41ac6f5c3f4c4151769d2954b2b3f405.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

Securing Remote Access With SSL VPNs: A Best Practice Primer Sikhi Gundu and Kartik Kumar, Juniper Networks India Pvt Ltd
Preliminaries • Target audience: IT org managers, admins; not developers/implementers • Introductory/high level overview • Essentially tutorial

Agenda Motivation 30000 ft view of SSLVPN Technology Security with SSLVPN: Athentication Security with SSLVPN: Endpoint Integrity • Security with SSLVPN: Authorization • Security with SSLVPN: User Education • •

Agenda Motivation 30000 ft view of SSLVPN Technology Security with SSLVPN: Authentication Security with SSLVPN: Endpoint Integrity • Security with SSLVPN: Authorization • Security with SSLVPN: User Education • •

Motivation • Usecase • Remote access for Employees, Partners & Customers • Why not IPSEC • Requires client software to be installed. • IPSEC VPNs are good for site-to-site, not so good for clients to server • is layer 3; remote access users get layer 3 access! • Why SSL VPN • Client less remote access (browser is the client) • Easy on the IT shop (roll-out, config) • Layer 4 access with notion of a " user "

Agenda Motivation 30000 ft view of SSLVPN Technology Security with SSLVPN: Authentication Security with SSLVPN: Endpoint Integrity • Security with SSLVPN: Authorization • Security with SSLVPN: User Education • •
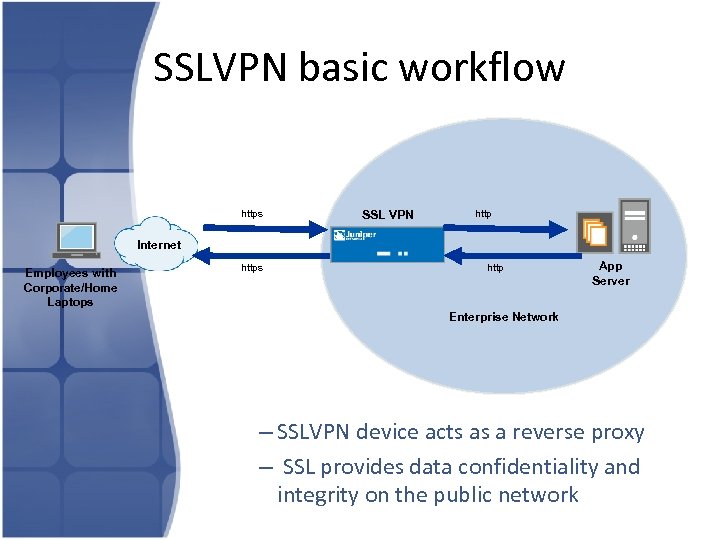
SSLVPN basic workflow https SSL VPN http Internet Employees with Corporate/Home Laptops http App Server Enterprise Network – SSLVPN device acts as a reverse proxy – SSL provides data confidentiality and integrity on the public network
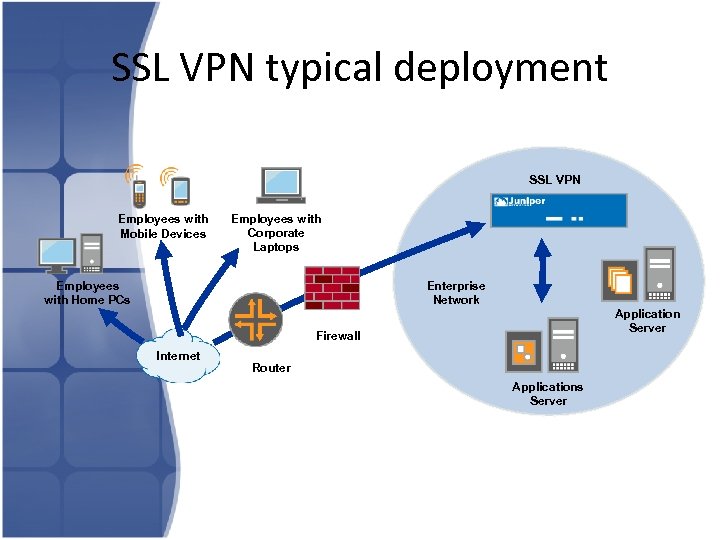
SSL VPN typical deployment SSL VPN Employees with Mobile Devices Employees with Corporate Laptops Employees with Home PCs Enterprise Network Application Server Firewall Internet Router Applications Server
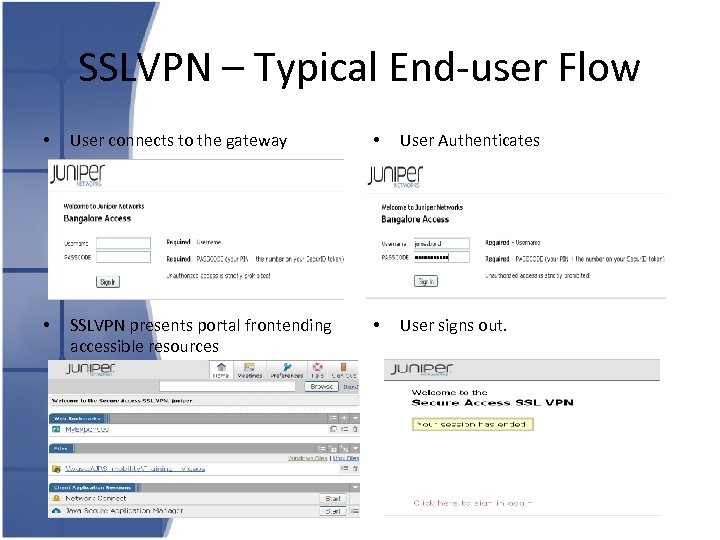
SSLVPN – Typical End-user Flow • User connects to the gateway • User Authenticates • SSLVPN presents portal frontending accessible resources • User signs out.

