9b4953aa93d8d69c90fdf8cfa8ca5ca6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Securing Access to Data Using IPsec Josh Jones Cosc 352
Securing Access to Data Using IPsec Josh Jones Cosc 352
 Introduction l Internet was originally designed to link educational and government facilities together (Small Scale) – – – TCP/IP Protocols were not made with built in security Data is being sent without any filters as clear text Easily monitored by others
Introduction l Internet was originally designed to link educational and government facilities together (Small Scale) – – – TCP/IP Protocols were not made with built in security Data is being sent without any filters as clear text Easily monitored by others
 Introduction (Cont. ) l Rapidly increasing size of the internet as well as private networks – Called for greater security measures IPsec (IP Security) l SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) l TLS (Transport Layer Security) l
Introduction (Cont. ) l Rapidly increasing size of the internet as well as private networks – Called for greater security measures IPsec (IP Security) l SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) l TLS (Transport Layer Security) l
 What Is IPsec (IP Security) l l l A framework of open standards for helping to ensure private, secure communications over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. Based on cryptography, used to encrypt data so that it cannot be read or tampered with during its journey across an IP network. Operates at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model.
What Is IPsec (IP Security) l l l A framework of open standards for helping to ensure private, secure communications over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. Based on cryptography, used to encrypt data so that it cannot be read or tampered with during its journey across an IP network. Operates at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model.
 What Is IPsec (IP Security) (Cont. ) l Designed to provide the following: – – – l authentication (verification of the identity of the sender). integrity (assurance that the data was not changed in transit). confidentiality (encryption of the data so that it can’t be read by anyone who doesn’t have the correct key). Provides security for almost all protocols in the TCP/IP suite.
What Is IPsec (IP Security) (Cont. ) l Designed to provide the following: – – – l authentication (verification of the identity of the sender). integrity (assurance that the data was not changed in transit). confidentiality (encryption of the data so that it can’t be read by anyone who doesn’t have the correct key). Provides security for almost all protocols in the TCP/IP suite.
 What Is IPsec (IP Security) (Cont. ) l IPsec is composed of three main protocols. – Authentication Header (AH). l – Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP). l – used to authenticate the identity of the sender, and to provide integrity of the data to ensure that it hasn’t been modified. can provide confidentiality by encrypting the data itself, along with authentication and integrity. Internet Key Exchange (IKE). l the protocol used to set up a security association (SA) in the IPsec.
What Is IPsec (IP Security) (Cont. ) l IPsec is composed of three main protocols. – Authentication Header (AH). l – Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP). l – used to authenticate the identity of the sender, and to provide integrity of the data to ensure that it hasn’t been modified. can provide confidentiality by encrypting the data itself, along with authentication and integrity. Internet Key Exchange (IKE). l the protocol used to set up a security association (SA) in the IPsec.
 Benefits of IPsec l Transparency of IPsec to users and applications. – IPsec is integrated at the Network layer (layer 3), there is no need to configure separate security for each application that uses TCP/IP.
Benefits of IPsec l Transparency of IPsec to users and applications. – IPsec is integrated at the Network layer (layer 3), there is no need to configure separate security for each application that uses TCP/IP.
 Benefits of IPsec (Cont. ) l Defense-in-depth against vulnerabilities in upper-layer protocols and applications. – – IPsec protects upper layer protocols, services, and applications. With IPsec enabled, initial packets to access an application or service running on a server.
Benefits of IPsec (Cont. ) l Defense-in-depth against vulnerabilities in upper-layer protocols and applications. – – IPsec protects upper layer protocols, services, and applications. With IPsec enabled, initial packets to access an application or service running on a server.
 Benefits of IPsec (Cont. ) l Restricted access to servers. – – Using IPsec policy, you can configure a server to only accept specific types of traffic. For example, you can configure an email server to accept only secured email traffic from client computers. The email server discards all other traffic from client computers.
Benefits of IPsec (Cont. ) l Restricted access to servers. – – Using IPsec policy, you can configure a server to only accept specific types of traffic. For example, you can configure an email server to accept only secured email traffic from client computers. The email server discards all other traffic from client computers.
