b0af9ed7a57981b9f39e0700b5e85eb0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

SECTION 1&2: THE SIMPLE PRESENT OF TO BE

Nouns Singular: (the indefinite article a or an) Ø Nouns are used to name people, animals and things. Like: girl , fish , car, table Ø Nouns can be singular or plural. We put a or an in front of a singular noun. A or an have the same meaning. The mean (1).
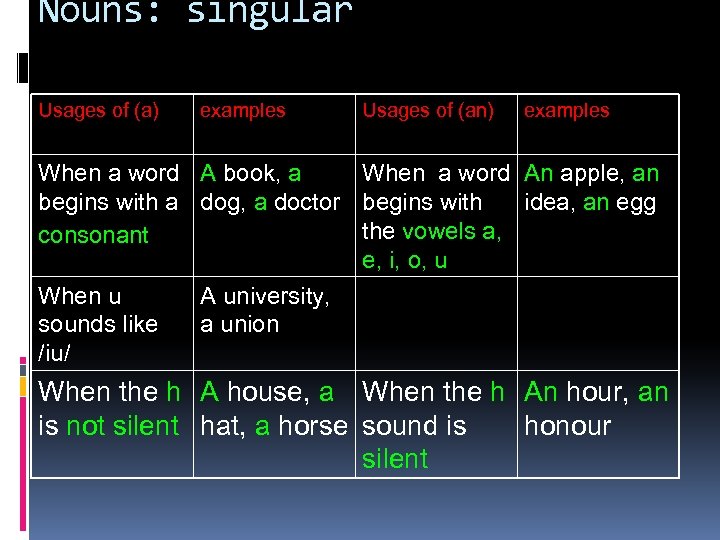
Nouns: singular Usages of (a) examples Usages of (an) examples When a word A book, a When a word An apple, an begins with a dog, a doctor begins with idea, an egg the vowels a, consonant e, i, o, u When u sounds like /iu/ A university, a union When the h A house, a When the h An hour, an is not silent hat, a horse sound is honour silent
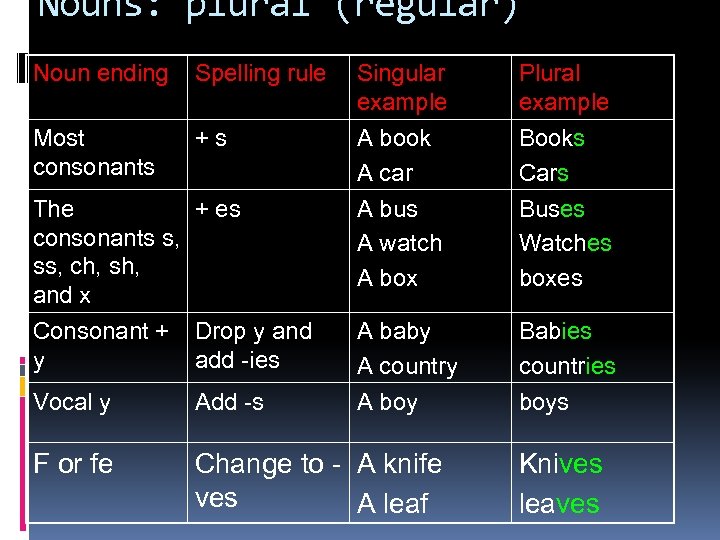
Nouns: plural (regular) Noun ending Spelling rule Singular example A book A car Plural example Books Cars Most consonants +s The + es consonants s, ss, ch, sh, and x A bus A watch A box Buses Watches boxes Consonant + y Drop y and add -ies Vocal y Add -s A baby A country A boy Babies countries boys F or fe Change to - A knife ves A leaf Knives leaves
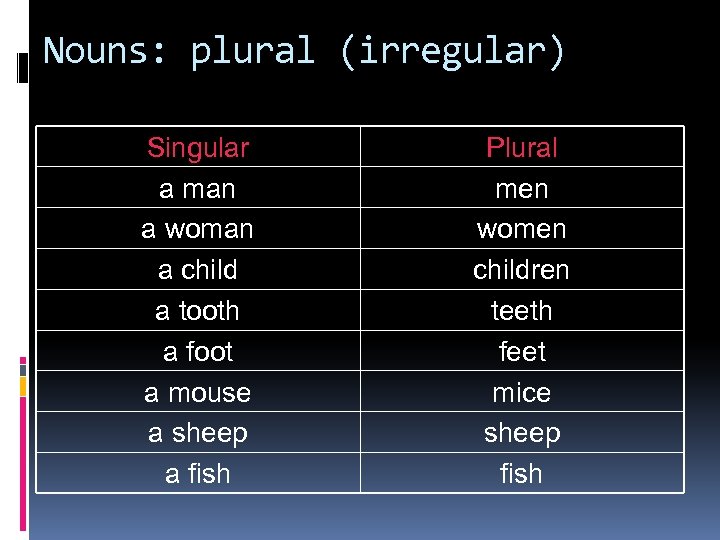
Nouns: plural (irregular) Singular a man a woman a child a tooth a foot a mouse a sheep a fish Plural men women children teeth feet mice sheep fish

Subject pronouns Ø Singular subject pronouns: I, you, he, she, it Ø Plural subject pronouns: we, you, they n Subject pronoun + simple present of to be: Pronoun + to be I = am He, she, it = is We, you, they = are Contractions I’m He’s / she’s You’re / they’re

Usages of verb to be To say who we are: Ø I am Aisha. / He’s Ahmad. n To say what we are: Ø We are students. / They are teachers. n To talk about nationality: Ø I’m Turkish. / They’re Brazilian. n To describe people, things or places: Ø He’s hungry. / She’s beautiful.

