f1cc9d5da9a457053463c8fc7396e394.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65
 Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Final Report Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellowship Program 2004 - 2005
Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Final Report Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellowship Program 2004 - 2005
 Agenda Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Background • Common Findings/Recommendations • Individual Experiences (time permitting) 2
Agenda Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Background • Common Findings/Recommendations • Individual Experiences (time permitting) 2
 SDCFP Background Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • SECDEF concerns for future Service leaders - Open to organizational and operational change - Recognize opportunities made possible by info tech - Appreciate resulting revolutionary changes underway l l Affecting society and business now Affecting culture and operations of Do. D in future • Businesses outside Do. D successful in: - Adapting to changing global environment Exploiting information revolution Structural reshaping/reorganizing Developing innovative processes 3
SDCFP Background Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • SECDEF concerns for future Service leaders - Open to organizational and operational change - Recognize opportunities made possible by info tech - Appreciate resulting revolutionary changes underway l l Affecting society and business now Affecting culture and operations of Do. D in future • Businesses outside Do. D successful in: - Adapting to changing global environment Exploiting information revolution Structural reshaping/reorganizing Developing innovative processes 3
 SDCFP Organization Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Two officers from each Service - High flag/general officer potential - O-6 or O-5 - Senior Service College credit • Group Education - Current political/military issues; leading edge technologies - Meetings with senior Do. D officials, business executives, Members of Congress, the press, former sponsors, alumni - Graduate business school executive education • Eleven months at Sponsoring Company • Permanent Staff - SDCFP Director, Admin Assistant - Net Assessment for oversight - National Defense University for Admin support 4
SDCFP Organization Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Two officers from each Service - High flag/general officer potential - O-6 or O-5 - Senior Service College credit • Group Education - Current political/military issues; leading edge technologies - Meetings with senior Do. D officials, business executives, Members of Congress, the press, former sponsors, alumni - Graduate business school executive education • Eleven months at Sponsoring Company • Permanent Staff - SDCFP Director, Admin Assistant - Net Assessment for oversight - National Defense University for Admin support 4
 SDCFP Sponsors Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • 1995 - 2004 – 3 M, ABB, Accenture, Agilent Technologies, American Management Systems, Amgen, Boeing, Cisco, Direc. TV, Du. Pont, Enron, Fed. Ex, General Dynamics, Hewlett-Packard, Human Genome Sciences, IBM, Lockheed Martin, Loral, Mc. Donnell Douglas, Mc. Kinsey & Co. , Merck, Microsoft, Mobil, Netscape, Northrop Grumman, Oracle, Pfizer, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers, Raytheon, Sarnoff, Sears, Southern Company, Sun Microsystems, United Technologies • 2004 -2005 – 3 M, Caterpillar, Cisco, Hewlett-Packard, Honeywell, Lockheed Martin, SRA International • 2005 – 2006 – Fed. Ex, Insitu Group, Johnson & Johnson, Raytheon, Southern Company, Sun, Symbol Technologies, United Technologies 5
SDCFP Sponsors Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • 1995 - 2004 – 3 M, ABB, Accenture, Agilent Technologies, American Management Systems, Amgen, Boeing, Cisco, Direc. TV, Du. Pont, Enron, Fed. Ex, General Dynamics, Hewlett-Packard, Human Genome Sciences, IBM, Lockheed Martin, Loral, Mc. Donnell Douglas, Mc. Kinsey & Co. , Merck, Microsoft, Mobil, Netscape, Northrop Grumman, Oracle, Pfizer, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers, Raytheon, Sarnoff, Sears, Southern Company, Sun Microsystems, United Technologies • 2004 -2005 – 3 M, Caterpillar, Cisco, Hewlett-Packard, Honeywell, Lockheed Martin, SRA International • 2005 – 2006 – Fed. Ex, Insitu Group, Johnson & Johnson, Raytheon, Southern Company, Sun, Symbol Technologies, United Technologies 5
 SDCFP Results Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Program objectives fulfilled - Education - Do. D, Individual officers, Sponsors - More Sponsors than Fellows available - Intra-group experience sharing • Unique corporate experience - Strong corporate support - Executive/operational level mix - Mergers/restructuring 6
SDCFP Results Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Program objectives fulfilled - Education - Do. D, Individual officers, Sponsors - More Sponsors than Fellows available - Intra-group experience sharing • Unique corporate experience - Strong corporate support - Executive/operational level mix - Mergers/restructuring 6
 SDCFP Products Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Build a cadre of future leaders who: – – – Understand more than the profession of arms Understand adaptive and innovative business culture Recognize organizational and operational opportunities Understand skills required to implement change Will motivate innovative changes throughout career • Report and Briefings directly to Sec. Def, others – – Business insights relevant to Do. D culture/operations Recommended process/organization changes 7
SDCFP Products Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Build a cadre of future leaders who: – – – Understand more than the profession of arms Understand adaptive and innovative business culture Recognize organizational and operational opportunities Understand skills required to implement change Will motivate innovative changes throughout career • Report and Briefings directly to Sec. Def, others – – Business insights relevant to Do. D culture/operations Recommended process/organization changes 7
 Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows “And we must transform not only our own forces, but also the department that serves them by encouraging a culture of creativity and intelligent risk taking. We need to promote a more entrepreneurial approach to developing military capabilities, one that encourages people—all people—to be more proactive and not reactive, to behave somewhat less like bureaucrats and more like venture capitalists…” Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld Remarks to The National Defense University 31 January 2002
Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows “And we must transform not only our own forces, but also the department that serves them by encouraging a culture of creativity and intelligent risk taking. We need to promote a more entrepreneurial approach to developing military capabilities, one that encourages people—all people—to be more proactive and not reactive, to behave somewhat less like bureaucrats and more like venture capitalists…” Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld Remarks to The National Defense University 31 January 2002
 2004 - 2005 Fellows Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Col John Clark Lockheed Martin Corporation Dallas, TX • Col Scott Vander Hamm 3 M Company St. Paul, MN • CAPT Mark Rich Honeywell International, Inc. Columbia, MD • LTC(P) Dennis Slagter SRA International, Inc. Fairfax, VA • Col (S) Ed Wilson Cisco Systems, Inc. San Jose, CA • CDR Mike Murphy Hewlett-Packard Company Reston, VA • Lt Col Howard Parker Caterpillar, Inc. Peoria, IL 9
2004 - 2005 Fellows Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Col John Clark Lockheed Martin Corporation Dallas, TX • Col Scott Vander Hamm 3 M Company St. Paul, MN • CAPT Mark Rich Honeywell International, Inc. Columbia, MD • LTC(P) Dennis Slagter SRA International, Inc. Fairfax, VA • Col (S) Ed Wilson Cisco Systems, Inc. San Jose, CA • CDR Mike Murphy Hewlett-Packard Company Reston, VA • Lt Col Howard Parker Caterpillar, Inc. Peoria, IL 9
 Agenda Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Background • Common Findings/Recommendations • Individual Experiences (time permitting) 10
Agenda Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Background • Common Findings/Recommendations • Individual Experiences (time permitting) 10
 Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Two Distinct Cultures… Corporate America Do. D • Profit and growth • Mission accomplishment • Market centric/customer focused • Service centric • Cost conscious (profit/loss) culture • Spend culture • “Street”/competition drive urgency • Politics/budget/ops drive urgency • Ruthless advocate for efficiency • Tenacious advocate for warfighter • Continuously reinventing tech base • Develop in blocks and spirals . . . with Best Practices to Share 11
Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Two Distinct Cultures… Corporate America Do. D • Profit and growth • Mission accomplishment • Market centric/customer focused • Service centric • Cost conscious (profit/loss) culture • Spend culture • “Street”/competition drive urgency • Politics/budget/ops drive urgency • Ruthless advocate for efficiency • Tenacious advocate for warfighter • Continuously reinventing tech base • Develop in blocks and spirals . . . with Best Practices to Share 11
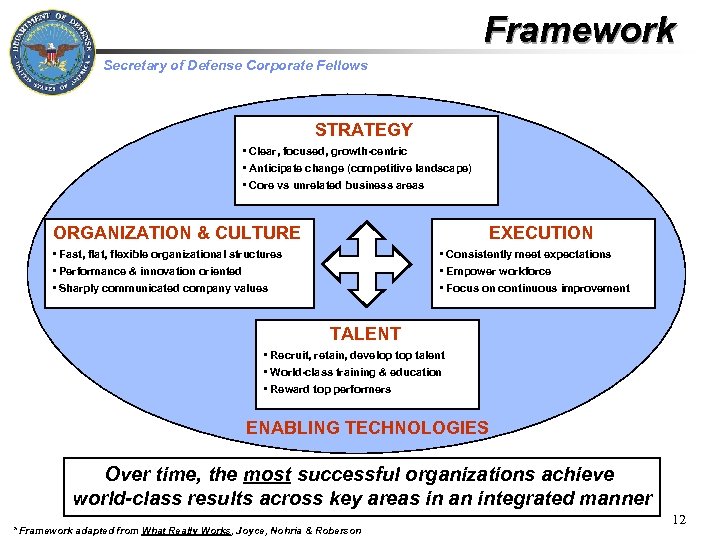 Framework Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows STRATEGY • Clear, focused, growth-centric • Anticipate change (competitive landscape) • Core vs unrelated business areas ORGANIZATION & CULTURE EXECUTION • Fast, flat, flexible organizational structures • Performance & innovation oriented • Sharply communicated company values • Consistently meet expectations • Empower workforce Technology • Focus on continuous improvement TALENT • Recruit, retain, develop talent • World-class training & education • Reward top performers ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES Over time, the most successful organizations achieve world-class results across key areas in an integrated manner * Framework adapted from What Really Works, Joyce, Nohria & Roberson 12
Framework Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows STRATEGY • Clear, focused, growth-centric • Anticipate change (competitive landscape) • Core vs unrelated business areas ORGANIZATION & CULTURE EXECUTION • Fast, flat, flexible organizational structures • Performance & innovation oriented • Sharply communicated company values • Consistently meet expectations • Empower workforce Technology • Focus on continuous improvement TALENT • Recruit, retain, develop talent • World-class training & education • Reward top performers ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES Over time, the most successful organizations achieve world-class results across key areas in an integrated manner * Framework adapted from What Really Works, Joyce, Nohria & Roberson 12
 Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows STRATEGY ORGANIZATION & CULTURE EXECUTION TALENT ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES Where Great Companies Put their Emphasis * Adapted from What Really Works 13
Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows STRATEGY ORGANIZATION & CULTURE EXECUTION TALENT ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES Where Great Companies Put their Emphasis * Adapted from What Really Works 13
 Strategy Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Do. D Relevance – – Increasing customer value in the requirements process Clarifying and focusing the budget cycle Anticipating changes in the security environment Increasing returns on R&D investments • Recommendations - Apply marketing methodologies to requirements development - Manage anticipated changes in the security environment - Review and manage “core” capabilities 14
Strategy Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Do. D Relevance – – Increasing customer value in the requirements process Clarifying and focusing the budget cycle Anticipating changes in the security environment Increasing returns on R&D investments • Recommendations - Apply marketing methodologies to requirements development - Manage anticipated changes in the security environment - Review and manage “core” capabilities 14
 Strategy Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Apply Marketing Methodologies to Requirements Development • Observations – Why Marketing? l l l – Not selling – deciding what to sell to whom Define the business, segment the market, ID target segment, develop value proposition and go-to-market plan Requires & enables true understanding of the customer & competition Industry tools get at “customer value” l l Feature/Benefit/Value relationship Voice of the Customer, Employee Satisfaction, Customer Strategic Review, data analysis tools, application methodology • Do. D should – Apply Marketing methodology to Service Requirements processes • • Understand stakeholder relationships, interdependencies better Increased Requirements specifications fidelity Increase Requirements process value Promote transparency between Services 15
Strategy Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Apply Marketing Methodologies to Requirements Development • Observations – Why Marketing? l l l – Not selling – deciding what to sell to whom Define the business, segment the market, ID target segment, develop value proposition and go-to-market plan Requires & enables true understanding of the customer & competition Industry tools get at “customer value” l l Feature/Benefit/Value relationship Voice of the Customer, Employee Satisfaction, Customer Strategic Review, data analysis tools, application methodology • Do. D should – Apply Marketing methodology to Service Requirements processes • • Understand stakeholder relationships, interdependencies better Increased Requirements specifications fidelity Increase Requirements process value Promote transparency between Services 15
 Strategy Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Manage Anticipated Changes in the Security Environment • Observations – – Corporate mindset to be alert for market transitions Change usually begins on the edges Stable investment streams important Industry moving to outcome based research investment process l l l Interdependent vice individual projects prioritized Business outcome driven ~ effects based decision-making Industries with similar decision criteria benchmarked • Do. D should – – Accommodate Do. D’s broader focus, different time horizon Increase Return on (R & D) Investment (ROI) l l Stay committed to & stabilize long-term R&D funding Apply Marketing processes to ACTD process Apply Six Sigma tools & methodology to R&D investment decision processes Benchmark industry leaders 16
Strategy Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Manage Anticipated Changes in the Security Environment • Observations – – Corporate mindset to be alert for market transitions Change usually begins on the edges Stable investment streams important Industry moving to outcome based research investment process l l l Interdependent vice individual projects prioritized Business outcome driven ~ effects based decision-making Industries with similar decision criteria benchmarked • Do. D should – – Accommodate Do. D’s broader focus, different time horizon Increase Return on (R & D) Investment (ROI) l l Stay committed to & stabilize long-term R&D funding Apply Marketing processes to ACTD process Apply Six Sigma tools & methodology to R&D investment decision processes Benchmark industry leaders 16
 Strategy Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Review & Manage “Core” Capabilities • Observations – Corporations constantly adjust to changing environment l – Leverage transition periods for competitive advantage In-house, outsource, or out-task decisions l l Core or context (relative to business) gap evaluation Mission critical or non-mission critical evaluation • Do. D should – Review Command/Service/Agency capabilities l – Assess processes - core vs context Apply Build/Partner/Acquire decision to core/context evaluation l l l Build to close gaps in core mission critical capabilities Acquire (outsource) non-core where capability exists affordably Partner (out-task) where gaps are common or cost-prohibitive 17
Strategy Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Review & Manage “Core” Capabilities • Observations – Corporations constantly adjust to changing environment l – Leverage transition periods for competitive advantage In-house, outsource, or out-task decisions l l Core or context (relative to business) gap evaluation Mission critical or non-mission critical evaluation • Do. D should – Review Command/Service/Agency capabilities l – Assess processes - core vs context Apply Build/Partner/Acquire decision to core/context evaluation l l l Build to close gaps in core mission critical capabilities Acquire (outsource) non-core where capability exists affordably Partner (out-task) where gaps are common or cost-prohibitive 17
 Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows STRATEGY ORGANIZATION & CULTURE EXECUTION TALENT ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES Where Great Companies Put their Emphasis * Adapted from What Really Works 18
Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows STRATEGY ORGANIZATION & CULTURE EXECUTION TALENT ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES Where Great Companies Put their Emphasis * Adapted from What Really Works 18
 Execution Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Do. D Relevance - Flawless execution = mission success - Supporting troops, meeting needs of combatant commanders - Quest for excellence in all areas – Eliminating waste frees dollars for critical priorities • Recommendations - Improve Information and Supply Chain Management – Adjust Acquisition Reform – Implement process improvement methodology 19
