3470730d70264c2aff07611be7eef974.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Securing Email Using PGP and Digital Certificates Putting together cipher, digital signature, and MD 5 one-way hashing - email/PGP - Network security
Securing Email Using PGP and Digital Certificates Putting together cipher, digital signature, and MD 5 one-way hashing - email/PGP - Network security
 Outline How email works? n Signing email n Securing contents n PGP -- Pretty Good Privacy and PEM -- Privacy Enhanced Mail n Public Key Certificates n 2 - email/PGP - Network security
Outline How email works? n Signing email n Securing contents n PGP -- Pretty Good Privacy and PEM -- Privacy Enhanced Mail n Public Key Certificates n 2 - email/PGP - Network security
 How does email work? n Suppose that Alice in Australia wants to send a message to Bob in USA via email ç Alice starts an email program on her computer, and types in Bob’s email address ç Alice composes (writes) the message ç Alice hits a special key to tell the computer that the message is ready to go! 3 - email/PGP - Network security
How does email work? n Suppose that Alice in Australia wants to send a message to Bob in USA via email ç Alice starts an email program on her computer, and types in Bob’s email address ç Alice composes (writes) the message ç Alice hits a special key to tell the computer that the message is ready to go! 3 - email/PGP - Network security
 How does email work ? (2) ç Alice’s email system adds a header to the message (including destination, return address, time stamp etc), and sends it to the nearest email gateway (a computer) ç The message is relayed from computer to computer before finally reaching Bob’s computer 4 - email/PGP - Network security
How does email work ? (2) ç Alice’s email system adds a header to the message (including destination, return address, time stamp etc), and sends it to the nearest email gateway (a computer) ç The message is relayed from computer to computer before finally reaching Bob’s computer 4 - email/PGP - Network security
 A sample message to: bob@xyz. com. us from: alice@abc. com. au subject: hello date: Mon, 26 Aug 2001 13: 23: 47 Hi Bob, I am coming down to states in January. Alice 5 - email/PGP - Network security
A sample message to: bob@xyz. com. us from: alice@abc. com. au subject: hello date: Mon, 26 Aug 2001 13: 23: 47 Hi Bob, I am coming down to states in January. Alice 5 - email/PGP - Network security
 header + message header message 6 - email/PGP - Network security
header + message header message 6 - email/PGP - Network security
 Possible attacks n spoofing ç third party may impersonate Alice and a send a fake/modified message to Bob n Eavesdropping ç party sitting between Alice and Bob may a peep communications between them n Replay ç party sitting between Alice and Bob may a re-send to Bob an old message from Alice 7 - email/PGP - Network security
