4ee4f6c6596b4fd458affd692e6ca5d8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Secure Software Design with UML Secure UML: Requirements System Architecture/Design Test
Secure Software Design with UML Secure UML: Requirements System Architecture/Design Test
 Acknowledgments References are provided per page. Most diagrams are original, but ideas are adapted from references. Author: Susan J Lincke, Ph. D Univ. of Wisconsin-Parkside Contributors/Reviewers: Tim Knautz, Janine Spears Ph. D, David Green Ph. D, Megan Reid Funded by National Science Foundation (NSF) Course, Curriculum and Laboratory Improvement (CCLI) grant 0837574: Information Security: Audit, Case Study, and Service Learning. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and/or source(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Acknowledgments References are provided per page. Most diagrams are original, but ideas are adapted from references. Author: Susan J Lincke, Ph. D Univ. of Wisconsin-Parkside Contributors/Reviewers: Tim Knautz, Janine Spears Ph. D, David Green Ph. D, Megan Reid Funded by National Science Foundation (NSF) Course, Curriculum and Laboratory Improvement (CCLI) grant 0837574: Information Security: Audit, Case Study, and Service Learning. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and/or source(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
 Security Assures … CIA Confidentiality: Limits access of authorized users and prevents access to unauthorized users Integrity: The reliability of information resources and data have not been changed inappropriately Availability: When something needs to be accessed by the user, it is available
Security Assures … CIA Confidentiality: Limits access of authorized users and prevents access to unauthorized users Integrity: The reliability of information resources and data have not been changed inappropriately Availability: When something needs to be accessed by the user, it is available
 Security Vocabulary Asset: Diamonds Threat: Theft Vulnerability: Open door or windows Threat agent: Burglar Owner: Those accountable or who value the asset Risk: Danger to assets
Security Vocabulary Asset: Diamonds Threat: Theft Vulnerability: Open door or windows Threat agent: Burglar Owner: Those accountable or who value the asset Risk: Danger to assets
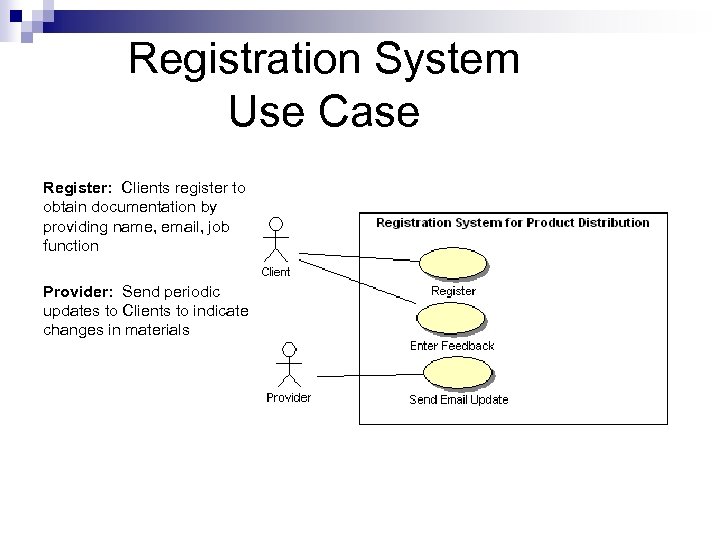 Registration System Use Case Register: Clients register to obtain documentation by providing name, email, job function Provider: Send periodic updates to Clients to indicate changes in materials
Registration System Use Case Register: Clients register to obtain documentation by providing name, email, job function Provider: Send periodic updates to Clients to indicate changes in materials
 OCTAVE Security Requirements Process Risk: Threat and vulnerability(s) -> negative impact 1. Identify critical assets 2. Define security goals 3. Identify threats 4. Analyze risks 5. Define security requirements
OCTAVE Security Requirements Process Risk: Threat and vulnerability(s) -> negative impact 1. Identify critical assets 2. Define security goals 3. Identify threats 4. Analyze risks 5. Define security requirements
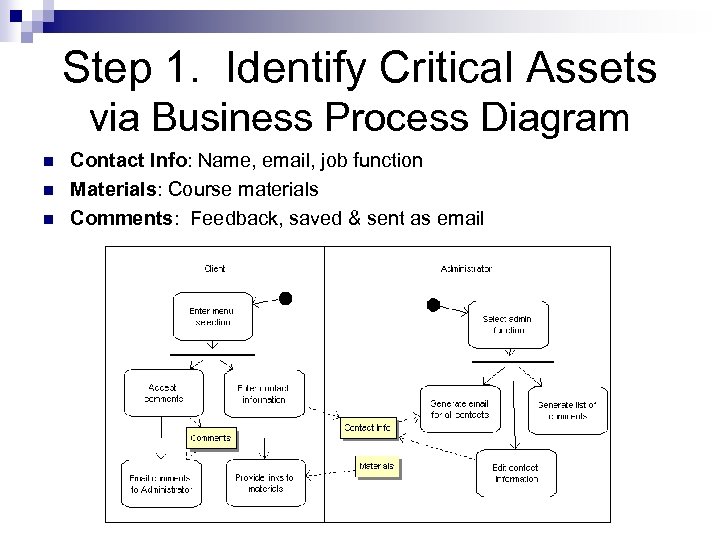 Step 1. Identify Critical Assets via Business Process Diagram n n n Contact Info: Name, email, job function Materials: Course materials Comments: Feedback, saved & sent as email
Step 1. Identify Critical Assets via Business Process Diagram n n n Contact Info: Name, email, job function Materials: Course materials Comments: Feedback, saved & sent as email