Execution Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Do. D Relevance - Flawless execution = mission success - Supporting troops, meeting needs of combatant commanders - Quest for excellence in all areas – Eliminating waste frees dollars for critical priorities • Recommendations - Improve Information and Supply Chain Management – Adjust Acquisition Reform – Implement process improvement methodology 19
 Execution Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Improve Info and Supply Chain Management • Observations - Ops, Info Management, Supply Chain Management converging • IT no longer a “support tool” - Information is the business • Supply Chain Management vital to operational success • Do. D should - Push convergence - Navy N 6 (C 4 I)/N 7(Requirements) good example Strengthen Do. D CIO’s role Do. D-wide IT architecture stds that encompass entire operational scope Continue Supply Chain improvement implementation • Cross service collaboration of best practices 20
Execution Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Improve Info and Supply Chain Management • Observations - Ops, Info Management, Supply Chain Management converging • IT no longer a “support tool” - Information is the business • Supply Chain Management vital to operational success • Do. D should - Push convergence - Navy N 6 (C 4 I)/N 7(Requirements) good example Strengthen Do. D CIO’s role Do. D-wide IT architecture stds that encompass entire operational scope Continue Supply Chain improvement implementation • Cross service collaboration of best practices 20
 Execution Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Adjust Acquisition Reform • Observations - Corporate America believes Acquisition Reform on track, but… • Pendulum has swung too far in some areas • Do. D should - Make Quality Assurance part of the contract; not assumed • Mandate First Article Inspections and physical configuration audits Both sides determine what is “good enough” • Larger role for DCMA in Tier II/III risk management and quality control Better quality from Subs/Suppliers to Primes - Require subcontractor, supplier management plan from Prime - Continue to foster closer partnerships with industry 21
Execution Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Adjust Acquisition Reform • Observations - Corporate America believes Acquisition Reform on track, but… • Pendulum has swung too far in some areas • Do. D should - Make Quality Assurance part of the contract; not assumed • Mandate First Article Inspections and physical configuration audits Both sides determine what is “good enough” • Larger role for DCMA in Tier II/III risk management and quality control Better quality from Subs/Suppliers to Primes - Require subcontractor, supplier management plan from Prime - Continue to foster closer partnerships with industry 21
 Execution Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Implement Process Improvement Methodology • Observations – Corporations adapt to change in disciplined manner • Common language, common metrics • 4 -6 year commitment required for organizational DNA change – – – Top level support imperative Change driven by change agent teams Annual budget savings of 2– 3 % • Do. D should - Develop / implement a formal process improvement methodology • Dedicated fully resourced effort • Eliminate inefficiencies and improve process quality • Teach in leadership training and at all levels of PME 22
Execution Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Implement Process Improvement Methodology • Observations – Corporations adapt to change in disciplined manner • Common language, common metrics • 4 -6 year commitment required for organizational DNA change – – – Top level support imperative Change driven by change agent teams Annual budget savings of 2– 3 % • Do. D should - Develop / implement a formal process improvement methodology • Dedicated fully resourced effort • Eliminate inefficiencies and improve process quality • Teach in leadership training and at all levels of PME 22
 Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows STRATEGY ORGANIZATION & CULTURE EXECUTION TALENT ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES Where Great Companies Put their Emphasis * Adapted from What Really Works 23
Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows STRATEGY ORGANIZATION & CULTURE EXECUTION TALENT ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES Where Great Companies Put their Emphasis * Adapted from What Really Works 23
 Talent Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Do. D Relevance – – Do. D OPTEMPO can stress service-level manning Do. D must compete for talent with private industry Do. D’s NSPS applies some of private industry’s best practices Private Industry focus on execution is the “bottom line” • Recommendations - Increase leader stability and continuity - Continue focus on leader development - Develop management skills as a core competency 24
Talent Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Do. D Relevance – – Do. D OPTEMPO can stress service-level manning Do. D must compete for talent with private industry Do. D’s NSPS applies some of private industry’s best practices Private Industry focus on execution is the “bottom line” • Recommendations - Increase leader stability and continuity - Continue focus on leader development - Develop management skills as a core competency 24
 Talent Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Increase Leader Stability and Continuity • Observations - CEOs emphasize importance of senior leader commitment to change - Leader continuity is key to winning business strategies of: • Agility and adapting to market place changes • Creating a culture for change and transformation • Constantly communicating organization’s values and vision • Do. D Should - Increase tour lengths for key leaders (military & civilian) - Recognize and reward all players on the team (line & staff) equally - Drive performance improvement for GS ranks • Institutionalize incentives for top performers • Improve or out 25
Talent Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Increase Leader Stability and Continuity • Observations - CEOs emphasize importance of senior leader commitment to change - Leader continuity is key to winning business strategies of: • Agility and adapting to market place changes • Creating a culture for change and transformation • Constantly communicating organization’s values and vision • Do. D Should - Increase tour lengths for key leaders (military & civilian) - Recognize and reward all players on the team (line & staff) equally - Drive performance improvement for GS ranks • Institutionalize incentives for top performers • Improve or out 25
 Talent Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Continue Focus on Leader Development • Observations - Emerging focus in Industry lacks “up or out” pressures Industry constrained by individual mobility options Team based and collaborative across boundaries Often involves mentoring by senior leadership (imprints subordinates) • Do. D should - Partner with Industry for leadership exchanges at junior officer levels Leverage early successes from NSPS across the Services quickly Develop short-duration leader training programs Continue leader development training investment; even during GWOT “We needed to excite the talented middle in our ranks” – 3 M Executive 26
Talent Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Continue Focus on Leader Development • Observations - Emerging focus in Industry lacks “up or out” pressures Industry constrained by individual mobility options Team based and collaborative across boundaries Often involves mentoring by senior leadership (imprints subordinates) • Do. D should - Partner with Industry for leadership exchanges at junior officer levels Leverage early successes from NSPS across the Services quickly Develop short-duration leader training programs Continue leader development training investment; even during GWOT “We needed to excite the talented middle in our ranks” – 3 M Executive 26
 Talent Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Management (not just leadership) a Core Competency • Observations - Corporations emphasize both leadership & management Flawless execution is the key to achieving “bottom line” growth Metrics, process improvement, instrumentation are best practices Do. D emphasizes leadership over management skills…rightly but balance may help • Do. D should - Recognize that both skill sets are complementary Incorporate executive MBA training into existing education programs Outsource management training Build a bench of management excellence outside of acquisition field “What’s important? How well your machine works and how well you relate to others” – Lockheed Executive 27
Talent Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Management (not just leadership) a Core Competency • Observations - Corporations emphasize both leadership & management Flawless execution is the key to achieving “bottom line” growth Metrics, process improvement, instrumentation are best practices Do. D emphasizes leadership over management skills…rightly but balance may help • Do. D should - Recognize that both skill sets are complementary Incorporate executive MBA training into existing education programs Outsource management training Build a bench of management excellence outside of acquisition field “What’s important? How well your machine works and how well you relate to others” – Lockheed Executive 27
 Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows STRATEGY ORGANIZATION & CULTURE EXECUTION TALENT ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES Where Great Companies Put their Emphasis * Adapted from What Really Works 28
Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows STRATEGY ORGANIZATION & CULTURE EXECUTION TALENT ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES Where Great Companies Put their Emphasis * Adapted from What Really Works 28
 Organization & Culture Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Do. D Relevance – – Importance of strong core values Simplify – ability to eliminate redundant organizations Keep raising the bar – reward achievement with praise & pay Harness innovation as catalyst for transformation efforts • Recommendations - Continue strong emphasis on core values - Institutionalize disciplined change management - Drive cost conscious vs. spend culture 29
Organization & Culture Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Do. D Relevance – – Importance of strong core values Simplify – ability to eliminate redundant organizations Keep raising the bar – reward achievement with praise & pay Harness innovation as catalyst for transformation efforts • Recommendations - Continue strong emphasis on core values - Institutionalize disciplined change management - Drive cost conscious vs. spend culture 29
 Organization & Culture Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Continue Strong Emphasis on Core Values • Observations - Pervasive commitment to doing the right thing for customers • Ethical standards, honesty, trust, quality - Dedicated members in our Nation’s defense - Strong commitment to corporate citizenship…globally • Do. D should - Continue strong support to Services for core value efforts • Invest in Do. D’s success, as well as our Nation, by exporting core values • Increase visibility to public sector “There’s never a right way to do something wrong. ” – SRA Int’l Executive 30
Organization & Culture Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Continue Strong Emphasis on Core Values • Observations - Pervasive commitment to doing the right thing for customers • Ethical standards, honesty, trust, quality - Dedicated members in our Nation’s defense - Strong commitment to corporate citizenship…globally • Do. D should - Continue strong support to Services for core value efforts • Invest in Do. D’s success, as well as our Nation, by exporting core values • Increase visibility to public sector “There’s never a right way to do something wrong. ” – SRA Int’l Executive 30
 Organization & Culture Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Institutionalize Disciplined Change Management • Observations - Successful corporations adapt to change • Disciplined part of enterprise processes • Constantly learning at all levels of the organization • Understand remaining static is not an option due to competition - Successful change management requires • People, process, technology…in this order • Leadership commitment & ability to communicate vision & strategy • New approaches anchored in the corporation’s culture • Do. D should - Leverage common Process Improvement methodologies - Continue broad-based improvement actions • Eliminate regulation, policy, organizational, etc. , obstacles - Identify and measure key performance metrics 31
Organization & Culture Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Institutionalize Disciplined Change Management • Observations - Successful corporations adapt to change • Disciplined part of enterprise processes • Constantly learning at all levels of the organization • Understand remaining static is not an option due to competition - Successful change management requires • People, process, technology…in this order • Leadership commitment & ability to communicate vision & strategy • New approaches anchored in the corporation’s culture • Do. D should - Leverage common Process Improvement methodologies - Continue broad-based improvement actions • Eliminate regulation, policy, organizational, etc. , obstacles - Identify and measure key performance metrics 31
 Organization & Culture Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Drive Cost Conscious vs. Spend Culture • Observations - Corporations focus on cost reduction - Process improvement methodology (Lean, Six Sigma) • Lower costs, increased productivity - Performance-based compensation • Tied to increased profits • 10 -60% of total, depending on pay grade • Do. D should - Incentivize commanders at all levels to control costs • Allow unit savings to be used locally - mission, Qo. L, etc. • Unit working capital funds appear a ready-made solution • Goal-based approach most successful -Strategically aligned, clearly communicated, routinely reported - Include cost savings In performance appraisals • Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) when assessing alternatives 32
Organization & Culture Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Drive Cost Conscious vs. Spend Culture • Observations - Corporations focus on cost reduction - Process improvement methodology (Lean, Six Sigma) • Lower costs, increased productivity - Performance-based compensation • Tied to increased profits • 10 -60% of total, depending on pay grade • Do. D should - Incentivize commanders at all levels to control costs • Allow unit savings to be used locally - mission, Qo. L, etc. • Unit working capital funds appear a ready-made solution • Goal-based approach most successful -Strategically aligned, clearly communicated, routinely reported - Include cost savings In performance appraisals • Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) when assessing alternatives 32
 Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows STRATEGY ORGANIZATION & CULTURE EXECUTION TALENT ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES Where Great Companies Put their Emphasis * Adapted from What Really Works 33
Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows STRATEGY ORGANIZATION & CULTURE EXECUTION TALENT ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES Where Great Companies Put their Emphasis * Adapted from What Really Works 33
 Enabling Technologies Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Do. D Relevance – – – Large, diverse enterprises require the right tools IT tools changing work environment, individual expectations Interface with industry/allies requires interoperable IT/other tools • Recommendations - Leverage emerging work-support technologies - Use standard, electronic organizational processes - Optimize facilities for the future environment 34
Enabling Technologies Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Do. D Relevance – – – Large, diverse enterprises require the right tools IT tools changing work environment, individual expectations Interface with industry/allies requires interoperable IT/other tools • Recommendations - Leverage emerging work-support technologies - Use standard, electronic organizational processes - Optimize facilities for the future environment 34
 Enabling Technologies Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Leverage Emerging Work-Support Technologies • Observations - Advanced IT accelerating virtual collaboration, matrixed teams International diversity key to success, yet remains challenging High technology corporations cultivating a culture of empowerment Complete network access driving strong work ethic (50 -80 hrs/wk) • Do. D should - Use mobile/wireless technologies to increase productivity - Adopt telecommuting guidance, virtual collaboration tool standards - Continue transformation to Internet-based solutions 35
Enabling Technologies Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Leverage Emerging Work-Support Technologies • Observations - Advanced IT accelerating virtual collaboration, matrixed teams International diversity key to success, yet remains challenging High technology corporations cultivating a culture of empowerment Complete network access driving strong work ethic (50 -80 hrs/wk) • Do. D should - Use mobile/wireless technologies to increase productivity - Adopt telecommuting guidance, virtual collaboration tool standards - Continue transformation to Internet-based solutions 35
 Enabling Technologies Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Use Standard, Electronic Organizational Processes • Observations - Several high tech corporations have made transition to “paperless” - Strong productivity gains by developing paperless processes • Not just duplicating paper forms on-line - Broad application to operational and support organizations • Travel planning, reservations, vouchers, etc. • Human Resource activities (job openings, performance ratings) • Meeting scheduling, agendas, conduct, follow-up • Do. D should - Implement paperless processes wherever possible - Implement virtual, collaborative processes • Process first, then technology solution “If it isn’t on the web, people don’t take it seriously…” – Cisco Sr. Director 36
