36c0f99f181f7ec0e91709b8f6bc3b2e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 88

Securing Databases in the Cloud Steven C. Markey, MSIS, PMP, CISSP, CIPP, CISM, CISA, STS-EV, CCSK, Comp. TIA Cloud Essentials Principal, n. Control, LLC Adjunct Professor President, Cloud Security Alliance – Delaware Valley Chapter (CSA-Del. Val)

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Presentation Overview – Cloud Overview – Database Overview – Big Data Overview – Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Securing Cloud-Based DB Solutions • Vulnerabilities Found in Cloud-Based Offerings • Securing Your Relational Cloud-Based Offerings • Securing Your Non-Relational Cloud-Based Offerings – Privacy & Data Protection for Cloud-Based DBs – Case Study: My. SQL & Simple. DB in the Cloud
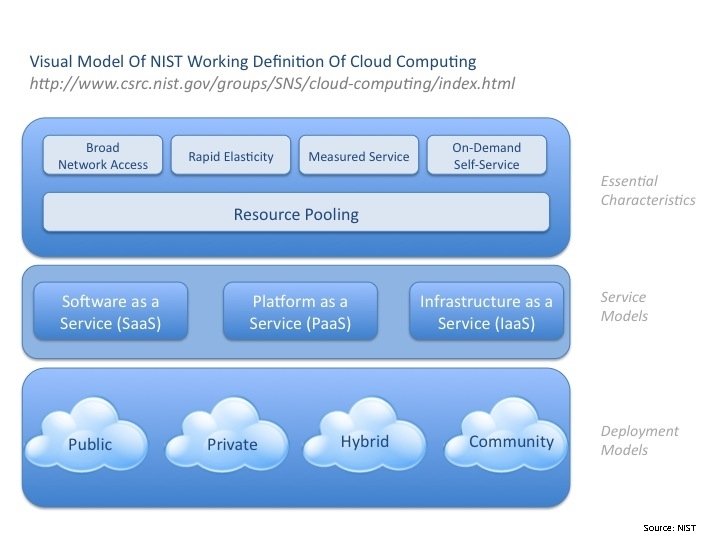
Source: NIST
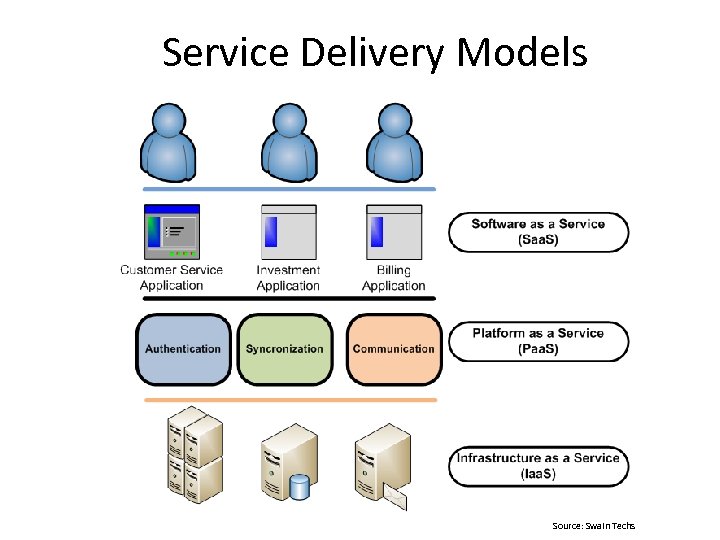
Service Delivery Models Source: Swain Techs

Source: Matthew Gardiner, Computer Associates

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Database Overview – Database Management Systems • Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) • Object-Oriented Database Management Systems (OODBMS) • Non-Relational, Distributed DB Mgmt Systems (NRDBMS) – Not only – Structured Query Language (No. SQL) – Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) • Real-time Data Warehousing – Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) • Operational Data Stores (ODS) • Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW)

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Database Overview – Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) • Business Intelligence (BI) – Data Mining – Reporting – OLAP
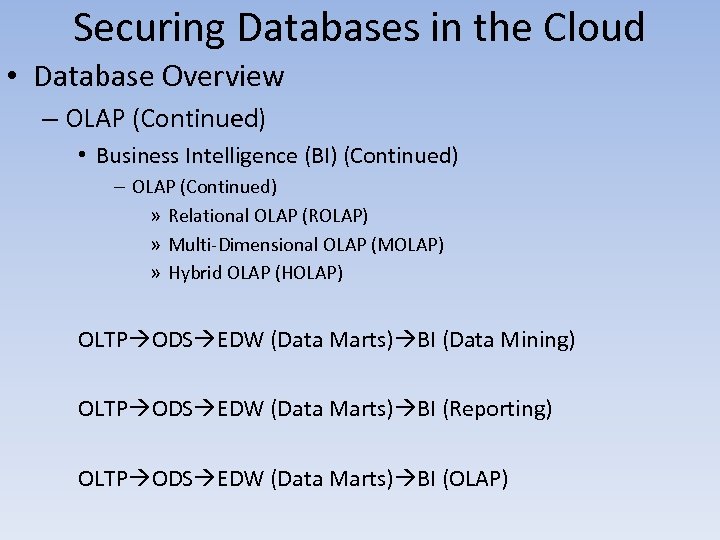
Securing Databases in the Cloud • Database Overview – OLAP (Continued) • Business Intelligence (BI) (Continued) – OLAP (Continued) » Relational OLAP (ROLAP) » Multi-Dimensional OLAP (MOLAP) » Hybrid OLAP (HOLAP) OLTP ODS EDW (Data Marts) BI (Data Mining) OLTP ODS EDW (Data Marts) BI (Reporting) OLTP ODS EDW (Data Marts) BI (OLAP)

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Big Data Overview – Aggregated Data From the Following Sources: • Traditional • Sensory • Social – Aggregators • Predominantly: NRDBMS – Column Family Stores: Cassandra (FB), Big. Table (Google), HBase (Apache) – Key-Values Stores: App Engine Data. Store (Google), Dynamo. DB & Simple. DB (AWS) – Document Databases: Couch. DB, Mongo. DB – Graph Databases: Neo 4 J

