fae6cafaeaaf20e076c49e50c693fd35.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 95
 Secured Transactions Assignment 29 Lienors vs. Secured Creditors: Future Advances 1
Secured Transactions Assignment 29 Lienors vs. Secured Creditors: Future Advances 1
 The Big Picture Part Two: The Creditor Third Party Relationship Chapter 9: Competitions for Collateral Assignment 28: Lien Creditors vs. Secureds: The Basics Assignment 29: Lien Creditors vs. Secured: Future Advances Assignment 31: Preferences Assignment 32: Secured Creditors vs. Secured Creditors Assignment 36: Buyers vs. Secured Creditors Land, Fixtures, Agriculture, and Minerals 2
The Big Picture Part Two: The Creditor Third Party Relationship Chapter 9: Competitions for Collateral Assignment 28: Lien Creditors vs. Secureds: The Basics Assignment 29: Lien Creditors vs. Secured: Future Advances Assignment 31: Preferences Assignment 32: Secured Creditors vs. Secured Creditors Assignment 36: Buyers vs. Secured Creditors Land, Fixtures, Agriculture, and Minerals 2
 Definitions “Advance” means payment of money to borrower as a loan 3
Definitions “Advance” means payment of money to borrower as a loan 3
 Definitions “Advance” means payment of money to borrower as a loan “Future advance” means an advance made after (1) the initial advance or (2) the note and security agreement are signed. 4
Definitions “Advance” means payment of money to borrower as a loan “Future advance” means an advance made after (1) the initial advance or (2) the note and security agreement are signed. 4
 Definitions “Advance” means payment of money to borrower as a loan “Future advance” means an advance made after (1) the initial advance or (2) the note and security agreement are signed. “Non-advance” means an amount that was not advanced to the borrower, but that the borrower is obligated to pay 5
Definitions “Advance” means payment of money to borrower as a loan “Future advance” means an advance made after (1) the initial advance or (2) the note and security agreement are signed. “Non-advance” means an amount that was not advanced to the borrower, but that the borrower is obligated to pay 5
 Definitions “Advance” means payment of money to borrower as a loan “Future advance” means an advance made after (1) the initial advance or (2) the note and security agreement are signed. “Non-advance” means an amount that was not advanced to the borrower, but that the borrower is obligated to pay Interest 6
Definitions “Advance” means payment of money to borrower as a loan “Future advance” means an advance made after (1) the initial advance or (2) the note and security agreement are signed. “Non-advance” means an amount that was not advanced to the borrower, but that the borrower is obligated to pay Interest 6
 Definitions “Advance” means payment of money to borrower as a loan “Future advance” means an advance made after (1) the initial advance or (2) the note and security agreement are signed. “Non-advance” means an amount that was not advanced to the borrower, but that the borrower is obligated to pay Interest Attorneys fees incurred in collection 7
Definitions “Advance” means payment of money to borrower as a loan “Future advance” means an advance made after (1) the initial advance or (2) the note and security agreement are signed. “Non-advance” means an amount that was not advanced to the borrower, but that the borrower is obligated to pay Interest Attorneys fees incurred in collection 7
 Definitions “Advance” means payment of money to borrower as a loan “Future advance” means an advance made after (1) the initial advance or (2) the note and security agreement are signed. “Non-advance” means an amount that was not advanced to the borrower, but that the borrower is obligated to pay Interest Attorneys fees incurred in collection Other expenses of the loan paid to third parties 8
Definitions “Advance” means payment of money to borrower as a loan “Future advance” means an advance made after (1) the initial advance or (2) the note and security agreement are signed. “Non-advance” means an amount that was not advanced to the borrower, but that the borrower is obligated to pay Interest Attorneys fees incurred in collection Other expenses of the loan paid to third parties 8
 Priority Rules General rule (UCC and Real Estate law): All advances and nonadvances have the same priority. Shutze v. Credithrift. 9
Priority Rules General rule (UCC and Real Estate law): All advances and nonadvances have the same priority. Shutze v. Credithrift. 9
 Priority Rules General rule (UCC and Real Estate law): All advances and nonadvances have the same priority. Shutze v. Credithrift. UCC exception: Future advances have priority over intervening liens only if made: 1. Within 45 days after lienor “became a lien creditor” 10
Priority Rules General rule (UCC and Real Estate law): All advances and nonadvances have the same priority. Shutze v. Credithrift. UCC exception: Future advances have priority over intervening liens only if made: 1. Within 45 days after lienor “became a lien creditor” 10
 Priority Rules General rule (UCC and Real Estate law): All advances and nonadvances have the same priority. Shutze v. Credithrift. UCC exception: Future advances have priority over intervening liens only if made: 1. Within 45 days after lienor “became a lien creditor” 2. Without knowledge of the lien, or 11
Priority Rules General rule (UCC and Real Estate law): All advances and nonadvances have the same priority. Shutze v. Credithrift. UCC exception: Future advances have priority over intervening liens only if made: 1. Within 45 days after lienor “became a lien creditor” 2. Without knowledge of the lien, or 11
 Priority Rules General rule (UCC and Real Estate law): All advances and nonadvances have the same priority. Shutze v. Credithrift. UCC exception: Future advances have priority over intervening liens only if made: 1. Within 45 days after lienor “became a lien creditor” 2. Without knowledge of the lien, or 3. Pursuant to commitment entered into without knowledge of the lien 12
Priority Rules General rule (UCC and Real Estate law): All advances and nonadvances have the same priority. Shutze v. Credithrift. UCC exception: Future advances have priority over intervening liens only if made: 1. Within 45 days after lienor “became a lien creditor” 2. Without knowledge of the lien, or 3. Pursuant to commitment entered into without knowledge of the lien 12
 Priority Rules General rule (UCC and Real Estate law): All advances and nonadvances have the same priority. Shutze v. Credithrift. UCC exception: Future advances have priority over intervening liens only if made: 1. Within 45 days after lienor “became a lien creditor” 2. Without knowledge of the lien, or 3. Pursuant to commitment entered into without knowledge of the lien Real estate exception (minority rule): Future advances have priority over intervening liens only if made: 2. Without knowledge of the lien, or 3. Pursuant to commitment without knowledge of the lien. 13
