6e3f6ee021f1aef75505bcc40668c542.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47

SECURING CYBERSPACE: THE OM-AM, RBAC AND PKI ROADMAP Prof. Ravi Sandhu Laboratory for Information Security Technology George Mason University sandhu@gmu. edu www. list. gmu. edu

INTERNET INSECURITY u Internet l l l Morris worm of 1987 Password sniffing attacks in 1994 IP spoofing attacks in 1995 Denial of service attacks in 1996 Email borne viruses 1999 Distributed denial of service attacks 2000 u Internet l insecurity spreads at Internet speed insecurity grows at super-Internet speed security incidents are growing faster than the Internet (which has roughly doubled every year since 1988) © Ravi Sandhu 2000 2

INTERNET INSECURITY u Its only going to get worse © Ravi Sandhu 2000 3

INTERNET SECURITY u There are no clear cut boundaries in modern cyberspace AOL-Microsoft instant messaging war of 1999 l Hotmail password bypass of 1999 l Ticketmaster deep web links l ebay versus auction aggregators l © Ravi Sandhu 2000 4
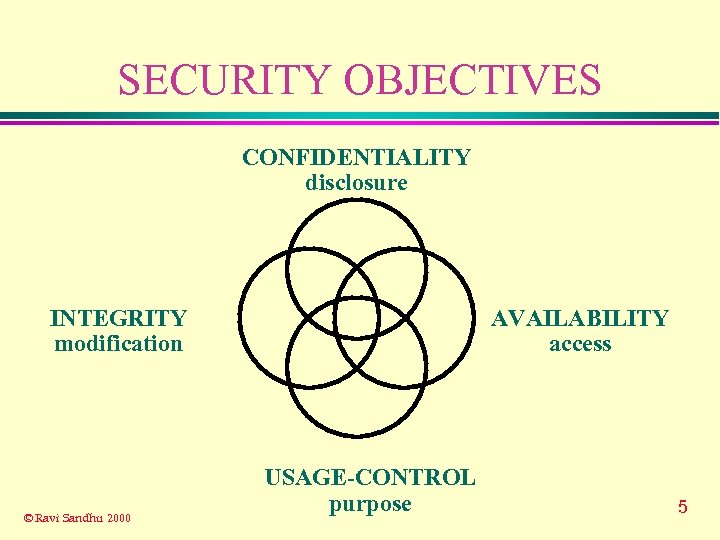
SECURITY OBJECTIVES CONFIDENTIALITY disclosure INTEGRITY modification © Ravi Sandhu 2000 AVAILABILITY access USAGE-CONTROL purpose 5

AUTHORIZATION, TRUST AND RISK u Information security is fundamentally about managing authorization and l trust l so as to manage risk © Ravi Sandhu 2000 6

SECURITY DOCTRINE u Prevent u Detect u Correct u Accept © Ravi Sandhu 2000 7

SECURITY DOCTRINE u absolute security is impossible does not mean absolute insecurity is acceptable u security is a journey not a destination © Ravi Sandhu 2000 8