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Big Data Overview – Serial Processing • Hadoop – Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) – Hive – DW – Pig – Querying Language • Riak – Parallel Processing • Hadoop. DB – Analytics • Google Map. Reduce • Apache Map. Reduce • Splunk (for Security Information / Event Management [SIEM])
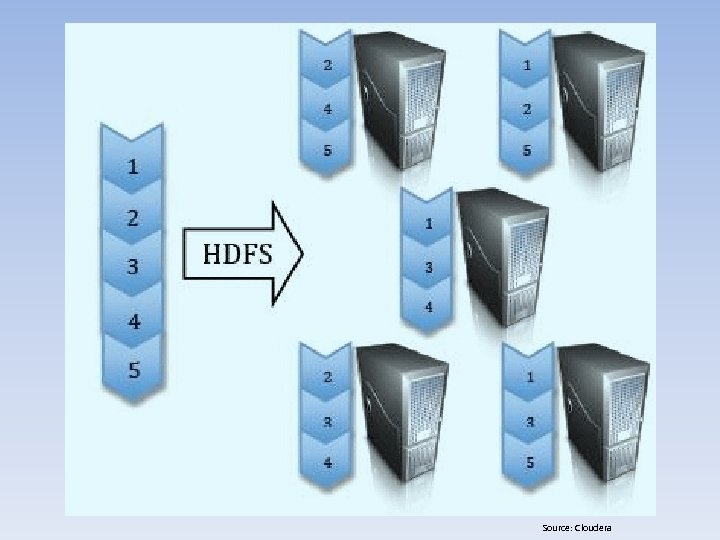
Source: Cloudera
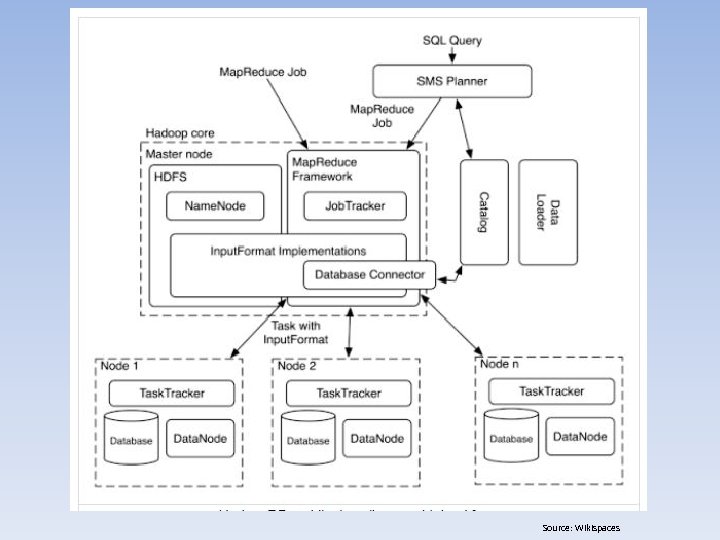
Source: Wikispaces
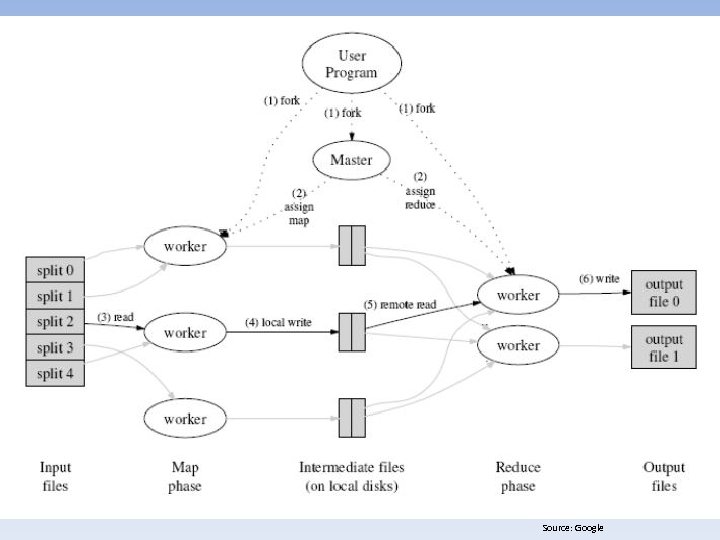
Source: Google
Source: Cloudera

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Cloud-Based Database Solutions – Paa. S • DBaa. S – Force. com – Intuit Quick. Base – Amazon Web Services (AWS) » Relational Database Service (RDS) Oracle 11 g / My. SQL » Dynamo. DB » Simple. DB – Google App Engine » Datastore – Oracle Public Cloud » 11 g

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Cloud-Based Database Solutions – Iaa. S • Build My. SQL, Microsoft SQL Server, or Oracle 11 g Instance • Leverage Compute Node & Storage Node Effectively – – AWS Elastic Compute Cloud (EC 2) AWS Elastic Block Store (EBS) Open. Stack Compute (Nova) Open. Stack Storage (Swift)

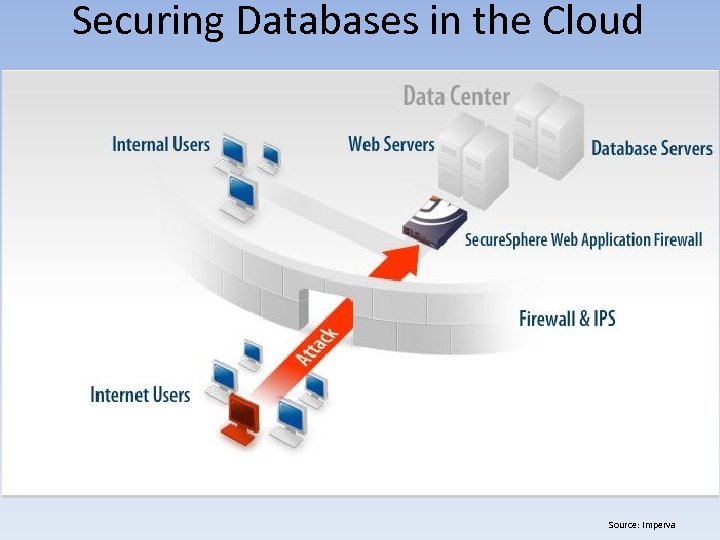
Securing Databases in the Cloud • Vulnerabilities Found in Cloud-Based DB Solutions – General Cloud Service • Middleware Vulnerabilities » Open / Java Database Connectivity (ODBC / JDBC) Attacks • Database Vulnerabilities » » Improper (Logical) Access Controls Change / Configuration Management Backups Multi-Tenancy • Virtualization Vulnerabilities – Insecure Hypervisor / Management Backplane » Hyperjacking – Rogue Hypervisor » Virtual Machine (VM) Theft – Data Loss » VM Hopping – One VM to Another » VM Sprawl – Unmanaged (Legacy VMs) » VM Escape – One VM to Another

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Vulnerabilities Found in Cloud-Based DB Solutions – General Cloud Service (Continued) • Internal (Cloud Service Provider) Attack Vectors: – Legacy Accounts » Automate Provisioning / De-Provisioning – Lack of Segregation / Separation of Duties – Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Injection • Application Vulnerabilities: – SQL Injection – Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) – Cross-Site Request Forgery (XSRF)

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Vulnerabilities Found in Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Iaa. S • Infrastructure: – Improper Physical Access Controls – Change / Configuration Management – Physical Separation of Compute & Storage Nodes » Performance Degradation – Backups » VM Backup Location, Jurisdiction » Data File Backup Location, Jurisdiction • Operating System (OS): – Improper (Logical) & Physical Access Controls – Change / Configuration Management

