1acfa736da9de1c3cea1738cc281e7b8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 100
 Sections Covered in 1 st Part of Course MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Sections Covered in 1 st Part of Course MIS 300 Midterm Summary
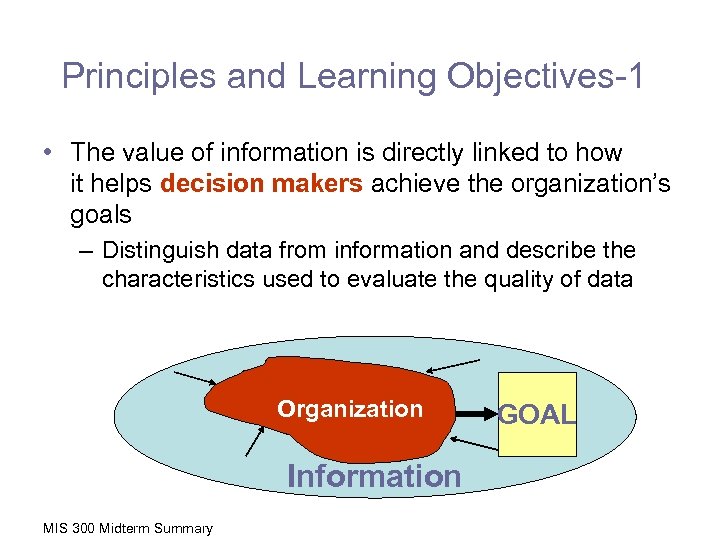 Principles and Learning Objectives-1 • The value of information is directly linked to how it helps decision makers achieve the organization’s goals – Distinguish data from information and describe the characteristics used to evaluate the quality of data Organization Information MIS 300 Midterm Summary GOAL
Principles and Learning Objectives-1 • The value of information is directly linked to how it helps decision makers achieve the organization’s goals – Distinguish data from information and describe the characteristics used to evaluate the quality of data Organization Information MIS 300 Midterm Summary GOAL
 Principles and Learning Objectives -2 • Knowing the potential impact of information systems and having the ability to put this knowledge to work can result in a successful personal career, organizations that reach their goals, and a society with a higher quality of life – Identify the basic types of business information systems and discuss who uses them, how they are used, and what kinds of benefits they deliver MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Principles and Learning Objectives -2 • Knowing the potential impact of information systems and having the ability to put this knowledge to work can result in a successful personal career, organizations that reach their goals, and a society with a higher quality of life – Identify the basic types of business information systems and discuss who uses them, how they are used, and what kinds of benefits they deliver MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Chapter 1 Provides a Preview of All the Concepts Covered in the Course. Note these especially MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Chapter 1 Provides a Preview of All the Concepts Covered in the Course. Note these especially MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Introduction • Information system (IS) – Set of interrelated components: collect, manipulate, disseminate data and information – Provide feedback to meet an objective – Examples: ATMs, airline reservation systems, course reservation systems What is Information, really? Why have it? MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Introduction • Information system (IS) – Set of interrelated components: collect, manipulate, disseminate data and information – Provide feedback to meet an objective – Examples: ATMs, airline reservation systems, course reservation systems What is Information, really? Why have it? MIS 300 Midterm Summary
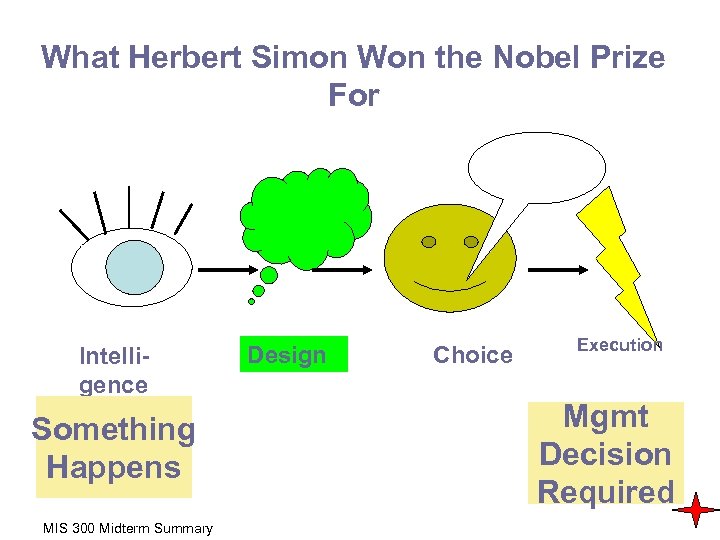 What Herbert Simon Won the Nobel Prize For Intelligence Something Happens MIS 300 Midterm Summary Design Choice Execution Mgmt Decision Required
What Herbert Simon Won the Nobel Prize For Intelligence Something Happens MIS 300 Midterm Summary Design Choice Execution Mgmt Decision Required
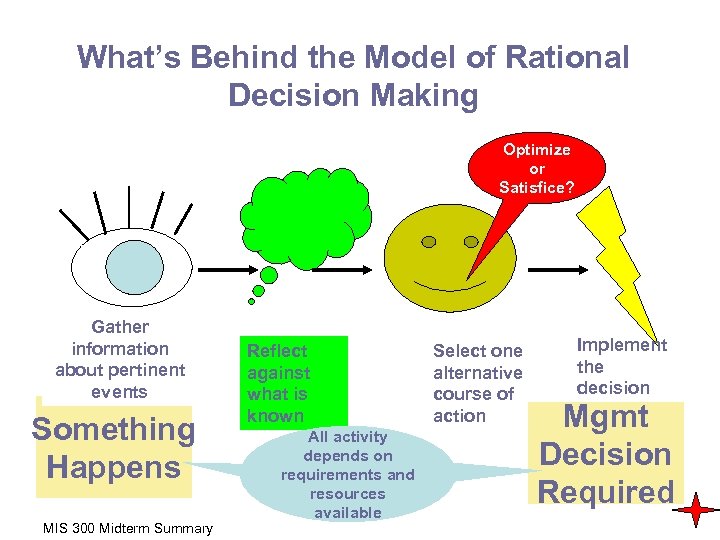 What’s Behind the Model of Rational Decision Making Optimize or Satisfice? Gather information Intelliabout pertinent gence events Something Happens MIS 300 Midterm Summary Reflect against what is known All activity depends on requirements and resources available Select one alternative course of action Implement the decision Mgmt Decision Required
What’s Behind the Model of Rational Decision Making Optimize or Satisfice? Gather information Intelliabout pertinent gence events Something Happens MIS 300 Midterm Summary Reflect against what is known All activity depends on requirements and resources available Select one alternative course of action Implement the decision Mgmt Decision Required
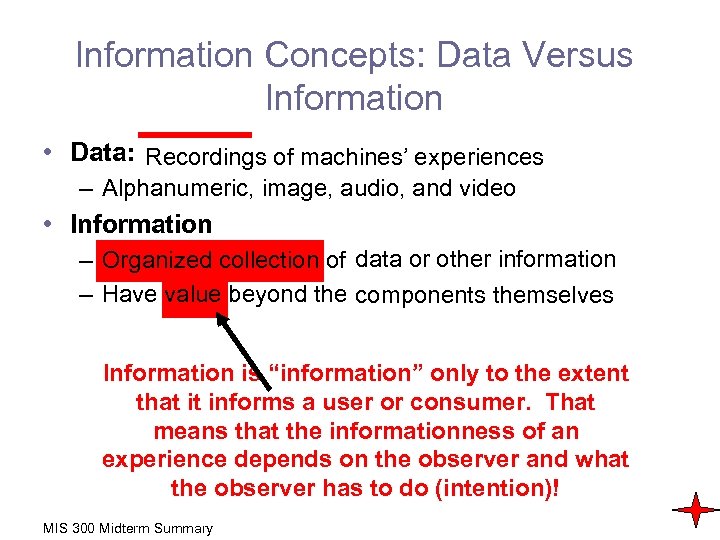 Information Concepts: Data Versus Information • Data: raw facts of machines’ experiences Recordings – Alphanumeric, image, audio, and video • Information data – Organized collection of facts or other information – Have value beyond the facts themselves components themselves Information is “information” only to the extent that it informs a user or consumer. That means that the informationness of an experience depends on the observer and what the observer has to do (intention)! MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Information Concepts: Data Versus Information • Data: raw facts of machines’ experiences Recordings – Alphanumeric, image, audio, and video • Information data – Organized collection of facts or other information – Have value beyond the facts themselves components themselves Information is “information” only to the extent that it informs a user or consumer. That means that the informationness of an experience depends on the observer and what the observer has to do (intention)! MIS 300 Midterm Summary
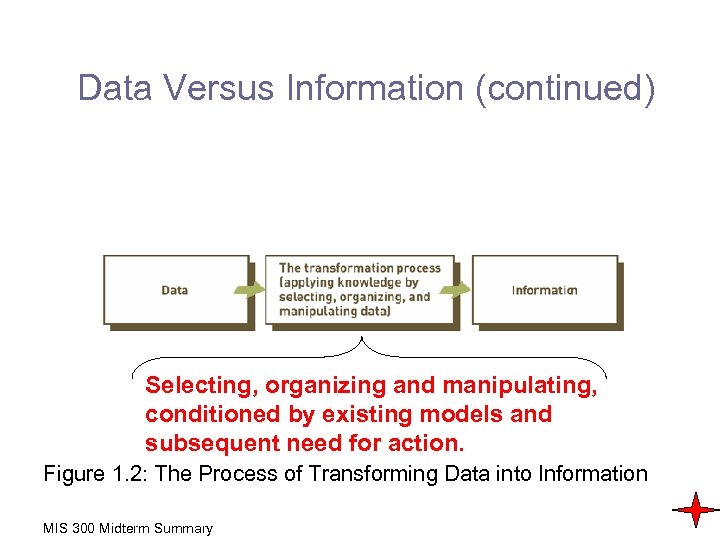 Data Versus Information (continued) Selecting, organizing and manipulating, conditioned by existing models and subsequent need for action. Figure 1. 2: The Process of Transforming Data into Information MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Data Versus Information (continued) Selecting, organizing and manipulating, conditioned by existing models and subsequent need for action. Figure 1. 2: The Process of Transforming Data into Information MIS 300 Midterm Summary
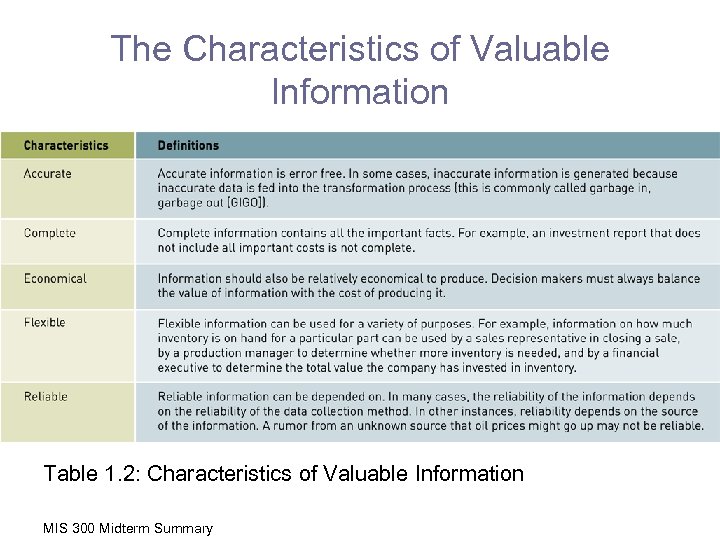 The Characteristics of Valuable Information Table 1. 2: Characteristics of Valuable Information MIS 300 Midterm Summary
The Characteristics of Valuable Information Table 1. 2: Characteristics of Valuable Information MIS 300 Midterm Summary
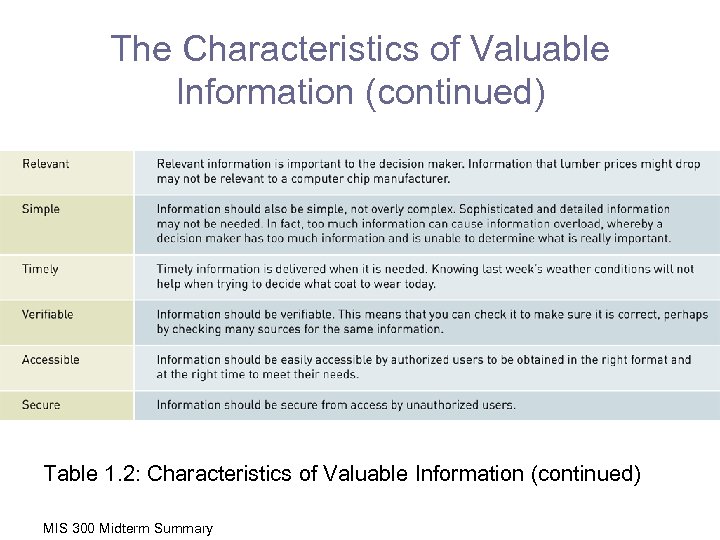 The Characteristics of Valuable Information (continued) Table 1. 2: Characteristics of Valuable Information (continued) MIS 300 Midterm Summary
