f7320b99533d3638feff286234d20f12.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Section 4 : Storage Security and Management Lecture 31 Storage Security and Management: Security Framework
Section 4 : Storage Security and Management Lecture 31 Storage Security and Management: Security Framework
 Chapter Objective Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to: Define storage security Discuss storage security framework Describe storage security domains ◦ Application, Management, Backup Recovery and Archive (BURA)
Chapter Objective Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to: Define storage security Discuss storage security framework Describe storage security domains ◦ Application, Management, Backup Recovery and Archive (BURA)
 Lesson: Building Storage Security Framework Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to: Define storage security Discuss the elements to build storage security framework ◦ Security services Define Risk triad
Lesson: Building Storage Security Framework Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to: Define storage security Discuss the elements to build storage security framework ◦ Security services Define Risk triad
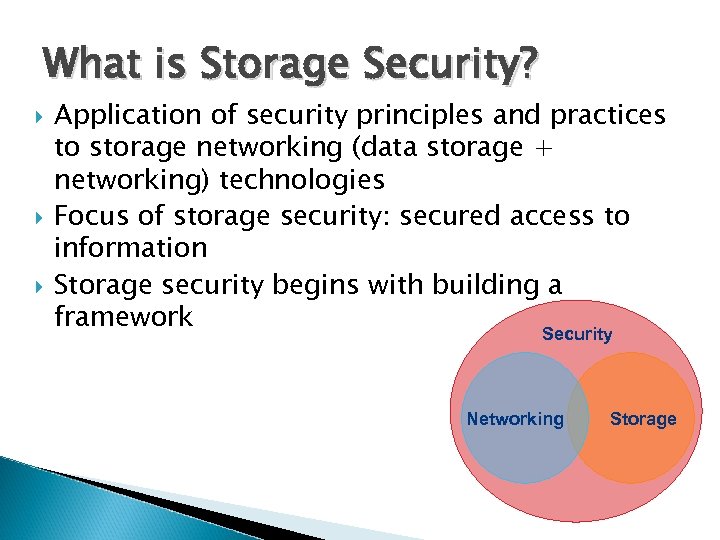 What is Storage Security? Application of security principles and practices to storage networking (data storage + networking) technologies Focus of storage security: secured access to information Storage security begins with building a framework Security Networking Storage
What is Storage Security? Application of security principles and practices to storage networking (data storage + networking) technologies Focus of storage security: secured access to information Storage security begins with building a framework Security Networking Storage
 Storage Security Framework A systematic way of defining security requirements Framework should incorporates: ◦ Anticipated security attacks Actions that compromise the security of information ◦ Security measures Control designed to protect from these security attacks Security framework must ensure: ◦ ◦ Confidentiality Integrity Availability Accountability