Possible attacks n spoofing ç third party may impersonate Alice and a send a fake/modified message to Bob n Eavesdropping ç party sitting between Alice and Bob may a peep communications between them n Replay ç party sitting between Alice and Bob may a re-send to Bob an old message from Alice 7 - email/PGP - Network security
 Preventing spoofing & replay n Use ç RSA digital signature ç MD 5 one-way hash algorithm 8 - email/PGP - Network security
Preventing spoofing & replay n Use ç RSA digital signature ç MD 5 one-way hash algorithm 8 - email/PGP - Network security
 What Alice has to do? n prepares a pair of public and secret keys ç public key: (ea, na) ç secret key: da registers her public key in a publicly available site and circulates it among friends (and also attaches it to the end of all her email messages). n composes a message. n 9 - email/PGP - Network security
What Alice has to do? n prepares a pair of public and secret keys ç public key: (ea, na) ç secret key: da registers her public key in a publicly available site and circulates it among friends (and also attaches it to the end of all her email messages). n composes a message. n 9 - email/PGP - Network security
 What Alice’s computer has to do? attaches to the message a header (to: , from: , date: subject: , etc) n uses MD 5 to hash the pair (message, header) into a 128 -bit value n uses Alice’s secret key da to sign (decrypt) the 128 -bit value n sends to the email gateway a triplet n ç (header, message, signature) 10 - email/PGP - Network security
What Alice’s computer has to do? attaches to the message a header (to: , from: , date: subject: , etc) n uses MD 5 to hash the pair (message, header) into a 128 -bit value n uses Alice’s secret key da to sign (decrypt) the 128 -bit value n sends to the email gateway a triplet n ç (header, message, signature) 10 - email/PGP - Network security
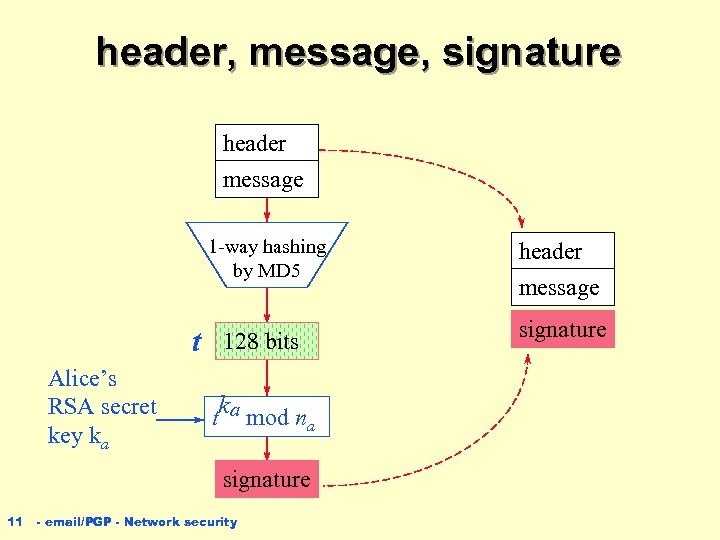 header, message, signature header message 1 -way hashing by MD 5 t Alice’s RSA secret key ka 128 bits tka mod na signature 11 - email/PGP - Network security header message signature
header, message, signature header message 1 -way hashing by MD 5 t Alice’s RSA secret key ka 128 bits tka mod na signature 11 - email/PGP - Network security header message signature
 What Bob’s computer has to do? finds out Alice’s public key (ea, na) n verifies (header, message, signature) n if OK, accepts that it is a message from Alice n Otherwise, informs Bob that it is NOT a genuine message from Alice n 12 - email/PGP - Network security
What Bob’s computer has to do? finds out Alice’s public key (ea, na) n verifies (header, message, signature) n if OK, accepts that it is a message from Alice n Otherwise, informs Bob that it is NOT a genuine message from Alice n 12 - email/PGP - Network security
