is normal. Otherwise, the fuse is blown. Replace the fuse. 4. If the alarm persists after the fuse is replaced, check the new fuse. If the newfuse is blown or the load circuit breaker is automatically switched to the OFF position, the load power on this route may be excessive or a short circuit mayoccur. In this case, you need to rectify the fault on this load loop. 1. Check the observation window on the AC surge protector. If the color of the window is red, replace the surge protector. 2. Check whether the fault detection cables of the AC surge protector are correctly connected or whether the cables are in good condition. If the cables are not in good condition, replace and reconnect them. 3. If the cable connection is proper, it indicates that the alarm loop is faulty. Replace the user interface module. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 68
6. 2 Rectifying Common Faults Symptom Possible Causes Ambient over humidity or under humidity alarm Improper setting of monitoring unit humidity 1. Check whether monitoring unit humidity alarm thresholds are set according to local conditions. If the alarm parameters Over humidity or under humidity in the shelter with the humidity sensor Humidity sensor fault (The alarm is generated only when the humidity sensor is installed. ) Battery over temperature or Battery cabin over temperature Improper setting of monitoring unit battery under temperature alarm parameters Battery charging overcurrent Temperature sensor fault Troubleshooting Measures thresholds are not proper, set the thresholds accordingly. 2. Check whether the floor of the shelter is wet. If the floor is wet, use a cotton cloth to wipe the floor and ensure it is dry or use other dehumidifiers. 3. If the alarm persists when the humidity is proper, check whether the humidity sensor is faulty. 1. Check whether monitoring unit battery temperature alarm thresholds are properly set. If the thresholds are not proper, set the thresholds accordingly. 2. Check whether the temperature in the battery room is excessively high. If the temperature is excessively high, the alarm can be cleared when the temperature is lowered. 3. Check the charging current. If the current is excessively strong, switch equalized charging to float charging and check whether the charging current is weakened. If the charging current is still excessively strong, adjust the current suppression to reduce the charging current. If the preceding steps do not work, replace the faulty battery. Door alarm(The alarm is generated only when the door status sensor is installed. ) Opened cabinet door Door status sensor fault 1. The alarm is cleared after the cabinet door is closed. 2. If the alarm persists after the cabinet door is closed, check whether the door status sensor is faulty. Water immersion alarm(The alarm is generated only when the water sensor is installed. ) Smoke alarm(The alarm is generated only when the smoke sensor is installed. ) Shelter water accumulation Water sensor fault 1. Check whether the floor of the shelter is wet. If the floor is wet, use a cotton cloth to wipe the floor Smoke in the shelter Smoke sensor fault 1. Check whether the smoke caused by fire pervades in the shelter. If there is fire, extinguish the fire Load Fuse Alarm The load fuse is faulty. Load circuit breaker set to OFF 1. Check whether the load fuse detection cable is securely connected. If the cable is not connected AC surge protector fault User interface module fault and ensure it is dry or use other dehumidifiers. 