f9694ea671a7f8bc6286a85d8a24f5ec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Security Administration Tools and Practices Amit Bhan Usable Privacy and Security

Agenda • • Security Administration Purpose of Security Tools Examples of Security Tools Security Incident Manager (SIM) – Security Monitoring • Cases from the Field • Problems with Security Administration • Improvements

Security Administration? • is the process of maintaining a safe computing environment. • Purpose? Need? • Security Administrator • Responsibilities?

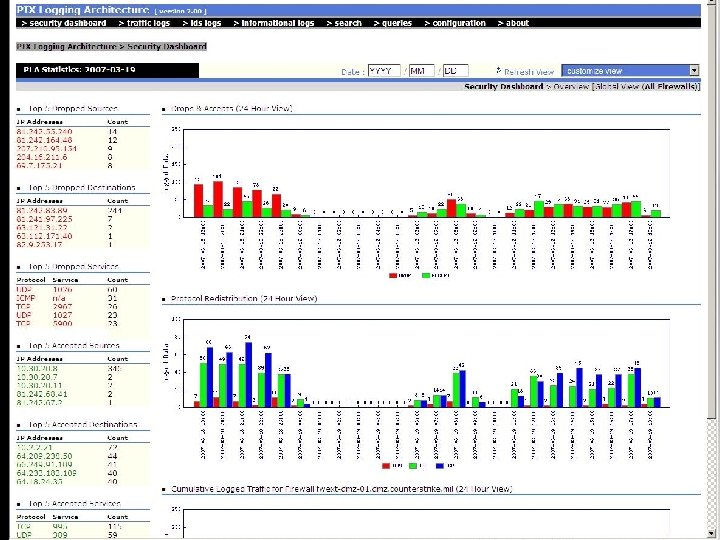
Purpose of Security Tools • • • Combining text and visuals Reporting Monitoring Correlating Simplify the life of a Security Administrator

Combining Text and Visuals • Size and complexity of networks • A System Administrator has a variety of responsibilities: install, configure, monitor, debug and patch • Visualization vs. Perl Scripts • Vis. Flow. Connect-IP (who is connecting to whom on my network? ) • Other tools (discuss later)

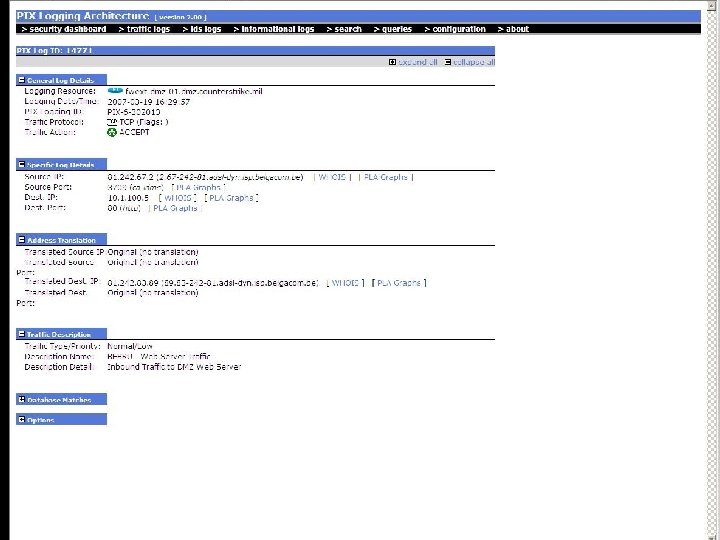
Reporting • Many security tools have an in built capability for reporting • Why is reporting important? • Examples: – Nessus (vulnerability information) – SIM (security incidents information)

Monitoring • Some security tools have live data feed for the network • Different types of monitoring – Network monitoring – Security event monitoring – Network Security Incident monitoring

Correlation • Correlation integrates the key security factors that are critical in determining the potential for significant damage within an organization. These factors are: – Real time events from heterogeneous devices – Results of vulnerability scans and other sources of threat data – The value of the host, database or application to the organization.

Life of a Security Administrator • According to the paper “Combining Text and Visual Interfaces for Security. System Administration”, Security administrators are very conservative when it comes to technology adoption. • Why?