The Characteristics of Valuable Information (continued) Table 1. 2: Characteristics of Valuable Information (continued) MIS 300 Midterm Summary
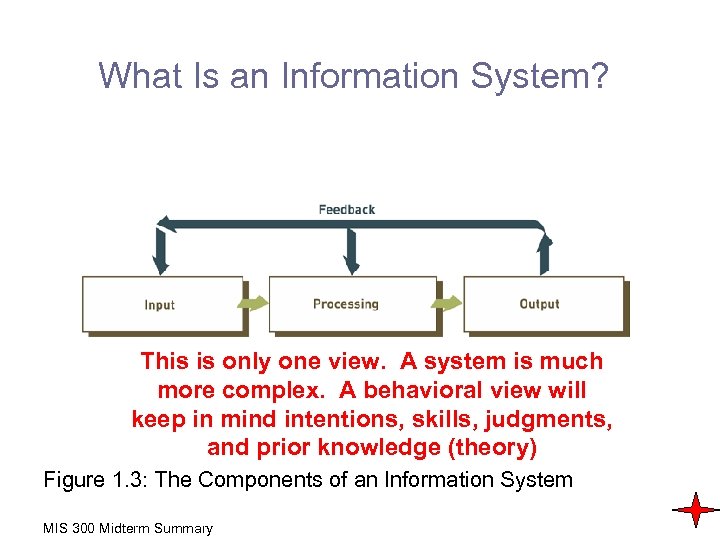 What Is an Information System? This is only one view. A system is much more complex. A behavioral view will keep in mind intentions, skills, judgments, and prior knowledge (theory) Figure 1. 3: The Components of an Information System MIS 300 Midterm Summary
What Is an Information System? This is only one view. A system is much more complex. A behavioral view will keep in mind intentions, skills, judgments, and prior knowledge (theory) Figure 1. 3: The Components of an Information System MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Computer-Based Information Systems • Manual versus computerized information systems • Computers are NOT necessary in information systems, but they have certain efficiencies • Computer-based information system (CBIS) – Hardware, software, databases, telecommunications, people, and procedures – Collect, manipulate, store, and process data into information MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Computer-Based Information Systems • Manual versus computerized information systems • Computers are NOT necessary in information systems, but they have certain efficiencies • Computer-based information system (CBIS) – Hardware, software, databases, telecommunications, people, and procedures – Collect, manipulate, store, and process data into information MIS 300 Midterm Summary
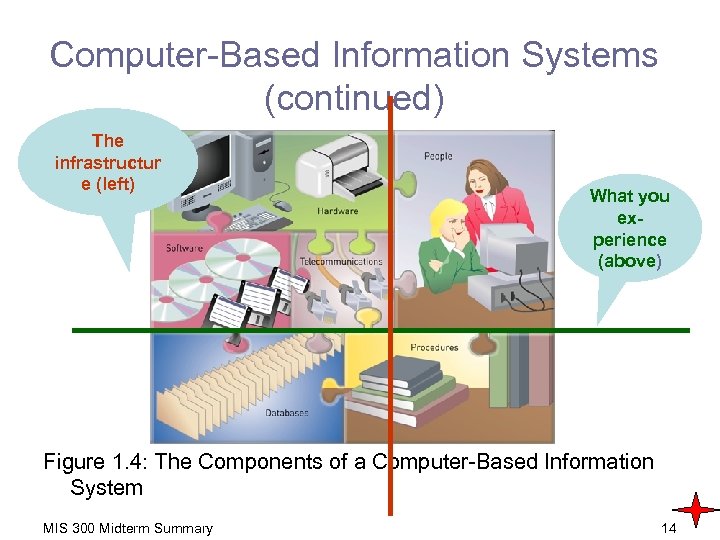 Computer-Based Information Systems (continued) The infrastructur e (left) What you experience (above) Figure 1. 4: The Components of a Computer-Based Information System MIS 300 Midterm Summary 14
Computer-Based Information Systems (continued) The infrastructur e (left) What you experience (above) Figure 1. 4: The Components of a Computer-Based Information System MIS 300 Midterm Summary 14
 Electronic and Mobile Commerce • E-commerce: any business transaction executed electronically between parties such as: – – – Companies (B 2 B) Companies and consumers (B 2 C) Consumers and other consumers (C 2 C) Business and the public sector Consumers and the public sector MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Electronic and Mobile Commerce • E-commerce: any business transaction executed electronically between parties such as: – – – Companies (B 2 B) Companies and consumers (B 2 C) Consumers and other consumers (C 2 C) Business and the public sector Consumers and the public sector MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Transaction Processing Systems • Transaction: business-related exchange – Payments to employees – Sales to customers – Payments to suppliers • Transaction processing system (TPS) – A collection of people, procedures, software, databases, devices – Records completed business transactions MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Transaction Processing Systems • Transaction: business-related exchange – Payments to employees – Sales to customers – Payments to suppliers • Transaction processing system (TPS) – A collection of people, procedures, software, databases, devices – Records completed business transactions MIS 300 Midterm Summary
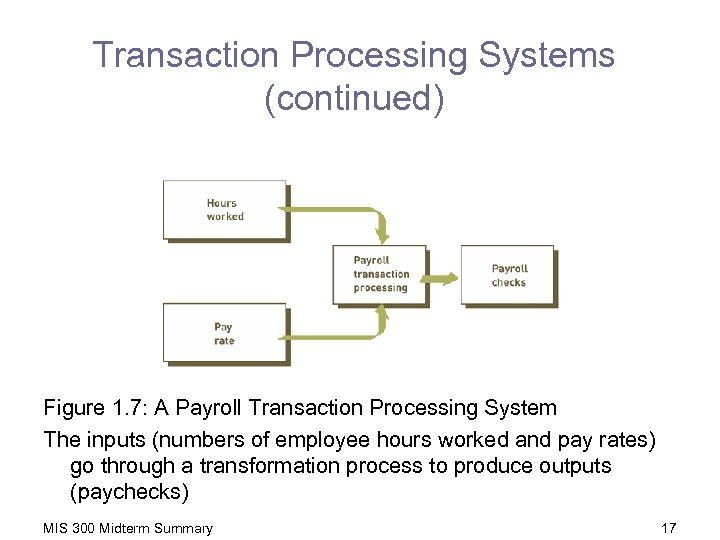 Transaction Processing Systems (continued) Figure 1. 7: A Payroll Transaction Processing System The inputs (numbers of employee hours worked and pay rates) go through a transformation process to produce outputs (paychecks) MIS 300 Midterm Summary 17
Transaction Processing Systems (continued) Figure 1. 7: A Payroll Transaction Processing System The inputs (numbers of employee hours worked and pay rates) go through a transformation process to produce outputs (paychecks) MIS 300 Midterm Summary 17
 Enterprise Resource Planning • Integrated programs that manage all business operations • Coordinate planning, inventory control, production, and ordering among others • Historically based in production systems • Hard to translate to other types of business • Necessarily complex MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Enterprise Resource Planning • Integrated programs that manage all business operations • Coordinate planning, inventory control, production, and ordering among others • Historically based in production systems • Hard to translate to other types of business • Necessarily complex MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Chapters 2 -5 Relate Material on These Topics • • Ch 2: Hardware (little emphasis) Ch 2: Software Ch 3: Data Management and Databases Ch 4: Networking Ch 5: E-Commerce Ch 5: Transaction Processing Systems Ch 5: Enterprise Resource Systems MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Chapters 2 -5 Relate Material on These Topics • • Ch 2: Hardware (little emphasis) Ch 2: Software Ch 3: Data Management and Databases Ch 4: Networking Ch 5: E-Commerce Ch 5: Transaction Processing Systems Ch 5: Enterprise Resource Systems MIS 300 Midterm Summary
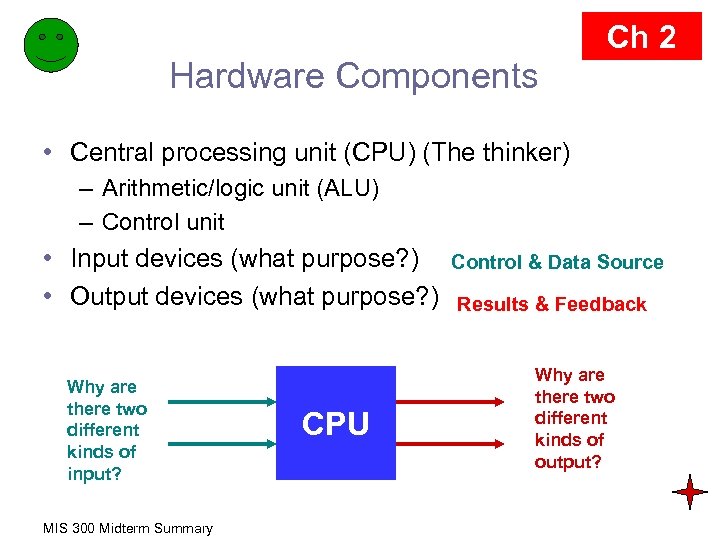 Ch 2 Hardware Components • Central processing unit (CPU) (The thinker) – Arithmetic/logic unit (ALU) – Control unit • Input devices (what purpose? ) • Output devices (what purpose? ) Why are there two different kinds of input? MIS 300 Midterm Summary CPU Control & Data Source Results & Feedback Why are there two different kinds of output?
Ch 2 Hardware Components • Central processing unit (CPU) (The thinker) – Arithmetic/logic unit (ALU) – Control unit • Input devices (what purpose? ) • Output devices (what purpose? ) Why are there two different kinds of input? MIS 300 Midterm Summary CPU Control & Data Source Results & Feedback Why are there two different kinds of output?
