 Secrets of using Can & May Only HERE and Only TODAY Can I? • What is the difference? • How to use modal verbs correctly? No, you may. Catherine Levchenko • How to say the same sentence with different emotional colouring changing only a modal verb? Catherine Ignatova
Secrets of using Can & May Only HERE and Only TODAY Can I? • What is the difference? • How to use modal verbs correctly? No, you may. Catherine Levchenko • How to say the same sentence with different emotional colouring changing only a modal verb? Catherine Ignatova
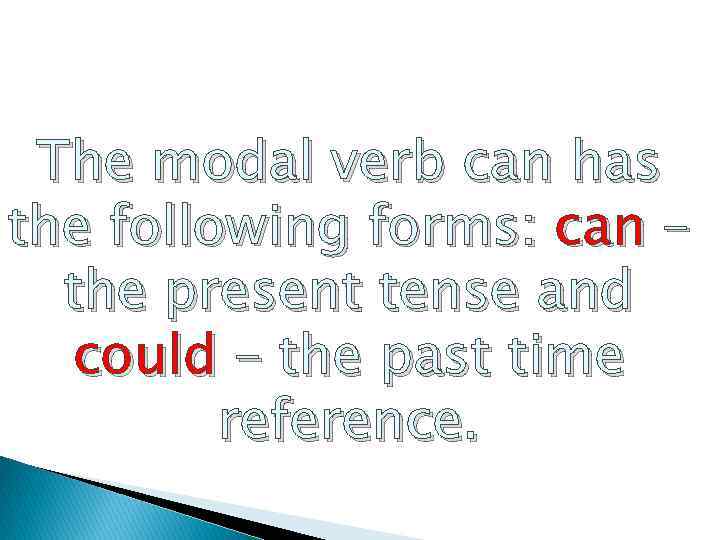 The modal verb can has the following forms: can – the present tense and could – the past time reference.
The modal verb can has the following forms: can – the present tense and could – the past time reference.
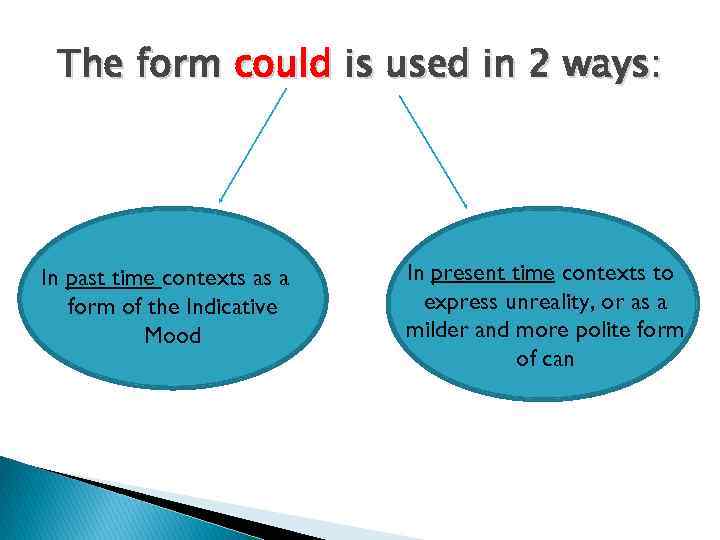 The form could is used in 2 ways: In past time contexts as a form of the Indicative Mood In present time contexts to express unreality, or as a milder and more polite form of can
The form could is used in 2 ways: In past time contexts as a form of the Indicative Mood In present time contexts to express unreality, or as a milder and more polite form of can
 The modal verb may has the following forms: may – the present tense and might – the past tense.
The modal verb may has the following forms: may – the present tense and might – the past tense.