Essential functionality: Rewriting • Layer 4 • <body bgcolor=#ffffff text=#000000 link=#0000 cc vlink=#551 a 8 b alink=#ff 0000 onload="try{!google. j. b&&document. f. q. focus()}catch(e){}; if(docum ent. images)Dana. Put. Src(new Image(), '/images/srpr/nav_logo 14. png', 0)" ><textarea id=csi style=display: none></textarea><script>if(google. j. b)document. body. style. visibility='hidden'; </script><iframe name=wgjf style=display: none src="/dana-cached/help/empty. html" onload="google. j. l()" onerror="google. j. e()"></iframe><textarea id=wgjc style=display: none></textarea><textarea id=wwcache style=display: none></textarea><textarea id=csi style=display: none></textarea><textarea id=hcache style=display: none></textarea><span id=main><div id=ghead><div id=gog><div id=gbar><nobr><b class=gb 1>Web</b> <a • href="https: //sslvpn. mycompnay. com/, Dana. In fo=10. 204. 50. 40+imghp? hl=en&tab=wi" <body bgcolor=#ffffff text=#000000 link=#0000 cc vlink=#551 a 8 b alink=#ff 0000 onload="try{!google. j. b&&document. f. q. focus()}catch(e){}; if(docum ent. images)new Image(). src='/images/srpr/nav_logo 14. png'" ><textarea id=csi style=display: none></textarea><script>if(google. j. b)document. body. style. visibility='hidden'; </script><iframe name=wgjf style=display: none src="" onload="google. j. l()" onerror="google. j. e()"></iframe><textarea id=wgjc style=display: none></textarea><textarea id=wwcache style=display: none></textarea><textarea id=csi style=display: none></textarea><textarea id=hcache style=display: none></textarea><span id=main><div id=ghead><div id=gog><div id=gbar><nobr><b class=gb 1>Web</b> <a href="http: //10. 204. 50. 40/imghp? hl=en&tab= wi" onclick=gbar. qs(this) class=gb 1>Images</a> <a href="https: //sslvpn. mycompnay. com/, Dana. Info=10. 204. 50. 40+? hl =en&tab=wv" onclick=gbar. qs(this) class=gb 1>Videos</a> <a href="https: //sslvpn. mycompnay. com/, Dana. Info=10. 204. 50. 40+ma ps? hl=en&tab=wl" onclick=gbar. qs(this) class=gb 1>Maps</a> <a href="https: //sslvpn. mycompnay. com/, Dana. Info=10. 204. 50. 40+nw shp? hl=en&tab=wn" onclick=gbar. qs(this) class=gb 1>News</a> <a • href="http: //10. 204. 50. 40/maps? hl=en&tab=wl" onclick=gbar. qs(this) class=gb 1>Maps</a> <a href="http: //10. 204. 50. 40/nwshp? hl=en&tab=wn" onclick=gbar. qs(this) class=gb 1>News</a> <a href="http: //10. 204. 50. 40/Home. aspx? hl=en&tab=w 0" class=gb 1>Arekkut</a> <a href="http: //10. 204. 50. 40/bkshp? hl=en&tab=wp"
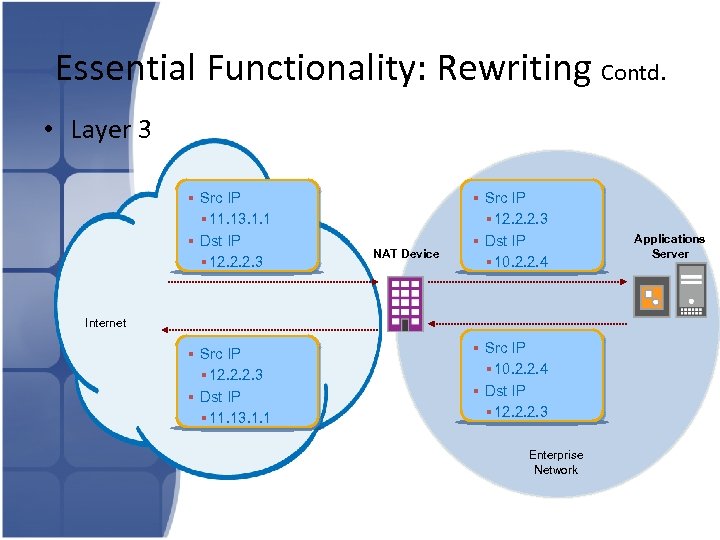
Essential Functionality: Rewriting Contd. • Layer 3 § Src IP § 11. 13. 1. 1 § Dst IP § 12. 2. 2. 3 NAT Device § Src IP § 12. 2. 2. 3 § Dst IP § 10. 2. 2. 4 Internet § Src IP § 12. 2. 2. 3 § Dst IP § 11. 13. 1. 1 § Src IP § 10. 2. 2. 4 § Dst IP § 12. 2. 2. 3 Enterprise Network Applications Server
Essential functionality: Granular Access Control • Policy based access control (based on identity & other factors) • For ex: assign role to user; assign resources to roles • Example policies: • • • Web Access UNIX file Access Windows File Access SSO Terminal Services
Essential functionality: Granualar Access Control Contd… • Example Role Assignments based on • • • Location Username Login time Group Etc etc. . Fine Grained Access control • SSL VPN being a layer 4 device, has an end user notion and thus Fine Grained Access control Is possible