 Overview of Software • Computer programs: sequences of instructions • Documentation: describes program functions • Systems software: coordinates the activities of hardware and programs: “To serve and protect” • Application software: helps users solve particular problems: “To get the job done” What is software really doing? Why is it important? MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Overview of Software • Computer programs: sequences of instructions • Documentation: describes program functions • Systems software: coordinates the activities of hardware and programs: “To serve and protect” • Application software: helps users solve particular problems: “To get the job done” What is software really doing? Why is it important? MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Systems Software: Operating Systems • Operating system (OS): set of programs that control and manage the hardware and act as an interface with applications • Common hardware functions – Get input (e. g. , keyboard) – Retrieve data from disks and store data on disks – Display information on a monitor or printer MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Systems Software: Operating Systems • Operating system (OS): set of programs that control and manage the hardware and act as an interface with applications • Common hardware functions – Get input (e. g. , keyboard) – Retrieve data from disks and store data on disks – Display information on a monitor or printer MIS 300 Midterm Summary
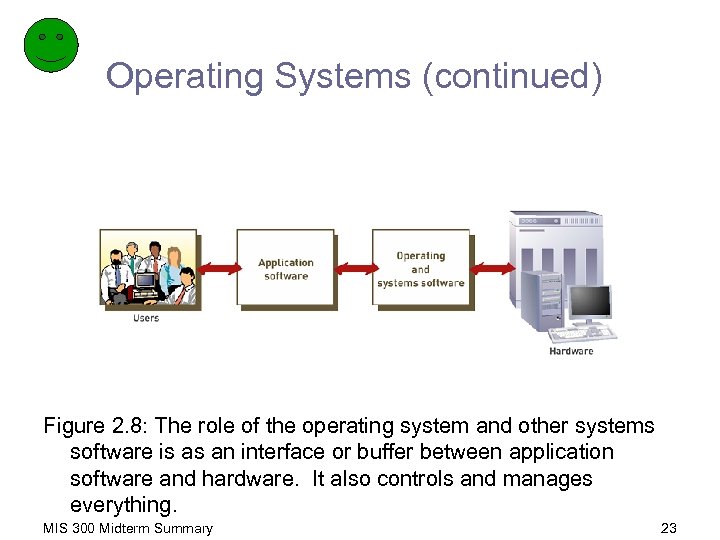 Operating Systems (continued) Figure 2. 8: The role of the operating system and other systems software is as an interface or buffer between application software and hardware. It also controls and manages everything. MIS 300 Midterm Summary 23
Operating Systems (continued) Figure 2. 8: The role of the operating system and other systems software is as an interface or buffer between application software and hardware. It also controls and manages everything. MIS 300 Midterm Summary 23
 Operating Systems (continued) • User interface – Allows individuals to access and command the computer system – Command-based user interface: uses text commands – Graphical user interface (GUI): uses icons and menus to send commands to the computer system – Smart interface: anticipates users’ needs MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Operating Systems (continued) • User interface – Allows individuals to access and command the computer system – Command-based user interface: uses text commands – Graphical user interface (GUI): uses icons and menus to send commands to the computer system – Smart interface: anticipates users’ needs MIS 300 Midterm Summary
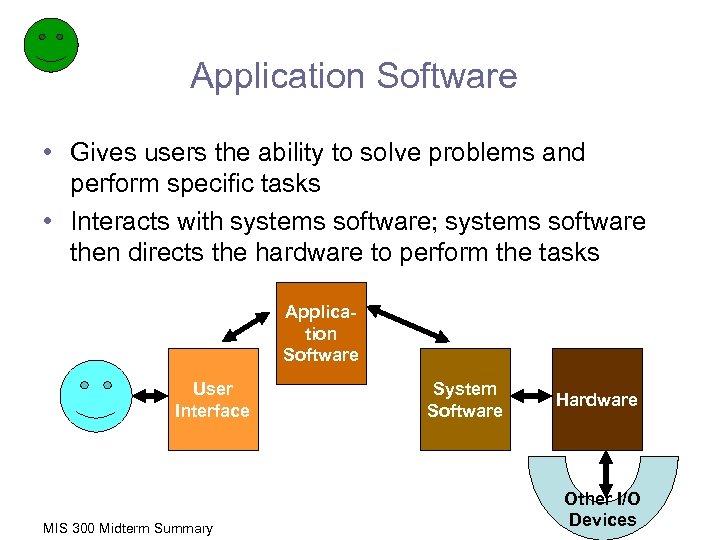 Application Software • Gives users the ability to solve problems and perform specific tasks • Interacts with systems software; systems software then directs the hardware to perform the tasks Application Software User Interface MIS 300 Midterm Summary System Software Hardware Other I/O Devices
Application Software • Gives users the ability to solve problems and perform specific tasks • Interacts with systems software; systems software then directs the hardware to perform the tasks Application Software User Interface MIS 300 Midterm Summary System Software Hardware Other I/O Devices
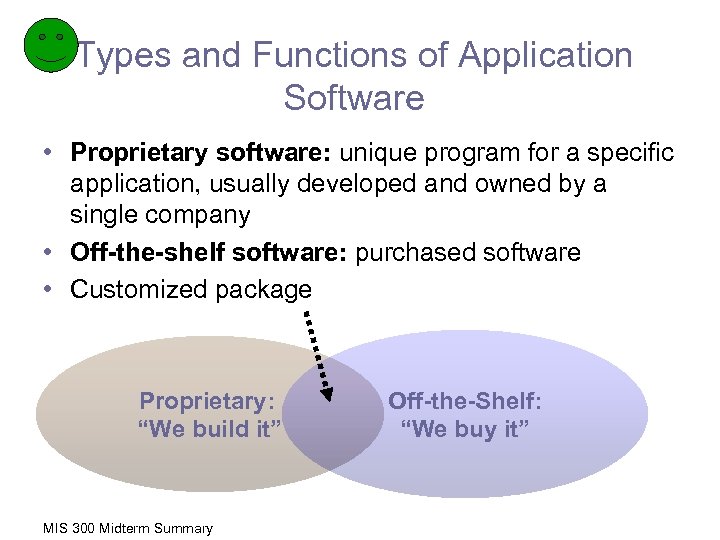 Types and Functions of Application Software • Proprietary software: unique program for a specific application, usually developed and owned by a single company • Off-the-shelf software: purchased software • Customized package Proprietary: “We build it” MIS 300 Midterm Summary Off-the-Shelf: “We buy it”
Types and Functions of Application Software • Proprietary software: unique program for a specific application, usually developed and owned by a single company • Off-the-shelf software: purchased software • Customized package Proprietary: “We build it” MIS 300 Midterm Summary Off-the-Shelf: “We buy it”
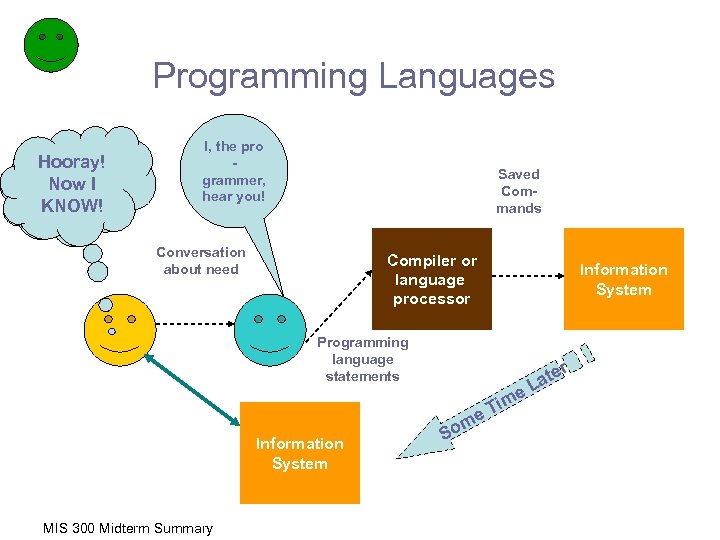 Programming Languages I need Hooray! informa. Now tion to. I solve a KNOW! problem! I, the pro grammer, hear you! Saved Commands Conversation about need Compiler or language processor Information System Programming language statements e e Information System MIS 300 Midterm Summary m So Tim r ate L
Programming Languages I need Hooray! informa. Now tion to. I solve a KNOW! problem! I, the pro grammer, hear you! Saved Commands Conversation about need Compiler or language processor Information System Programming language statements e e Information System MIS 300 Midterm Summary m So Tim r ate L
 Software Issues and Trends That Will Effect YOU! • Software bugs – Program defects that keep it from performing correctly • • Copyrights and licenses Global software support Obsolescence Outsourcing Legal issues Commoditization Security MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Software Issues and Trends That Will Effect YOU! • Software bugs – Program defects that keep it from performing correctly • • Copyrights and licenses Global software support Obsolescence Outsourcing Legal issues Commoditization Security MIS 300 Midterm Summary
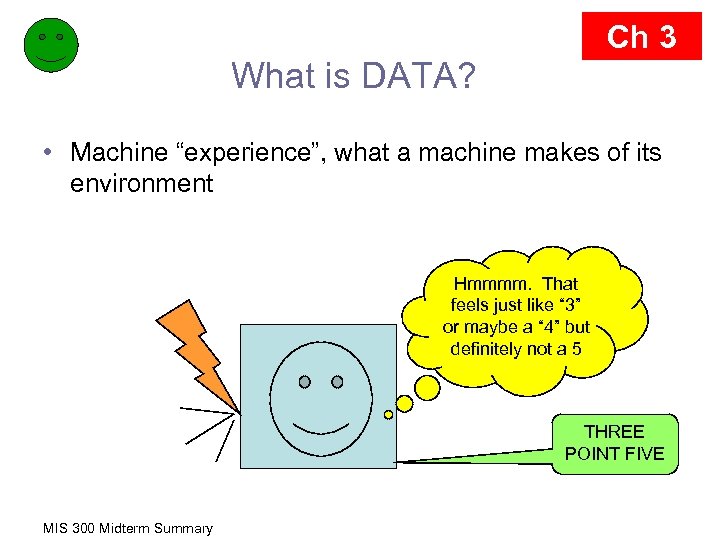 Ch 3 What is DATA? • Machine “experience”, what a machine makes of its environment Hmmmm. That feels just like “ 3” or maybe a “ 4” but definitely not a 5 THREE POINT FIVE MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Ch 3 What is DATA? • Machine “experience”, what a machine makes of its environment Hmmmm. That feels just like “ 3” or maybe a “ 4” but definitely not a 5 THREE POINT FIVE MIS 300 Midterm Summary
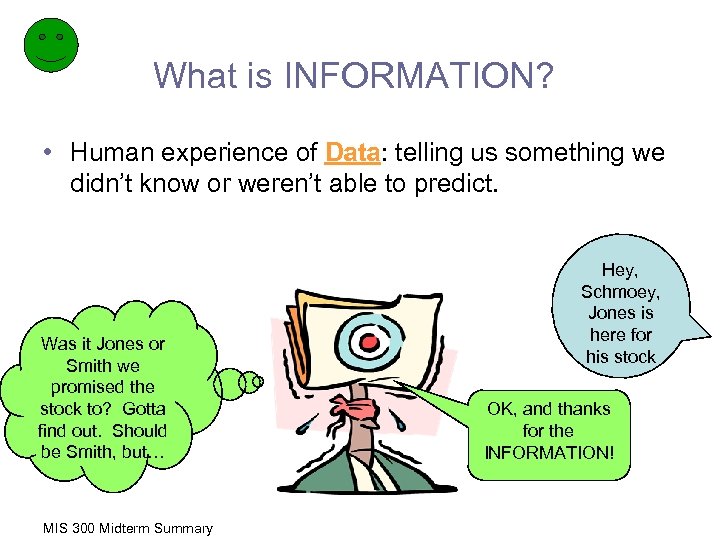 What is INFORMATION? • Human experience of Data: telling us something we didn’t know or weren’t able to predict. Was it Jones or Smith we promised the stock to? Gotta find out. Should be Smith, but… MIS 300 Midterm Summary Hey, Schmoey, Jones is here for his stock OK, and thanks for the INFORMATION!
What is INFORMATION? • Human experience of Data: telling us something we didn’t know or weren’t able to predict. Was it Jones or Smith we promised the stock to? Gotta find out. Should be Smith, but… MIS 300 Midterm Summary Hey, Schmoey, Jones is here for his stock OK, and thanks for the INFORMATION!