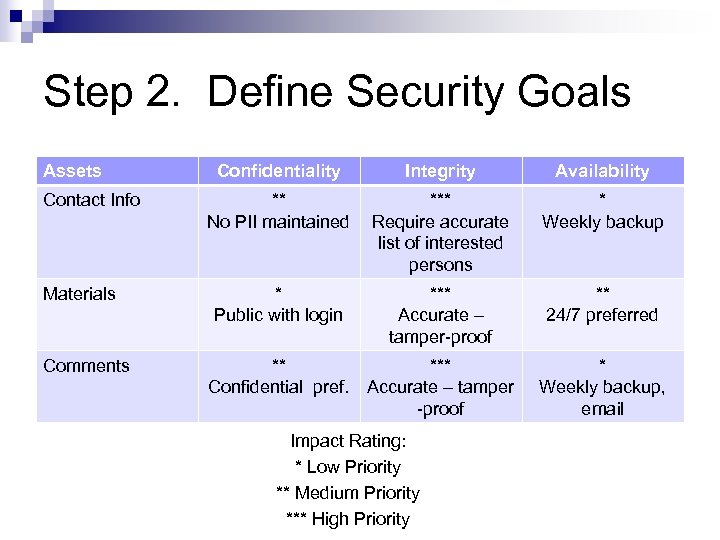 Step 2. Define Security Goals Assets Contact Info Materials Comments Confidentiality Integrity Availability ** No PII maintained *** Require accurate list of interested persons * Weekly backup * Public with login *** Accurate – tamper-proof ** 24/7 preferred ** Confidential pref. *** Accurate – tamper -proof * Weekly backup, email Impact Rating: * Low Priority ** Medium Priority *** High Priority
Step 2. Define Security Goals Assets Contact Info Materials Comments Confidentiality Integrity Availability ** No PII maintained *** Require accurate list of interested persons * Weekly backup * Public with login *** Accurate – tamper-proof ** 24/7 preferred ** Confidential pref. *** Accurate – tamper -proof * Weekly backup, email Impact Rating: * Low Priority ** Medium Priority *** High Priority
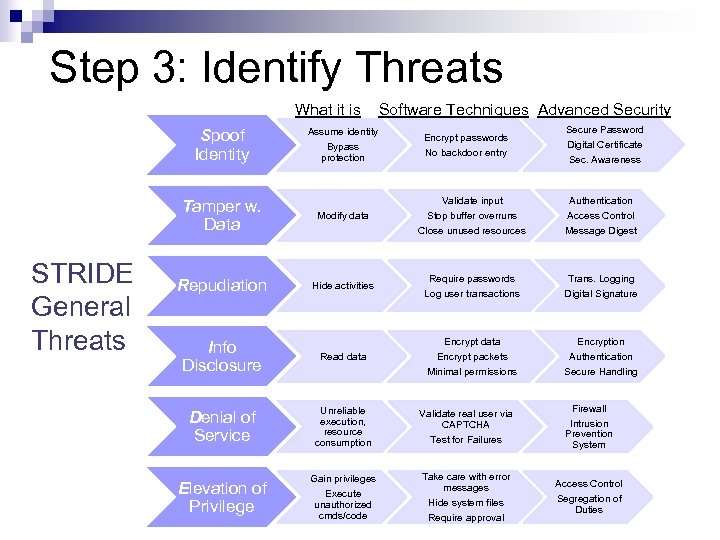 Step 3: Identify Threats What it is Spoof Identity Assume identity Bypass protection Software Techniques Advanced Security Encrypt passwords No backdoor entry Secure Password Digital Certificate Sec. Awareness Validate input Stop buffer overruns Authentication Access Control Close unused resources Message Digest Require passwords Log user transactions Trans. Logging Digital Signature Encrypt data Encrypt packets Encryption Authentication Minimal permissions Secure Handling Tamper w. Data STRIDE General Threats Modify data Repudiation Hide activities Info Disclosure Read data Denial of Service Unreliable execution, resource consumption Validate real user via CAPTCHA Test for Failures Firewall Intrusion Prevention System Elevation of Privilege Gain privileges Execute unauthorized cmds/code Take care with error messages Hide system files Require approval Access Control Segregation of Duties
Step 3: Identify Threats What it is Spoof Identity Assume identity Bypass protection Software Techniques Advanced Security Encrypt passwords No backdoor entry Secure Password Digital Certificate Sec. Awareness Validate input Stop buffer overruns Authentication Access Control Close unused resources Message Digest Require passwords Log user transactions Trans. Logging Digital Signature Encrypt data Encrypt packets Encryption Authentication Minimal permissions Secure Handling Tamper w. Data STRIDE General Threats Modify data Repudiation Hide activities Info Disclosure Read data Denial of Service Unreliable execution, resource consumption Validate real user via CAPTCHA Test for Failures Firewall Intrusion Prevention System Elevation of Privilege Gain privileges Execute unauthorized cmds/code Take care with error messages Hide system files Require approval Access Control Segregation of Duties
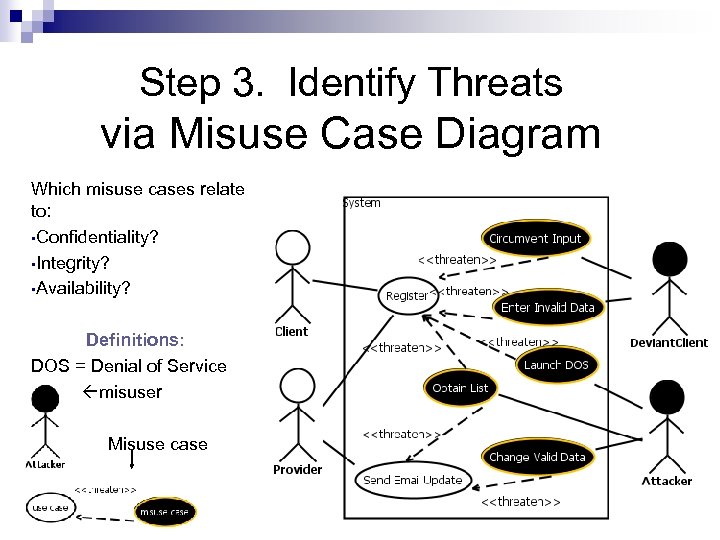 Step 3. Identify Threats via Misuse Case Diagram Which misuse cases relate to: • Confidentiality? • Integrity? • Availability? Definitions: DOS = Denial of Service misuser Misuse case
Step 3. Identify Threats via Misuse Case Diagram Which misuse cases relate to: • Confidentiality? • Integrity? • Availability? Definitions: DOS = Denial of Service misuser Misuse case
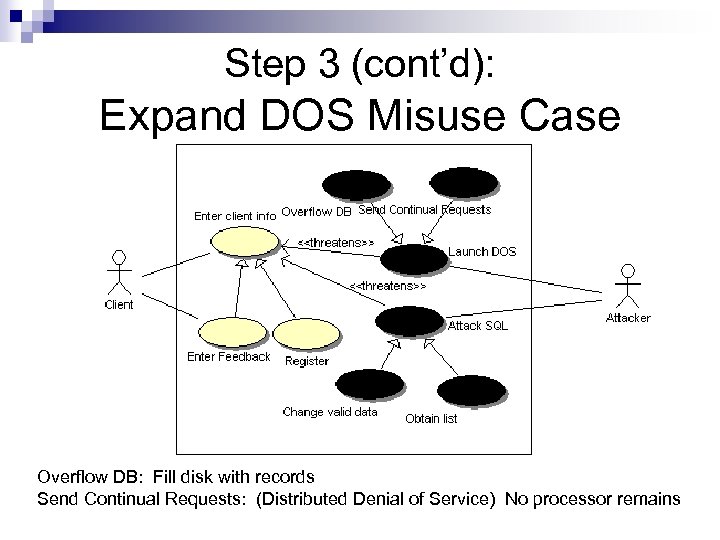 Step 3 (cont’d): Expand DOS Misuse Case Overflow DB: Fill disk with records Send Continual Requests: (Distributed Denial of Service) No processor remains
Step 3 (cont’d): Expand DOS Misuse Case Overflow DB: Fill disk with records Send Continual Requests: (Distributed Denial of Service) No processor remains
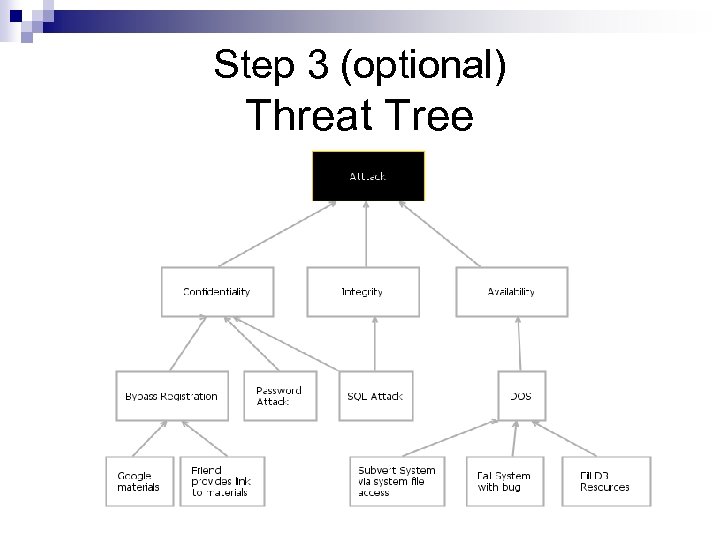 Step 3 (optional) Threat Tree
Step 3 (optional) Threat Tree
