parkinson.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 14
 SECHENOV FIRST MOSCOW STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF FOREIGN LANGUAGES Professional Communication Programme Parkinson's disease By forth-year student of farmacy Vladykova Kate
SECHENOV FIRST MOSCOW STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF FOREIGN LANGUAGES Professional Communication Programme Parkinson's disease By forth-year student of farmacy Vladykova Kate
 INTRODUCTION The history of Parkinson's disease expands from 1817, when British apothecary James Parkinson published An Essay on the Shaking Palsy, to modern times.
INTRODUCTION The history of Parkinson's disease expands from 1817, when British apothecary James Parkinson published An Essay on the Shaking Palsy, to modern times.
 INTRODUCTION Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic progressive neurodegenerative movement disorder characterized by a profound and selective loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons.
INTRODUCTION Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic progressive neurodegenerative movement disorder characterized by a profound and selective loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons.
 Signs of Parkinson’s disease Primary motor signs of Parkinson’s disease include the following: • tremor of the hands, arms, legs, jaw and face • bradykinesia or slowness of movement • rigidity or stiffness of the limbs and trunk • postural instability or impaired balance and coordination
Signs of Parkinson’s disease Primary motor signs of Parkinson’s disease include the following: • tremor of the hands, arms, legs, jaw and face • bradykinesia or slowness of movement • rigidity or stiffness of the limbs and trunk • postural instability or impaired balance and coordination
 TREATMENT Parkinson's disease can't be cured, but medications can help control your symptoms, often effective. In some later cases, surgery may be advised.
TREATMENT Parkinson's disease can't be cured, but medications can help control your symptoms, often effective. In some later cases, surgery may be advised.
 MEDICATIONS Levodopa, the most effective Parkinson's disease medication, is a natural chemical that passes into your brain and is converted to dopamine.
MEDICATIONS Levodopa, the most effective Parkinson's disease medication, is a natural chemical that passes into your brain and is converted to dopamine.
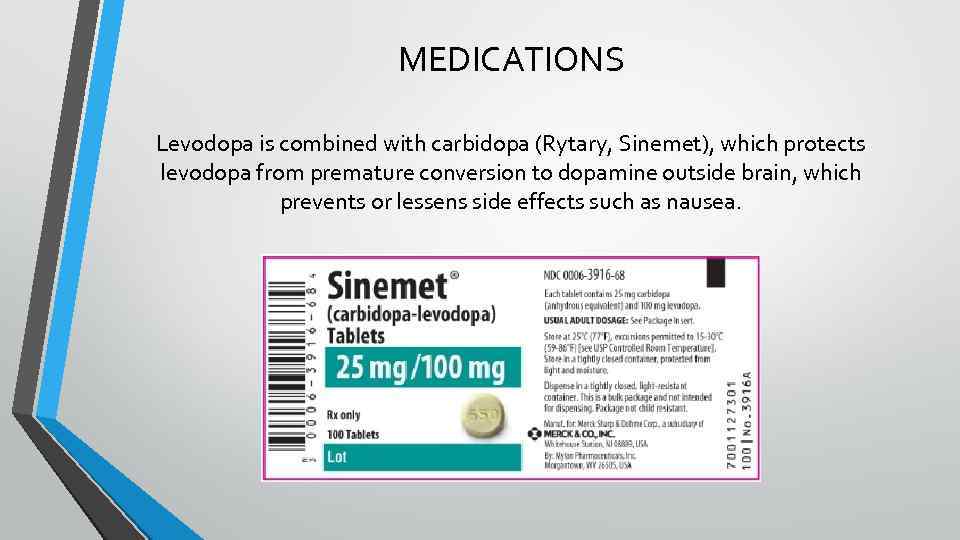 MEDICATIONS Levodopa is combined with carbidopa (Rytary, Sinemet), which protects levodopa from premature conversion to dopamine outside brain, which prevents or lessens side effects such as nausea.
MEDICATIONS Levodopa is combined with carbidopa (Rytary, Sinemet), which protects levodopa from premature conversion to dopamine outside brain, which prevents or lessens side effects such as nausea.
 MEDICATIONS Dopamine agonists • Unlike levodopa, dopamine agonists don't change into dopamine. Instead, they mimic dopamine effects in brain. • They aren't as effective as levodopa in treating symptoms. However, they last longer and may be used with levodopa to smooth the sometimes offand-on effect of levodopa.
MEDICATIONS Dopamine agonists • Unlike levodopa, dopamine agonists don't change into dopamine. Instead, they mimic dopamine effects in brain. • They aren't as effective as levodopa in treating symptoms. However, they last longer and may be used with levodopa to smooth the sometimes offand-on effect of levodopa.
 MEDICATIONS Anticholinergics • These medications were used for many years to help control the tremor associated with Parkinson's disease. Several anticholinergic medications are available, including benztropine (Cogentin) or trihexyphenidyl. • However, their modest benefits are often offset by side effects such as impaired memory, confusion, hallucinations, constipation, dry mouth and impaired urination.
MEDICATIONS Anticholinergics • These medications were used for many years to help control the tremor associated with Parkinson's disease. Several anticholinergic medications are available, including benztropine (Cogentin) or trihexyphenidyl. • However, their modest benefits are often offset by side effects such as impaired memory, confusion, hallucinations, constipation, dry mouth and impaired urination.
