dd7c9eb4ce2bc688837a54b708b4928d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Security and Privacy over the Internet Chan Hing Wing, Anthony Mphil Yr. 1, CSE, CUHK Oct 19, 1998
Security and Privacy over the Internet Chan Hing Wing, Anthony Mphil Yr. 1, CSE, CUHK Oct 19, 1998
 Presentation Overview n n n Introduction Public-key cryptography: RSA Secret-key cryptography: DES The SSL protocol Open discussion
Presentation Overview n n n Introduction Public-key cryptography: RSA Secret-key cryptography: DES The SSL protocol Open discussion
 Introduction n Privacy u Keeping communication contents secret, known to a predetermined set of people, unknown to others n Security u. A means to achieve privacy u An attempt against attacks like: eavesdropping, tampering, message replay u Tools: cryptography, secure protocol
Introduction n Privacy u Keeping communication contents secret, known to a predetermined set of people, unknown to others n Security u. A means to achieve privacy u An attempt against attacks like: eavesdropping, tampering, message replay u Tools: cryptography, secure protocol
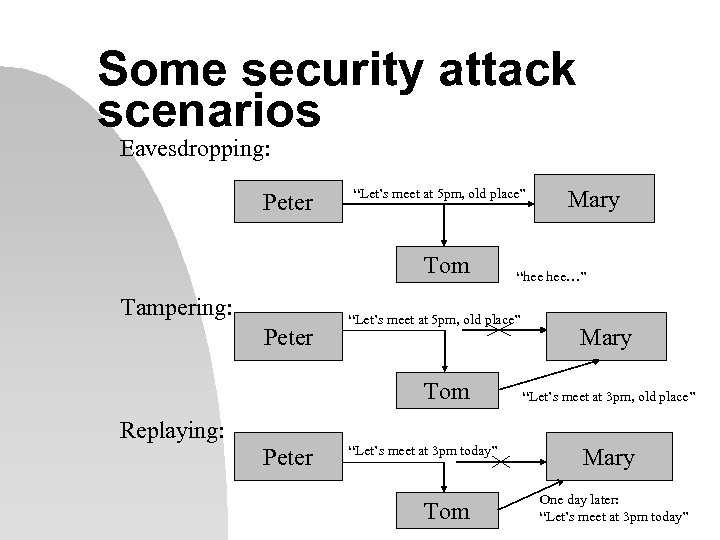 Some security attack scenarios Eavesdropping: Peter “Let’s meet at 5 pm, old place” Tom Tampering: Peter Replaying: Peter “hee hee…” “Let’s meet at 5 pm, old place” Tom “Let’s meet at 3 pm today” Tom Mary “Let’s meet at 3 pm, old place” Mary One day later: “Let’s meet at 3 pm today”
Some security attack scenarios Eavesdropping: Peter “Let’s meet at 5 pm, old place” Tom Tampering: Peter Replaying: Peter “hee hee…” “Let’s meet at 5 pm, old place” Tom “Let’s meet at 3 pm today” Tom Mary “Let’s meet at 3 pm, old place” Mary One day later: “Let’s meet at 3 pm today”
 Cryptography n Transformation of data into a secret form that is infeasible to read without knowledge of a shared secret (a key) encryption Data n n decryption Secret-form data Achieve privacy by making information hidden to people who don’t know the key Encryption key and decryption key may be the same (secret-key cryptography) or different (public-key cryptography)
Cryptography n Transformation of data into a secret form that is infeasible to read without knowledge of a shared secret (a key) encryption Data n n decryption Secret-form data Achieve privacy by making information hidden to people who don’t know the key Encryption key and decryption key may be the same (secret-key cryptography) or different (public-key cryptography)
