56888f93576e57382a085ce687843548.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 122

Section II and Final Papers 1. Fix problems with Section I and resubmit it with Section II as part of the final paper. 2. Make sure that you put a major emphasis on a business leader as part of Section II. 3. Complete the assignment on an individual basis.

Chapter 8 The Internet and Electronic Commerce

Internet and E-Commerce Two very hot topics. Two things that are having a huge impact on businesses in the US and around the world.

Chapter Objectives 1. Understand the significance of the Internet and its role in changing business strategies, structures and the business environment. 2. Understand the ways that Internet applications provide value to a company and more importantly its customers. 3. Appreciate the fact that business-to-business electronic commerce on the Internet is far more significant than business-to-consumer. 4. Appreciate both the strengths and the weaknesses of the Internet as a business resource.

Internet Perspective Roadmap • Making sense of the Internet as a business resource. • Understanding the value of information browsing and search engines (business and personal use). • Appreciating the difference and relationship between E-Business and E-Commerce. • Understanding the multiple roles of Internet technologies: (1) Traditional Internet use, (2) Internal business use (intranet), and (3)Business-to-business use (extranet or B 2 B).

Internet Perspective Roadmap • Recognizing its impact on major industries. • Appreciating the significance of Internet laws and public policies.

Jack Callon’s List of Important Business Issues How many of these factors are directly related to the Internet? • Direct Business Model • Extended Enterprise • Supply Chain Management • Outsourcing • Reengineering Business Processes • Managing Change

Important Chapter Topics • BUSINESS USE OF THE INTERNET - Businesses are broadening their use of the Internet from simple applications like E-mail and marketing themselves on the World Wide Web. Companies are deploying a range of applications that are intended to give them strategic capabilities. • INTERACTIVE MARKETING - The Internet, along with intranets and extranets, is enabling marketing, development and customer support people within a business to collaborate interactively with customers to provide top quality, personalized service and support.

BUSINESS VALUE OF THE INTERNET - Companies are deriving business value from the Internet. E-COMMERCE - Encompasses the entire online process of developing, marketing, selling, delivering, servicing and paying for products and services. E-COMMERCE APPLICATIONS - The Internet’s economic model encourages innovation and entrepreneurship. ELECTRONIC PAYMENT AND SECURITY - Presents a vital and complex challenge to business and financial institutions to develop efficient, flexible and secure payment systems for electronic funds transfers.

A New Competitive Environment Traditional brick-and-mortar (store front) companies competing with web-based retailers. What will prevail over time? Web-based retailers Brick-and-mortar retailers Brick-and-click retailers (combination of both)

Internet Search Engines and Browsers Do you understand the differences? Do you make the best use of browsers to help find the information that you need? Have you ever done an objective comparison of multiple browsers using the same compound search?

Amazon. com Is it realistic to conclude that Amazon. com is the standard by which other. com retailers are measured? If so, why? If not, then who is?

Possible Exam Questions 1. What ways can companies use the Internet as more than a communications network? 2. How can the Internet improve customer value?

The Internet What is it? What do you do with it? How do you join the Internet club? Who owns, runs and controls it? How big is it? How did it become what it is? What will it be like in the future?

Yahoo Softbank Priceline. com Morgan Stanley e. Bay Amazon. com 9/27/99

9/27/99

Dell Computer Michael Jordan Proxicom Micro. Strategy Amazon. com Gateway Broadcast. com No Limit Yahoo! Trilogy Software 9/27/99

Speed Knowledge Culture Technology Great People 9/13/99

Creative Destruction dyb. com 9/24/99

Business Health Sex Family Politics 9/20/ 99

The Dawn of E-Life Once a novelty, the Internet is now transforming how Americans live, think, talk and love; how we go to school, make money, see the doctor and elect presidents. It is crucial to assess this, because the digital revolution is more profound than a mere change of tools.

Internet Truths 1. The acceptance of the Internet as a new technology based on reaching fifty million users happened faster than any other technology in the history of the world. 2. The Internet as a business resource is having a dramatic impact on organizations through its use as an intranet and extranet. 3. Within the US, the Internet has already fundamentally changed some industries 4. The Internet has greatly influenced venture capital funding evaluations. 5. The Internet redefines itself every two years.

Ways to Win on the Web • Selling to Businesses - Dell Computer • Selling to Businesses - Cisco Systems • A Corporate Intranet - Sun Microsystems • Streamlining the Supply Chain - Pitney Bowes • Recruiting Online - Lots of Companies • Winning and Keeping Web Surfers - Yahoo • Selling to Consumers - Amazon. com • Customer Service - Federal Express • Online Auction - e. Bay

How significant is all of this? • To you personally? • To you in terms of career opportunities? • To businesses and public sector institutions? • To the US and its role as a global citizen?

