c217f9b8ccdd715ecc93a51e57a89d6f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 Search Mining Integration Mining in the Middle: From Search to Integration on the Web Kevin C. Chang Joint with: the UIUC and Cazoodle Teams
Search Mining Integration Mining in the Middle: From Search to Integration on the Web Kevin C. Chang Joint with: the UIUC and Cazoodle Teams
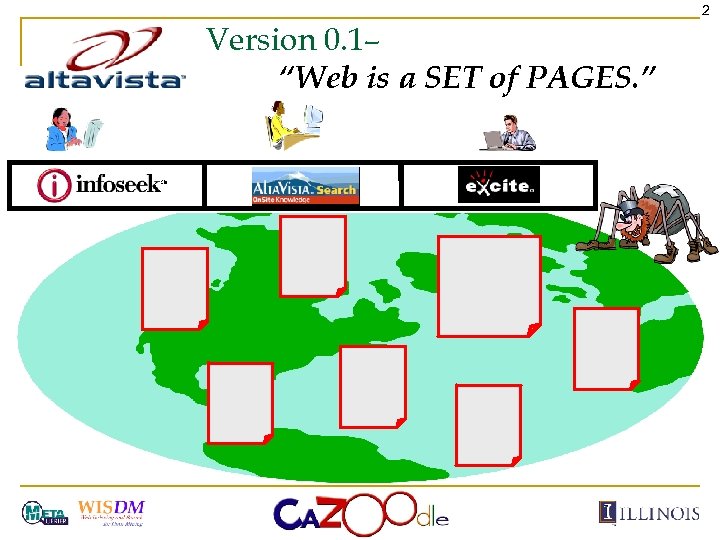 2 Version 0. 1– “Web is a SET of PAGES. ”
2 Version 0. 1– “Web is a SET of PAGES. ”
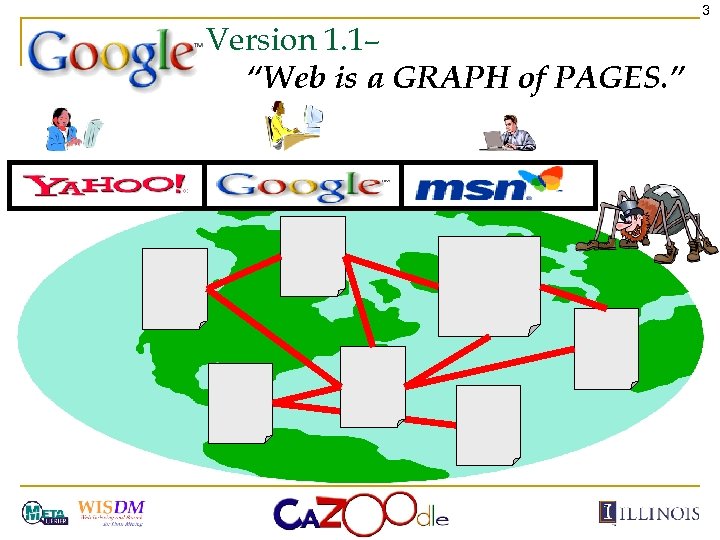 3 Version 1. 1– “Web is a GRAPH of PAGES. ”