 Check how does the previous scheme prevent spoofing and replaying ? n does Bob have to have his public and secret keys ? why ? n 13 - email/PGP - Network security
Check how does the previous scheme prevent spoofing and replaying ? n does Bob have to have his public and secret keys ? why ? n 13 - email/PGP - Network security
 Preventing peeping n the basic idea to encrypt each message by the use of hybrid RSA and IDEA ç IDEA is a private key cipher lkey: 128 bits, plain/ciphertext: 64 bits n an extra requirement: ç Bob should lpublish his public key (eb, nb) lkeeps his secret key db in a safe place 14 - email/PGP - Network security
Preventing peeping n the basic idea to encrypt each message by the use of hybrid RSA and IDEA ç IDEA is a private key cipher lkey: 128 bits, plain/ciphertext: 64 bits n an extra requirement: ç Bob should lpublish his public key (eb, nb) lkeeps his secret key db in a safe place 14 - email/PGP - Network security
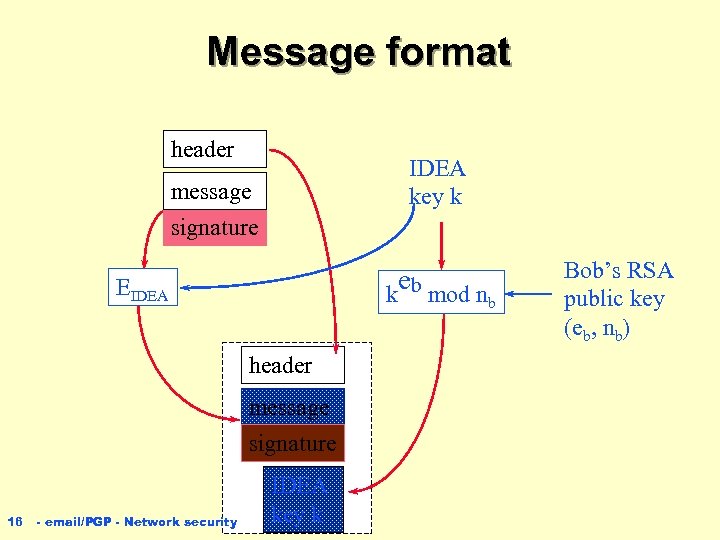
 Alice’s computer As before, uses Alice’s secret key da to sign a message and gets a triplet (header, message, signature) n picks a random 128 -bit IDEA key k n encrypts (message, signature) using IDEA under the key k n finds out Bob’s public key (eb, nb) n encrypts k using (eb, nb) n 15 - email/PGP - Network security
Alice’s computer As before, uses Alice’s secret key da to sign a message and gets a triplet (header, message, signature) n picks a random 128 -bit IDEA key k n encrypts (message, signature) using IDEA under the key k n finds out Bob’s public key (eb, nb) n encrypts k using (eb, nb) n 15 - email/PGP - Network security
 Message format header IDEA key k message signature e k b mod n EIDEA header message signature 16 - email/PGP - Network security IDEA key k b Bob’s RSA public key (eb, nb)
Message format header IDEA key k message signature e k b mod n EIDEA header message signature 16 - email/PGP - Network security IDEA key k b Bob’s RSA public key (eb, nb)
 Message sent by Alice n Alice’s computer sends to Bob’s computer four (4) parts ç header, un-encrypted ç message, encrypted using IDEA under k ç signature, encrypted using IDEA under k ç IDEA key k, encrypted using Bob’s RSA public key (eb, nb) 17 - email/PGP - Network security
Message sent by Alice n Alice’s computer sends to Bob’s computer four (4) parts ç header, un-encrypted ç message, encrypted using IDEA under k ç signature, encrypted using IDEA under k ç IDEA key k, encrypted using Bob’s RSA public key (eb, nb) 17 - email/PGP - Network security
 header + message to: bob@xyz. com. us from: alice@uvw. com. au subject: hello date: Mon, 26 Feb 1996 13: 23: 47 Hi Bob, Meet in January at home ? Alice 18 - email/PGP - Network security
