2c9050e2bcaf3ac5130eed115a3b5feb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

SECURITY FOR SMALL STATES IN A GLOBALIZED WORLD: AN ILLUSION? CLIVE ARCHER CLIVEARCHER 8@AOL. COM

Outline Contested concept 1: small states (again) Contested concept 2: security Contested concept 3: Globalized World (again) Small states in Europe & world Security checklists 10/20 years after Smallness & security Largeness & security Some key factors Where to now?

Contested concept 1: small state Subjective concept: seen as small Objective reality: population, area, GDP Contextual: ‘the weak part in any asymmetric relationship’ (Steinmetz & Wivel, 2010: 6). Smallness is defined through the relation between the state and external environment

Contested concept 2: security Traditional concept of security: Military: state must have enough military power to defend itself or buy it in Threat to existence of state: self-defence or alliance needed (then a choice of ‘bandwaggoning’ or ‘balancing’)

Contested concept 2: security New concepts of security: the middle range: New military insecurities; irregular armies, terrorism – need more than just military response Environmental security: specific/general: can still threaten existence of state, but military means not sufficient to ‘repel’ it; diplomacy Economic security: lack can threaten state & nation; non-military solutions Energy security: problems of lack of sources

Contested concept 2: security ‘Low level’ security Societal security: rights of groups, protect civilian population & infrastructure Human security: legal rights in war & conflict; living conditions

Contested concept 2: security Range of securities: traditional hard military; intermediate; low level, soft. Security complexes: Mixes of the range of securities (or insecurities) some of which react on each other Some elements re-inforce: use of hard security instruments to help environmental security. Others clash: hard vs societal
Contested concept 3: Globalized World Is the world more ‘global’ than 100 years ago? What has changed and what has stayed the same?

Small States in Europe Nordic-Baltic Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania CEEC Czech Republic, Hungary, Slovakia, Bulgaria, Romania, CIS/Ex-CIS Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, Alpines Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein Western Europe Belgium, Ireland, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Portugal, Balkans Albania, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro, Slovenia, Serbia, Mediterranean: Cyprus, Greece, Malta
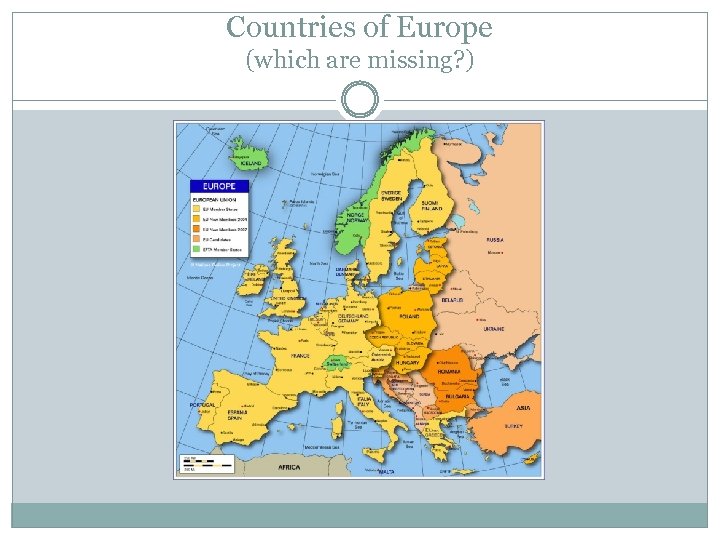
Countries of Europe (which are missing? )

Checklist: existential military threat (10 -20 years) Nordic-Baltic Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania CIS/Ex-CIS Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, Balkans Kosovo Mediterranean Cyprus Italics weakest threat, bold strongest

Checklist: internal military conflict CIS/Ex-CIS Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, Balkans Albania, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Kosovo, Macedonia, Serbia,
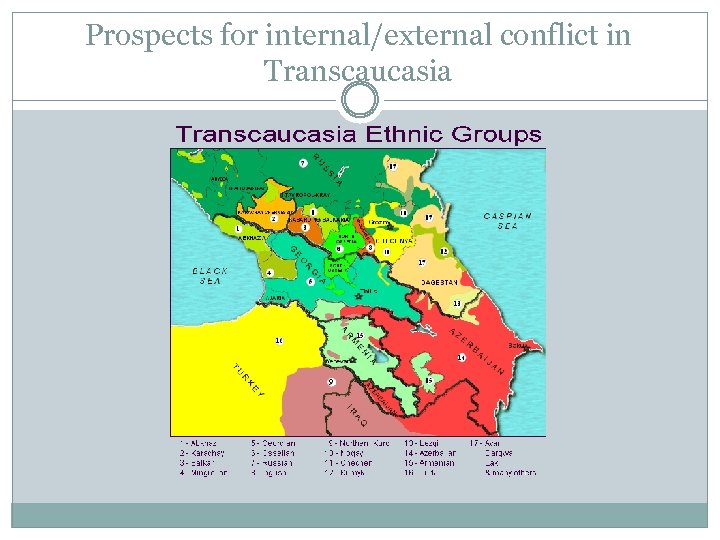
Prospects for internal/external conflict in Transcaucasia