Priority Rules General rule (UCC and Real Estate law): All advances and nonadvances have the same priority. Shutze v. Credithrift. UCC exception: Future advances have priority over intervening liens only if made: 1. Within 45 days after lienor “became a lien creditor” 2. Without knowledge of the lien, or 3. Pursuant to commitment entered into without knowledge of the lien Real estate exception (minority rule): Future advances have priority over intervening liens only if made: 2. Without knowledge of the lien, or 3. Pursuant to commitment without knowledge of the lien. 13
 Priority Rules Non-advances (real and personal property exceptions): A nonadvance has the priority of the advance to which it relates 14
Priority Rules Non-advances (real and personal property exceptions): A nonadvance has the priority of the advance to which it relates 14
 Uni Imports v. Exchange “The marshal’s service served the writ on Exchange, but Exchange refused to turn over any of Aparcor’s assets, contending that it had priority status. ” Page 482. 15
Uni Imports v. Exchange “The marshal’s service served the writ on Exchange, but Exchange refused to turn over any of Aparcor’s assets, contending that it had priority status. ” Page 482. 15
 Uni Imports v. Exchange “The marshal’s service served the writ on Exchange, but Exchange refused to turn over any of Aparcor’s assets, contending that it had priority status. ” Page 482. How can Exchange bank refuse to permit a levy? 16
Uni Imports v. Exchange “The marshal’s service served the writ on Exchange, but Exchange refused to turn over any of Aparcor’s assets, contending that it had priority status. ” Page 482. How can Exchange bank refuse to permit a levy? 16
 Uni Imports v. Exchange “The marshal’s service served the writ on Exchange, but Exchange refused to turn over any of Aparcor’s assets, contending that it had priority status. ” Page 482. How can Exchange bank refuse to permit a levy? Page 9: “An officer may force an entry into any enclosure except the dwelling house of the judgment debtor in order to levy. . . on the debtor’s goods. . ” 17
Uni Imports v. Exchange “The marshal’s service served the writ on Exchange, but Exchange refused to turn over any of Aparcor’s assets, contending that it had priority status. ” Page 482. How can Exchange bank refuse to permit a levy? Page 9: “An officer may force an entry into any enclosure except the dwelling house of the judgment debtor in order to levy. . . on the debtor’s goods. . ” 17
 Uni Imports v. Exchange “The marshal’s service served the writ on Exchange, but Exchange refused to turn over any of Aparcor’s assets, contending that it had priority status. ” Page 482. How can Exchange bank refuse to permit a levy? Page 9: “An officer may force an entry into any enclosure except the dwelling house of the judgment debtor in order to levy. . . on the debtor’s goods. . ” Page 8. “The sheriff’s duty is to execute the writ according to the plaintiff’s instructions. 18
Uni Imports v. Exchange “The marshal’s service served the writ on Exchange, but Exchange refused to turn over any of Aparcor’s assets, contending that it had priority status. ” Page 482. How can Exchange bank refuse to permit a levy? Page 9: “An officer may force an entry into any enclosure except the dwelling house of the judgment debtor in order to levy. . . on the debtor’s goods. . ” Page 8. “The sheriff’s duty is to execute the writ according to the plaintiff’s instructions. 18
 Uni Imports v. Exchange “The marshal’s service served the writ on Exchange, but Exchange refused to turn over any of Aparcor’s assets, contending that it had priority status. ” Page 482. How can Exchange bank refuse to permit a levy? Page 9: “An officer may force an entry into any enclosure except the dwelling house of the judgment debtor in order to levy. . . on the debtor’s goods. . ” Page 8. “The sheriff’s duty is to execute the writ according to the plaintiff’s instructions. The writ is in the ‘exclusive control’ of the judgment creditor; the sheriff must follow the creditor’s reasonable instructions regarding the time and manner of making the levy. . ” 19
Uni Imports v. Exchange “The marshal’s service served the writ on Exchange, but Exchange refused to turn over any of Aparcor’s assets, contending that it had priority status. ” Page 482. How can Exchange bank refuse to permit a levy? Page 9: “An officer may force an entry into any enclosure except the dwelling house of the judgment debtor in order to levy. . . on the debtor’s goods. . ” Page 8. “The sheriff’s duty is to execute the writ according to the plaintiff’s instructions. The writ is in the ‘exclusive control’ of the judgment creditor; the sheriff must follow the creditor’s reasonable instructions regarding the time and manner of making the levy. . ” 19
 Uni Imports v. Exchange “The marshal’s service served the writ on Exchange, but Exchange refused to turn over any of Aparcor’s assets, contending that it had priority status. ” Page 482. How can Exchange bank refuse to permit a levy? Page 9: “An officer may force an entry into any enclosure except the dwelling house of the judgment debtor in order to levy. . . on the debtor’s goods. . ” Page 8. “The sheriff’s duty is to execute the writ according to the plaintiff’s instructions. The writ is in the ‘exclusive control’ of the judgment creditor; the sheriff must follow the creditor’s reasonable instructions regarding the time and manner of making the levy. . ” Answer: Soft levy or this “execution” is garnishment. 20
Uni Imports v. Exchange “The marshal’s service served the writ on Exchange, but Exchange refused to turn over any of Aparcor’s assets, contending that it had priority status. ” Page 482. How can Exchange bank refuse to permit a levy? Page 9: “An officer may force an entry into any enclosure except the dwelling house of the judgment debtor in order to levy. . . on the debtor’s goods. . ” Page 8. “The sheriff’s duty is to execute the writ according to the plaintiff’s instructions. The writ is in the ‘exclusive control’ of the judgment creditor; the sheriff must follow the creditor’s reasonable instructions regarding the time and manner of making the levy. . ” Answer: Soft levy or this “execution” is garnishment. 20
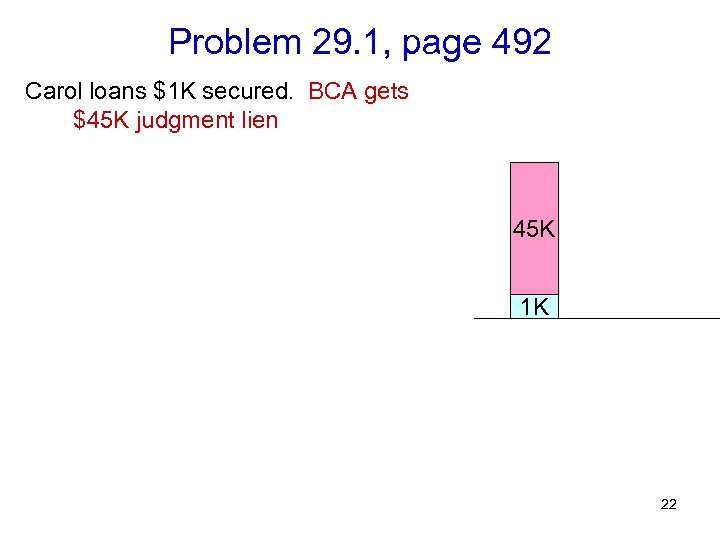
 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Assume boat worth about $32 K. What effect if Bob advances $31 K? 1 K 21
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Assume boat worth about $32 K. What effect if Bob advances $31 K? 1 K 21
 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Assume boat worth about $32 K. What effect if Bob advances $31 K? 45 K 1 K 22
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Assume boat worth about $32 K. What effect if Bob advances $31 K? 45 K 1 K 22
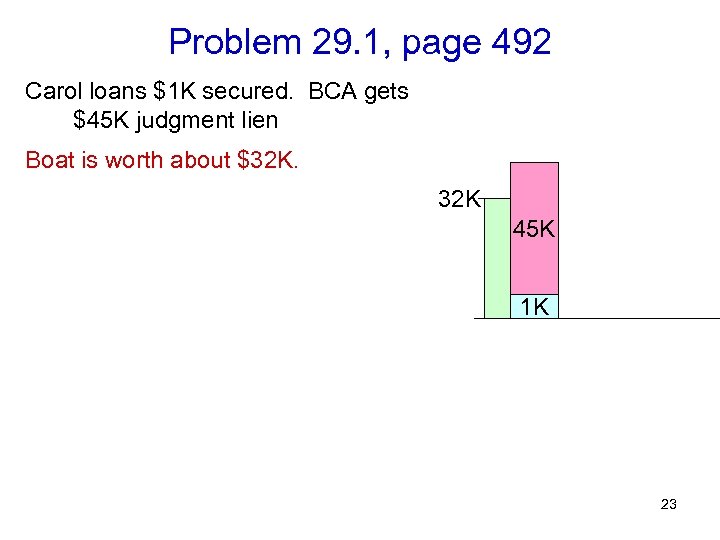 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. 32 K 45 K 1 K 23
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. 32 K 45 K 1 K 23
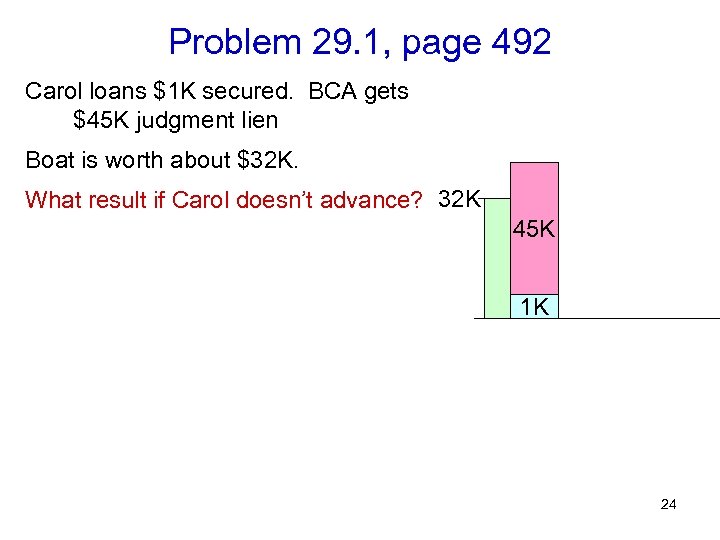 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol doesn’t advance? 32 K 45 K 1 K 24
