3b3e99c1b89c43c7aef971a6b37e651a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Securing Legacy Software So. Be. Net User group meeting 25/06/2004

Objectives • Existing applications are enabled to operate in a networked environment • Adapter Suites • Application Platform Suites (J 2 EE, . NET, …) • • • Application Servers Enterprise Portals Integration Suites • Message-Oriented Middleware • Object-Request Brokers • Transaction Processing Monitors Preserve Security Level Compliance with Security Standards and regulations Manageable

Ubizen – trusted partner in IT Security • Ubizen has a vast experience in Application Security • Via a highly qualified consultancy team • • • Via product development • • • Risk Management, Security Policies, Procedures and Standards Architecture Review and Infrastructure design Penetration testing Application Vulnerability Assessment Implementation of best of breed security products AAA products Web Shielding (DMZ/Shield. TM) Proven Track record in IT Security • Top-3 Managed Security Service Provider World-wide • Number 1 in Europe • > 3200 devices under management • Incident Response • Forensics Investigation

Three research tracks for securing existing applications • Protect all access paths to and from the application • • • Apply automatic protocol security • • Interception and validation of the communication between components, modules and systems Shielding components, module and systems from malicious traffic Moving to a more formal model for protocol description and automatic application of protocol security at different layers of the stack. Monitoring and managing • Introduction of security infrastructure is only the first step… Keeping it properly configured and monitored 24 by 7 by experienced security experts is the second.