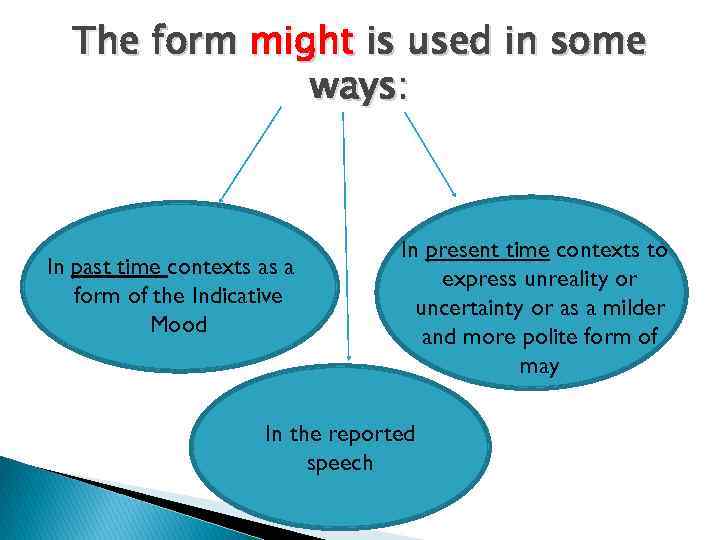 The form might is used in some ways: In past time contexts as a form of the Indicative Mood In present time contexts to express unreality or uncertainty or as a milder and more polite form of may In the reported speech
The form might is used in some ways: In past time contexts as a form of the Indicative Mood In present time contexts to express unreality or uncertainty or as a milder and more polite form of may In the reported speech
 The meanings of the modal verbs can & may
The meanings of the modal verbs can & may
 Concrete meaning Can
Concrete meaning Can
 Physical and mental ability The modal verb can is used in its concrete meaning to express physical and mental ability in the present and future tenses.
Physical and mental ability The modal verb can is used in its concrete meaning to express physical and mental ability in the present and future tenses.
 Hypothetical ability The modal verb can is used to express a hypothetical ability in all tenses. I could have gone to university but I decided to get a job. I could have eaten a horse! I was so hungry yesterday
Hypothetical ability The modal verb can is used to express a hypothetical ability in all tenses. I could have gone to university but I decided to get a job. I could have eaten a horse! I was so hungry yesterday
 Permanent and habitual ability The modal verb can is used in it’s concrete meaning to express permanent or habitual ability in the past time. He could play the piano when he was nine
Permanent and habitual ability The modal verb can is used in it’s concrete meaning to express permanent or habitual ability in the past time. He could play the piano when he was nine
 Theoretical possibility The modal verb can is used to express a theoretical possibility. Anybody can make mistakes.
Theoretical possibility The modal verb can is used to express a theoretical possibility. Anybody can make mistakes.
 Factual possibility The modal verb can is used to express a factual possibility. I wasn’t tired last night and we could go to the restaurant.
Factual possibility The modal verb can is used to express a factual possibility. I wasn’t tired last night and we could go to the restaurant.
 Possibility due to circumstances The modal verb can is used in it’s concrete meaning to express a possibility due to circumstances. You can see the forest through the other window.
Possibility due to circumstances The modal verb can is used in it’s concrete meaning to express a possibility due to circumstances. You can see the forest through the other window.
 If there is no indications of past time in the context but the speaker wishes to refer the action to the past , Was/were able to is used instead of could She was able to explain the mystery
If there is no indications of past time in the context but the speaker wishes to refer the action to the past , Was/were able to is used instead of could She was able to explain the mystery
 Imperative meaning Can
Imperative meaning Can
 Asking for permission The modal verb can/could is used in it’s imperative meaning to express asking of permission. Can I smoke here? (informal) Could I go out for a minute? (more polite)
Asking for permission The modal verb can/could is used in it’s imperative meaning to express asking of permission. Can I smoke here? (informal) Could I go out for a minute? (more polite)
 Granting/refusing permission The modal verb can is used in it’s imperative meaning to express a granting/refusing permission. You can(n’t) smoke here. The window is(n’t) open. (granting/refusing permission; informal)
Granting/refusing permission The modal verb can is used in it’s imperative meaning to express a granting/refusing permission. You can(n’t) smoke here. The window is(n’t) open. (granting/refusing permission; informal)
 How not to be ordinary in speaking? In other words: He wasn’t allowed to/couldn’t take my car. (past) I could always/was always allowed to stay up late on Saturdays when I was a child. (general permission in the past) He was allowed to take my car. (an action that really happened in the past) You are allowed to see the patient. (permission)
How not to be ordinary in speaking? In other words: He wasn’t allowed to/couldn’t take my car. (past) I could always/was always allowed to stay up late on Saturdays when I was a child. (general permission in the past) He was allowed to take my car. (an action that really happened in the past) You are allowed to see the patient. (permission)
 Prohibition The modal verb can is used in it’s imperative meaning to express a prohibition {depending on circumstances} You cannot walk on the grass!