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol doesn’t advance? 32 K 45 K 1 K 24
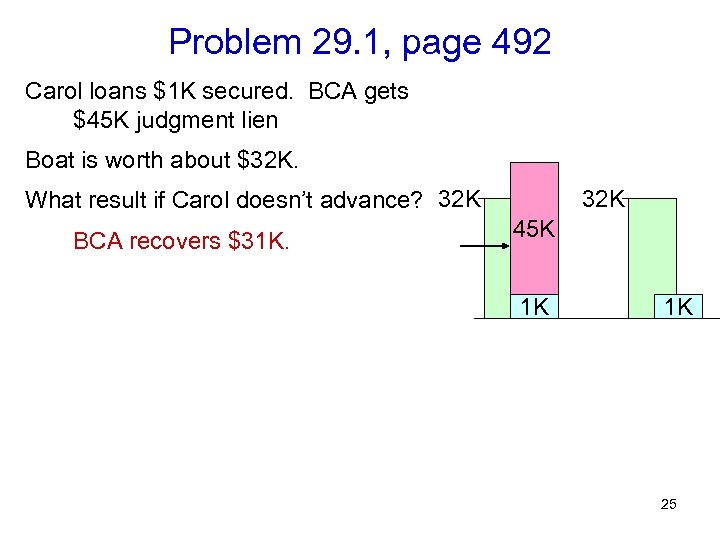 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol doesn’t advance? 32 K BCA recovers $31 K. 32 K 45 K 1 K 1 K 25
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol doesn’t advance? 32 K BCA recovers $31 K. 32 K 45 K 1 K 1 K 25
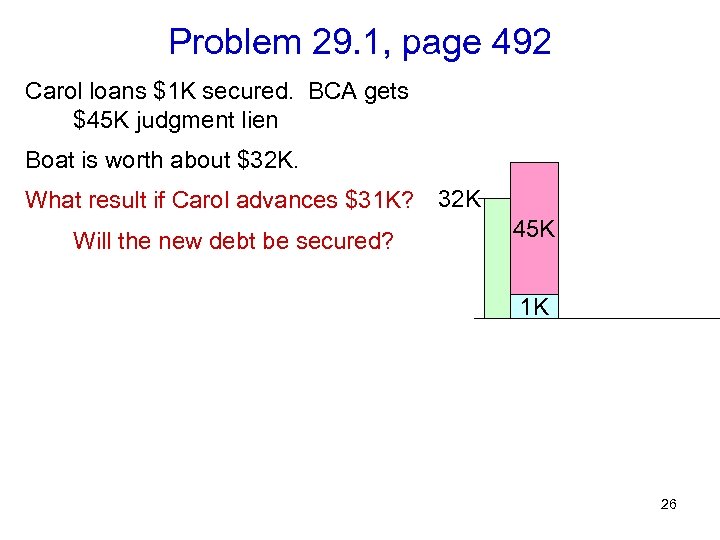 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K Will the new debt be secured? 45 K 1 K 26
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K Will the new debt be secured? 45 K 1 K 26
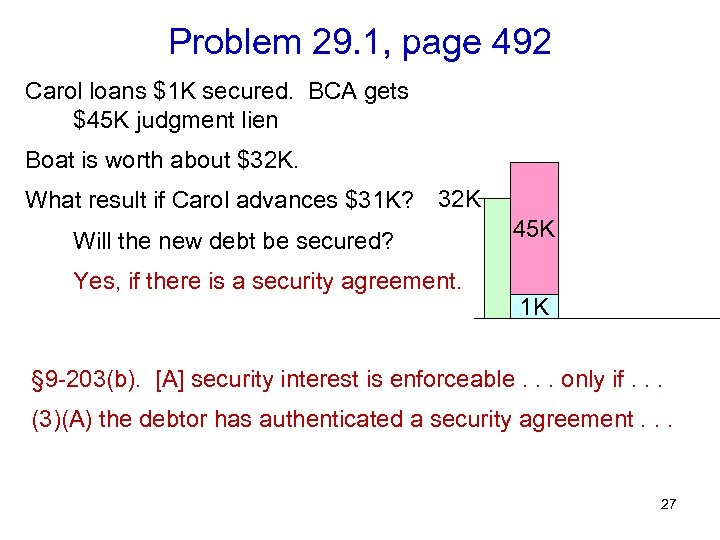 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K Will the new debt be secured? Yes, if there is a security agreement. 45 K 1 K § 9 -203(b). [A] security interest is enforceable. . . only if. . . (3)(A) the debtor has authenticated a security agreement. . . 27
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K Will the new debt be secured? Yes, if there is a security agreement. 45 K 1 K § 9 -203(b). [A] security interest is enforceable. . . only if. . . (3)(A) the debtor has authenticated a security agreement. . . 27
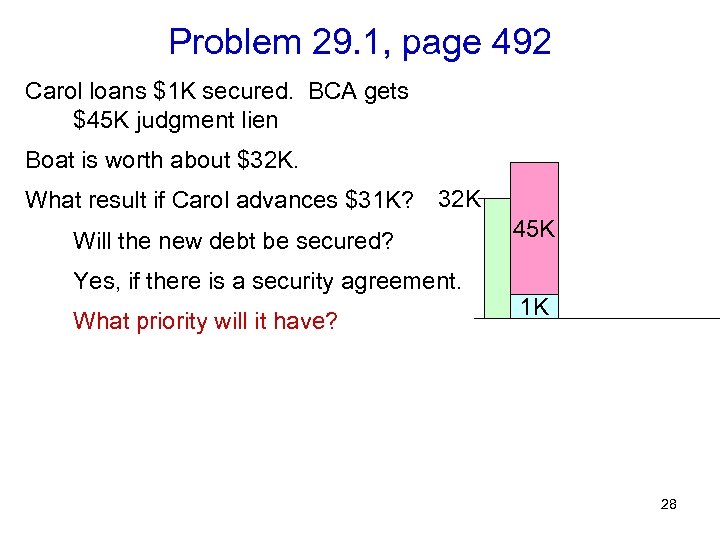 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K Will the new debt be secured? Yes, if there is a security agreement. What priority will it have? 45 K 1 K 28
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K Will the new debt be secured? Yes, if there is a security agreement. What priority will it have? 45 K 1 K 28
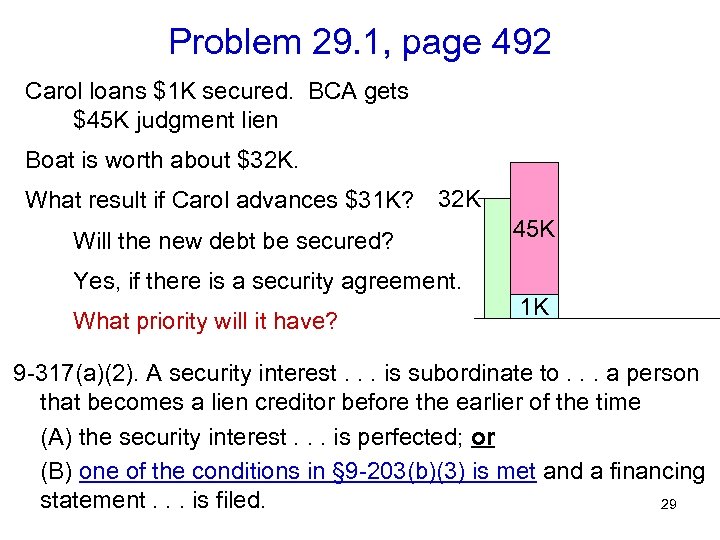 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K Will the new debt be secured? Yes, if there is a security agreement. What priority will it have? 45 K 1 K 9 -317(a)(2). A security interest. . . is subordinate to. . . a person that becomes a lien creditor before the earlier of the time (A) the security interest. . . is perfected; or (B) one of the conditions in § 9 -203(b)(3) is met and a financing statement. . . is filed. 29
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K Will the new debt be secured? Yes, if there is a security agreement. What priority will it have? 45 K 1 K 9 -317(a)(2). A security interest. . . is subordinate to. . . a person that becomes a lien creditor before the earlier of the time (A) the security interest. . . is perfected; or (B) one of the conditions in § 9 -203(b)(3) is met and a financing statement. . . is filed. 29
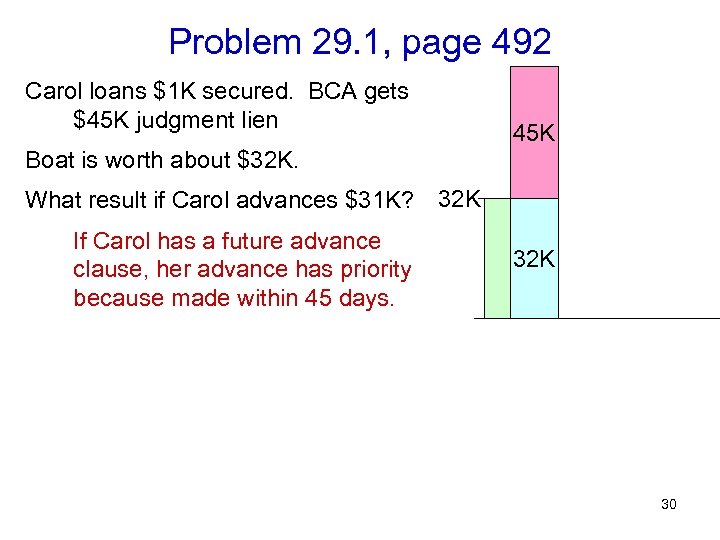 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. 32 K 30
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. 32 K 30
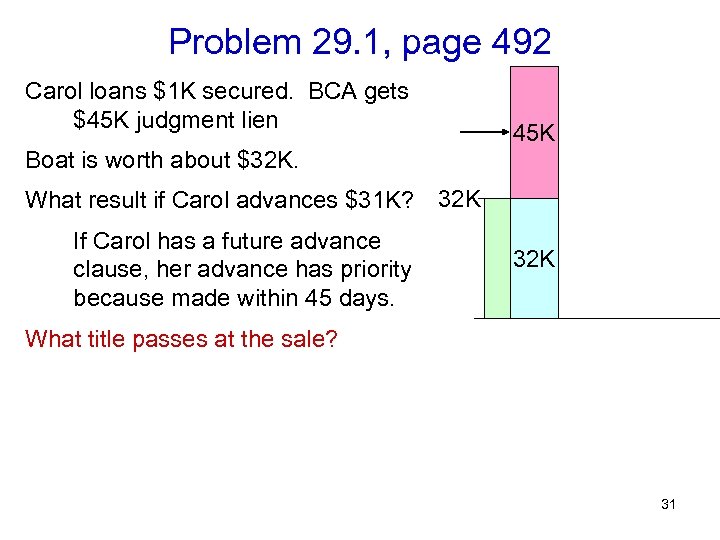 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. 32 K What title passes at the sale? 31
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. 32 K What title passes at the sale? 31
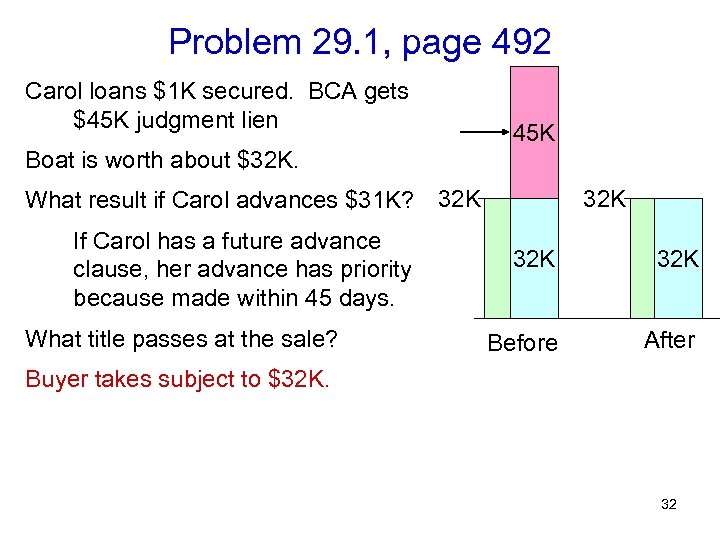 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. What title passes at the sale? 32 K 32 K Before After Buyer takes subject to $32 K. 32
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. What title passes at the sale? 32 K 32 K Before After Buyer takes subject to $32 K. 32
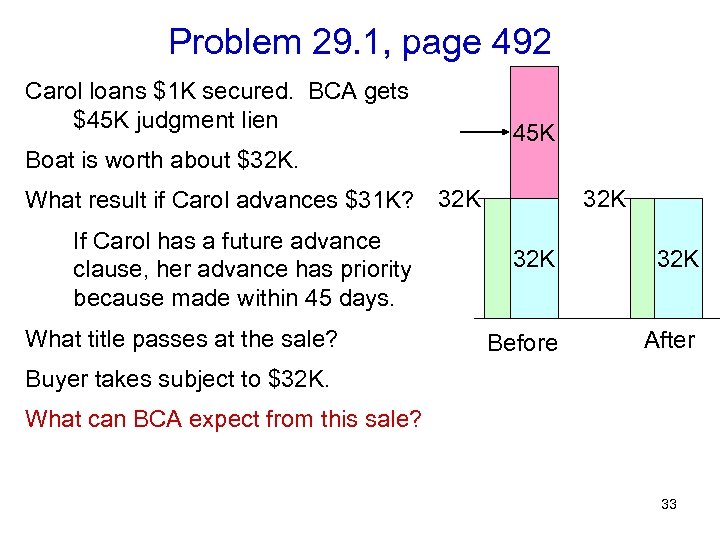 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. What title passes at the sale? 32 K 32 K Before After Buyer takes subject to $32 K. What can BCA expect from this sale? 33
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. What title passes at the sale? 32 K 32 K Before After Buyer takes subject to $32 K. What can BCA expect from this sale? 33
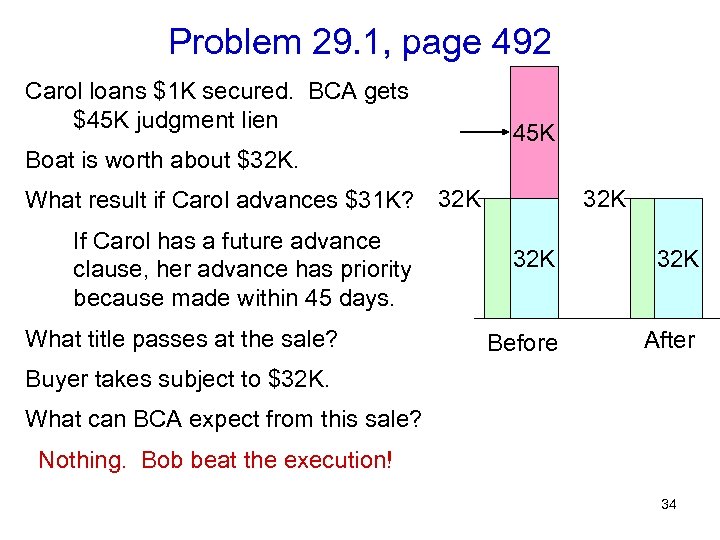 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. What title passes at the sale? 32 K 32 K Before After Buyer takes subject to $32 K. What can BCA expect from this sale? Nothing. Bob beat the execution! 34
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. What title passes at the sale? 32 K 32 K Before After Buyer takes subject to $32 K. What can BCA expect from this sale? Nothing. Bob beat the execution! 34
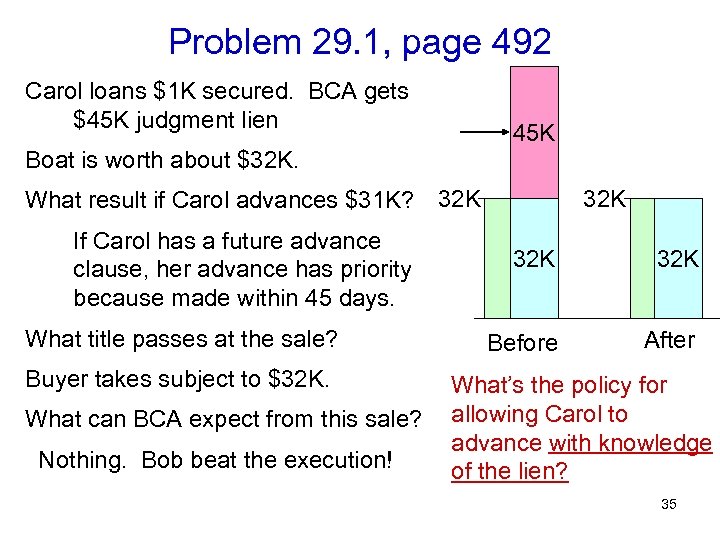 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. What title passes at the sale? Buyer takes subject to $32 K. What can BCA expect from this sale? Nothing. Bob beat the execution! 32 K 32 K Before After What’s the policy for allowing Carol to advance with knowledge of the lien? 35
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. What title passes at the sale? Buyer takes subject to $32 K. What can BCA expect from this sale? Nothing. Bob beat the execution! 32 K 32 K Before After What’s the policy for allowing Carol to advance with knowledge of the lien? 35
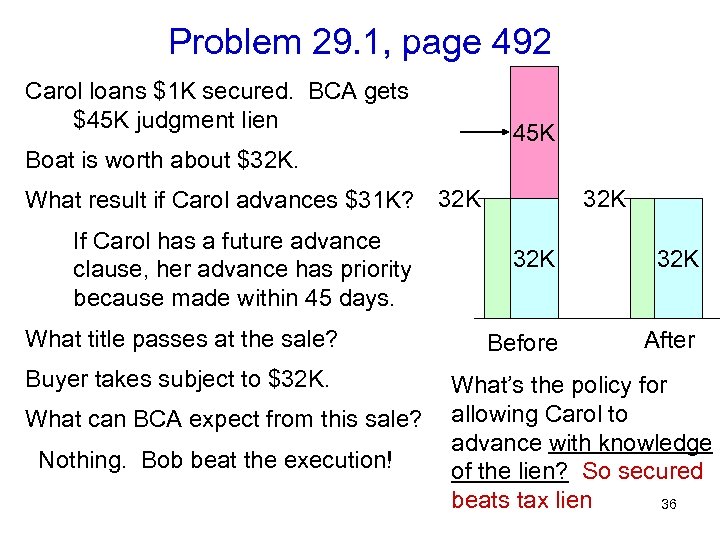 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. What title passes at the sale? Buyer takes subject to $32 K. What can BCA expect from this sale? Nothing. Bob beat the execution! 32 K 32 K Before After What’s the policy for allowing Carol to advance with knowledge of the lien? So secured beats tax lien 36
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Carol loans $1 K secured. BCA gets $45 K judgment lien 45 K Boat is worth about $32 K. What result if Carol advances $31 K? 32 K If Carol has a future advance clause, her advance has priority because made within 45 days. What title passes at the sale? Buyer takes subject to $32 K. What can BCA expect from this sale? Nothing. Bob beat the execution! 32 K 32 K Before After What’s the policy for allowing Carol to advance with knowledge of the lien? So secured beats tax lien 36
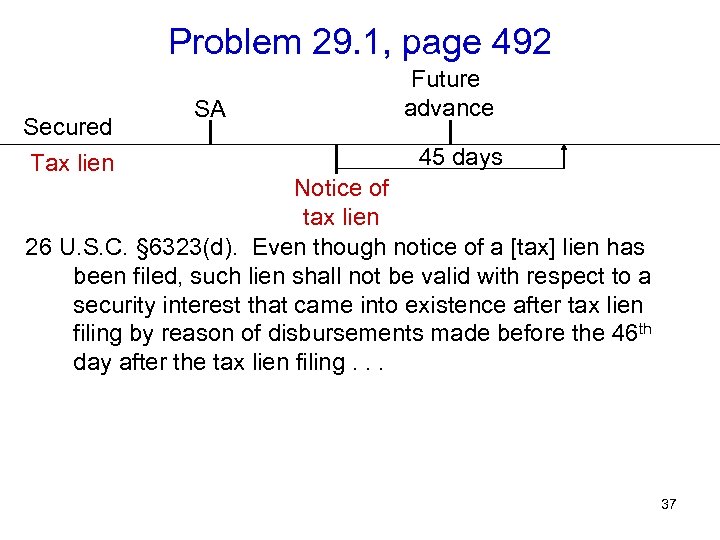 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Secured Tax lien SA Future advance 45 days Notice of tax lien 26 U. S. C. § 6323(d). Even though notice of a [tax] lien has been filed, such lien shall not be valid with respect to a security interest that came into existence after tax lien filing by reason of disbursements made before the 46 th day after the tax lien filing. . . 37
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Secured Tax lien SA Future advance 45 days Notice of tax lien 26 U. S. C. § 6323(d). Even though notice of a [tax] lien has been filed, such lien shall not be valid with respect to a security interest that came into existence after tax lien filing by reason of disbursements made before the 46 th day after the tax lien filing. . . 37
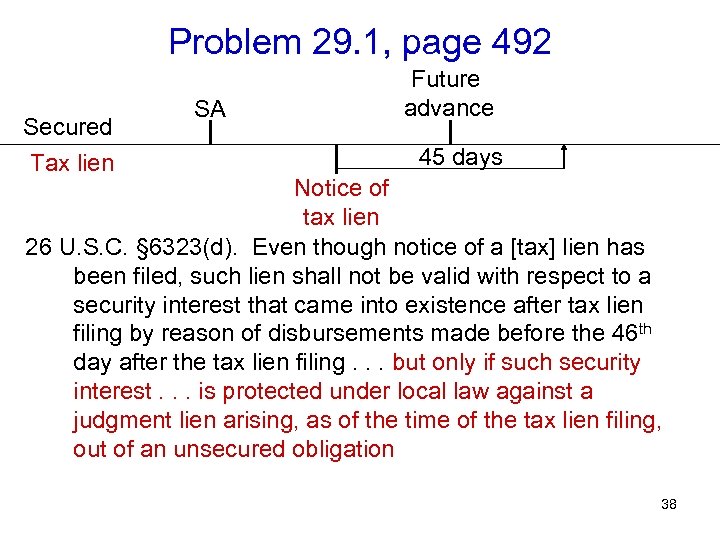 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Secured Tax lien SA Future advance 45 days Notice of tax lien 26 U. S. C. § 6323(d). Even though notice of a [tax] lien has been filed, such lien shall not be valid with respect to a security interest that came into existence after tax lien filing by reason of disbursements made before the 46 th day after the tax lien filing. . . but only if such security interest. . . is protected under local law against a judgment lien arising, as of the time of the tax lien filing, out of an unsecured obligation 38
