cc9fd3007c677f592b7b2c88f889e238.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Securing Large Applications CSCI 5931 Web Security Rungang Mo, Yingying Sun

Content – Designing an online banking application; – Setting up the keys and certificates; – Configuring the database; – Building a database access tier; – Developing a web tier; – Constructing a client application; – Looking at areas for improvements.
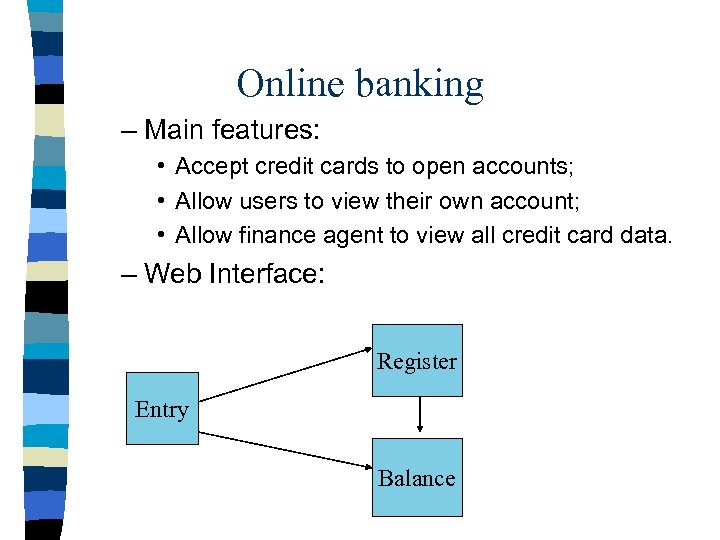
Online banking – Main features: • Accept credit cards to open accounts; • Allow users to view their own account; • Allow finance agent to view all credit card data. – Web Interface: Register Entry Balance
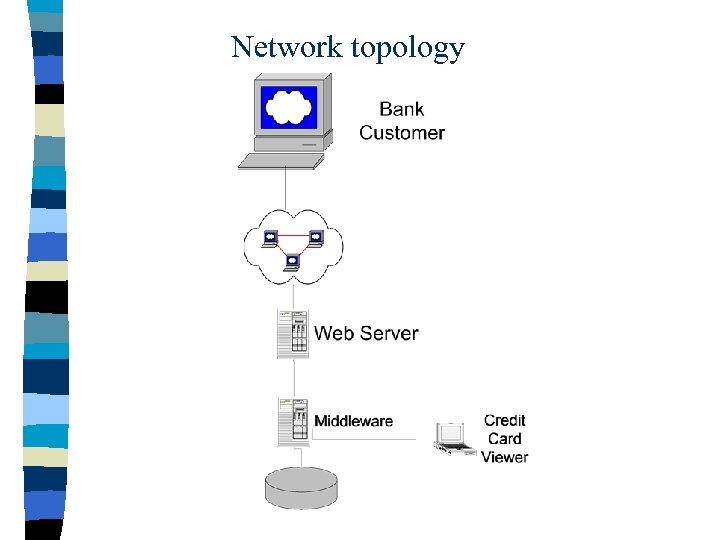
Network topology

Network connections – Customer to web server: • Most dangerous; • Using SSL with authentication. – Web server to middleware: • RMI over SSL. – Middleware to database: • RMI over SSL. – Credit card viewer to middleware: • Using SSL with authentication.
Application security – Database: • Encrypt credit card numbers by public key; • Run secure JDBC driver on the database. – Middleware (Bank): • Only allow connections from web server and credit card client. – Credit card client: • Decrypt and view credit cards
Application security (cont. ) – Web server: • Block access to most ports with a firewall. – Web browser: • Using client authentication; • The browser protects the private key with password-based encryption;
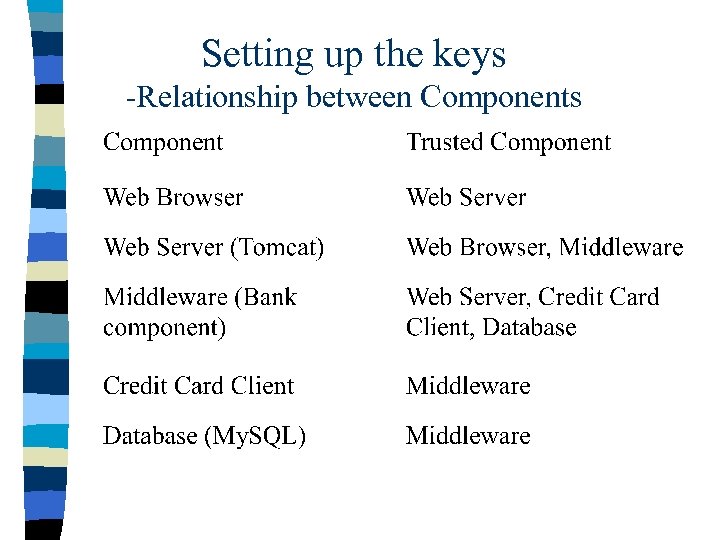
Setting up the keys -Relationship between Components
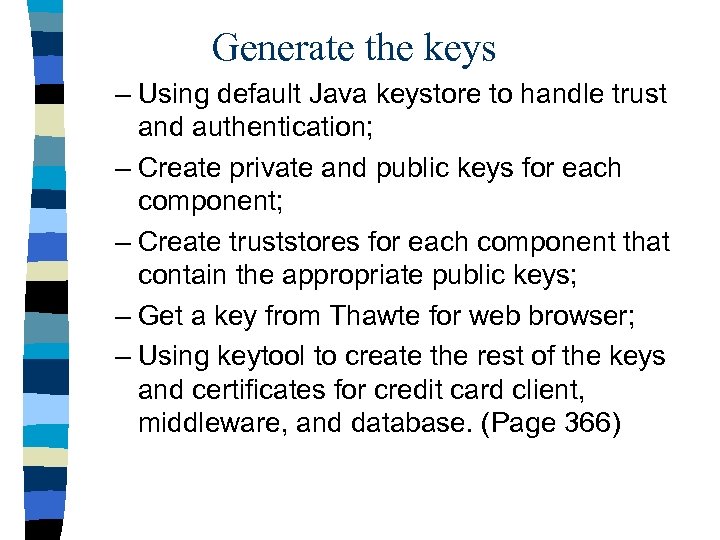
Generate the keys – Using default Java keystore to handle trust and authentication; – Create private and public keys for each component; – Create truststores for each component that contain the appropriate public keys; – Get a key from Thawte for web browser; – Using keytool to create the rest of the keys and certificates for credit card client, middleware, and database. (Page 366)