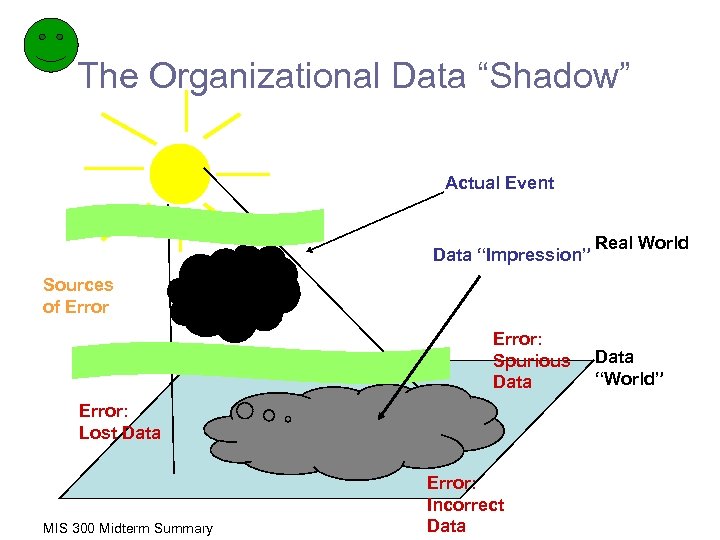 The Organizational Data “Shadow” Actual Event Data “Impression” Real World Sources of Error: Spurious Data Error: Lost Data MIS 300 Midterm Summary Error: Incorrect Data “World”
The Organizational Data “Shadow” Actual Event Data “Impression” Real World Sources of Error: Spurious Data Error: Lost Data MIS 300 Midterm Summary Error: Incorrect Data “World”
 Events as Data • Each event generates some data • The data are about the objects that play roles in the event • The data describe the objects and perhaps how they relate to one another • The events, too, relate to one another in various ways. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Events as Data • Each event generates some data • The data are about the objects that play roles in the event • The data describe the objects and perhaps how they relate to one another • The events, too, relate to one another in various ways. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Data Events • Consider a sales “event” • It involves a number of objects: items sold, salesperson, act of selling, customer, money (objects are also called “entities”) • Each event generates data that describe each of the objects…. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Data Events • Consider a sales “event” • It involves a number of objects: items sold, salesperson, act of selling, customer, money (objects are also called “entities”) • Each event generates data that describe each of the objects…. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Data Representation: The Hierarchy of Data • Bit (a binary digit): a circuit that is either on or off • Byte: 8 bits • Character: each byte represents a character; the basic building block of information • Field: name, number, or characters that describe an aspect of a business object or activity MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Data Representation: The Hierarchy of Data • Bit (a binary digit): a circuit that is either on or off • Byte: 8 bits • Character: each byte represents a character; the basic building block of information • Field: name, number, or characters that describe an aspect of a business object or activity MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 The Hierarchy of Data (continued) • • Record: a collection of related data fields File: a collection of related records Database: a collection of integrated and related files Hierarchy of data – Bits, characters, fields, records, files, and databases MIS 300 Midterm Summary
The Hierarchy of Data (continued) • • Record: a collection of related data fields File: a collection of related records Database: a collection of integrated and related files Hierarchy of data – Bits, characters, fields, records, files, and databases MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 The Traditional Approach Versus the Database Approach • Traditional approach: separate data files are created for each application, i. e. , each business problem – Results in data redundancy (duplication) – Data redundancy conflicts with data integrity • Database approach: pool of related data is shared by multiple applications – Significant advantages over traditional approach – Besides, all elements of business are related MIS 300 Midterm Summary
The Traditional Approach Versus the Database Approach • Traditional approach: separate data files are created for each application, i. e. , each business problem – Results in data redundancy (duplication) – Data redundancy conflicts with data integrity • Database approach: pool of related data is shared by multiple applications – Significant advantages over traditional approach – Besides, all elements of business are related MIS 300 Midterm Summary
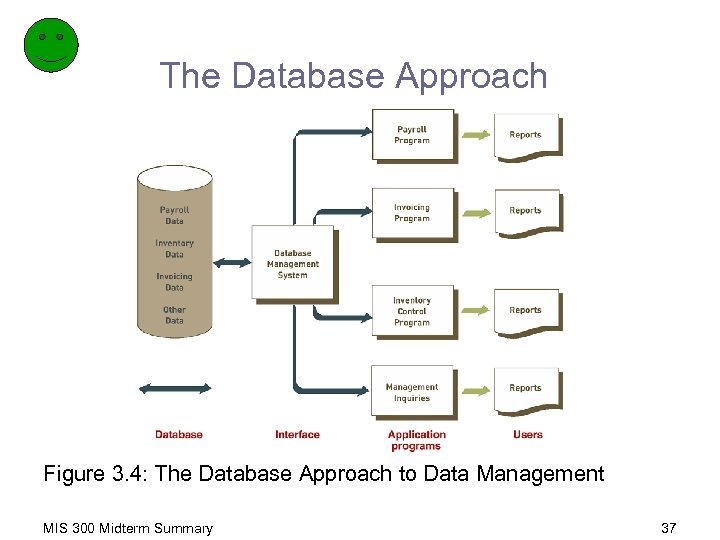 The Database Approach Figure 3. 4: The Database Approach to Data Management MIS 300 Midterm Summary 37
The Database Approach Figure 3. 4: The Database Approach to Data Management MIS 300 Midterm Summary 37
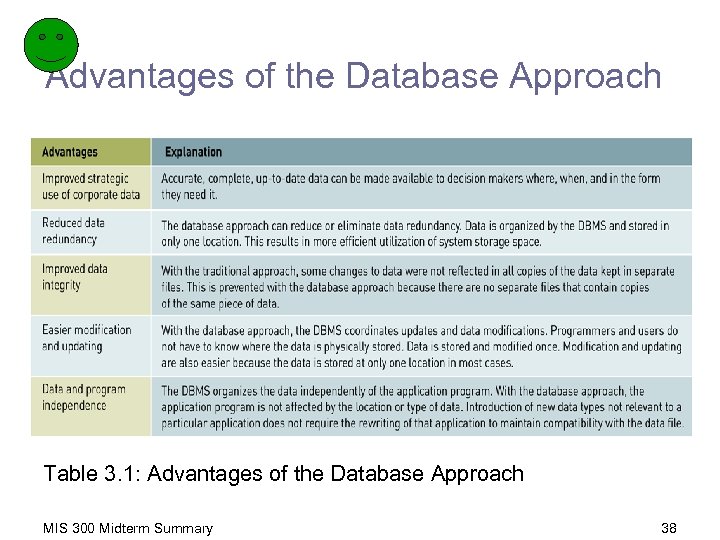 Advantages of the Database Approach Table 3. 1: Advantages of the Database Approach MIS 300 Midterm Summary 38
Advantages of the Database Approach Table 3. 1: Advantages of the Database Approach MIS 300 Midterm Summary 38
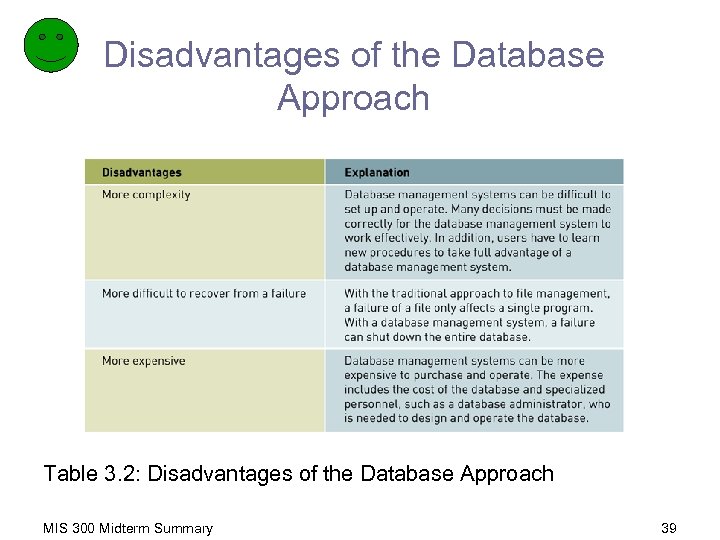 Disadvantages of the Database Approach Table 3. 2: Disadvantages of the Database Approach MIS 300 Midterm Summary 39
Disadvantages of the Database Approach Table 3. 2: Disadvantages of the Database Approach MIS 300 Midterm Summary 39
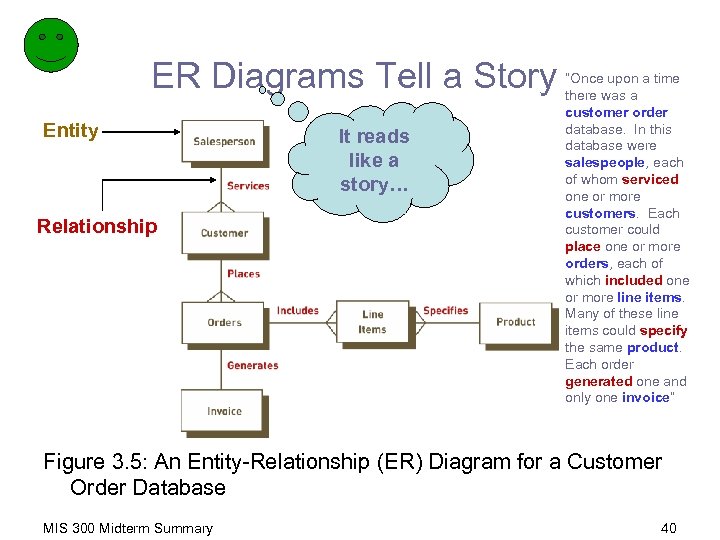 ER Diagrams Tell a Story Entity Relationship It reads like a story… “Once upon a time there was a customer order database. In this database were salespeople, each of whom serviced one or more customers. Each customer could place one or more orders, each of which included one or more line items. Many of these line items could specify the same product. Each order generated one and only one invoice” Figure 3. 5: An Entity-Relationship (ER) Diagram for a Customer Order Database MIS 300 Midterm Summary 40
ER Diagrams Tell a Story Entity Relationship It reads like a story… “Once upon a time there was a customer order database. In this database were salespeople, each of whom serviced one or more customers. Each customer could place one or more orders, each of which included one or more line items. Many of these line items could specify the same product. Each order generated one and only one invoice” Figure 3. 5: An Entity-Relationship (ER) Diagram for a Customer Order Database MIS 300 Midterm Summary 40
 Database Management Systems (DBMS) • Interface between – Database and application programs – Database and the user • Database types – Flat file – Single user – Multiple users MIS 300 Midterm Summary 41
Database Management Systems (DBMS) • Interface between – Database and application programs – Database and the user • Database types – Flat file – Single user – Multiple users MIS 300 Midterm Summary 41
 Data Warehouses, Data Marts, and Data Mining • Data warehouse: collects business information from many sources in the enterprise • Data mart: a subset of a data warehouse • Data mining: an information-analysis tool for discovering patterns and relationships in a data warehouse or a data mart MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Data Warehouses, Data Marts, and Data Mining • Data warehouse: collects business information from many sources in the enterprise • Data mart: a subset of a data warehouse • Data mining: an information-analysis tool for discovering patterns and relationships in a data warehouse or a data mart MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Business Intelligence • Business intelligence (BI): gathering the right information in a timely manner and usable form and analyzing it to have a positive impact on business • Knowledge management: capturing a company’s collective expertise and distributing it wherever it can help produce the biggest payoff MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Business Intelligence • Business intelligence (BI): gathering the right information in a timely manner and usable form and analyzing it to have a positive impact on business • Knowledge management: capturing a company’s collective expertise and distributing it wherever it can help produce the biggest payoff MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Distributed Databases • Distributed database – Data may be spread across several smaller databases connected via telecommunications devices – Corporations get more flexibility in how databases are organized and used • Replicated database – Holds a duplicate set of frequently used data MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Distributed Databases • Distributed database – Data may be spread across several smaller databases connected via telecommunications devices – Corporations get more flexibility in how databases are organized and used • Replicated database – Holds a duplicate set of frequently used data MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 An Overview of Telecommunications Ch 4 and Networks • Telecommunications: the electronic transmission of signals for communications • Telecommunications medium: anything that carries an electronic signal and interfaces between a sending device and a receiving device • Telecommunications carrier: any business that provides (leases, services) telecommunications media. • Telecommunications service: any service to customers at least partially facilitated by telecommunications MIS 300 Midterm Summary
An Overview of Telecommunications Ch 4 and Networks • Telecommunications: the electronic transmission of signals for communications • Telecommunications medium: anything that carries an electronic signal and interfaces between a sending device and a receiving device • Telecommunications carrier: any business that provides (leases, services) telecommunications media. • Telecommunications service: any service to customers at least partially facilitated by telecommunications MIS 300 Midterm Summary
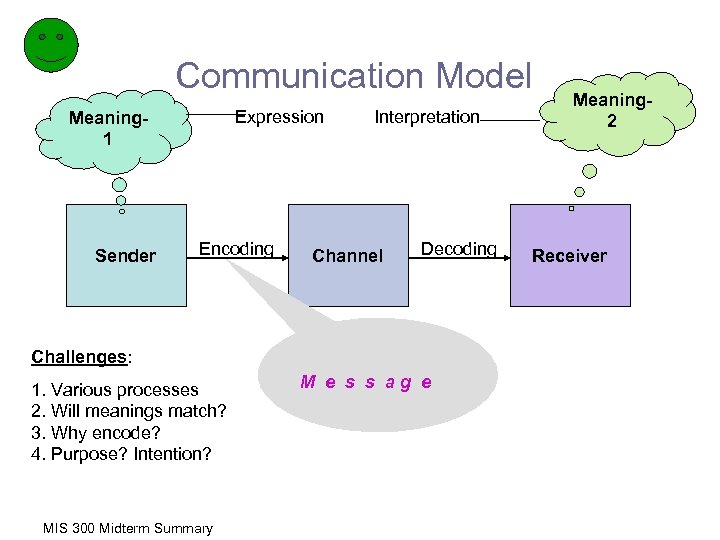 Communication Model Expression Meaning 1 Sender Encoding Interpretation Channel Decoding Challenges: 1. Various processes 2. Will meanings match? 3. Why encode? 4. Purpose? Intention? MIS 300 Midterm Summary M e s s ag e Meaning 2 Receiver
Communication Model Expression Meaning 1 Sender Encoding Interpretation Channel Decoding Challenges: 1. Various processes 2. Will meanings match? 3. Why encode? 4. Purpose? Intention? MIS 300 Midterm Summary M e s s ag e Meaning 2 Receiver