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Secured Tax lien SA Future advance 45 days Notice of tax lien 26 U. S. C. § 6323(d). Even though notice of a [tax] lien has been filed, such lien shall not be valid with respect to a security interest that came into existence after tax lien filing by reason of disbursements made before the 46 th day after the tax lien filing. . . but only if such security interest. . . is protected under local law against a judgment lien arising, as of the time of the tax lien filing, out of an unsecured obligation 38
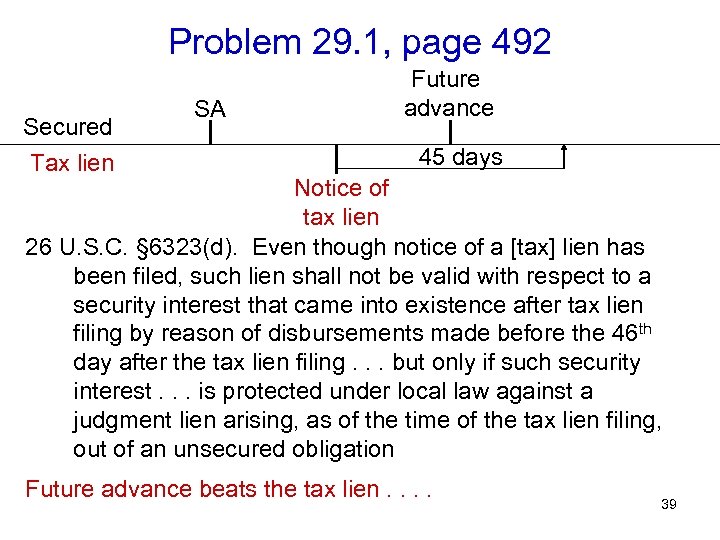 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Secured Tax lien SA Future advance 45 days Notice of tax lien 26 U. S. C. § 6323(d). Even though notice of a [tax] lien has been filed, such lien shall not be valid with respect to a security interest that came into existence after tax lien filing by reason of disbursements made before the 46 th day after the tax lien filing. . . but only if such security interest. . . is protected under local law against a judgment lien arising, as of the time of the tax lien filing, out of an unsecured obligation Future advance beats the tax lien. . 39
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Secured Tax lien SA Future advance 45 days Notice of tax lien 26 U. S. C. § 6323(d). Even though notice of a [tax] lien has been filed, such lien shall not be valid with respect to a security interest that came into existence after tax lien filing by reason of disbursements made before the 46 th day after the tax lien filing. . . but only if such security interest. . . is protected under local law against a judgment lien arising, as of the time of the tax lien filing, out of an unsecured obligation Future advance beats the tax lien. . 39
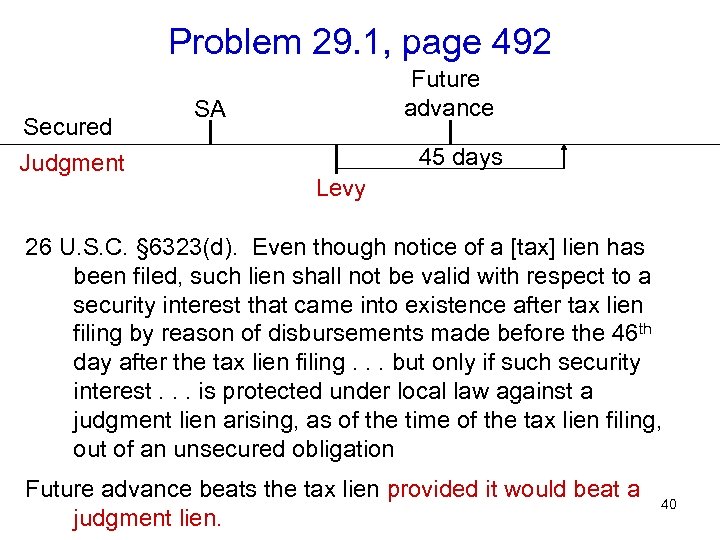 Problem 29. 1, page 492 Secured Judgment Future advance SA 45 days Levy 26 U. S. C. § 6323(d). Even though notice of a [tax] lien has been filed, such lien shall not be valid with respect to a security interest that came into existence after tax lien filing by reason of disbursements made before the 46 th day after the tax lien filing. . . but only if such security interest. . . is protected under local law against a judgment lien arising, as of the time of the tax lien filing, out of an unsecured obligation Future advance beats the tax lien provided it would beat a judgment lien. 40
Problem 29. 1, page 492 Secured Judgment Future advance SA 45 days Levy 26 U. S. C. § 6323(d). Even though notice of a [tax] lien has been filed, such lien shall not be valid with respect to a security interest that came into existence after tax lien filing by reason of disbursements made before the 46 th day after the tax lien filing. . . but only if such security interest. . . is protected under local law against a judgment lien arising, as of the time of the tax lien filing, out of an unsecured obligation Future advance beats the tax lien provided it would beat a judgment lien. 40
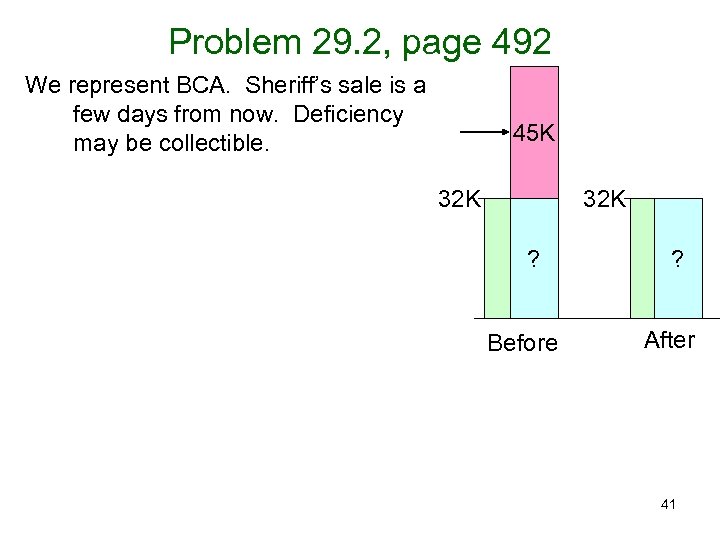 Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. 45 K 32 K ? Before ? After 41
Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. 45 K 32 K ? Before ? After 41
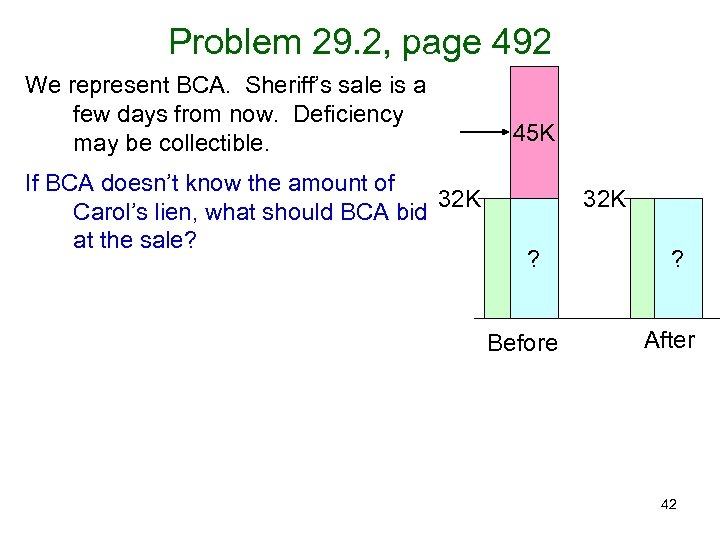 Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? 45 K 32 K ? Before ? After 42
Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? 45 K 32 K ? Before ? After 42
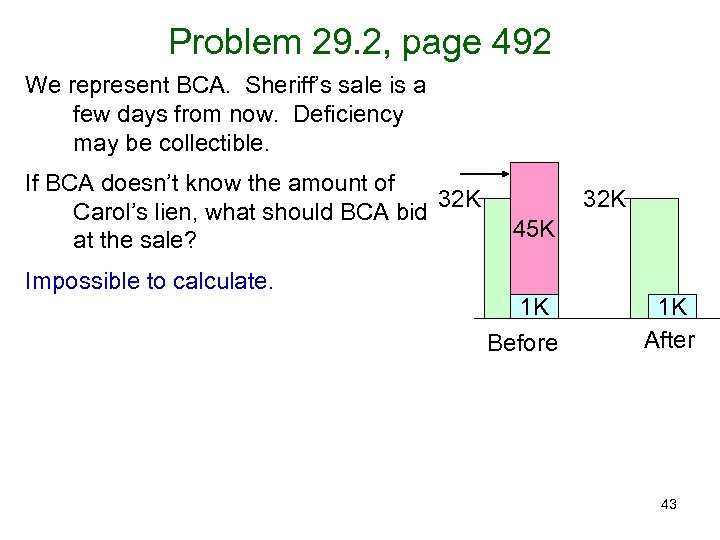 Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. 32 K 45 K 1 K Before 1 K After 43
Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. 32 K 45 K 1 K Before 1 K After 43
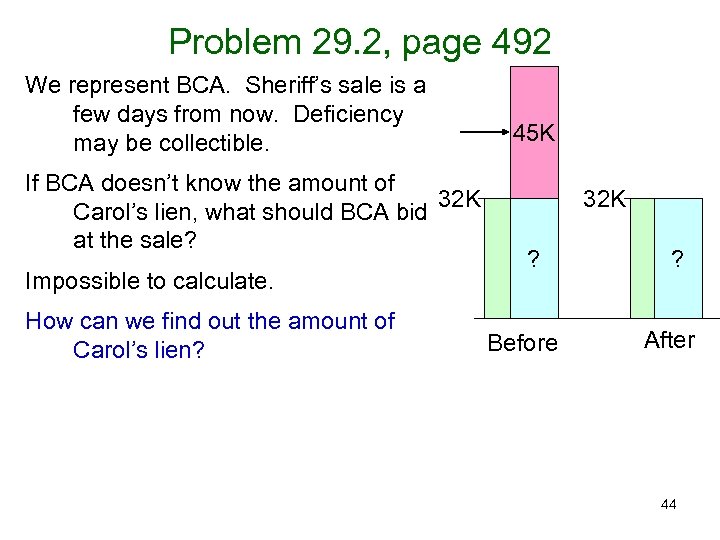 Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? 45 K 32 K ? Before ? After 44
Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? 45 K 32 K ? Before ? After 44
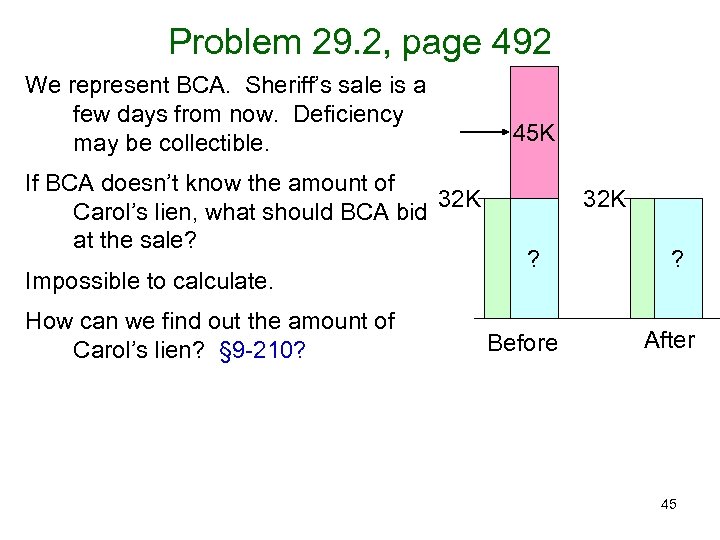 Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? 45 K 32 K ? Before ? After 45
Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? 45 K 32 K ? Before ? After 45
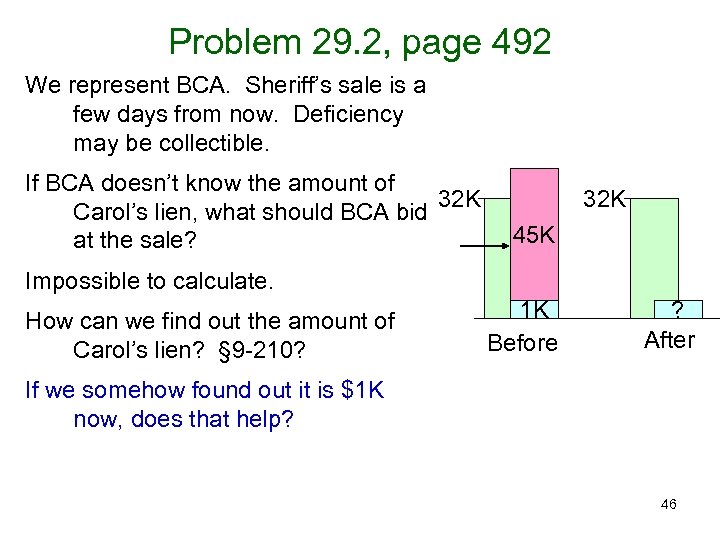 Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? 32 K 45 K Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? 1 K Before ? After If we somehow found out it is $1 K now, does that help? 46
Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? 32 K 45 K Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? 1 K Before ? After If we somehow found out it is $1 K now, does that help? 46
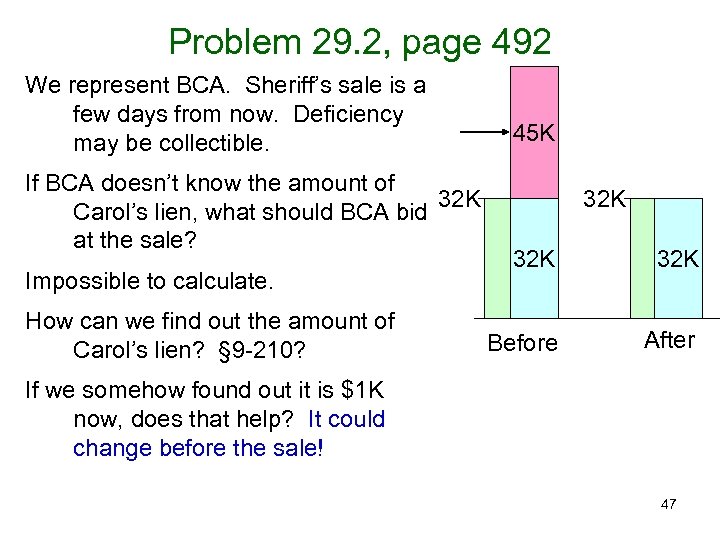 Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? 45 K 32 K 32 K Before After If we somehow found out it is $1 K now, does that help? It could change before the sale! 47
Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? 45 K 32 K 32 K Before After If we somehow found out it is $1 K now, does that help? It could change before the sale! 47
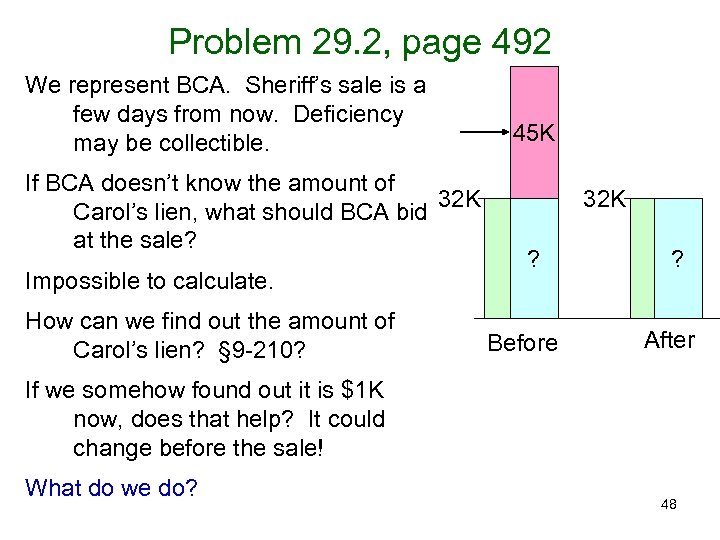 Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? 45 K 32 K ? Before ? After If we somehow found out it is $1 K now, does that help? It could change before the sale! What do we do? 48
Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? 45 K 32 K ? Before ? After If we somehow found out it is $1 K now, does that help? It could change before the sale! What do we do? 48
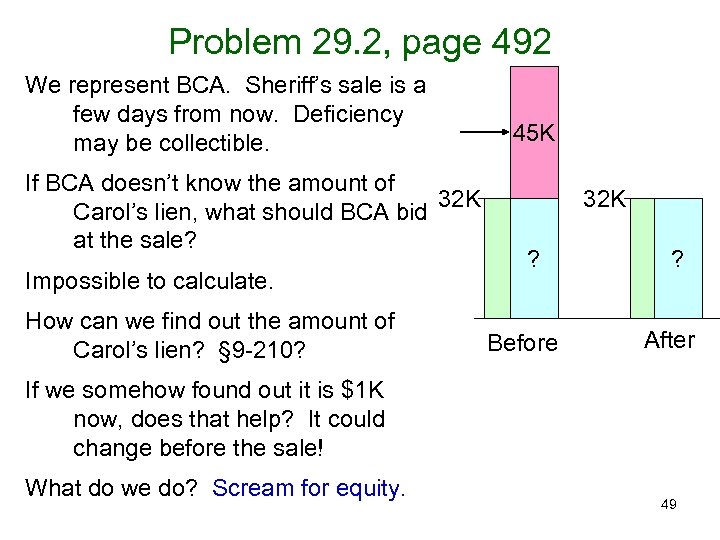 Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? 45 K 32 K ? Before ? After If we somehow found out it is $1 K now, does that help? It could change before the sale! What do we do? Scream for equity. 49
Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of 32 K Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? 45 K 32 K ? Before ? After If we somehow found out it is $1 K now, does that help? It could change before the sale! What do we do? Scream for equity. 49
 Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? § 9 -625(a). If it is established that a secured party is not proceeding in accordance with this article, a court may order or restrain. . . disposition of collateral on appropriate terms and conditions. If we somehow found out it is $1 K now, does that help? It could change before the sale! What do we do? Scream for equity. But see § 9 -625(a)! 50
Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? § 9 -625(a). If it is established that a secured party is not proceeding in accordance with this article, a court may order or restrain. . . disposition of collateral on appropriate terms and conditions. If we somehow found out it is $1 K now, does that help? It could change before the sale! What do we do? Scream for equity. But see § 9 -625(a)! 50
 Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? If we somehow found out it is $1 K now, does that help? It could change before the sale! What do we do? Scream for equity. But see § 9 -625(a)! § 9 -625(a). If it is established that a secured party is not proceeding in accordance with this article, a court may order or restrain. . . disposition of collateral on appropriate terms and conditions. Daniel’s solution: Delay the execution sale 45 days and then discover the balance 51 owing.