Prohibition The modal verb can is used in it’s imperative meaning to express a prohibition {depending on circumstances} You cannot walk on the grass!
 Request The modal verb can is used in it’s imperative meaning to express a request. Only in interrogative (? ) sentences. f o r m a l i t y Can you tell me the way to the Museum of Art? (informal) Could you tell me the way to the Museum of Art? (polite)
Request The modal verb can is used in it’s imperative meaning to express a request. Only in interrogative (? ) sentences. f o r m a l i t y Can you tell me the way to the Museum of Art? (informal) Could you tell me the way to the Museum of Art? (polite)
 How not to be ordinary in speaking? In other words: Will you do my shopping? (informal) Do/Would you mind working overtime? (polite; formal) We normally reply with: ‘Yes, I’d (would) be happy to. ’/’Yes, I’d be glad to. ’/’Certainly. ’/’Of course. ’/’I’m sorry, but I can’t. ’
How not to be ordinary in speaking? In other words: Will you do my shopping? (informal) Do/Would you mind working overtime? (polite; formal) We normally reply with: ‘Yes, I’d (would) be happy to. ’/’Yes, I’d be glad to. ’/’Certainly. ’/’Of course. ’/’I’m sorry, but I can’t. ’
 Suppositional meaning Can
Suppositional meaning Can
 Uncertainty/ Doubt The modal verb can is used in it’s suppositional meaning to express uncertainty/doubt. You could at least warn me that aliens are coming!! Can John have done all the exercises without my help? * *There is a slight reproach in this case.
Uncertainty/ Doubt The modal verb can is used in it’s suppositional meaning to express uncertainty/doubt. You could at least warn me that aliens are coming!! Can John have done all the exercises without my help? * *There is a slight reproach in this case.
 Strong doubt The modal verb can/could is used in it’s suppositional meaning to express a strong doubt {in negations (-) } Present time - He can’t be so old. Past time – He can’t/couldn’t have fallen ill. Future time – He can’t be playing now.
Strong doubt The modal verb can/could is used in it’s suppositional meaning to express a strong doubt {in negations (-) } Present time - He can’t be so old. Past time – He can’t/couldn’t have fallen ill. Future time – He can’t be playing now.
 Improbability The modal verb can is used to express improbability. It can’t be true!
Improbability The modal verb can is used to express improbability. It can’t be true!
 Astonishment The modal verb can is used in it’s suppositional meaning to express an astonishment {in interrogative sentences (? ) } Can it be so cold in the middle of July here?
Astonishment The modal verb can is used in it’s suppositional meaning to express an astonishment {in interrogative sentences (? ) } Can it be so cold in the middle of July here?
 Hypothetical possibility The modal verb can is used to express a hypothetical possibility. But for the rain we could go for a walk.
Hypothetical possibility The modal verb can is used to express a hypothetical possibility. But for the rain we could go for a walk.
 Could + perfect infinitive indicates that the action wasn’t carried out in the past She could have explained the mystery. (luckily she didn’t – past)
Could + perfect infinitive indicates that the action wasn’t carried out in the past She could have explained the mystery. (luckily she didn’t – past)
 How not to be ordinary in speaking? In other words: It is likely that Ann will offer to help. Ann is likely to offer to help. It was likely that she had missed the bus. (past) She was likely to have missed the bus. (past)
How not to be ordinary in speaking? In other words: It is likely that Ann will offer to help. Ann is likely to offer to help. It was likely that she had missed the bus. (past) She was likely to have missed the bus. (past)
 Set phrases with can I can’t help doing – Не могу удержаться от I can’t but do something – Мне ничего другого не остается, как I can’t possibly do – Просто не могу сделать
Set phrases with can I can’t help doing – Не могу удержаться от I can’t but do something – Мне ничего другого не остается, как I can’t possibly do – Просто не могу сделать
 Concrete meaning May
Concrete meaning May
 Theoretical possibility The modal verb may is used in the past time reference to express a theoretical possibility. He might come later. (40% certain; perhaps he will come later)
Theoretical possibility The modal verb may is used in the past time reference to express a theoretical possibility. He might come later. (40% certain; perhaps he will come later)
 Factual possibility The modal verb may is used in the present/future or past time reference to express a factual possibility. He could*/may be tired. (50% certain; it’s possible he is tired) *in such a case modal verbs could and may are used without difference in meaning.