3 Version 1. 1– “Web is a GRAPH of PAGES. ”
 4 But, … What have you been searching lately?
4 But, … What have you been searching lately?
 5 First Question: Where is U. of Illinois? Or: Is it in California? Let’s ask the Web…
5 First Question: Where is U. of Illinois? Or: Is it in California? Let’s ask the Web…
 6 Second Question: San Francisco to Chicago? AA. com or ? Let’s ask the Web…
6 Second Question: San Francisco to Chicago? AA. com or ? Let’s ask the Web…
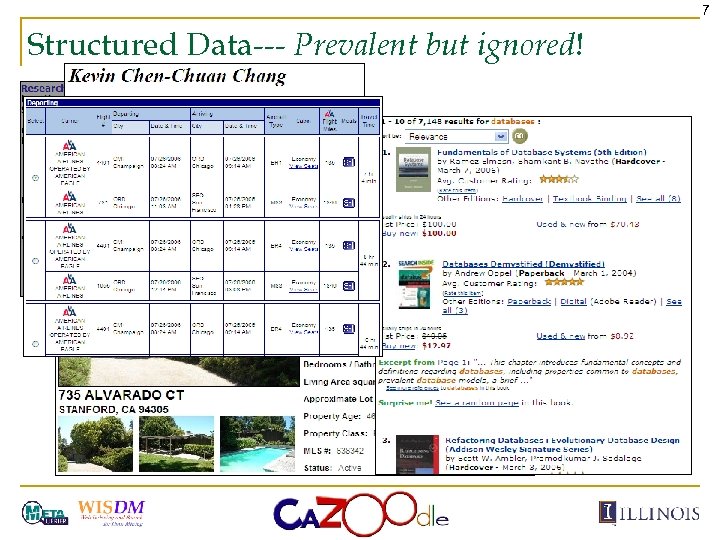 7 Structured Data--- Prevalent but ignored!
7 Structured Data--- Prevalent but ignored!
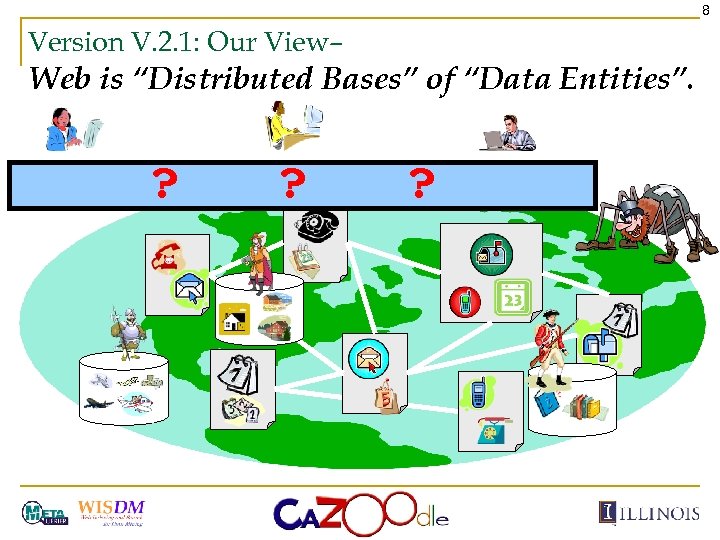 8 Version V. 2. 1: Our View– Web is “Distributed Bases” of “Data Entities”. ? ? ?
8 Version V. 2. 1: Our View– Web is “Distributed Bases” of “Data Entities”. ? ? ?
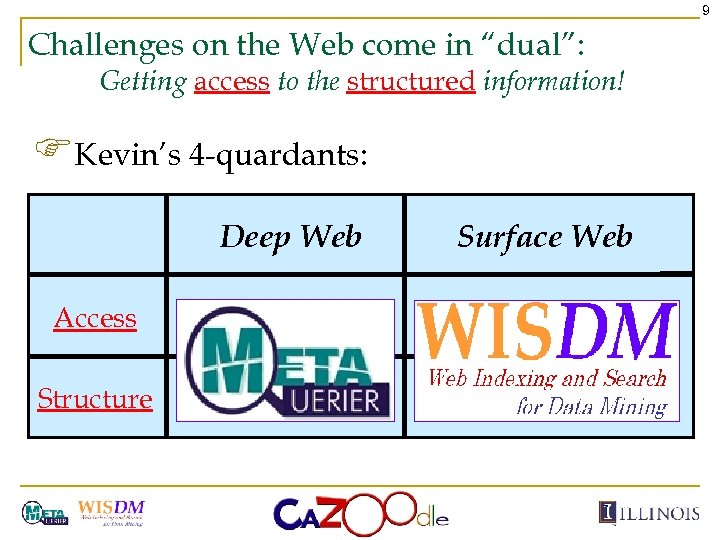 9 Challenges on the Web come in “dual”: Getting access to the structured information! FKevin’s 4 -quardants: Deep Web Access Structure Surface Web
9 Challenges on the Web come in “dual”: Getting access to the structured information! FKevin’s 4 -quardants: Deep Web Access Structure Surface Web