The Internet Is: Multidemensional -- It can be used one-to-one, one-to-many or many to many (community emphasis, bulletin boards). Multipurpose -- Can serve an organization in many different ways. There is no cookie cutter approach relative to the Internet. Multidisciplinary -- Talent, resources, control and responsibility within an organization.

The Internet Obliterates Traditional Barriers Geographic barriers: Online businesses can reach every corner of the globe without building physical facilities. Time barriers: People can research and buy 24 hours a day. Information barriers: Comparison shopping is a breeze, even for things that are tough to compare in the real world. Switching barriers: No longer are customers locked in by the time and hassle of finding another supplier, the competition is just a click away.

The Internet Has Created New Models: • Business Strategies and Organization • Consumer Shopping and Purchasing • Advertising • Government Policies and Legislation • Educating K-12 and University Students • Entertaining Children and Adults • Investing and/or Gambling • Information Sources • Communication

Jack Callon’s List of Important Business Issues • Direct Business Model • Extended Enterprise • Supply Chain Management • Outsourcing • Reengineering Business Processes • Managing Change
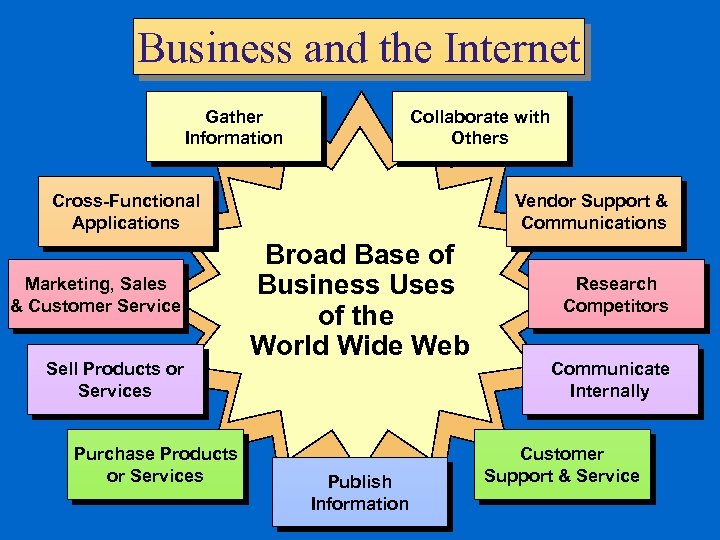
Business and the Internet Gather Information Collaborate with Others Cross-Functional Applications Marketing, Sales & Customer Service Sell Products or Services Purchase Products or Services Vendor Support & Communications Broad Base of Business Uses of the World Wide Web Publish Information Research Competitors Communicate Internally Customer Support & Service

Intel Internet Definition The Internet is a global web of networks and servers. It connects people to people, businesses to people and businesses to businesses.

A Composite Internet Profile • A network of networks. • Uses standards out of necessity. • A surprising architecture for its time. • It is relatively easy to link to it. • It is a classic example of decentralization and independence since no one really owns or controls it. • Growth was initially driven by email. • Has become commercialized.
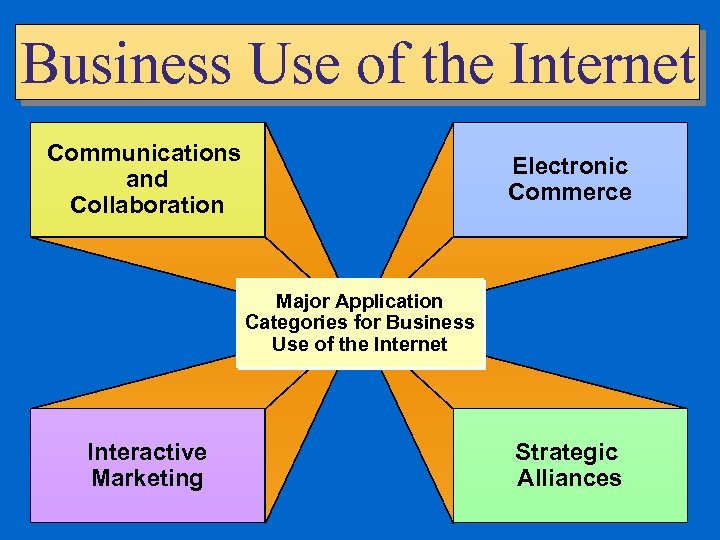
Business Use of the Internet Communications and Collaboration Electronic Commerce Major Application Categories for Business Use of the Internet Interactive Marketing Strategic Alliances
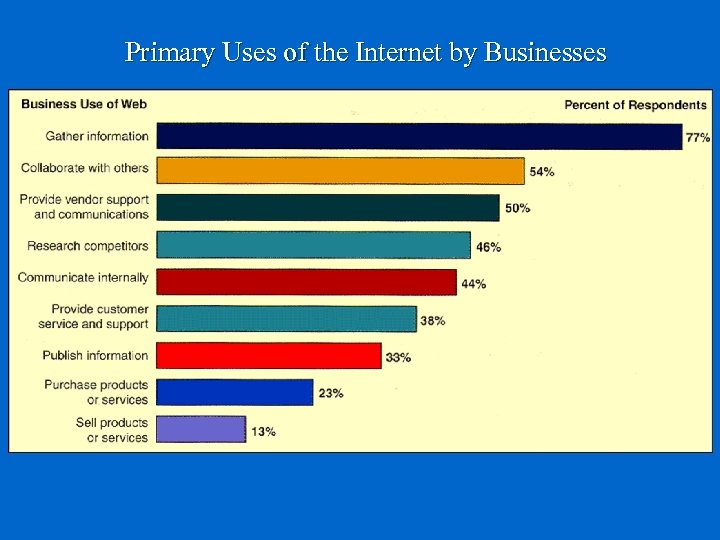
Primary Uses of the Internet by Businesses