Problem 29. 2, page 492 We represent BCA. Sheriff’s sale is a few days from now. Deficiency may be collectible. If BCA doesn’t know the amount of Carol’s lien, what should BCA bid at the sale? Impossible to calculate. How can we find out the amount of Carol’s lien? § 9 -210? If we somehow found out it is $1 K now, does that help? It could change before the sale! What do we do? Scream for equity. But see § 9 -625(a)! § 9 -625(a). If it is established that a secured party is not proceeding in accordance with this article, a court may order or restrain. . . disposition of collateral on appropriate terms and conditions. Daniel’s solution: Delay the execution sale 45 days and then discover the balance 51 owing.
 Problem 29. 2, page 492 Uni Imports, page 485 (indented text) quoting the Article 9 drafters (1972): It seems unfair to make it possible for a debtor and secured party with knowledge of the judgment lien to squeeze out a judgment creditor who has successfully levied on a valuable equity subject to a security interest 52
Problem 29. 2, page 492 Uni Imports, page 485 (indented text) quoting the Article 9 drafters (1972): It seems unfair to make it possible for a debtor and secured party with knowledge of the judgment lien to squeeze out a judgment creditor who has successfully levied on a valuable equity subject to a security interest 52
 Problem 29. 2, page 492 Uni Imports, page 485 (indented text) quoting the Article 9 drafters (1972): It seems unfair to make it possible for a debtor and secured party with knowledge of the judgment lien to squeeze out a judgment creditor who has successfully levied on a valuable equity subject to a security interest by permitting later enlargement of the security interest, by an additional advance. . 53
Problem 29. 2, page 492 Uni Imports, page 485 (indented text) quoting the Article 9 drafters (1972): It seems unfair to make it possible for a debtor and secured party with knowledge of the judgment lien to squeeze out a judgment creditor who has successfully levied on a valuable equity subject to a security interest by permitting later enlargement of the security interest, by an additional advance. . 53
 Problem 29. 2, page 492 Uni Imports, page 485 (indented text) quoting the Article 9 drafters (1972): It seems unfair to make it possible for a debtor and secured party with knowledge of the judgment lien to squeeze out a judgment creditor who has successfully levied on a valuable equity subject to a security interest by permitting later enlargement of the security interest, by an additional advance. 54
Problem 29. 2, page 492 Uni Imports, page 485 (indented text) quoting the Article 9 drafters (1972): It seems unfair to make it possible for a debtor and secured party with knowledge of the judgment lien to squeeze out a judgment creditor who has successfully levied on a valuable equity subject to a security interest by permitting later enlargement of the security interest, by an additional advance. 54
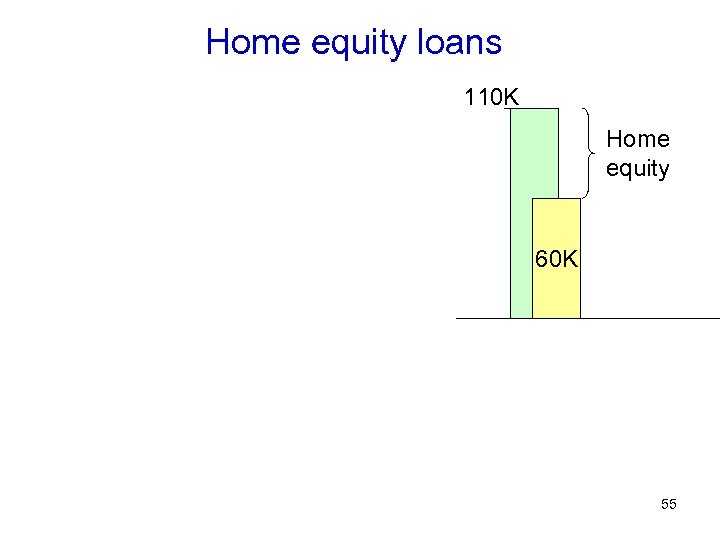 Home equity loans 110 K Home equity 60 K 55
Home equity loans 110 K Home equity 60 K 55
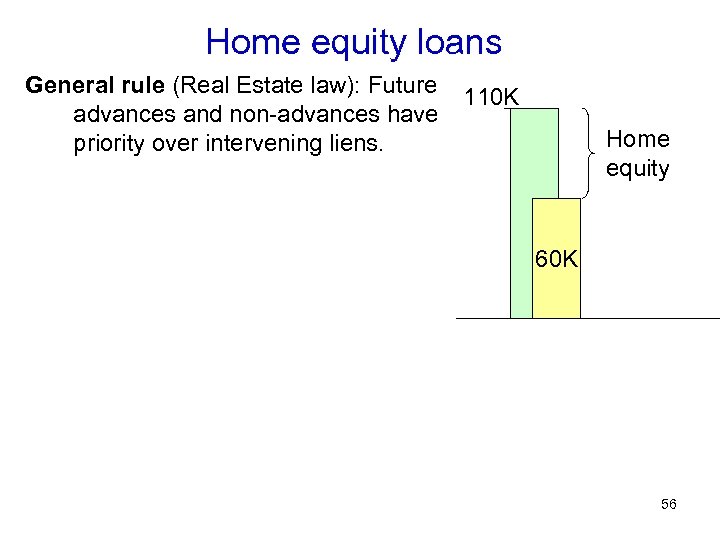 Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. 110 K Home equity 60 K 56
Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. 110 K Home equity 60 K 56
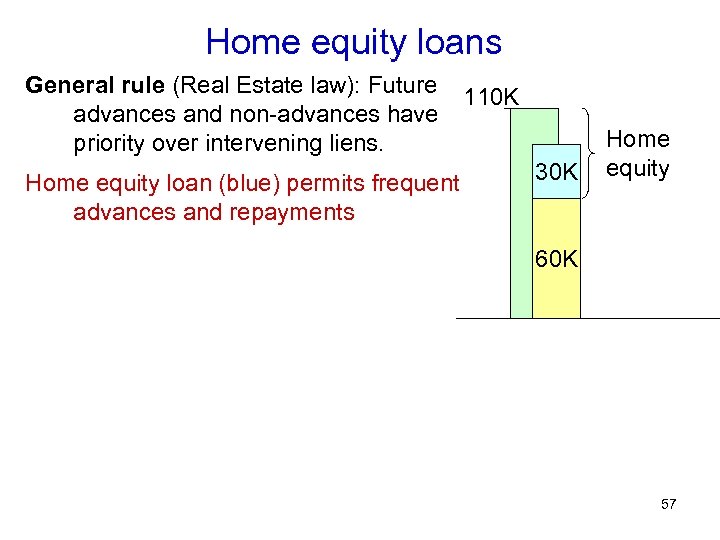 Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments 110 K 30 K Home equity 60 K 57
Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments 110 K 30 K Home equity 60 K 57
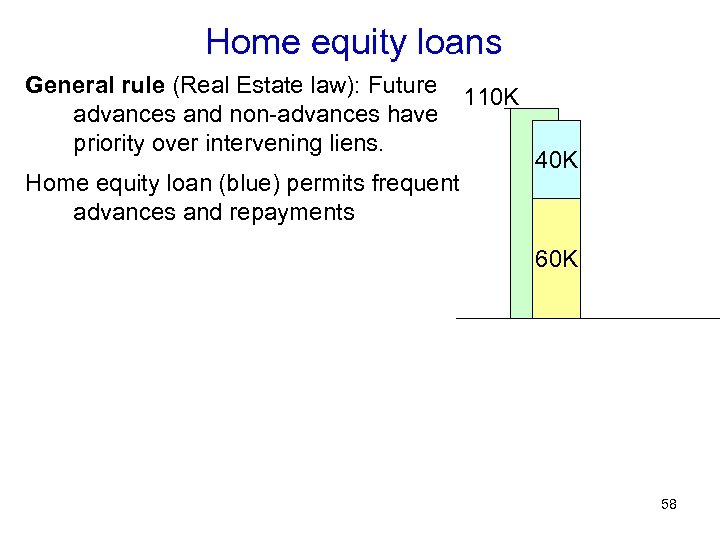 Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments 110 K 40 K 60 K 58
Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments 110 K 40 K 60 K 58
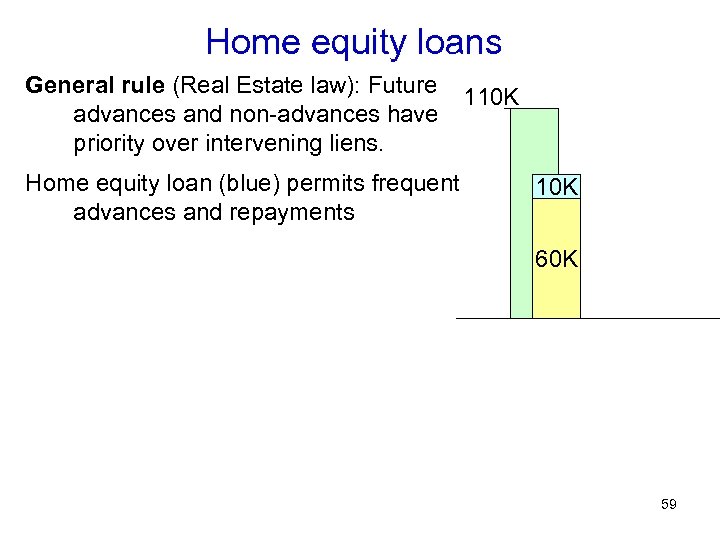 Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments 110 K 60 K 59
Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments 110 K 60 K 59
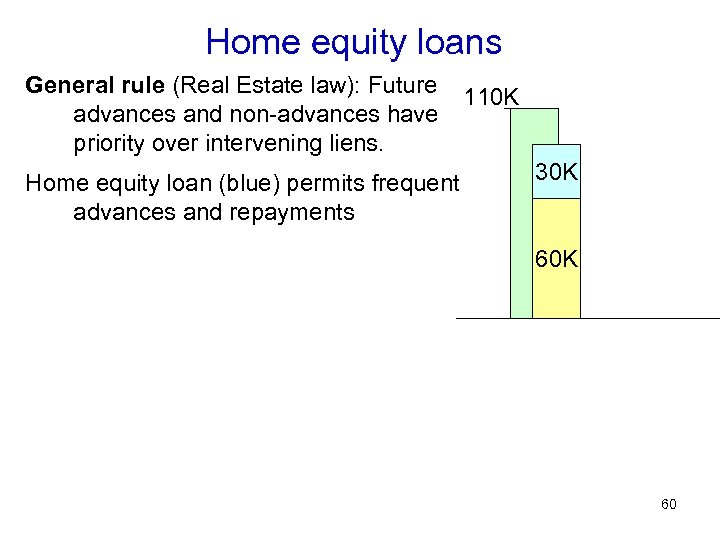 Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments 110 K 30 K 60
Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments 110 K 30 K 60
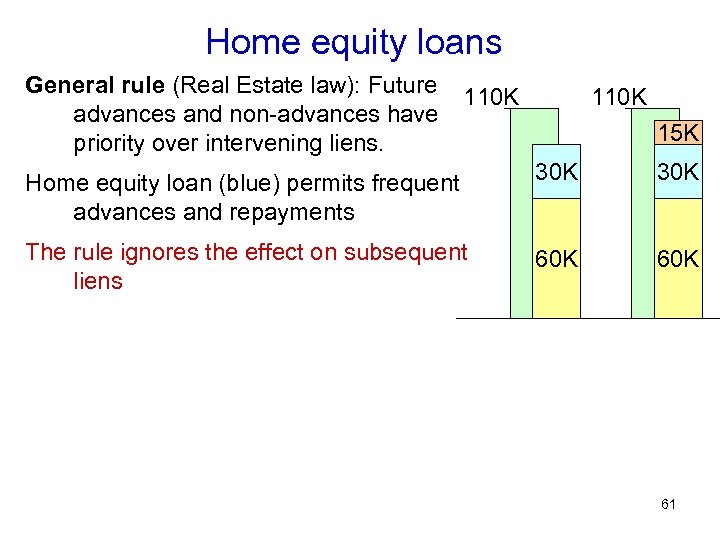 Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. 110 K 15 K Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments 30 K The rule ignores the effect on subsequent liens 60 K 61
Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. 110 K 15 K Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments 30 K The rule ignores the effect on subsequent liens 60 K 61
 Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. 110 K 15 K 50 K Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments The rule ignores the effect on subsequent liens. 60 K 62
Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. 110 K 15 K 50 K Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments The rule ignores the effect on subsequent liens. 60 K 62
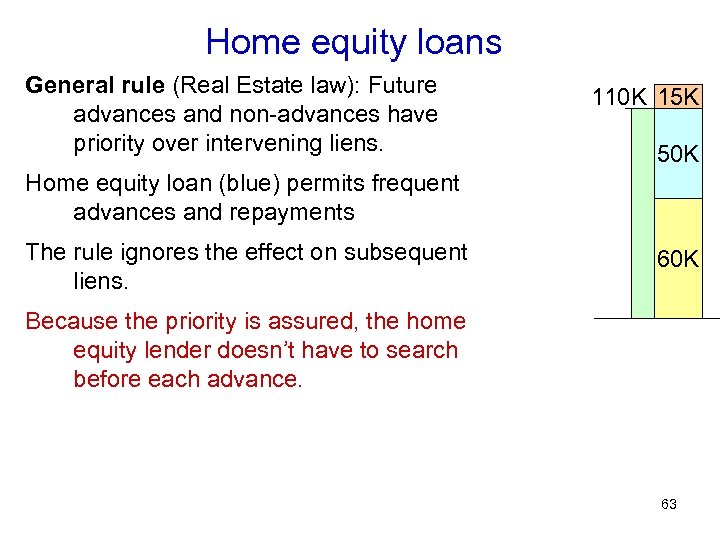 Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. 110 K 15 K 50 K Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments The rule ignores the effect on subsequent liens. 60 K Because the priority is assured, the home equity lender doesn’t have to search before each advance. 63
Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. 110 K 15 K 50 K Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments The rule ignores the effect on subsequent liens. 60 K Because the priority is assured, the home equity lender doesn’t have to search before each advance. 63
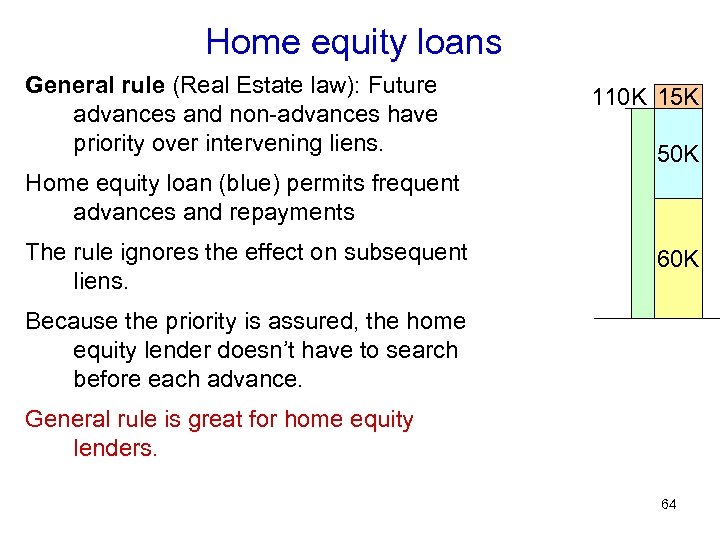 Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. 110 K 15 K 50 K Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments The rule ignores the effect on subsequent liens. 60 K Because the priority is assured, the home equity lender doesn’t have to search before each advance. General rule is great for home equity lenders. 64
Home equity loans General rule (Real Estate law): Future advances and non-advances have priority over intervening liens. 110 K 15 K 50 K Home equity loan (blue) permits frequent advances and repayments The rule ignores the effect on subsequent liens. 60 K Because the priority is assured, the home equity lender doesn’t have to search before each advance. General rule is great for home equity lenders. 64
 Home equity loans Optional advance rule: If the future advance is “optional” and made with knowledge of the lien, the advance is subordinate. 110 K 15 K 30 K 65
Home equity loans Optional advance rule: If the future advance is “optional” and made with knowledge of the lien, the advance is subordinate. 110 K 15 K 30 K 65
 Home equity loans Optional advance rule: If the future advance is “optional” and made with knowledge of the lien, the advance is subordinate. 110 K 20 K 15 K 30 K 66
Home equity loans Optional advance rule: If the future advance is “optional” and made with knowledge of the lien, the advance is subordinate. 110 K 20 K 15 K 30 K 66
 Home equity loans Optional advance rule: If the future advance is “optional” and made with knowledge of the lien, the advance is subordinate. 110 K 20 K 15 K Shutze: “Many Mississippians need to borrow substantial sums with which to educate their offspring. . They and their lenders need the security of the knowledge that their priority position will remain fixed to the date of the original deed of trust. . Any other view could imperil the student’s education. . . ” 30 K 67
Home equity loans Optional advance rule: If the future advance is “optional” and made with knowledge of the lien, the advance is subordinate. 110 K 20 K 15 K Shutze: “Many Mississippians need to borrow substantial sums with which to educate their offspring. . They and their lenders need the security of the knowledge that their priority position will remain fixed to the date of the original deed of trust. . Any other view could imperil the student’s education. . . ” 30 K 67
 Home equity loans Optional advance rule: If the future advance is “optional” and made with knowledge of the lien, the advance is subordinate. 110 K 20 K 15 K Shutze: “Many Mississippians need to borrow substantial sums with which to educate their offspring. . They and their lenders need the security of the knowledge that their priority position will remain fixed to the date of the original deed of trust. . Any other view could imperil the student’s education. . . ” 30 K 60 K Can home equity lenders live with the optional advance rule? 68
Home equity loans Optional advance rule: If the future advance is “optional” and made with knowledge of the lien, the advance is subordinate. 110 K 20 K 15 K Shutze: “Many Mississippians need to borrow substantial sums with which to educate their offspring. . They and their lenders need the security of the knowledge that their priority position will remain fixed to the date of the original deed of trust. . Any other view could imperil the student’s education. . . ” 30 K 60 K Can home equity lenders live with the optional advance rule? 68
 Home equity loans Optional advance rule: If the future advance is “optional” and made with knowledge of the lien, the advance is subordinate. 110 K 20 K 15 K Shutze: “Many Mississippians need to borrow substantial sums with which to educate their offspring. . They and their lenders need the security of the knowledge that their priority position will remain fixed to the date of the original deed of trust. . Any other view could imperil the student’s education. . . ” 30 K Can home equity lenders live with the optional advance rule? 60 K Don’t lend with knowledge of a lien? 69
Home equity loans Optional advance rule: If the future advance is “optional” and made with knowledge of the lien, the advance is subordinate. 110 K 20 K 15 K Shutze: “Many Mississippians need to borrow substantial sums with which to educate their offspring. . They and their lenders need the security of the knowledge that their priority position will remain fixed to the date of the original deed of trust. . Any other view could imperil the student’s education. . . ” 30 K Can home equity lenders live with the optional advance rule? 60 K Don’t lend with knowledge of a lien? 69
 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Mortgagee Note, mortgage $50 K advance 70
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Mortgagee Note, mortgage $50 K advance 70
