ae1993052b5912320d492c275049eb08.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 Security in 802. 16 d and 802. 16 e Advisor: Dr. Kai-Wei Ke Speaker: Yen-Jen Chen Date: 03/04/2008 1
Security in 802. 16 d and 802. 16 e Advisor: Dr. Kai-Wei Ke Speaker: Yen-Jen Chen Date: 03/04/2008 1
 Outline n n n Overview of 802. 16 d Security Architecture in the 802. 16 e Authentication in the 802. 16 e Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e Conclusion References 2
Outline n n n Overview of 802. 16 d Security Architecture in the 802. 16 e Authentication in the 802. 16 e Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e Conclusion References 2
 Overview of 802. 16 d Security 3
Overview of 802. 16 d Security 3
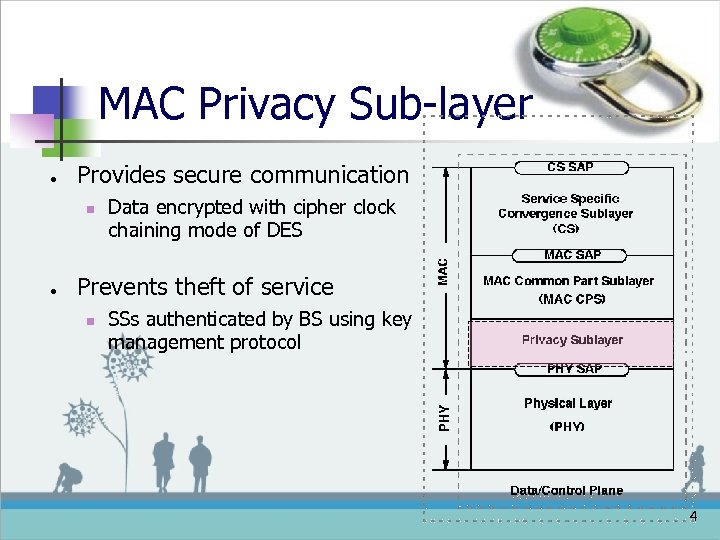 MAC Privacy Sub-layer ● Provides secure communication n ● Data encrypted with cipher clock chaining mode of DES Prevents theft of service n SSs authenticated by BS using key management protocol 4
MAC Privacy Sub-layer ● Provides secure communication n ● Data encrypted with cipher clock chaining mode of DES Prevents theft of service n SSs authenticated by BS using key management protocol 4
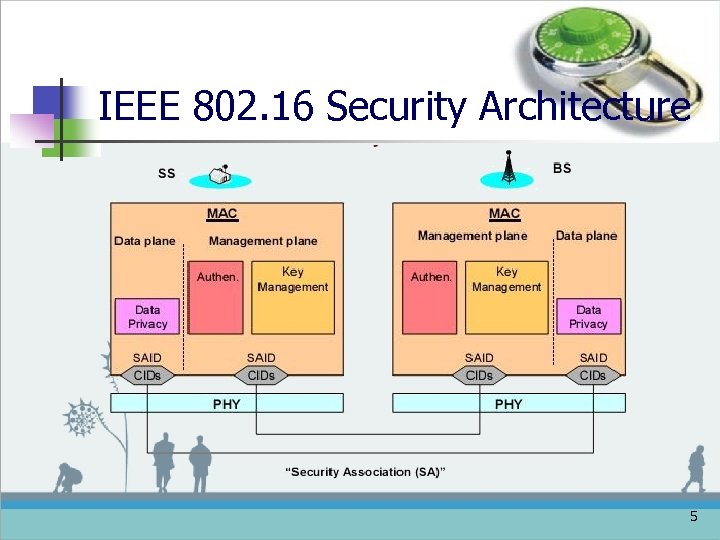 IEEE 802. 16 Security Architecture 5
IEEE 802. 16 Security Architecture 5
 X. 509 certificate 6
X. 509 certificate 6
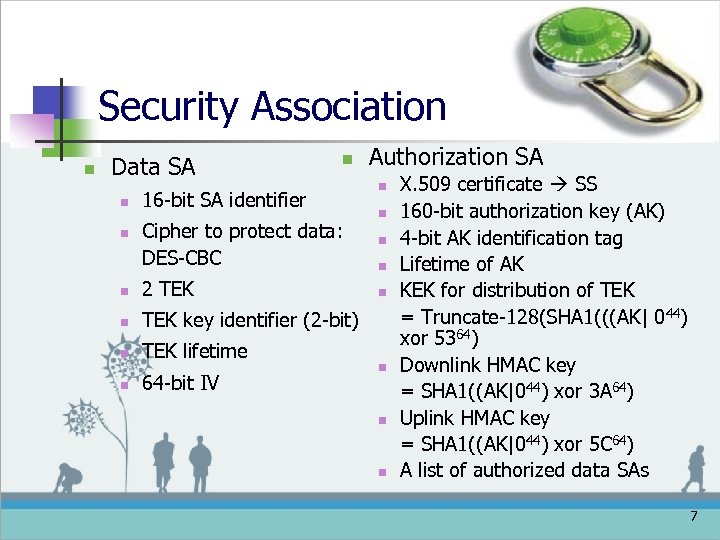 Security Association n Data SA n n n 16 -bit SA identifier Cipher to protect data: DES-CBC n 2 TEK n TEK lifetime n n TEK key identifier (2 -bit) n Authorization SA n 64 -bit IV n n X. 509 certificate SS 160 -bit authorization key (AK) 4 -bit AK identification tag Lifetime of AK KEK for distribution of TEK = Truncate-128(SHA 1(((AK| 044) xor 5364) Downlink HMAC key = SHA 1((AK|044) xor 3 A 64) Uplink HMAC key = SHA 1((AK|044) xor 5 C 64) A list of authorized data SAs 7
Security Association n Data SA n n n 16 -bit SA identifier Cipher to protect data: DES-CBC n 2 TEK n TEK lifetime n n TEK key identifier (2 -bit) n Authorization SA n 64 -bit IV n n X. 509 certificate SS 160 -bit authorization key (AK) 4 -bit AK identification tag Lifetime of AK KEK for distribution of TEK = Truncate-128(SHA 1(((AK| 044) xor 5364) Downlink HMAC key = SHA 1((AK|044) xor 3 A 64) Uplink HMAC key = SHA 1((AK|044) xor 5 C 64) A list of authorized data SAs 7
 Security Association n n BS use the X. 509 certificate from SS to authenticate. No BS authentication Negotiate security capabilities between BS and SS Authentication Key (AK) n n n exchange AK serves as authorization token AK is encrypted using public key cryptography Authentication is done when both SS and BS possess AK 8