E-Business and E-Commerce

Objective To effectively define E-Commerce and E-Business, to understand the differences and appreciate how one relates to and enhances the possibility of success of the other.

What is E-Commerce? Formal definition: The buying and selling, marketing and servicing, and delivery and payment of products, services, and information over the Internet, intranets, extranets, and other networks, between an inter-networked enterprise and its prospects, customers, suppliers, and other business partners. What it really means: It is the way companies do business with customers and other businesses by using computer-based (web-based in most cases) systems.

What is E-Business? E-Business enables businesses and organizations to realize the potential of E-Commerce through the creation of business processes and strategies geared to this objective. In other words… it helps position organizations with better business processes and strategies to successfully realize E-Commerce potential through web-based systems.

E-Commerce Elements I II III Success with I and II can depend greatly on effectively doing III.

E-Commerce Characteristics • Barriers to entry are low. • Everyone utilizes the same technology. • Marketing niches abound. • Access is becoming universal. • Revenue sources are many. • No dominance in the market. • There is room for teams of successful players.

Business to Consumer Commerce This segment is the retail businesses on the Internet. The major factors that optimizes a successful retailing website: – Performance and service – Personalization – Socialization – Visual presentation of website – Incentives – Security and reliability

Business to Business Commerce Enables businesses to seek, find, buy and pay for raw materials, products and services from vendors by using -Commerce. E Example: Electronic data interchange (EDI) Many companies rely on this form of transaction from other businesses to effectively manipulate and process each data into information that is relevant to their business needs.

Supply Chain Management • • Supplier management Inventory management Distribution management Channel management Payment management Financial management Sales force management The goal is to systematize and integrate as many of these processes as possible as webbased applications.

Internal Business Processes By using intranets, companies regulate and monitor online information about customers, clients, suppliers, and competitors from websites and discussion groups This information is vital to a company since it helps it shape and improve products and services with customer input.
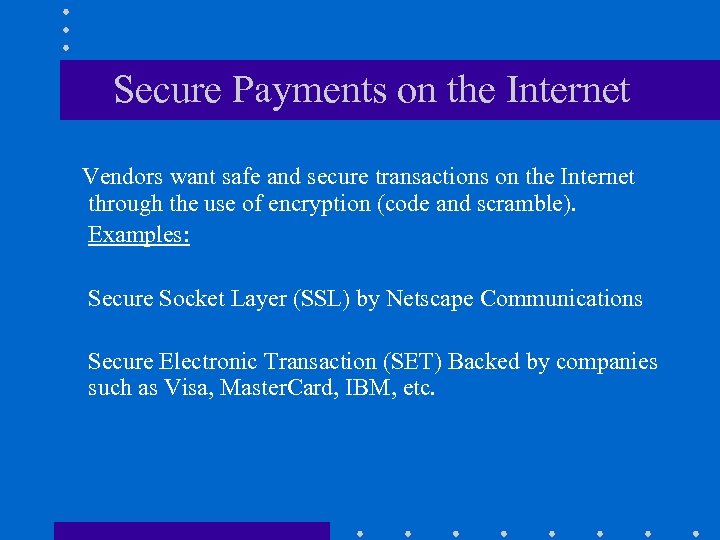
Secure Payments on the Internet Vendors want safe and secure transactions on the Internet through the use of encryption (code and scramble). Examples: Secure Socket Layer (SSL) by Netscape Communications Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) Backed by companies such as Visa, Master. Card, IBM, etc.

Conclusion Many businesses and vendors find E-Business and E-Commerce the best choice to help make their strategic business models competitive and effective. The Internet’s Web browser and networks of hypermedia databases on the World Wide Web is the backbone of electronic commerce that keeps businesses and customers internetworked.

Two Possible Exam Questions 1. Describe a company’s business model approach with E-Commerce using the Internet, intranet, and extranet terms. 2. Describe how E-Business and E-Commerce relate to each other and the important elements of each approach.