 Benefits of IPsec (Cont. ) l Customizable security configuration. – Administrators can configure IPsec policies to meet the security requirements of an application, computer, group of computers, domain, site, or global organization. IPsec can be customized for use in a wide range of scenarios, including packet filtering, securing host-to-host traffic on specific paths, securing traffic to servers, Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L 2 TP)/IPsec for virtual private network (VPN) connections, and site-to-site (also known as gateway-to-gateway) tunneling.
Benefits of IPsec (Cont. ) l Customizable security configuration. – Administrators can configure IPsec policies to meet the security requirements of an application, computer, group of computers, domain, site, or global organization. IPsec can be customized for use in a wide range of scenarios, including packet filtering, securing host-to-host traffic on specific paths, securing traffic to servers, Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L 2 TP)/IPsec for virtual private network (VPN) connections, and site-to-site (also known as gateway-to-gateway) tunneling.
 Modes of IPsec l Tunnel Mode: – l the entire IP packet (data plus the message headers) is encrypted and/or authenticated; provides gateway to gateway (or server to server) protection. Transportation Mode: – used to encrypt data inside a tunnel that is created by L 2 TP (the layer 2 tunneling protocol). Transport mode provides end-to-end security, all the way from the sending computer to the final destination.
Modes of IPsec l Tunnel Mode: – l the entire IP packet (data plus the message headers) is encrypted and/or authenticated; provides gateway to gateway (or server to server) protection. Transportation Mode: – used to encrypt data inside a tunnel that is created by L 2 TP (the layer 2 tunneling protocol). Transport mode provides end-to-end security, all the way from the sending computer to the final destination.
 Recommended Scenarios for IPsec l l Packet filtering End-to-end security between specific hosts End-to-end traffic through an ISA-secured NAT Secure server
Recommended Scenarios for IPsec l l Packet filtering End-to-end security between specific hosts End-to-end traffic through an ISA-secured NAT Secure server
 Recommended Scenarios for IPsec (Cont. ) l l Server isolation Domain isolation L 2 TP/IPsec for remote access and site-to-site VPN connections Gateway-to-gateway IPsec tunneling with thirdparty IPsec gateways
Recommended Scenarios for IPsec (Cont. ) l l Server isolation Domain isolation L 2 TP/IPsec for remote access and site-to-site VPN connections Gateway-to-gateway IPsec tunneling with thirdparty IPsec gateways
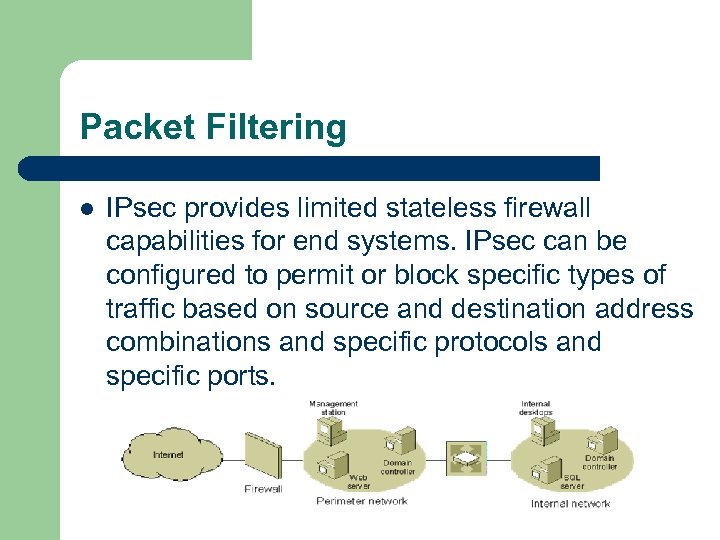 Packet Filtering l IPsec provides limited stateless firewall capabilities for end systems. IPsec can be configured to permit or block specific types of traffic based on source and destination address combinations and specific protocols and specific ports.