SOLUTIONS u OM-AM u RBAC u PKI u and © Ravi Sandhu 2000 others 9
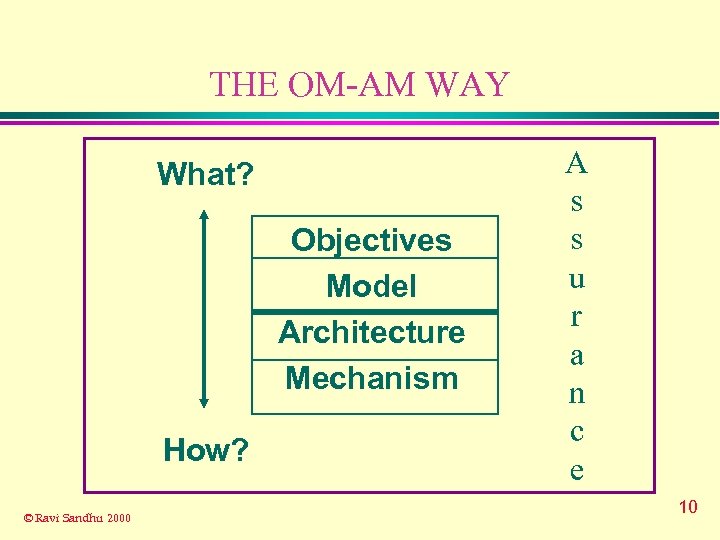
THE OM-AM WAY What? Objectives Model Architecture Mechanism How? © Ravi Sandhu 2000 A s s u r a n c e 10
LAYERS AND LAYERS u Multics rings u Layered abstractions u Waterfall model u Network protocol stacks u OM-AM © Ravi Sandhu 2000 11
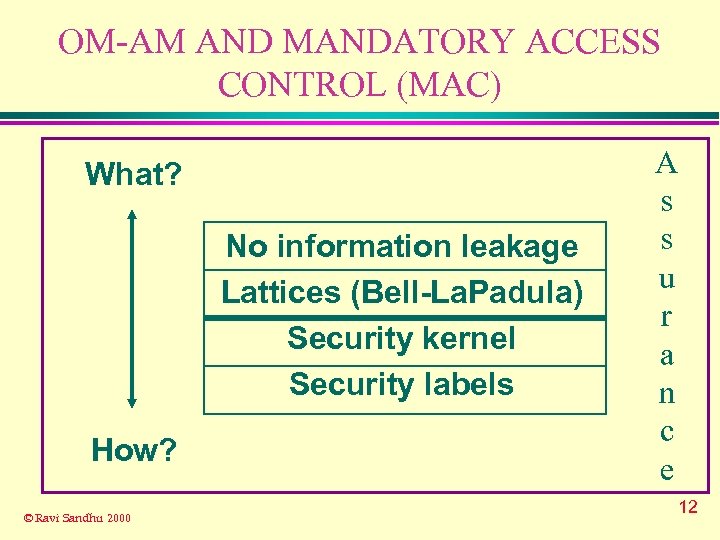
OM-AM AND MANDATORY ACCESS CONTROL (MAC) What? No information leakage Lattices (Bell-La. Padula) Security kernel Security labels How? © Ravi Sandhu 2000 A s s u r a n c e 12
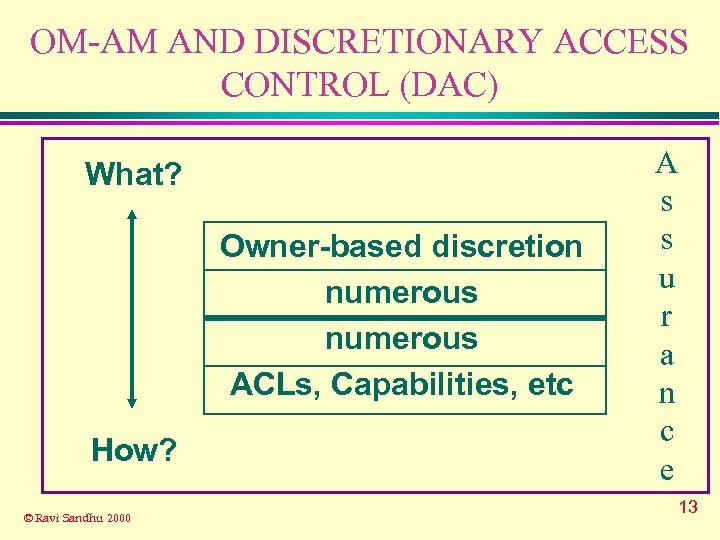
OM-AM AND DISCRETIONARY ACCESS CONTROL (DAC) What? Owner-based discretion numerous ACLs, Capabilities, etc How? © Ravi Sandhu 2000 A s s u r a n c e 13
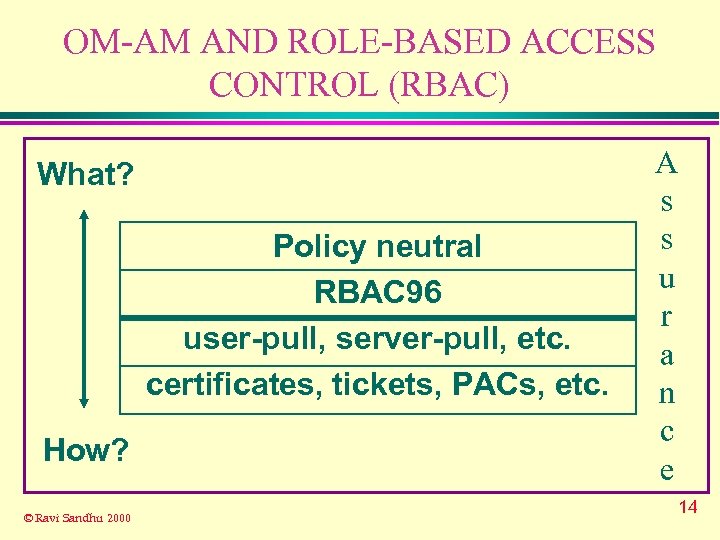
OM-AM AND ROLE-BASED ACCESS CONTROL (RBAC) What? Policy neutral RBAC 96 user-pull, server-pull, etc. certificates, tickets, PACs, etc. How? © Ravi Sandhu 2000 A s s u r a n c e 14
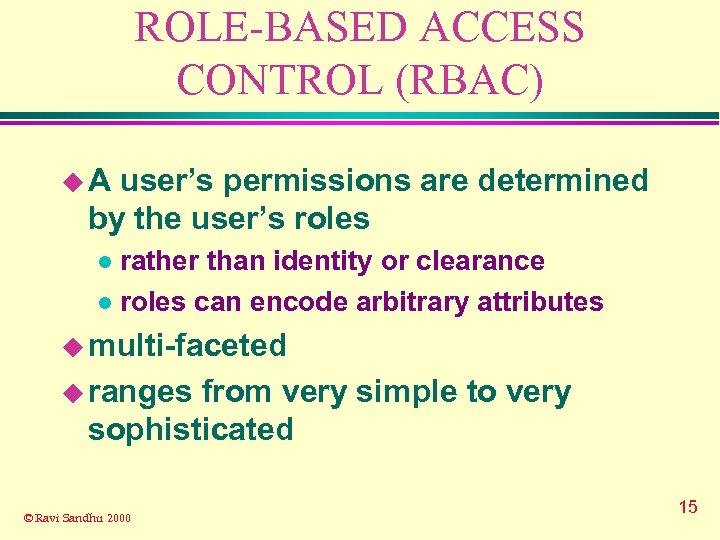
ROLE-BASED ACCESS CONTROL (RBAC) u. A user’s permissions are determined by the user’s roles rather than identity or clearance l roles can encode arbitrary attributes l u multi-faceted u ranges from very simple to very sophisticated © Ravi Sandhu 2000 15