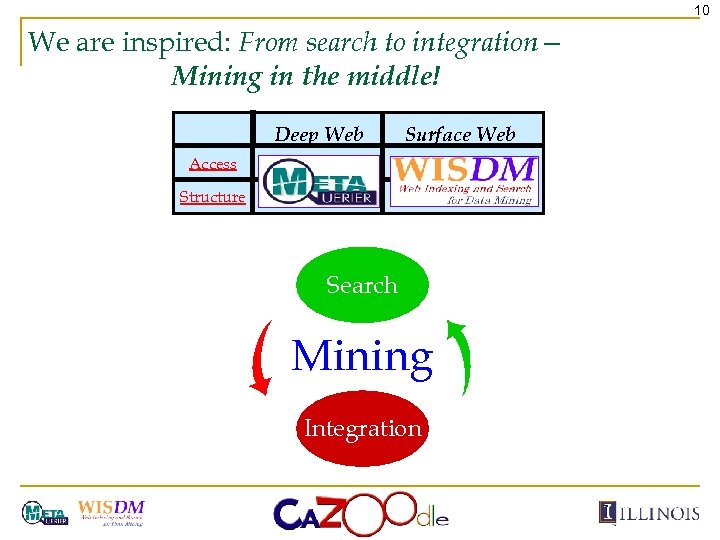 10 We are inspired: From search to integration— Mining in the middle! Deep Web Surface Web Access Structure Search Mining Integration
10 We are inspired: From search to integration— Mining in the middle! Deep Web Surface Web Access Structure Search Mining Integration
 11 Challenge of the Deep Web: Access: How to Get There? Meta. Querier: Holistic Integration over the Deep Web.
11 Challenge of the Deep Web: Access: How to Get There? Meta. Querier: Holistic Integration over the Deep Web.
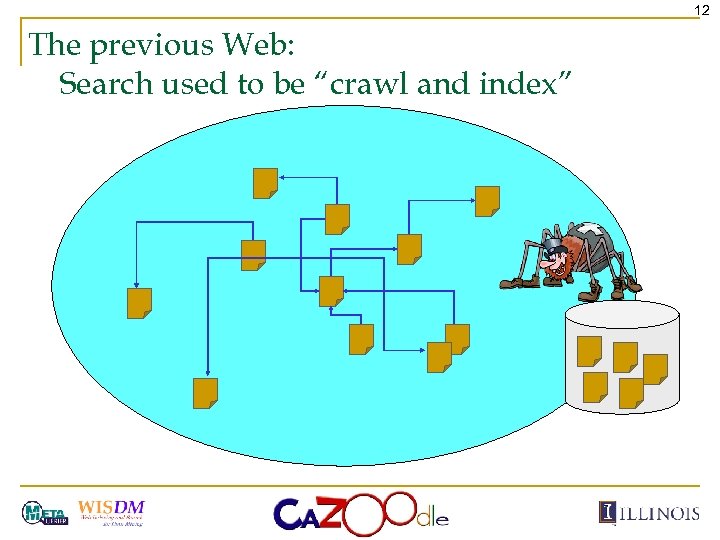 12 The previous Web: Search used to be “crawl and index”
12 The previous Web: Search used to be “crawl and index”
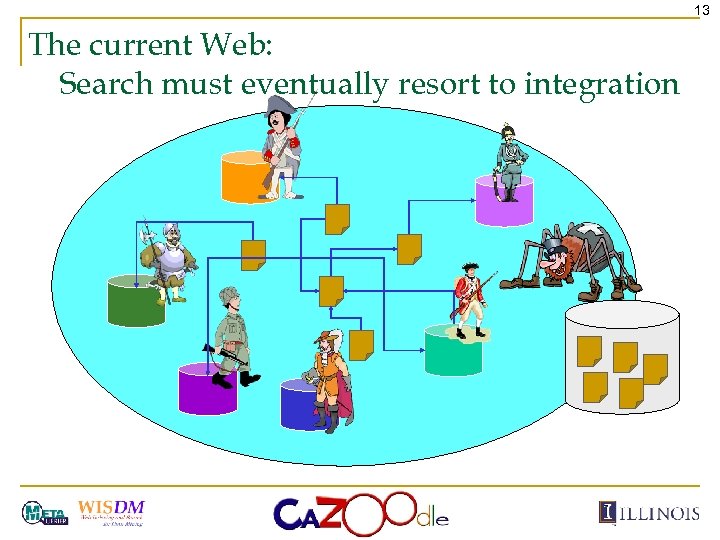 13 The current Web: Search must eventually resort to integration
13 The current Web: Search must eventually resort to integration
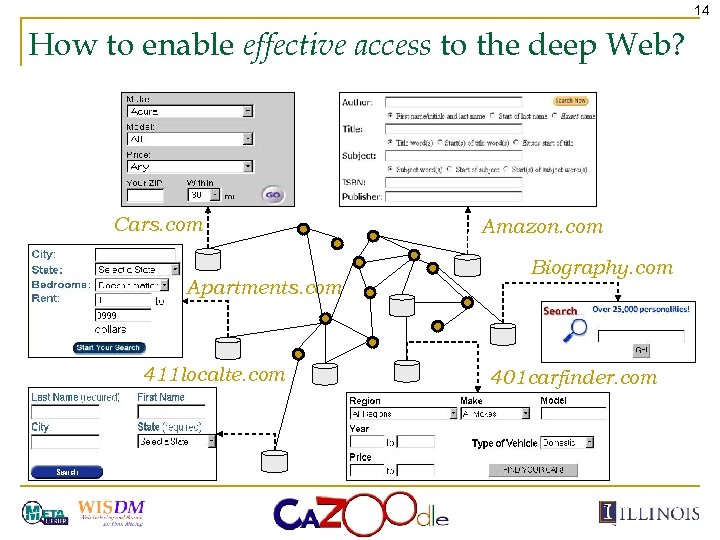 14 How to enable effective access to the deep Web? Cars. com Apartments. com 411 localte. com Amazon. com Biography. com 401 carfinder. com