Security Association n n BS use the X. 509 certificate from SS to authenticate. No BS authentication Negotiate security capabilities between BS and SS Authentication Key (AK) n n n exchange AK serves as authorization token AK is encrypted using public key cryptography Authentication is done when both SS and BS possess AK 8
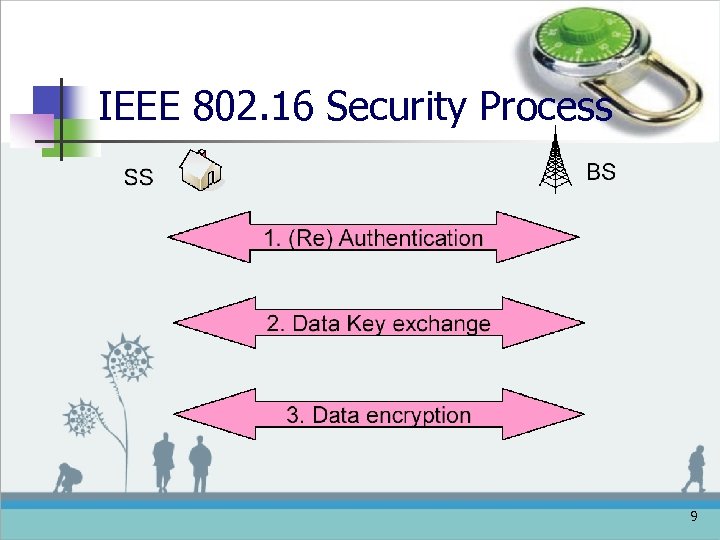 IEEE 802. 16 Security Process 9
IEEE 802. 16 Security Process 9
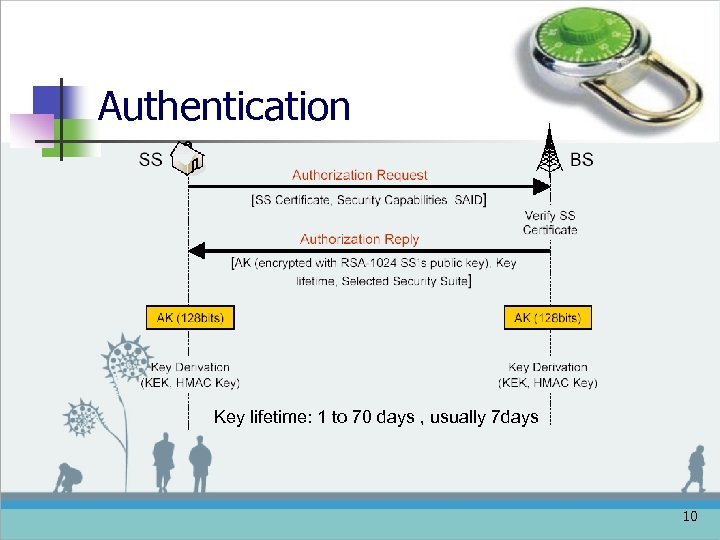 Authentication Key lifetime: 1 to 70 days , usually 7 days 10
Authentication Key lifetime: 1 to 70 days , usually 7 days 10
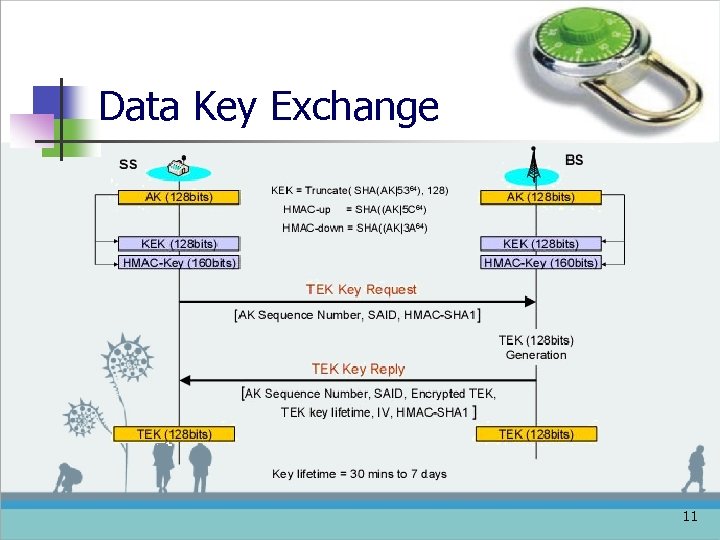 Data Key Exchange 11
Data Key Exchange 11
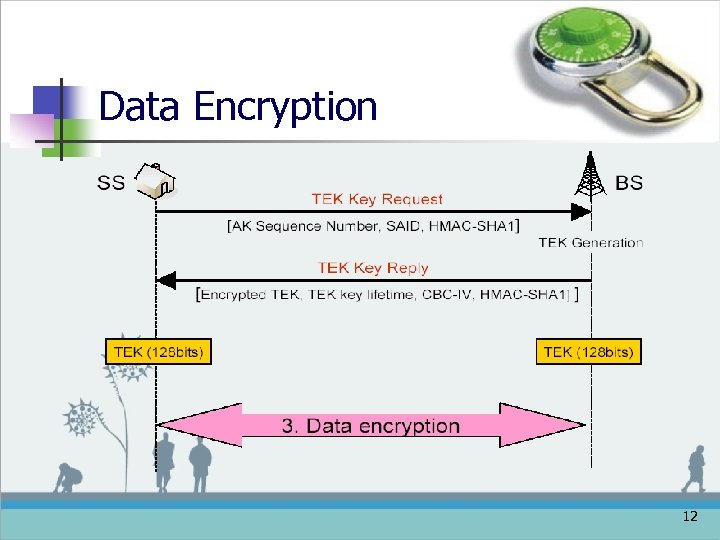 Data Encryption 12
Data Encryption 12
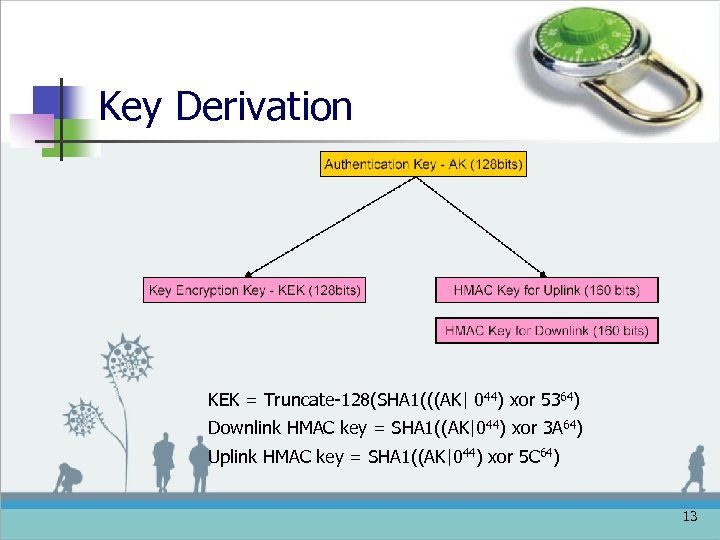 Key Derivation KEK = Truncate-128(SHA 1(((AK| 044) xor 5364) Downlink HMAC key = SHA 1((AK|044) xor 3 A 64) Uplink HMAC key = SHA 1((AK|044) xor 5 C 64) 13
Key Derivation KEK = Truncate-128(SHA 1(((AK| 044) xor 5364) Downlink HMAC key = SHA 1((AK|044) xor 3 A 64) Uplink HMAC key = SHA 1((AK|044) xor 5 C 64) 13
 IEEE 802. 16 d Security Flaws n Lack of Explicit Definitions n Lack of the mutual authentication n n Limited authentication method–SS certification Authentication Key (AK) generation 14
IEEE 802. 16 d Security Flaws n Lack of Explicit Definitions n Lack of the mutual authentication n n Limited authentication method–SS certification Authentication Key (AK) generation 14
 Security Architecture in the 802. 16 e 15
Security Architecture in the 802. 16 e 15
 Simple 802. 16 e Network topology 16
Simple 802. 16 e Network topology 16
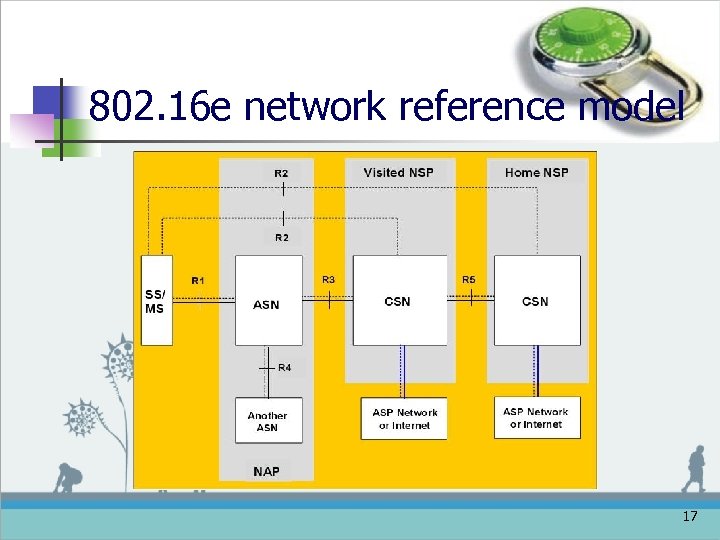 802. 16 e network reference model 17
802. 16 e network reference model 17
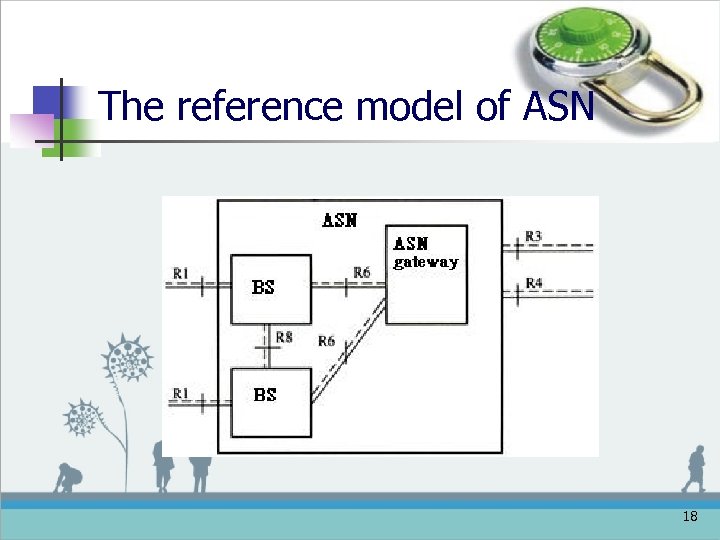 The reference model of ASN 18
The reference model of ASN 18
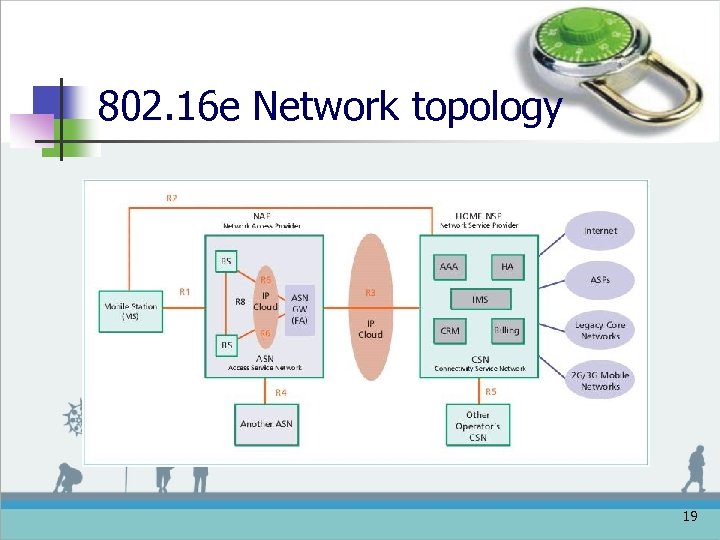 802. 16 e Network topology 19
802. 16 e Network topology 19
 Security Architecture n Encapsulation protocol n n n A set of cryptographic suites The rules for applying those algorithm Key management protocol n PKM for distributing key data n n n AK 160 bits share key for ss and bs TEK 128 bits PKM exchange key Authentication (PKMv 2 protocol) n n n To get AK (Authorization key) RSA authentication EAP authentication 20
Security Architecture n Encapsulation protocol n n n A set of cryptographic suites The rules for applying those algorithm Key management protocol n PKM for distributing key data n n n AK 160 bits share key for ss and bs TEK 128 bits PKM exchange key Authentication (PKMv 2 protocol) n n n To get AK (Authorization key) RSA authentication EAP authentication 20
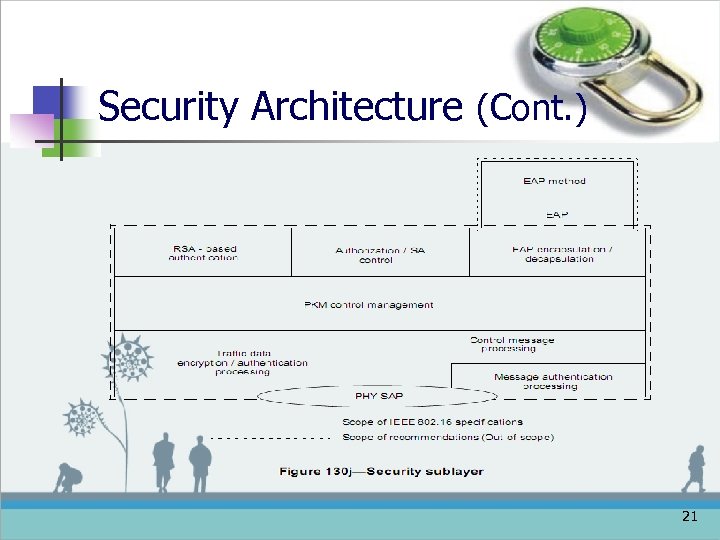 Security Architecture (Cont. ) 21
Security Architecture (Cont. ) 21
 Authentication in the 802. 16 e 22
Authentication in the 802. 16 e 22
 RSA authentication protocol n n n 802. 16 d uses this one BS uses the PKI mechanism to verify the Certificate BS uses the CTL (Certificate trust list) 23