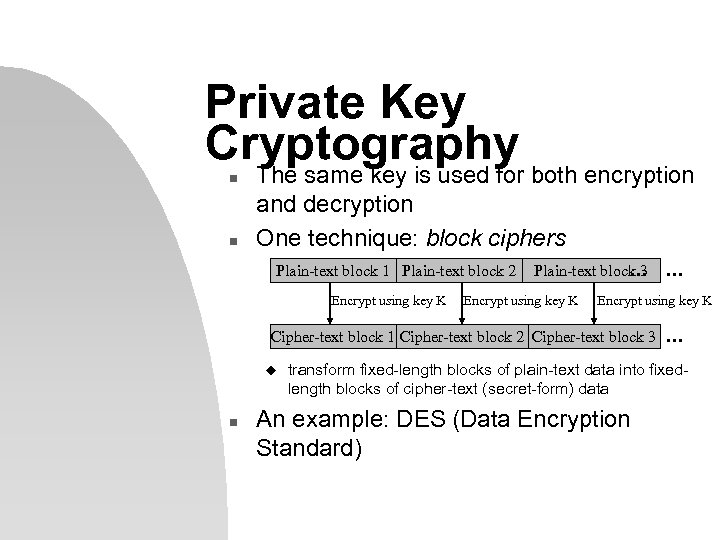 Private Key Cryptography n n The same key is used for both encryption and decryption One technique: block ciphers Plain-text block 1 Plain-text block 2 Plain-text block 3. . . Encrypt using key K Cipher-text block 1 Cipher-text block 2 Cipher-text block 3 u n . . . transform fixed-length blocks of plain-text data into fixedlength blocks of cipher-text (secret-form) data An example: DES (Data Encryption Standard)
Private Key Cryptography n n The same key is used for both encryption and decryption One technique: block ciphers Plain-text block 1 Plain-text block 2 Plain-text block 3. . . Encrypt using key K Cipher-text block 1 Cipher-text block 2 Cipher-text block 3 u n . . . transform fixed-length blocks of plain-text data into fixedlength blocks of cipher-text (secret-form) data An example: DES (Data Encryption Standard)
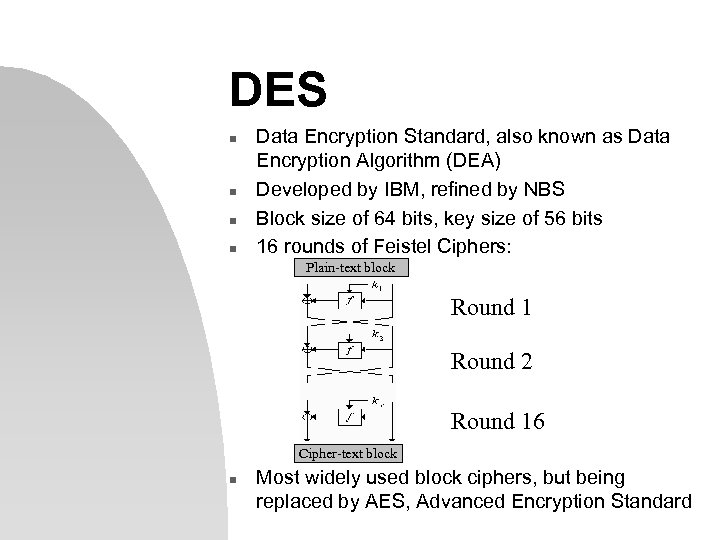 DES n n Data Encryption Standard, also known as Data Encryption Algorithm (DEA) Developed by IBM, refined by NBS Block size of 64 bits, key size of 56 bits 16 rounds of Feistel Ciphers: Plain-text block Round 1 Round 2 Round 16 Cipher-text block n Most widely used block ciphers, but being replaced by AES, Advanced Encryption Standard
DES n n Data Encryption Standard, also known as Data Encryption Algorithm (DEA) Developed by IBM, refined by NBS Block size of 64 bits, key size of 56 bits 16 rounds of Feistel Ciphers: Plain-text block Round 1 Round 2 Round 16 Cipher-text block n Most widely used block ciphers, but being replaced by AES, Advanced Encryption Standard
 Private Key cryptography n Stream ciphers (e. g. , RC 4) transform plain-text data into cipher-text data bit by bit, and vice versa u can be much faster than block ciphers, but less secure u n Message Authentication Codes (MAC) a checksum obtained by applying an authentication scheme (DES, RC 4, etc. ) and a secret key to a message u the recipient verifies the integrity of the message by calculating the MAC with the secret key again u