14 How to enable effective access to the deep Web? Cars. com Apartments. com 411 localte. com Amazon. com Biography. com 401 carfinder. com
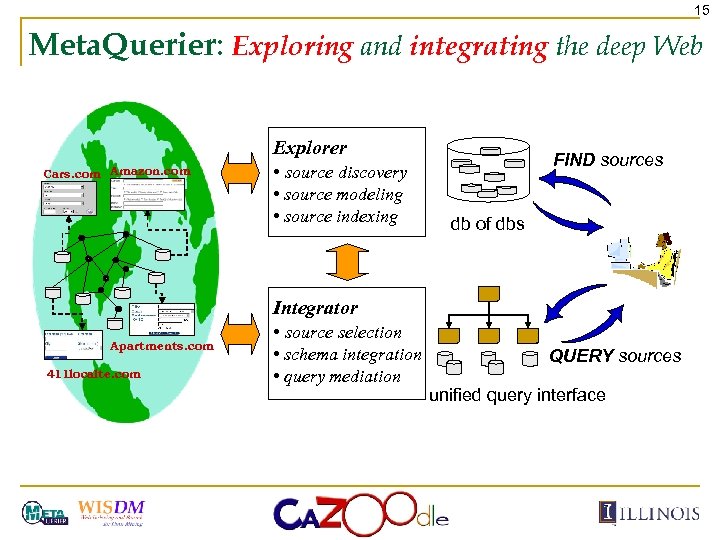 15 Meta. Querier: Exploring and integrating the deep Web Cars. com Amazon. com Explorer • source discovery • source modeling • source indexing Apartments. com 411 localte. com FIND sources db of dbs Integrator • source selection • schema integration • query mediation QUERY sources unified query interface
15 Meta. Querier: Exploring and integrating the deep Web Cars. com Amazon. com Explorer • source discovery • source modeling • source indexing Apartments. com 411 localte. com FIND sources db of dbs Integrator • source selection • schema integration • query mediation QUERY sources unified query interface
 16 The challenge – How to deal with “deep” semantics across a large scale? “Semantics” is the key in integration! n How to understand a query interface? q n How to match query interfaces? q n Where is the first condition? What’s its attribute? What does “author” on this source match on that? How to translate queries? q How to ask this query on that source?