Enabling Technologies Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Use Standard, Electronic Organizational Processes • Observations - Several high tech corporations have made transition to “paperless” - Strong productivity gains by developing paperless processes • Not just duplicating paper forms on-line - Broad application to operational and support organizations • Travel planning, reservations, vouchers, etc. • Human Resource activities (job openings, performance ratings) • Meeting scheduling, agendas, conduct, follow-up • Do. D should - Implement paperless processes wherever possible - Implement virtual, collaborative processes • Process first, then technology solution “If it isn’t on the web, people don’t take it seriously…” – Cisco Sr. Director 36
 Enabling Technologies Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Optimize Facilities for the Future Environment • Observations - Fusion of wireless voice, data, & video; collaborative workspaces • Drives more careful facilities management - Creative workspaces can increase productivity, generate savings • Small mobile team concepts • Do. D should - Ensure facilities planning includes entire requirements spectrum • Present and future; especially communications and power - Implement flexible workspace utilization modes • Small team staff and back office organizations - Acquisition offices, PME, headquarters staff, etc. 37
Enabling Technologies Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Optimize Facilities for the Future Environment • Observations - Fusion of wireless voice, data, & video; collaborative workspaces • Drives more careful facilities management - Creative workspaces can increase productivity, generate savings • Small mobile team concepts • Do. D should - Ensure facilities planning includes entire requirements spectrum • Present and future; especially communications and power - Implement flexible workspace utilization modes • Small team staff and back office organizations - Acquisition offices, PME, headquarters staff, etc. 37
 Enabling Technologies Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Specific Technological Opportunities • • Advanced Video Conferencing Technology Natural Language Processing Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Internet Protocols – – • • • Voice Over IP (VOIP) Blackberry wireless VOIP Identity Management Hyperspectral imagery Storage Area Networking (SAN) Broadband into the home Instant Messaging / Chat Virtual Modeling and Simulation e. Paper Multi-layer film Laser protection Electronic Dashboard (for metrics measuring) 38
Enabling Technologies Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Specific Technological Opportunities • • Advanced Video Conferencing Technology Natural Language Processing Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Internet Protocols – – • • • Voice Over IP (VOIP) Blackberry wireless VOIP Identity Management Hyperspectral imagery Storage Area Networking (SAN) Broadband into the home Instant Messaging / Chat Virtual Modeling and Simulation e. Paper Multi-layer film Laser protection Electronic Dashboard (for metrics measuring) 38
 Summary of Recommendations Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Strategy - Apply marketing methodologies to requirements development - Manage anticipated changes in the security environment - Review and manage “core” capabilities • Execution – – – Improve Information and Supply Chain Management Adjust Acquisition Reform Implement process improvement methodology • Talent - Increase leader stability and continuity - Continue focus on leader development - Management (not just leadership) is a core competency 39
Summary of Recommendations Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Strategy - Apply marketing methodologies to requirements development - Manage anticipated changes in the security environment - Review and manage “core” capabilities • Execution – – – Improve Information and Supply Chain Management Adjust Acquisition Reform Implement process improvement methodology • Talent - Increase leader stability and continuity - Continue focus on leader development - Management (not just leadership) is a core competency 39
 Summary of Recommendations Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Organization & Culture - Continue strong emphasis on core values - Institutionalize disciplined change management - Drive cost conscious vs. spend culture • Enabling Technologies - Leverage emerging work-support technologies - Use standard, electronic organizational processes - Optimize facilities for the future environment 40
Summary of Recommendations Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Organization & Culture - Continue strong emphasis on core values - Institutionalize disciplined change management - Drive cost conscious vs. spend culture • Enabling Technologies - Leverage emerging work-support technologies - Use standard, electronic organizational processes - Optimize facilities for the future environment 40
 Agenda Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Background • Common Findings/Recommendations • Individual Experiences (time permitting) 41
Agenda Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Background • Common Findings/Recommendations • Individual Experiences (time permitting) 41
 Lockheed Martin Corporation Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • World's largest defense contractor – – – 132 K employees (85 K scientists and engineers) $35. 5 B 2004 sales, $73 B backlog, $2. 9 B cash Main business segments l Aeronautics, Electronic Systems, Space Systems, Integrated Systems and Solutions, and Information &Technology Services • Corporate Strategy: Disciplined growth to increase shareholder value – – – Operational performance and customer satisfaction as top priorities Consistent financial performance including strong cash flow Focus on profitable growth in core markets (DOD, Homeland Security, IT) • Assignment: President, Missiles and Fire Control business area – Strategic plans and PAC-3 program office 42
Lockheed Martin Corporation Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • World's largest defense contractor – – – 132 K employees (85 K scientists and engineers) $35. 5 B 2004 sales, $73 B backlog, $2. 9 B cash Main business segments l Aeronautics, Electronic Systems, Space Systems, Integrated Systems and Solutions, and Information &Technology Services • Corporate Strategy: Disciplined growth to increase shareholder value – – – Operational performance and customer satisfaction as top priorities Consistent financial performance including strong cash flow Focus on profitable growth in core markets (DOD, Homeland Security, IT) • Assignment: President, Missiles and Fire Control business area – Strategic plans and PAC-3 program office 42
 Observations (LM) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • LM employees: Dedicated members in our nation’s defense • Strategy: Clearly stated & focused on customer value – IR&D, Shared Vision, Lab insertion • Execution: Flawless operational execution – Executive leadership Council, rigorous metrics, cost consciousness, – Lean/Six Sigma • Culture: Performance based, firm commitments, ethical • Structure: Matrix org -- Fast, flexible, and flat • People: recruit, retain, reward, and develop leaders – Intern program, development programs, pay linked to performance • Innovation: 30% IR&D invested in new tech -- passion for invention 43
Observations (LM) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • LM employees: Dedicated members in our nation’s defense • Strategy: Clearly stated & focused on customer value – IR&D, Shared Vision, Lab insertion • Execution: Flawless operational execution – Executive leadership Council, rigorous metrics, cost consciousness, – Lean/Six Sigma • Culture: Performance based, firm commitments, ethical • Structure: Matrix org -- Fast, flexible, and flat • People: recruit, retain, reward, and develop leaders – Intern program, development programs, pay linked to performance • Innovation: 30% IR&D invested in new tech -- passion for invention 43
 Recommendations (LM) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • • • Ensure sufficient funds for Contract R&D through labs, DARPA Review core competencies and reduce duplication and redundancy Continue to aggressively pursue outsourcing opportunities Implement a formal process for process improvement Management skills are as important as leadership skills – Incorporate executive MBA training in our PME • Encourage commanders to save resources and manpower – – Provide incentives to save $$$ and measure on performance reports Transform from a spend culture to a cost conscious culture • Institute a formal mentorship program for scientists and engineers • Focus on stabilizing key leadership positions to drive transformation 44
Recommendations (LM) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • • • Ensure sufficient funds for Contract R&D through labs, DARPA Review core competencies and reduce duplication and redundancy Continue to aggressively pursue outsourcing opportunities Implement a formal process for process improvement Management skills are as important as leadership skills – Incorporate executive MBA training in our PME • Encourage commanders to save resources and manpower – – Provide incentives to save $$$ and measure on performance reports Transform from a spend culture to a cost conscious culture • Institute a formal mentorship program for scientists and engineers • Focus on stabilizing key leadership positions to drive transformation 44