Negative of to be I am not a teacher. OR I’m not a teacher. You are not from Spain. OR You’re not from Spain. OR You aren’t from Spain. Subject + verb to be + not + additional information
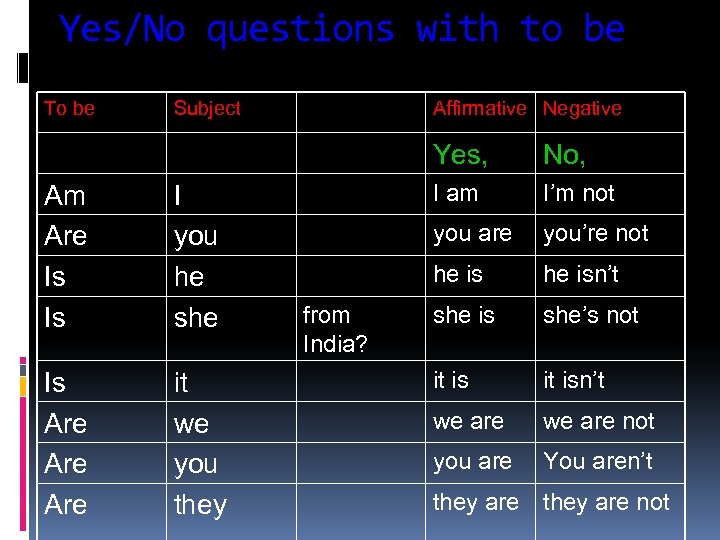
Yes/No questions with to be To be Subject Affirmative Negative Yes, Am Are Is Is I you he she Is Are Are it we you they I am I’m not you are you’re not he is from India? No, he isn’t she is she’s not it isn’t we are not you are You aren’t they are not

To be + adjective n Nationality adjective: Ø He is Turkish. / He is from Turkey. Ø I am Italian. / I am from Italy. n Descriptive adjectives: Ø Lemons are yellow. / A giraffe is tall. Ø Adjectives describes people, things or places.

Possessive adjectives We use possessive adjectives before nouns to show that something belongs to someone. My book / his name / our house Pronouns I Possessive adjectives My Your He His She Her It its We Our They Their

Demonstrative adjectives This is my book (singular). These are my books (plural). Ø We use this & these for people or things that are near to us. n That is your book (singular). Those are books (plural). Ø We use that & those for things that are not near.

Question with what, where, and who What is that? It is a pen. Ø We use what to ask about things. n Where is Sylvia? She is in the kitchen. Ø We use where to ask about location. n Who is he? He is my teacher. Ø We use who to ask about people.

Yes / no questions with to be Are you a student? Yes, I am / No, I am not. Is he from India? Yes, he is / No he is not.

Section 2: it, there, the simple past of to be What is the weather like today? It’s sunny / hot / cold / rainy / windy n What is the temperature today? It’s is 90 degrees Fahrenheit/ 32 degrees centigrade.

It to tell the time & the date What time is it? It is two / it is 2 o’clock / it is 2 p. m. n What day is it? It is Wednesday. n What month is it? It is July. n What year is it? It is 2002. n What is the date today? It is July 6 th.

Read 2. 15 10. 35 1986 1820 2005

Questions with when & what. Prepositions of time We use when & what for questions about time. Ø When is your birthday? What time is the party? n We use in for parts of the day and with months, seasons, and years Ø In July/ in the afternoon/ in the summer/ in 1786 n We use on with dates and days Ø On Monday/ on the 12 th of May n We use at for times & for the expression at night Ø At 2 o’clock/ at night

Statements with there + to be We use there is/ there are to say that something exists. Ø There is a computer in the room. There are books on the desk. n We use there isn’t/ there aren’t to say that something doesn’t exist. Ø There isn’t a waiter in the picture. The aren’t any glasses on the table. n We use any before nouns in the plural, both in yes/no questions and in negatives. Ø Are there any cookies on the table? No, there aren’t any cookies on the table.

Questions with there Is there a bank in the town? Ø Yes, there is. No, there is not. n Are there any shops in the town? Ø Yes, there are. No, there aren’t.

The conjunctions and, but, or We use a comma before the conjunctions when we connect 2 sentences. Ø The food is cheap, but it’s not good. n We don’t use a comma when the conjunction separates 2 adjectives. Ø She is tired but happy. n We don’t use a comma when the conjunction separates 2 nouns. Ø Are you busy on Saturday or Sunday?

The conjunctions and, but, or We use and to add information. Ø The coat is beautiful , and it is warm. Ø The coat is beautiful and warm. n We use but to give a contrasting idea. Ø I want to go skiing, but I haven’t got any money. n We use or to give a choice. Ø We go, or we stay.

The simple the past of to be I, he, she, it = was or was not We, you, they = were or were not The time expression of the past: yesterday, two hours ago, 5 five months ago, last night, last year, in 1980

The simple past of to be: questions Was (he, she, it, I) here yesterday? Ø Yes, she was. No, it wasn’t. n Were (we, you, they) here yesterday? Ø Yes, we were. No, you weren’t.

Possessive adjectives We use possessive adjectives before nouns to show that something belongs to someone. pronouns Possessive adjectives I you he she it we you they my your his her its our your their

Demonstrative adjectives We use this and these for people and things that are near us. Singular We use that and those for people and things This book that are not near. That book Plural These books Those books

Questions with what, where, and who Wh- word To be subject What is Your name? My name is Kelly What are these? They’re pens Where is Joe? He’s at home Where are you from? I’m from Spain Who is he? He’s my brother Who are they? They’re visitors
b0af9ed7a57981b9f39e0700b5e85eb0.ppt