16 The challenge – How to deal with “deep” semantics across a large scale? “Semantics” is the key in integration! n How to understand a query interface? q n How to match query interfaces? q n Where is the first condition? What’s its attribute? What does “author” on this source match on that? How to translate queries? q How to ask this query on that source?
 17 Survey the frontier before going to the battle. n Challenge reassured: q q n 450, 000 online databases 1, 258, 000 query interfaces 307, 000 deep web sites 3 -7 times increase in 4 years Insight revealed: q q Web sources are not arbitrarily complex “Amazon effect” – convergence and regularity naturally emerge
17 Survey the frontier before going to the battle. n Challenge reassured: q q n 450, 000 online databases 1, 258, 000 query interfaces 307, 000 deep web sites 3 -7 times increase in 4 years Insight revealed: q q Web sources are not arbitrarily complex “Amazon effect” – convergence and regularity naturally emerge
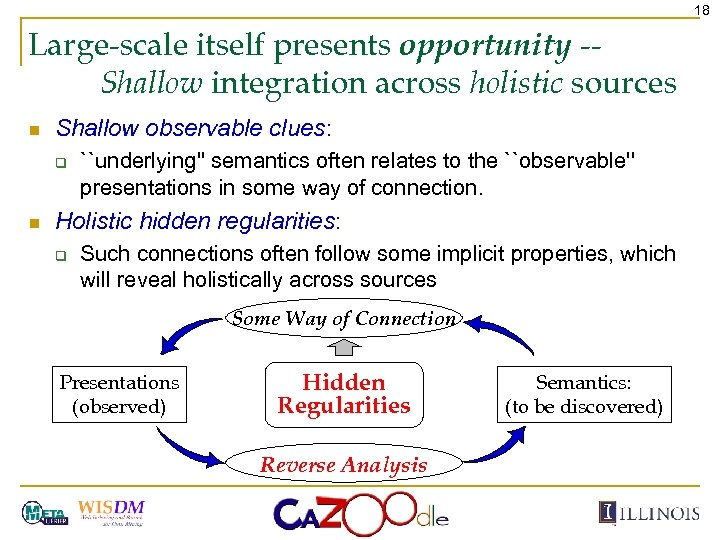 18 Large-scale itself presents opportunity -Shallow integration across holistic sources n Shallow observable clues: q n ``underlying'' semantics often relates to the ``observable'' presentations in some way of connection. Holistic hidden regularities: q Such connections often follow some implicit properties, which will reveal holistically across sources Some Way of Connection Presentations (observed) Hidden Regularities Reverse Analysis Semantics: (to be discovered)
18 Large-scale itself presents opportunity -Shallow integration across holistic sources n Shallow observable clues: q n ``underlying'' semantics often relates to the ``observable'' presentations in some way of connection. Holistic hidden regularities: q Such connections often follow some implicit properties, which will reveal holistically across sources Some Way of Connection Presentations (observed) Hidden Regularities Reverse Analysis Semantics: (to be discovered)