 DOD Acquisition Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Program stability is key to delivering a successful program • Acquisition reform receives high marks but need to add: – Physical Configuration Audits and First Article Inspections – Improve communication w/ industry while protecting proprietary data • Knowledge Transfer major issue with ageing workforce • Supplier base demands a great deal of LM’s attention – COTS, parts obsolescence, quality controls create supplier issues – Make subcontractor and supplier management plan part of bid • Benchmark DCMA’s risk assessment for LMMFC programs 45
DOD Acquisition Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Program stability is key to delivering a successful program • Acquisition reform receives high marks but need to add: – Physical Configuration Audits and First Article Inspections – Improve communication w/ industry while protecting proprietary data • Knowledge Transfer major issue with ageing workforce • Supplier base demands a great deal of LM’s attention – COTS, parts obsolescence, quality controls create supplier issues – Make subcontractor and supplier management plan part of bid • Benchmark DCMA’s risk assessment for LMMFC programs 45
 3 M Company Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Innovative Diversified Technology company – – – Revenues $20. 1 B (61% international) 67 K employees (51% international) Operations in 60+ countries; products sold in 200+ • Seven businesses; 40 units – – – – Health Care Industrial Display and Graphics Consumer and Office Electro and Communications Safety, Security, and Protection Services Transportation • Corporate Strategy Delivering solid, consistent profit growth, driven by organic top-line growth and continuous improvements in operational efficiency • Assignment - Six Sigma Operations – Black Belt, Master Black Belt, Design for Six Sigma Champion 46
3 M Company Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Innovative Diversified Technology company – – – Revenues $20. 1 B (61% international) 67 K employees (51% international) Operations in 60+ countries; products sold in 200+ • Seven businesses; 40 units – – – – Health Care Industrial Display and Graphics Consumer and Office Electro and Communications Safety, Security, and Protection Services Transportation • Corporate Strategy Delivering solid, consistent profit growth, driven by organic top-line growth and continuous improvements in operational efficiency • Assignment - Six Sigma Operations – Black Belt, Master Black Belt, Design for Six Sigma Champion 46
 Observations (3 M) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Six Sigma driving results in cost, cash, growth – Common language, established channels, measured performance • Aggressive business initiatives optimize processes – – – Six Sigma e-Productivity Global Sourcing Global Business Processes 3 M Acceleration $1. 7 B combined Operating Income impact of five initiatives sinception • Entrepreneurial Leadership – – Utilizing Six Sigma and leadership development opportunities Performance management focus Stretch assignments Top management engagement in growth 47
Observations (3 M) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Six Sigma driving results in cost, cash, growth – Common language, established channels, measured performance • Aggressive business initiatives optimize processes – – – Six Sigma e-Productivity Global Sourcing Global Business Processes 3 M Acceleration $1. 7 B combined Operating Income impact of five initiatives sinception • Entrepreneurial Leadership – – Utilizing Six Sigma and leadership development opportunities Performance management focus Stretch assignments Top management engagement in growth 47
 Recommendations (3 M) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Deploy a Do. D process improvement discipline similar to Six Sigma – – – Top level support Beware superficially applied, under-resourced “quality programs” Common language, common metrics • Leverage Do. D size in “back room” processes • Incorporate Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology – – Where 100% accountability is critical Medical, Personal Reliability Program (PRP), logistics, intel • Partner with the services to provide comprehensive DOD solution to protecting cockpits, tanks, and vehicles with multi-layer film to protect eyes from outside lasers • Consider synergy of establishing joint labs, acquisition offices, joint requirements offices, joint research and development organizations 48
Recommendations (3 M) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Deploy a Do. D process improvement discipline similar to Six Sigma – – – Top level support Beware superficially applied, under-resourced “quality programs” Common language, common metrics • Leverage Do. D size in “back room” processes • Incorporate Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology – – Where 100% accountability is critical Medical, Personal Reliability Program (PRP), logistics, intel • Partner with the services to provide comprehensive DOD solution to protecting cockpits, tanks, and vehicles with multi-layer film to protect eyes from outside lasers • Consider synergy of establishing joint labs, acquisition offices, joint requirements offices, joint research and development organizations 48
 Honeywell International Inc. Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Fortune 100 Company – – – $25 B sales, $31 B market capitalization 108 K employees in nearly 100 countries Business segments l l • Corporate Strategy – “Five Initiatives” to drive success – – Growth, Productivity, Cash, People, Enablers (Digital. Works & 6 +) Principal interrelated key processes l l l • Aerospace Automation and Control Solutions Transportation Systems Specialty Materials Strategic Planning Process (STRAP) for direction Annual Operating Plan (AOP) for budget Management Resource Review (MRR) for people Assignment - Honeywell Technology Solutions, Inc (HTSI) – – Aerospace Sector, Aerospace Electronic Systems Business Development & Military Segment 49
Honeywell International Inc. Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Fortune 100 Company – – – $25 B sales, $31 B market capitalization 108 K employees in nearly 100 countries Business segments l l • Corporate Strategy – “Five Initiatives” to drive success – – Growth, Productivity, Cash, People, Enablers (Digital. Works & 6 +) Principal interrelated key processes l l l • Aerospace Automation and Control Solutions Transportation Systems Specialty Materials Strategic Planning Process (STRAP) for direction Annual Operating Plan (AOP) for budget Management Resource Review (MRR) for people Assignment - Honeywell Technology Solutions, Inc (HTSI) – – Aerospace Sector, Aerospace Electronic Systems Business Development & Military Segment 49
 Observations (Honeywell) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • History and heritage – – • Globalization – • Engineering, HR, IT, Program Management, Supply Chain Marketing Transformation – • Expanding overseas, going where the customers are Functionalization – • Allied. Signal & Honeywell merger New CEO in 2002 brought Five Initiatives Deeper understanding of customers & competitors HTSI – – – Focusing on growth Organizational realignment Government Services division of a product-centric company l Return on Investment (ROI) vs. Return on Sales (ROS) 50
Observations (Honeywell) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • History and heritage – – • Globalization – • Engineering, HR, IT, Program Management, Supply Chain Marketing Transformation – • Expanding overseas, going where the customers are Functionalization – • Allied. Signal & Honeywell merger New CEO in 2002 brought Five Initiatives Deeper understanding of customers & competitors HTSI – – – Focusing on growth Organizational realignment Government Services division of a product-centric company l Return on Investment (ROI) vs. Return on Sales (ROS) 50
 Observations (Honeywell) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Honeywell (Allied. Signal) leader of Six Sigma – – – Senior leadership buy-in Across entire business (organization) Dedicated resources Best people in Six Sigma billets Efforts linked to critical needs 6 + includes Six Sigma, Lean, Design for Six Sigma • Functionalization key to flattening the organization • Key issues for Honeywell / HTSI – Driving profitable growth l – Integrating the sectors, segments and businesses l – Changing environment Cross-Honeywell strategy, product pull-through, joint initiatives Mindset l l Conservative approach Prime or sub dilemma 51