2. If the alarm persists after the water is drained, check whether the water sensor is faulty. and ventilate the shelter. 2. If the alarm persists when there is no smoke, check whether the smoke sensor is faulty. securely, connect it correctly. 2. Check whether the load circuit breaker is in the OFF position. If it is, switch it to the ON position. 3. Check whether the load fuse is damaged. Use a multimeter to measure the voltageat both ends of the fuse. If the voltage is close to 0 V, the fuse is normal. Otherwise, the fuse is blown. Replace the fuse. 4. If the alarm persists after the fuse is replaced, check the new fuse. If the newfuse is blown or the load circuit breaker is automatically switched to the OFF position, the load power on this route may be excessive or a short circuit mayoccur. In this case, you need to rectify the fault on this load loop. 1. Check the observation window on the AC surge protector. If the color of the window is red, replace the surge protector. 2. Check whether the fault detection cables of the AC surge protector are correctly connected or whether the cables are in good condition. If the cables are not in good condition, replace and reconnect them. 3. If the cable connection is proper, it indicates that the alarm loop is faulty. Replace the user interface module. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 68
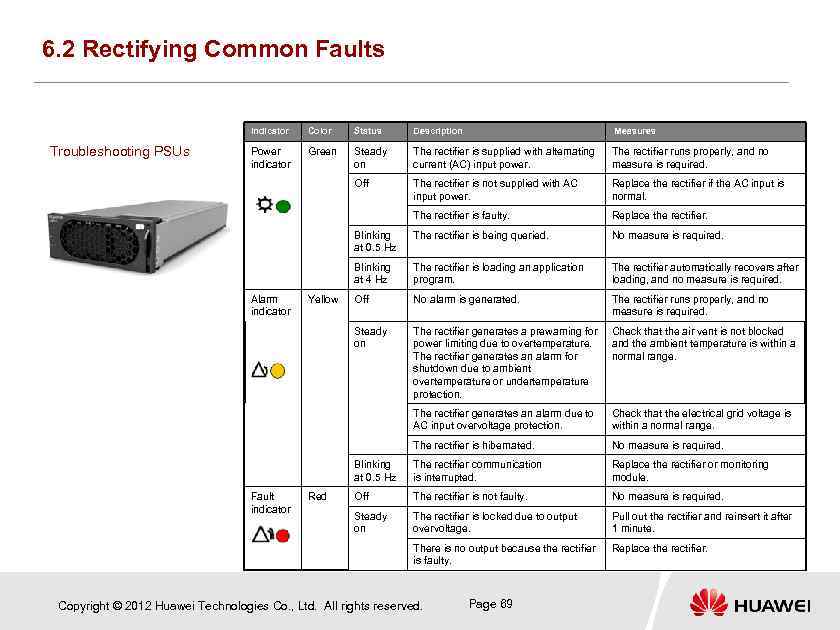 6. 2 Rectifying Common Faults Indicator Status Description Measures Power indicator Green Steady on The rectifier is supplied with alternating current (AC) input power. The rectifier runs properly, and no measure is required. Off The rectifier is not supplied with AC input power. Replace the rectifier if the AC input is normal. The rectifier is faulty. Replace the rectifier. Blinking at 0. 5 Hz The rectifier is being queried. No measure is required. Blinking at 4 Hz The rectifier is loading an application program. The rectifier automatically recovers after loading, and no measure is required. Off No alarm is generated. The rectifier runs properly, and no measure is required. Steady on The rectifier generates a prewarning for power limiting due to overtemperature. The rectifier generates an alarm for shutdown due to ambient overtemperature or undertemperature protection. Check that the air vent is not blocked and the ambient temperature is within a normal range. The rectifier generates an alarm due to AC input overvoltage protection. Check that the electrical grid voltage is within a normal range. The rectifier is hibernated. No measure is required. Blinking at 0. 5 Hz The rectifier communication is interrupted. Replace the rectifier or monitoring module. Off The rectifier is not faulty. No measure is required. Steady on The rectifier is locked due to output overvoltage. Pull out the rectifier and reinsert it after 1 minute. There is no output because the rectifier is faulty. Troubleshooting PSUs Color Replace the rectifier. Alarm indicator Fault indicator Yellow Red Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 69