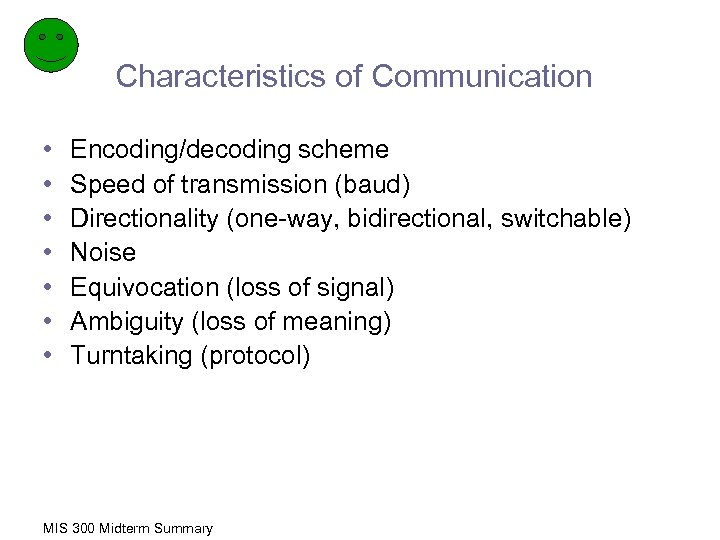 Characteristics of Communication • • Encoding/decoding scheme Speed of transmission (baud) Directionality (one-way, bidirectional, switchable) Noise Equivocation (loss of signal) Ambiguity (loss of meaning) Turntaking (protocol) MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Characteristics of Communication • • Encoding/decoding scheme Speed of transmission (baud) Directionality (one-way, bidirectional, switchable) Noise Equivocation (loss of signal) Ambiguity (loss of meaning) Turntaking (protocol) MIS 300 Midterm Summary
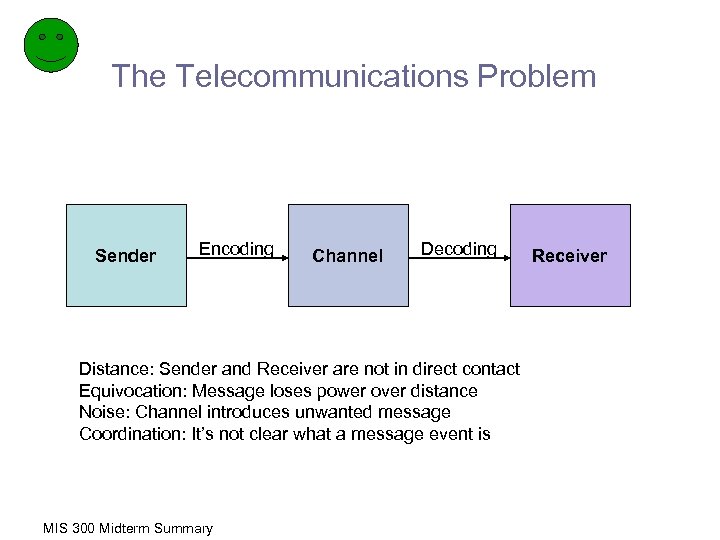 The Telecommunications Problem Sender Encoding Channel Decoding Distance: Sender and Receiver are not in direct contact Equivocation: Message loses power over distance Noise: Channel introduces unwanted message Coordination: It’s not clear what a message event is MIS 300 Midterm Summary Receiver
The Telecommunications Problem Sender Encoding Channel Decoding Distance: Sender and Receiver are not in direct contact Equivocation: Message loses power over distance Noise: Channel introduces unwanted message Coordination: It’s not clear what a message event is MIS 300 Midterm Summary Receiver
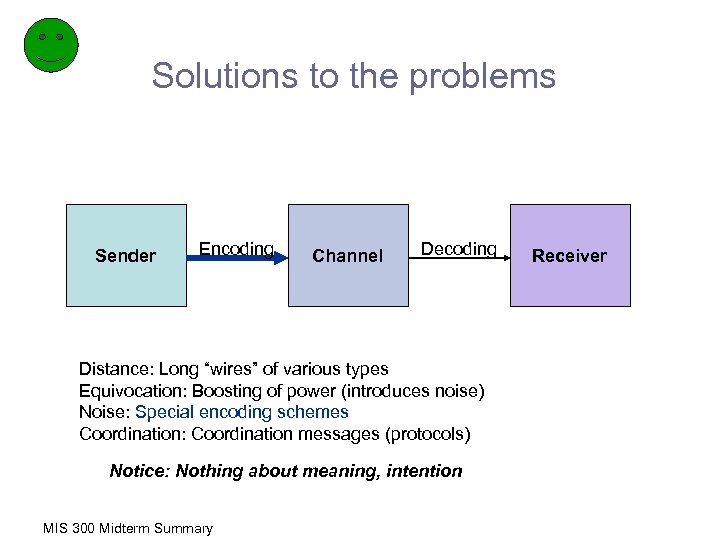 Solutions to the problems Sender Encoding Channel Decoding Distance: Long “wires” of various types Equivocation: Boosting of power (introduces noise) Noise: Special encoding schemes Coordination: Coordination messages (protocols) Notice: Nothing about meaning, intention MIS 300 Midterm Summary Receiver
Solutions to the problems Sender Encoding Channel Decoding Distance: Long “wires” of various types Equivocation: Boosting of power (introduces noise) Noise: Special encoding schemes Coordination: Coordination messages (protocols) Notice: Nothing about meaning, intention MIS 300 Midterm Summary Receiver
 Basic Economics • • Sources aren’t “on” all the time Sources make mistakes; repetition is dangerous and costly Channels are usually relatively expensive Sharing channels is a good use of an expensive resource; sharing is costly • All channels are error-prone; the way to compensate is redundancy • The more complex the scheme, the higher the cost and the more likely is failure or error. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Basic Economics • • Sources aren’t “on” all the time Sources make mistakes; repetition is dangerous and costly Channels are usually relatively expensive Sharing channels is a good use of an expensive resource; sharing is costly • All channels are error-prone; the way to compensate is redundancy • The more complex the scheme, the higher the cost and the more likely is failure or error. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
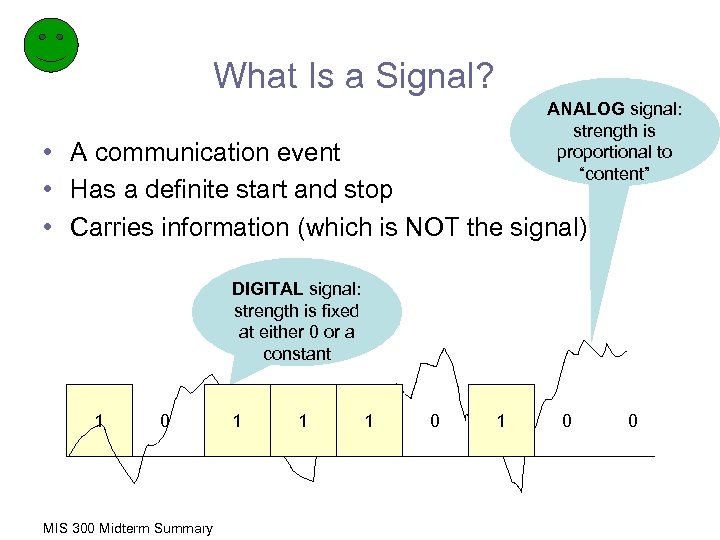 What Is a Signal? ANALOG signal: strength is proportional to “content” • A communication event • Has a definite start and stop • Carries information (which is NOT the signal) DIGITAL signal: strength is fixed at either 0 or a constant 1 0 MIS 300 Midterm Summary 1 1 1 0 0
What Is a Signal? ANALOG signal: strength is proportional to “content” • A communication event • Has a definite start and stop • Carries information (which is NOT the signal) DIGITAL signal: strength is fixed at either 0 or a constant 1 0 MIS 300 Midterm Summary 1 1 1 0 0
 What Is the Advantage of Digital Signalling? • First, simplicity, only two signal levels • Second, resistance to noise • Third, amplification can work without amplifying noise • Fourth, potential to add check bits to reconstruct byte in the event of errors (for example, parity checking). MIS 300 Midterm Summary
What Is the Advantage of Digital Signalling? • First, simplicity, only two signal levels • Second, resistance to noise • Third, amplification can work without amplifying noise • Fourth, potential to add check bits to reconstruct byte in the event of errors (for example, parity checking). MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Carriers and Services • Local exchange carrier (LEC): a public telephone company in the United States that provides service to homes and businesses within its defined geographical area • Competitive local exchange carrier (CLEC): a company that is allowed to compete with the LECs, such as a wireless, satellite, or cable service provider • Long-distance carrier: a traditional long-distance phone provider, such as AT&T, Sprint, or MCI MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Carriers and Services • Local exchange carrier (LEC): a public telephone company in the United States that provides service to homes and businesses within its defined geographical area • Competitive local exchange carrier (CLEC): a company that is allowed to compete with the LECs, such as a wireless, satellite, or cable service provider • Long-distance carrier: a traditional long-distance phone provider, such as AT&T, Sprint, or MCI MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 What Are Networks For? • At an electrical level, networks move electrons along paths between nodes • At a signal level, networks move coded characters along links connecting nodes • At a transportation level, networks move packages or packets of characters between source and destination along paths within the network • At a session level, networks move messages from sender to receiver. • At the application level, networks move information from a server to a client. Businesses can select various ways for this to happen. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
What Are Networks For? • At an electrical level, networks move electrons along paths between nodes • At a signal level, networks move coded characters along links connecting nodes • At a transportation level, networks move packages or packets of characters between source and destination along paths within the network • At a session level, networks move messages from sender to receiver. • At the application level, networks move information from a server to a client. Businesses can select various ways for this to happen. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
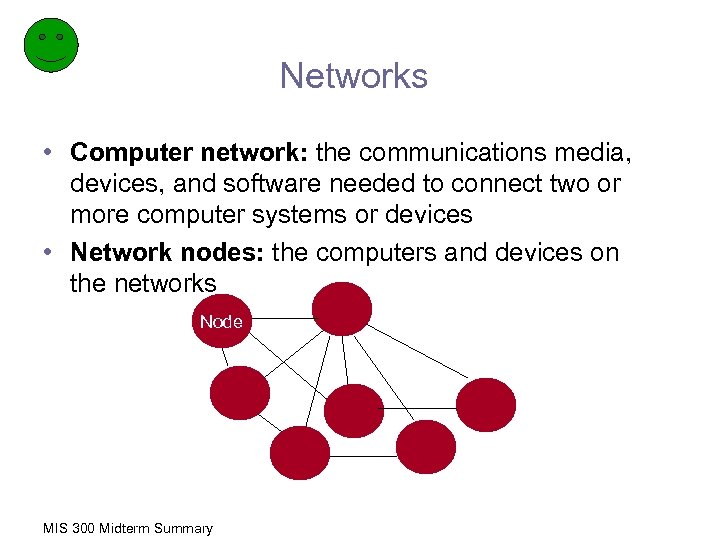 Networks • Computer network: the communications media, devices, and software needed to connect two or more computer systems or devices • Network nodes: the computers and devices on the networks Node MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Networks • Computer network: the communications media, devices, and software needed to connect two or more computer systems or devices • Network nodes: the computers and devices on the networks Node MIS 300 Midterm Summary
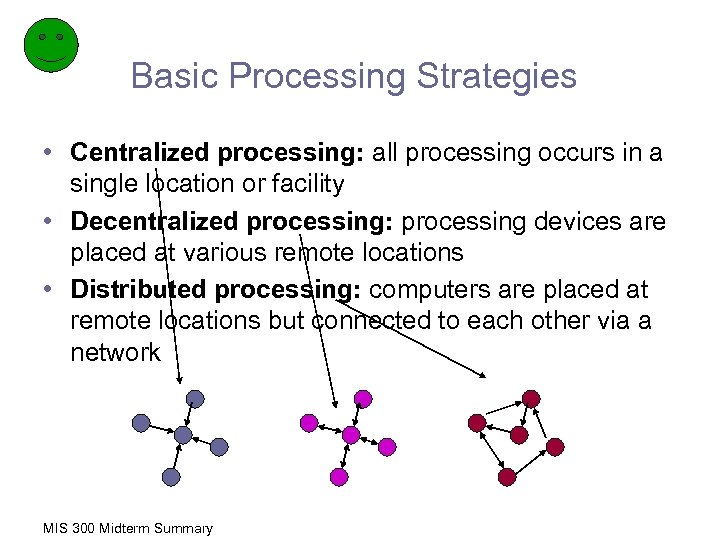 Basic Processing Strategies • Centralized processing: all processing occurs in a single location or facility • Decentralized processing: processing devices are placed at various remote locations • Distributed processing: computers are placed at remote locations but connected to each other via a network MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Basic Processing Strategies • Centralized processing: all processing occurs in a single location or facility • Decentralized processing: processing devices are placed at various remote locations • Distributed processing: computers are placed at remote locations but connected to each other via a network MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Terminal-to-Host, File Server, and Client/Server Systems • Connecting computers in distributed information processing: – Terminal-to-host: the application and database reside on one host computer, and the user interacts with the application and data using a “dumb” terminal – File server: the application and database reside on the one host computer, called the file server – Client/server: multiple computer platforms are dedicated to special functions, such as database management, printing, communications, and program execution MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Terminal-to-Host, File Server, and Client/Server Systems • Connecting computers in distributed information processing: – Terminal-to-host: the application and database reside on one host computer, and the user interacts with the application and data using a “dumb” terminal – File server: the application and database reside on the one host computer, called the file server – Client/server: multiple computer platforms are dedicated to special functions, such as database management, printing, communications, and program execution MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Communications Software and Protocols • Communications software: software that provides a number of important functions in a network, such as error checking and data security • Network operating system (NOS) • Network management software • Communications protocol: a standard set of rules that controls a telecommunications connection MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Communications Software and Protocols • Communications software: software that provides a number of important functions in a network, such as error checking and data security • Network operating system (NOS) • Network management software • Communications protocol: a standard set of rules that controls a telecommunications connection MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Packet Switching • Sender’s message is broken into (generally short, fixed-length) packets • Each packet is numbered and sent “into” the network • The network transmits the packets • The node assembles the packets in order (not an easy task) • The receiver gets the message from the node. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Packet Switching • Sender’s message is broken into (generally short, fixed-length) packets • Each packet is numbered and sent “into” the network • The network transmits the packets • The node assembles the packets in order (not an easy task) • The receiver gets the message from the node. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 How the Internet Works • The Internet transmits data from one computer (called a host) to another • If the receiving computer is on a network to which the first computer is directly connected, it can send the message directly • If the receiving computer is not on a network to which the sending computer is connected, the sending computer relays the message to another computer that can forward it MIS 300 Midterm Summary