Storage Security Framework A systematic way of defining security requirements Framework should incorporates: ◦ Anticipated security attacks Actions that compromise the security of information ◦ Security measures Control designed to protect from these security attacks Security framework must ensure: ◦ ◦ Confidentiality Integrity Availability Accountability
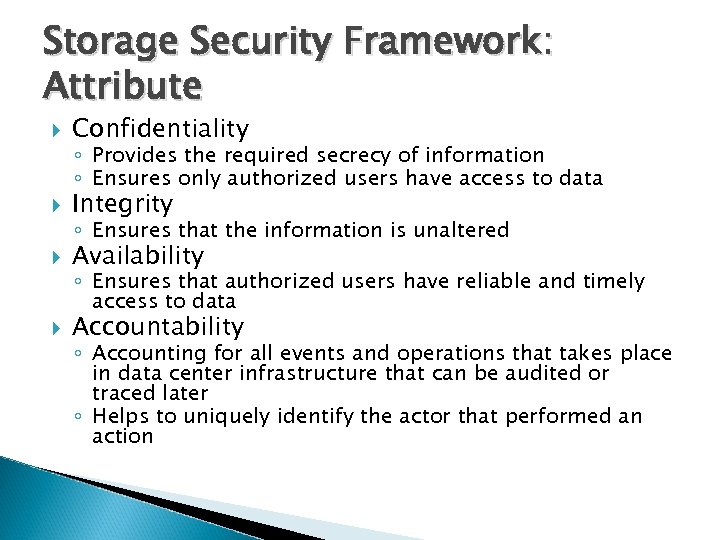 Storage Security Framework: Attribute Confidentiality Integrity Availability Accountability ◦ Provides the required secrecy of information ◦ Ensures only authorized users have access to data ◦ Ensures that the information is unaltered ◦ Ensures that authorized users have reliable and timely access to data ◦ Accounting for all events and operations that takes place in data center infrastructure that can be audited or traced later ◦ Helps to uniquely identify the actor that performed an action
Storage Security Framework: Attribute Confidentiality Integrity Availability Accountability ◦ Provides the required secrecy of information ◦ Ensures only authorized users have access to data ◦ Ensures that the information is unaltered ◦ Ensures that authorized users have reliable and timely access to data ◦ Accounting for all events and operations that takes place in data center infrastructure that can be audited or traced later ◦ Helps to uniquely identify the actor that performed an action
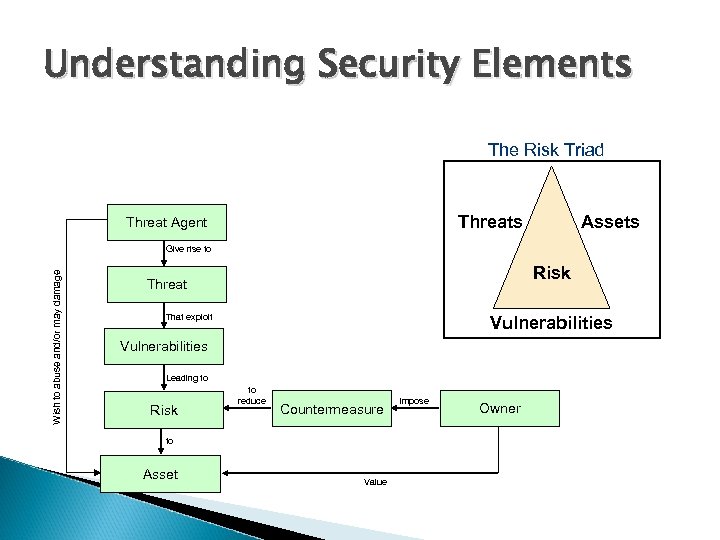 Understanding Security Elements The Risk Triad Threats Threat Agent Assets Wish to abuse and/or may damage Give rise to Risk Threat That exploit Vulnerabilities Leading to Risk to reduce Countermeasure to Asset Value impose Owner
Understanding Security Elements The Risk Triad Threats Threat Agent Assets Wish to abuse and/or may damage Give rise to Risk Threat That exploit Vulnerabilities Leading to Risk to reduce Countermeasure to Asset Value impose Owner
 Security Elements: Assets ◦ ◦ ◦ “Information” – The most important asset Other assets Hardware, software, and network infrastructure Protecting assets is the primary concern Security mechanism considerations: Must provide easy access to information assets for authorized users Make it very difficult for potential attackers to access and compromise the system Should only cost a small fraction of the value of protected asset Should cost a potential attacker more, in terms of money and time, to compromise the system than the protected data is worth