Internet Fraud Credit card fraud on the Internet is 12 times higher than at conventional stores. This translates into higher merchant fees to credit card companies and costs to resolve disputes. These are high enough to hurt the profitability of an E-Business.

Transition to E-Commerce • E-Commerce has huge potential but probably needs the foundation of an E-Business approach to be truly successful. • Business-to-business E-Commerce continues to be the largest segment of this approach and this is expected to continue.

For Instance • It was much easier for Dell Computer to use a web-based direct marketing approach since it had emphasized such an approach with an earlier Electronic Data Interchange system. • Dell’s advantage was that it had a significant amount of experience with a similar approach. It internal processes, employee knowledge and experience and even its corporate culture was geared to a direct marketing business model. • A similar case can be made for Charles Schwab.

Making Money Via the Internet 1. Sales Transactions 2. Advertising Revenue 3. Subscription Fees 4. Sales Transaction Partnership “Linkage Finder Fees. ”

Brick-and-Mortar Versus E-Commerce

What is the point? What happened to the days when people were predicting the demise of large brick-and-mortar retailers? Is the bloom really off the bush relative to Internet-only based retailers? What happened to their low cost advantage? Is the best strategy of brick-and-mortar retailers based on an established reputation and a combination of both webbased and brick-and-mortar outlets?

Brick-and-Mortar Retailers Traditional store front retailers that come in all shapes and sizes under the umbrella of general merchandising: • Large chain discounters like Wal-Mart, Target and Kmart. • Established good reputation department stores like Nordstroms. • Thousands of mom-and-pop single location retailers that tend to be specialty stores.

Internet Only Retailers Many of the top web sites still only run webbased operations.

Top Web Retailers - Sept. 2000 1. Amazon. com 2. Ticketmaster. com 3. Buy. com 4. * JCPenney 5. Drugstore. com 6. * Barnes&Noble 7. CDNow 8. Pets. com 9. * Sears 10. Planet. R. com 11. e. Toys 12. half. com 13. Egghead. com 14. Real. com 15. Gateway 16. Landsend 17. i. Print. com 18. Outpost. com 19. More. com 20. * Spiegel. com * Both brick and mortar and Web sites

Christmas 2000 Outlook Number of people projected to be shopping online from home during the holiday season - 55 million. US population that this represents - 20% Number that shopped online from home in 1999 - 14 million Number of people with web access in Aug. 2000 - 146 million Increase in people with web access - 35% Average time spent online in Aug. 2000 - 31 minutes +15% Toys are hot with projected growth of 270% based on a projection of 10 million shoppers. Source: Nielsen/Net Ratings

But These numbers don’t say whose web site will gain the most shoppers. For instance, who are the world’s largest toy sellers? 1. Toys R Us 2. Wal-Mart 3. Kmart

Internet Retailer Demographics Cities with most on-line users with incomes over $75, 000 San Francisco - 42. 8%, New York - 39. 2% Cities with most on-line users with incomes less than $25, 000 - Pittsburgh - 10. 3%, Portland - 8. 5% City with most surfers with advanced degrees - Raleigh, N. C. 19. 6% City with most surfers ages 18 -24 - Raleigh, N. C. 17. 6%, Pittsburgh - 17% Cities with most surfers older than 55 - New York - 17. 7%, Portland - 15. 8% Does knowing this really matter?

Don’t Forget Many web sites spend money on radio, TV, bill boards and printed media to advertise their business.

Is Brand Identity a Key Factor? Amazon. com certainly pursued this as a high priority strategy. “It would be a mistake to make a profit instead of spending all the money we can to establish a brand identity. ” A path to profitability that emphasizes planning and patience versus an ROI for now mentality. Profit seems to have become a recent, important consideration.

Considerations Amazon. com is not going to put Barnes and Noble out of business. Both of them can and have had a very negative impact on the small mom-and-pop retail book store.

A Small Brick-and-Mortar Retailer Vern Mastel Sales Manager Team Electronics Bismark, North Dakota

A Small Brick-and-Mortar Retailer Has five employees and nearly 30 years in electronics retailing. Used to fight the mail-order catalogs. Now fights both the mail-order and Internet retailers. “There isn’t a product that I sell that can’t be found cheaper and in greater quantity in a mass merchant, mail-order or Internet retailer. ” In today’s market, inventory control is the difference between survival and going out of business.