![19 Some evidences for “holistic integration” n Evidence 1: [SIGMOD 04] Query Interface Understanding 19 Some evidences for “holistic integration” n Evidence 1: [SIGMOD 04] Query Interface Understanding](https://present5.com/presentation/c217f9b8ccdd715ecc93a51e57a89d6f/image-19.jpg) 19 Some evidences for “holistic integration” n Evidence 1: [SIGMOD 04] Query Interface Understanding Hidden-syntax parsing attribute operator value n Evidence 2: [SIGMOD 03, KDD 04, KDD 05] Matching Query Interfaces Hidden-model discovery
19 Some evidences for “holistic integration” n Evidence 1: [SIGMOD 04] Query Interface Understanding Hidden-syntax parsing attribute operator value n Evidence 2: [SIGMOD 03, KDD 04, KDD 05] Matching Query Interfaces Hidden-model discovery
 20 Demo. Knocking the Door to the Deep Web
20 Demo. Knocking the Door to the Deep Web
 21 Meta. Querier: Technology transfer in progress Need for domain-based integration pervasive! n In Jobs domain: q q n With Soc. Sec. Admin for “Job-Demands” A few days crawling collected ~4000 sources In Real-Estate domain: q q With Homestore. com for vertical search engine A few days crawling collected ~15, 000 sources
21 Meta. Querier: Technology transfer in progress Need for domain-based integration pervasive! n In Jobs domain: q q n With Soc. Sec. Admin for “Job-Demands” A few days crawling collected ~4000 sources In Real-Estate domain: q q With Homestore. com for vertical search engine A few days crawling collected ~15, 000 sources
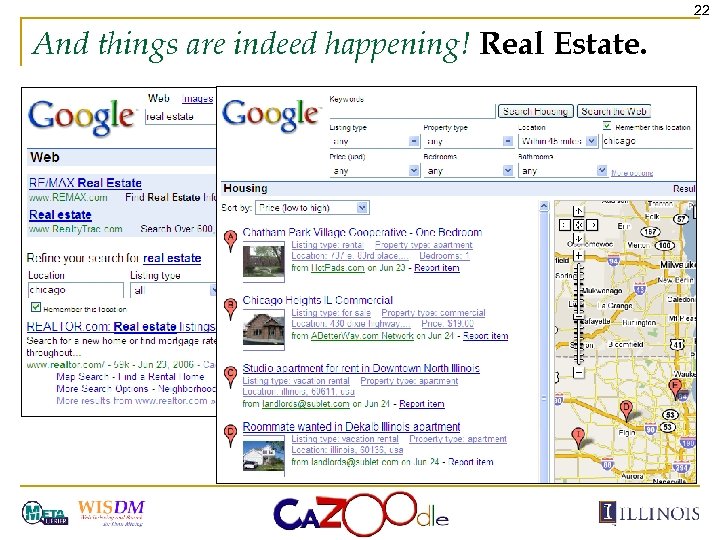 22 And things are indeed happening! Real Estate.
22 And things are indeed happening! Real Estate.
 23 Jobs
23 Jobs
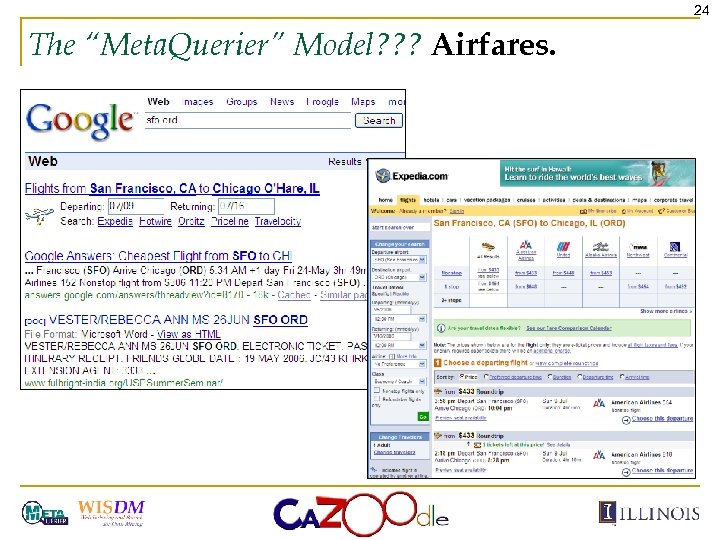 24 The “Meta. Querier” Model? ? ? Airfares.