Security Elements: Assets ◦ ◦ ◦ “Information” – The most important asset Other assets Hardware, software, and network infrastructure Protecting assets is the primary concern Security mechanism considerations: Must provide easy access to information assets for authorized users Make it very difficult for potential attackers to access and compromise the system Should only cost a small fraction of the value of protected asset Should cost a potential attacker more, in terms of money and time, to compromise the system than the protected data is worth
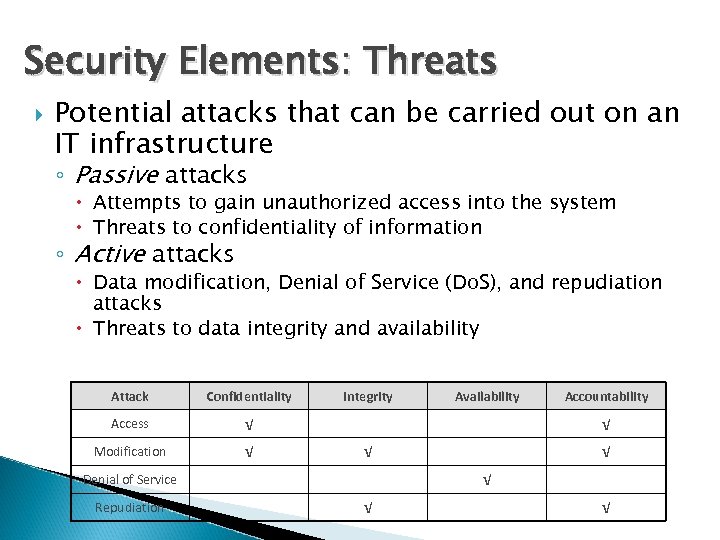 Security Elements: Threats Potential attacks that can be carried out on an IT infrastructure ◦ Passive attacks Attempts to gain unauthorized access into the system Threats to confidentiality of information ◦ Active attacks Data modification, Denial of Service (Do. S), and repudiation attacks Threats to data integrity and availability Attack Confidentiality Access √ Modification √ Integrity Accountability √ √ Denial of Service Repudiation Availability √ √
Security Elements: Threats Potential attacks that can be carried out on an IT infrastructure ◦ Passive attacks Attempts to gain unauthorized access into the system Threats to confidentiality of information ◦ Active attacks Data modification, Denial of Service (Do. S), and repudiation attacks Threats to data integrity and availability Attack Confidentiality Access √ Modification √ Integrity Accountability √ √ Denial of Service Repudiation Availability √ √
 Security Elements: Vulnerabilities can occur anywhere in the system ◦ An attacker can bypass controls implemented at a single point in the system ◦ Requires “defense in depth” – implementing security controls at each access point of every access path Failure anywhere in the system can jeopardize the security of information assets ◦ Loss of authentication may jeopardize confidentiality ◦ Loss of a device jeopardizes availability
Security Elements: Vulnerabilities can occur anywhere in the system ◦ An attacker can bypass controls implemented at a single point in the system ◦ Requires “defense in depth” – implementing security controls at each access point of every access path Failure anywhere in the system can jeopardize the security of information assets ◦ Loss of authentication may jeopardize confidentiality ◦ Loss of a device jeopardizes availability