Packet Filtering l IPsec provides limited stateless firewall capabilities for end systems. IPsec can be configured to permit or block specific types of traffic based on source and destination address combinations and specific protocols and specific ports.
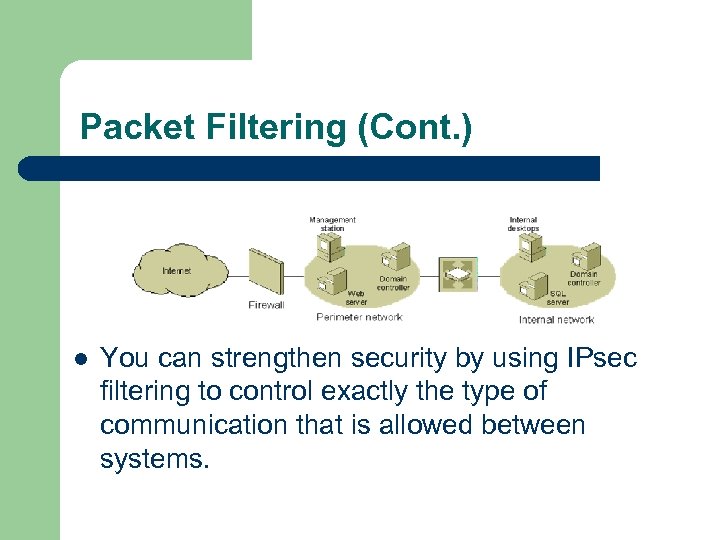 Packet Filtering (Cont. ) l You can strengthen security by using IPsec filtering to control exactly the type of communication that is allowed between systems.
Packet Filtering (Cont. ) l You can strengthen security by using IPsec filtering to control exactly the type of communication that is allowed between systems.
 Secure Server l l Allows IPsec authentication and protection for traffic between specific sets of servers Secures communication in environments that are not secure Complements firewalls by requiring authentication of all traffic Reduces firewall exceptions to IPsec traffic
Secure Server l l Allows IPsec authentication and protection for traffic between specific sets of servers Secures communication in environments that are not secure Complements firewalls by requiring authentication of all traffic Reduces firewall exceptions to IPsec traffic
 Domain Isolation l l Allows host to host communication to be limited to domain members (managed computers) Requires IPsec authentication and protection for any communication with domain members (managed computers) – – Managed computers can initiate communication with managed and unmanaged computers Unmanaged computers cannot initiate communication with managed computers
Domain Isolation l l Allows host to host communication to be limited to domain members (managed computers) Requires IPsec authentication and protection for any communication with domain members (managed computers) – – Managed computers can initiate communication with managed and unmanaged computers Unmanaged computers cannot initiate communication with managed computers
 Server Isolation l Requires IPsec authentication and protection for communications from hosts to specific servers – – Managed computers can initiate communication with specific servers Unmanaged computers cannot initiate communication with specific servers
Server Isolation l Requires IPsec authentication and protection for communications from hosts to specific servers – – Managed computers can initiate communication with specific servers Unmanaged computers cannot initiate communication with specific servers
 Server Isolation (Cont. ) l Group-specific server isolation. – Only managed computers that are members of a specific security group can initiate communication with specific servers.
Server Isolation (Cont. ) l Group-specific server isolation. – Only managed computers that are members of a specific security group can initiate communication with specific servers.
 When NOT to Use IPsec. l IPsec can reduce processing performance and increase network bandwidth consumption. Additionally, IPsec policies can be quite complex to configure and manage. Finally, the use of IPsec can introduce application compatibility issues
When NOT to Use IPsec. l IPsec can reduce processing performance and increase network bandwidth consumption. Additionally, IPsec policies can be quite complex to configure and manage. Finally, the use of IPsec can introduce application compatibility issues
 When NOT to Use IPsec. (Cont. ) l Securing traffic between domain controllers and domain members. – In addition to reduced network performance, using IPsec for this scenario is not recommended because of the complexity of the required IPsec policy configuration and management.
When NOT to Use IPsec. (Cont. ) l Securing traffic between domain controllers and domain members. – In addition to reduced network performance, using IPsec for this scenario is not recommended because of the complexity of the required IPsec policy configuration and management.