Source: Flickr

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Paa. S • DBaa. S – SIEM – Logical Segregation / Separation of Duties (DBA, Developer) – Enforce Logical Access Controls » Virtual Firewalls – Encryption » Enforce Compliance Encryption Requirements for Data » Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): Remote & Application Access » Key Management – User Rights Management (URM) » Identity & Access Management (IAM)
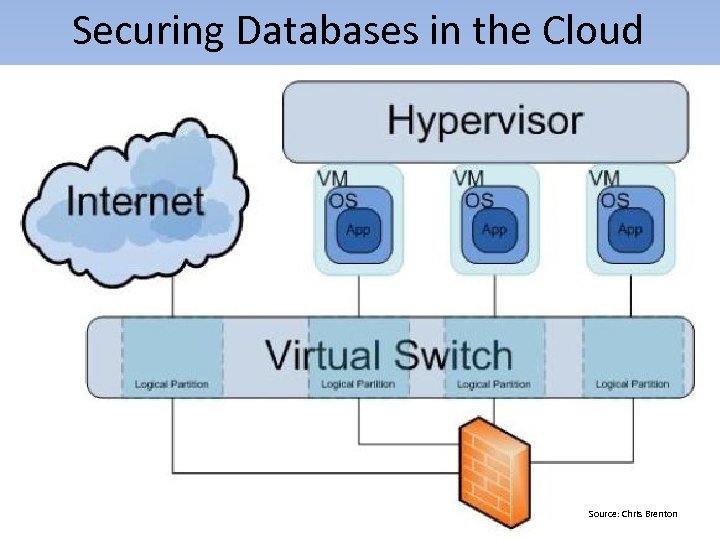
Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: Chris Brenton
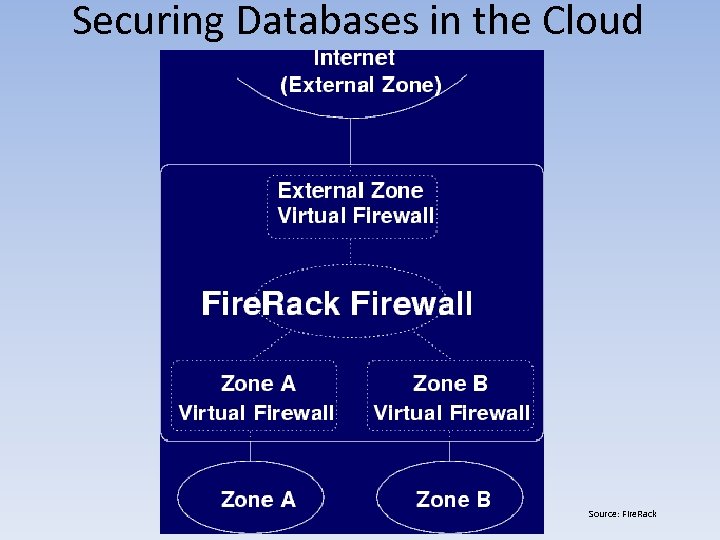
Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: Fire. Rack
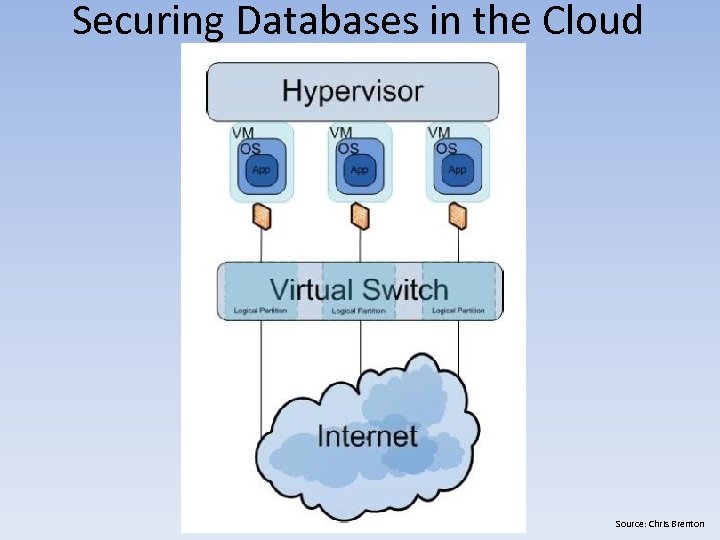
Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: Chris Brenton
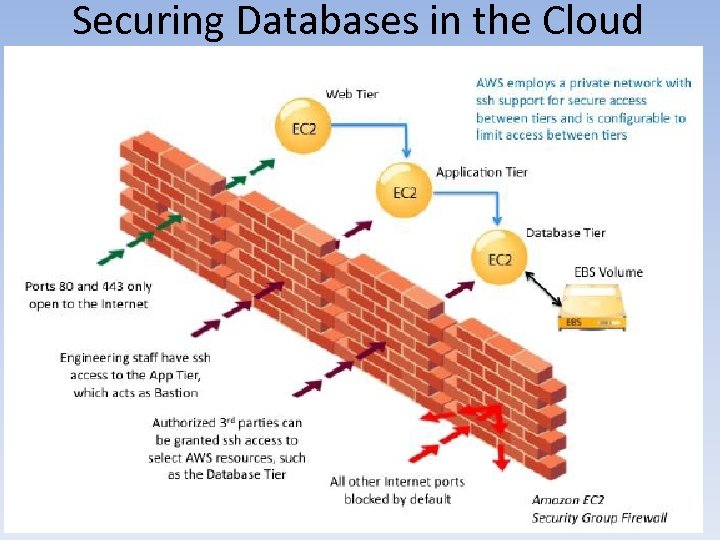
Securing Databases in the Cloud
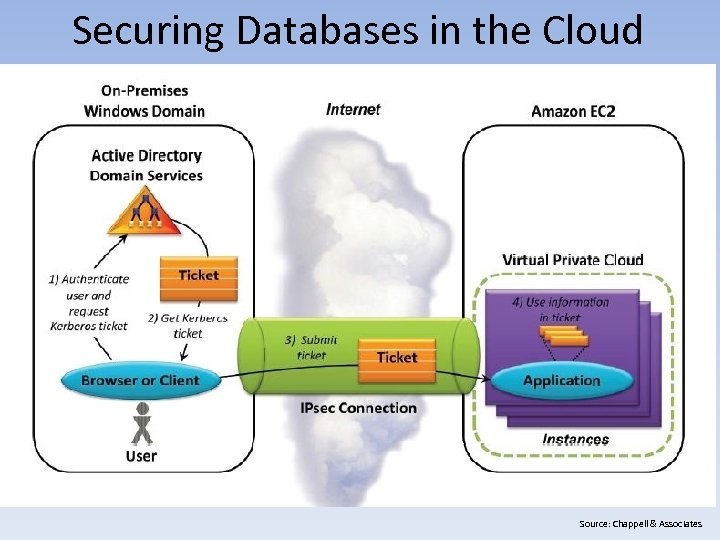
Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: Chappell & Associates
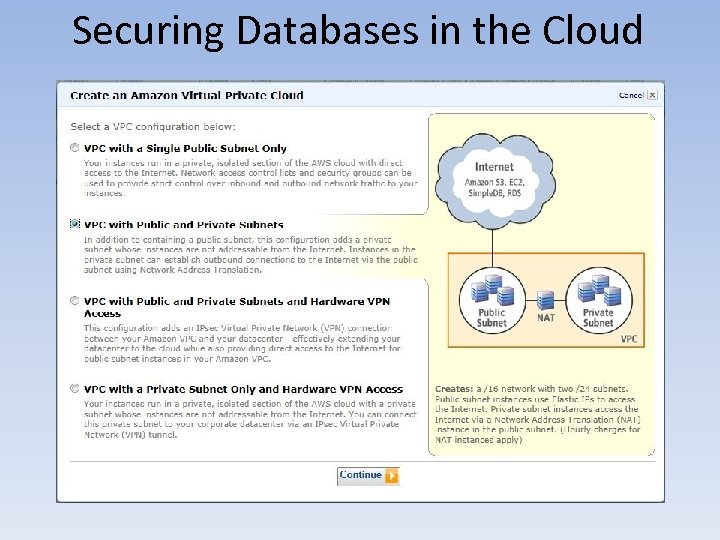
Securing Databases in the Cloud