 Security Elements: Vulnerabilities (cont. ) ◦ ◦ ◦ Understanding Vulnerabilities Attack surface Refers to various access points/interfaces that an attacker can use to launch an attack Attack vector A path or means by which an attacker can gain access to a system Work factor Amount of time and effort required to exploit an attack vector Solution to protect critical assets: Minimize the attack surface Maximize the work factor Manage vulnerabilities Detect and remove the vulnerabilities, or Install countermeasures to lessen the impact
Security Elements: Vulnerabilities (cont. ) ◦ ◦ ◦ Understanding Vulnerabilities Attack surface Refers to various access points/interfaces that an attacker can use to launch an attack Attack vector A path or means by which an attacker can gain access to a system Work factor Amount of time and effort required to exploit an attack vector Solution to protect critical assets: Minimize the attack surface Maximize the work factor Manage vulnerabilities Detect and remove the vulnerabilities, or Install countermeasures to lessen the impact
 Countermeasures to Vulnerability Implement countermeasures (safeguards or controls) in order to lessen the impact of vulnerabilities Controls are technical or non-technical ◦ Technical implemented in computer hardware, software, or firmware ◦ Non-technical Administrative (policies, standards) Physical (guards, gates) Controls provide different functions ◦ Preventive – prevent an attack ◦ Corrective – reduce the effect of an attack ◦ Detective – discover attacks and trigger preventive/corrective controls
Countermeasures to Vulnerability Implement countermeasures (safeguards or controls) in order to lessen the impact of vulnerabilities Controls are technical or non-technical ◦ Technical implemented in computer hardware, software, or firmware ◦ Non-technical Administrative (policies, standards) Physical (guards, gates) Controls provide different functions ◦ Preventive – prevent an attack ◦ Corrective – reduce the effect of an attack ◦ Detective – discover attacks and trigger preventive/corrective controls