Observations (Honeywell) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Honeywell (Allied. Signal) leader of Six Sigma – – – Senior leadership buy-in Across entire business (organization) Dedicated resources Best people in Six Sigma billets Efforts linked to critical needs 6 + includes Six Sigma, Lean, Design for Six Sigma • Functionalization key to flattening the organization • Key issues for Honeywell / HTSI – Driving profitable growth l – Integrating the sectors, segments and businesses l – Changing environment Cross-Honeywell strategy, product pull-through, joint initiatives Mindset l l Conservative approach Prime or sub dilemma 51
 SRA International Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • A Fortune “ 100 Best Company to Work For” - Winner for last 6 years; 4, 100 employees nation-wide - 2004 Revenues: $615 M / 2005 Projected: $850 M - Growth from 2003 to 2004: 49% - Company founded by a Mc. Namara Whiz Kid (USAF Colonel) • Corporate Strategy - Provide IT Services & Solutions to Federal Government only - 65% Do. D/DHS; 35% Civil Government - Hire employees “for a career” - Innovation in C 3 I and Data/Text mining • Assignment - Defense Sector x 3 months (Business Unit / Project Level) - Civil Sector x 5 months (Sector / Senior VP level) 52
SRA International Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • A Fortune “ 100 Best Company to Work For” - Winner for last 6 years; 4, 100 employees nation-wide - 2004 Revenues: $615 M / 2005 Projected: $850 M - Growth from 2003 to 2004: 49% - Company founded by a Mc. Namara Whiz Kid (USAF Colonel) • Corporate Strategy - Provide IT Services & Solutions to Federal Government only - 65% Do. D/DHS; 35% Civil Government - Hire employees “for a career” - Innovation in C 3 I and Data/Text mining • Assignment - Defense Sector x 3 months (Business Unit / Project Level) - Civil Sector x 5 months (Sector / Senior VP level) 52
 Observations (SRA) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Corporate Strategy working thru… - Selective acquisitions based on “values”; not just “of value” - Internal investments in explosive external growth - Development of horizontal expertise to increase agility - Persistent and insistent adherence to SRA Culture & Values • Corporate Execution focused on… - Genuine desire to add value for the customer…ethically - Reaching for higher purpose goals (national interests) - Caring for their people who provide the “services” • Evidence? - 80% win rate on new contracts; 90% on re-competes - Less than 12% personnel turn-over rate - Demonstrated willingness to “invest $” to maintain customer satisfaction - Employee incentives found at all levels of the company 53
Observations (SRA) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Corporate Strategy working thru… - Selective acquisitions based on “values”; not just “of value” - Internal investments in explosive external growth - Development of horizontal expertise to increase agility - Persistent and insistent adherence to SRA Culture & Values • Corporate Execution focused on… - Genuine desire to add value for the customer…ethically - Reaching for higher purpose goals (national interests) - Caring for their people who provide the “services” • Evidence? - 80% win rate on new contracts; 90% on re-competes - Less than 12% personnel turn-over rate - Demonstrated willingness to “invest $” to maintain customer satisfaction - Employee incentives found at all levels of the company 53
 Recommendations (SRA) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Transformation - Change is occurring and will continue in Do. D - Rapid change requires incentives - Effective change requires focus • Industry focuses on… - Helping Do. D identify its requirements and solutions - Incentives for their people - Being agile and responsive - Investment in internal growth and processes • What can or should Do. D learn from industry? - Investments in people + Incentives for people = Rapid Transformation 54
Recommendations (SRA) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Transformation - Change is occurring and will continue in Do. D - Rapid change requires incentives - Effective change requires focus • Industry focuses on… - Helping Do. D identify its requirements and solutions - Incentives for their people - Being agile and responsive - Investment in internal growth and processes • What can or should Do. D learn from industry? - Investments in people + Incentives for people = Rapid Transformation 54
 Cisco Systems Inc. Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Global leader in Internet innovation, equipment, services – – Revenue $23 B; profit $15 B (+ $6. 8 B cash) Market Capitalization $132 B (2: 1 WRT top 11 competitors combined) 35 K employees worldwide ($657 K profit/employee) Primary business segments l l l Core - routers & switches Advanced Technologies - Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP), optical, wireless, etc Service Provider - tech support, manufacturing, training, etc • Corporate Vision - “Changing the way we work, live, play and learn” – – – Unprecedented value & opportunity - Cisco synonymous with productivity Customer partner status - technology + business success = trust Network evolution leader - End-to-End Net of Nets Intelligent Network Expand, grow Advanced Technologies - 4 new business areas $2 B, 8 $1 B Drive quality, security, systems, processes into culture • Assignment: IT/Infrastructure Business Practices – – Program management improvements Strategic planning initiatives 55
Cisco Systems Inc. Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Global leader in Internet innovation, equipment, services – – Revenue $23 B; profit $15 B (+ $6. 8 B cash) Market Capitalization $132 B (2: 1 WRT top 11 competitors combined) 35 K employees worldwide ($657 K profit/employee) Primary business segments l l l Core - routers & switches Advanced Technologies - Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP), optical, wireless, etc Service Provider - tech support, manufacturing, training, etc • Corporate Vision - “Changing the way we work, live, play and learn” – – – Unprecedented value & opportunity - Cisco synonymous with productivity Customer partner status - technology + business success = trust Network evolution leader - End-to-End Net of Nets Intelligent Network Expand, grow Advanced Technologies - 4 new business areas $2 B, 8 $1 B Drive quality, security, systems, processes into culture • Assignment: IT/Infrastructure Business Practices – – Program management improvements Strategic planning initiatives 55
 Observations (Cisco) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Strategy: Pioneer use of Internet for all business activities – – Generate 95+% of sales via www. cisco. com website ($40 K/minute) Showcase internal IT Internet solutions revenue generation • Execution: Build, acquire, partner – – Leader in business acquisition 90+ companies in last 10 yrs ~1, 000 new employees/month over 3 yr period in late ‘ 90 s • Organization: Empowerment via virtual collaboration, matrixed teams – – International diversity key to success; remains challenging Reward success (top 20%) Aggressively manage poor performance (bottom 5%) Actively build consensus (recurring 1: 1 s); use 360 degree feedback sessions • Culture: Intense organizational commitment to “Cisco Culture” – – Customer success, innovation, stretch goals, integrity, corporate citizenship Complete network access drives strong work ethic (50 -80 hrs/wk typical) 56
Observations (Cisco) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Strategy: Pioneer use of Internet for all business activities – – Generate 95+% of sales via www. cisco. com website ($40 K/minute) Showcase internal IT Internet solutions revenue generation • Execution: Build, acquire, partner – – Leader in business acquisition 90+ companies in last 10 yrs ~1, 000 new employees/month over 3 yr period in late ‘ 90 s • Organization: Empowerment via virtual collaboration, matrixed teams – – International diversity key to success; remains challenging Reward success (top 20%) Aggressively manage poor performance (bottom 5%) Actively build consensus (recurring 1: 1 s); use 360 degree feedback sessions • Culture: Intense organizational commitment to “Cisco Culture” – – Customer success, innovation, stretch goals, integrity, corporate citizenship Complete network access drives strong work ethic (50 -80 hrs/wk typical) 56
 Recommendations (Cisco) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Continue transformation to Internet-based business solutions – – – Leverage corporate investment in robust IT foundation & lessons learned Virtual collaboration holds potential for rapid change at all levels Drive towards increased info accessibility/availability l Balance with info security • Strengthen (potentially elevate) CIO role within Do. D organization – – – Enable stronger partnerships with tech industry leaders Provide focal point for spending authority, interoperability, standardization Potential to leverage lower cost, overseas solutions l Balance with procurement regulations, security, Congressional oversight • Assess benefit of proactively identifying/separating low performers – – Build strong incentives for higher performance Additional tool to manage reductions in force when required 57