Securing Databases in the Cloud
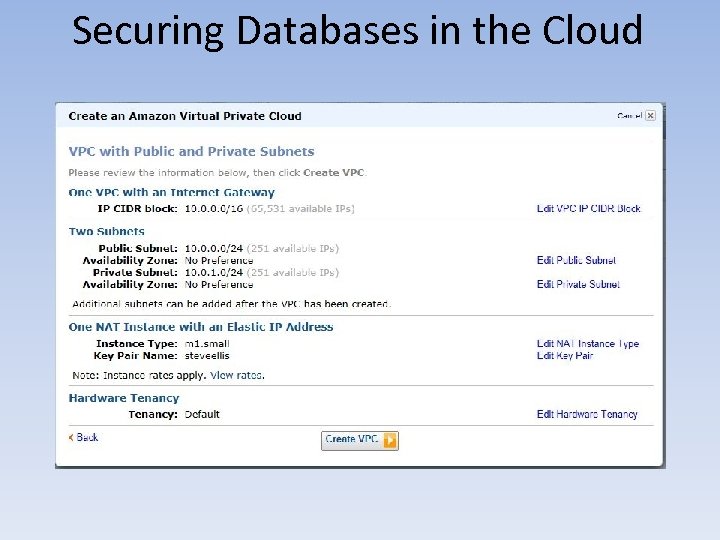
Securing Databases in the Cloud

Securing Databases in the Cloud
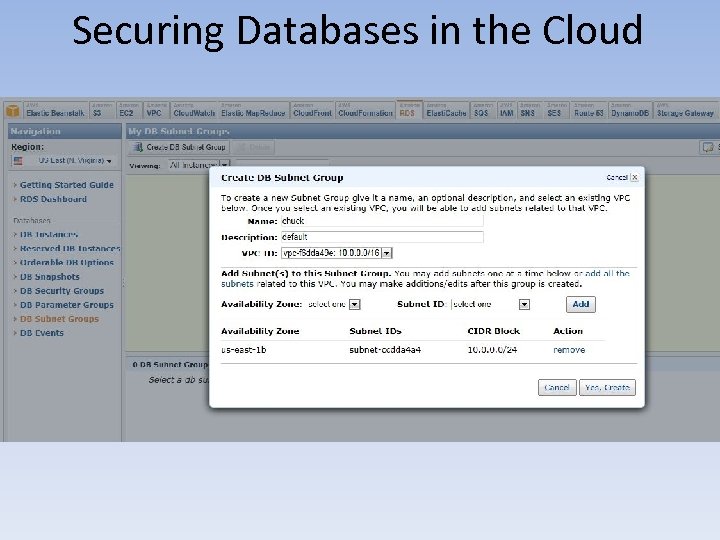
Securing Databases in the Cloud
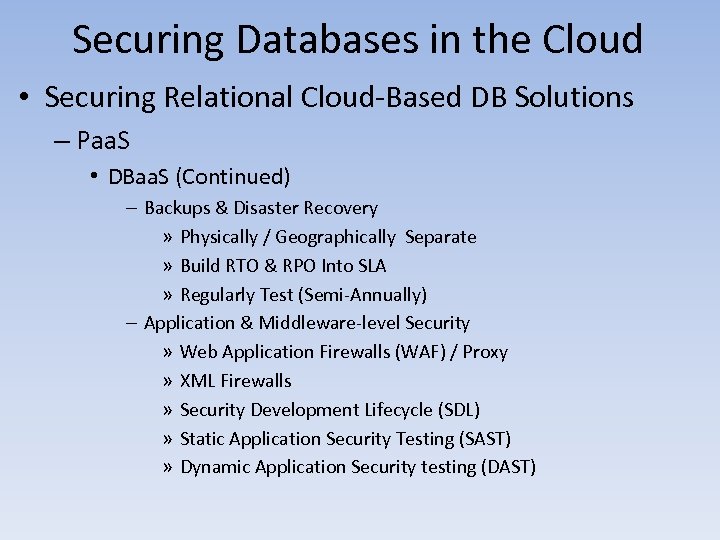
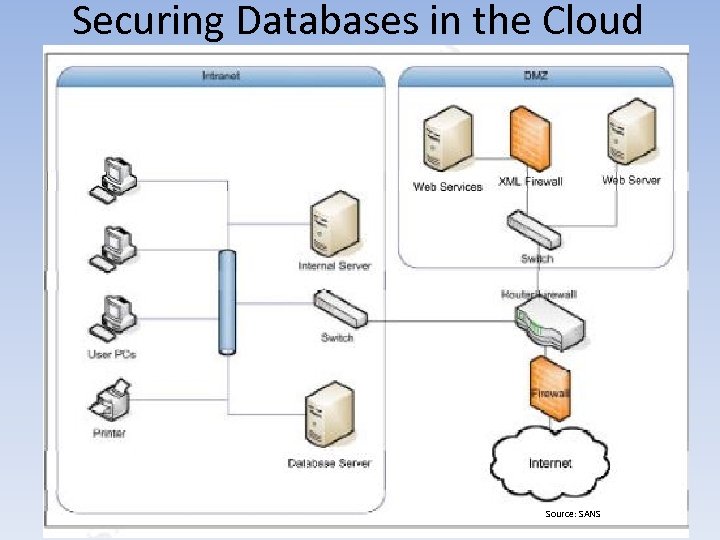
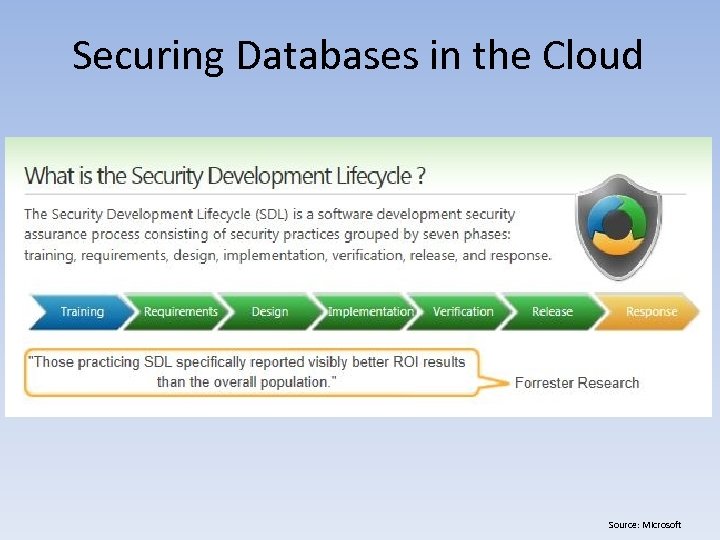
Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Paa. S • DBaa. S (Continued) – Backups & Disaster Recovery » Physically / Geographically Separate » Build RTO & RPO Into SLA » Regularly Test (Semi-Annually) – Application & Middleware-level Security » Web Application Firewalls (WAF) / Proxy » XML Firewalls » Security Development Lifecycle (SDL) » Static Application Security Testing (SAST) » Dynamic Application Security testing (DAST)
Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: Imperva
Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: SANS
Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: Microsoft