 Lesson Summary Key topics covered in this lesson: Storage security framework ◦ Security attributes Security elements Security controls
Lesson Summary Key topics covered in this lesson: Storage security framework ◦ Security attributes Security elements Security controls
 Lecture 32 Storage security domains, List and analyzes the common threats in each domain
Lecture 32 Storage security domains, List and analyzes the common threats in each domain
 Lesson: Storage Security Domains Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to: Describe three security domains ◦ Application ◦ Management ◦ Backup & Data Storage List the security threats in each domain Describe the controls that can be applied
Lesson: Storage Security Domains Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to: Describe three security domains ◦ Application ◦ Management ◦ Backup & Data Storage List the security threats in each domain Describe the controls that can be applied
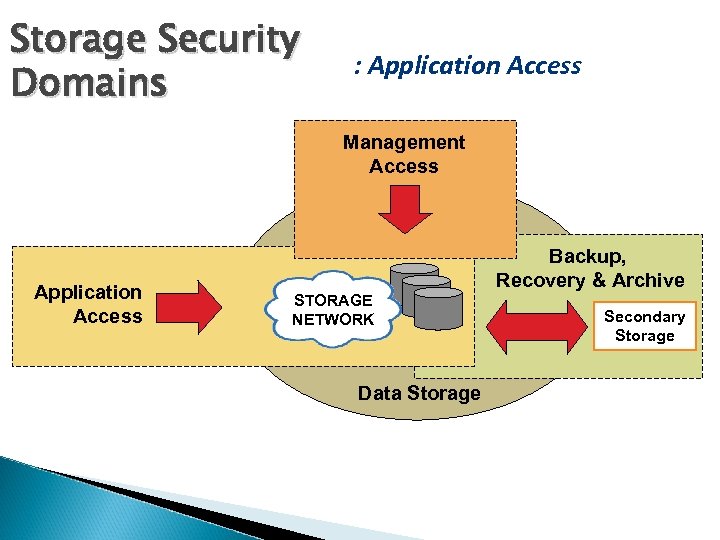 Storage Security Domains : Application Access Management Access Application Access Backup, Recovery & Archive STORAGE NETWORK Data Storage Secondary Storage
Storage Security Domains : Application Access Management Access Application Access Backup, Recovery & Archive STORAGE NETWORK Data Storage Secondary Storage
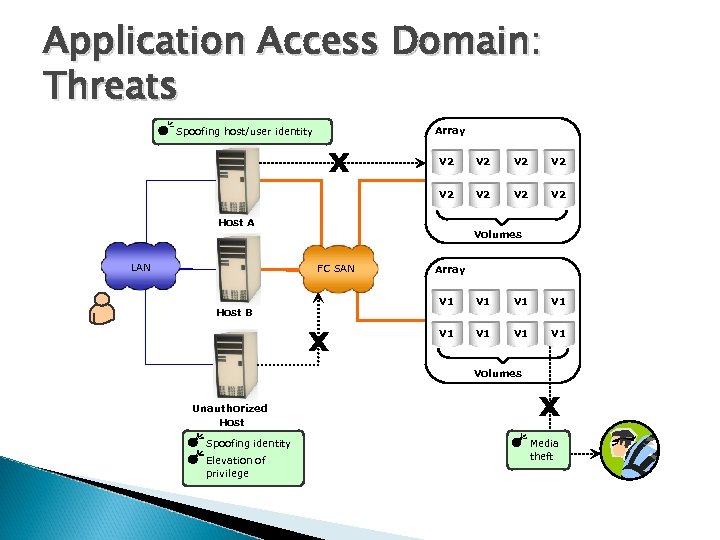 Application Access Domain: Threats Array Spoofing host/user identity V 2 V 2 Host A LAN Volumes FC SAN Array V 1 V 1 V 1 Host B V 1 V 1 Volumes Unauthorized Host Spoofing identity Elevation of privilege Media theft
Application Access Domain: Threats Array Spoofing host/user identity V 2 V 2 Host A LAN Volumes FC SAN Array V 1 V 1 V 1 Host B V 1 V 1 Volumes Unauthorized Host Spoofing identity Elevation of privilege Media theft
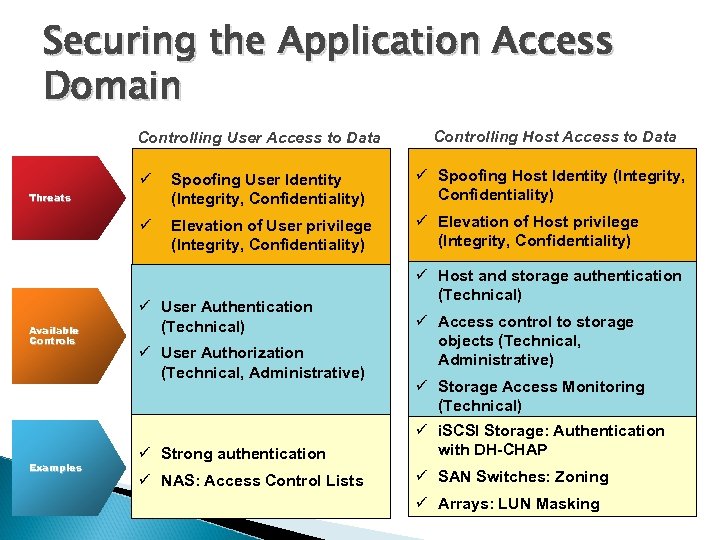 Securing the Application Access Domain Controlling User Access to Data Controlling Host Access to Data ü Spoofing User Identity (Integrity, Confidentiality) ü Spoofing Host Identity (Integrity, Confidentiality) ü Elevation of User privilege (Integrity, Confidentiality) ü Elevation of Host privilege (Integrity, Confidentiality) Threats Available Controls Examples ü User Authentication (Technical) ü User Authorization (Technical, Administrative) ü Host and storage authentication (Technical) ü Access control to storage objects (Technical, Administrative) ü Strong authentication ü Storage Access Monitoring (Technical) ü i. SCSI Storage: Authentication with DH-CHAP ü NAS: Access Control Lists ü SAN Switches: Zoning ü Arrays: LUN Masking