6. 2 Rectifying Common Faults Indicator Status Description Measures Power indicator Green Steady on The rectifier is supplied with alternating current (AC) input power. The rectifier runs properly, and no measure is required. Off The rectifier is not supplied with AC input power. Replace the rectifier if the AC input is normal. The rectifier is faulty. Replace the rectifier. Blinking at 0. 5 Hz The rectifier is being queried. No measure is required. Blinking at 4 Hz The rectifier is loading an application program. The rectifier automatically recovers after loading, and no measure is required. Off No alarm is generated. The rectifier runs properly, and no measure is required. Steady on The rectifier generates a prewarning for power limiting due to overtemperature. The rectifier generates an alarm for shutdown due to ambient overtemperature or undertemperature protection. Check that the air vent is not blocked and the ambient temperature is within a normal range. The rectifier generates an alarm due to AC input overvoltage protection. Check that the electrical grid voltage is within a normal range. The rectifier is hibernated. No measure is required. Blinking at 0. 5 Hz The rectifier communication is interrupted. Replace the rectifier or monitoring module. Off The rectifier is not faulty. No measure is required. Steady on The rectifier is locked due to output overvoltage. Pull out the rectifier and reinsert it after 1 minute. There is no output because the rectifier is faulty. Troubleshooting PSUs Color Replace the rectifier. Alarm indicator Fault indicator Yellow Red Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 69
 Questions What is the basic procedure to troubleshoot the ETP 48200? How to rectify common faults? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 70
Questions What is the basic procedure to troubleshoot the ETP 48200? How to rectify common faults? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 70
 Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 71
Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 71
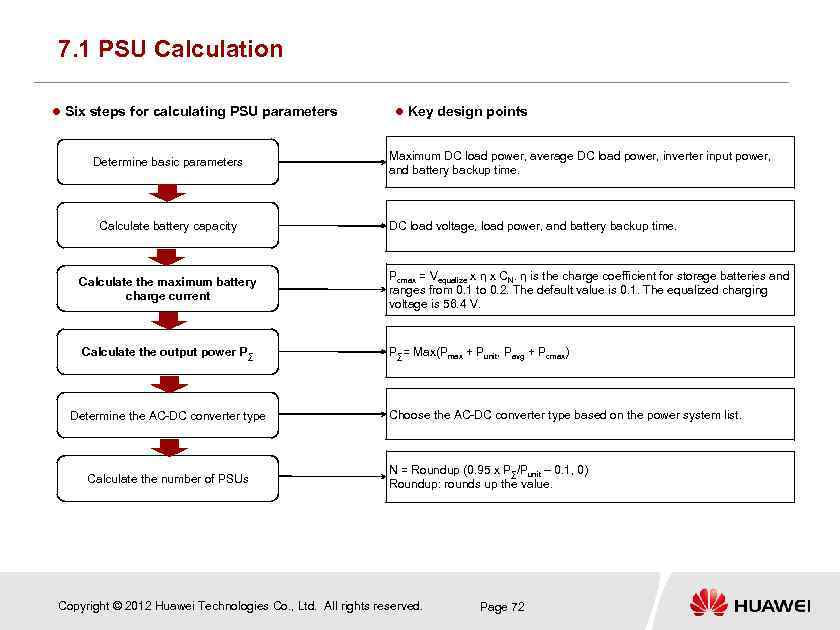 7. 1 PSU Calculation Six steps for calculating PSU parameters Determine basic parameters Calculate battery capacity Key design points Maximum DC load power, average DC load power, inverter input power, and battery backup time. DC load voltage, load power, and battery backup time. Calculate the maximum battery charge current Pcmax = Vequalize x η x CN. η is the charge coefficient for storage batteries and ranges from 0. 1 to 0. 2. The default value is 0. 1. The equalized charging voltage is 56. 4 V. Calculate the output power P ∑ P∑= Max(Pmax + Punit, Pavg + Pcmax) Determine the AC-DC converter type Calculate the number of PSUs Choose the AC-DC converter type based on the power system list. N = Roundup (0. 95 x P∑/Punit – 0. 1, 0) Roundup: rounds up the value. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 72
7. 1 PSU Calculation Six steps for calculating PSU parameters Determine basic parameters Calculate battery capacity Key design points Maximum DC load power, average DC load power, inverter input power, and battery backup time. DC load voltage, load power, and battery backup time. Calculate the maximum battery charge current Pcmax = Vequalize x η x CN. η is the charge coefficient for storage batteries and ranges from 0. 1 to 0. 2. The default value is 0. 1. The equalized charging voltage is 56. 4 V. Calculate the output power P ∑ P∑= Max(Pmax + Punit, Pavg + Pcmax) Determine the AC-DC converter type Calculate the number of PSUs Choose the AC-DC converter type based on the power system list. N = Roundup (0. 95 x P∑/Punit – 0. 1, 0) Roundup: rounds up the value. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 72