Securing Databases in the Cloud

Securing Databases in the Cloud

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Paa. S • DBaa. S (Continued) – AWS RDS Oracle 11 g & Java Apache Tomcat EC 2 Scenario: » Setup VPC Public & Private via NAT w/ IPSec VPN » Setup App Security Group » Build Public App Instance on EC 2 w/ Java & Apache Tomcat » Setup DB Security Group w/ App Security Group Added » Build Private AWS RDS Oracle 11 g DB » Leverage PL/SQL Audit Triggers for Compliance » Leverage Cloud. Watch for App & DB Instances » Leverage Prepared Statements & Error / Exception Handling

Securing Databases in the Cloud
Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Iaa. S • Server / Infrastructure – Physical Access Controls – Hypervisor / Management Backplane » Grouping – Segmenting VMs » Generalization – Leveraging a Template » Aspect-Oriented Management – Tiering » Automation Provisioning » Air Gapping – Siloed Virtual Networks (VLANs)

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Iaa. S • OS OS Firewalls (Windows) Patching / Configuration Management (Chef / Puppet) PKI Encryption Key Management Logical Access Controls Anti-Virus (AV) Authentication, Authorization & Accounting (AAA) » IAM – Vulnerability Assessment Scanning » Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC 2) Instance: Cloud. Inspect – – –
Securing Databases in the Cloud
Securing Databases in the Cloud
Securing Databases in the Cloud

Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: CORE
Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Iaa. S • Database Backups URM Segregation / Separation of Duties Vulnerability Scanning » Mc. Afee Database Security Scanner (DSS) for MS SQL Azure – Database Activity Monitoring (DAM) » Database Firewall – IAM – –
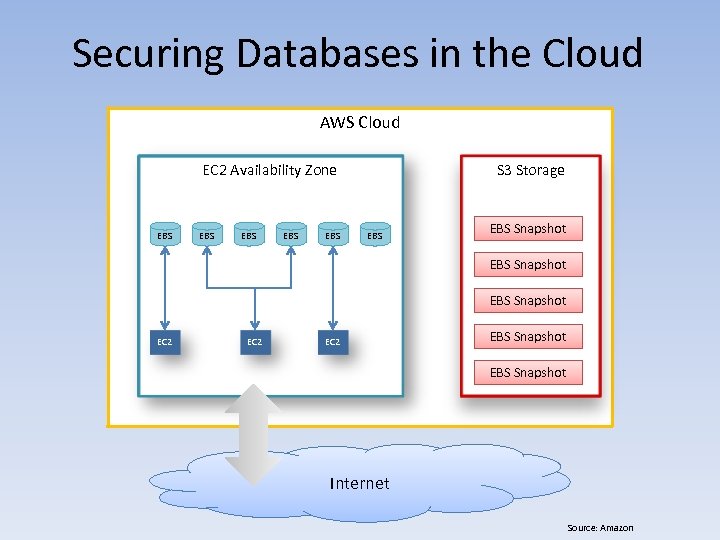
Securing Databases in the Cloud AWS Cloud EC 2 Availability Zone EBS EBS EBS S 3 Storage EBS Snapshot EC 2 EBS Snapshot Internet Source: Amazon
Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: Mc. Afee
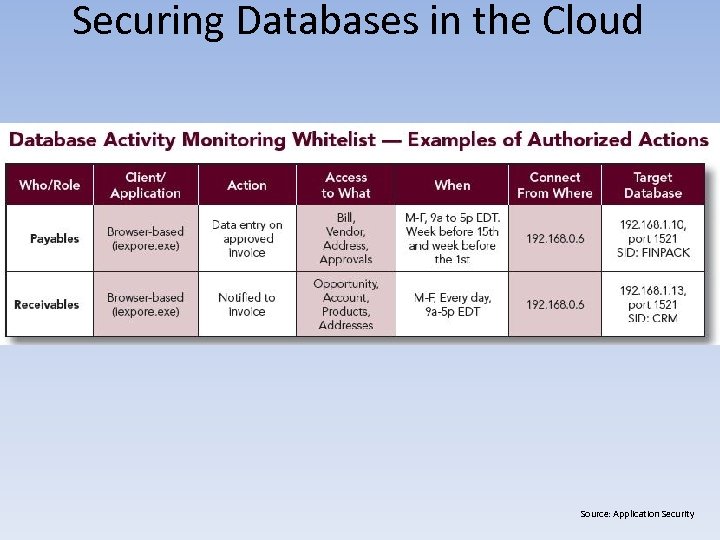
Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: Application Security
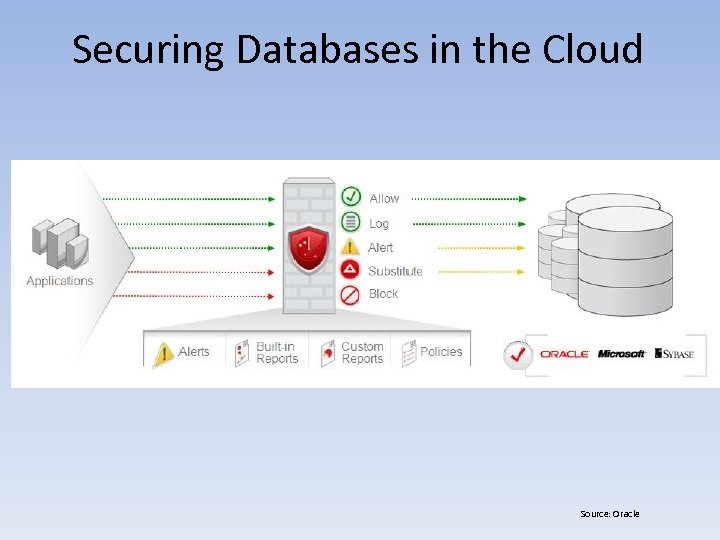
Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: Oracle

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Iaa. S • Database – LAMP Stack & php. My. Admin Scenario: » Setup VPC Public & Private via NAT » Setup App Security Group » Build Public App Instance on EC 2 w/ LAP & php. My. Admin » Setup DB Security Group w/ App Security Group Added » Build Private My. SQL DB Instance on EC 2 w/ Encrypted EBS » Leverage Cloud. Watch for App & DB Instances
Securing Databases in the Cloud

Securing Databases in the Cloud

Securing Databases in the Cloud

Securing Databases in the Cloud

Securing Databases in the Cloud

Securing Databases in the Cloud

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Iaa. S • Storage – PKI Encryption Key Management – Logical Access Controls » RBAC Groups (Open. Stack Swift) – Authentication, Authorization & Accounting (AAA) » IAM – Monitoring – Information Governance » Lifecycle
Securing Databases in the Cloud
Securing Databases in the Cloud