RSA authentication protocol n n n 802. 16 d uses this one BS uses the PKI mechanism to verify the Certificate BS uses the CTL (Certificate trust list) 23
 RSA authentication protocol (Cont. ) 24
RSA authentication protocol (Cont. ) 24
 EAP authentication protocol n n EAP is a authentication framework not a specially authentication mechanism the four methods in 802. 16 e n n RSA based authentication One level EAP based authentication Two level EAP based authentication RSA based authentication followed by EAP authentication 25
EAP authentication protocol n n EAP is a authentication framework not a specially authentication mechanism the four methods in 802. 16 e n n RSA based authentication One level EAP based authentication Two level EAP based authentication RSA based authentication followed by EAP authentication 25
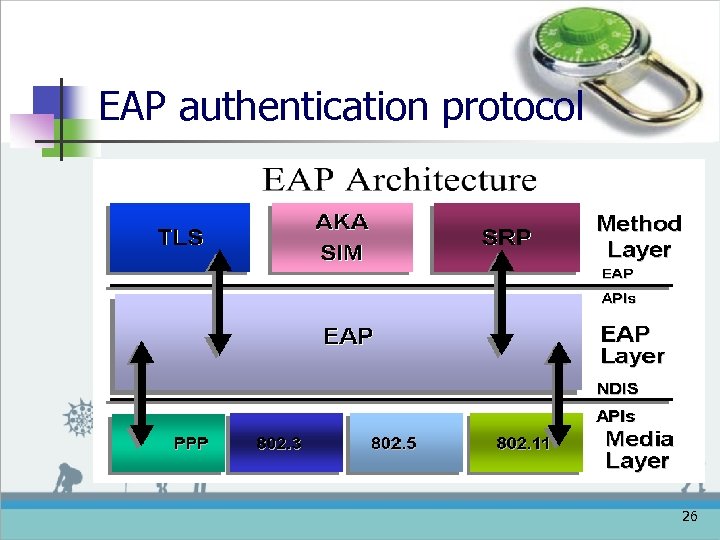 EAP authentication protocol 26
EAP authentication protocol 26
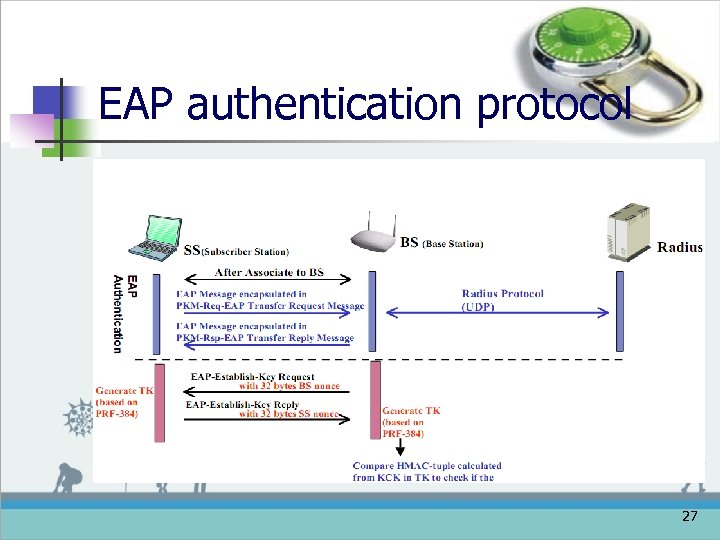 EAP authentication protocol 27
EAP authentication protocol 27
 EAP authentication protocol n RSA based authentication n n Use the PKMv 2 RSA-Request、PKMv 2 RSA-Reply、 PKMv 2 RSA-Reject、PKMv 2 RSA-acknowledgement messages to get pre-PAK Using the public key of SS to encrypt the pre-PAK and send back to SS pre-PAK generates the PAK (Primary Authorization key) and EIK(EAP integrity Key) PAK generates the AK 28
EAP authentication protocol n RSA based authentication n n Use the PKMv 2 RSA-Request、PKMv 2 RSA-Reply、 PKMv 2 RSA-Reject、PKMv 2 RSA-acknowledgement messages to get pre-PAK Using the public key of SS to encrypt the pre-PAK and send back to SS pre-PAK generates the PAK (Primary Authorization key) and EIK(EAP integrity Key) PAK generates the AK 28
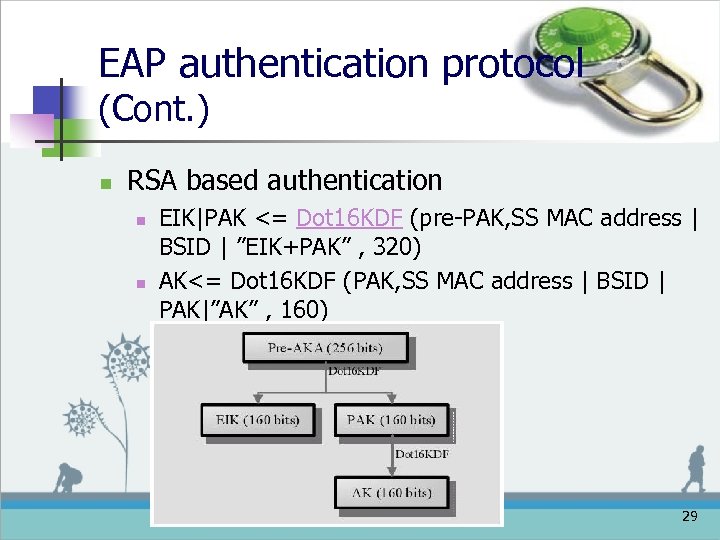 EAP authentication protocol (Cont. ) n RSA based authentication n n EIK|PAK <= Dot 16 KDF (pre-PAK, SS MAC address | BSID | ”EIK+PAK” , 320) AK<= Dot 16 KDF (PAK, SS MAC address | BSID | PAK|”AK” , 160) 29
EAP authentication protocol (Cont. ) n RSA based authentication n n EIK|PAK <= Dot 16 KDF (pre-PAK, SS MAC address | BSID | ”EIK+PAK” , 320) AK<= Dot 16 KDF (PAK, SS MAC address | BSID | PAK|”AK” , 160) 29
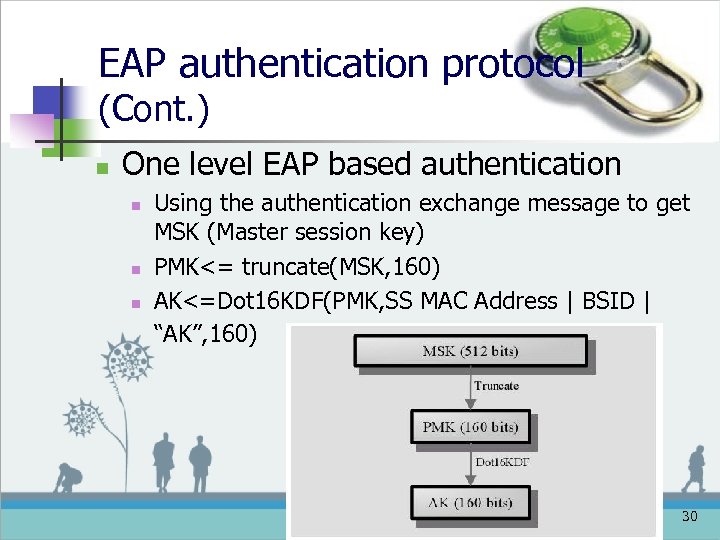 EAP authentication protocol (Cont. ) n One level EAP based authentication n Using the authentication exchange message to get MSK (Master session key) PMK<= truncate(MSK, 160) AK<=Dot 16 KDF(PMK, SS MAC Address | BSID | “AK”, 160) 30
EAP authentication protocol (Cont. ) n One level EAP based authentication n Using the authentication exchange message to get MSK (Master session key) PMK<= truncate(MSK, 160) AK<=Dot 16 KDF(PMK, SS MAC Address | BSID | “AK”, 160) 30