Checklist: major civil unrest (next 10 -20 years) Nordic-Baltic Latvia CEEC Hungary, Slovakia, Bulgaria, Romania, CIS/Ex-CIS Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, Balkans Albania, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Mediterranean Cyprus, Greece, Spain, Portugal
Checklist: international terrorism Nordic-Baltic Denmark CIS/Ex-CIS Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Moldova, Balkans Albania, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Kosovo, Macedonia, Serbia Mediterranean Cyprus, Greece
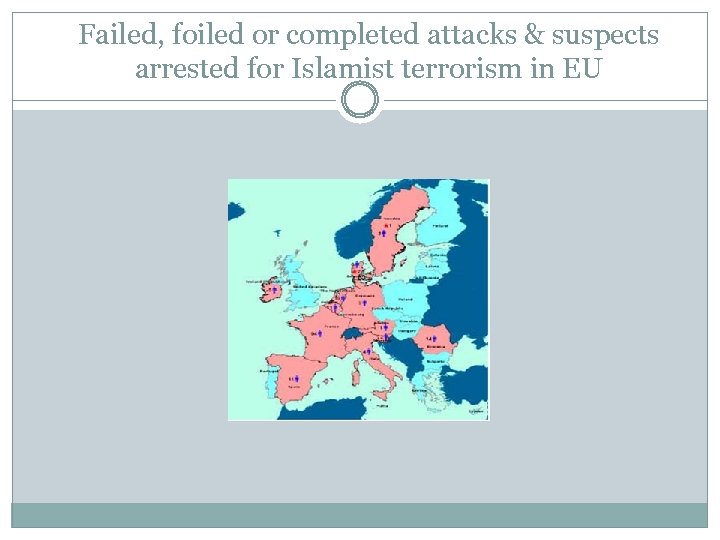
Failed, foiled or completed attacks & suspects arrested for Islamist terrorism in EU

Checklist: major environmental problems Nordic-Baltic Lithuania CEEC Hungary, Slovakia, Bulgaria, Romania, CIS/Ex-CIS Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, Western Europe Netherlands, Portugal, Balkans Albania, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Mediterranean Cyprus, Greece, Malta

Youth & Environment Europe July 2011

Checklist: major economic/social breakdown Nordic-Baltic Latvia CEEC Czech Republic, Hungary, Slovakia, Bulgaria, Romania, CIS/Ex-CIS Armenia, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, Western Europe Ireland, Portugal, Spain Balkans Albania, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Mediterranean Cyprus, Greece, Malta
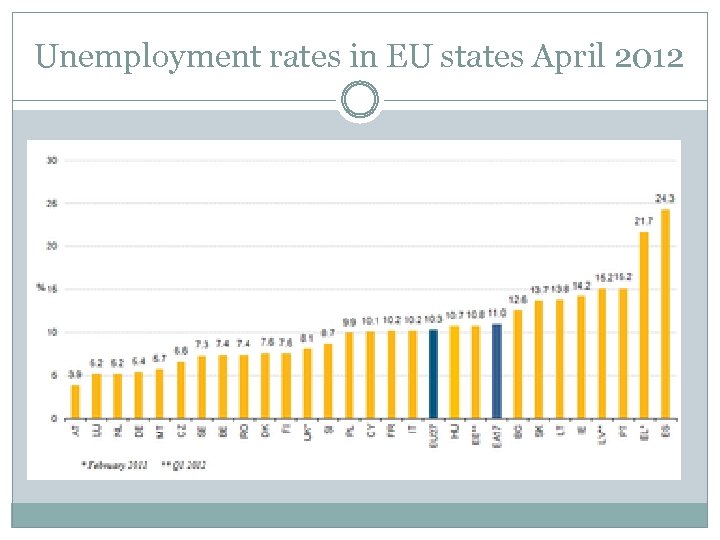
Unemployment rates in EU states April 2012

Smallness & security Most secure Most insecure Nordic states, Be. Ne. Lux, Alpines Ireland Czech Rep, Slovenia, Slovakia, Croatia CIS/Ex-CIS states Albania, Kosovo, Macedonia, Serbia, B-H Bulgaria, Romania, Hungary Cyprus Greece
Largeness & Security Most secure Least secure Germany UK France Ukraine Russia Poland Italy Spain

Some key factors History: ex-USSR, ex-Yugoslavia (shadow of the past) Geography: Mediterranean, Balkan Not-EU member : causal? ? Not-Eurozone member: causal? Not-NATO member : causal? ? Level of democracy: causal? ? Underdevelopment of civil society BUT size?

Some key factors Clearly small states in Europe can be secure and are probably as secure now as ever BUT other factors help sustain this security AND other factors help undermine it What about elsewhere in world? Caribbean, Africa, Middle east, Asia-Pacific A key factor for small state: alliance A key factor for small nation: civil society

Where to now? Look at how states bind themselves into state system Look at society not just the state

After the break…. Identify your state (where you come from, one that you like, Iceland…) Make up groups of 4 -6 Identify: what makes it Secure Insecure Should it join/remain part of an alliance? Why?
2c9050e2bcaf3ac5130eed115a3b5feb.ppt