24 The “Meta. Querier” Model? ? ? Airfares.
 25 Challenge of the Surface Web: Structure: What to look for? WISDM: Holistic Search over the Surface Web.
25 Challenge of the Surface Web: Structure: What to look for? WISDM: Holistic Search over the Surface Web.
 26 What have you been searching lately? n n n n What is the email of Marc Snir? What is Marc Snir’s research area? Who are Marc Snir’s coauthors? What are the phones of CS database faculty? How much is “Canon Power. Shot A 400”? Where is SIGMOD 2006 to be held? When is the due date of SIGMOD 2006? Find PDF files of “SIGMOD 2006”?
26 What have you been searching lately? n n n n What is the email of Marc Snir? What is Marc Snir’s research area? Who are Marc Snir’s coauthors? What are the phones of CS database faculty? How much is “Canon Power. Shot A 400”? Where is SIGMOD 2006 to be held? When is the due date of SIGMOD 2006? Find PDF files of “SIGMOD 2006”?
 27 NO! Regardless of what you want, you are searching for pages…
27 NO! Regardless of what you want, you are searching for pages…
 28 We take an entity view of the Web:
28 We take an entity view of the Web:
 29 What is an “entity”? Your target of information– or, anything. n n n n Phone number Email address PDF Image Person name Book title, author, … Price (of something)
29 What is an “entity”? Your target of information– or, anything. n n n n Phone number Email address PDF Image Person name Book title, author, … Price (of something)