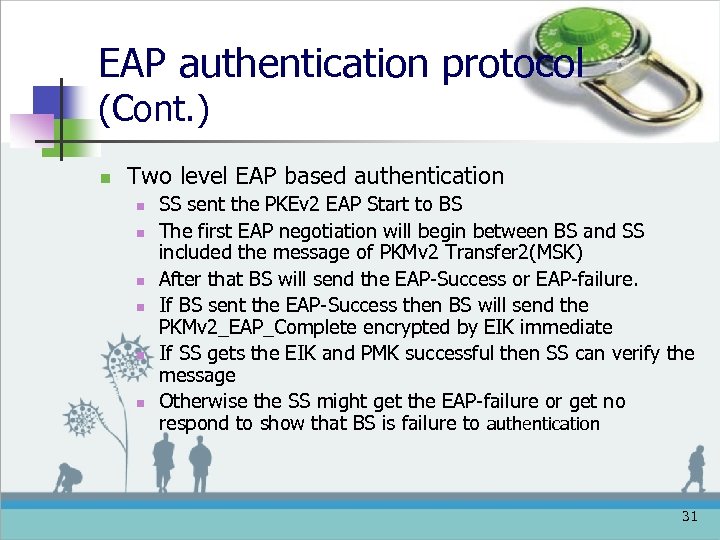 EAP authentication protocol (Cont. ) n Two level EAP based authentication n n n SS sent the PKEv 2 EAP Start to BS The first EAP negotiation will begin between BS and SS included the message of PKMv 2 Transfer 2(MSK) After that BS will send the EAP-Success or EAP-failure. If BS sent the EAP-Success then BS will send the PKMv 2_EAP_Complete encrypted by EIK immediate If SS gets the EIK and PMK successful then SS can verify the message Otherwise the SS might get the EAP-failure or get no respond to show that BS is failure to authentication 31
EAP authentication protocol (Cont. ) n Two level EAP based authentication n n n SS sent the PKEv 2 EAP Start to BS The first EAP negotiation will begin between BS and SS included the message of PKMv 2 Transfer 2(MSK) After that BS will send the EAP-Success or EAP-failure. If BS sent the EAP-Success then BS will send the PKMv 2_EAP_Complete encrypted by EIK immediate If SS gets the EIK and PMK successful then SS can verify the message Otherwise the SS might get the EAP-failure or get no respond to show that BS is failure to authentication 31
 EAP authentication protocol (Cont. ) n Two level EAP based authentication n n After SS finished the first EAP negotiation successful , the SS will send “PKMv 2 Authenticated EAP Start” to start the second EAP negotiation When BS got this message, BS will check the message by EIK. If BS check ok then BS will start the second EAP negotiation, otherwise BS will think the Authenticated failure. The related messages of PKM is protected by EIK in the second EAP negotiation If BS and SS competed second EAP negotiation, then BS and SS can get the AK form PMK( pairwise authorization key) and PMK 2 32
EAP authentication protocol (Cont. ) n Two level EAP based authentication n n After SS finished the first EAP negotiation successful , the SS will send “PKMv 2 Authenticated EAP Start” to start the second EAP negotiation When BS got this message, BS will check the message by EIK. If BS check ok then BS will start the second EAP negotiation, otherwise BS will think the Authenticated failure. The related messages of PKM is protected by EIK in the second EAP negotiation If BS and SS competed second EAP negotiation, then BS and SS can get the AK form PMK( pairwise authorization key) and PMK 2 32
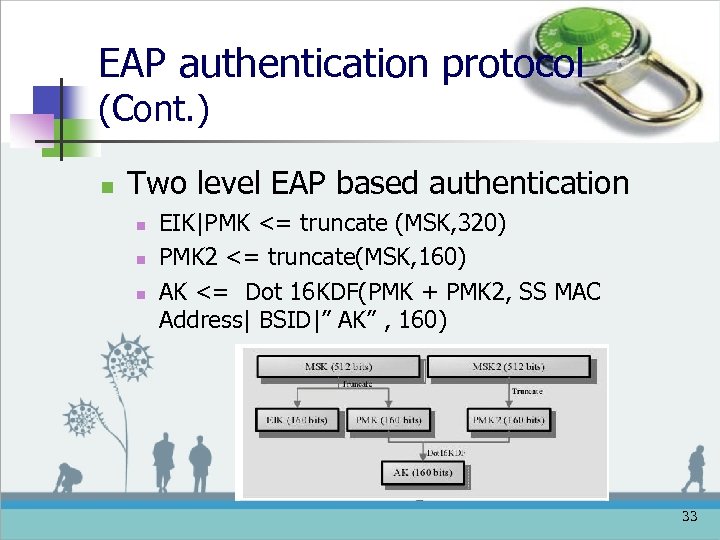 EAP authentication protocol (Cont. ) n Two level EAP based authentication n EIK|PMK <= truncate (MSK, 320) PMK 2 <= truncate(MSK, 160) AK <= Dot 16 KDF(PMK + PMK 2, SS MAC Address| BSID|” AK” , 160) 33
EAP authentication protocol (Cont. ) n Two level EAP based authentication n EIK|PMK <= truncate (MSK, 320) PMK 2 <= truncate(MSK, 160) AK <= Dot 16 KDF(PMK + PMK 2, SS MAC Address| BSID|” AK” , 160) 33