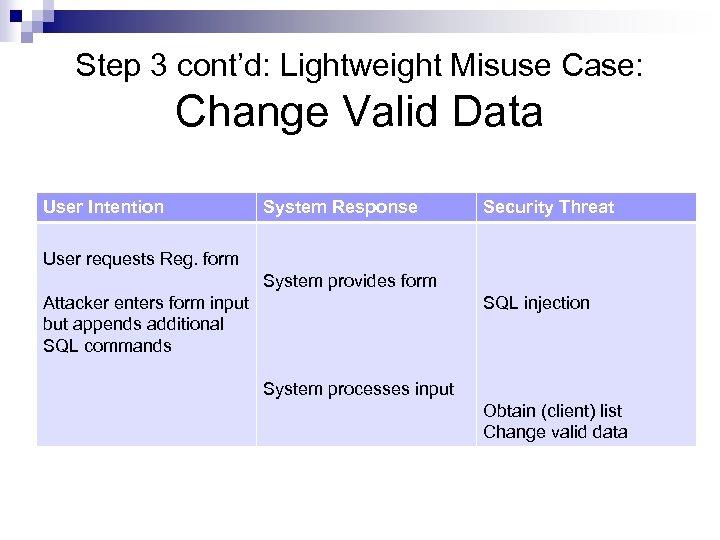 Step 3 cont’d: Lightweight Misuse Case: Change Valid Data User Intention System Response Security Threat User requests Reg. form System provides form Attacker enters form input but appends additional SQL commands SQL injection System processes input Obtain (client) list Change valid data
Step 3 cont’d: Lightweight Misuse Case: Change Valid Data User Intention System Response Security Threat User requests Reg. form System provides form Attacker enters form input but appends additional SQL commands SQL injection System processes input Obtain (client) list Change valid data
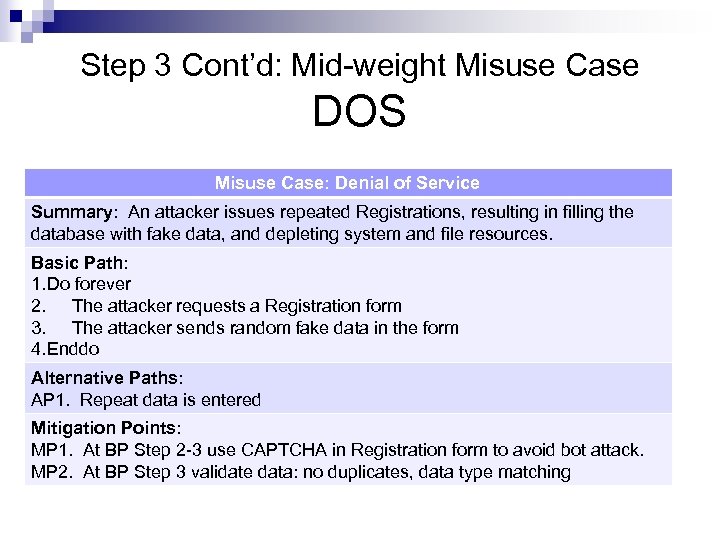 Step 3 Cont’d: Mid-weight Misuse Case DOS Misuse Case: Denial of Service Summary: An attacker issues repeated Registrations, resulting in filling the database with fake data, and depleting system and file resources. Basic Path: 1. Do forever 2. The attacker requests a Registration form 3. The attacker sends random fake data in the form 4. Enddo Alternative Paths: AP 1. Repeat data is entered Mitigation Points: MP 1. At BP Step 2 -3 use CAPTCHA in Registration form to avoid bot attack. MP 2. At BP Step 3 validate data: no duplicates, data type matching
Step 3 Cont’d: Mid-weight Misuse Case DOS Misuse Case: Denial of Service Summary: An attacker issues repeated Registrations, resulting in filling the database with fake data, and depleting system and file resources. Basic Path: 1. Do forever 2. The attacker requests a Registration form 3. The attacker sends random fake data in the form 4. Enddo Alternative Paths: AP 1. Repeat data is entered Mitigation Points: MP 1. At BP Step 2 -3 use CAPTCHA in Registration form to avoid bot attack. MP 2. At BP Step 3 validate data: no duplicates, data type matching
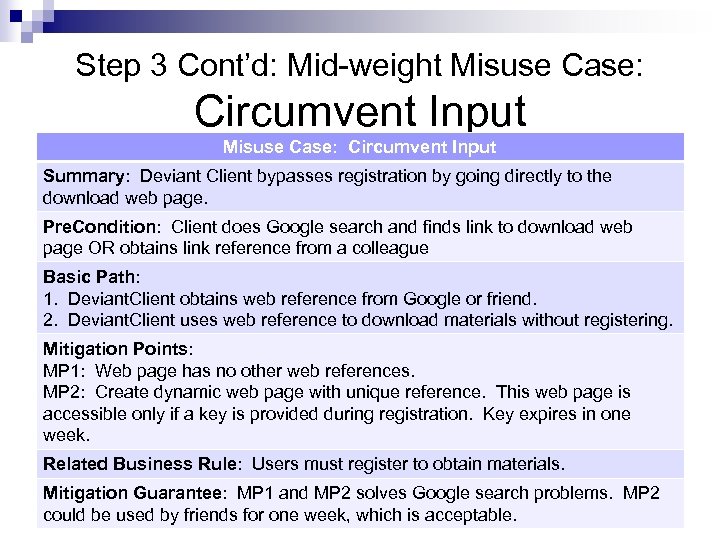 Step 3 Cont’d: Mid-weight Misuse Case: Circumvent Input Misuse Case: Circumvent Input Summary: Deviant Client bypasses registration by going directly to the download web page. Pre. Condition: Client does Google search and finds link to download web page OR obtains link reference from a colleague Basic Path: 1. Deviant. Client obtains web reference from Google or friend. 2. Deviant. Client uses web reference to download materials without registering. Mitigation Points: MP 1: Web page has no other web references. MP 2: Create dynamic web page with unique reference. This web page is accessible only if a key is provided during registration. Key expires in one week. Related Business Rule: Users must register to obtain materials. Mitigation Guarantee: MP 1 and MP 2 solves Google search problems. MP 2 could be used by friends for one week, which is acceptable.
Step 3 Cont’d: Mid-weight Misuse Case: Circumvent Input Misuse Case: Circumvent Input Summary: Deviant Client bypasses registration by going directly to the download web page. Pre. Condition: Client does Google search and finds link to download web page OR obtains link reference from a colleague Basic Path: 1. Deviant. Client obtains web reference from Google or friend. 2. Deviant. Client uses web reference to download materials without registering. Mitigation Points: MP 1: Web page has no other web references. MP 2: Create dynamic web page with unique reference. This web page is accessible only if a key is provided during registration. Key expires in one week. Related Business Rule: Users must register to obtain materials. Mitigation Guarantee: MP 1 and MP 2 solves Google search problems. MP 2 could be used by friends for one week, which is acceptable.