 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Mortgagee Judgment Note, mortgage $50 K advance Records $100 K 71
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Mortgagee Judgment Note, mortgage $50 K advance Records $100 K 71
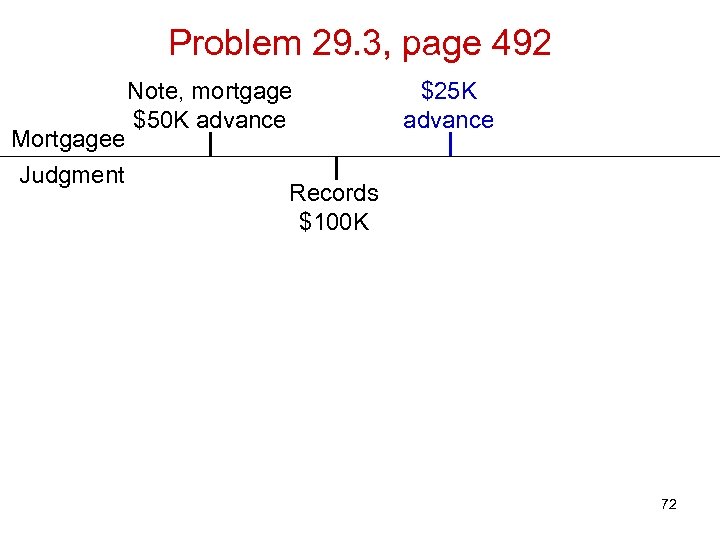 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Mortgagee Judgment Note, mortgage $50 K advance $25 K advance Records $100 K 72
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Mortgagee Judgment Note, mortgage $50 K advance $25 K advance Records $100 K 72
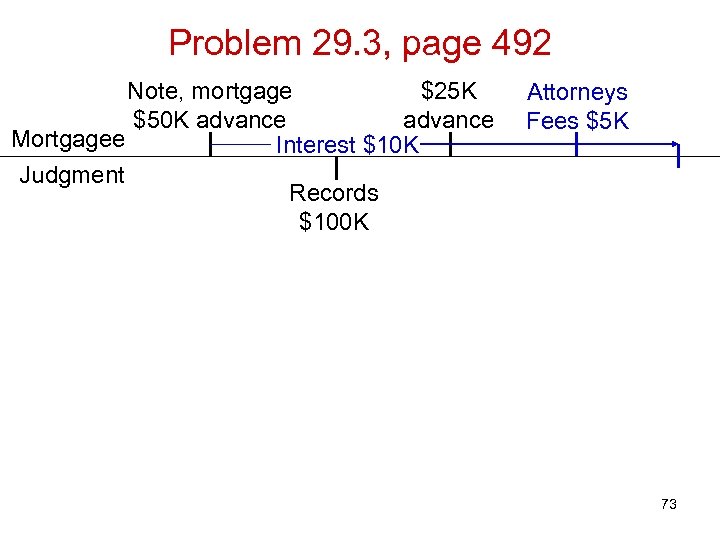 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K 73
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K 73
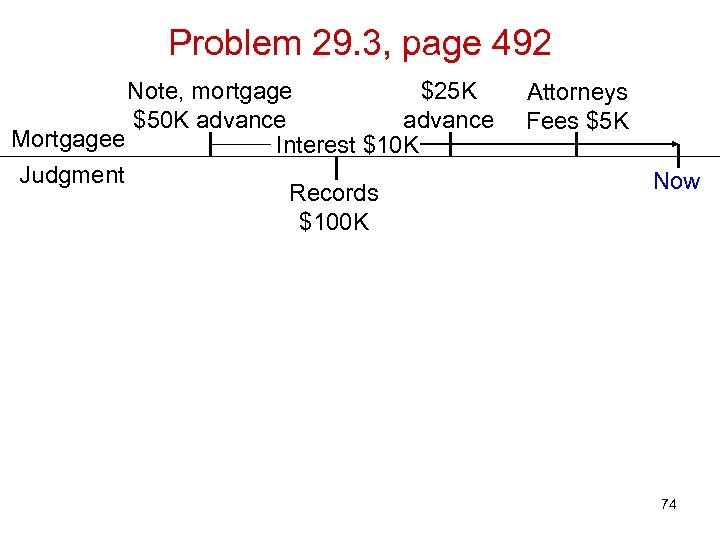 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now 74
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now 74
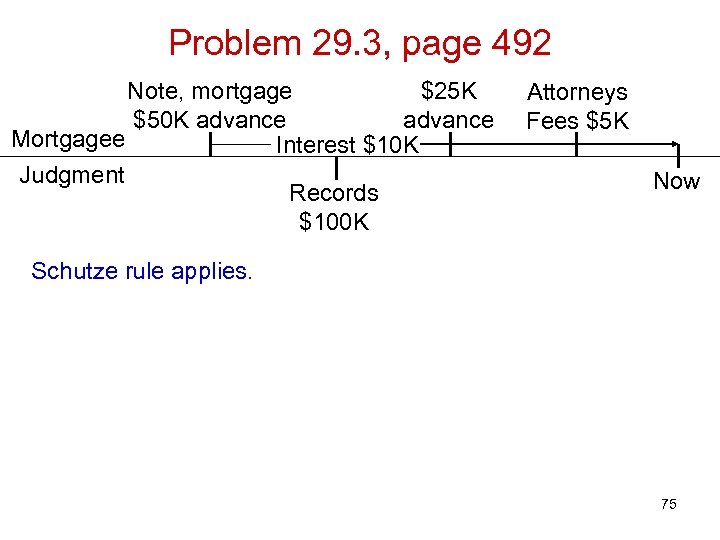 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Schutze rule applies. 75
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Schutze rule applies. 75
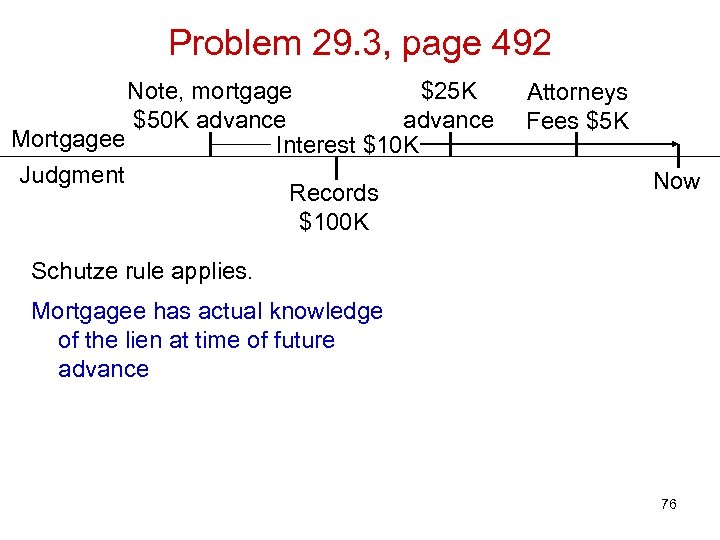 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Schutze rule applies. Mortgagee has actual knowledge of the lien at time of future advance 76
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Schutze rule applies. Mortgagee has actual knowledge of the lien at time of future advance 76
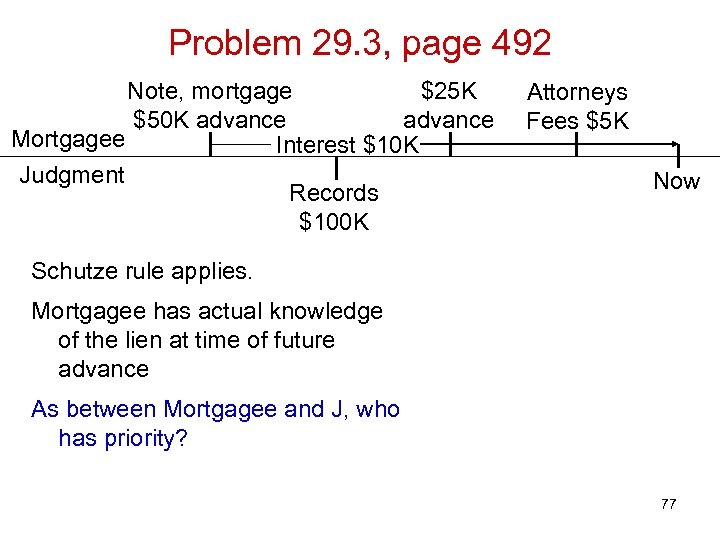 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Schutze rule applies. Mortgagee has actual knowledge of the lien at time of future advance As between Mortgagee and J, who has priority? 77
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Schutze rule applies. Mortgagee has actual knowledge of the lien at time of future advance As between Mortgagee and J, who has priority? 77
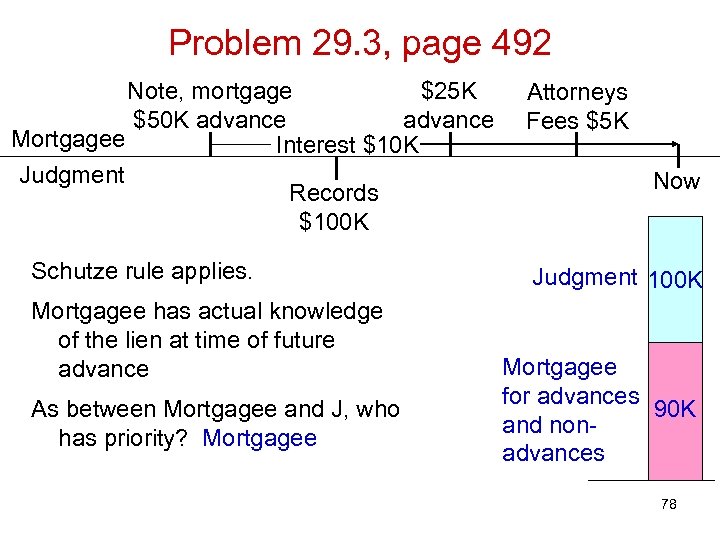 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Schutze rule applies. Mortgagee has actual knowledge of the lien at time of future advance As between Mortgagee and J, who has priority? Mortgagee Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Judgment 100 K Mortgagee for advances 90 K and nonadvances 78
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Schutze rule applies. Mortgagee has actual knowledge of the lien at time of future advance As between Mortgagee and J, who has priority? Mortgagee Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Judgment 100 K Mortgagee for advances 90 K and nonadvances 78
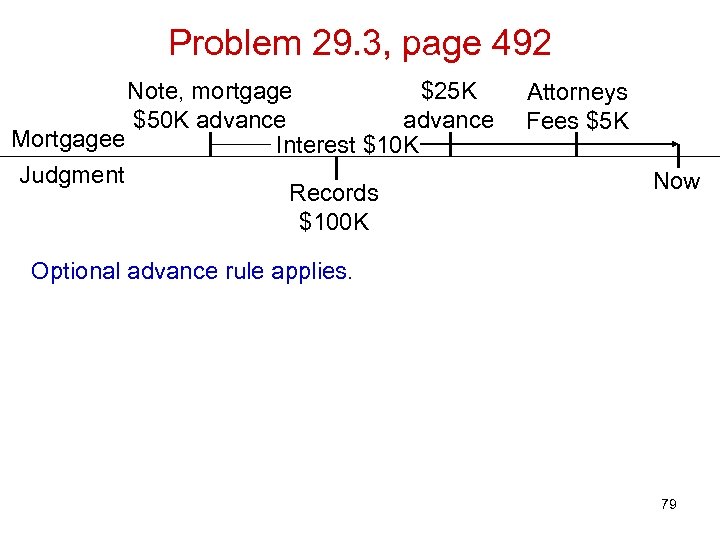 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Optional advance rule applies. 79
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Optional advance rule applies. 79
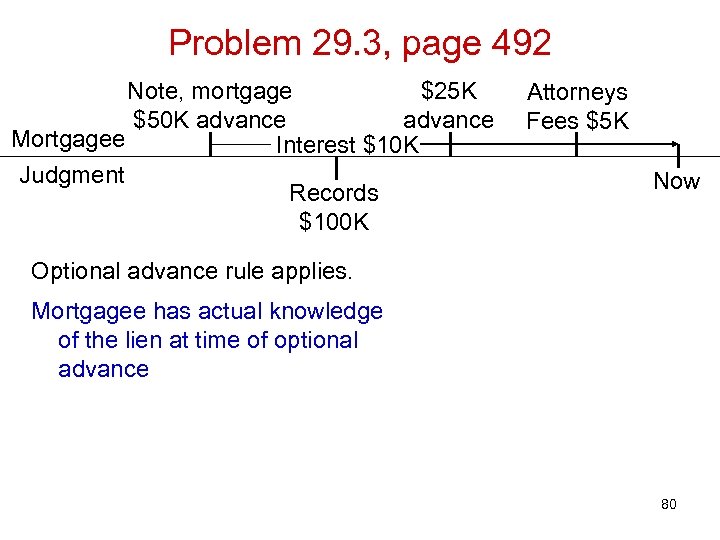 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Optional advance rule applies. Mortgagee has actual knowledge of the lien at time of optional advance 80
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Optional advance rule applies. Mortgagee has actual knowledge of the lien at time of optional advance 80
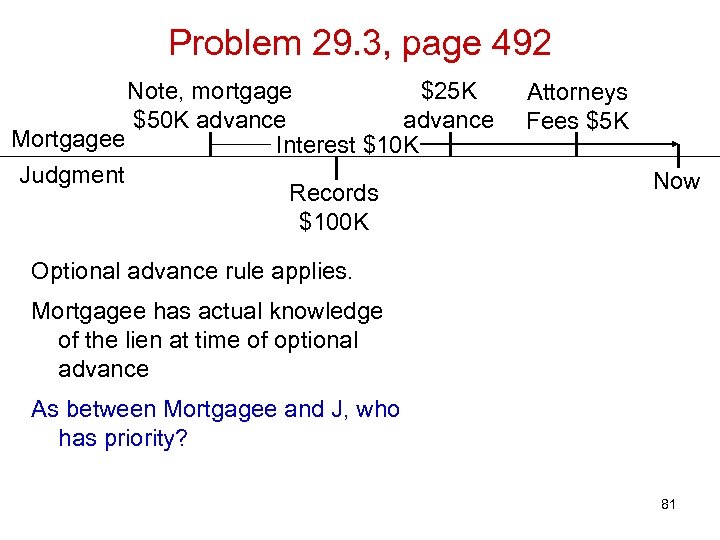 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Optional advance rule applies. Mortgagee has actual knowledge of the lien at time of optional advance As between Mortgagee and J, who has priority? 81
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K $50 K advance Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Records $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now Optional advance rule applies. Mortgagee has actual knowledge of the lien at time of optional advance As between Mortgagee and J, who has priority? 81
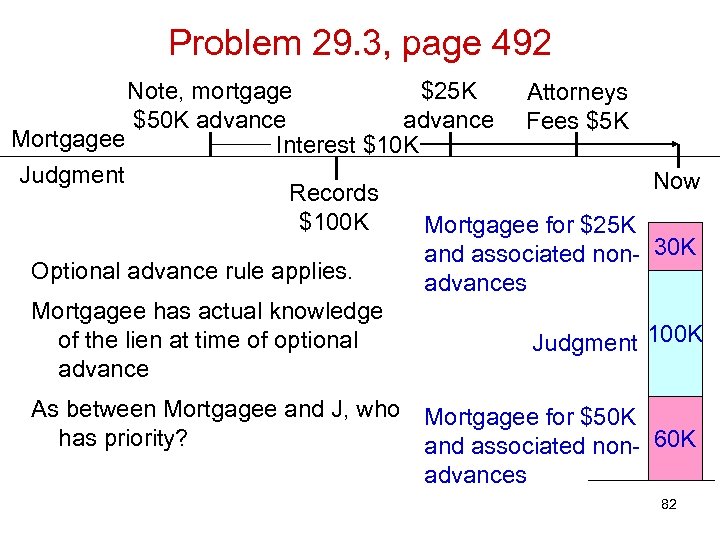 Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K Attorneys $50 K advance Fees $5 K Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Now Records $100 K Mortgagee for $25 K and associated non- 30 K Optional advance rule applies. advances Mortgagee has actual knowledge of the lien at time of optional Judgment 100 K advance As between Mortgagee and J, who Mortgagee for $50 K has priority? and associated non- 60 K advances 82
Problem 29. 3, page 492 Note, mortgage $25 K Attorneys $50 K advance Fees $5 K Mortgagee Interest $10 K Judgment Now Records $100 K Mortgagee for $25 K and associated non- 30 K Optional advance rule applies. advances Mortgagee has actual knowledge of the lien at time of optional Judgment 100 K advance As between Mortgagee and J, who Mortgagee for $50 K has priority? and associated non- 60 K advances 82
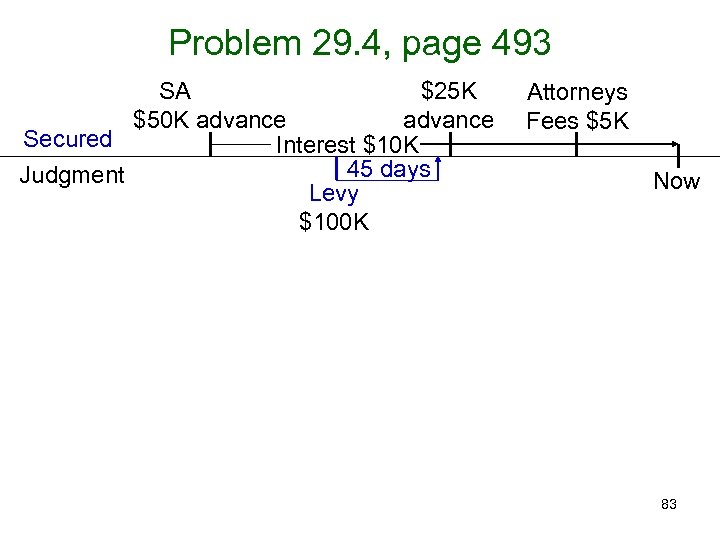 Problem 29. 4, page 493 SA, filing, $25 K $50 K advance Secured Interest $10 K 45 days Judgment Levy $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now 83
Problem 29. 4, page 493 SA, filing, $25 K $50 K advance Secured Interest $10 K 45 days Judgment Levy $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now 83
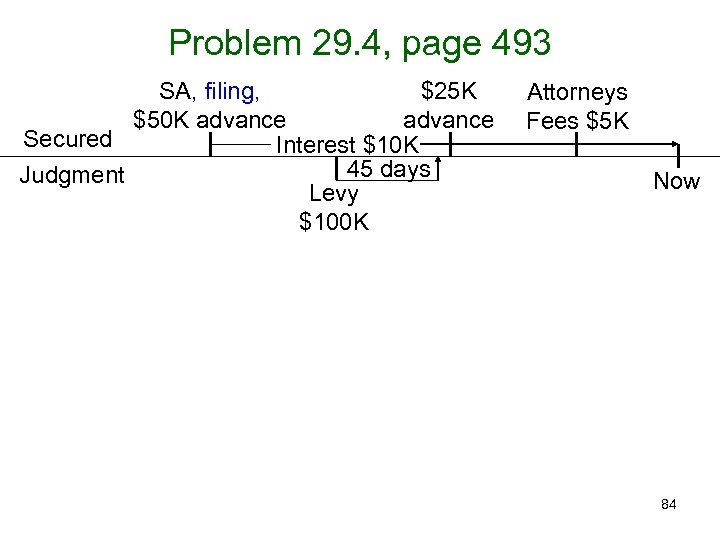 Problem 29. 4, page 493 SA, filing, $25 K $50 K advance Secured Interest $10 K 45 days Judgment Levy $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now 84