header + message to: bob@xyz. com. us from: alice@uvw. com. au subject: hello date: Mon, 26 Feb 1996 13: 23: 47 Hi Bob, Meet in January at home ? Alice 18 - email/PGP - Network security
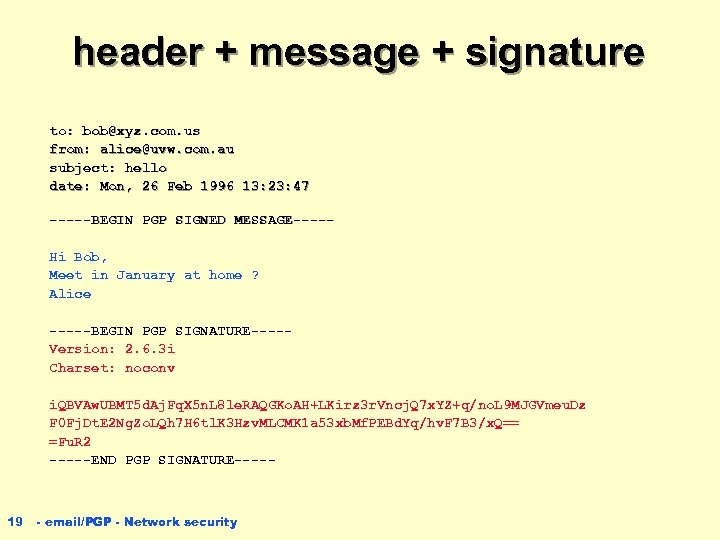 header + message + signature to: bob@xyz. com. us from: alice@uvw. com. au subject: hello date: Mon, 26 Feb 1996 13: 23: 47 -----BEGIN PGP SIGNED MESSAGE----Hi Bob, Meet in January at home ? Alice -----BEGIN PGP SIGNATURE----Version: 2. 6. 3 i Charset: noconv i. QBVAw. UBMT 5 d. Aj. Fq. X 5 n. L 8 le. RAQGKo. AH+LKirz 3 r. Vncj. Q 7 x. YZ+q/no. L 9 MJGVmeu. Dz F 0 Fj. Dt. E 2 Ng. Zo. LQh 7 H 6 tl. K 3 Hzv. MLCMK 1 a 53 xb. Mf. PEBd. Yq/hv. F 7 B 3/x. Q== =Fu. R 2 -----END PGP SIGNATURE----- 19 - email/PGP - Network security
header + message + signature to: bob@xyz. com. us from: alice@uvw. com. au subject: hello date: Mon, 26 Feb 1996 13: 23: 47 -----BEGIN PGP SIGNED MESSAGE----Hi Bob, Meet in January at home ? Alice -----BEGIN PGP SIGNATURE----Version: 2. 6. 3 i Charset: noconv i. QBVAw. UBMT 5 d. Aj. Fq. X 5 n. L 8 le. RAQGKo. AH+LKirz 3 r. Vncj. Q 7 x. YZ+q/no. L 9 MJGVmeu. Dz F 0 Fj. Dt. E 2 Ng. Zo. LQh 7 H 6 tl. K 3 Hzv. MLCMK 1 a 53 xb. Mf. PEBd. Yq/hv. F 7 B 3/x. Q== =Fu. R 2 -----END PGP SIGNATURE----- 19 - email/PGP - Network security
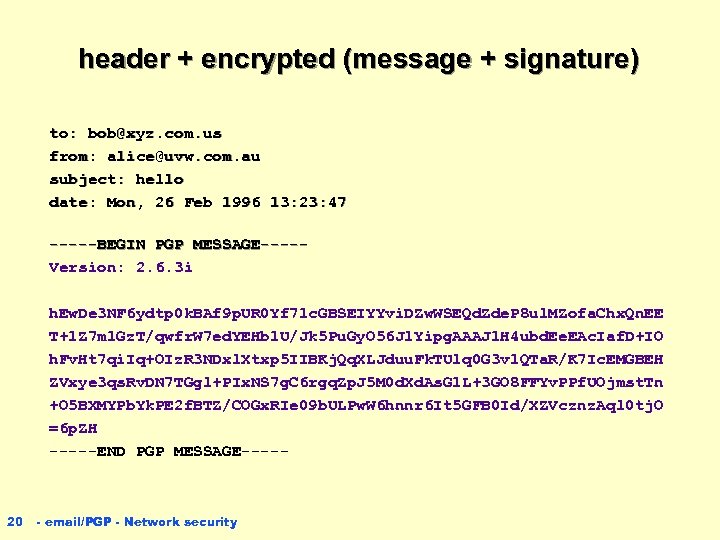 header + encrypted (message + signature) to: bob@xyz. com. us from: alice@uvw. com. au subject: hello date: Mon, 26 Feb 1996 13: 23: 47 -----BEGIN PGP MESSAGE----Version: 2. 6. 3 i h. Ew. De 3 NF 6 ydtp 0 k. BAf 9 p. UR 0 Yf 71 c. GBSEIYYvi. DZw. WSEQd. Zde. P 8 ul. MZofa. Chx. Qn. EE T+1 Z 7 m 1 Gz. T/qwfr. W 7 ed. YEHb 1 U/Jk 5 Pu. Gy. O 56 Jl. Yipg. AAAJ 1 H 4 ubd. Ee. EAc. Iaf. D+IO h. Fv. Ht 7 qi. Iq+OIz. R 3 NDxl. Xtxp 5 IIBKj. Qq. XLJduu. Fk. TUlq 0 G 3 v 1 QTa. R/K 7 Ic. EMGBEH ZVxye 3 qs. Rv. DN 7 TGgl+PIx. NS 7 g. C 6 rgq. Zp. J 5 M 0 d. Xd. As. G 1 L+3 GO 8 FFYv. PPf. UOjmst. Tn +O 5 BXMYPb. Yk. PE 2 f. BTZ/COGx. RIe 09 b. ULPw. W 6 hnnr 6 It 5 GFB 0 Id/XZVcznz. Aql 0 tj. O =6 p. ZH -----END PGP MESSAGE----- 20 - email/PGP - Network security
header + encrypted (message + signature) to: bob@xyz. com. us from: alice@uvw. com. au subject: hello date: Mon, 26 Feb 1996 13: 23: 47 -----BEGIN PGP MESSAGE----Version: 2. 6. 3 i h. Ew. De 3 NF 6 ydtp 0 k. BAf 9 p. UR 0 Yf 71 c. GBSEIYYvi. DZw. WSEQd. Zde. P 8 ul. MZofa. Chx. Qn. EE T+1 Z 7 m 1 Gz. T/qwfr. W 7 ed. YEHb 1 U/Jk 5 Pu. Gy. O 56 Jl. Yipg. AAAJ 1 H 4 ubd. Ee. EAc. Iaf. D+IO h. Fv. Ht 7 qi. Iq+OIz. R 3 NDxl. Xtxp 5 IIBKj. Qq. XLJduu. Fk. TUlq 0 G 3 v 1 QTa. R/K 7 Ic. EMGBEH ZVxye 3 qs. Rv. DN 7 TGgl+PIx. NS 7 g. C 6 rgq. Zp. J 5 M 0 d. Xd. As. G 1 L+3 GO 8 FFYv. PPf. UOjmst. Tn +O 5 BXMYPb. Yk. PE 2 f. BTZ/COGx. RIe 09 b. ULPw. W 6 hnnr 6 It 5 GFB 0 Id/XZVcznz. Aql 0 tj. O =6 p. ZH -----END PGP MESSAGE----- 20 - email/PGP - Network security