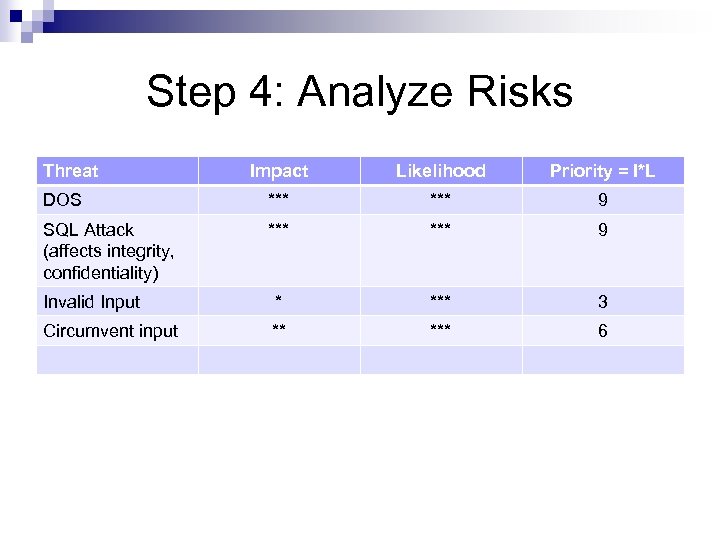 Step 4: Analyze Risks Threat Impact Likelihood Priority = I*L DOS *** 9 SQL Attack (affects integrity, confidentiality) *** 9 Invalid Input * *** 3 Circumvent input ** *** 6
Step 4: Analyze Risks Threat Impact Likelihood Priority = I*L DOS *** 9 SQL Attack (affects integrity, confidentiality) *** 9 Invalid Input * *** 3 Circumvent input ** *** 6
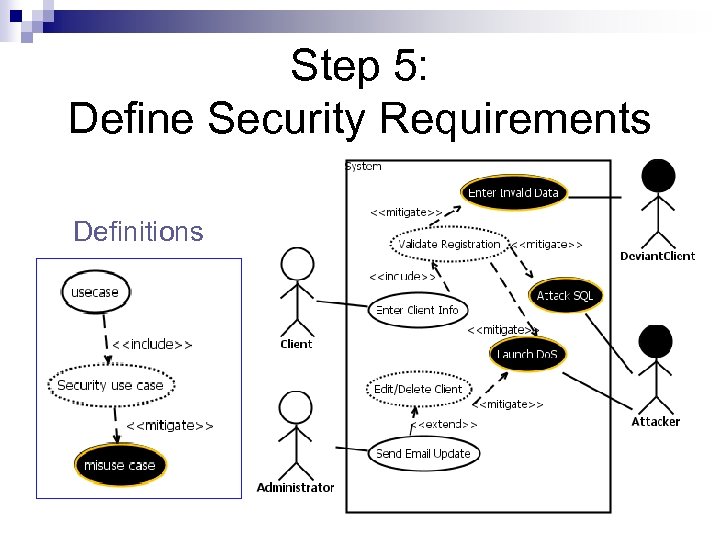 Step 5: Define Security Requirements Definitions
Step 5: Define Security Requirements Definitions
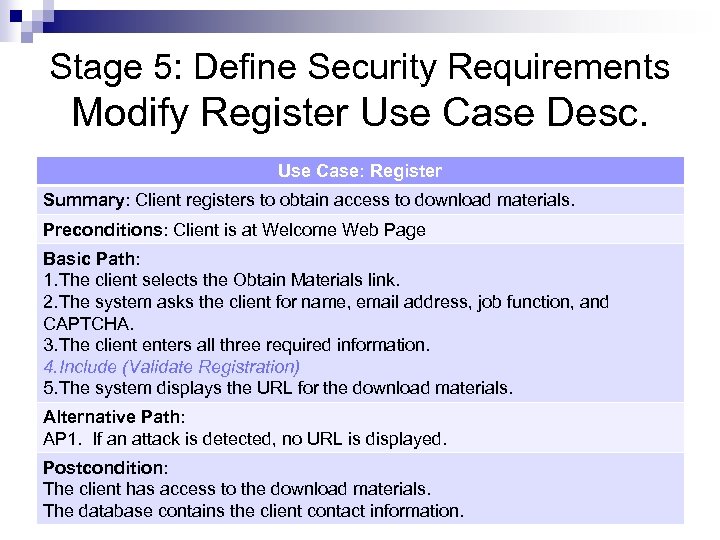 Stage 5: Define Security Requirements Modify Register Use Case Desc. Use Case: Register Summary: Client registers to obtain access to download materials. Preconditions: Client is at Welcome Web Page Basic Path: 1. The client selects the Obtain Materials link. 2. The system asks the client for name, email address, job function, and CAPTCHA. 3. The client enters all three required information. 4. Include (Validate Registration) 5. The system displays the URL for the download materials. Alternative Path: AP 1. If an attack is detected, no URL is displayed. Postcondition: The client has access to the download materials. The database contains the client contact information.
Stage 5: Define Security Requirements Modify Register Use Case Desc. Use Case: Register Summary: Client registers to obtain access to download materials. Preconditions: Client is at Welcome Web Page Basic Path: 1. The client selects the Obtain Materials link. 2. The system asks the client for name, email address, job function, and CAPTCHA. 3. The client enters all three required information. 4. Include (Validate Registration) 5. The system displays the URL for the download materials. Alternative Path: AP 1. If an attack is detected, no URL is displayed. Postcondition: The client has access to the download materials. The database contains the client contact information.
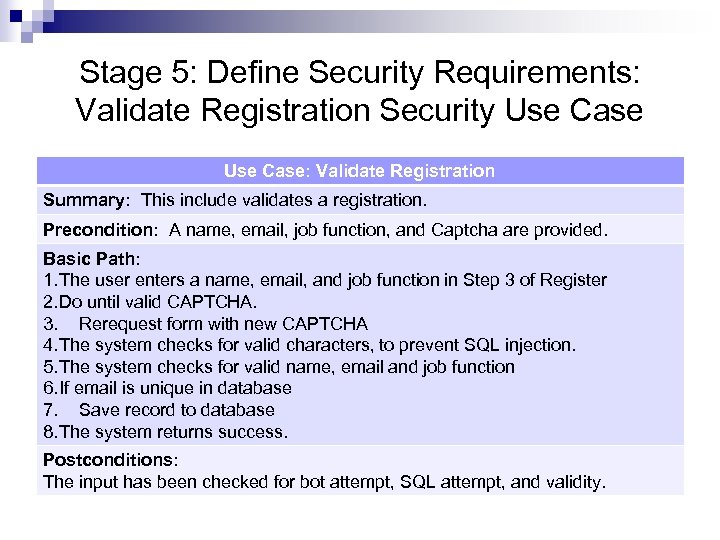 Stage 5: Define Security Requirements: Validate Registration Security Use Case: Validate Registration Summary: This include validates a registration. Precondition: A name, email, job function, and Captcha are provided. Basic Path: 1. The user enters a name, email, and job function in Step 3 of Register 2. Do until valid CAPTCHA. 3. Rerequest form with new CAPTCHA 4. The system checks for valid characters, to prevent SQL injection. 5. The system checks for valid name, email and job function 6. If email is unique in database 7. Save record to database 8. The system returns success. Postconditions: The input has been checked for bot attempt, SQL attempt, and validity.
Stage 5: Define Security Requirements: Validate Registration Security Use Case: Validate Registration Summary: This include validates a registration. Precondition: A name, email, job function, and Captcha are provided. Basic Path: 1. The user enters a name, email, and job function in Step 3 of Register 2. Do until valid CAPTCHA. 3. Rerequest form with new CAPTCHA 4. The system checks for valid characters, to prevent SQL injection. 5. The system checks for valid name, email and job function 6. If email is unique in database 7. Save record to database 8. The system returns success. Postconditions: The input has been checked for bot attempt, SQL attempt, and validity.