Problem 29. 4, page 493 SA, filing, $25 K $50 K advance Secured Interest $10 K 45 days Judgment Levy $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now 84
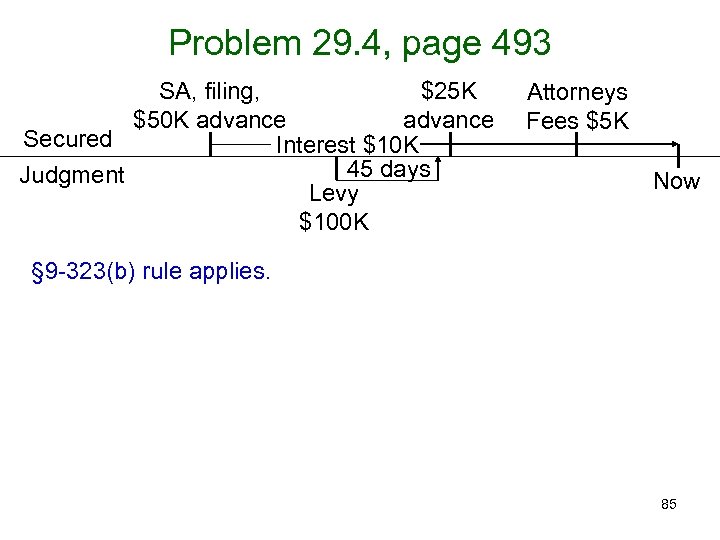 Problem 29. 4, page 493 SA, filing, $25 K $50 K advance Secured Interest $10 K 45 days Judgment Levy $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now § 9 -323(b) rule applies. 85
Problem 29. 4, page 493 SA, filing, $25 K $50 K advance Secured Interest $10 K 45 days Judgment Levy $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now § 9 -323(b) rule applies. 85
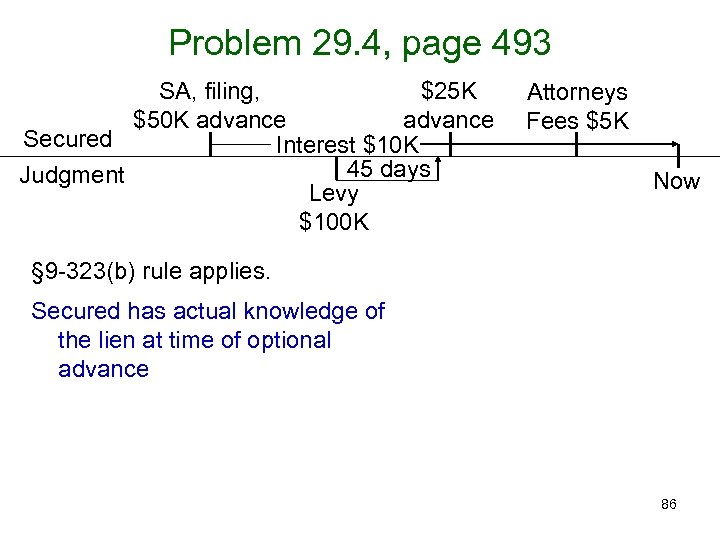 Problem 29. 4, page 493 SA, filing, $25 K $50 K advance Secured Interest $10 K 45 days Judgment Levy $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now § 9 -323(b) rule applies. Secured has actual knowledge of the lien at time of optional advance 86
Problem 29. 4, page 493 SA, filing, $25 K $50 K advance Secured Interest $10 K 45 days Judgment Levy $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now § 9 -323(b) rule applies. Secured has actual knowledge of the lien at time of optional advance 86
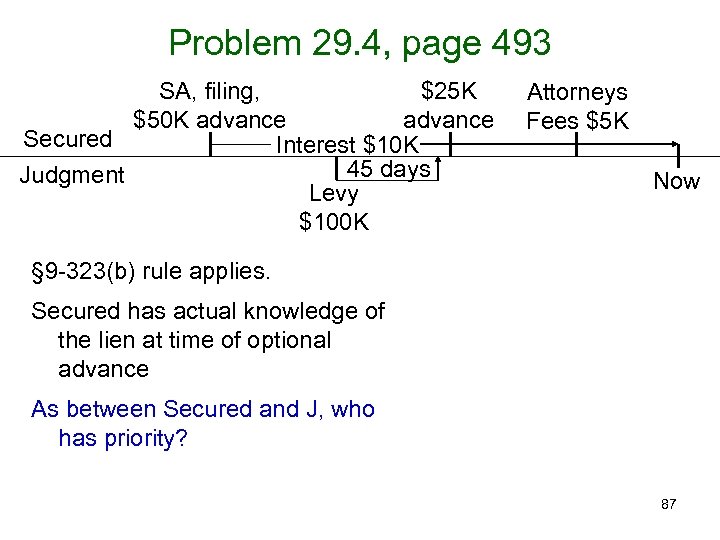 Problem 29. 4, page 493 SA, filing, $25 K $50 K advance Secured Interest $10 K 45 days Judgment Levy $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now § 9 -323(b) rule applies. Secured has actual knowledge of the lien at time of optional advance As between Secured and J, who has priority? 87
Problem 29. 4, page 493 SA, filing, $25 K $50 K advance Secured Interest $10 K 45 days Judgment Levy $100 K Attorneys Fees $5 K Now § 9 -323(b) rule applies. Secured has actual knowledge of the lien at time of optional advance As between Secured and J, who has priority? 87
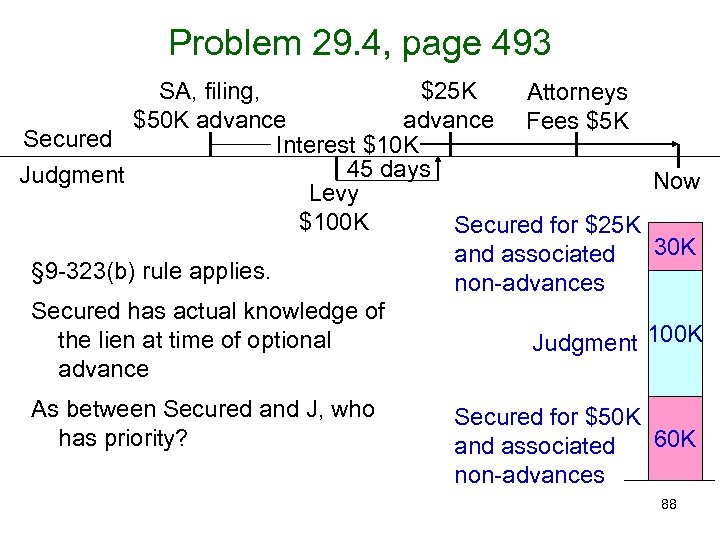 Problem 29. 4, page 493 SA, filing, $25 K Attorneys $50 K advance Fees $5 K Secured Interest $10 K 45 days Judgment Now Levy $100 K Secured for $25 K 30 K and associated § 9 -323(b) rule applies. non-advances Secured has actual knowledge of the lien at time of optional Judgment 100 K advance As between Secured and J, who has priority? Secured for $50 K 60 K and associated non-advances 88
Problem 29. 4, page 493 SA, filing, $25 K Attorneys $50 K advance Fees $5 K Secured Interest $10 K 45 days Judgment Now Levy $100 K Secured for $25 K 30 K and associated § 9 -323(b) rule applies. non-advances Secured has actual knowledge of the lien at time of optional Judgment 100 K advance As between Secured and J, who has priority? Secured for $50 K 60 K and associated non-advances 88
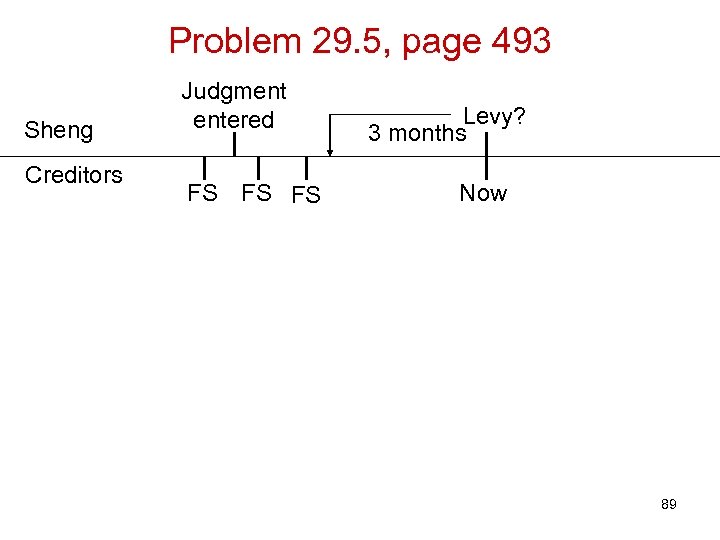 Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now 89
Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now 89
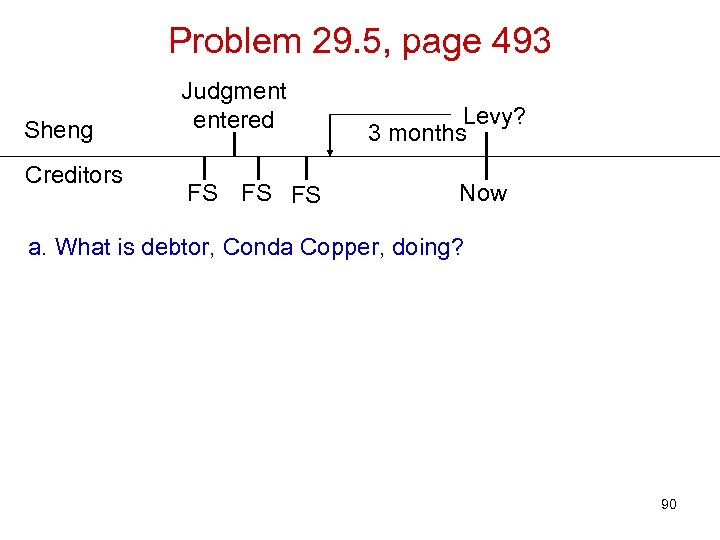 Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now a. What is debtor, Conda Copper, doing? 90
Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now a. What is debtor, Conda Copper, doing? 90
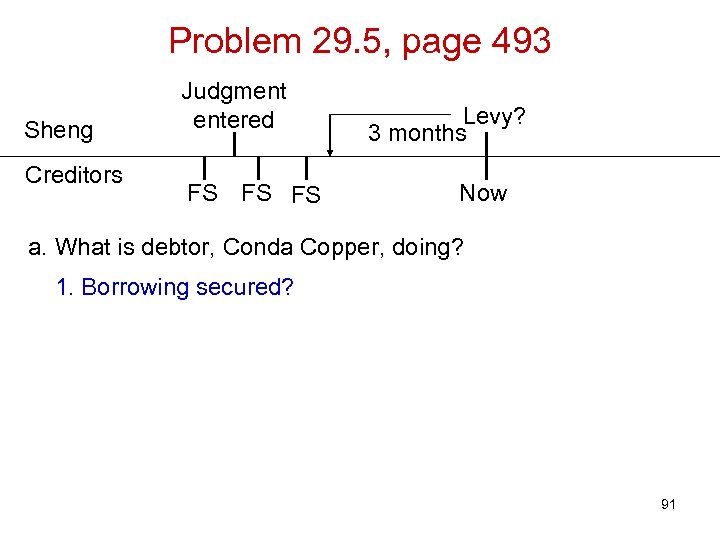 Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now a. What is debtor, Conda Copper, doing? 1. Borrowing secured? 91
Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now a. What is debtor, Conda Copper, doing? 1. Borrowing secured? 91
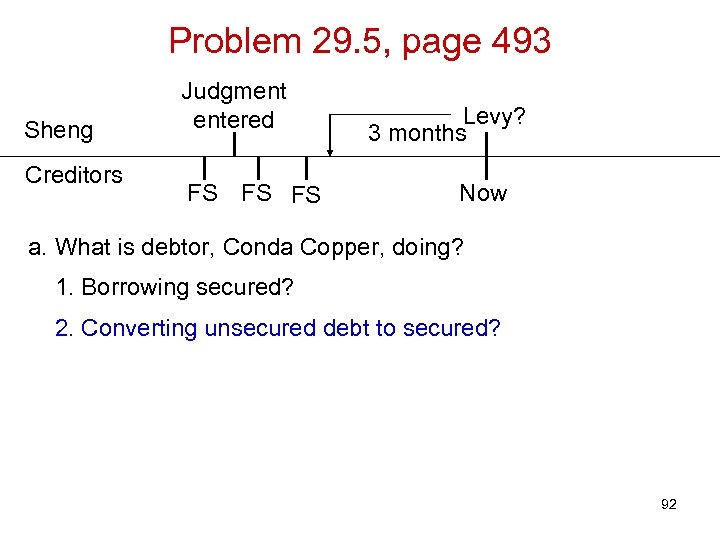 Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now a. What is debtor, Conda Copper, doing? 1. Borrowing secured? 2. Converting unsecured debt to secured? 92
Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now a. What is debtor, Conda Copper, doing? 1. Borrowing secured? 2. Converting unsecured debt to secured? 92
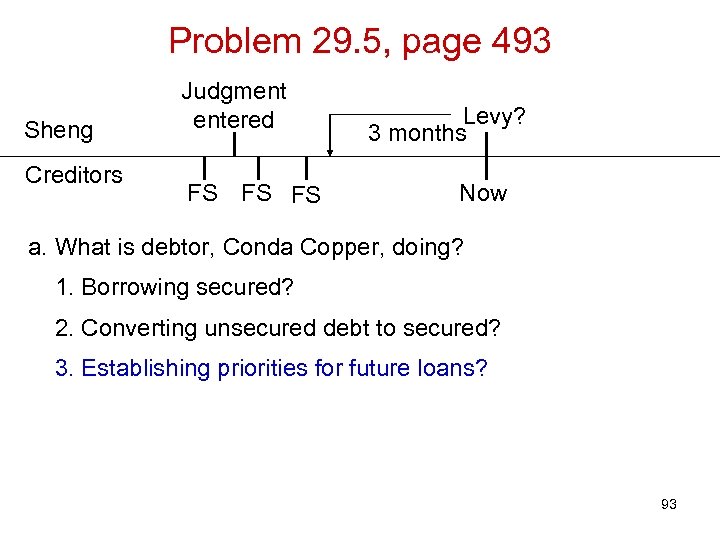 Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now a. What is debtor, Conda Copper, doing? 1. Borrowing secured? 2. Converting unsecured debt to secured? 3. Establishing priorities for future loans? 93
Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now a. What is debtor, Conda Copper, doing? 1. Borrowing secured? 2. Converting unsecured debt to secured? 3. Establishing priorities for future loans? 93
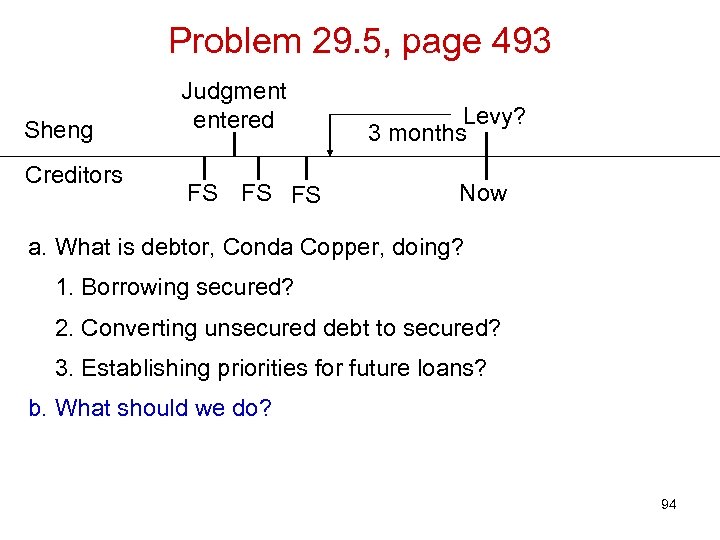 Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now a. What is debtor, Conda Copper, doing? 1. Borrowing secured? 2. Converting unsecured debt to secured? 3. Establishing priorities for future loans? b. What should we do? 94
Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now a. What is debtor, Conda Copper, doing? 1. Borrowing secured? 2. Converting unsecured debt to secured? 3. Establishing priorities for future loans? b. What should we do? 94
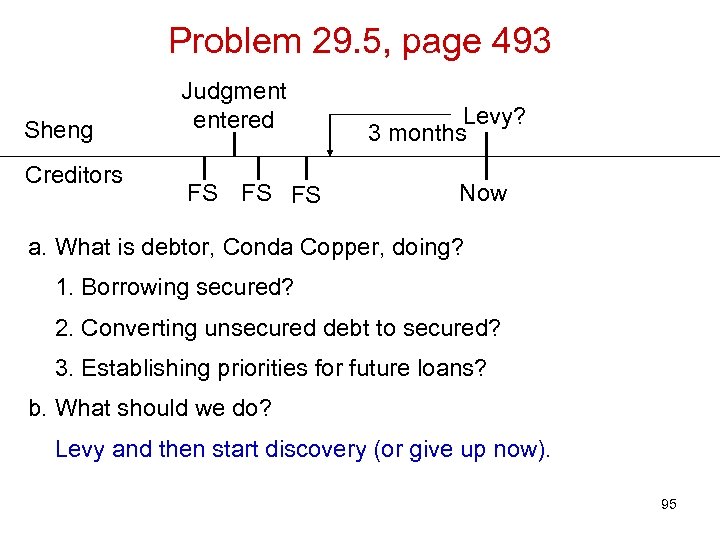 Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now a. What is debtor, Conda Copper, doing? 1. Borrowing secured? 2. Converting unsecured debt to secured? 3. Establishing priorities for future loans? b. What should we do? Levy and then start discovery (or give up now). 95
Problem 29. 5, page 493 Sheng Creditors Judgment entered FS FS FS Levy? 3 months Now a. What is debtor, Conda Copper, doing? 1. Borrowing secured? 2. Converting unsecured debt to secured? 3. Establishing priorities for future loans? b. What should we do? Levy and then start discovery (or give up now). 95