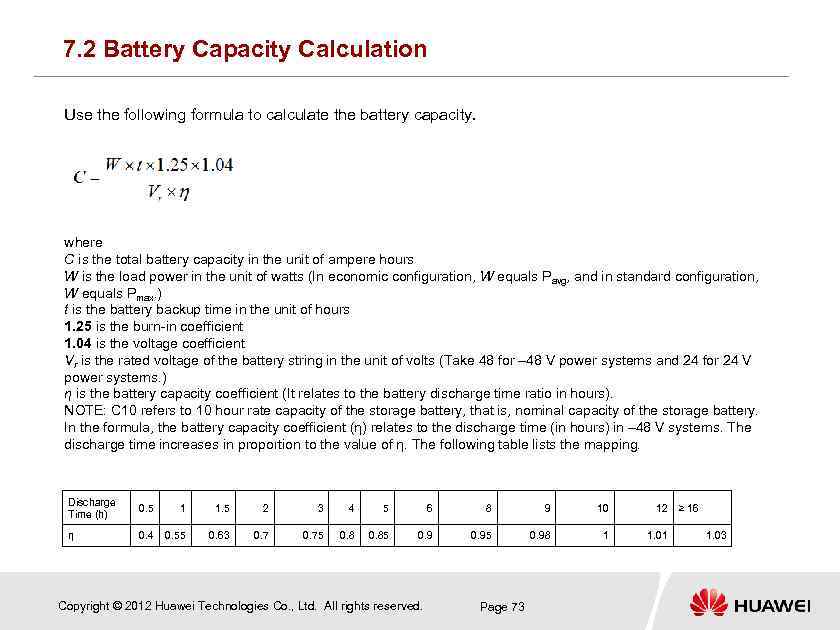 7. 2 Battery Capacity Calculation Use the following formula to calculate the battery capacity. where C is the total battery capacity in the unit of ampere hours W is the load power in the unit of watts (In economic configuration, W equals Pavg, and in standard configuration, W equals Pmax. ) t is the battery backup time in the unit of hours 1. 25 is the burn-in coefficient 1. 04 is the voltage coefficient Vr is the rated voltage of the battery string in the unit of volts (Take 48 for – 48 V power systems and 24 for 24 V power systems. ) η is the battery capacity coefficient (It relates to the battery discharge time ratio in hours). NOTE: C 10 refers to 10 hour rate capacity of the storage battery, that is, nominal capacity of the storage battery. In the formula, the battery capacity coefficient (η) relates to the discharge time (in hours) in – 48 V systems. The discharge time increases in proportion to the value of η. The following table lists the mapping. Discharge Time (h) 0. 5 1 1. 5 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 12 η 0. 4 0. 55 0. 63 0. 75 0. 85 0. 95 0. 98 1 1. 01 Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 73 ≥ 16 1. 03
7. 2 Battery Capacity Calculation Use the following formula to calculate the battery capacity. where C is the total battery capacity in the unit of ampere hours W is the load power in the unit of watts (In economic configuration, W equals Pavg, and in standard configuration, W equals Pmax. ) t is the battery backup time in the unit of hours 1. 25 is the burn-in coefficient 1. 04 is the voltage coefficient Vr is the rated voltage of the battery string in the unit of volts (Take 48 for – 48 V power systems and 24 for 24 V power systems. ) η is the battery capacity coefficient (It relates to the battery discharge time ratio in hours). NOTE: C 10 refers to 10 hour rate capacity of the storage battery, that is, nominal capacity of the storage battery. In the formula, the battery capacity coefficient (η) relates to the discharge time (in hours) in – 48 V systems. The discharge time increases in proportion to the value of η. The following table lists the mapping. Discharge Time (h) 0. 5 1 1. 5 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 12 η 0. 4 0. 55 0. 63 0. 75 0. 85 0. 95 0. 98 1 1. 01 Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 73 ≥ 16 1. 03
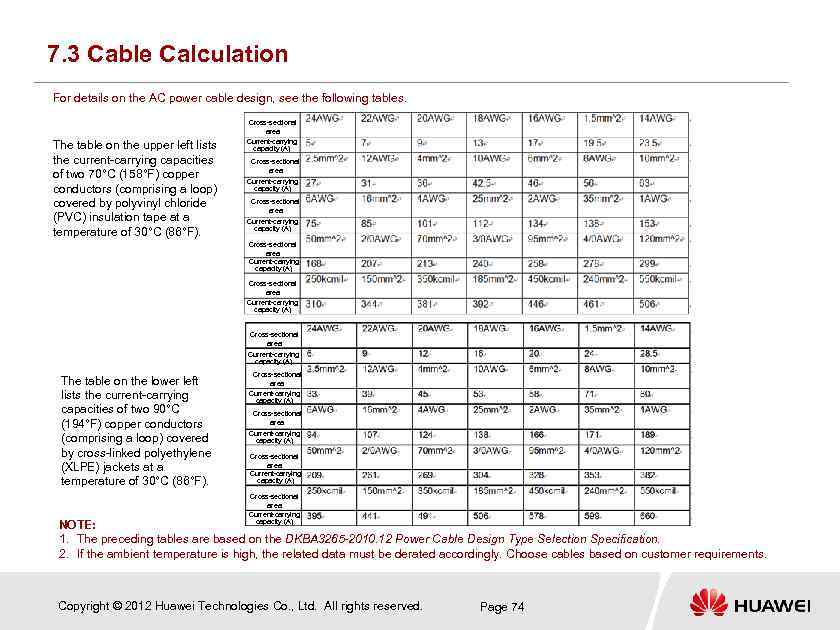 7. 3 Cable Calculation For details on the AC power cable design, see the following tables. Cross-sectional area The table on the upper left lists the current-carrying capacities of two 70°C (158°F) copper conductors (comprising a loop) covered by polyvinyl chloride (PVC) insulation tape at a temperature of 30°C (86°F). Current-carrying capacity (A) Cross-sectional area Current-carrying capacity (A) Cross-sectional area Current-carrying capacity (A) The table on the lower left lists the current-carrying capacities of two 90°C (194°F) copper conductors (comprising a loop) covered by cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) jackets at a temperature of 30°C (86°F). Cross-sectional area Current-carrying capacity (A) NOTE: 1. The preceding tables are based on the DKBA 3265 -2010. 12 Power Cable Design Type Selection Specification. 2. If the ambient temperature is high, the related data must be derated accordingly. Choose cables based on customer requirements. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 74