RBAC SECURITY PRINCIPLES u least privilege u separation of duties u separation of administration and access u abstract operations © Ravi Sandhu 2000 16
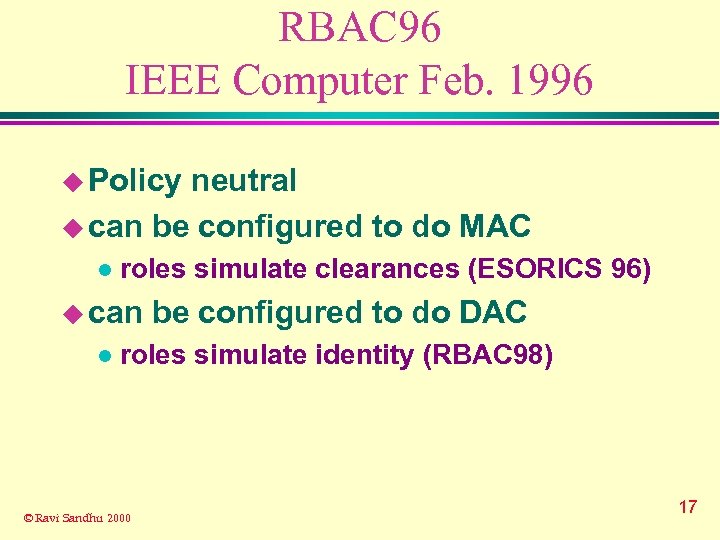
RBAC 96 IEEE Computer Feb. 1996 u Policy neutral u can be configured to do MAC l roles simulate clearances (ESORICS 96) u can l be configured to do DAC roles simulate identity (RBAC 98) © Ravi Sandhu 2000 17
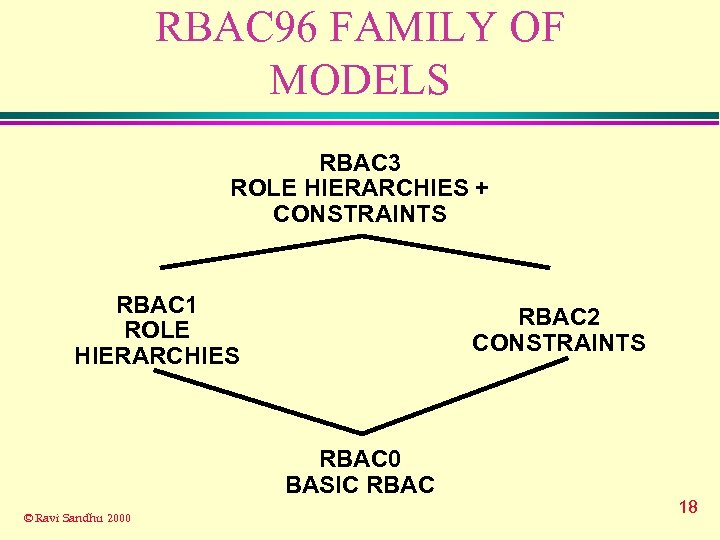
RBAC 96 FAMILY OF MODELS RBAC 3 ROLE HIERARCHIES + CONSTRAINTS RBAC 1 ROLE HIERARCHIES RBAC 2 CONSTRAINTS RBAC 0 BASIC RBAC © Ravi Sandhu 2000 18
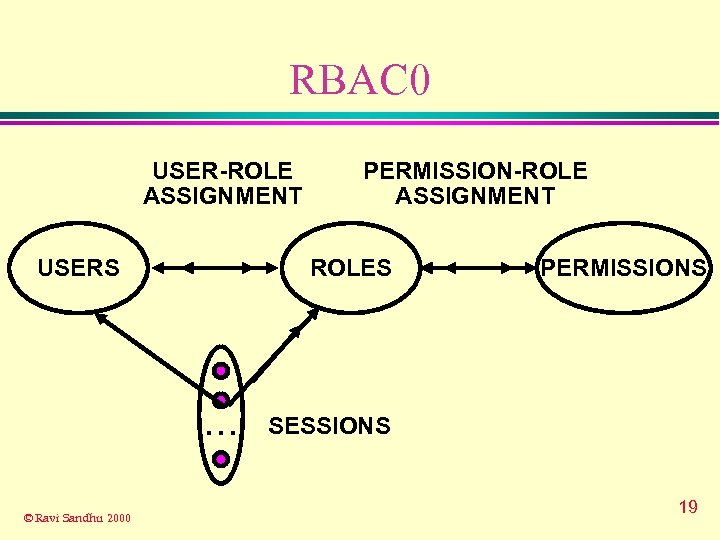
RBAC 0 USER-ROLE ASSIGNMENT USERS ROLES . . . © Ravi Sandhu 2000 PERMISSION-ROLE ASSIGNMENT PERMISSIONS SESSIONS 19
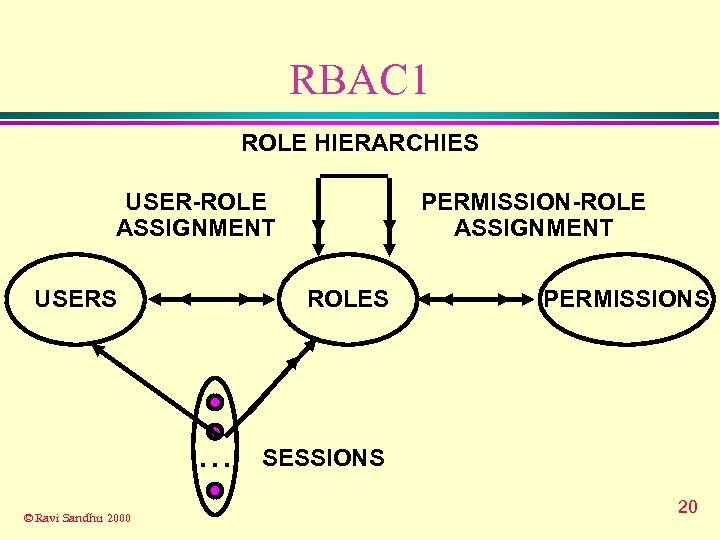
RBAC 1 ROLE HIERARCHIES USER-ROLE ASSIGNMENT USERS ROLES . . . © Ravi Sandhu 2000 PERMISSION-ROLE ASSIGNMENT PERMISSIONS SESSIONS 20
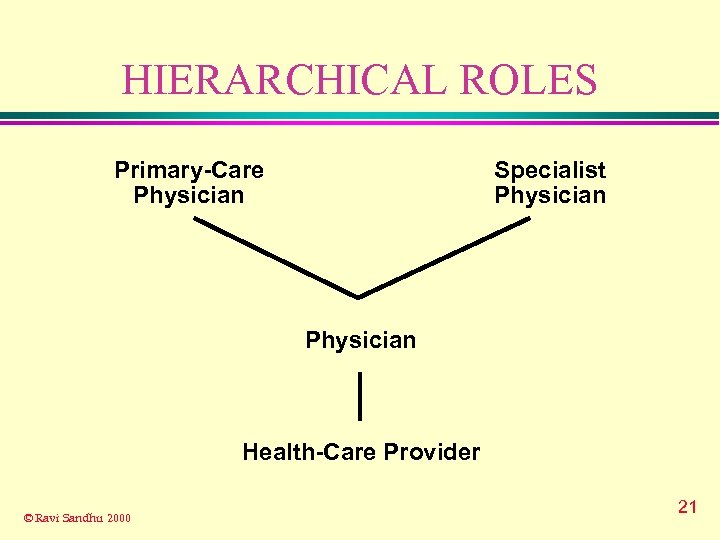
HIERARCHICAL ROLES Primary-Care Physician Specialist Physician Health-Care Provider © Ravi Sandhu 2000 21