 Bob’s computer n When receiving the parts from Alice, Bob’s computer ç uses Bob’s secret key db to decrypt the 4 th part and extract IDEA key k ç uses k and IDEA to decrypt the 2 nd & 3 rd parts ç uses Alice’s public key (ea, na) to check Alice’s signature on the 1 st & 2 nd parts ç OK, accepts it as a genuine message if from Alice 21 - email/PGP - Network security
Bob’s computer n When receiving the parts from Alice, Bob’s computer ç uses Bob’s secret key db to decrypt the 4 th part and extract IDEA key k ç uses k and IDEA to decrypt the 2 nd & 3 rd parts ç uses Alice’s public key (ea, na) to check Alice’s signature on the 1 st & 2 nd parts ç OK, accepts it as a genuine message if from Alice 21 - email/PGP - Network security
 Check by yourself n explain how ç spoofing ç eavesdropping ç replay are prevented n 22 why the 1 st part (the header) is NOT encrypted ? - email/PGP - Network security
Check by yourself n explain how ç spoofing ç eavesdropping ç replay are prevented n 22 why the 1 st part (the header) is NOT encrypted ? - email/PGP - Network security
 Signature-and-encryption or encryption-and-signature n 2 alternative approaches to achieving authenticity and confidentiality ç Signature-and-encryption Signing the message first, followed by “sealing” the message-signature pair ç Encryption-and-signature “scrambling” the message first, following by signing the ciphertext 23 - email/PGP - Network security
Signature-and-encryption or encryption-and-signature n 2 alternative approaches to achieving authenticity and confidentiality ç Signature-and-encryption Signing the message first, followed by “sealing” the message-signature pair ç Encryption-and-signature “scrambling” the message first, following by signing the ciphertext 23 - email/PGP - Network security
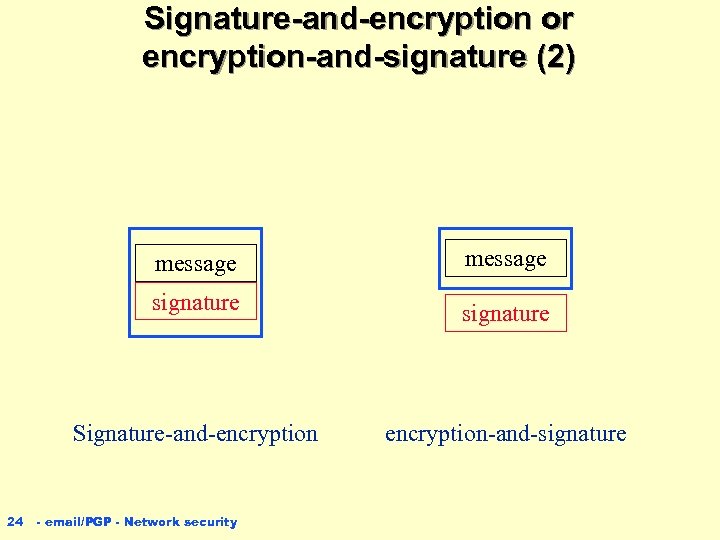 Signature-and-encryption or encryption-and-signature (2) message signature Signature-and-encryption 24 message encryption-and-signature - email/PGP - Network security
Signature-and-encryption or encryption-and-signature (2) message signature Signature-and-encryption 24 message encryption-and-signature - email/PGP - Network security
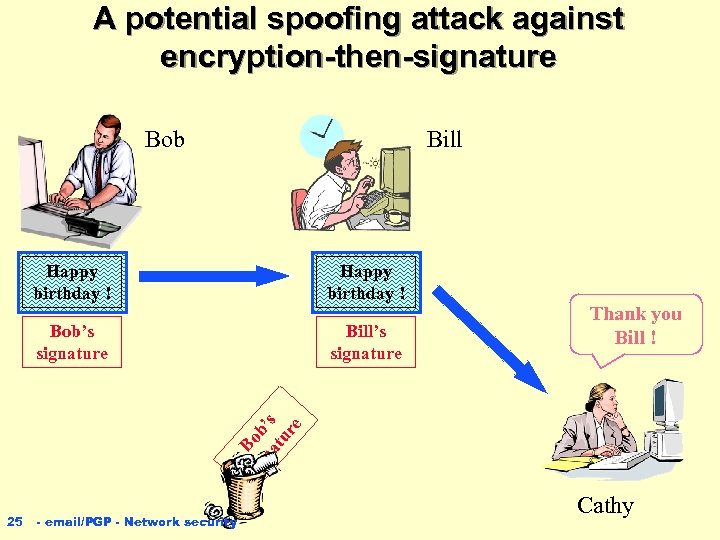 A potential spoofing attack against encryption-then-signature Bob Bill Happy birthday ! Bob’s signature Bill’s signature Thank you Bill ! sig Bob na ’s tu re Happy birthday ! 25 - email/PGP - Network security Cathy
A potential spoofing attack against encryption-then-signature Bob Bill Happy birthday ! Bob’s signature Bill’s signature Thank you Bill ! sig Bob na ’s tu re Happy birthday ! 25 - email/PGP - Network security Cathy
 The importance of order n 26 Use “signature followed by encryption” in your applications ! - email/PGP - Network security
The importance of order n 26 Use “signature followed by encryption” in your applications ! - email/PGP - Network security