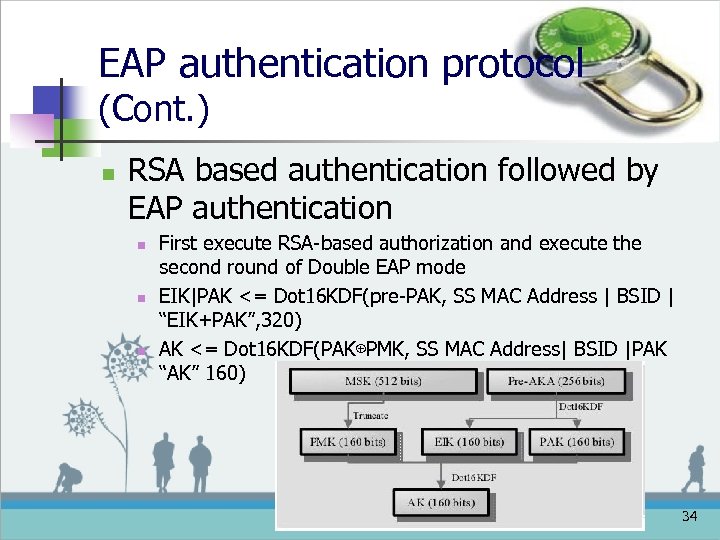 EAP authentication protocol (Cont. ) n RSA based authentication followed by EAP authentication n First execute RSA-based authorization and execute the second round of Double EAP mode EIK|PAK <= Dot 16 KDF(pre-PAK, SS MAC Address | BSID | “EIK+PAK”, 320) AK <= Dot 16 KDF(PAK⊕PMK, SS MAC Address| BSID |PAK “AK” 160) 34
EAP authentication protocol (Cont. ) n RSA based authentication followed by EAP authentication n First execute RSA-based authorization and execute the second round of Double EAP mode EIK|PAK <= Dot 16 KDF(pre-PAK, SS MAC Address | BSID | “EIK+PAK”, 320) AK <= Dot 16 KDF(PAK⊕PMK, SS MAC Address| BSID |PAK “AK” 160) 34
 Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e 35
Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e 35
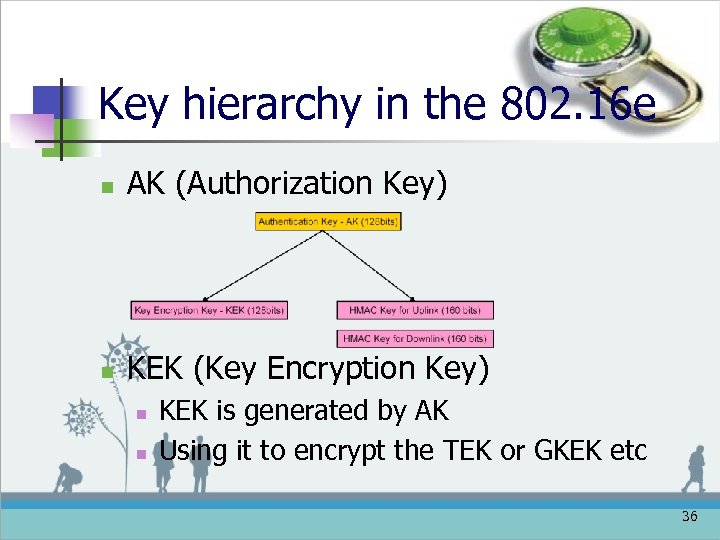 Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n AK (Authorization Key) n KEK (Key Encryption Key) n n KEK is generated by AK Using it to encrypt the TEK or GKEK etc 36
Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n AK (Authorization Key) n KEK (Key Encryption Key) n n KEK is generated by AK Using it to encrypt the TEK or GKEK etc 36
 Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n GKEK (group KEK) n n One GSA has one GKEK is generated by random number of BS BS uses the KEK to encrypt GKEK and send to SS GKEK encrypted the GTEK when GTEK updated and send it to all SS in the group 37
Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n GKEK (group KEK) n n One GSA has one GKEK is generated by random number of BS BS uses the KEK to encrypt GKEK and send to SS GKEK encrypted the GTEK when GTEK updated and send it to all SS in the group 37
 Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n TEK (Traffic Encryption Key) n n n TEK is generated by random number of BS BS use the KEK to encrypt the TEK and send to SS TEK is used to encrypt the message or data between BS and SS 38
Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n TEK (Traffic Encryption Key) n n n TEK is generated by random number of BS BS use the KEK to encrypt the TEK and send to SS TEK is used to encrypt the message or data between BS and SS 38
 Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n GTEK (Group TEK) n n TEK is generated by random number of BS or some nodes in the group GTEK is used to encrypt the broadcast messages Using the KEK as the encryption key When request the GTEK Using the GKEK as the encryption key When update the GTEK 39
Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n GTEK (Group TEK) n n TEK is generated by random number of BS or some nodes in the group GTEK is used to encrypt the broadcast messages Using the KEK as the encryption key When request the GTEK Using the GKEK as the encryption key When update the GTEK 39