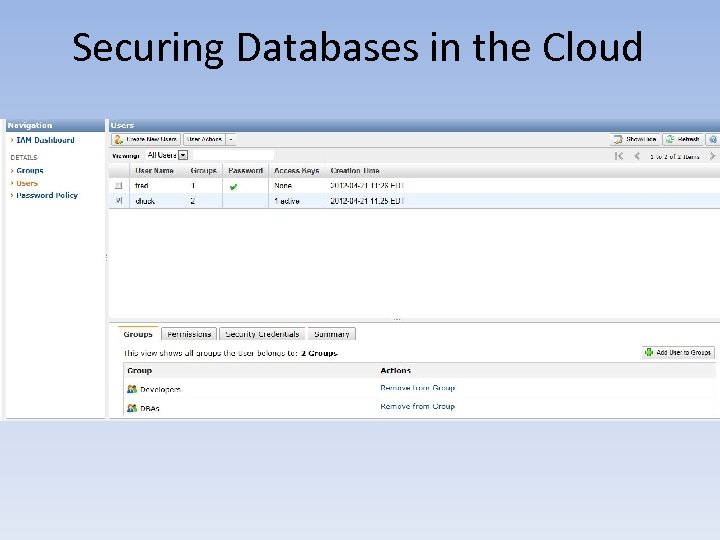
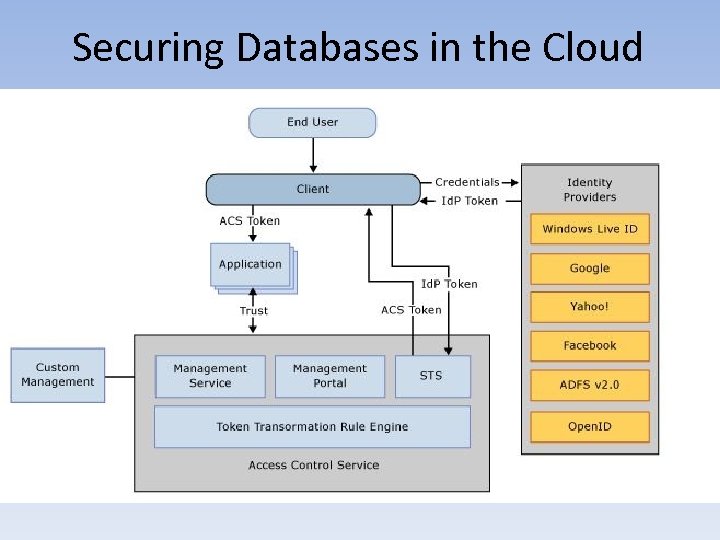
Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Iaa. S • Database – IAM » Federated Identity -Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) -Open Authorization (OAuth) -Representational State Transfer (REST) -AWS IAM -Windows Azure Access Control Service (ACS) -Web Services – Trust Language (WS-Trust) -Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) -Microsoft Federation Gateway (MFG)
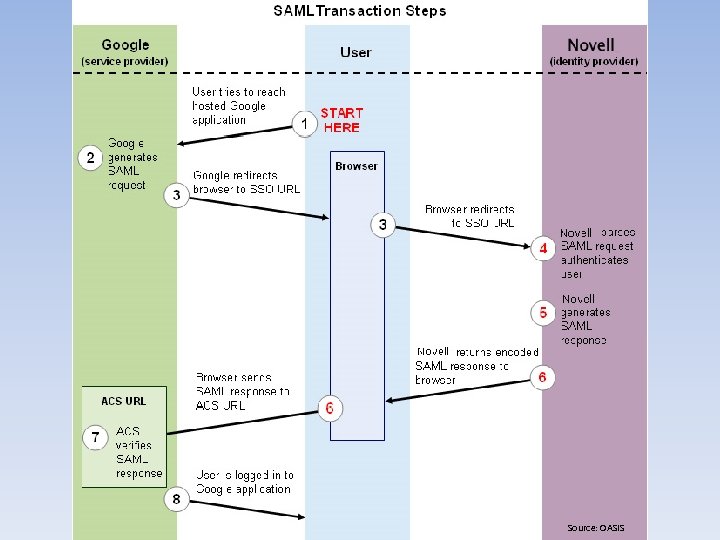
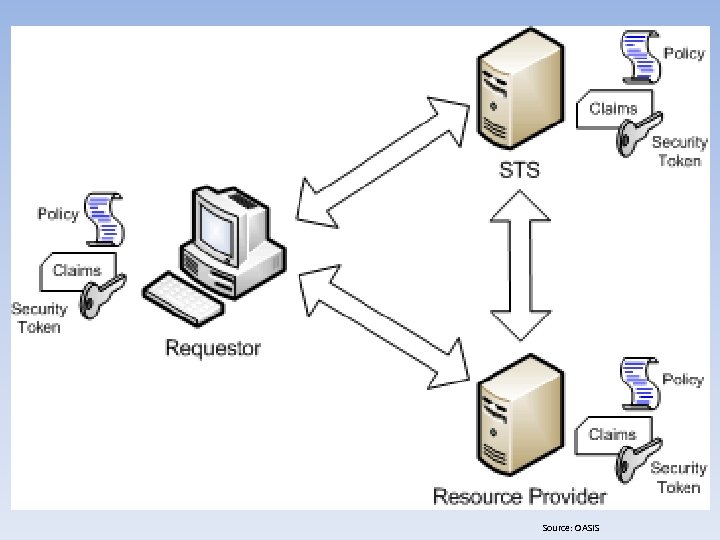
Source: OASIS
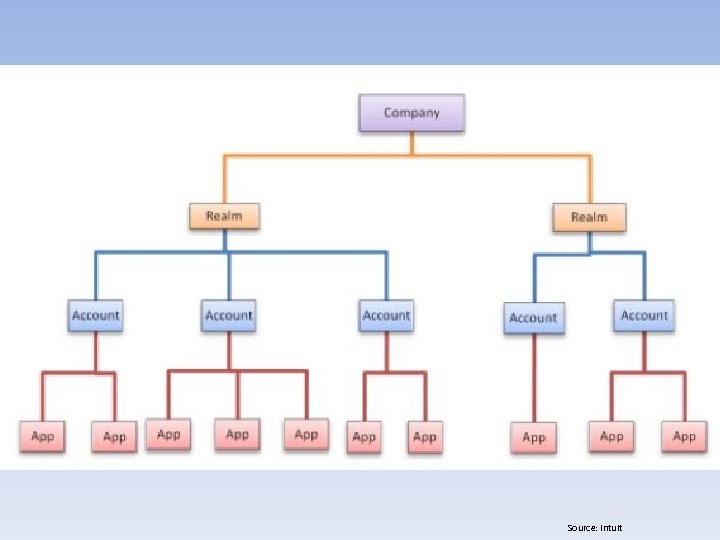
Source: Intuit