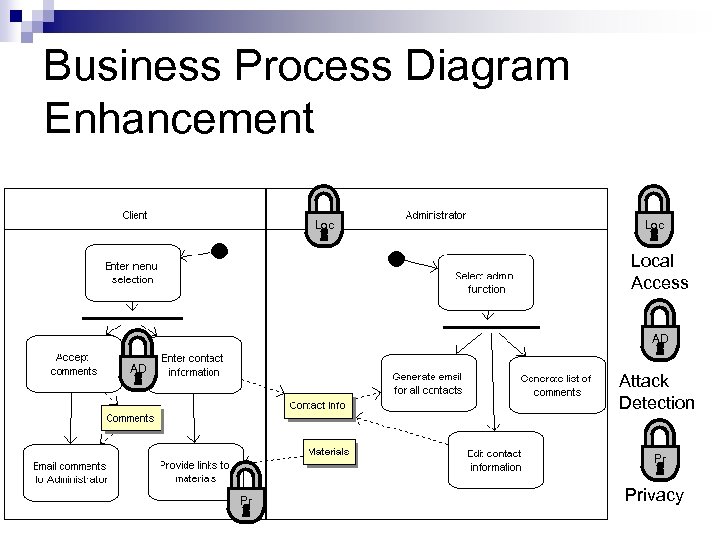 Business Process Diagram Enhancement Loc Local Access AD AD Attack Detection Pr Pr Privacy
Business Process Diagram Enhancement Loc Local Access AD AD Attack Detection Pr Pr Privacy
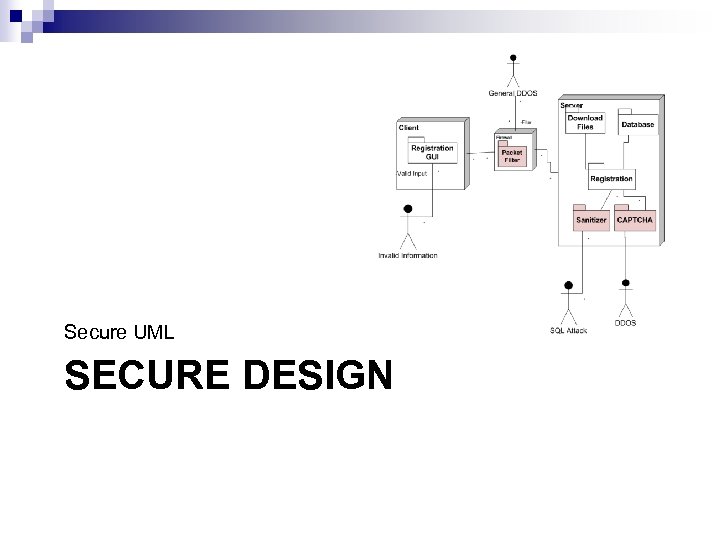 Secure UML SECURE DESIGN
Secure UML SECURE DESIGN
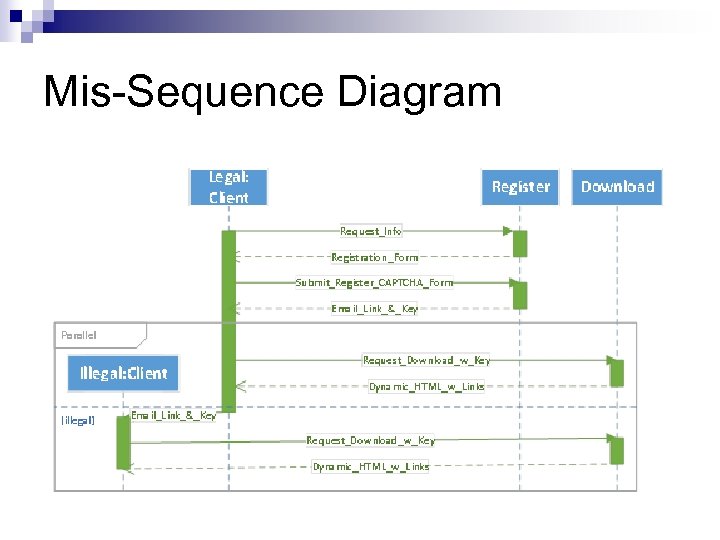 Mis-Sequence Diagram
Mis-Sequence Diagram
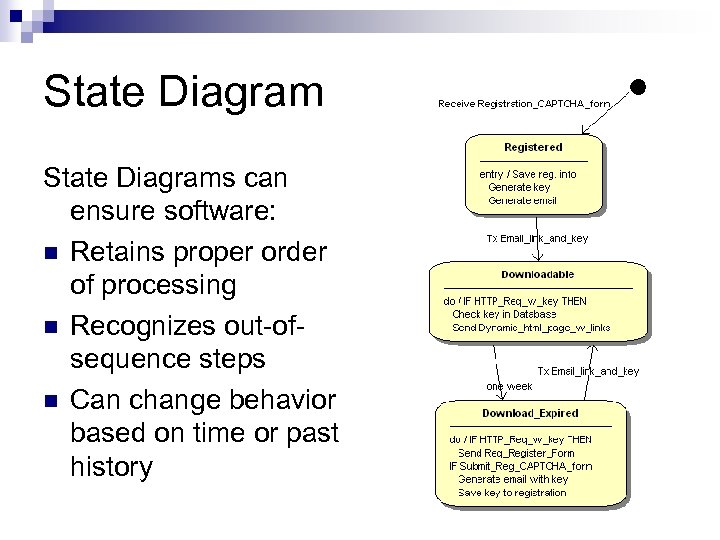 State Diagrams can ensure software: n Retains proper order of processing n Recognizes out-ofsequence steps n Can change behavior based on time or past history
State Diagrams can ensure software: n Retains proper order of processing n Recognizes out-ofsequence steps n Can change behavior based on time or past history
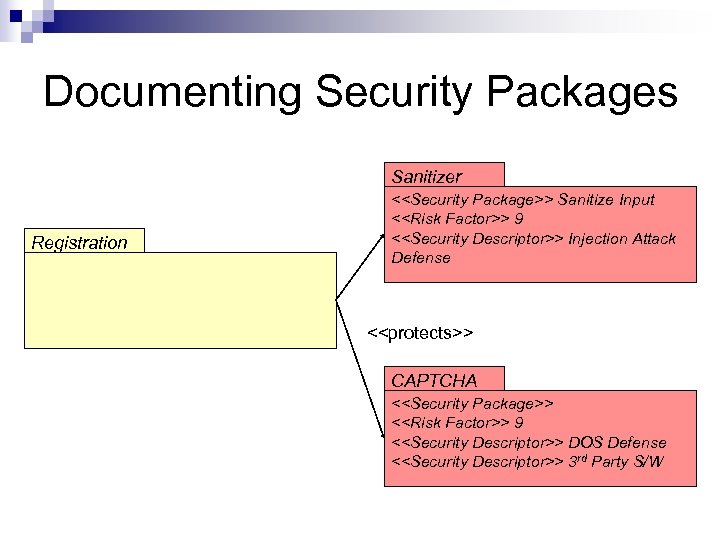 Documenting Security Packages Sanitizer Registration <
Documenting Security Packages Sanitizer Registration <
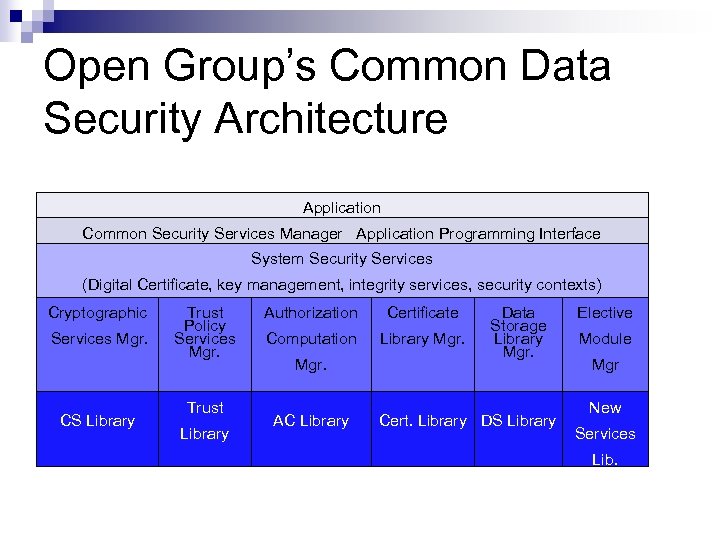 Open Group’s Common Data Security Architecture Application Common Security Services Manager Application Programming Interface System Security Services (Digital Certificate, key management, integrity services, security contexts) Cryptographic Services Mgr. CS Library Trust Policy Services Mgr. Trust Library Authorization Certificate Computation Library Mgr. AC Library Data Storage Library Mgr. Cert. Library DS Library Elective Module Mgr New Services Lib.
Open Group’s Common Data Security Architecture Application Common Security Services Manager Application Programming Interface System Security Services (Digital Certificate, key management, integrity services, security contexts) Cryptographic Services Mgr. CS Library Trust Policy Services Mgr. Trust Library Authorization Certificate Computation Library Mgr. AC Library Data Storage Library Mgr. Cert. Library DS Library Elective Module Mgr New Services Lib.