Securing the Application Access Domain Controlling User Access to Data Controlling Host Access to Data ü Spoofing User Identity (Integrity, Confidentiality) ü Spoofing Host Identity (Integrity, Confidentiality) ü Elevation of User privilege (Integrity, Confidentiality) ü Elevation of Host privilege (Integrity, Confidentiality) Threats Available Controls Examples ü User Authentication (Technical) ü User Authorization (Technical, Administrative) ü Host and storage authentication (Technical) ü Access control to storage objects (Technical, Administrative) ü Strong authentication ü Storage Access Monitoring (Technical) ü i. SCSI Storage: Authentication with DH-CHAP ü NAS: Access Control Lists ü SAN Switches: Zoning ü Arrays: LUN Masking
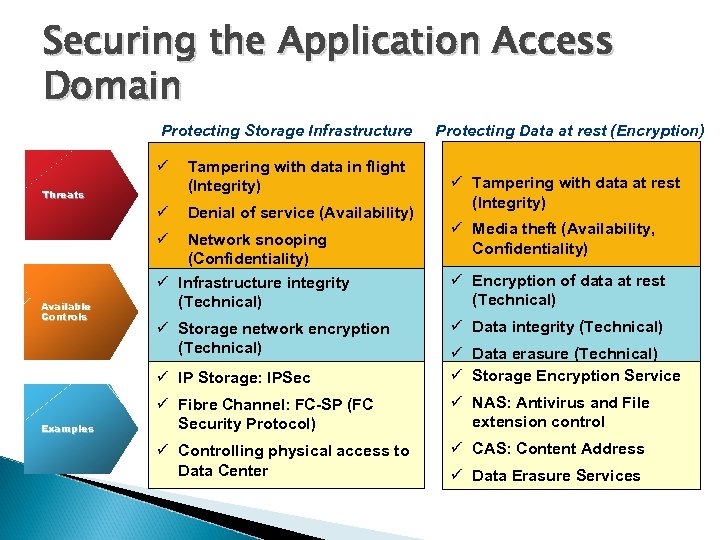 Securing the Application Access Domain Protecting Storage Infrastructure ü Tampering with data in flight (Integrity) ü Denial of service (Availability) ü Network snooping (Confidentiality) Threats Available Controls Protecting Data at rest (Encryption) ü Tampering with data at rest (Integrity) ü Media theft (Availability, Confidentiality) ü Infrastructure integrity (Technical) ü Encryption of data at rest (Technical) ü Storage network encryption (Technical) ü Data integrity (Technical) ü IP Storage: IPSec Examples ü Data erasure (Technical) ü Storage Encryption Service ü Fibre Channel: FC-SP (FC Security Protocol) ü NAS: Antivirus and File extension control ü Controlling physical access to Data Center ü CAS: Content Address ü Data Erasure Services
Securing the Application Access Domain Protecting Storage Infrastructure ü Tampering with data in flight (Integrity) ü Denial of service (Availability) ü Network snooping (Confidentiality) Threats Available Controls Protecting Data at rest (Encryption) ü Tampering with data at rest (Integrity) ü Media theft (Availability, Confidentiality) ü Infrastructure integrity (Technical) ü Encryption of data at rest (Technical) ü Storage network encryption (Technical) ü Data integrity (Technical) ü IP Storage: IPSec Examples ü Data erasure (Technical) ü Storage Encryption Service ü Fibre Channel: FC-SP (FC Security Protocol) ü NAS: Antivirus and File extension control ü Controlling physical access to Data Center ü CAS: Content Address ü Data Erasure Services