 Reminder: Marvin’s “Public Key Faking” Attack n n Instead of just eavesdropping, Marvin can try a more active attack! Outline of the New Attack: ç Marvin generates an RSA key pair l Public key = Kpub_* = (N_*, e_*) l Secret key = Ksec_* = d_* ç Marvin sends the following email to Alice, pretending to be Bob: l Hi Alice, ¥ Please use my new public key from now on to encrypt messages to me. My new public key is Kpub_*. ¥ Yours sincerely, Bob. 27 ç Marvin decrypts any messages Alice sends to Bob (encrypted with Kpub_*), using Ksec_*. - email/PGP - Network security
Reminder: Marvin’s “Public Key Faking” Attack n n Instead of just eavesdropping, Marvin can try a more active attack! Outline of the New Attack: ç Marvin generates an RSA key pair l Public key = Kpub_* = (N_*, e_*) l Secret key = Ksec_* = d_* ç Marvin sends the following email to Alice, pretending to be Bob: l Hi Alice, ¥ Please use my new public key from now on to encrypt messages to me. My new public key is Kpub_*. ¥ Yours sincerely, Bob. 27 ç Marvin decrypts any messages Alice sends to Bob (encrypted with Kpub_*), using Ksec_*. - email/PGP - Network security
 Preventing Marvin’s Attack (1) n Marvin’s Attack illustrates that: çIn the context of Public Key Encryption, Alice must make sure she is not using a “fake public key” produced by Marvin (like Kpub_*) to encrypt messages to Bob çIn the context of Digital Signatures, Alice must make sure she is not using a “fake public key” produced by Marvin to verify digital signatures on documents claimed to be produced by Bob. 28 - email/PGP - Network security
Preventing Marvin’s Attack (1) n Marvin’s Attack illustrates that: çIn the context of Public Key Encryption, Alice must make sure she is not using a “fake public key” produced by Marvin (like Kpub_*) to encrypt messages to Bob çIn the context of Digital Signatures, Alice must make sure she is not using a “fake public key” produced by Marvin to verify digital signatures on documents claimed to be produced by Bob. 28 - email/PGP - Network security
 Preventing Marvin’s Attack (2) n n n 29 When Alice obtains Bob’s public key from some source, she is really receiving a document C containing a statement of the form “Bob’s public key is X”. To prevent Marvin’s attack, Alice wants to check the integrity of the document C before she believes the statement it contains. This is commonly done using a “Public Key Certification” system in conjunction with a digital signature scheme - This system is described in the following slides. - email/PGP - Network security