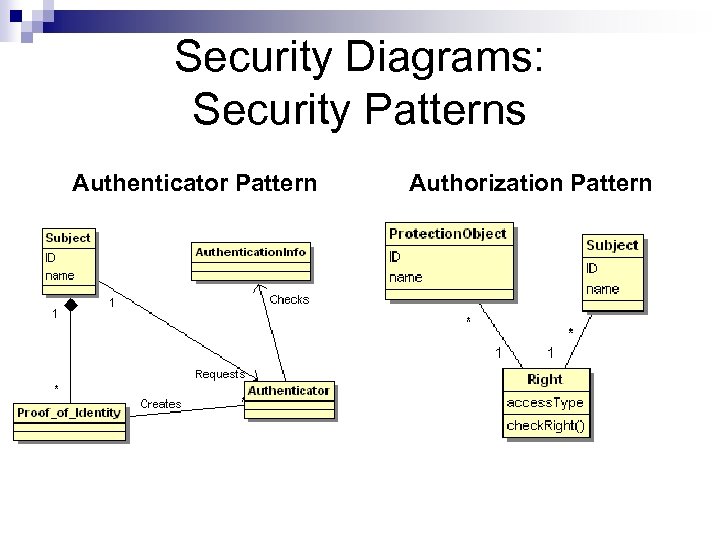 Security Diagrams: Security Patterns Authenticator Pattern Authorization Pattern
Security Diagrams: Security Patterns Authenticator Pattern Authorization Pattern
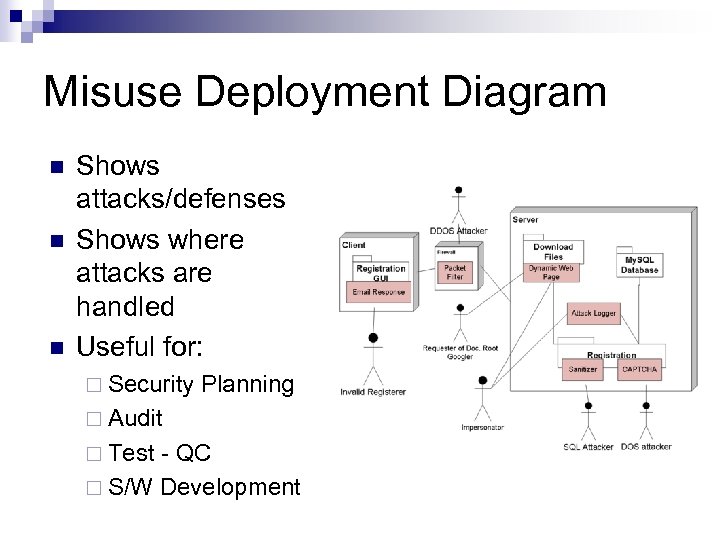 Misuse Deployment Diagram n n n Shows attacks/defenses Shows where attacks are handled Useful for: ¨ Security Planning ¨ Audit ¨ Test - QC ¨ S/W Development
Misuse Deployment Diagram n n n Shows attacks/defenses Shows where attacks are handled Useful for: ¨ Security Planning ¨ Audit ¨ Test - QC ¨ S/W Development
 Confidentiality Integrity Secure UML SECURE TEST Availability
Confidentiality Integrity Secure UML SECURE TEST Availability
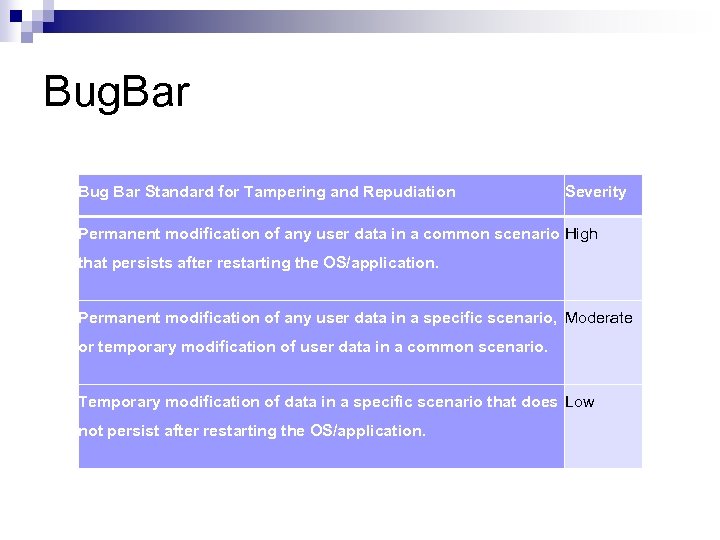 Bug. Bar Bug Bar Standard for Tampering and Repudiation Severity Permanent modification of any user data in a common scenario High that persists after restarting the OS/application. Permanent modification of any user data in a specific scenario, Moderate or temporary modification of user data in a common scenario. Temporary modification of data in a specific scenario that does Low not persist after restarting the OS/application.
Bug. Bar Bug Bar Standard for Tampering and Repudiation Severity Permanent modification of any user data in a common scenario High that persists after restarting the OS/application. Permanent modification of any user data in a specific scenario, Moderate or temporary modification of user data in a common scenario. Temporary modification of data in a specific scenario that does Low not persist after restarting the OS/application.
 When to Release Software? Attack Surface n n Knight: suit of armor protects attack surface by covering most of his body Software: where are (new) vulnerabilities that are not mitigated? Bug Bar n Security threshold that must be achieved for release
When to Release Software? Attack Surface n n Knight: suit of armor protects attack surface by covering most of his body Software: where are (new) vulnerabilities that are not mitigated? Bug Bar n Security threshold that must be achieved for release
 Testing Software Testing = Software works as it should Vulnerability Testing = Automated testing checks for holes Penetration Testing = Probes security risks addressing threats to policy Reliability testing: Can s/w survive unusual conditions: faults or unusual operating conditions?
Testing Software Testing = Software works as it should Vulnerability Testing = Automated testing checks for holes Penetration Testing = Probes security risks addressing threats to policy Reliability testing: Can s/w survive unusual conditions: faults or unusual operating conditions?
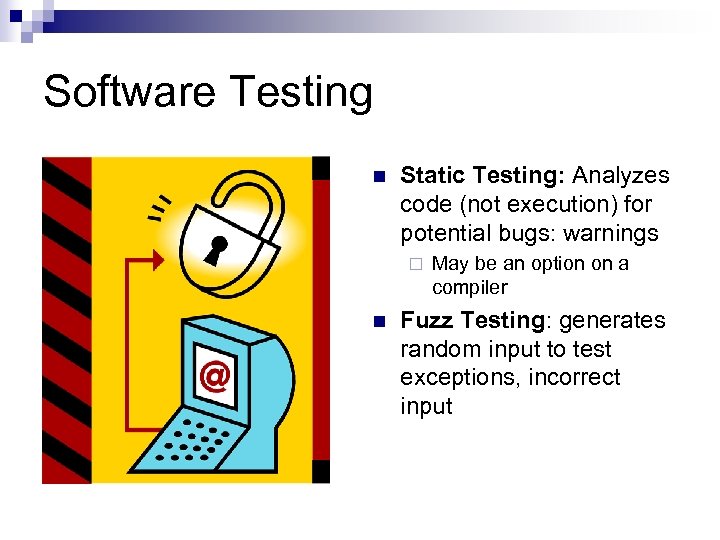 Software Testing n Static Testing: Analyzes code (not execution) for potential bugs: warnings ¨ n May be an option on a compiler Fuzz Testing: generates random input to test exceptions, incorrect input
Software Testing n Static Testing: Analyzes code (not execution) for potential bugs: warnings ¨ n May be an option on a compiler Fuzz Testing: generates random input to test exceptions, incorrect input
 Vulnerability Testing Buffer Overflow: Can long input affect service? Script Injection: Can input with scripts execute? Numeric Overflow: Can a large number become a negative or small number? Race Condition: Can multiple threads cause errors? Configuration Issues: Can software be installed improperly, causing abuse? Programmer Backdoors: Have programmers left hooks providing entry or information?