Private Key cryptography n Stream ciphers (e. g. , RC 4) transform plain-text data into cipher-text data bit by bit, and vice versa u can be much faster than block ciphers, but less secure u n Message Authentication Codes (MAC) a checksum obtained by applying an authentication scheme (DES, RC 4, etc. ) and a secret key to a message u the recipient verifies the integrity of the message by calculating the MAC with the secret key again u
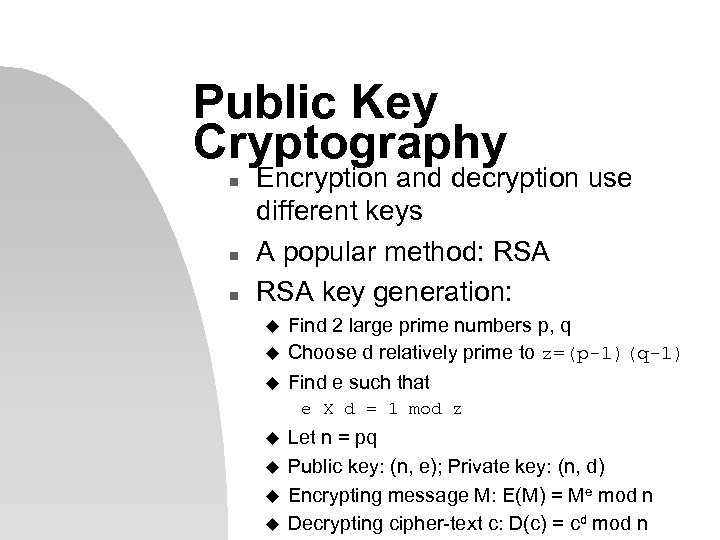 Public Key Cryptography n n n Encryption and decryption use different keys A popular method: RSA key generation: u Find 2 large prime numbers p, q Choose d relatively prime to z=(p-1)(q-1) u Find e such that u e X d = 1 mod z u u Let n = pq Public key: (n, e); Private key: (n, d) Encrypting message M: E(M) = Me mod n Decrypting cipher-text c: D(c) = cd mod n
Public Key Cryptography n n n Encryption and decryption use different keys A popular method: RSA key generation: u Find 2 large prime numbers p, q Choose d relatively prime to z=(p-1)(q-1) u Find e such that u e X d = 1 mod z u u Let n = pq Public key: (n, e); Private key: (n, d) Encrypting message M: E(M) = Me mod n Decrypting cipher-text c: D(c) = cd mod n
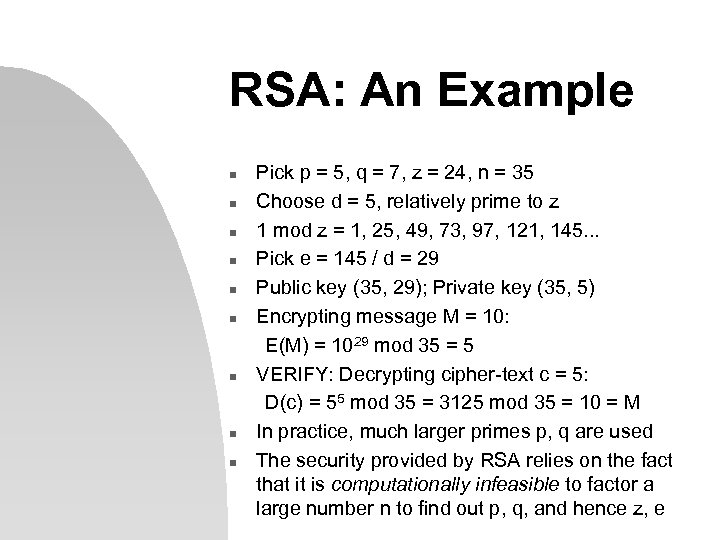 RSA: An Example n n n n n Pick p = 5, q = 7, z = 24, n = 35 Choose d = 5, relatively prime to z 1 mod z = 1, 25, 49, 73, 97, 121, 145. . . Pick e = 145 / d = 29 Public key (35, 29); Private key (35, 5) Encrypting message M = 10: E(M) = 1029 mod 35 = 5 VERIFY: Decrypting cipher-text c = 5: D(c) = 55 mod 35 = 3125 mod 35 = 10 = M In practice, much larger primes p, q are used The security provided by RSA relies on the fact that it is computationally infeasible to factor a large number n to find out p, q, and hence z, e
RSA: An Example n n n n n Pick p = 5, q = 7, z = 24, n = 35 Choose d = 5, relatively prime to z 1 mod z = 1, 25, 49, 73, 97, 121, 145. . . Pick e = 145 / d = 29 Public key (35, 29); Private key (35, 5) Encrypting message M = 10: E(M) = 1029 mod 35 = 5 VERIFY: Decrypting cipher-text c = 5: D(c) = 55 mod 35 = 3125 mod 35 = 10 = M In practice, much larger primes p, q are used The security provided by RSA relies on the fact that it is computationally infeasible to factor a large number n to find out p, q, and hence z, e
 Digital Signatures, Certificates n Digital signature Message M u n M encrypted with sender’s private key The recipient verifies the signature by decrypting the signature with sender’s public key, and compares decrypted message with M Certificate A digitally signed public key u Used to verify a claimed-to-be public key of an entity u