Agenda Motivation 30000 ft view of SSLVPN Technology Security with SSLVPN: Authentication Security with SSLVPN: Endpoint Integrity • Security with SSLVPN: Authorization • Security with SSLVPN: User Education • •

Security with SSL VPN: Authentication • Remember: Internet-facing device! • Ensure Strong Authentication • Strength of a password policy – Password strength – Password expiry – Blacklisted pin dictionary • Typically, device vendor would ensure protection against: • Dictionary attacks • Brute force attacks • Denial of service attacks

Strong Authentication, Contd • Single factor Authentication • Two factor

Strength of Authentication Contd. • Secondary Authentication • Adaptive authentication

Strength of Authentication Contd. • Secondary Authentication – Can be used where stronger auth mechanism is required. – For example : • User does primary authentication to a Auth Server [could be certificate or Machine Auth] • Once Primary auth succeeds, he has to authenticate again to a Secondary Auth Server [which could be AD or LDAP or radius auth] • Secondary authentication combined with 2 factor, will be even more stronger, but an overkill.

Agenda Motivation 30000 ft view of SSLVPN Technology Security with SSLVPN: Authentication Security with SSLVPN: Endpoint Integrity • Security with SSLVPN: Authorization • Security with SSLVPN: User Education • •
Assess Endpoint’s security posture • Enable this feature, most vendors provide it • Enforce policy not to allow login if client not clean • Makes sure that the client has – – Trusted anitivirus software (eg: Norton AV 2010) Trusted Anti-Mal. Ware Updated database virus signatures for the antivirus. Availabilty of OS Patches. • Ensure file system has no suspicious content or processes. • Ensure file system has the content it is supposed to have; ie, not tampered with

Clean session termination • Data is left behind by the session! – – – Browser History Browser Cache Saved password and forms Keystroke loggers Cookies • Use cache cleaning functionality – Cleans up all Browser data on logout • Enable virtual keyboards during authentication
![Clean session termination Contd. • SVW [Secure virtual workspace] – Restricted, transient shell Clean session termination Contd. • SVW [Secure virtual workspace] – Restricted, transient shell](https://present5.com/presentation/41ac6f5c3f4c4151769d2954b2b3f405/image-22.jpg)
Clean session termination Contd. • SVW [Secure virtual workspace] – Restricted, transient shell – Created when user login-in – Destroyed on logout – Ensures no upload of dangerous content or download of critical data
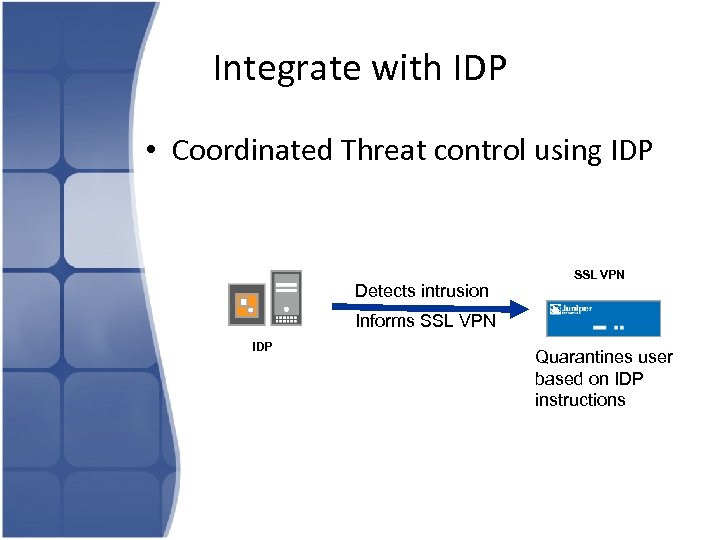
Integrate with IDP • Coordinated Threat control using IDP Detects intrusion SSL VPN Informs SSL VPN IDP Quarantines user based on IDP instructions

Agenda Motivation 30000 ft view of SSLVPN Technology Security with SSLVPN: Authentication Security with SSLVPN: Endpoint Integrity • Security with SSLVPN: Authorization • Security with SSLVPN: User Education • •

Security with SSLVPN: Authorization • Can remote users have the same level of access privilege as local users? Maybe not! • Exploit RBAC to the fullest • Role is a group of policies • Policies govern access to resources – – – Web Recource Access File Resource access [Both windows/UNIX] Telnet/SSH Access SSO Terminal Services access
Role Based Access Control Contd. • Vendors provide the ability to define roles as a function of several attributes • For example: – – – – Endpoint security posture Login time Login IP Login Name Directory attributes Group For ex: same user gets different privileges during office hours as opposed to off-hours

Agenda Motivation 30000 ft view of SSLVPN Technology Security with SSLVPN: Authentication Security with SSLVPN: Endpoint Integrity • Security with SSLVPN: Authorization • Security with SSLVPN: User Education • •

Bad people: evil outsiders and disgruntled insiders • Remember: internet-facing web device • Vulnerable to the usual set of web attacks • Injection Attacks – Most Common: Cross-site scripting • Parsing and detecting malicious script • Have multiple admins to verify config. – New one XSRF • Cross site Request forgery • Frame busting • Vendor provides some form of defence; but beware your customization may open up holes!
Key is: Train your users • Educate Users – Always ensure graceful exit – Don’t leave sessions unattended – Avoid logging in via Shared Computers – Don’t cache Password on browsers – Use Virtual keyboards for login

Thank you
41ac6f5c3f4c4151769d2954b2b3f405.ppt