MULTI LAYER approach to Application Security • Deep Packet Inspection • • Protection at the transport layer • • Protection at the network layer Protection at the application layer Defense in depth • Perimeter • Demilitarized Zone Transactional Zone • Multi-tier architecture • • Coordination of Security Information between # tiers (e. g. SAML) Protection of end points • Not all layers on the #tiers are under control (e. g. OS, Language execution environment, App Server) Introduction of HIDS, Policy Compliance Modules, …
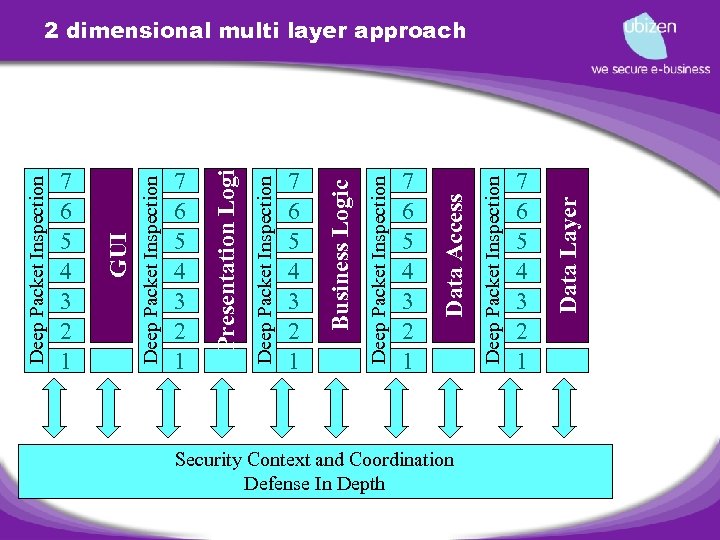
Deep Packet Inspection 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Deep Packet Inspection GUI 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Deep Packet Inspection Presentation Logic 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Deep Packet Inspection Business Logic 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Security Context and Coordination Defense In Depth Deep Packet Inspection Data Access 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Data Layer 2 dimensional multi layer approach
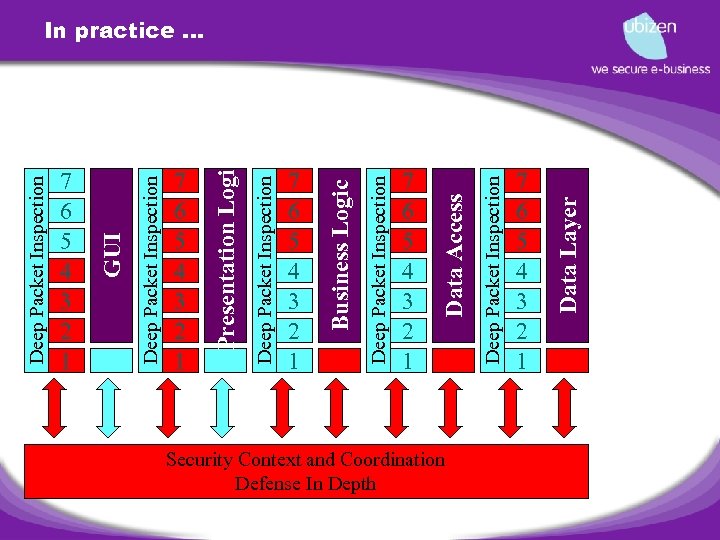
Deep Packet Inspection 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Deep Packet Inspection GUI 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Deep Packet Inspection Presentation Logic 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Deep Packet Inspection Business Logic 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Security Context and Coordination Defense In Depth Deep Packet Inspection Data Access 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Data Layer In practice …
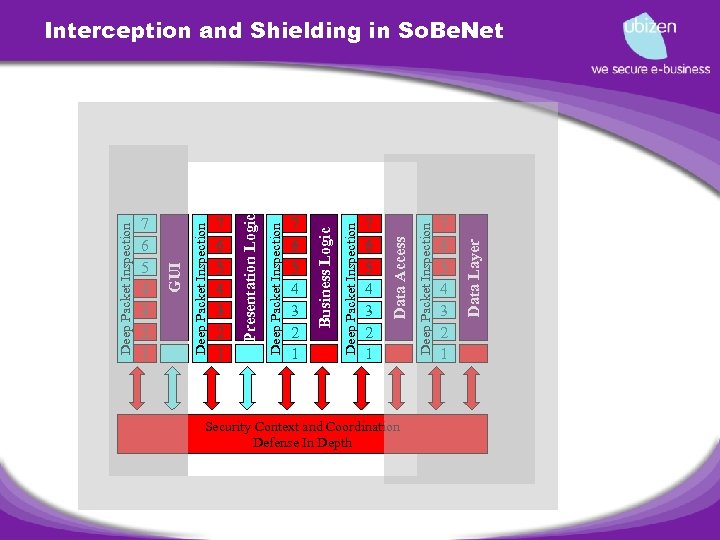
Deep Packet Inspection 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Deep Packet Inspection GUI 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Deep Packet Inspection Presentation Logic 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Deep Packet Inspection Business Logic 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Security Context and Coordination Defense In Depth Deep Packet Inspection Data Access 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Data Layer Interception and Shielding in So. Be. Net
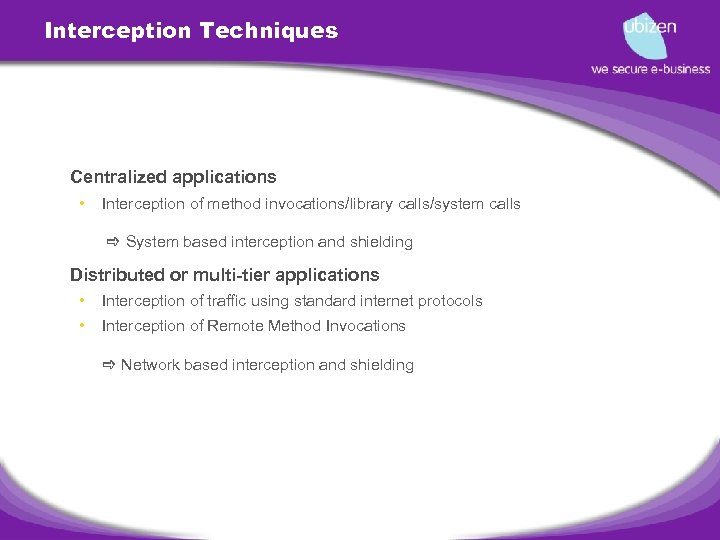
Interception Techniques • Centralized applications • Interception of method invocations/library calls/system calls System based interception and shielding • Distributed or multi-tier applications • Interception of traffic using standard internet protocols • Interception of Remote Method Invocations Network based interception and shielding