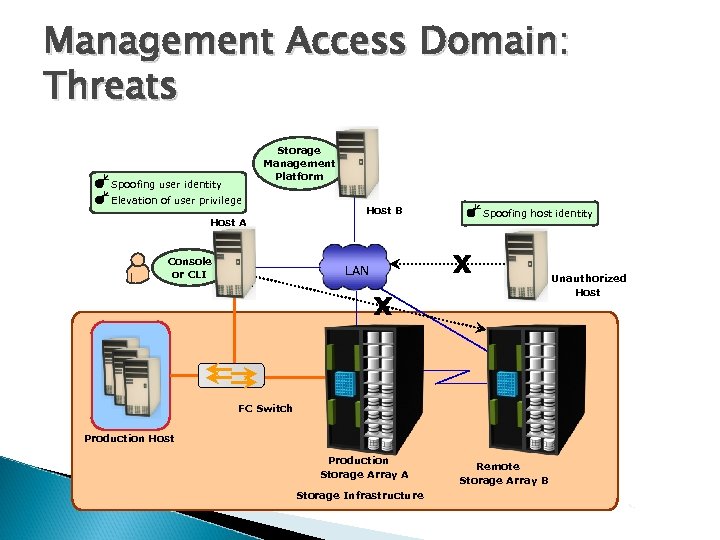 Management Access Domain: Threats Storage Management Platform Spoofing user identity Elevation of user privilege Host A Console or CLI Host B Spoofing host identity LAN Unauthorized Host FC Switch Production Host Production Storage Array A Storage Infrastructure Remote Storage Array B
Management Access Domain: Threats Storage Management Platform Spoofing user identity Elevation of user privilege Host A Console or CLI Host B Spoofing host identity LAN Unauthorized Host FC Switch Production Host Production Storage Array A Storage Infrastructure Remote Storage Array B
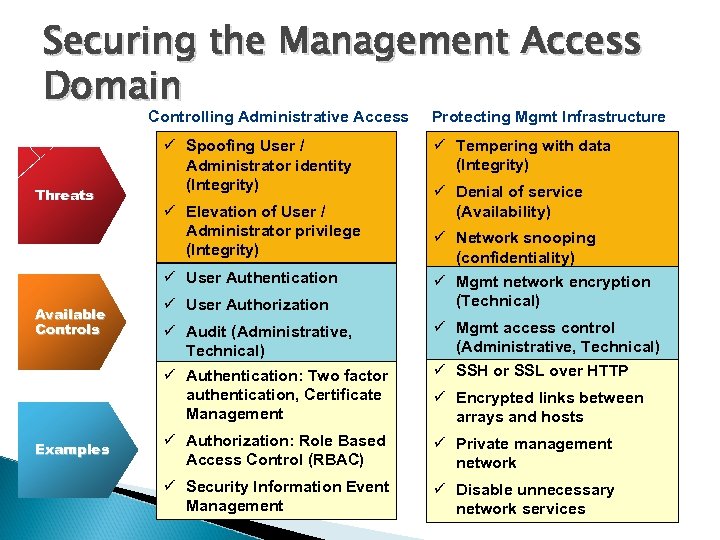 Securing the Management Access Domain Controlling Administrative Access Threats ü Spoofing User / Administrator identity (Integrity) ü Elevation of User / Administrator privilege (Integrity) ü User Authentication Available Controls ü User Authorization ü Audit (Administrative, Technical) ü Authentication: Two factor authentication, Certificate Management Examples Protecting Mgmt Infrastructure ü Tempering with data (Integrity) ü Denial of service (Availability) ü Network snooping (confidentiality) ü Mgmt network encryption (Technical) ü Mgmt access control (Administrative, Technical) ü SSH or SSL over HTTP ü Encrypted links between arrays and hosts ü Authorization: Role Based Access Control (RBAC) ü Private management network ü Security Information Event Management ü Disable unnecessary network services
Securing the Management Access Domain Controlling Administrative Access Threats ü Spoofing User / Administrator identity (Integrity) ü Elevation of User / Administrator privilege (Integrity) ü User Authentication Available Controls ü User Authorization ü Audit (Administrative, Technical) ü Authentication: Two factor authentication, Certificate Management Examples Protecting Mgmt Infrastructure ü Tempering with data (Integrity) ü Denial of service (Availability) ü Network snooping (confidentiality) ü Mgmt network encryption (Technical) ü Mgmt access control (Administrative, Technical) ü SSH or SSL over HTTP ü Encrypted links between arrays and hosts ü Authorization: Role Based Access Control (RBAC) ü Private management network ü Security Information Event Management ü Disable unnecessary network services