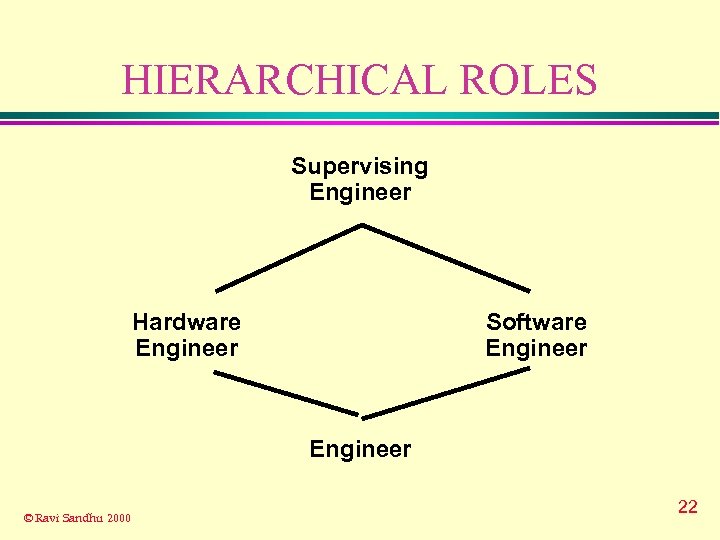
HIERARCHICAL ROLES Supervising Engineer Hardware Engineer Software Engineer © Ravi Sandhu 2000 22
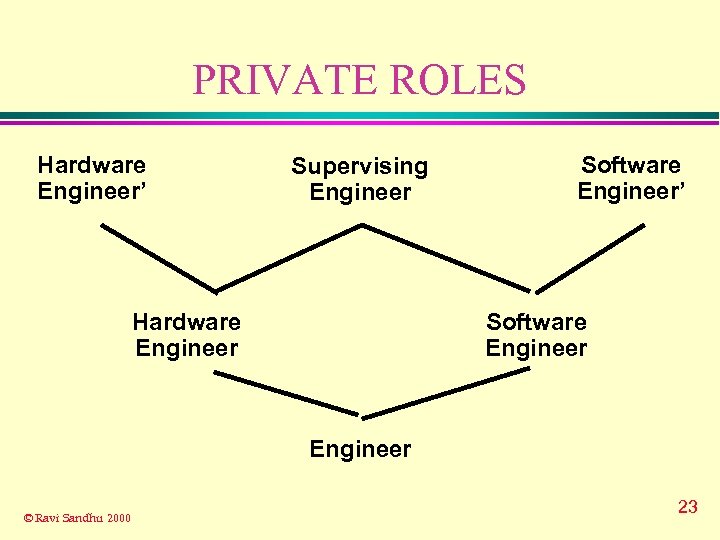
PRIVATE ROLES Hardware Engineer’ Supervising Engineer Hardware Engineer Software Engineer’ Software Engineer © Ravi Sandhu 2000 23
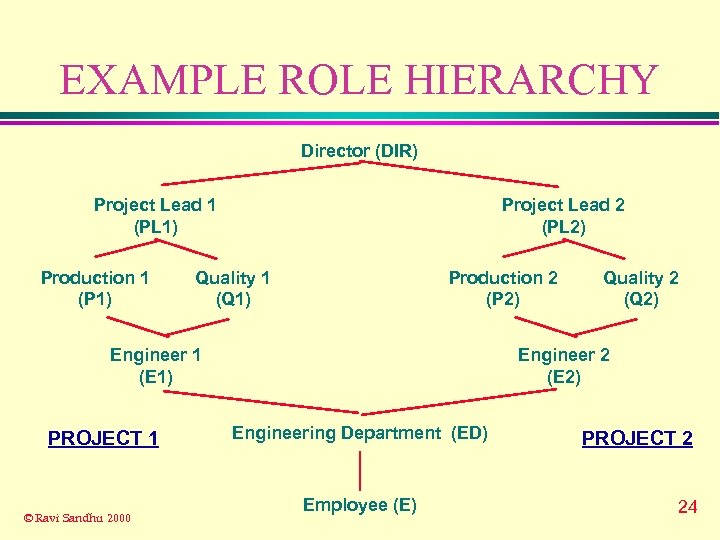
EXAMPLE ROLE HIERARCHY Director (DIR) Project Lead 1 (PL 1) Production 1 (P 1) Project Lead 2 (PL 2) Quality 1 (Q 1) Production 2 (P 2) Engineer 1 (E 1) PROJECT 1 © Ravi Sandhu 2000 Quality 2 (Q 2) Engineer 2 (E 2) Engineering Department (ED) Employee (E) PROJECT 2 24
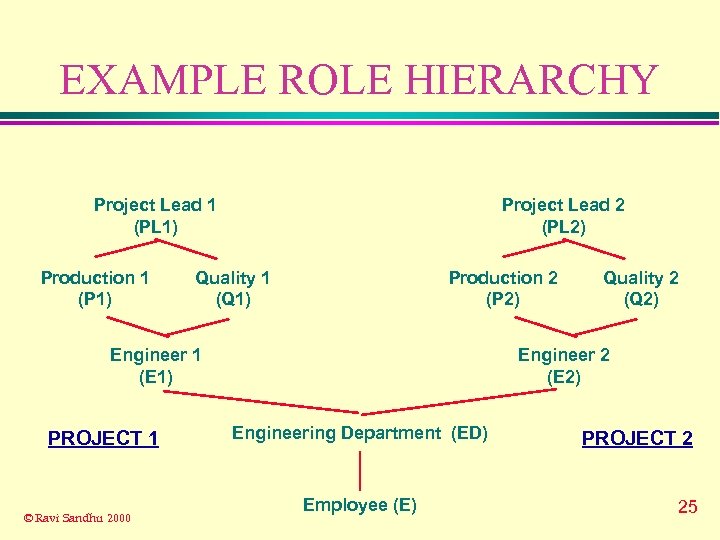
EXAMPLE ROLE HIERARCHY Project Lead 1 (PL 1) Production 1 (P 1) Project Lead 2 (PL 2) Quality 1 (Q 1) Production 2 (P 2) Engineer 1 (E 1) PROJECT 1 © Ravi Sandhu 2000 Quality 2 (Q 2) Engineer 2 (E 2) Engineering Department (ED) Employee (E) PROJECT 2 25
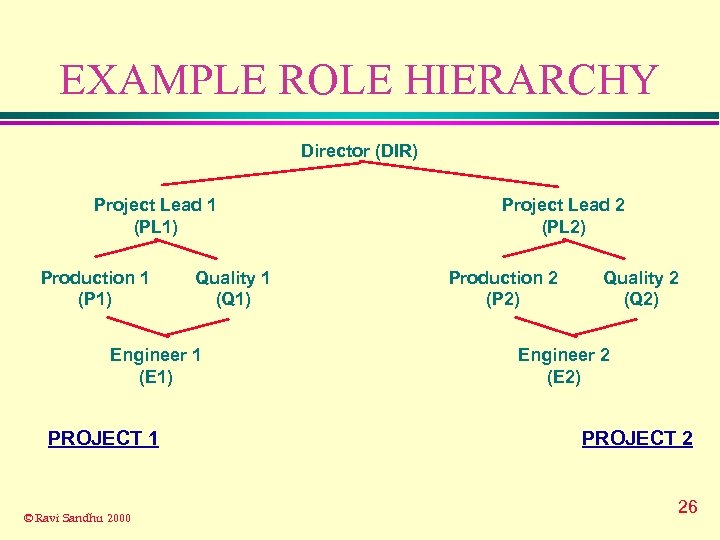