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Iaa. S • Database – IAM » Federated Identity -Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) -Open Authorization (OAuth) -Representational State Transfer (REST) -AWS IAM -Windows Azure Access Control Service (ACS) -Web Services – Trust Language (WS-Trust) -Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) -Microsoft Federation Gateway (MFG)
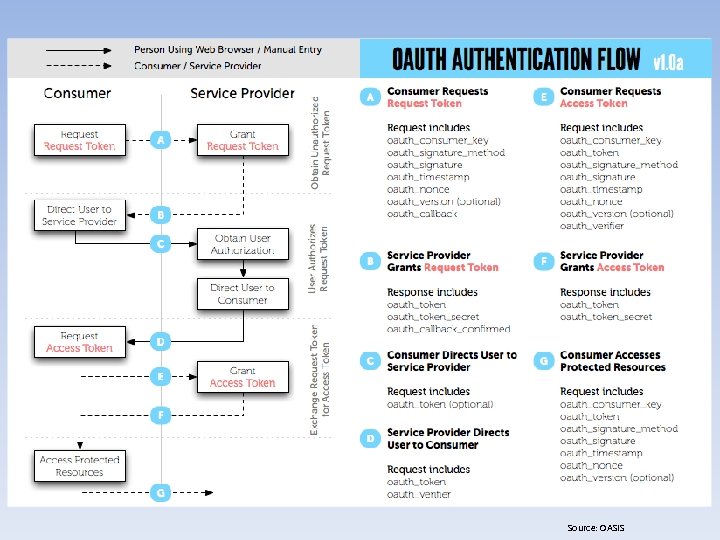
Source: OASIS

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Iaa. S • Database – IAM » Federated Identity -Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) -Open Authorization (OAuth) -Representational State Transfer (REST) -AWS IAM -Windows Azure Access Control Service (ACS) -Web Services – Trust Language (WS-Trust) -Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) -Microsoft Federation Gateway (MFG)
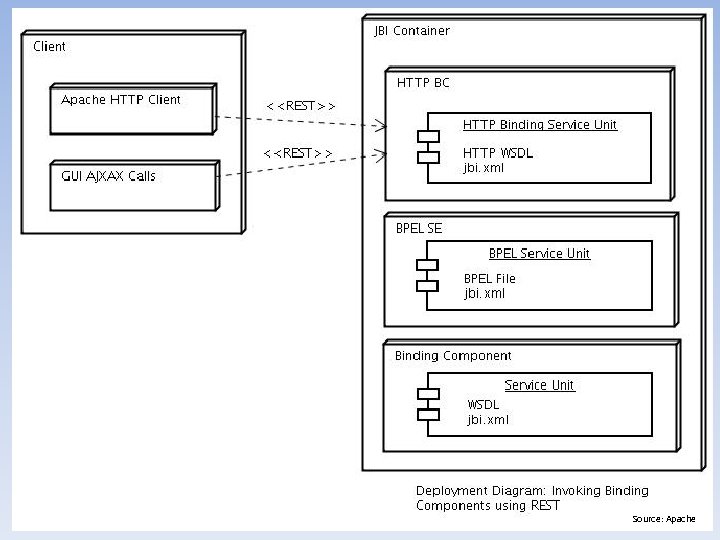
Source: Apache

Securing Databases in the Cloud
Securing Databases in the Cloud
Securing Databases in the Cloud

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Iaa. S • Database – IAM » Federated Identity -Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) -Open Authorization (OAuth) -Representational State Transfer (REST) -AWS IAM -Windows Azure Access Control Service (ACS) -Web Services – Trust Language (WS-Trust) -Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) -Microsoft Federation Gateway (MFG)
Source: OASIS
Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Iaa. S • Database – IAM » Federated Identity -Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) -Open Authorization (OAuth) -Representational State Transfer (REST) -AWS IAM -Windows Azure Access Control Service (ACS) -Web Services – Trust Language (WS-Trust) -Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) -Microsoft Federation Gateway (MFG)
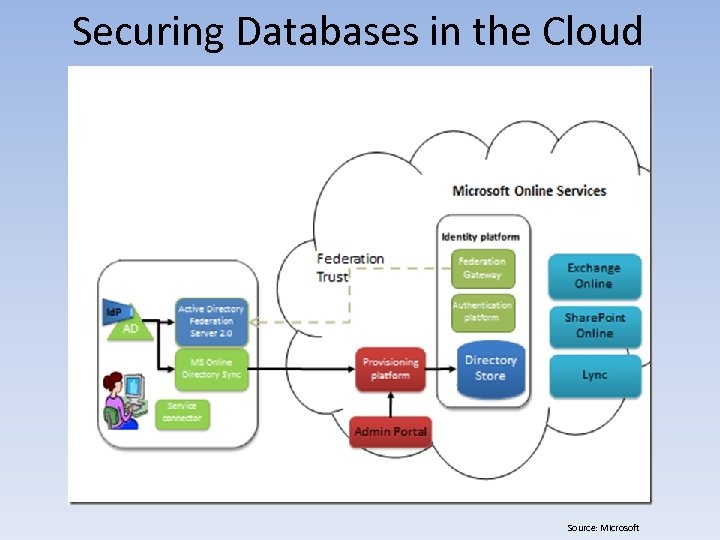
Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: Microsoft
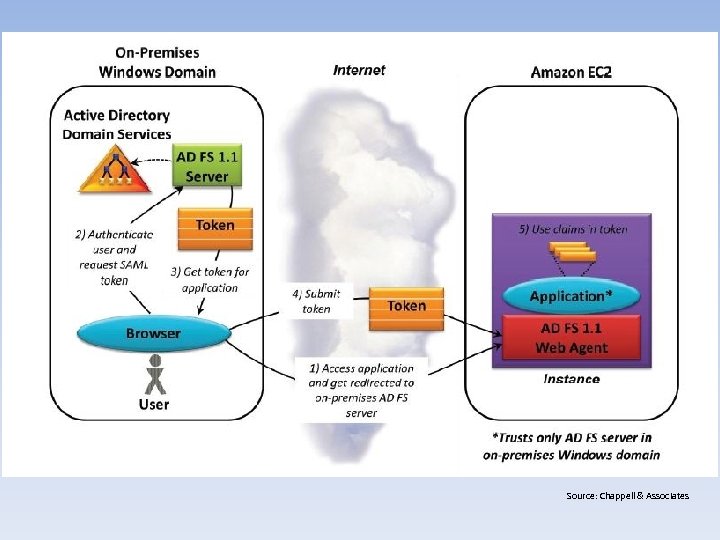
Source: Chappell & Associates
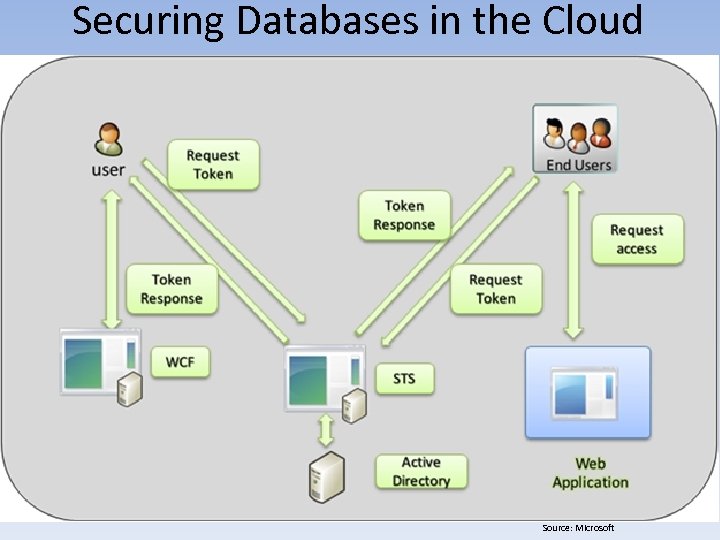
Securing Databases in the Cloud Source: Microsoft
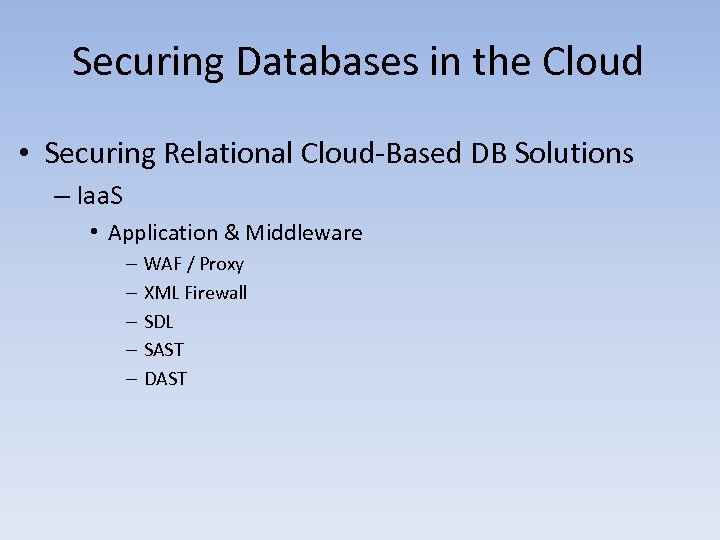
Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing Relational Cloud-Based DB Solutions – Iaa. S • Application & Middleware – – – WAF / Proxy XML Firewall SDL SAST DAST