Factual possibility The modal verb may is used in the present/future or past time reference to express a factual possibility. He could*/may be tired. (50% certain; it’s possible he is tired) *in such a case modal verbs could and may are used without difference in meaning.
 Hypothetical possibility The modal verb may is used in the present/future or past time reference to express a hypothetical possibility. He may/might have sold his house. (perhaps he sold it – past)
Hypothetical possibility The modal verb may is used in the present/future or past time reference to express a hypothetical possibility. He may/might have sold his house. (perhaps he sold it – past)
 Imperative meaning May
Imperative meaning May
 Asking for permission The modal verb may/might is used in it’s imperative meaning to express asking of permission. May I leave class early today? I’ve got a job interview. (Asking for permission – for more formal situations) *may/might are used to ask for permission when we do not know the other person very well.
Asking for permission The modal verb may/might is used in it’s imperative meaning to express asking of permission. May I leave class early today? I’ve got a job interview. (Asking for permission – for more formal situations) *may/might are used to ask for permission when we do not know the other person very well.
 Granting/refusing permission The modal verb may is used in it’s imperative meaning to express granting/refusing permission. You may go out for a minute. (formal; giving permission, the speaker allows to perform an action) Visitors may not take pictures of the statues. (formal; refusing permission, written notice)
Granting/refusing permission The modal verb may is used in it’s imperative meaning to express granting/refusing permission. You may go out for a minute. (formal; giving permission, the speaker allows to perform an action) Visitors may not take pictures of the statues. (formal; refusing permission, written notice)
 Request The modal verb may is used in it’s imperative meaning to express a request. Only in interrogative (? ) sentences. f o r m a l i t y May you tell me the way to the Museum of Art, please? (formal) Might you tell me the way to the Museum of Art? (very formal) *We use this structure to ask for smth politely. Might is formal and is not often used.
Request The modal verb may is used in it’s imperative meaning to express a request. Only in interrogative (? ) sentences. f o r m a l i t y May you tell me the way to the Museum of Art, please? (formal) Might you tell me the way to the Museum of Art? (very formal) *We use this structure to ask for smth politely. Might is formal and is not often used.
 Prohibition The modal verb may is used in it’s imperative meaning to express a prohibition {depending on circumstances} Candidates may not leave the room during the exam. (prohibition depending on the will of the speaker) You may not talk in the library. (formal; often written)
Prohibition The modal verb may is used in it’s imperative meaning to express a prohibition {depending on circumstances} Candidates may not leave the room during the exam. (prohibition depending on the will of the speaker) You may not talk in the library. (formal; often written)
 Ironic advice The modal verb may is used in it’s suppositional meaning to express an ironic advice Don’t wait for her. You might do it yourself.
Ironic advice The modal verb may is used in it’s suppositional meaning to express an ironic advice Don’t wait for her. You might do it yourself.
 Reproach The modal verb may is used in it’s suppositional meaning to express a reproach You might have phoned me last night.
Reproach The modal verb may is used in it’s suppositional meaning to express a reproach You might have phoned me last night.
 Suppositional meaning May
Suppositional meaning May
 Uncertainty/ Doubt The modal verb may is used in it’s suppositional meaning to express uncertainty/doubt. He may/might* (not) come tomorrow. He may/might* be skating now. He may/might* (not) have recovered yet. He may/might* have been skating for 2 hours. *Might is more uncertain.
Uncertainty/ Doubt The modal verb may is used in it’s suppositional meaning to express uncertainty/doubt. He may/might* (not) come tomorrow. He may/might* be skating now. He may/might* (not) have recovered yet. He may/might* have been skating for 2 hours. *Might is more uncertain.
 Set phrases with may May as well(might as well, might just as well) + inf – mild/unemphatic way of expressing an intention/to suggest or recommend an action It might have been worse = Things are not so bad after all He might have been a… =He might have been taken for a… He looked like a… If I may so… = a stereotyped phrase in which the meaning of permission is considerably weakened
Set phrases with may May as well(might as well, might just as well) + inf – mild/unemphatic way of expressing an intention/to suggest or recommend an action It might have been worse = Things are not so bad after all He might have been a… =He might have been taken for a… He looked like a… If I may so… = a stereotyped phrase in which the meaning of permission is considerably weakened
 THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION!
THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION!