EXAMPLE ROLE HIERARCHY Director (DIR) Project Lead 1 (PL 1) Production 1 (P 1) Quality 1 (Q 1) Engineer 1 (E 1) PROJECT 1 © Ravi Sandhu 2000 Project Lead 2 (PL 2) Production 2 (P 2) Quality 2 (Q 2) Engineer 2 (E 2) PROJECT 2 26
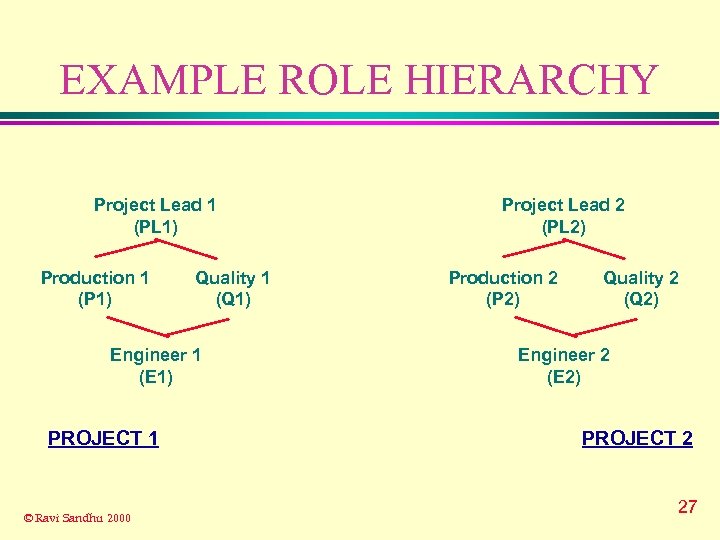
EXAMPLE ROLE HIERARCHY Project Lead 1 (PL 1) Production 1 (P 1) Quality 1 (Q 1) Engineer 1 (E 1) PROJECT 1 © Ravi Sandhu 2000 Project Lead 2 (PL 2) Production 2 (P 2) Quality 2 (Q 2) Engineer 2 (E 2) PROJECT 2 27
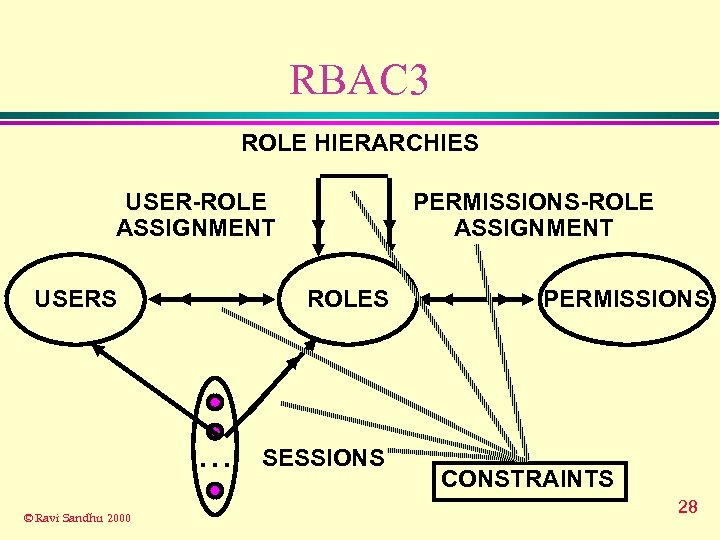
RBAC 3 ROLE HIERARCHIES USER-ROLE ASSIGNMENT USERS ROLES . . . © Ravi Sandhu 2000 PERMISSIONS-ROLE ASSIGNMENT SESSIONS PERMISSIONS CONSTRAINTS 28
CONSTRAINTS u Mutually Exclusive Roles l l u u u Static: The same individual can never hold both roles Dynamic: The same individual can never activate both roles in the same context Mutually Exclusive Permissions Cardinality Constraints on User-Role Assignment Cardinality Constraints on Permissions-Role Assignment © Ravi Sandhu 2000 29
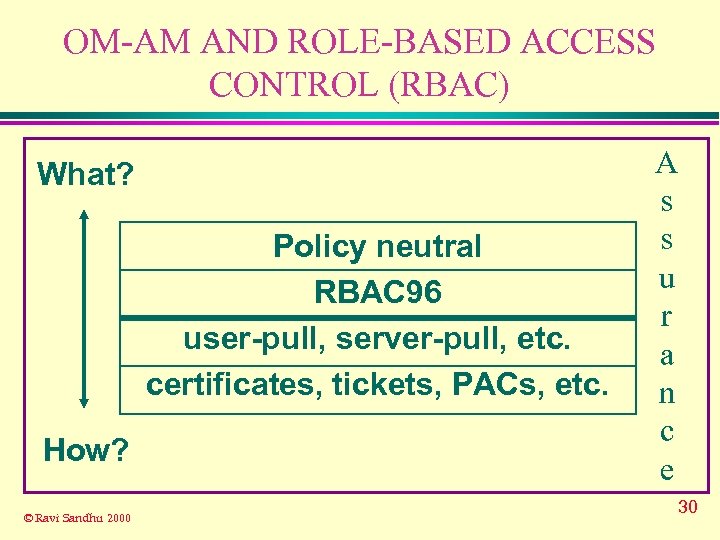
OM-AM AND ROLE-BASED ACCESS CONTROL (RBAC) What? Policy neutral RBAC 96 user-pull, server-pull, etc. certificates, tickets, PACs, etc. How? © Ravi Sandhu 2000 A s s u r a n c e 30