A Small Brick-and-Mortar Retailer “I do not dare stock in depth or in quantity because of the extremely short life span of products. Many models have a life span of 3 to 6 months. ” Customer loyalty is at rock bottom. With so many places to buy the same products, the only criteria that really matters is price. We used to average five shoppers to one buyer. Now the average is about 25 shoppers to one buyer. Small brick-and-mortar stores have the worse to fear. Many of us will not be in business in five years.
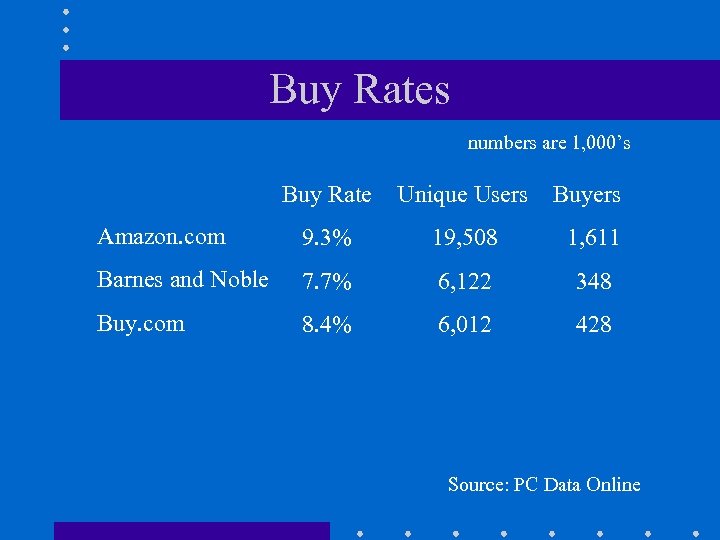
Buy Rates numbers are 1, 000’s Buy Rate Unique Users Buyers Amazon. com 9. 3% 19, 508 1, 611 Barnes and Noble 7. 7% 6, 122 348 Buy. com 8. 4% 6, 012 428 Source: PC Data Online

Large Brick-and-Mortar Companies Advantages: 1. Reputation and customer confidence. 2. Financial staying power. 3. Volume buying power results in lower prices. 4. Can combine the strengths of brick-and-mortar and web-based retailing which many have not done very well in the past. Challenges: 1. A fundamental change in business model. 2. A question of priorities: B&M versus web.

Conclusions 1. The Internet retailer fall-out has happened and seems to be continuing. 2. Small specialty retailers face major challenges to even survive. 3. The experts are predicting that “the big guys with both store fronts and good web operations (bricksand-clicks) will win in the long run. ” 4. Number of e-marketplace companies expected to survive by 2002: 5, 000. Source: Jupiter, AMR Research

Possible Exam Questions 1. Why would a brick-and-mortar retailer have an advantage over an exclusively web-based company? 2. How could the reverse also be the case?

Internet Strategies • Marrying the new with the old. • Selling the business case for financing. • Selling the business model to customers. • Managing the process and measuring the results.

Internet Principles The Internet is not a strategy: It serves the business strategy. Internet initiatives require commitment and leadership. The Internet requires the re-examination of intermediate relationships. Internet technology advances are not enough: It is business model advances that count. Partnering is the key to success in the Internet’s multifunctional environment.

Some Good Questions How can the Internet help reach our business objectives in a way that is better, delivers more revenue and/or reduces costs? In what way does the Internet enhance what I am already doing? Is anyone doing this with any success? What commitment are we willing to make to enhance our chances of success? Do we have the right resources in house?
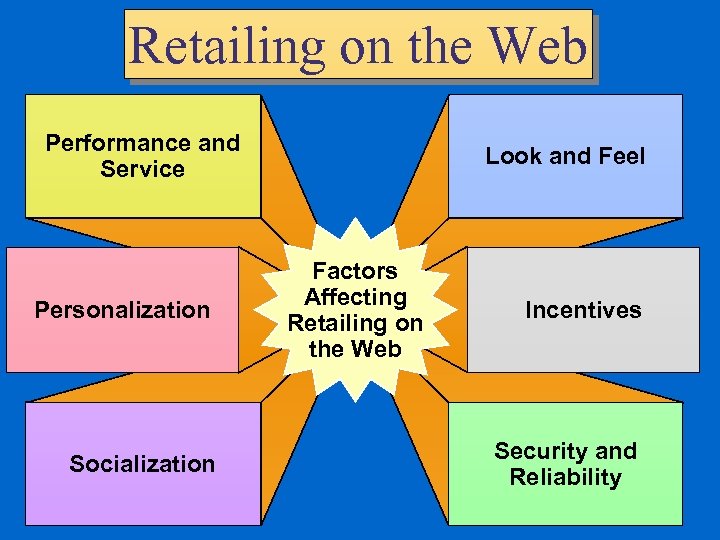
Retailing on the Web Performance and Service Personalization Socialization Look and Feel Factors Affecting Retailing on the Web Incentives Security and Reliability

Amazon. com

Topics Covered • • What is Amazon. com? What they offer. . . Where they started… Where they are today… Amazon. com progress Foreign Markets Summary Possible exam questions

What is Amazon. com? Amazon. com is one of the biggest and best virtual book stores on the web. The site is designed to speed you through the purchase of browsing and ordering books, while giving you reassuring, personal services at discount prices.