How the Internet Works • The Internet transmits data from one computer (called a host) to another • If the receiving computer is on a network to which the first computer is directly connected, it can send the message directly • If the receiving computer is not on a network to which the sending computer is connected, the sending computer relays the message to another computer that can forward it MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 How the Internet Works (continued) • Data is passed in chunks called packets • Internet Protocol (IP): communications standard that enables traffic to be routed from one network to another as needed • Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): widely used transport-layer protocol that is used in combination with IP by most Internet applications • Uniform Resource Locator (URL): an assigned address on the Internet for each computer MIS 300 Midterm Summary
How the Internet Works (continued) • Data is passed in chunks called packets • Internet Protocol (IP): communications standard that enables traffic to be routed from one network to another as needed • Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): widely used transport-layer protocol that is used in combination with IP by most Internet applications • Uniform Resource Locator (URL): an assigned address on the Internet for each computer MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Internet Service Providers • Internet service provider (ISP): any company that provides individuals or organizations with access to the Internet • Most charge a monthly fee • Many ISPs and online services offer broadband Internet access through digital subscriber lines (DSLs), cable, or satellite transmission MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Internet Service Providers • Internet service provider (ISP): any company that provides individuals or organizations with access to the Internet • Most charge a monthly fee • Many ISPs and online services offer broadband Internet access through digital subscriber lines (DSLs), cable, or satellite transmission MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 The World Wide Web • The Web, WWW or W 3 • A menu-based system that uses the client/server model • Organizes Internet resources throughout the world into a series of menu pages, or screens, that appear on your computer • Hypermedia: tools that connect the data on Web pages, allowing users to access topics in whatever order they want MIS 300 Midterm Summary
The World Wide Web • The Web, WWW or W 3 • A menu-based system that uses the client/server model • Organizes Internet resources throughout the world into a series of menu pages, or screens, that appear on your computer • Hypermedia: tools that connect the data on Web pages, allowing users to access topics in whatever order they want MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 The World Wide Web (continued) • Hypertext Markup Language (HTML): the standard page description language for Web pages • HTML tags: codes that let the browser know how to format the text on a Web page and whether images, sound, and other elements should be inserted MIS 300 Midterm Summary
The World Wide Web (continued) • Hypertext Markup Language (HTML): the standard page description language for Web pages • HTML tags: codes that let the browser know how to format the text on a Web page and whether images, sound, and other elements should be inserted MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Web Browsers • Web browser: software that creates a unique, hypermedia-based menu on a computer screen, providing a graphical interface to the Web • The menu consists of graphics, titles, and text with hypertext links • Ubiquitous and non-proprietary web browsers make it possible for the Internet to be a business platform. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Web Browsers • Web browser: software that creates a unique, hypermedia-based menu on a computer screen, providing a graphical interface to the Web • The menu consists of graphics, titles, and text with hypertext links • Ubiquitous and non-proprietary web browsers make it possible for the Internet to be a business platform. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Search Engines • • Search engine: a Web search tool Examples: Yahoo. com, Google. com Most search engines are free Searches can use words, such as AND and OR, to refine the search MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Search Engines • • Search engine: a Web search tool Examples: Yahoo. com, Google. com Most search engines are free Searches can use words, such as AND and OR, to refine the search MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Intranets and Extranets • Intranet – Internal corporate network built using Internet and World Wide Web standards and products – Used by employees to gain access to corporate information – Slashes the need for paper MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Intranets and Extranets • Intranet – Internal corporate network built using Internet and World Wide Web standards and products – Used by employees to gain access to corporate information – Slashes the need for paper MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Intranets and Extranets (continued) • Extranet – A network based on Web technologies that links selected resources of a company’s intranet with its customers, suppliers, or other business partners • Virtual private network (VPN): a secure connection between two points across the Internet • Tunneling: the process by which VPNs transfer information by encapsulating traffic in IP packets over the Internet MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Intranets and Extranets (continued) • Extranet – A network based on Web technologies that links selected resources of a company’s intranet with its customers, suppliers, or other business partners • Virtual private network (VPN): a secure connection between two points across the Internet • Tunneling: the process by which VPNs transfer information by encapsulating traffic in IP packets over the Internet MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Net Issues • Management issues – No centralized governing body controls the Internet • Service and speed issues – Web server computers can be overwhelmed by the amount of “hits” (requests for pages) – More and more Web sites have video, audio clips, or other features that require faster Internet speeds MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Net Issues • Management issues – No centralized governing body controls the Internet • Service and speed issues – Web server computers can be overwhelmed by the amount of “hits” (requests for pages) – More and more Web sites have video, audio clips, or other features that require faster Internet speeds MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Net Issues (continued) • Privacy – Spyware: hidden files and information trackers that install themselves secretly when you visit some Internet sites – Cookie: a text file that an Internet company can place on the hard disk of a computer system • Fraud – Phishing MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Net Issues (continued) • Privacy – Spyware: hidden files and information trackers that install themselves secretly when you visit some Internet sites – Cookie: a text file that an Internet company can place on the hard disk of a computer system • Fraud – Phishing MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Net Issues (continued) • Security with encryption and firewalls – Cryptography: converting a message into a secret code and changing the encoded message back to regular text – Digital signature: encryption technique used to verify the identity of a message sender for processing online financial transactions – Firewall: a device that sits between an internal network and the Internet, limiting access into and out of a network based on access policies MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Net Issues (continued) • Security with encryption and firewalls – Cryptography: converting a message into a secret code and changing the encoded message back to regular text – Digital signature: encryption technique used to verify the identity of a message sender for processing online financial transactions – Firewall: a device that sits between an internal network and the Internet, limiting access into and out of a network based on access policies MIS 300 Midterm Summary
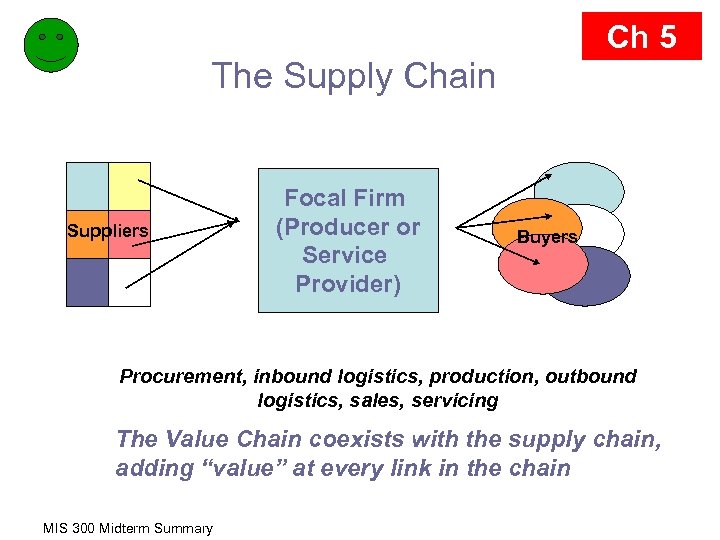 Ch 5 The Supply Chain Suppliers Focal Firm (Producer or Service Provider) Buyers Procurement, inbound logistics, production, outbound logistics, sales, servicing The Value Chain coexists with the supply chain, adding “value” at every link in the chain MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Ch 5 The Supply Chain Suppliers Focal Firm (Producer or Service Provider) Buyers Procurement, inbound logistics, production, outbound logistics, sales, servicing The Value Chain coexists with the supply chain, adding “value” at every link in the chain MIS 300 Midterm Summary