Digital Signatures, Certificates n Digital signature Message M u n M encrypted with sender’s private key The recipient verifies the signature by decrypting the signature with sender’s public key, and compares decrypted message with M Certificate A digitally signed public key u Used to verify a claimed-to-be public key of an entity u
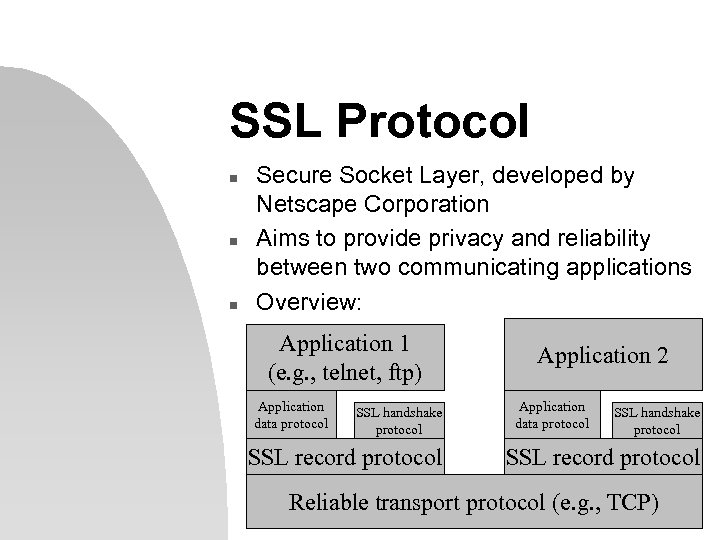 SSL Protocol n n n Secure Socket Layer, developed by Netscape Corporation Aims to provide privacy and reliability between two communicating applications Overview: Application 1 (e. g. , telnet, ftp) Application data protocol SSL handshake protocol SSL record protocol Application 2 Application data protocol SSL handshake protocol SSL record protocol Reliable transport protocol (e. g. , TCP)
SSL Protocol n n n Secure Socket Layer, developed by Netscape Corporation Aims to provide privacy and reliability between two communicating applications Overview: Application 1 (e. g. , telnet, ftp) Application data protocol SSL handshake protocol SSL record protocol Application 2 Application data protocol SSL handshake protocol SSL record protocol Reliable transport protocol (e. g. , TCP)
 SSL Protocol n Record protocol u u u n SSL handshake protocol u u n encapsulate higher level protocols divide messages into blocks compresses message blocks applies MAC to message blocks encrypts and transmits message blocks allow the client to authenticate the server, and the server to authenticate the client negotiate an encryption algorithm and key for application data transmission Application data protocol u transmits data from applications to the record layer, which then sends the data securely
SSL Protocol n Record protocol u u u n SSL handshake protocol u u n encapsulate higher level protocols divide messages into blocks compresses message blocks applies MAC to message blocks encrypts and transmits message blocks allow the client to authenticate the server, and the server to authenticate the client negotiate an encryption algorithm and key for application data transmission Application data protocol u transmits data from applications to the record layer, which then sends the data securely