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Securing NRDBMS Cloud-Based DB Solutions – General • Focus on Application / Middleware-Level Security – SQL Injections Are Still Possible – Leverage Application IAM for NRDBMS URM – Leverage Application & System Logging for AAA • Segregation of Duties – Read / Write Namespaces – Read-Only Namespaces – Specific • Document – Consistency Assurance • Key / Value – Ensure Referential Integrity

Securing Databases in the Cloud
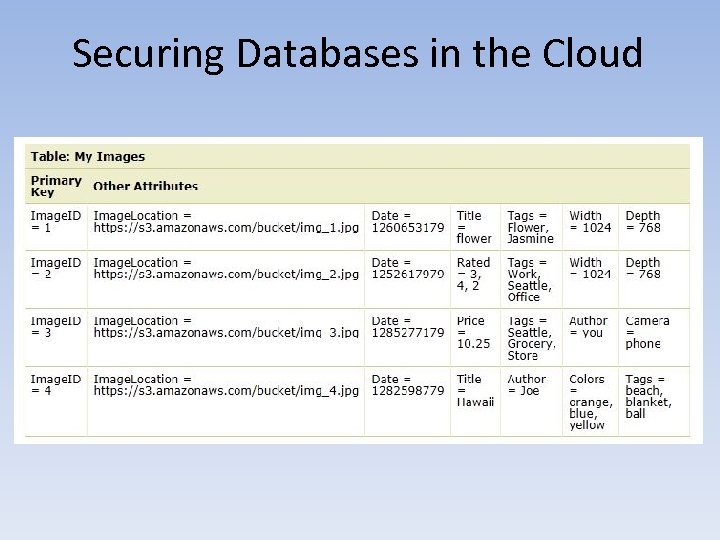
Securing Databases in the Cloud

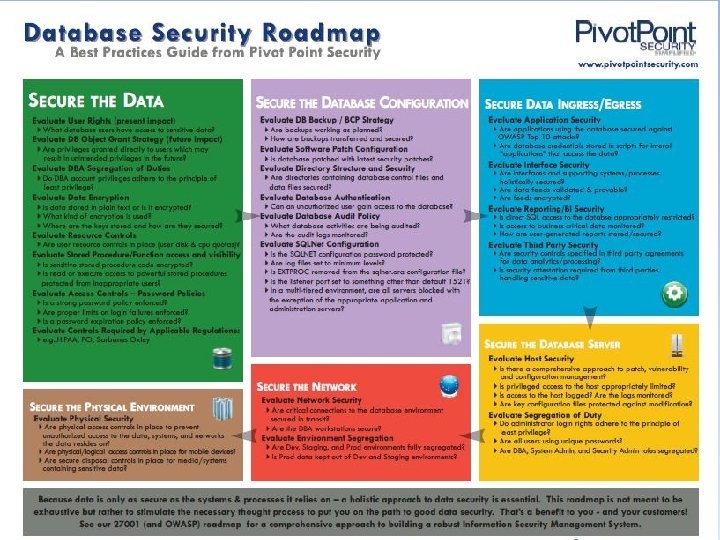
Securing Databases in the Cloud • Privacy & Data Protection for Cloud-Based DBs – Jurisdictions* • Regional: EU DPA • National: PIPEDA, GLBA, HIPAA / HITECH, COPPA, Safe Harbor • Statutory: Bavarian, CA SB 1386 / 24, MA 201 CMR 17, NV SB 227 – Data Flow & Jurisdictional Adherence • Data Sharing with Third Parties – Pseudonymization / De-Identification • Consent & Notices – Contract Clauses • Model Contracts – Privacy Best Practices • Generally Accepted Privacy Principles (GAPP) * Not all inclusive.

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Case Study: My. SQL & Simple. DB in the Cloud – Background • SMB Healthcare Service Provider (HIPAA Business Associate) • Providing Services for Larger HIPAA Covered Entities • Fall 2011 Project – Drivers • • Cost Savings HIPAA / HITECH Compliance More Cost Effective & Simplistic BCP / DRP Planning Parse Out Non-Protected Health Information (PHI)
Securing Databases in the Cloud • Case Study: My. SQL & Simple. DB in the Cloud – Technologies • AWS: – – EC 2 EBS Simple Storage Service (S 3) Simple. DB • Linux (Ubuntu AMI), Apache, My. SQL, & PHP (LAMP) Stack • Open. LDAP • Splunk – Limitations • Skill-Sets (AWS EC 2, Simple. DB) • Risk Posture • Vendor Management
Securing Databases in the Cloud • Case Study: My. SQL & Simple. DB in the Cloud – Risks • Vendor Lock-In – AWS EC 2 and / or Simple. DB • Legal Concerns – Lack of Bargaining Power – Service Level Agreements (SLAs) • Data Security & Privacy Concerns – Geographic Jurisdiction • Business Continuity / Availability – Data. Com Circuits • Variable Costs – Data Transfer

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Case Study: My. SQL & Simple. DB in the Cloud – Lessons Learned • Cloud Strategy / Roadmap Matters • Availability Issues w/ Simple. DB • Learning Curve – Simple. DB – Elastic Block Store (EBS) • Not as Cost Effective as First Thought – Backups & S 3 – Next Steps • Leveraging No. SQL for More Log Data • Enhanced use of Splunk for SIEM • Splunk to the Cloud (on AWS EC 2)

Securing Databases in the Cloud • Presentation Take-Aways – Databases in the Cloud are Here to Stay – Secure Cloud-Based DBs Through Defense-in-Depth – Application / Database – Middleware – OS – (Virtual) Infrastructure – Stay Abreast of New Technologies / Services – Big Data – Federated Identities

• Questions? • Contact – – Email: steve@ncontrol-llc. com Twitter: markes 1 LI: http: //www. linkedin. com/in/smarkey CSA-Del. Val: http: //www. csadelval. org/
36c0f99f181f7ec0e91709b8f6bc3b2e.ppt