What they offer. . . • A quick and accurate search engine to find the books you are looking for • A quick and easy ordering process • Quick order confirmations • Accurate and friendly email notifications • Prompt delivery • Carefully wrapped orders accompanied by handwritten notes • Book reviews by other customers • A complete money-back guarantee

Where they started…… • Amazon. com opened its virtual doors in Seattle in July 1995 with a mission to use the Internet to transform book buying into the fastest, easiest, and most enjoyable shopping experience possible. • While its customer base and product offerings have grown considerably since its early days, they still maintain a founding commitment to customer satisfaction and the delivery of an educational and inspiring shopping experience.

Would the Amazon. com Business Model Work? The issue was not whether the technology would work, but whether customers would want to shop for books online.

Where they are today… Today, Amazon. com is the place to find and discover anything you want to buy online. Twenty million people in more than 160 countries have made them the leading online shopping site. They have Earth's Biggest Selection of products, including free electronic greeting cards, online auctions, millions of books, CDs, videos, DVDs, toys, games, and electronics.

What they offer…. • • Convenience A huge selection Quickness and accuracy Prompt delivery Personal notification system Gift-wrapped books with a personalized note Discounted prices Confirmation process

Foreign Markets • Amazon. com operates two international Web sites: www. amazon. co. uk for the UK, and www. amazon. de for Germany. • Aug. 29, 2000 --Leading online retailer Amazon. com announced it will launch Amazon. fr, a French-language site offering books, music CDs, DVDs and videos dedicated to customers in France and to French-speaking customers around the world. • November 1, 2000—Leading online retailer Amazon. com launched Amazon. co. jp, a Japanese-language site, to serve Japan and Japanese-language speakers around the world. Amazon. co. jp enters Japan’s market with a comprehensive books catalog, offering more than 1. 7 million Japanese and English-language titles and extensive editorial content.

Summary • Amazon. com’s combination of efficiency, discount prices, and great customer service is why it is frequently mentioned as a model of customer service for businesses on the Web. • Amazon. com is the place to find and discover anything you want to buy online. • Amazon. com’s progress is strong and growing as it expands into more foreign markets.

Possible Exam Questions 1. What qualities do Amazon. com have that signify why they are such a dominant web-based company? 2. How does globalization play a part of Amazon. com’s marketing strategies?
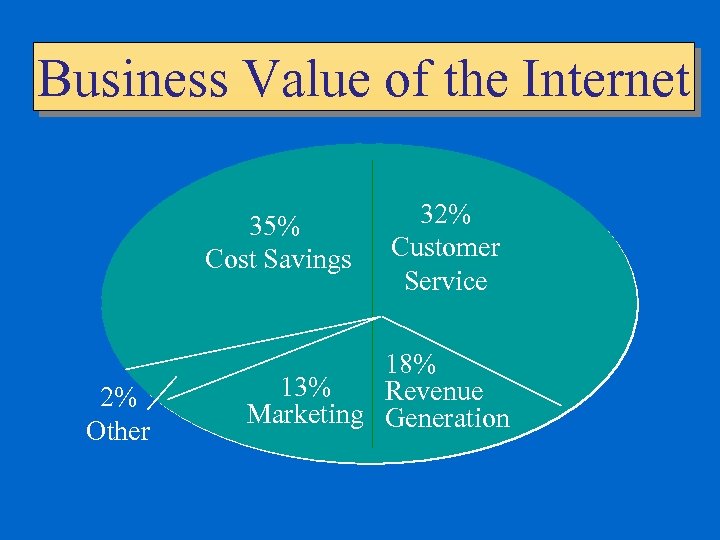
Business Value of the Internet 35% Cost Savings 2% Other 32% Customer Service 18% 13% Revenue Marketing Generation

Customer Value & the Internet

Customer Value The driving force behind world economic growth has evolved from volume manufacturing following World War II to quality manufacturing during the 1980 s and 1990 s to improving customer value. As a result, the key success factor for many firms is maximizing customer value.

Customer Value • The concept is based on the principle that customers make buying decisions based on relative value perceptions in the marketplace. • The challenge is to measure the customers' needs and wants and find ways to serve those expectations better than the competition.

Customer Value Fast, responsive service with quality products has replaced price as the determinants of a customer’s perception of value. Results include increased market share, competitive advantage, and significantly improved return on assets.

What Customers Want A Company that: • Consistently offers the best value. • Keeps track of the customer’s preferences and needs. • Keeps up with market trends. • Makes information available any where, any time. • Is both responsive yet flexible.

How the Internet Increases Customer Value • Responds to Customer Concerns • Helps gain customer loyalty • Improves Customer Service • Anticipates future needs of the customers All of these factors are directly or indirectly related to the communication dimension of the Internet.