Vulnerability Testing Buffer Overflow: Can long input affect service? Script Injection: Can input with scripts execute? Numeric Overflow: Can a large number become a negative or small number? Race Condition: Can multiple threads cause errors? Configuration Issues: Can software be installed improperly, causing abuse? Programmer Backdoors: Have programmers left hooks providing entry or information?
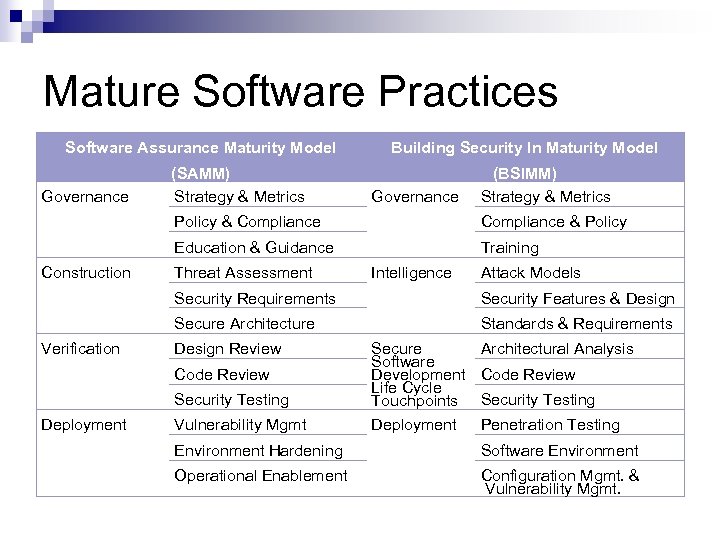 Mature Software Practices Software Assurance Maturity Model Governance (SAMM) Strategy & Metrics Building Security In Maturity Model Governance (BSIMM) Strategy & Metrics Policy & Compliance Education & Guidance Construction Compliance & Policy Training Threat Assessment Intelligence Attack Models Security Requirements Secure Architecture Verification Security Features & Design Standards & Requirements Design Review Security Testing Secure Architectural Analysis Software Development Code Review Life Cycle Touchpoints Security Testing Vulnerability Mgmt Deployment Code Review Deployment Penetration Testing Environment Hardening Software Environment Operational Enablement Configuration Mgmt. & Vulnerability Mgmt.
Mature Software Practices Software Assurance Maturity Model Governance (SAMM) Strategy & Metrics Building Security In Maturity Model Governance (BSIMM) Strategy & Metrics Policy & Compliance Education & Guidance Construction Compliance & Policy Training Threat Assessment Intelligence Attack Models Security Requirements Secure Architecture Verification Security Features & Design Standards & Requirements Design Review Security Testing Secure Architectural Analysis Software Development Code Review Life Cycle Touchpoints Security Testing Vulnerability Mgmt Deployment Code Review Deployment Penetration Testing Environment Hardening Software Environment Operational Enablement Configuration Mgmt. & Vulnerability Mgmt.
 Agile Development n n Security training is important! Include Evil User Stories in every Sprint ¨ n n Analyze risk at start of sprint, backlog change Address Security features ¨ n n "As a hacker, I send bad data in forms, so I can modify the database in unauthorized ways. " authentication, access control, input validation, output encoding, error/exception handling, encryption, data integrity, logging and alarms, and data communication security Review code for security Test using code analyzers, fuzz testing, auto/manual penetration tests
Agile Development n n Security training is important! Include Evil User Stories in every Sprint ¨ n n Analyze risk at start of sprint, backlog change Address Security features ¨ n n "As a hacker, I send bad data in forms, so I can modify the database in unauthorized ways. " authentication, access control, input validation, output encoding, error/exception handling, encryption, data integrity, logging and alarms, and data communication security Review code for security Test using code analyzers, fuzz testing, auto/manual penetration tests
 Jamie Ramon MD Doctor Chris Ramon RD Dietician Terry Medical Admin Pat Software Consultant HEALTH FIRST CASE STUDY Security Requirements
Jamie Ramon MD Doctor Chris Ramon RD Dietician Terry Medical Admin Pat Software Consultant HEALTH FIRST CASE STUDY Security Requirements
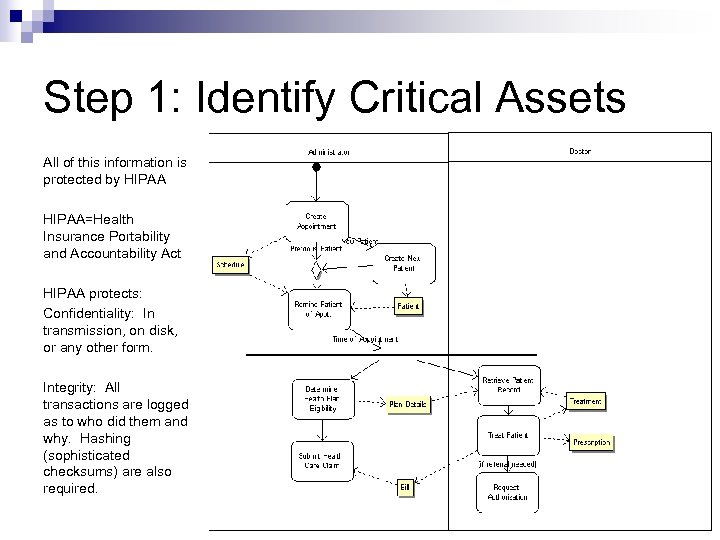 Step 1: Identify Critical Assets All of this information is protected by HIPAA=Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act HIPAA protects: Confidentiality: In transmission, on disk, or any other form. Integrity: All transactions are logged as to who did them and why. Hashing (sophisticated checksums) are also required.
Step 1: Identify Critical Assets All of this information is protected by HIPAA=Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act HIPAA protects: Confidentiality: In transmission, on disk, or any other form. Integrity: All transactions are logged as to who did them and why. Hashing (sophisticated checksums) are also required.