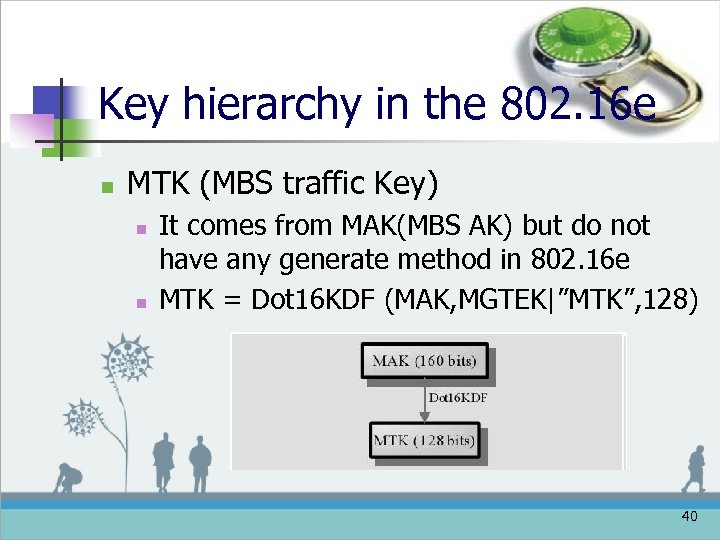 Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n MTK (MBS traffic Key) n n It comes from MAK(MBS AK) but do not have any generate method in 802. 16 e MTK = Dot 16 KDF (MAK, MGTEK|”MTK”, 128) 40
Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n MTK (MBS traffic Key) n n It comes from MAK(MBS AK) but do not have any generate method in 802. 16 e MTK = Dot 16 KDF (MAK, MGTEK|”MTK”, 128) 40
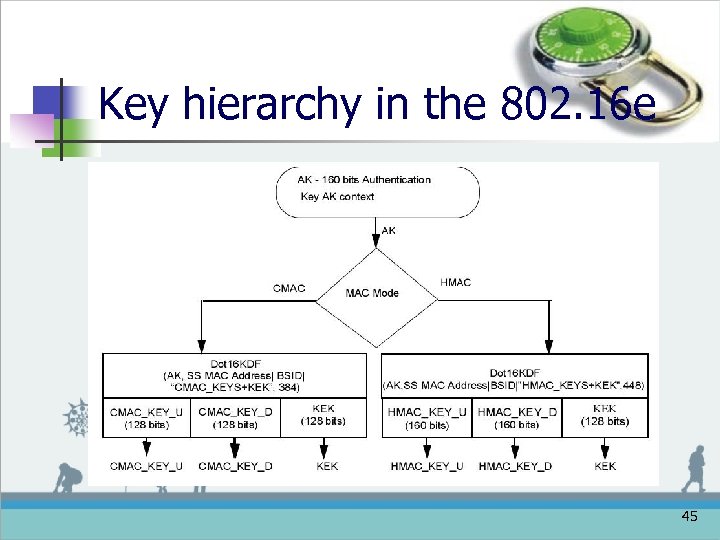
 Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n HMAC (HMAC Digests) n n n Using the AK as the material HMAC_KEY_U | HMAC_KEY_D | KEK <=Dot 16 KDF(AK, SS MAC Address | BSID | “HMAC_KEYS+KEK”, 448) HMAC_KEY_GD <= Dot 16 KDF (GKEK, ”GROUP HMAC KEY”, 160) 41
Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n HMAC (HMAC Digests) n n n Using the AK as the material HMAC_KEY_U | HMAC_KEY_D | KEK <=Dot 16 KDF(AK, SS MAC Address | BSID | “HMAC_KEYS+KEK”, 448) HMAC_KEY_GD <= Dot 16 KDF (GKEK, ”GROUP HMAC KEY”, 160) 41
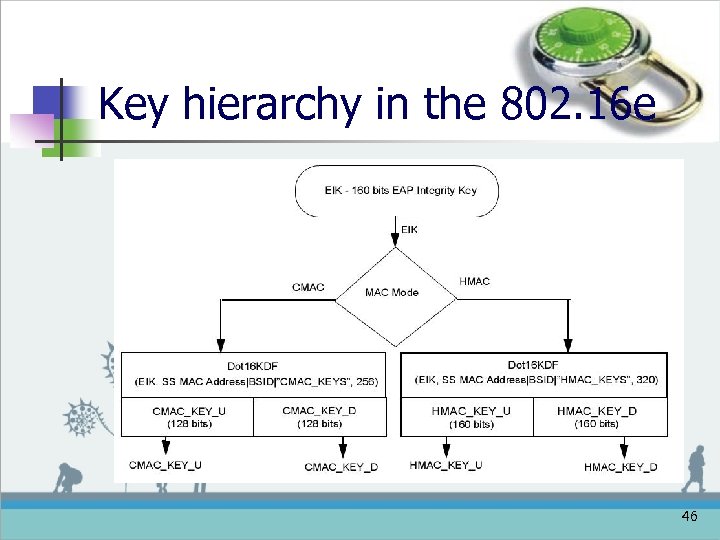
 Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n HMAC (HMAC Digests) n n Using the EIK as the material HMAC_KEY_U | HMAC_KEY_D | KEK <=Dot 16 KDF(EIK, SS MAC Address | BSID | “HMAC_KEYS+KEK”, 320) 42
Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n HMAC (HMAC Digests) n n Using the EIK as the material HMAC_KEY_U | HMAC_KEY_D | KEK <=Dot 16 KDF(EIK, SS MAC Address | BSID | “HMAC_KEYS+KEK”, 320) 42
 Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n CMAC (Cipher-based MAC) n n n Using the AK as the material CMAC_KEY_U | CMAC_KEY_D | KEK <=Dot 16 KDF(AK, SS MAC Address | BSID | “CMAC_KEYS+KEK”, 384) CMAC_KEY_GD <= Dot 16 KDF (GKEK, ”GROUP CMAC KEY”, 128) 43
Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n CMAC (Cipher-based MAC) n n n Using the AK as the material CMAC_KEY_U | CMAC_KEY_D | KEK <=Dot 16 KDF(AK, SS MAC Address | BSID | “CMAC_KEYS+KEK”, 384) CMAC_KEY_GD <= Dot 16 KDF (GKEK, ”GROUP CMAC KEY”, 128) 43
 Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n CMAC (Cipher-based MAC) n n Using the EIK as the material CMAC_KEY_U | CMAC_KEY_D | KEK<=Dot 16 KDF(EIK, SS MAC Address | BSID | “CMAC_KEYS + KEK” , 256) 44
Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e n CMAC (Cipher-based MAC) n n Using the EIK as the material CMAC_KEY_U | CMAC_KEY_D | KEK<=Dot 16 KDF(EIK, SS MAC Address | BSID | “CMAC_KEYS + KEK” , 256) 44
 Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e 45
Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e 45
 Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e 46
Key hierarchy in the 802. 16 e 46
 Conclusion 47
Conclusion 47