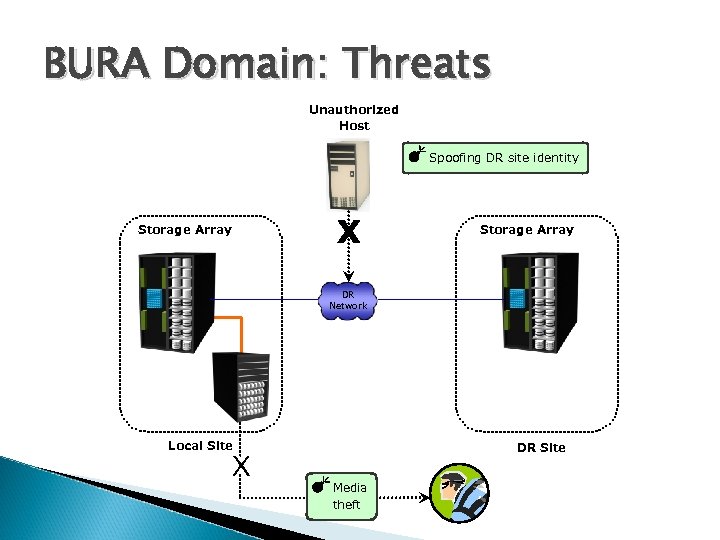 BURA Domain: Threats Unauthorized Host Spoofing DR site identity Storage Array DR Network Local Site DR Site Media theft
BURA Domain: Threats Unauthorized Host Spoofing DR site identity Storage Array DR Network Local Site DR Site Media theft
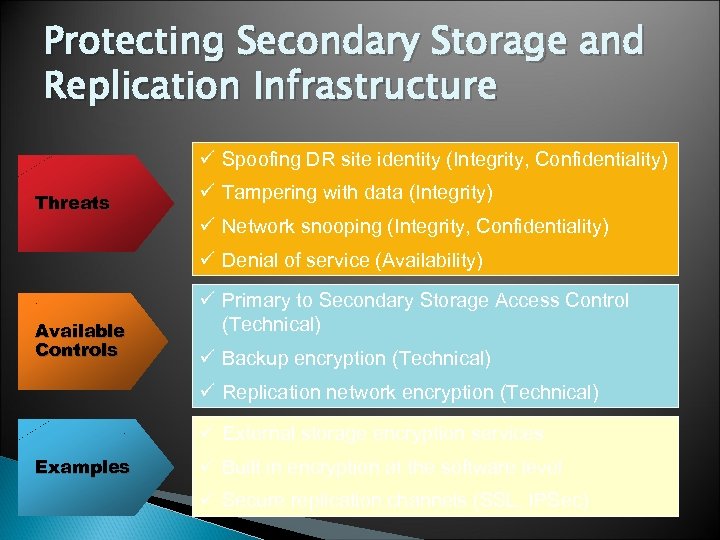 Protecting Secondary Storage and Replication Infrastructure ü Spoofing DR site identity (Integrity, Confidentiality) Threats ü Tampering with data (Integrity) ü Network snooping (Integrity, Confidentiality) ü Denial of service (Availability) Available Controls ü Primary to Secondary Storage Access Control (Technical) ü Backup encryption (Technical) ü Replication network encryption (Technical) ü External storage encryption services Examples ü Built in encryption at the software level ü Secure replication channels (SSL, IPSec)
Protecting Secondary Storage and Replication Infrastructure ü Spoofing DR site identity (Integrity, Confidentiality) Threats ü Tampering with data (Integrity) ü Network snooping (Integrity, Confidentiality) ü Denial of service (Availability) Available Controls ü Primary to Secondary Storage Access Control (Technical) ü Backup encryption (Technical) ü Replication network encryption (Technical) ü External storage encryption services Examples ü Built in encryption at the software level ü Secure replication channels (SSL, IPSec)
 Lesson Summary Key topics covered in this lesson: The three security domains ◦ Application ◦ Management ◦ Backup & Data Storage Security threats in each domain Security controls
Lesson Summary Key topics covered in this lesson: The three security domains ◦ Application ◦ Management ◦ Backup & Data Storage Security threats in each domain Security controls
 Check Your Knowledge What are the primary security attributes? What are three data security domains?
Check Your Knowledge What are the primary security attributes? What are three data security domains?