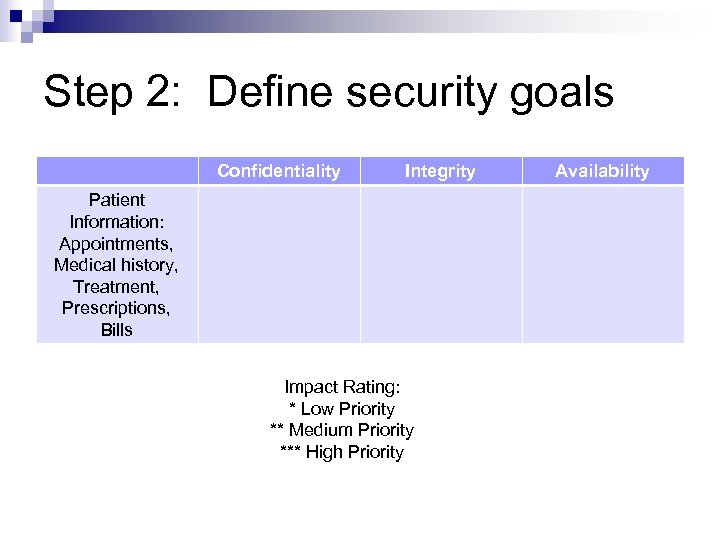 Step 2: Define security goals Confidentiality Integrity Patient Information: Appointments, Medical history, Treatment, Prescriptions, Bills Impact Rating: * Low Priority ** Medium Priority *** High Priority Availability
Step 2: Define security goals Confidentiality Integrity Patient Information: Appointments, Medical history, Treatment, Prescriptions, Bills Impact Rating: * Low Priority ** Medium Priority *** High Priority Availability
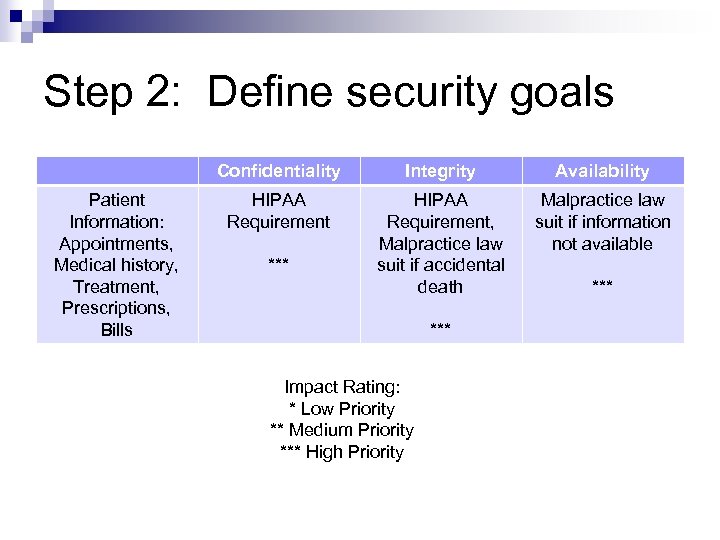 Step 2: Define security goals Confidentiality Patient Information: Appointments, Medical history, Treatment, Prescriptions, Bills Integrity Availability HIPAA Requirement, Malpractice law suit if accidental death Malpractice law suit if information not available *** Impact Rating: * Low Priority ** Medium Priority *** High Priority ***
Step 2: Define security goals Confidentiality Patient Information: Appointments, Medical history, Treatment, Prescriptions, Bills Integrity Availability HIPAA Requirement, Malpractice law suit if accidental death Malpractice law suit if information not available *** Impact Rating: * Low Priority ** Medium Priority *** High Priority ***
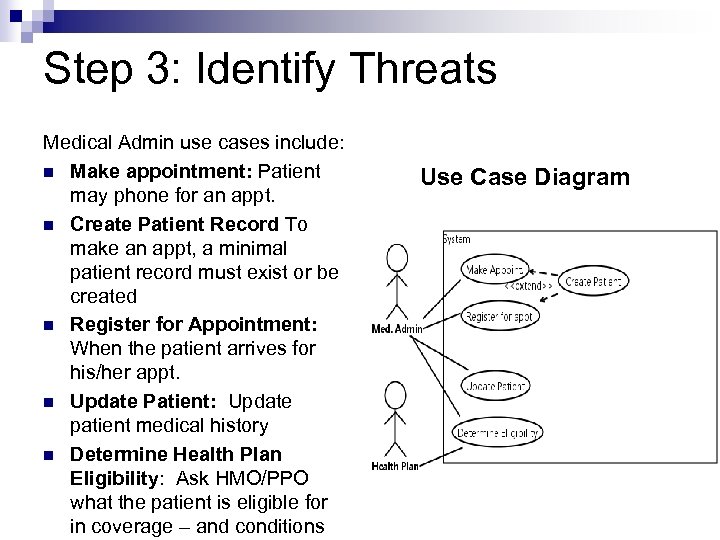 Step 3: Identify Threats Medical Admin use cases include: n Make appointment: Patient may phone for an appt. n Create Patient Record To make an appt, a minimal patient record must exist or be created n Register for Appointment: When the patient arrives for his/her appt. n Update Patient: Update patient medical history n Determine Health Plan Eligibility: Ask HMO/PPO what the patient is eligible for in coverage – and conditions Use Case Diagram
Step 3: Identify Threats Medical Admin use cases include: n Make appointment: Patient may phone for an appt. n Create Patient Record To make an appt, a minimal patient record must exist or be created n Register for Appointment: When the patient arrives for his/her appt. n Update Patient: Update patient medical history n Determine Health Plan Eligibility: Ask HMO/PPO what the patient is eligible for in coverage – and conditions Use Case Diagram
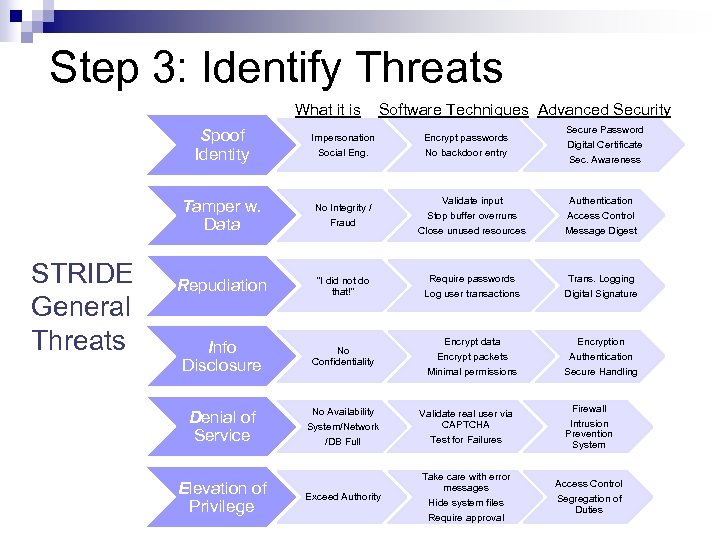 Step 3: Identify Threats What it is Spoof Identity STRIDE General Threats Impersonation Social Eng. Tamper w. Data No Integrity / Fraud Repudiation “I did not do that!” Info Disclosure Software Techniques Advanced Security No Confidentiality Denial of Service Elevation of Privilege No Availability System/Network /DB Full Exceed Authority Encrypt passwords No backdoor entry Secure Password Digital Certificate Sec. Awareness Validate input Stop buffer overruns Authentication Access Control Close unused resources Message Digest Require passwords Log user transactions Trans. Logging Digital Signature Encrypt data Encrypt packets Encryption Authentication Minimal permissions Secure Handling Validate real user via CAPTCHA Test for Failures Firewall Intrusion Prevention System Take care with error messages Hide system files Require approval Access Control Segregation of Duties
Step 3: Identify Threats What it is Spoof Identity STRIDE General Threats Impersonation Social Eng. Tamper w. Data No Integrity / Fraud Repudiation “I did not do that!” Info Disclosure Software Techniques Advanced Security No Confidentiality Denial of Service Elevation of Privilege No Availability System/Network /DB Full Exceed Authority Encrypt passwords No backdoor entry Secure Password Digital Certificate Sec. Awareness Validate input Stop buffer overruns Authentication Access Control Close unused resources Message Digest Require passwords Log user transactions Trans. Logging Digital Signature Encrypt data Encrypt packets Encryption Authentication Minimal permissions Secure Handling Validate real user via CAPTCHA Test for Failures Firewall Intrusion Prevention System Take care with error messages Hide system files Require approval Access Control Segregation of Duties
 Security Requirements Process OCTAVE Security Requirements Process ü Identify critical assets ü Define security goals 3. Identify threats ¨ 4. Analyze risks: ¨ 5. Draw Misuse Diagram from Use Case Diagram Priority = Impact * Likelihood Define security requirements ¨ ¨ Draw Misuse Diagram with Security Use Cases Define one Misuse Description (Lightweight or Midweight)
Security Requirements Process OCTAVE Security Requirements Process ü Identify critical assets ü Define security goals 3. Identify threats ¨ 4. Analyze risks: ¨ 5. Draw Misuse Diagram from Use Case Diagram Priority = Impact * Likelihood Define security requirements ¨ ¨ Draw Misuse Diagram with Security Use Cases Define one Misuse Description (Lightweight or Midweight)