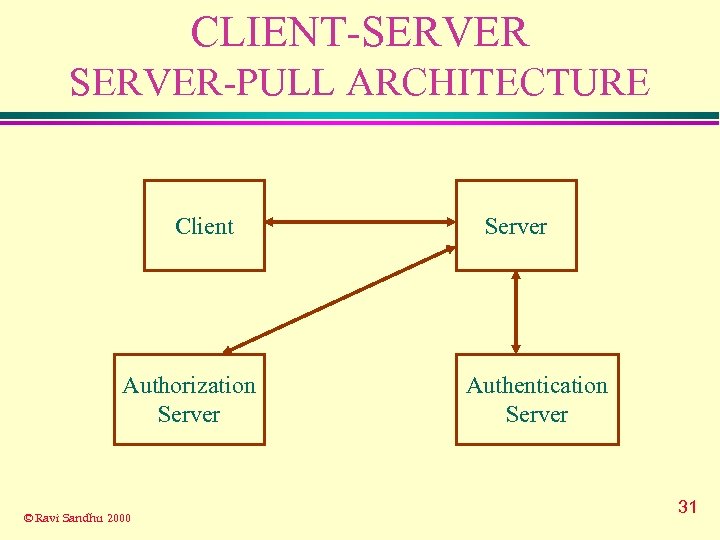
CLIENT-SERVER-PULL ARCHITECTURE Client Authorization Server © Ravi Sandhu 2000 Server Authentication Server 31
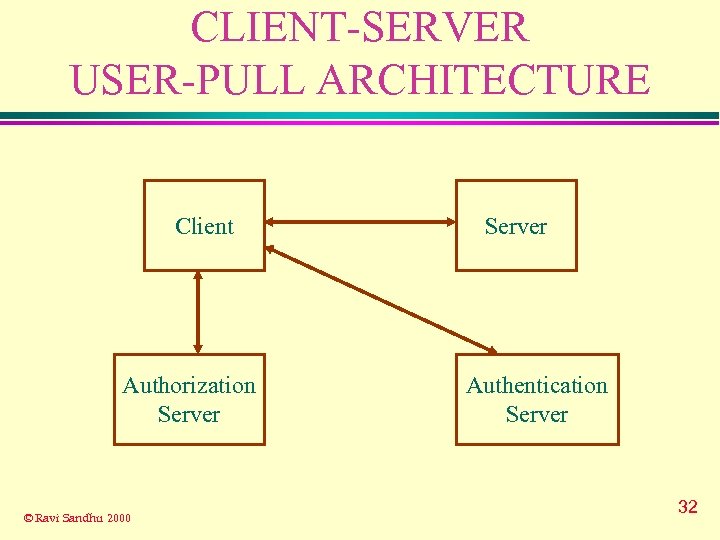
CLIENT-SERVER USER-PULL ARCHITECTURE Client Authorization Server © Ravi Sandhu 2000 Server Authentication Server 32
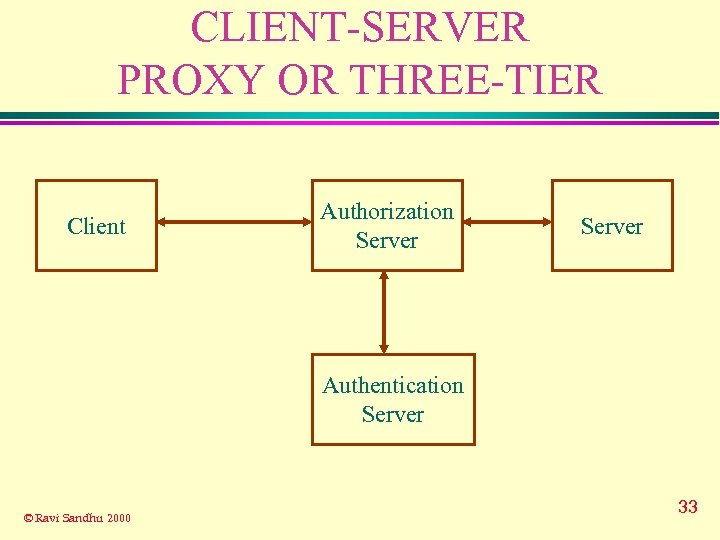
CLIENT-SERVER PROXY OR THREE-TIER Client Authorization Server Authentication Server © Ravi Sandhu 2000 33
OM-AM AND ROLE-BASED ACCESS CONTROL (RBAC) What? Policy neutral RBAC 96 user-pull, server-pull, etc. certificates, tickets, PACs, etc. How? © Ravi Sandhu 2000 A s s u r a n c e 34
Related Mechanisms u Cookies l l l in widespread current use for maintaining state of HTTP becoming a standard not secure u Public-Key l l Certificates (X. 509) support security on the Web based on PKI standard simply, bind users to keys have the ability to be extended © Ravi Sandhu 2000 35
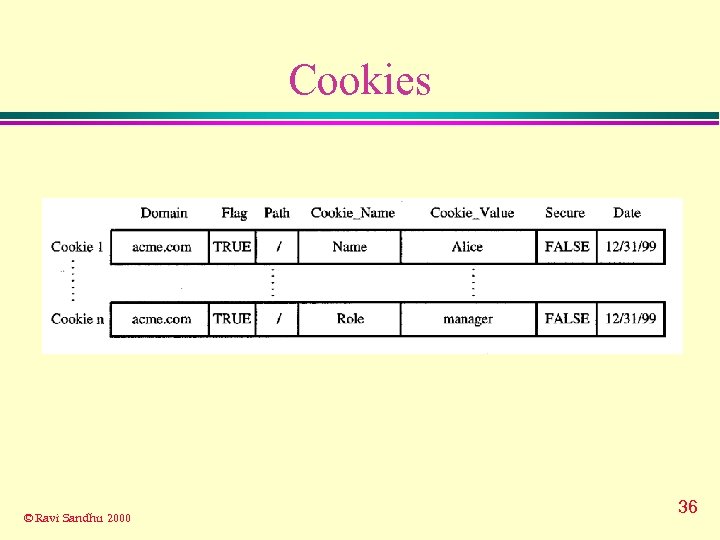
Cookies © Ravi Sandhu 2000 36