Preventing Marvin’s Attack (2) n n n 29 When Alice obtains Bob’s public key from some source, she is really receiving a document C containing a statement of the form “Bob’s public key is X”. To prevent Marvin’s attack, Alice wants to check the integrity of the document C before she believes the statement it contains. This is commonly done using a “Public Key Certification” system in conjunction with a digital signature scheme - This system is described in the following slides. - email/PGP - Network security
 Public Key Certification System (1) n n A Public Key Certification System requires the establishment of (at least one) Trusted Certification Authority (CA). The CA is an organization known to all users and trusted by the users to: ç Issue Certificates by following properly the procedure described in following slide ç Guard its secret digital signature key SK_CA very well! n 30 All users obtain the CA’s public digital signature key PK_CA directly from the CA. - email/PGP - Network security
Public Key Certification System (1) n n A Public Key Certification System requires the establishment of (at least one) Trusted Certification Authority (CA). The CA is an organization known to all users and trusted by the users to: ç Issue Certificates by following properly the procedure described in following slide ç Guard its secret digital signature key SK_CA very well! n 30 All users obtain the CA’s public digital signature key PK_CA directly from the CA. - email/PGP - Network security
 Issuing Digital Certificates (1) n The CA issues Digital Certificates to users as follows: çA user Bob generates a key pair (Kpub, Ksec). çBob goes (ideally physically) to the CA, gives his public key Kpub, and declares “I’m Bob Smith, and Kpub is my public key!” çThe CA asks Bob to present strong proof of identity (eg Passport, driver’s licence), to ensure that CA is really talking to Bob Smith (and not Marvin, for example). çIf CA is convinced it is really talking to Bob Smith, the CA produces a digital certificate for Bob (see next slide for detailed content). 31 - email/PGP - Network security
Issuing Digital Certificates (1) n The CA issues Digital Certificates to users as follows: çA user Bob generates a key pair (Kpub, Ksec). çBob goes (ideally physically) to the CA, gives his public key Kpub, and declares “I’m Bob Smith, and Kpub is my public key!” çThe CA asks Bob to present strong proof of identity (eg Passport, driver’s licence), to ensure that CA is really talking to Bob Smith (and not Marvin, for example). çIf CA is convinced it is really talking to Bob Smith, the CA produces a digital certificate for Bob (see next slide for detailed content). 31 - email/PGP - Network security
 Issuing Digital Certificates (2) n The Digital Certificate C_Bob given to Bob by CA consists of essentially FIVE parts: çPart A. Bob’s unique identification information (eg Full name, address, etc) çPart B. Bob’s public key, Kpub çPart C. A unique certificate serial no. çPart D. Issue time, Expiry time, and any other conditions of use. çPart E. The CA’s digital signature on the document consisting of Parts (A, B, C, D). n 32 So C_Bob = (A, B, C, D, E). - email/PGP - Network security