 When NOT to Use IPsec. (Cont. ) l IPsec tunnel mode for remote access VPN connections. – IPsec tunnel mode is not a recommended technology for remote access VPN connections because there are no standard methods for user authentication, IP address assignment, and name server address assignment.
When NOT to Use IPsec. (Cont. ) l IPsec tunnel mode for remote access VPN connections. – IPsec tunnel mode is not a recommended technology for remote access VPN connections because there are no standard methods for user authentication, IP address assignment, and name server address assignment.
 Creating IPsec Policies l An IPsec policy is a collection of general settings and rules that are used to configure IPsec services and that determine behavior. – General IPsec policy settings. l Settings that determine the name of the policy, its description, key exchange settings, and key exchange methods. General IPsec policy settings apply regardless of which rules are configured.
Creating IPsec Policies l An IPsec policy is a collection of general settings and rules that are used to configure IPsec services and that determine behavior. – General IPsec policy settings. l Settings that determine the name of the policy, its description, key exchange settings, and key exchange methods. General IPsec policy settings apply regardless of which rules are configured.
 Creating IPsec Policies (Cont. ) l Rules. – l One or more IPsec rules that determine which traffic IPsec examines, how that traffic is secured and encrypted, and how IPsec peers are authenticated. After the policies are created, they can be assigned to individual Active Directory domain system containers (domains, sites, organizational units). This allows the IPsec policy to be assigned at the domain, site, or organizational unit level, eliminating the administrative overhead of configuring each computer separately.
Creating IPsec Policies (Cont. ) l Rules. – l One or more IPsec rules that determine which traffic IPsec examines, how that traffic is secured and encrypted, and how IPsec peers are authenticated. After the policies are created, they can be assigned to individual Active Directory domain system containers (domains, sites, organizational units). This allows the IPsec policy to be assigned at the domain, site, or organizational unit level, eliminating the administrative overhead of configuring each computer separately.
 Defining IPsec Policy Rules l Filter list. – l A single filter list is selected that contains one or more predefined packet filters that describe the types of traffic to which the configured filter action for this rule is applied. Authentication methods. – One or more authentication methods are configured (in order of preference) and used for authentication of IPsec peers during main mode negotiations. The available authentication methods are the Kerberos V 5 protocol (used in Active Directory environments), use of a certificate issued from a specified certification authority (CA), or a preshared key.
Defining IPsec Policy Rules l Filter list. – l A single filter list is selected that contains one or more predefined packet filters that describe the types of traffic to which the configured filter action for this rule is applied. Authentication methods. – One or more authentication methods are configured (in order of preference) and used for authentication of IPsec peers during main mode negotiations. The available authentication methods are the Kerberos V 5 protocol (used in Active Directory environments), use of a certificate issued from a specified certification authority (CA), or a preshared key.
 Defining IPsec Policy Rules (Cont. ) l Filter action. – – A single filter action is selected that includes the type of action required (permit, block, or secure) for packets that match the filter list. For the secure filter action, the negotiation data contains one or more security methods that are used (in order of preference) during IKE negotiations and other IPsec settings. Each security method determines the security protocol (such as AH or ESP), the specific cryptographic algorithms, and session key regeneration settings.
Defining IPsec Policy Rules (Cont. ) l Filter action. – – A single filter action is selected that includes the type of action required (permit, block, or secure) for packets that match the filter list. For the secure filter action, the negotiation data contains one or more security methods that are used (in order of preference) during IKE negotiations and other IPsec settings. Each security method determines the security protocol (such as AH or ESP), the specific cryptographic algorithms, and session key regeneration settings.
 Conclusion l l l IPsec is a versatile way of providing security for you network. Many different scenarios for in-depth defense are available from Microsoft. However, you are free to create and customize your own policies as well.
Conclusion l l l IPsec is a versatile way of providing security for you network. Many different scenarios for in-depth defense are available from Microsoft. However, you are free to create and customize your own policies as well.