Export/ Import the certificates – In order to establish trust, we need to export all the certificate that need to be trusted: • c: > keytool -export -keystore bank. Key. Store file bank. cer – Set up trust by creating trust store: • Web Server: need to trust a number of certificates • Certificate Recognition in Internet Explorer: Page 367.
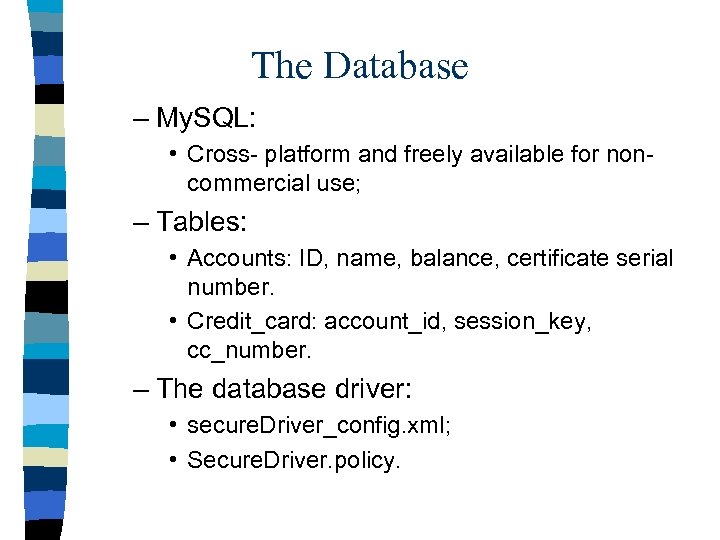
The Database – My. SQL: • Cross- platform and freely available for noncommercial use; – Tables: • Accounts: ID, name, balance, certificate serial number. • Credit_card: account_id, session_key, cc_number. – The database driver: • secure. Driver_config. xml; • Secure. Driver. policy.
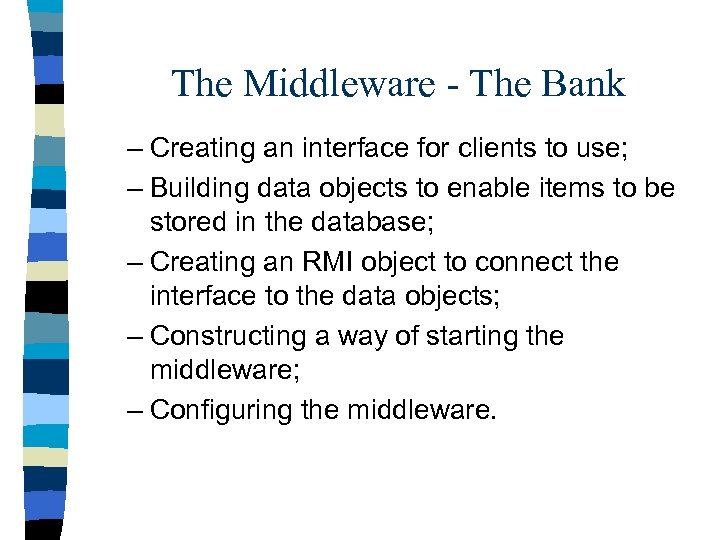
The Middleware - The Bank – Creating an interface for clients to use; – Building data objects to enable items to be stored in the database; – Creating an RMI object to connect the interface to the data objects; – Constructing a way of starting the middleware; – Configuring the middleware.