7. 3 Cable Calculation For details on the AC power cable design, see the following tables. Cross-sectional area The table on the upper left lists the current-carrying capacities of two 70°C (158°F) copper conductors (comprising a loop) covered by polyvinyl chloride (PVC) insulation tape at a temperature of 30°C (86°F). Current-carrying capacity (A) Cross-sectional area Current-carrying capacity (A) Cross-sectional area Current-carrying capacity (A) The table on the lower left lists the current-carrying capacities of two 90°C (194°F) copper conductors (comprising a loop) covered by cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) jackets at a temperature of 30°C (86°F). Cross-sectional area Current-carrying capacity (A) NOTE: 1. The preceding tables are based on the DKBA 3265 -2010. 12 Power Cable Design Type Selection Specification. 2. If the ambient temperature is high, the related data must be derated accordingly. Choose cables based on customer requirements. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 74
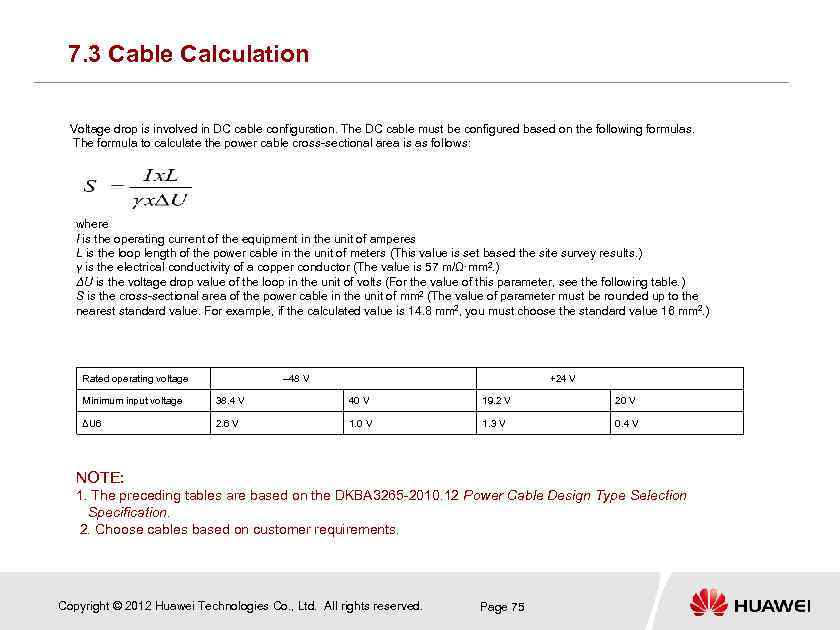 7. 3 Cable Calculation Voltage drop is involved in DC cable configuration. The DC cable must be configured based on the following formulas. The formula to calculate the power cable cross-sectional area is as follows: where I is the operating current of the equipment in the unit of amperes L is the loop length of the power cable in the unit of meters (This value is set based the site survey results. ) γ is the electrical conductivity of a copper conductor (The value is 57 m/Ω·mm 2. ) ΔU is the voltage drop value of the loop in the unit of volts (For the value of this parameter, see the following table. ) S is the cross-sectional area of the power cable in the unit of mm 2 (The value of parameter must be rounded up to the nearest standard value. For example, if the calculated value is 14. 8 mm 2, you must choose the standard value 16 mm 2. ) Rated operating voltage – 48 V +24 V Minimum input voltage 38. 4 V 40 V 19. 2 V 20 V ΔU 6 2. 6 V 1. 0 V 1. 3 V 0. 4 V NOTE: 1. The preceding tables are based on the DKBA 3265 -2010. 12 Power Cable Design Type Selection Specification. 2. Choose cables based on customer requirements. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 75
7. 3 Cable Calculation Voltage drop is involved in DC cable configuration. The DC cable must be configured based on the following formulas. The formula to calculate the power cable cross-sectional area is as follows: where I is the operating current of the equipment in the unit of amperes L is the loop length of the power cable in the unit of meters (This value is set based the site survey results. ) γ is the electrical conductivity of a copper conductor (The value is 57 m/Ω·mm 2. ) ΔU is the voltage drop value of the loop in the unit of volts (For the value of this parameter, see the following table. ) S is the cross-sectional area of the power cable in the unit of mm 2 (The value of parameter must be rounded up to the nearest standard value. For example, if the calculated value is 14. 8 mm 2, you must choose the standard value 16 mm 2. ) Rated operating voltage – 48 V +24 V Minimum input voltage 38. 4 V 40 V 19. 2 V 20 V ΔU 6 2. 6 V 1. 0 V 1. 3 V 0. 4 V NOTE: 1. The preceding tables are based on the DKBA 3265 -2010. 12 Power Cable Design Type Selection Specification. 2. Choose cables based on customer requirements. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 75