The World Wide Web • A global network of multimedia Internet information sources, which are stored on hyperlinked pages and accessed through Web Browsers. • Long term prospects: is to form a base information infrastructure on a national level in order to increase the efficiency and competitiveness of businesses. • Increases business value through: improving communications, implementing electronic commerce and collaboration, and improving the gathering of information.

The World Wide Web • WWW, also known as THE WEB, is the leading information retrieval service of the Internet (the worldwide computer network). The Web gives users access to a vast array of documents that are connected to each other by means of hypertext or hypermedia links--i. e. , hyperlinks. • The Web operates within the Internet's basic client-server format; servers are computer programs that store and transmit documents to other computers on the network when requested, while clients are programs that request documents from a server as the user asks for them. Web Browsers allows users to view the retrieved documents.

History of the WWW • The development of the World Wide Web was begun in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee and his colleagues at CERN, an international scientific organization based in Geneva, Switzerland. They created a protocol called Hyper. Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which standardized communication between servers and clients. This communication is done through web browser.

Web Browsers e. g. Netscape Navigator, Microsoft Internet Explorer • Provide the user interface for accessing Web sites on the Internet, intranet, and extranet sites. • Trend is for browsers to become universal clients, expanding beyond being mere vehicles of Web surfing. • Perform multiple functions: sending and receiving e-mail, downloading files, accessing Java applets, participating in discussion groups, developing web pages. • The model for how networked computers will be used in the future as a vital component of the new communication and collaboration software suites.

Web Browsers • Provide the user interface for accessing Web sites on the Internet, intranet, and extranet sites. • Works by using a protocol called Hyper. Text Transport Protocol (HTTP) to request a specially encoded text document from a web server. • Its usage expands from web browsing to email, downloading files, participating in discussion groups, developing web pages, etc.

Search Engine Definition • The software used on a server or a collection of servers dedicated to indexing Internet web pages, storing the results and returning lists of pages which match particular queries. • Search engine is often used synonymously with spider and index, although these are separate components that work with the engine.

Search Engine • Assist end users finding almost all types of information they need on the Internet. • Examples of search engine: Yahoo, Excite, MSN Search, Lycos, Google, Ask. Jeeves, etc. • Each search engine has its own method of searching.

Search Engine Components 1) The spider, also called the crawler. The spider visits a web page, reads it, and then follows links to other pages within the site. The spider returns to the site on a regular basis, such as every month or two, to look for changes. 2) The index. Everything the spider finds goes into this second part of a search engine. The index, sometimes called the catalog, is like a giant book containing a copy of every web page that the spider finds. 3) Search engine software. This is the program that sifts through the millions of pages recorded in the index to find matches to a search and rank them in order of what it believes is most relevant.

Spider Technology • Spider software perpetually crawls from site to site, taking a complete measure of the Web. Once it finds a new site or one that has changed, it sends material back to the search engine. While some spiders grab every site they find, others prioritize their efforts by determining a site’s popularity or how frequently it has changed. The assumption is that popular and frequently changed sites are more likely to be the most useful.

Search Engines • To get gold, you must sift through mounds of raw ore. To find valuable nuggets of information on the Internet, you have to sift through an almost unfathomable number of Web pages--which explains the popularity of Web search engines. • These search sites are information refineries, helping us quickly distill useful material from the mountains of data that comprises the Internet.

Top Search Engines • Google: Google is a search engine that makes heavy use of link popularity as a primary way to rank web sites. • Yahoo: The secret to Yahoo's success is human beings. It is the largest human-compiled guide to the web, employing about 150 editors in an effort to categorize the web. Yahoo has over 1 million sites listed. • MSN Search: Microsoft's MSN Search service is a Look. Smart-powered directory of web sites, with secondary results that come from Inktomi. MSN Search also offers a unique way for Internet Explorer 5 users to save past searches

Summary • The World Wide Web is expanding in character and scope as the vehicles by which users access it, search engines and web browsers, increase their multimedia sophistication, and information resources and applications. • Browser’s capability has expanded to email, web page development, discussion groups, video/audio, etc. • There are many search engines to choose from: Lycos, Excite, Alta. Vista, Netscape Search, with Google, Yahoo, and MSN Search being the top search engines. Each of these search engines has their own method of searching web pages.

Possible Exam Questions 1. Explain the roles of the World Wide Web, browsers and search engines. 1. Why do different search engines produce very different results?

Search Engines Which one do YOU use? Why? Does a single search engine address all of your needs?

Search Engines Any idiot can write a search engine, the World Wide Web was a real challenge. Tim Berners-Lee 1, 550 search engines!

Search Engines Search engines are intensely competitive products, trying to win loyalty both with fast-and-furious marketing campaigns and by constantly improving their technology. The hot search engine of last year is not necessarily this year’s best.

A Logical Approach Experiment with different search engines. Even though they are all similar, they can have important differences. A search engine that is quick, but returns 40, 000 pages may not be as effective as one that may be slower but returns only 30 pages. Find the search engine that is best suited for your needs.