System based interception • Interception at the Operating System Level • • • Library Level • • Dynamical loaded libraries can be replaced with more secure versions Language Runtime Support • • Plug-able services of the OS (e. g. network or file io) Host Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems work at this level E. g. Load time modification of binary code Validation of pre and post conditions Audit-ability and forensics Application Platform Suite • • J 2 EE container services and components Microsoft. NET services and components
Network based interception • Proxy Architectures… • • Reverse Proxy • • Asymmetric Proxy (protocol encapsulates proxy support), no modification of client software Symmetric Proxy (general applicable but has influence on client software) Transparency • Link, network, transport level • Application Protocol level (e. g. HTTP, …) • User Application level
Scope definition for maximum valorization of the results? • Target is “Protecting” Legacy Applications … • … but these are built on evolving components Fall back on industry adapted standards • Web Application HTTP Firewalls • Service Oriented Architectures XML Firewalls • Application Platform Suites J 2 EE, . NET

Internet Application Protocols … • The most important internet protocols were never designed with security in mind • RFC’s describing the protocols allow often ambiguous interpretation Vendors choose for interoperability instead of security • Most applications use only a small part of the protocol definition … and vulnerabilities are often in the nonused protocol functionality

User Application Protocols … • Communication protocols at application level are rarely specified, nor formalized • User Application protocols get less attention because they are typically used once for a specific application • User Application protocols are more complex because of their dependency of a (huge) internal state combinatorial explosion of cases
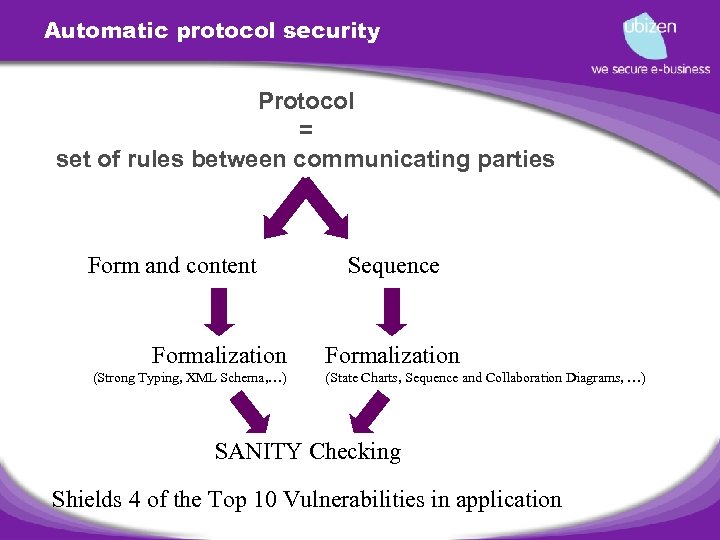
Automatic protocol security Protocol = set of rules between communicating parties Form and content Formalization (Strong Typing, XML Schema, …) Sequence Formalization (State Charts, Sequence and Collaboration Diagrams, …) SANITY Checking Shields 4 of the Top 10 Vulnerabilities in application

Manageability and Monitoring • Keeping the configuration up to date • • Default Deny Policy Automatic Learning of normal behavior Configuration automation policy proposals Monitoring of all the alerts triggered by the devices • Correlation of events from security components • • • Anomaly detection Audit Trail • • Coordination and exchange of security state between devices reduces the false positives What information is required for Forensics Performance Management

www. ubizen. com
3b3e99c1b89c43c7aef971a6b37e651a.ppt