Security Threats to Cookies u Cookies are not secure No authentication l No integrity l No confidentiality l u can be easily attacked by Network Security Threats l End-System Threats l Cookie Harvesting Threats l © Ravi Sandhu 2000 37
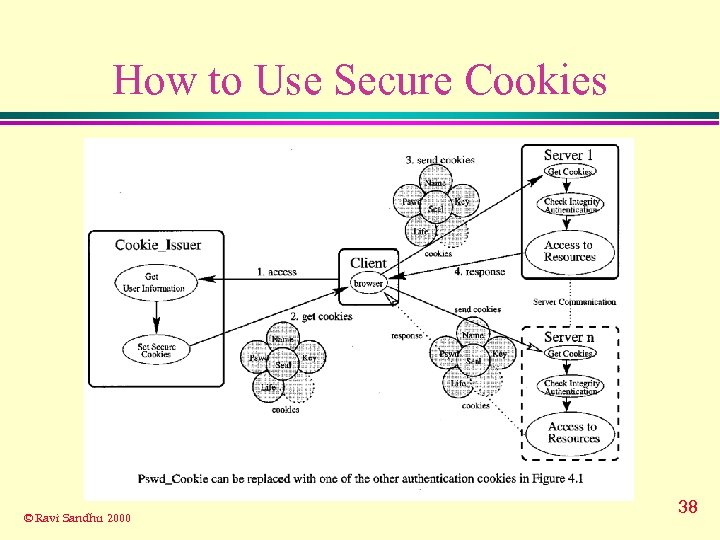
How to Use Secure Cookies © Ravi Sandhu 2000 38
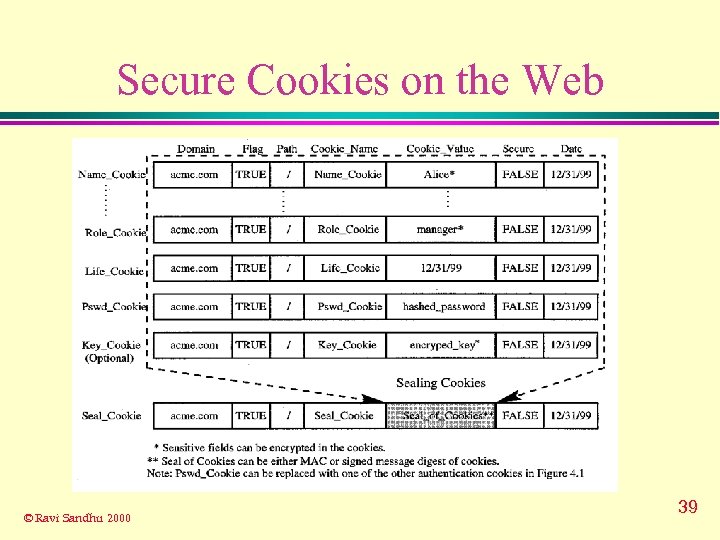
Secure Cookies on the Web © Ravi Sandhu 2000 39