Search Engine Assignment Conduct a compound search using a subject that is of use to you in this or another class. Use four different search engines and evaluate the results according to the following four criteria: 1. Ease of use. 2. Accuracy 3. Advanced Search Capabilities 4. Extra Features/Functions

URL "URL" stands for Uniform Resource Locator. A URL is a Web page's address on the Internet. It is how you find a desired Web page.

URL HTTP//: Here comes an Internet compliant message. WWW It is intended for use with the World Wide Web. . SOE. UCSC It is to go to Web page of the School of Engineering at UCSC. EDU UCSC has an Education domain name. /FAQ page. A specific page within the SOE Web JP Country designation.

Domain Names • . com - commercial • . edu - educational institution • . gov - governmental body • . org - nonprofit organization • . mil - military • . net - network

Country Designation The scheme in countries other than the U. S. is a two-character name that identifies the country. A few sites in the U. S. follow this method, and sometimes add an additional two characters for the state, i. e. , "somebody. us. ca" Country Examples: au: Australia at: Austria be: Belgium br: Brazil ca: Canada cn: China co: Columbia jp: Japan
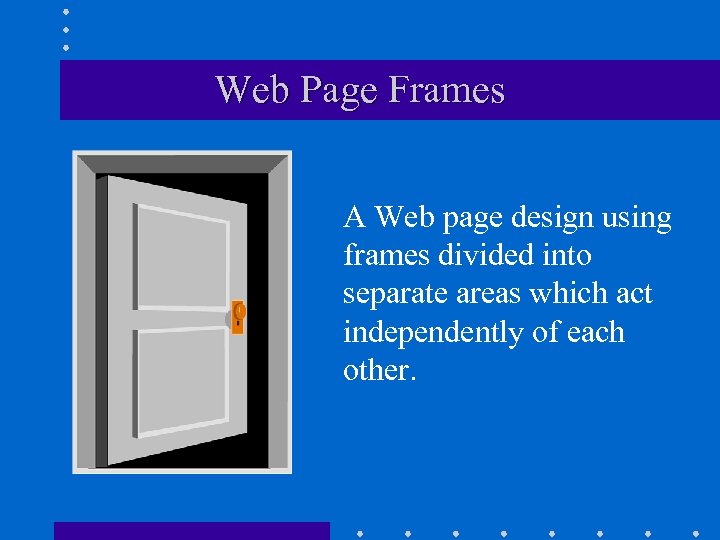
Web Page Frames A Web page design using frames divided into separate areas which act independently of each other.

Web Page Plug-In A "plug-in" is a program, usually shareware, that adds function to your Web browser, such as a sound player, video player or compression utility. A plug-in is set up within the browser so that its functions occur right in the browser. This is preferable to a helper application, which provides similar functions, but is launched separately from the browser when needed.

Search Engine Techniques Be as specific as you can be. Use + and - symbols to better define what you really want. +clinton +starr -lewinsky Use quotations for a phrase versus a word search. “Sam Walton” “Whirlpool Corporation” You can combine the two search techniques. “Robert E. Lee” +”Ulysses S. Grant” +surrender +”Appomattox Court House” Most search engines support these techniques.

Search Engine Info Sources Search Engine Watch Web Page: http: //www. searchenginewatch. com

Internet Service Providers 7, 800 ISPs and growing!

How Much Info is There? There were 800 million indexable pages and 180 million images on the web, as of February 1999. "Indexable" means pages that weren't hidden behind password protection, excluded from indexing by robots. txt files, locked away in databases or basically inaccessible to search engines for other reasons. An earlier study found that there were 320 million pages as of December 1997, so it sounds as if the web has more than doubled in size in just over a year. However, the two studies cannot be compared fairly because they used completely different methods of estimating the size of the web.

Industry Impact of the Internet Impact varies by industry. In some cases the impact has been dramatic: • Automotive • Financial Services • Travel • Newspapers and Books • Advertising • Education

So at this point we conclude that: • The Internet is having a dramatic impact on how we work, live and play. • It is growing like a weed. • People talk about it, use it and invest in it. • The key role that it plays is one of connecting people and businesses to communicate, interact and in some cases to buy and sell things. • It accomplishes all of these things as a “network of networks. ”

Key Terms in Chapter 8 Business Uses of the Internet Business Value of the Internet Customer Value of the Internet Electronic Commerce Business-to-Business-to-Consumer Economic Model Technology Architecture Electronic Data Interchange Electronic Funds Transfer Electronic Payment Systems Interactive Marketing Pull Marketing Push Marketing Retailing on the Web Security of Electronic Commerce Supply Chain Management Virtual Communities Virtual Companies Virtual Shopping Malls Virtual Storefronts Virtual Teams Wholesaling on the Web
56888f93576e57382a085ce687843548.ppt