The Bank Interface – Four methods contained in the Bank class: • register(): register a new account given basic user information. • get. Account(): find the account for a given client certificate serial number. • get. Credit. Card. DBO(): fetch the encrypted credit card information for a given account ID. • get. All. Credit. Card. Account. IDs(): get a list of all the account Ids in the database.
Data objects – Account class: • Hold information, which is not encrypted; • Contains account. ID, balance, customer name, certificate serial number; – Registration. Information class: • Wrap up all of the user-entered information; • Contains credit card number, balance, name, certificate serial number; – Credit. Card. DBO class:
Data objects (cont. ) – Database. Operations class: • Class for performing database operations; • Use the JDBC proxy to encrypt the connection using RMI over SSL; • Store Credit. Card. DBO object and Account object in the database separately; • Use the BASE 64 encoder and decoder classes;
Bank Implementation – Creating an RMI object: Bank. Impl to connect the interface to the data objects; – Extend Unicast. Remote. Object so that it can be used over RMI; – Important methods: • • • Bank. Impl (); register (); get. Account (); get. All. Credit. Card. Account. IDs (); get. Credit. Card. DBO ();

Starting the Bank – The Bank. Init class: • Construct a Bank. Impl object with a Properties object that we read off the file system; • Commond-line argument indicates the properties file to read; • Call Naming. rebind () on it so that it becomes available for RMI client; • A bug in JSSE v. 1. 0. 2 and earlier.
Configuration – config. properties: define JDBC configuration and the location of the public key; – Bank. Init. policy: start up the bank; – Collecting the files: • Secure. Driver. Client. jar; • Bank. jar; • Associated data: keystore/ truststore/ creditcard. cer – Running the Bank:
The Web Server – Main functions: • Registration; • Account viewing. – Using SSL client authentication to identify users; – Build the servlets and JSPs for the web tier; – Look at packaging the web application and deploying to Tomcat; – Run the application;
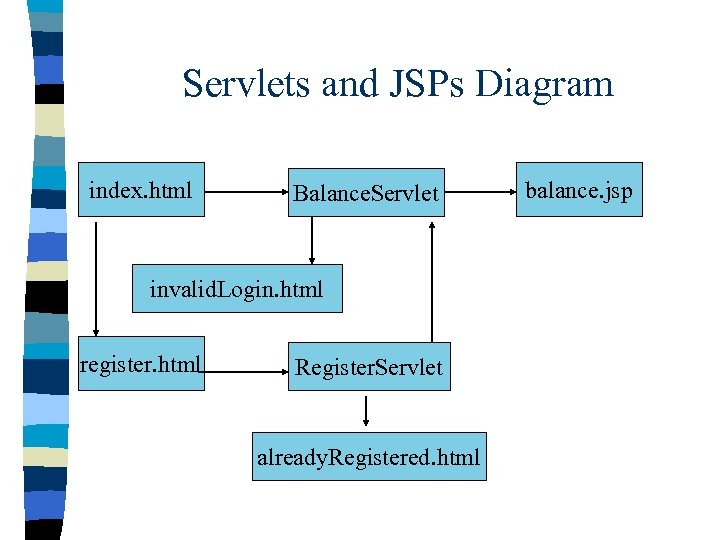
Servlets and JSPs Diagram index. html Balance. Servlet invalid. Login. html register. html Register. Servlet already. Registered. html balance. jsp
Servlets and JSPs – HTMLs: • Register: sends data to Register. Servlet; • Login: takes users to the Balance. Servlet; – Servlets: • Register. Servlet: handles creating account; • Balance. Servlet: loads account information, and sends it to a JSP for display • Abstract. Ecommerce. Servlet: – init(); – get. Certificate(); – get. Redirect. URL(); – balance. jsp:

Packaging the web application – Policy file for Tomcat: tomcat. policy – Modifying web. xml; – Build the WAR file; – Copy the WAR file into Tomcat; – Delete other Webapps and Add the Bank. App; – Enable SSL; – Enable policy support; – Add support file – Edit web server startup scripts

Start the application – Start the RMI registry on the database server; – Start the database driver; – Start the RMI registry on the bank; – Start the web server.
Credit Card Client – Allows a user to view all of the credit cards in the database, decrypting them with the private key; – Modifications on Chapter 10 example: • The GUI for password instead of setting the keystore password on the command line; • Adding support for RMI: Credit. Card. Client class: – decrypt. Credit. Card. DBO(); – main(); – get. Password();

Credit Card Client (Cont. ) – Credit card client policy file: Credit. Card. Client. policy (Page 409); – Packaging the credit card client: • create a JAR file, Credit. Card. Client. jar; • create a directory for the credit card client; – Running the credit card client:

Possible Modifications – Logging: – Using SSL: – Web browser authentication: – The database: – Encrypting SSL keys:

Reference – Jess Garms, Daniel Somerfield-Professional Java Security; – http: //www. wrox. com; – http: //xml. apache. org/xerces-j/index. html; – http: //jakarta. apache. org/tomcat/index. html; – http: //www. mysql. com – http: //www. thawte. com/certs/personal – http: //www. bouncycastle. org
cc9fd3007c677f592b7b2c88f889e238.ppt