Applications of Secure Cookies u User Authentication u Electronic Transaction u Pay-Per-Access u Attribute-based Access Control © Ravi Sandhu 2000 40

X. 509 Certificate u Digitally l signed by a certificate authority to confirm the information in the certificate belongs to the holder of the corresponding private key u Contents l l version, serial number, subject, validity period, issuer, optional fields (v 2) subject’s public key and algorithm info. extension fields (v 3) digital signature of CA u Binding users to keys u Certificate Revocation © Ravi Sandhu 2000 List (CRL) 41

X. 509 Certificate © Ravi Sandhu 2000 42

Smart Certificates u Short-Lived l Lifetime More secure n typical validity period for X. 509 is months (years) n the longer-lived certificates have a higher probability of being attacked – users may leave copies of the corresponding keys behind l No Certificate Revocation List (CRL) n supports © Ravi Sandhu 2000 simple and less expensive PKI 43

Smart Certificates u Containing Attributes Securely Web servers can use secure attributes for their purposes l Each authority has independent control on the corresponding information l n basic certificate (containing identity information) n each attribute can be added, changed, revoked, or re-issued by the appropriate authority – e. g. , role, credit card number, clearance, etc. © Ravi Sandhu 2000 44

Applications of Smart Certificates u Very similar to applications of secure cookies © Ravi Sandhu 2000 45
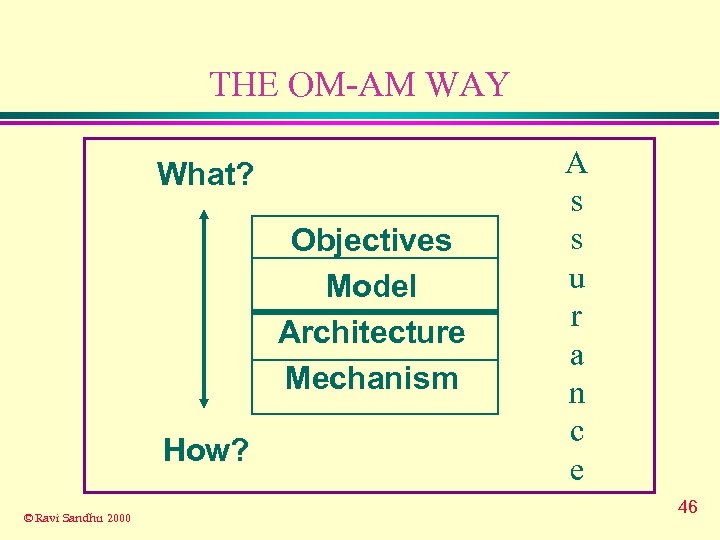
THE OM-AM WAY What? Objectives Model Architecture Mechanism How? © Ravi Sandhu 2000 A s s u r a n c e 46

INTERNET INSECURITY u Its only going to get worse u But security is a fun and profitable business and will get more so © Ravi Sandhu 2000 47
6e3f6ee021f1aef75505bcc40668c542.ppt