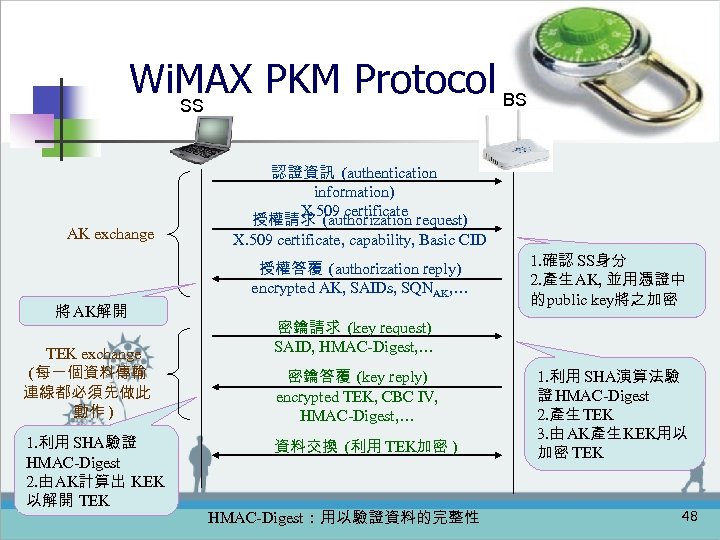 Wi. MAX PKM Protocol BS SS AK exchange 認證資訊 (authentication information) X. 509 certificate 授權請求 (authorization request) X. 509 certificate, capability, Basic CID 授權答覆 (authorization reply) encrypted AK, SAIDs, SQNAK, … 將 AK解開 TEK exchange (每一個資料傳輸 連線都必須先做此 動作 ) 1. 利用 SHA驗證 HMAC-Digest 2. 由 AK計算出 KEK 以解開 TEK 1. 確認 SS身分 2. 產生 AK, 並用憑證中 的 public key將之加密 密鑰請求 (key request) SAID, HMAC-Digest, … 密鑰答覆 (key reply) encrypted TEK, CBC IV, HMAC-Digest, … 資料交換 (利用 TEK加密 ) HMAC-Digest:用以驗證資料的完整性 1. 利用 SHA演算法驗 證 HMAC-Digest 2. 產生 TEK 3. 由 AK產生 KEK用以 加密 TEK 48
Wi. MAX PKM Protocol BS SS AK exchange 認證資訊 (authentication information) X. 509 certificate 授權請求 (authorization request) X. 509 certificate, capability, Basic CID 授權答覆 (authorization reply) encrypted AK, SAIDs, SQNAK, … 將 AK解開 TEK exchange (每一個資料傳輸 連線都必須先做此 動作 ) 1. 利用 SHA驗證 HMAC-Digest 2. 由 AK計算出 KEK 以解開 TEK 1. 確認 SS身分 2. 產生 AK, 並用憑證中 的 public key將之加密 密鑰請求 (key request) SAID, HMAC-Digest, … 密鑰答覆 (key reply) encrypted TEK, CBC IV, HMAC-Digest, … 資料交換 (利用 TEK加密 ) HMAC-Digest:用以驗證資料的完整性 1. 利用 SHA演算法驗 證 HMAC-Digest 2. 產生 TEK 3. 由 AK產生 KEK用以 加密 TEK 48
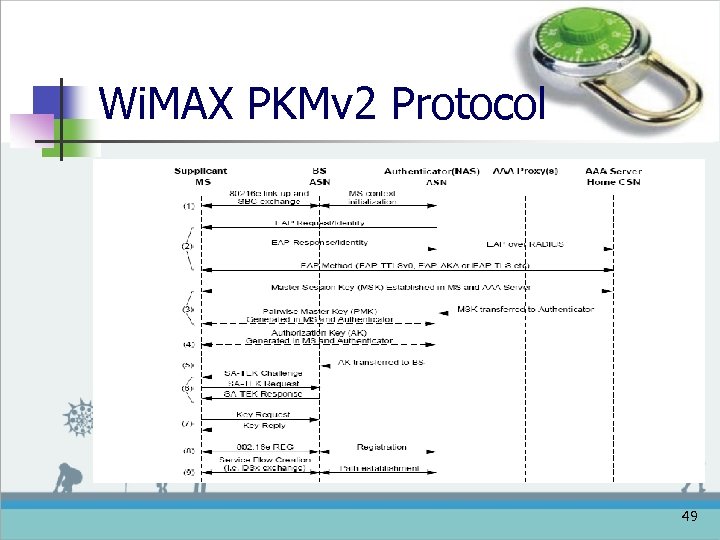 Wi. MAX PKMv 2 Protocol 49
Wi. MAX PKMv 2 Protocol 49
 Conclusion n Authentication & Authorization more robust n n Data Privacy n n Using the bidirectional Authentication to avoid the rude base station and support the different Authentication policy。 802. 16 e add more encryption algorithm (Advanced Encryption Standard, AES) to enhance the security Key’s generation n Using the robust solution to generate the AK 50
Conclusion n Authentication & Authorization more robust n n Data Privacy n n Using the bidirectional Authentication to avoid the rude base station and support the different Authentication policy。 802. 16 e add more encryption algorithm (Advanced Encryption Standard, AES) to enhance the security Key’s generation n Using the robust solution to generate the AK 50
 References n n n n IEEE Std 802. 16 -2001 standard for the local and metropolitan Area Networks, part 16 “ZAir interface for Fixed Broad. Band Wireless Access Systems, ” IEEE Press , 2001 IEEE Std 802. 16 -2004(Revision of IEEE Std 802. 16 -2001) Johnson, David and Walker, Jesse of Intel (2004), “Overview of IEEE 802. 16 Security” , published by the IEEE computer society http: //www. seas. gwu. edu/~cheng/388/Lec. Notes 2006/ IEEE Std 802. 16 e Wi. MAX 安全問題之研究 IEEE 802. 16 e-2005 Wi. MAX安全子層初探 51
References n n n n IEEE Std 802. 16 -2001 standard for the local and metropolitan Area Networks, part 16 “ZAir interface for Fixed Broad. Band Wireless Access Systems, ” IEEE Press , 2001 IEEE Std 802. 16 -2004(Revision of IEEE Std 802. 16 -2001) Johnson, David and Walker, Jesse of Intel (2004), “Overview of IEEE 802. 16 Security” , published by the IEEE computer society http: //www. seas. gwu. edu/~cheng/388/Lec. Notes 2006/ IEEE Std 802. 16 e Wi. MAX 安全問題之研究 IEEE 802. 16 e-2005 Wi. MAX安全子層初探 51
 Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) n n It is a security mechanism which uses the public and private keys The five components of PKI n n n Security Policy Certificate Authority;CA Registration Authority;RA Certificate Revocation List;CRL Directory Service; DS 52
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) n n It is a security mechanism which uses the public and private keys The five components of PKI n n n Security Policy Certificate Authority;CA Registration Authority;RA Certificate Revocation List;CRL Directory Service; DS 52
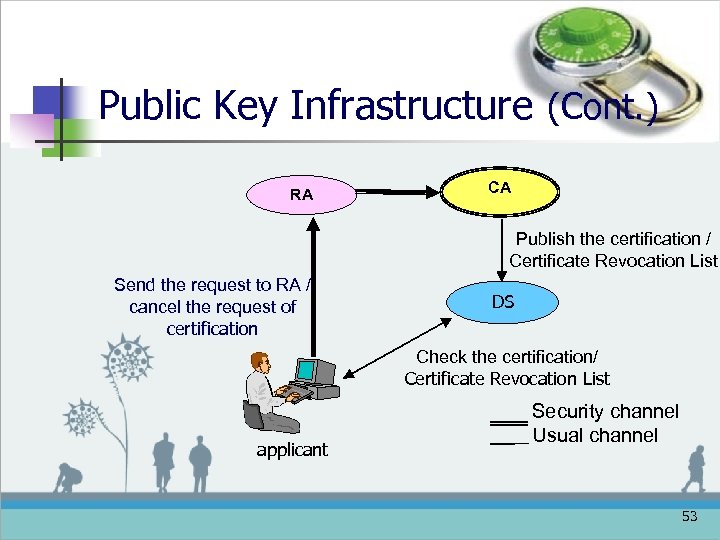 Public Key Infrastructure (Cont. ) RA CA Publish the certification / Certificate Revocation List Send the request to RA / cancel the request of certification DS Check the certification/ Certificate Revocation List applicant Security channel Usual channel 53
Public Key Infrastructure (Cont. ) RA CA Publish the certification / Certificate Revocation List Send the request to RA / cancel the request of certification DS Check the certification/ Certificate Revocation List applicant Security channel Usual channel 53
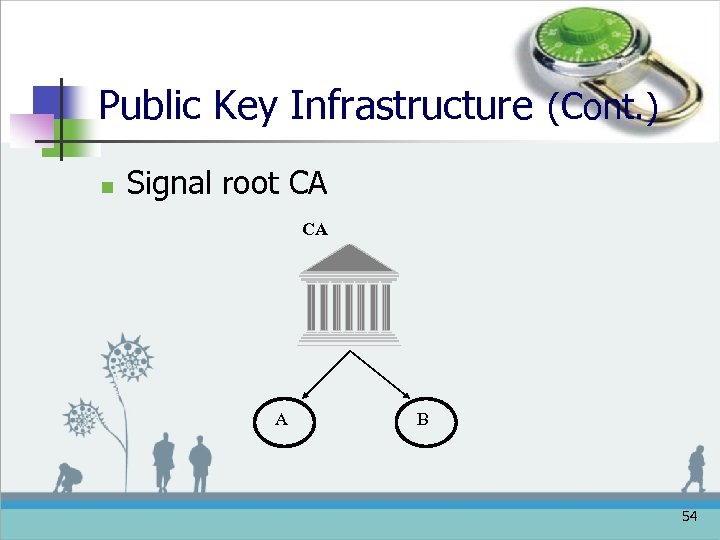 Public Key Infrastructure (Cont. ) n Signal root CA CA A B 54
Public Key Infrastructure (Cont. ) n Signal root CA CA A B 54
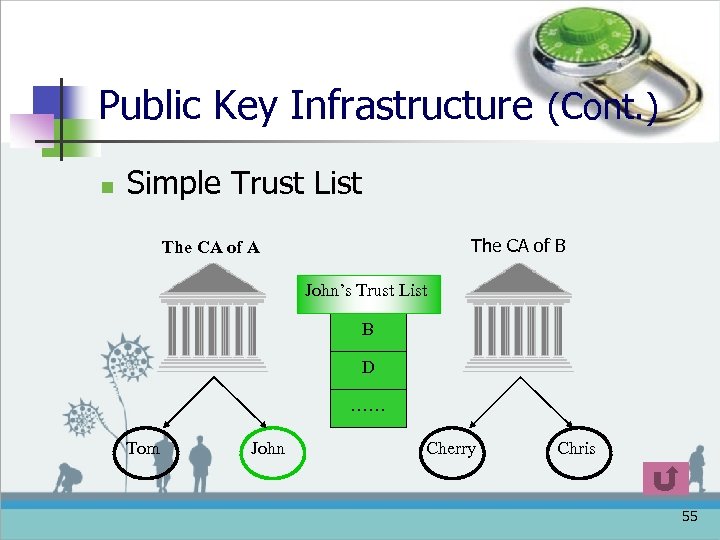 Public Key Infrastructure (Cont. ) n Simple Trust List The CA of B The CA of A John’s Trust List B D …… Tom John Cherry Chris 55
Public Key Infrastructure (Cont. ) n Simple Trust List The CA of B The CA of A John’s Trust List B D …… Tom John Cherry Chris 55
 Dot 16 KDF algorithm n n n CRT (counter mode encryption) uses the input material to generate the designed length key input material (key, astring, keylength) Output key length is keylength*2 56
Dot 16 KDF algorithm n n n CRT (counter mode encryption) uses the input material to generate the designed length key input material (key, astring, keylength) Output key length is keylength*2 56
 Dot 16 KDF algorithm (Cont. ) n CMAC n n Kin = Truncate (key, 128) get the leftmost 128 bits of key as the Kin Output key = (CMAC(Kin, 0| astring | keylength) || CMAC(Kin, 1| astring | keylength) || CMAC(Kin, 2| astring | keylength) …………) 57
Dot 16 KDF algorithm (Cont. ) n CMAC n n Kin = Truncate (key, 128) get the leftmost 128 bits of key as the Kin Output key = (CMAC(Kin, 0| astring | keylength) || CMAC(Kin, 1| astring | keylength) || CMAC(Kin, 2| astring | keylength) …………) 57
 Dot 16 KDF algorithm (Cont. ) n HMAC n n Kin = Truncate (key, 160) get the leftmost 160 bits of key as the Kin Output key = SHA-1(Kin , i | astring | keylength) 58
Dot 16 KDF algorithm (Cont. ) n HMAC n n Kin = Truncate (key, 160) get the leftmost 160 bits of key as the Kin Output key = SHA-1(Kin , i | astring | keylength) 58