 7. 4 Site Survey The site survey is performed by Huawei and customer engineers. During the site survey, Huawei and customer engineers should determine the installation site, cable routing and layout, installation material, and specifications. After finishing the site survey and data collection, Huawei and customer representatives should sign on the Site Survey Report and Data Collection Report. Installation position and environment of the ETP 48200: describes the altitude, position, and surrounding environment of the equipment room. Power supply: involves the power supply mode, position of the AC power distribution cabinet or PDF, cable routing, and cabling distance. Power load: involves the load position and distance between the load and the power system. Installation materials: involves the calculation of installation materials. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 76
7. 4 Site Survey The site survey is performed by Huawei and customer engineers. During the site survey, Huawei and customer engineers should determine the installation site, cable routing and layout, installation material, and specifications. After finishing the site survey and data collection, Huawei and customer representatives should sign on the Site Survey Report and Data Collection Report. Installation position and environment of the ETP 48200: describes the altitude, position, and surrounding environment of the equipment room. Power supply: involves the power supply mode, position of the AC power distribution cabinet or PDF, cable routing, and cabling distance. Power load: involves the load position and distance between the load and the power system. Installation materials: involves the calculation of installation materials. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 76
 Questions How to calculate the number of PSUs? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 77
Questions How to calculate the number of PSUs? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 77
 Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 78
Contents Chapter 1 Working Principles Chapter 2 ETP 48200 Introduction Chapter 3 Installation and Commissioning Chapter 4 Acceptance Chapter 5 Routine Maintenance Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Chapter 7 Project Design Chapter 8 Test Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 78
 Chapter 8 Test The system test is to verify product performance, functions, and serviceability by observation or using tool. Product tests after GA are to verify that the tested device complies with the specifications specified by the customer and to gain customers' trust. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 79
Chapter 8 Test The system test is to verify product performance, functions, and serviceability by observation or using tool. Product tests after GA are to verify that the tested device complies with the specifications specified by the customer and to gain customers' trust. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 79
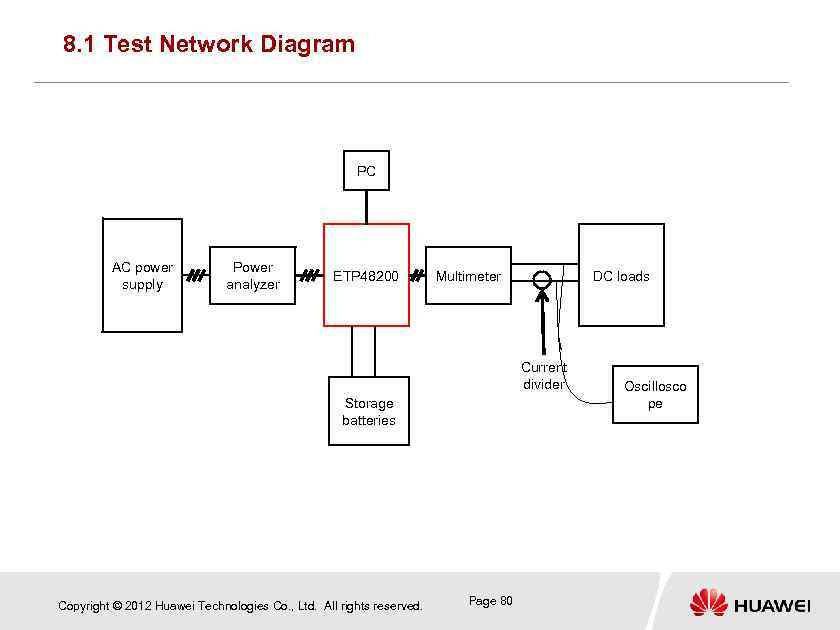 8. 1 Test Network Diagram PC AC power supply Power analyzer ETP 48200 Multimeter DC loads Current divider Storage batteries Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 80 Oscillosco pe
8. 1 Test Network Diagram PC AC power supply Power analyzer ETP 48200 Multimeter DC loads Current divider Storage batteries Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 80 Oscillosco pe