Security Admin Tools • Mentioned in Text: – Bro – Nessus – Symantec Anti-virus – Tripwire – Rootkit – Sebek

Bro • Bro (http: //www. bro-ids. org/) is a NIDS. • Bro supports signature analysis, and in fact can read Snort signatures. (Snort is one of the most popular NIDS available. ) • Bro also performs (a limited form of) anomaly detection, looking for activity that resembles an intrusion.

Structure of Bro

Nessus • Nessus is a free comprehensive vulnerability scanning software. • Its goal is to detect potential vulnerabilities on the tested systems
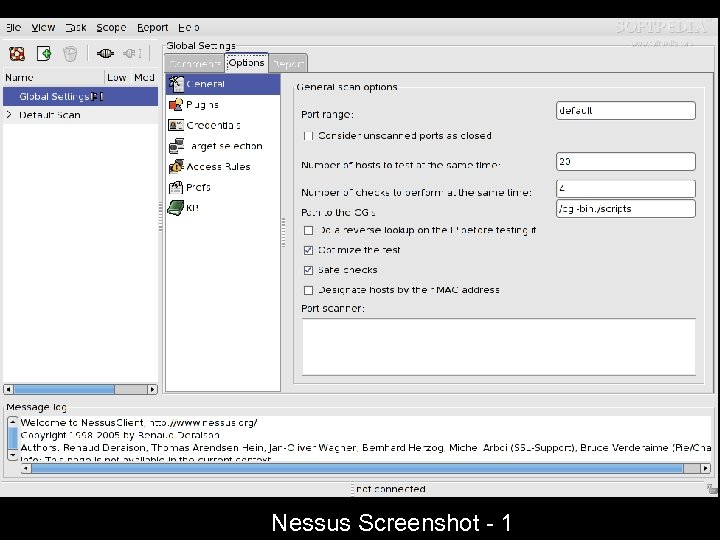
Nessus Screenshot - 1
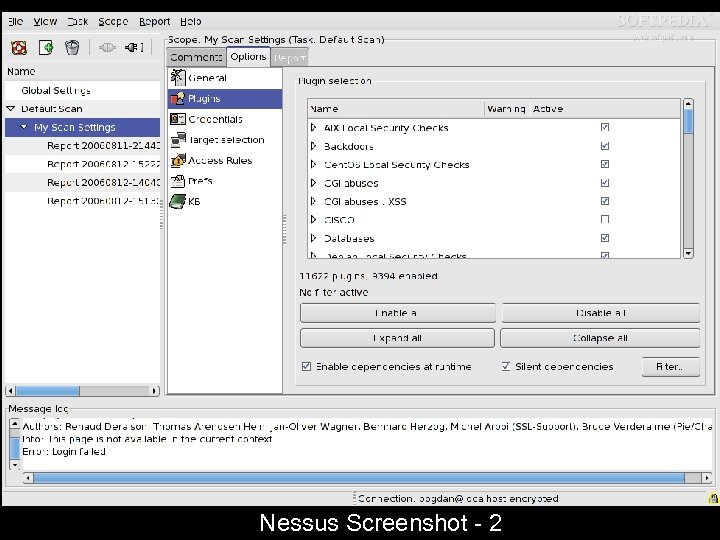
Nessus Screenshot - 2
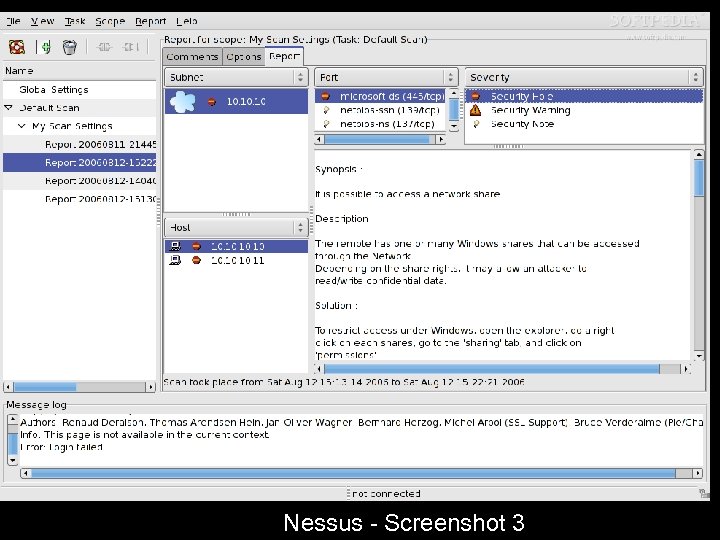
Nessus Screenshot - 3 Nessus - Screenshot 3