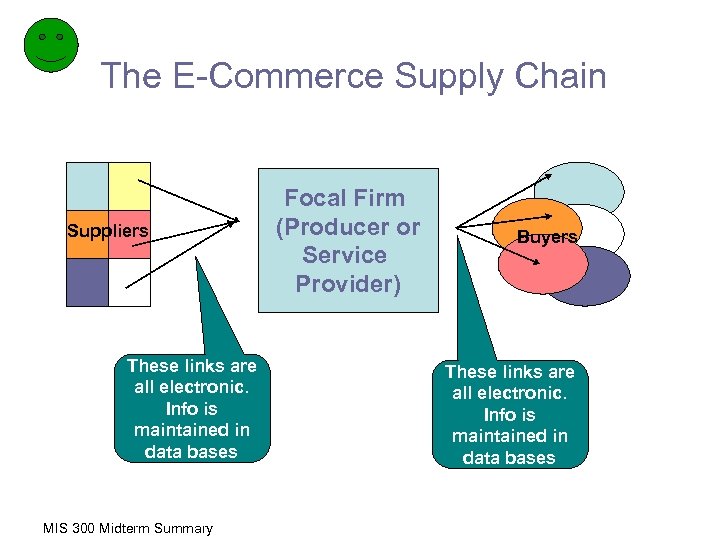 The E-Commerce Supply Chain Suppliers These links are all electronic. Info is maintained in data bases MIS 300 Midterm Summary Focal Firm (Producer or Service Provider) Buyers These links are all electronic. Info is maintained in data bases
The E-Commerce Supply Chain Suppliers These links are all electronic. Info is maintained in data bases MIS 300 Midterm Summary Focal Firm (Producer or Service Provider) Buyers These links are all electronic. Info is maintained in data bases
 E-Commerce Supply Chain Management • Supply chain management is a key value chain composed of: – Demand planning – Supply planning – Demand fulfillment • It’s actually a supply network. • The supply chain is the upstream aspect of the value chain. • The value chain is actually a value network. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
E-Commerce Supply Chain Management • Supply chain management is a key value chain composed of: – Demand planning – Supply planning – Demand fulfillment • It’s actually a supply network. • The supply chain is the upstream aspect of the value chain. • The value chain is actually a value network. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Mobile Commerce • Mobile commerce (m-commerce) relies on the use of wireless devices, such as personal digital assistants, cell phones, and smart phones, to place orders and conduct business • What does it mean to “be mobile”? • Issues confronting m-commerce – User-friendliness of the wireless device – Network speed – Security MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Mobile Commerce • Mobile commerce (m-commerce) relies on the use of wireless devices, such as personal digital assistants, cell phones, and smart phones, to place orders and conduct business • What does it mean to “be mobile”? • Issues confronting m-commerce – User-friendliness of the wireless device – Network speed – Security MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Mobile Commerce (continued) • Handheld devices used for m-commerce have limitations that complicate their use • Wireless application protocol (WAP): a standard set of specifications for Internet applications that run on handheld, wireless devices MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Mobile Commerce (continued) • Handheld devices used for m-commerce have limitations that complicate their use • Wireless application protocol (WAP): a standard set of specifications for Internet applications that run on handheld, wireless devices MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Electronic Payment Systems • Digital certificate: an attachment to an e-mail message or data embedded in a Web page that verifies the identity of a sender or a Web site • Electronic cash: an amount of money that is computerized, stored, and used as cash for e-commerce transactions MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Electronic Payment Systems • Digital certificate: an attachment to an e-mail message or data embedded in a Web page that verifies the identity of a sender or a Web site • Electronic cash: an amount of money that is computerized, stored, and used as cash for e-commerce transactions MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Electronic Payment Systems (continued) • Electronic wallet: a computerized stored value that holds credit card information, electronic cash, owner identification, and address information • Credit card • Charge card • Debit card • Smart card MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Electronic Payment Systems (continued) • Electronic wallet: a computerized stored value that holds credit card information, electronic cash, owner identification, and address information • Credit card • Charge card • Debit card • Smart card MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 An Overview of Transaction Processing Systems • Provide data for other business processes: – Management information system/decision support system (MIS/DSS) – Special-purpose information systems • Process the detailed data necessary to update records about the fundamental business operations • Include order entry, inventory control, payroll, accounts payable, accounts receivable, and the general ledger. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
An Overview of Transaction Processing Systems • Provide data for other business processes: – Management information system/decision support system (MIS/DSS) – Special-purpose information systems • Process the detailed data necessary to update records about the fundamental business operations • Include order entry, inventory control, payroll, accounts payable, accounts receivable, and the general ledger. MIS 300 Midterm Summary
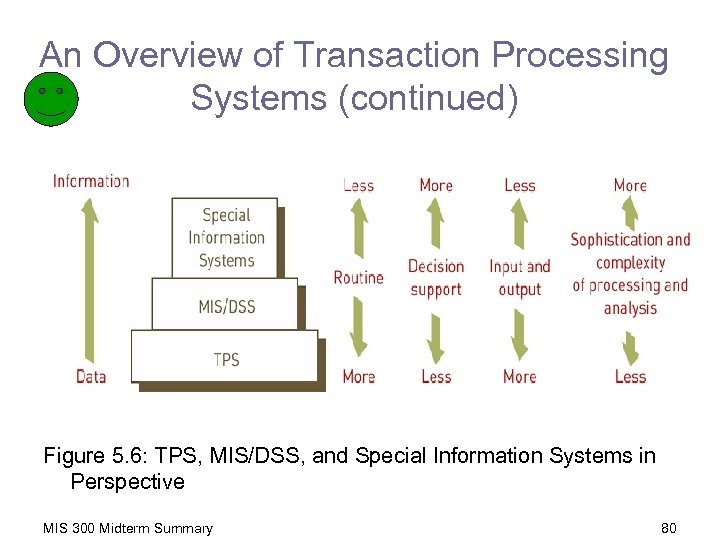 An Overview of Transaction Processing Systems (continued) Figure 5. 6: TPS, MIS/DSS, and Special Information Systems in Perspective MIS 300 Midterm Summary 80
An Overview of Transaction Processing Systems (continued) Figure 5. 6: TPS, MIS/DSS, and Special Information Systems in Perspective MIS 300 Midterm Summary 80
 Traditional Transaction Processing Methods and Objectives • Batch processing system: method of computerized processing in which business transactions are accumulated over a period of time and prepared for processing as a single unit or batch • Online transaction processing (OLTP): computerized processing in which each transaction is processed immediately, without the delay of accumulating transactions into a batch MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Traditional Transaction Processing Methods and Objectives • Batch processing system: method of computerized processing in which business transactions are accumulated over a period of time and prepared for processing as a single unit or batch • Online transaction processing (OLTP): computerized processing in which each transaction is processed immediately, without the delay of accumulating transactions into a batch MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Transaction Processing Activities • TPSs – Capture and process data that describes fundamental business transactions – Update databases – Produce a variety of reports • Transaction processing cycle: the process of data collection, data editing, data correction, data manipulation, data storage, and document production MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Transaction Processing Activities • TPSs – Capture and process data that describes fundamental business transactions – Update databases – Produce a variety of reports • Transaction processing cycle: the process of data collection, data editing, data correction, data manipulation, data storage, and document production MIS 300 Midterm Summary
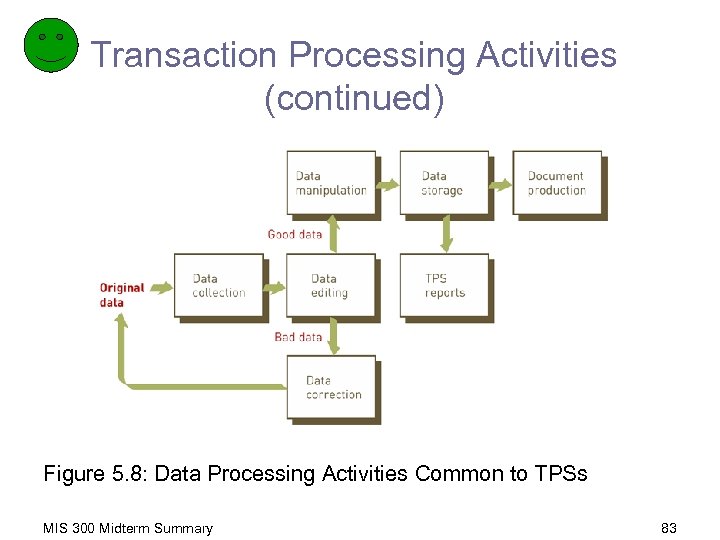 Transaction Processing Activities (continued) Figure 5. 8: Data Processing Activities Common to TPSs MIS 300 Midterm Summary 83
Transaction Processing Activities (continued) Figure 5. 8: Data Processing Activities Common to TPSs MIS 300 Midterm Summary 83
 Transaction Processing Activities (continued) • Data collection – Should be collected at source – Should be recorded accurately, in a timely fashion • Data editing • Data correction MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Transaction Processing Activities (continued) • Data collection – Should be collected at source – Should be recorded accurately, in a timely fashion • Data editing • Data correction MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Transaction Processing Activities (continued) • Data manipulation • Data storage • Document production and reports MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Transaction Processing Activities (continued) • Data manipulation • Data storage • Document production and reports MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 International Issues • Issues that multinational corporations face in planning, building, and operating their TPSs – – Different languages and cultures Disparities in IS infrastructure Varying laws and customs rules Multiple currencies MIS 300 Midterm Summary
International Issues • Issues that multinational corporations face in planning, building, and operating their TPSs – – Different languages and cultures Disparities in IS infrastructure Varying laws and customs rules Multiple currencies MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Enterprise Resource Planning: An Overview of Enterprise Resource Planning • Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems are used in large, midsized, and small companies • Real-time monitoring of business functions • Timely analysis of key issues, such as quality, availability, customer satisfaction, performance, and profitability MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Enterprise Resource Planning: An Overview of Enterprise Resource Planning • Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems are used in large, midsized, and small companies • Real-time monitoring of business functions • Timely analysis of key issues, such as quality, availability, customer satisfaction, performance, and profitability MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Definition • The adoption of an integrated, comprehensive set of applications that communicate easily with one another to handle all of a firm’s business MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Definition • The adoption of an integrated, comprehensive set of applications that communicate easily with one another to handle all of a firm’s business MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Basic Philosophy • Division of labor, basis of bureaucracy isn’t whole story • Business is an integrated, tightly cohesive system • Structure follows form follows function follows information! • Redundancy, duplication are bad • Variety is the enemy MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Basic Philosophy • Division of labor, basis of bureaucracy isn’t whole story • Business is an integrated, tightly cohesive system • Structure follows form follows function follows information! • Redundancy, duplication are bad • Variety is the enemy MIS 300 Midterm Summary