 8. 2 Test Instrument Introduction Power analyzer: obtains AC input information, such as AC input voltage, current, power, THD, and PF, and is mandatory. A WT 1600 power analyzer is recommended. Multimeter: obtains the output voltage, input voltage, and dry contact status. A Fluke 87 multimeter is recommended. Current divider: obtains the system output current for efficiency tests. Use a clamp meter (such as Fluke 337) instead if the customer approves. Oscilloscope: displays the system output voltage and typically is not required. An Agilent 5014 oscilloscope is recommended. DC load: can be resistance loads or electronic loads. PC: monitors the system, communicates with the PMU, and verifies communication with the host. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 81
8. 2 Test Instrument Introduction Power analyzer: obtains AC input information, such as AC input voltage, current, power, THD, and PF, and is mandatory. A WT 1600 power analyzer is recommended. Multimeter: obtains the output voltage, input voltage, and dry contact status. A Fluke 87 multimeter is recommended. Current divider: obtains the system output current for efficiency tests. Use a clamp meter (such as Fluke 337) instead if the customer approves. Oscilloscope: displays the system output voltage and typically is not required. An Agilent 5014 oscilloscope is recommended. DC load: can be resistance loads or electronic loads. PC: monitors the system, communicates with the PMU, and verifies communication with the host. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 81
 8. 3 Common Test Item Introduction Energy conversion efficiency [ The energy conversion efficiency is calculated based on the formula ŋ=Po/Pin [ Obtain the system input power Pin on the power analyzer. [ Obtain the system output current Io on the current divider and the output voltage Uo on the multimeter Po=Uo x Io. [ Obtain the system input THD and power factor on the power analyzer. [ Calculate and record the test efficiency, THD, and power factor under various voltage modes (such as 85% Un, and 110% Un) and loads (10%– 100%). Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 82
8. 3 Common Test Item Introduction Energy conversion efficiency [ The energy conversion efficiency is calculated based on the formula ŋ=Po/Pin [ Obtain the system input power Pin on the power analyzer. [ Obtain the system output current Io on the current divider and the output voltage Uo on the multimeter Po=Uo x Io. [ Obtain the system input THD and power factor on the power analyzer. [ Calculate and record the test efficiency, THD, and power factor under various voltage modes (such as 85% Un, and 110% Un) and loads (10%– 100%). Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 82
 8. 3 Common Test Item Introduction Imbalance degree of current equalization [ The imbalance degree of current equalization identifies load balance degree of PSUs and typically is less than 5%. [ Read the output current (Io 1, Io 2, …Ion) of each PSU on the PMU. [ Read the system output current Io on the current divider. [ Record the rated current (In 1, In 2, …Inn) of each PSU. [ I=In 1+In 2+…+Inn [ The imbalance degree of current equalization is equal to max(abs(Io 1/In 1 Io/I), abs(Io 2 -Io/I), …, abs(Ion/Inn-Io/I) [ Test and record the imbalance degree of current equalization under various voltages and load combination. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 83