Issuing Digital Certificates (2) n The Digital Certificate C_Bob given to Bob by CA consists of essentially FIVE parts: çPart A. Bob’s unique identification information (eg Full name, address, etc) çPart B. Bob’s public key, Kpub çPart C. A unique certificate serial no. çPart D. Issue time, Expiry time, and any other conditions of use. çPart E. The CA’s digital signature on the document consisting of Parts (A, B, C, D). n 32 So C_Bob = (A, B, C, D, E). - email/PGP - Network security
 Using Digital Certificates (1) n n Bob distributes his digital certificate C_Bob. Note that: çThe certificate C_Bob is NOT secret çBob CANNOT use the certificate C_Bob by itself as a proof of identity (since anyone can get a copy of it). n 33 When Alice needs Bob’s public key (eg to encrypt a message to Bob, or to verify Bob’s signature on a document) she obtains Bob’s digital certificate C_Bob (eg from Bob’s web server). - email/PGP - Network security
Using Digital Certificates (1) n n Bob distributes his digital certificate C_Bob. Note that: çThe certificate C_Bob is NOT secret çBob CANNOT use the certificate C_Bob by itself as a proof of identity (since anyone can get a copy of it). n 33 When Alice needs Bob’s public key (eg to encrypt a message to Bob, or to verify Bob’s signature on a document) she obtains Bob’s digital certificate C_Bob (eg from Bob’s web server). - email/PGP - Network security
 Using Digital Certificates (2) n n From Part B of the certificate C_Bob, Alice extracts Bob’s public key PK_Bob. But before using PK_Bob, Alice verifies that the certificate C_Bob is a valid certificate for Bob - This means that Alice verifies that: ç 1. C_Bob contains (in part E) a valid signature by CA on the rest of the certificate (parts A, B, C, D). ç 2. Part A of C_Bob contains Bob’s correct (unique) identification details (name, address, …). ç 3. All the conditions stated in part D of the certificate C_Bob are valid (eg certificate has not expired yet). 34 Alice rejects C_Bob if it fails the test above! - email/PGP - Network security n
Using Digital Certificates (2) n n From Part B of the certificate C_Bob, Alice extracts Bob’s public key PK_Bob. But before using PK_Bob, Alice verifies that the certificate C_Bob is a valid certificate for Bob - This means that Alice verifies that: ç 1. C_Bob contains (in part E) a valid signature by CA on the rest of the certificate (parts A, B, C, D). ç 2. Part A of C_Bob contains Bob’s correct (unique) identification details (name, address, …). ç 3. All the conditions stated in part D of the certificate C_Bob are valid (eg certificate has not expired yet). 34 Alice rejects C_Bob if it fails the test above! - email/PGP - Network security n