 MEDICATIONS Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors • Entacapone (Comtan) is the primary medication from this class. This medication mildly prolongs the effect of levodopa therapy by blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine. • Side effects, including an increased risk of involuntary movements (dyskinesias), mainly result from an enhanced levodopa effect. Other side effects include diarrhea or other enhanced levodopa side effects.
MEDICATIONS Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors • Entacapone (Comtan) is the primary medication from this class. This medication mildly prolongs the effect of levodopa therapy by blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine. • Side effects, including an increased risk of involuntary movements (dyskinesias), mainly result from an enhanced levodopa effect. Other side effects include diarrhea or other enhanced levodopa side effects.
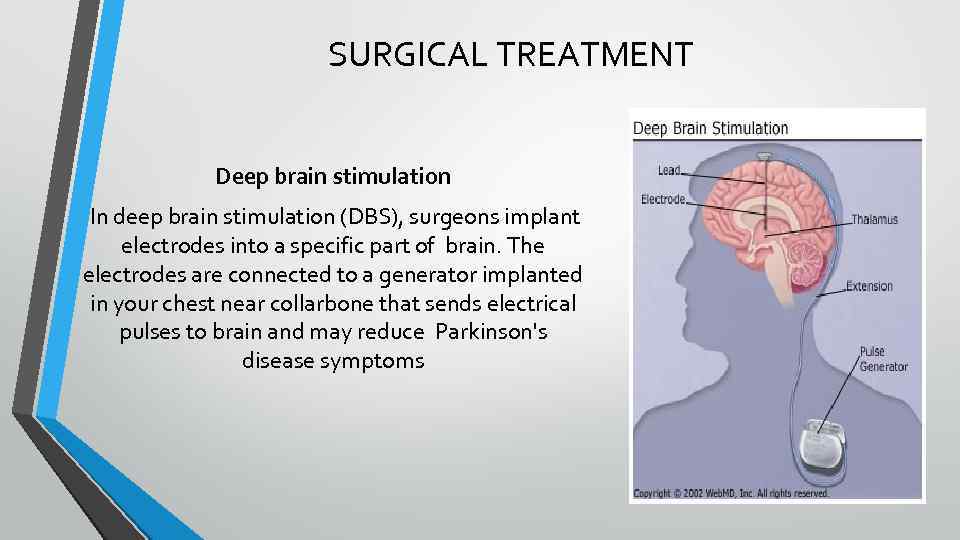 SURGICAL TREATMENT Deep brain stimulation In deep brain stimulation (DBS), surgeons implant electrodes into a specific part of brain. The electrodes are connected to a generator implanted in your chest near collarbone that sends electrical pulses to brain and may reduce Parkinson's disease symptoms
SURGICAL TREATMENT Deep brain stimulation In deep brain stimulation (DBS), surgeons implant electrodes into a specific part of brain. The electrodes are connected to a generator implanted in your chest near collarbone that sends electrical pulses to brain and may reduce Parkinson's disease symptoms
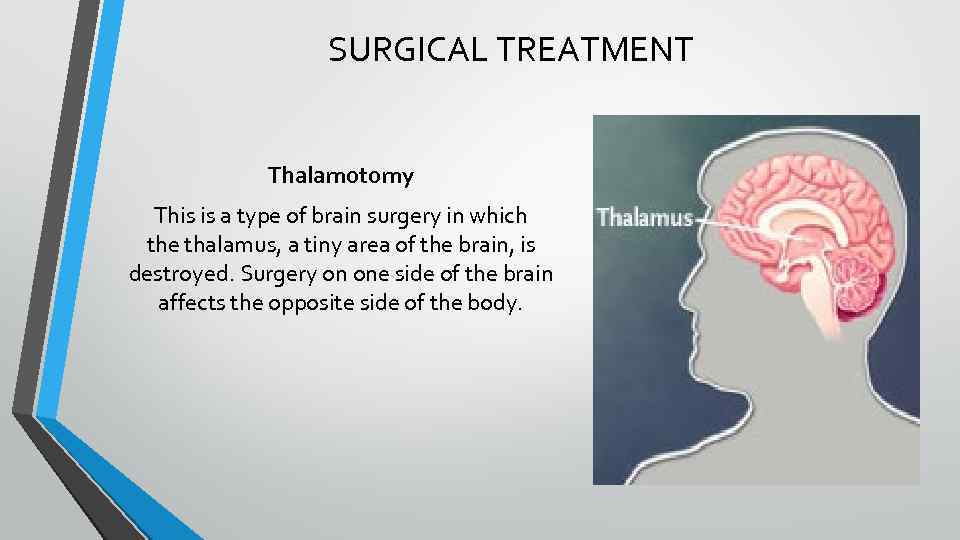 SURGICAL TREATMENT Thalamotomy This is a type of brain surgery in which the thalamus, a tiny area of the brain, is destroyed. Surgery on one side of the brain affects the opposite side of the body.
SURGICAL TREATMENT Thalamotomy This is a type of brain surgery in which the thalamus, a tiny area of the brain, is destroyed. Surgery on one side of the brain affects the opposite side of the body.
 SUMMARY Parkinson's disease itself is not fatal. Unfortunately, there is currently no cure for Parkinson's disease, but treatments are available to help relieve the symptoms and maintain quality of life. These include supportive therapies (such as physiotherapy), medication and, for some people, surgery.
SUMMARY Parkinson's disease itself is not fatal. Unfortunately, there is currently no cure for Parkinson's disease, but treatments are available to help relieve the symptoms and maintain quality of life. These include supportive therapies (such as physiotherapy), medication and, for some people, surgery.
 Thank You!
Thank You!