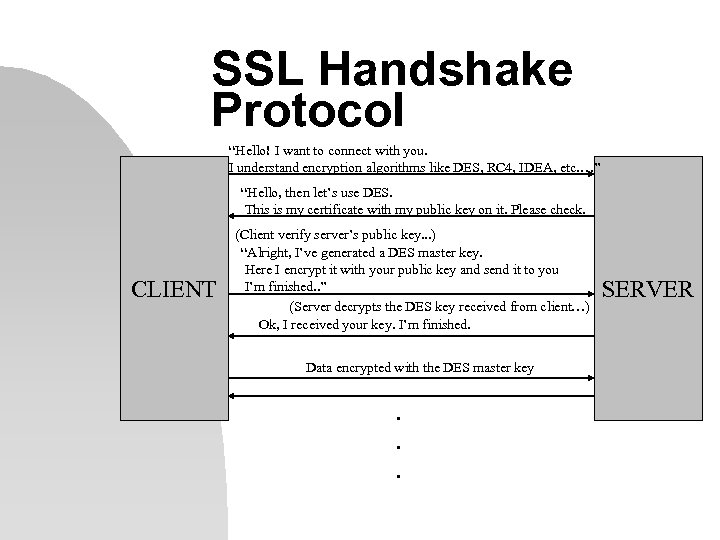 SSL Handshake Protocol “Hello! I want to connect with you. I understand encryption algorithms like DES, RC 4, IDEA, etc. …” “Hello, then let’s use DES. This is my certificate with my public key on it. Please check. CLIENT (Client verify server’s public key. . . ) “Alright, I’ve generated a DES master key. Here I encrypt it with your public key and send it to you I’m finished. . ” (Server decrypts the DES key received from client…) Ok, I received your key. I’m finished. Data encrypted with the DES master key . . . SERVER
SSL Handshake Protocol “Hello! I want to connect with you. I understand encryption algorithms like DES, RC 4, IDEA, etc. …” “Hello, then let’s use DES. This is my certificate with my public key on it. Please check. CLIENT (Client verify server’s public key. . . ) “Alright, I’ve generated a DES master key. Here I encrypt it with your public key and send it to you I’m finished. . ” (Server decrypts the DES key received from client…) Ok, I received your key. I’m finished. Data encrypted with the DES master key . . . SERVER
 SSL Protocol n How does it achieve privacy? u u u All data are encrypted during transmission, therefore, eavesdropping is useless unless the eavesdropper knows how to decrypt the message Moreover, an attacker will not be able to tamper a message because he does not know how to encrypt it A session-id is assigned by the server to each connection, so that an attacker cannot pretend the client later by replaying the message
SSL Protocol n How does it achieve privacy? u u u All data are encrypted during transmission, therefore, eavesdropping is useless unless the eavesdropper knows how to decrypt the message Moreover, an attacker will not be able to tamper a message because he does not know how to encrypt it A session-id is assigned by the server to each connection, so that an attacker cannot pretend the client later by replaying the message
 Summary n n We introduced basic cryptographic techniques, DES and RSA, and their application in MAC, digital signatures and certificates We introduced the SSL protocol developed by Netscape Corp. as a secure protocol for data transmission
Summary n n We introduced basic cryptographic techniques, DES and RSA, and their application in MAC, digital signatures and certificates We introduced the SSL protocol developed by Netscape Corp. as a secure protocol for data transmission