Other tools • Security Incident Management System – Arc. Sight – Novell e-Security Sentinel • Network Incident Management System – Whatsup Gold – IBM Tivoli

Arc. Sight • Large Enterprises and Governments infrastructures are growing increasingly dynamic and complex • Arc. Sight ESM is an event management tool • Different capabilities: filters, correlation, reporting, threat monitor, vulnerability knowledge base, asset information, risk management, zones, etc.

Architecture - Arc. Sight ESM • Smart. Agents (residing on remote systems or on a separate layer) • Devices or Remote Systems (Firewalls, IDSs etc. ) • Correlation engine • Central database • Arc. Sight Manager (console/browser)

Testing Arc. Sight • Real strength - analyzing huge volumes at data • When tested at an ISP that provided managed services to many corporate clients, generating millions of events a day (stress test), Arc. Sight had no hiccups. • Biggest advantage: Scaling
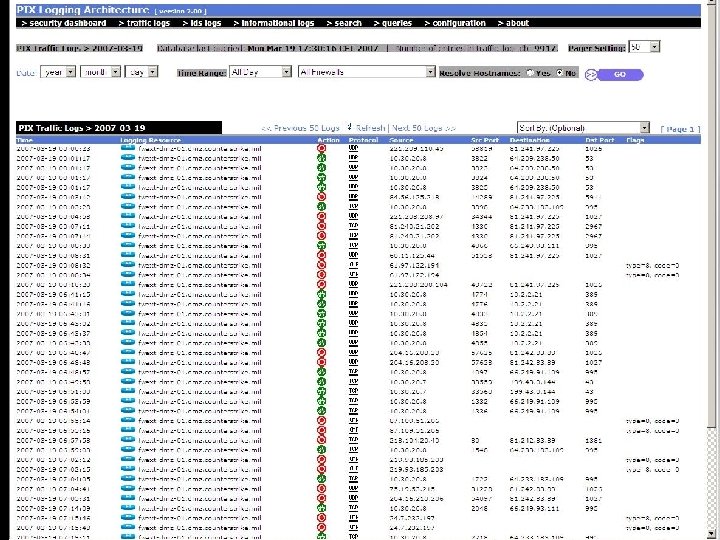
Arc. Sight screenshot 1
Arc. Sight screenshot 2
Arc. Sight screenshot 3

e-Security Sentinel • Competitor of Arc. Sight, Network Intelligence, Symantec Security Information Manager • Event collector • Analyses and correlates events to determine if an event violates a predetermined condition or acceptable threshold. • Control Center & Correlation Engine • Unlike Arcsight, e-Security Sentinel has an i. Scale Message Bus that is based on the Sonic JMS* bus architecture. – Highly scalable – Doesn’t rely on a relational database

E-Sentinel Screenshot 1

E-Security Screenshot 2

Cases from the Field • Security Checkup – Latest fixes/patches – Use of IDS + regular scanning of network – Security Engineers need to be well informed (discussions on forums)

Case 1 - virus/worm/spyware on the network

Case 2 - false alarms

Case 3 - Real time network security monitoring

Case 4 - Security Scans

Problems with Security Administration • Integration is required – From firewalls to IDSs to Websense to vulnerability information to KB • Challenges – Too much to look at – No single standard data format – Out of sync system clocks • Correlation becomes difficult

Problems cont. • Information asymmetry – Use of manual tools (location, address books, information directories) • Process is slow because of very little integration – A problem in times of actual attacks • Critical factor - “Time” • New vulnerabilities - proactive work pays • Administrator motto - “Know Thy Network”

Improvements • New tools to help security administrators need to be developed – Standardization of event formats for easier integration – Application of data mining in event classification, analysis and noise reduction – Automated event stream processing – Improved information management tools

Questions ? ? ? ? ?
f9694ea671a7f8bc6286a85d8a24f5ec.ppt