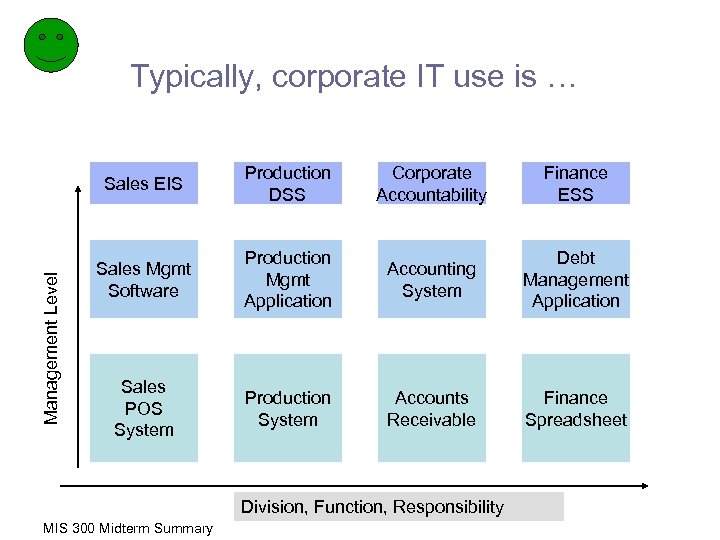 Typically, corporate IT use is … Management Level Sales EIS Production DSS Corporate Accountability Finance ESS Sales Mgmt Software Production Mgmt Application Accounting System Debt Management Application Sales POS System Production System Accounts Receivable Finance Spreadsheet Division, Function, Responsibility MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Typically, corporate IT use is … Management Level Sales EIS Production DSS Corporate Accountability Finance ESS Sales Mgmt Software Production Mgmt Application Accounting System Debt Management Application Sales POS System Production System Accounts Receivable Finance Spreadsheet Division, Function, Responsibility MIS 300 Midterm Summary
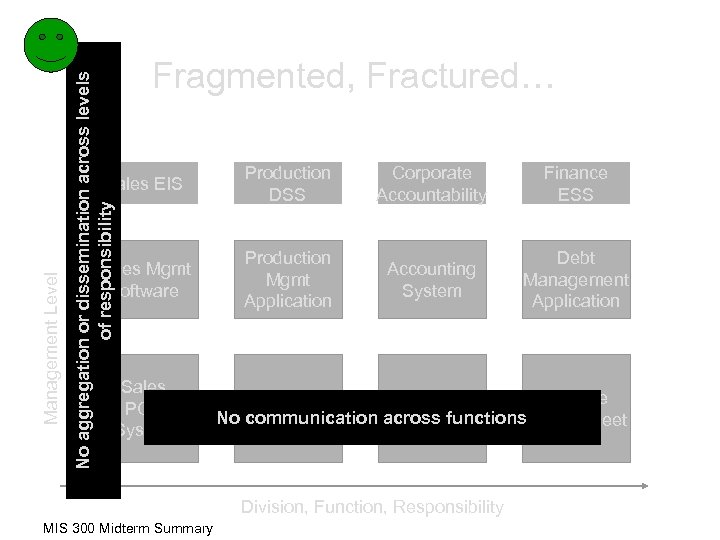 No aggregation or dissemination across levels of responsibility Fragmented, Fractured… Management Level Sales EIS Production DSS Corporate Accountability Finance ESS Sales Mgmt Software Production Mgmt Application Accounting System Debt Management Application Sales POS System Production Accounts Finance No communication across functions. Spreadsheet System Receivable Division, Function, Responsibility MIS 300 Midterm Summary
No aggregation or dissemination across levels of responsibility Fragmented, Fractured… Management Level Sales EIS Production DSS Corporate Accountability Finance ESS Sales Mgmt Software Production Mgmt Application Accounting System Debt Management Application Sales POS System Production Accounts Finance No communication across functions. Spreadsheet System Receivable Division, Function, Responsibility MIS 300 Midterm Summary
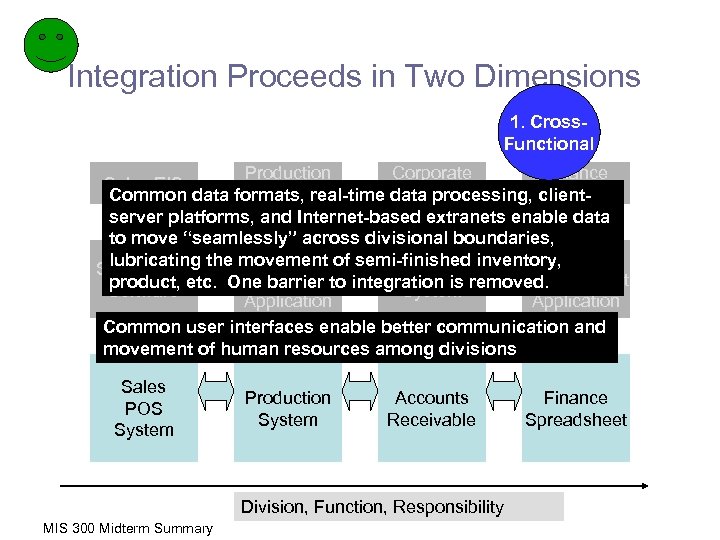 Integration Proceeds in Two Dimensions 1. Cross. Functional Production Corporate Finance Sales EIS DSS Accountability ESS Common data formats, real-time data processing, clientserver platforms, and Internet-based extranets enable data to move “seamlessly” across divisional boundaries, Production Debt lubricating Sales Mgmt the movement of semi-finished inventory, Accounting Mgmt Management product, Software etc. One barrier to integration is removed. System Application Common user interfaces enable better communication and movement of human resources among divisions Sales POS System Production System Accounts Receivable Division, Function, Responsibility MIS 300 Midterm Summary Finance Spreadsheet
Integration Proceeds in Two Dimensions 1. Cross. Functional Production Corporate Finance Sales EIS DSS Accountability ESS Common data formats, real-time data processing, clientserver platforms, and Internet-based extranets enable data to move “seamlessly” across divisional boundaries, Production Debt lubricating Sales Mgmt the movement of semi-finished inventory, Accounting Mgmt Management product, Software etc. One barrier to integration is removed. System Application Common user interfaces enable better communication and movement of human resources among divisions Sales POS System Production System Accounts Receivable Division, Function, Responsibility MIS 300 Midterm Summary Finance Spreadsheet
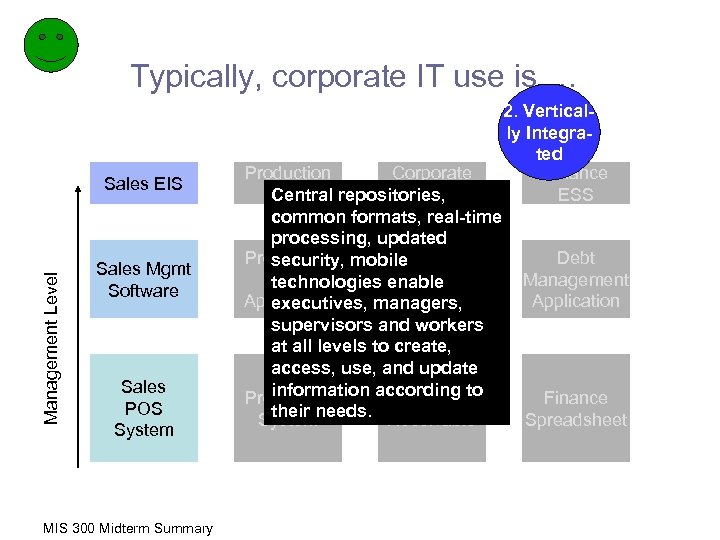 Typically, corporate IT use is … Management Level Sales EIS Sales Mgmt Software Sales POS System MIS 300 Midterm Summary 2. Vertically Integrated Production Corporate Finance DSS Accountability ESS Central repositories, common formats, real-time processing, updated Production mobile Debt security, Accounting Mgmt Management technologies enable System Application executives, managers, supervisors and workers at all levels to create, access, use, and update information according to Production Accounts Finance their Systemneeds. Receivable Spreadsheet
Typically, corporate IT use is … Management Level Sales EIS Sales Mgmt Software Sales POS System MIS 300 Midterm Summary 2. Vertically Integrated Production Corporate Finance DSS Accountability ESS Central repositories, common formats, real-time processing, updated Production mobile Debt security, Accounting Mgmt Management technologies enable System Application executives, managers, supervisors and workers at all levels to create, access, use, and update information according to Production Accounts Finance their Systemneeds. Receivable Spreadsheet
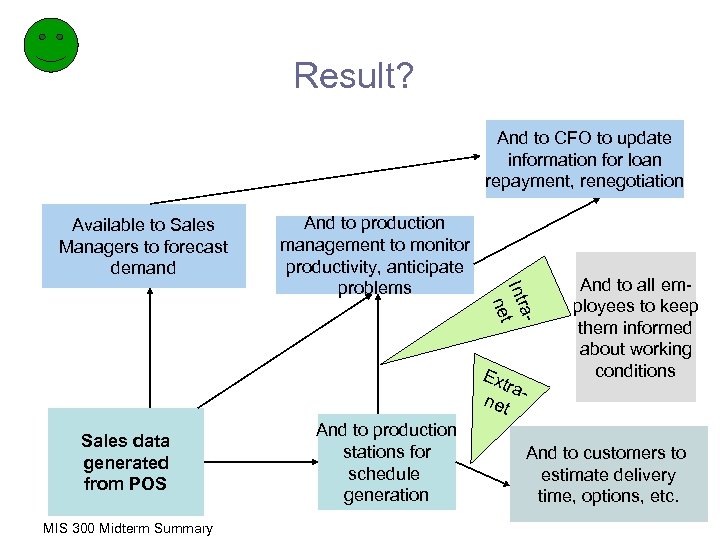 Result? And to CFO to update information for loan repayment, renegotiation Available to Sales Managers to forecast demand a. Intr net And to production management to monitor productivity, anticipate problems Ext ranet Sales data generated from POS MIS 300 Midterm Summary And to production stations for schedule generation And to all employees to keep them informed about working conditions And to customers to estimate delivery time, options, etc.
Result? And to CFO to update information for loan repayment, renegotiation Available to Sales Managers to forecast demand a. Intr net And to production management to monitor productivity, anticipate problems Ext ranet Sales data generated from POS MIS 300 Midterm Summary And to production stations for schedule generation And to all employees to keep them informed about working conditions And to customers to estimate delivery time, options, etc.
 Why Is Enterprise Computing Important? • Integrates the supply chain • Provides for organizational learning • Introduces strong IT efficiencies through common approaches • Solves management problems of burgeoning IT costs (consolidation) • Recognizes IT’s central role in integration, lubrication of business processes MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Why Is Enterprise Computing Important? • Integrates the supply chain • Provides for organizational learning • Introduces strong IT efficiencies through common approaches • Solves management problems of burgeoning IT costs (consolidation) • Recognizes IT’s central role in integration, lubrication of business processes MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 What Makes ERP/EC Difficult? • • Sheer volume of data Divisional lore Actual divisions of labor Human nature (undesirability of change) Poorly thought-through problem statement High initial cost Legacy systems, sunk costs Near-monopoly supplier situation (SAP, Bahn, Peoplesoft, Oracle are really only suppliers) MIS 300 Midterm Summary
What Makes ERP/EC Difficult? • • Sheer volume of data Divisional lore Actual divisions of labor Human nature (undesirability of change) Poorly thought-through problem statement High initial cost Legacy systems, sunk costs Near-monopoly supplier situation (SAP, Bahn, Peoplesoft, Oracle are really only suppliers) MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Advantages and Disadvantages of ERP • Elimination of costly, inflexible legacy systems • Improvement of work processes • Increase in access to data for operational decision making • Upgrade of technology infrastructure • Expense and time in implementation MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Advantages and Disadvantages of ERP • Elimination of costly, inflexible legacy systems • Improvement of work processes • Increase in access to data for operational decision making • Upgrade of technology infrastructure • Expense and time in implementation MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Advantages and Disadvantages of ERP (continued) • • Difficulty implementing change Difficulty integrating with other systems Risks in using one vendor Risk of implementation failure MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Advantages and Disadvantages of ERP (continued) • • Difficulty implementing change Difficulty integrating with other systems Risks in using one vendor Risk of implementation failure MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Plus Material NOT in the Book • *Internet as E-Commerce Platform (. asp) • *The Business Platform Idea (. ppt) What business needs to function • *The Computer Idea (. ppt) Computers as ideal office assistants • *The Database Idea (. ppt) Integrating data • *The Economy of Style Idea (. ppt) Another basis for competition • *Transaction Processing Systems (. ppt) Gold in old transactions MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Plus Material NOT in the Book • *Internet as E-Commerce Platform (. asp) • *The Business Platform Idea (. ppt) What business needs to function • *The Computer Idea (. ppt) Computers as ideal office assistants • *The Database Idea (. ppt) Integrating data • *The Economy of Style Idea (. ppt) Another basis for competition • *Transaction Processing Systems (. ppt) Gold in old transactions MIS 300 Midterm Summary
 Information Laws • Conservation: Information cannot come from nowhere • Utilization: Data cannot go nowhere • Logical Data Flow: Outputs must be completely determined by inputs plus processing • Data Integrity: All changes to data stores must be made by processes inside a system MIS 300 Midterm Summary
Information Laws • Conservation: Information cannot come from nowhere • Utilization: Data cannot go nowhere • Logical Data Flow: Outputs must be completely determined by inputs plus processing • Data Integrity: All changes to data stores must be made by processes inside a system MIS 300 Midterm Summary