8. 3 Common Test Item Introduction Imbalance degree of current equalization [ The imbalance degree of current equalization identifies load balance degree of PSUs and typically is less than 5%. [ Read the output current (Io 1, Io 2, …Ion) of each PSU on the PMU. [ Read the system output current Io on the current divider. [ Record the rated current (In 1, In 2, …Inn) of each PSU. [ I=In 1+In 2+…+Inn [ The imbalance degree of current equalization is equal to max(abs(Io 1/In 1 Io/I), abs(Io 2 -Io/I), …, abs(Ion/Inn-Io/I) [ Test and record the imbalance degree of current equalization under various voltages and load combination. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 83
 8. 3 Common Test Item Introduction Peak-to-peak noise voltage test [ The peak-to-peak noise voltage identifies ripple content. [ Test the peak-to-peak noise voltage by using an oscilloscope. [ Set the oscilloscope bandwidth to 20 MHz and select the AC coupling mode. (For details about how to operate various oscilloscopes, see associated documents. ) [ Push the time axis to 5 s. The value displayed on the oscilloscope is the peak-to-peak noise voltage. [ The peak-to-peak noise voltage should be tested under different output voltages and loads. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 84
8. 3 Common Test Item Introduction Peak-to-peak noise voltage test [ The peak-to-peak noise voltage identifies ripple content. [ Test the peak-to-peak noise voltage by using an oscilloscope. [ Set the oscilloscope bandwidth to 20 MHz and select the AC coupling mode. (For details about how to operate various oscilloscopes, see associated documents. ) [ Push the time axis to 5 s. The value displayed on the oscilloscope is the peak-to-peak noise voltage. [ The peak-to-peak noise voltage should be tested under different output voltages and loads. Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 84
 Questions What is the purpose to perform the system test? What basic test instruments are required to perform a system test? How to perform an efficiency test? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 86
Questions What is the purpose to perform the system test? What basic test instruments are required to perform a system test? How to perform an efficiency test? Copyright © 2012 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 86
 Summary The slides introduces the history of AC-DC power supplies and Huawei power systems, and their location. It describes the ETP 48200 in terms of its working principles, composition, installation, commissioning, acceptance, maintenance, troubleshooting, project design, and tests, which provides guidelines for engineers to perform site designs, install, maintain, and troubleshoot the ETP 48200, and perform system tests. Copyright © 2008 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 88
Summary The slides introduces the history of AC-DC power supplies and Huawei power systems, and their location. It describes the ETP 48200 in terms of its working principles, composition, installation, commissioning, acceptance, maintenance, troubleshooting, project design, and tests, which provides guidelines for engineers to perform site designs, install, maintain, and troubleshoot the ETP 48200, and perform system tests. Copyright © 2008 Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 88
 Thank you www. huawei. com
Thank you www. huawei. com