Recommendations (Cisco) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Continue transformation to Internet-based business solutions – – – Leverage corporate investment in robust IT foundation & lessons learned Virtual collaboration holds potential for rapid change at all levels Drive towards increased info accessibility/availability l Balance with info security • Strengthen (potentially elevate) CIO role within Do. D organization – – – Enable stronger partnerships with tech industry leaders Provide focal point for spending authority, interoperability, standardization Potential to leverage lower cost, overseas solutions l Balance with procurement regulations, security, Congressional oversight • Assess benefit of proactively identifying/separating low performers – – Build strong incentives for higher performance Additional tool to manage reductions in force when required 57
 Hewlett-Packard Company Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows l World’s leading consumer and small/med business IT company – $80 B Sales (#11 on Fortune 500) 152 K employees worldwide – Business segments – Imaging & Printing l Personal Computing l Enterprise Systems l HP Services l l Corporate strategy - Increase value through growth & innovation “Reliable innovation at a price our customers can afford, delivered with an experience that sets us apart. We deliver high tech, low cost and best customer experience” ● Assignment - VP Federal Sales 58
Hewlett-Packard Company Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows l World’s leading consumer and small/med business IT company – $80 B Sales (#11 on Fortune 500) 152 K employees worldwide – Business segments – Imaging & Printing l Personal Computing l Enterprise Systems l HP Services l l Corporate strategy - Increase value through growth & innovation “Reliable innovation at a price our customers can afford, delivered with an experience that sets us apart. We deliver high tech, low cost and best customer experience” ● Assignment - VP Federal Sales 58
 Observations (HP) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Much of the “HP Way” remains intact – – Left to themselves, employees will do the right thing Departure of CEO Fiorina had cultural overtones • Similar to US Services – – Size, worldwide reach, team diversity Challenges l l l Employee integration Team building Communication and horizontal integration • Acquisition of Compaq – Resembles integration of US Services in joint environment l CNO has had this discussion with HP CEO 59
Observations (HP) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Much of the “HP Way” remains intact – – Left to themselves, employees will do the right thing Departure of CEO Fiorina had cultural overtones • Similar to US Services – – Size, worldwide reach, team diversity Challenges l l l Employee integration Team building Communication and horizontal integration • Acquisition of Compaq – Resembles integration of US Services in joint environment l CNO has had this discussion with HP CEO 59
 Observations (HP) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows l Commitment to doing the right thing for the customer is pervasive – Historically, no aggressive lobbying or direct attacks l Share of direct business with Do. D relatively small – Plan for public sector growth being debated internally l Strong commitment to global citizenship – l More than traditional philanthropy (not just writing checks) New CEO is much more hands-on, operationally oriented – Well-received by analyst community and by employees 60
Observations (HP) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows l Commitment to doing the right thing for the customer is pervasive – Historically, no aggressive lobbying or direct attacks l Share of direct business with Do. D relatively small – Plan for public sector growth being debated internally l Strong commitment to global citizenship – l More than traditional philanthropy (not just writing checks) New CEO is much more hands-on, operationally oriented – Well-received by analyst community and by employees 60
 Caterpillar Inc. Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • World’s largest heavy equipment producer – – – • Heart of Illinois - Peoria – – – • $30. 25 B sales; $2. 03 B profits 77 K + employees (38 K U. S. ); 198 dealers worldwide Main business segments: Machinery, Engines, Financial Products Professional corporate culture – – – • Construction equipment Mining equipment Natural gas engines Industrial gas turbines Diesel engines Steeped in Midwestern values; grows own leaders Positive work environment - trust, quality, community involvement Ethical standards and honesty in dealing with customers Assignment – CAT Logistics VP, Human Resources Division l – Strategic projects in leadership training, recruitment, employment, retention Operations Area next 61
Caterpillar Inc. Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • World’s largest heavy equipment producer – – – • Heart of Illinois - Peoria – – – • $30. 25 B sales; $2. 03 B profits 77 K + employees (38 K U. S. ); 198 dealers worldwide Main business segments: Machinery, Engines, Financial Products Professional corporate culture – – – • Construction equipment Mining equipment Natural gas engines Industrial gas turbines Diesel engines Steeped in Midwestern values; grows own leaders Positive work environment - trust, quality, community involvement Ethical standards and honesty in dealing with customers Assignment – CAT Logistics VP, Human Resources Division l – Strategic projects in leadership training, recruitment, employment, retention Operations Area next 61
 Observations (CAT) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Cat employees - dedicated, innovative and professional. – Relationship with company characterized as “Partnership”; Very Patriotic • Strategy - articulated top down; executed bottom up – Focused on 3 Ps l Profitable growth, Performance through Six Sigma and People • Execution: Operational excellence in all areas – Involved senior leadership • Professional corporate culture – – Positive work environment-trust, quality, community involvement Ethical standards and honesty in dealing with each other and customers • Structure - Matrix org w/ 26 business units • People – Diversity focused; getting “right people on the bus” is corporate critical success factor 62
Observations (CAT) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Cat employees - dedicated, innovative and professional. – Relationship with company characterized as “Partnership”; Very Patriotic • Strategy - articulated top down; executed bottom up – Focused on 3 Ps l Profitable growth, Performance through Six Sigma and People • Execution: Operational excellence in all areas – Involved senior leadership • Professional corporate culture – – Positive work environment-trust, quality, community involvement Ethical standards and honesty in dealing with each other and customers • Structure - Matrix org w/ 26 business units • People – Diversity focused; getting “right people on the bus” is corporate critical success factor 62
 Recommendations (CAT) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Deploy Six Sigma or similar process improvement methodology for elimination of inefficiencies and process quality improvements • Conducted “top to bottom” force structure review to ensure we are getting right people with rights skills to meet future challenges • Conduct comprehensive pay study to close pay gap with civilian sector • Restructure benefit packages • Adapt Shared Services Model; focus on core functions/enablers • Conduct study to assess implementing Behavior Based Safety Methodology 63
Recommendations (CAT) Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows • Deploy Six Sigma or similar process improvement methodology for elimination of inefficiencies and process quality improvements • Conducted “top to bottom” force structure review to ensure we are getting right people with rights skills to meet future challenges • Conduct comprehensive pay study to close pay gap with civilian sector • Restructure benefit packages • Adapt Shared Services Model; focus on core functions/enablers • Conduct study to assess implementing Behavior Based Safety Methodology 63
 Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Backup 64
Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Backup 64
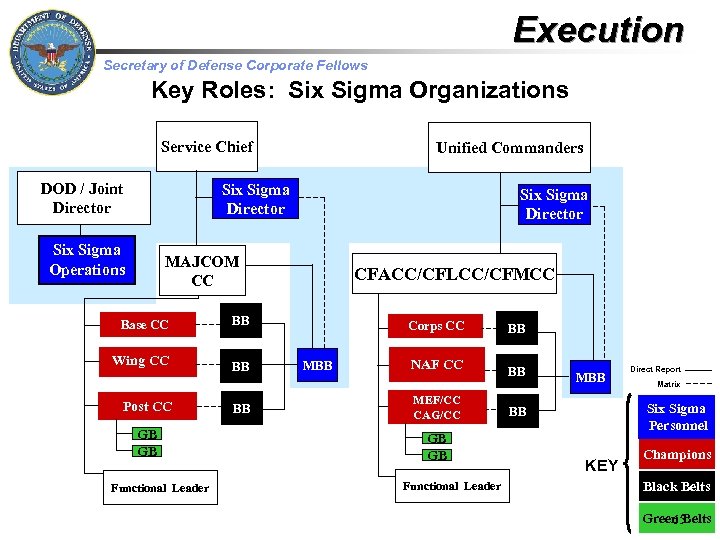 Execution Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Key Roles: Six Sigma Organizations Service Chief DOD / Joint Director Unified Commanders Six Sigma Director Six Sigma Operations Six Sigma Director MAJCOM CC Base CC BB Wing CC BB CFACC/CFLCC/CFMCC Post CC GB GB Functional Leader BB Corps CC MBB BB NAF CC BB MEF/CC CAG/CC GB GB Functional Leader MBB Direct Report Matrix Sigma Personnel BB KEY Champions Black Belts Green Belts 65
Execution Secretary of Defense Corporate Fellows Key Roles: Six Sigma Organizations Service Chief DOD / Joint Director Unified Commanders Six Sigma Director Six Sigma Operations Six Sigma Director MAJCOM CC Base CC BB Wing CC BB CFACC/CFLCC/CFMCC Post CC GB GB Functional Leader BB Corps CC MBB BB NAF CC BB MEF/CC CAG/CC GB GB Functional Leader MBB Direct Report Matrix Sigma Personnel BB KEY Champions Black Belts Green Belts 65