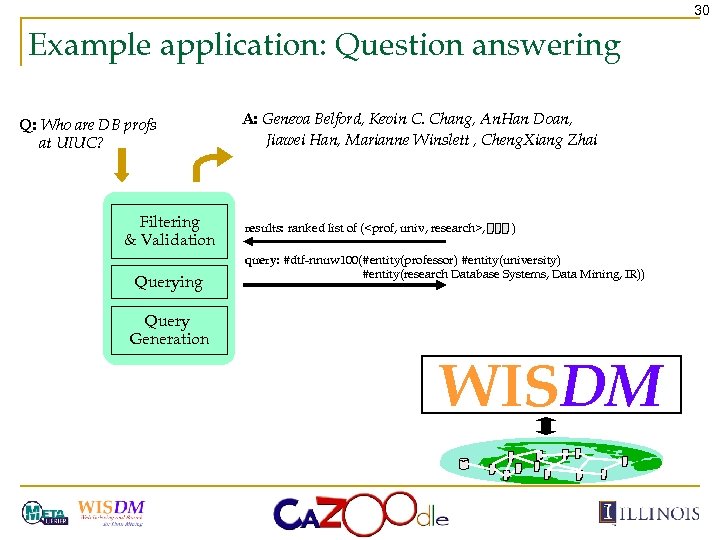 30 Example application: Question answering Q: Who are DB profs at UIUC? Filtering & Validation Querying A: Geneva Belford, Kevin C. Chang, An. Han Doan, Jiawei Han, Marianne Winslett , Cheng. Xiang Zhai results: ranked list of (
30 Example application: Question answering Q: Who are DB profs at UIUC? Filtering & Validation Querying A: Geneva Belford, Kevin C. Chang, An. Han Doan, Jiawei Han, Marianne Winslett , Cheng. Xiang Zhai results: ranked list of (
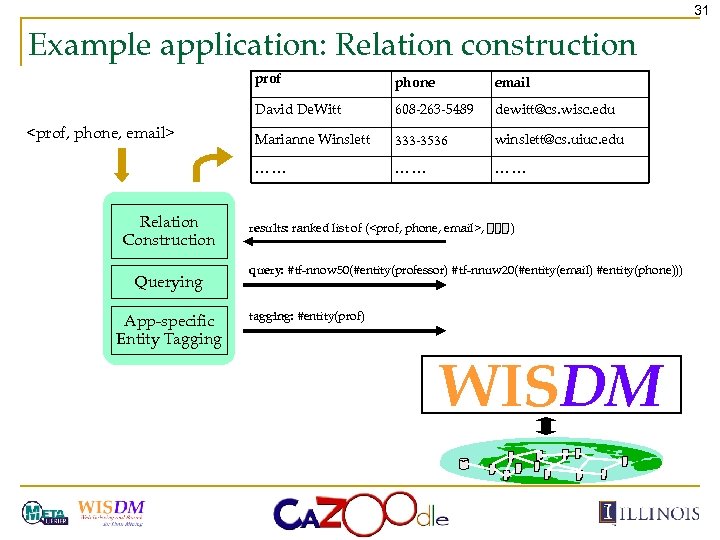 31 Example application: Relation construction prof Querying App-specific Entity Tagging 608 -263 -5489 dewitt@cs. wisc. edu Marianne Winslett 333 -3536 winslett@cs. uiuc. edu …… Relation Construction email David De. Witt
31 Example application: Relation construction prof Querying App-specific Entity Tagging 608 -263 -5489 dewitt@cs. wisc. edu Marianne Winslett 333 -3536 winslett@cs. uiuc. edu …… Relation Construction email David De. Witt
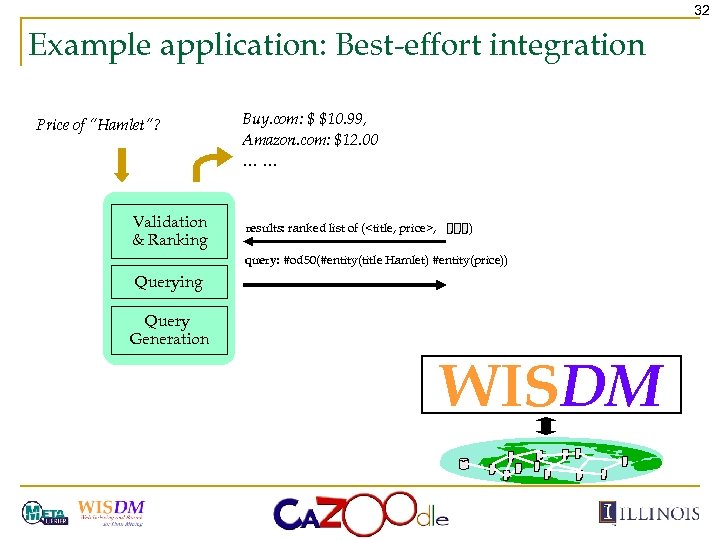 32 Example application: Best-effort integration Price of “Hamlet”? Validation & Ranking Buy. com: $ $10. 99, Amazon. com: $12. 00 …… results: ranked list of (
32 Example application: Best-effort integration Price of “Hamlet”? Validation & Ranking Buy. com: $ $10. 99, Amazon. com: $12. 00 …… results: ranked list of (
 33 How different is “entity search”? How to define such searches?
33 How different is “entity search”? How to define such searches?
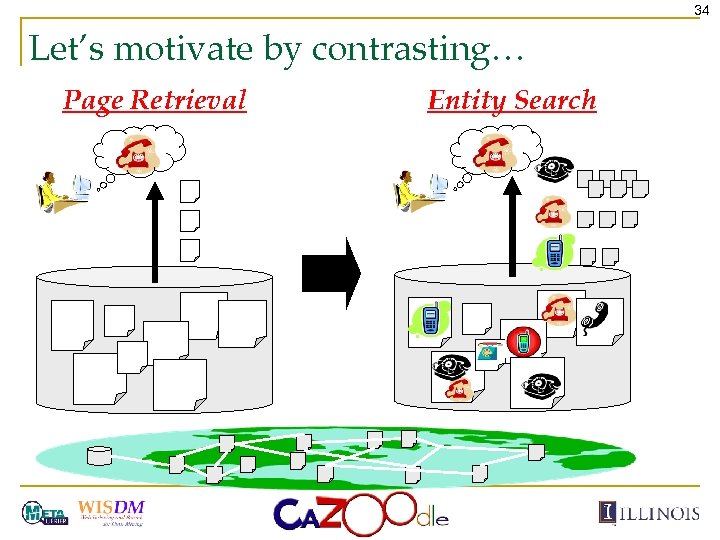 34 Let’s motivate by contrasting… Page Retrieval Entity Search
34 Let’s motivate by contrasting… Page Retrieval Entity Search
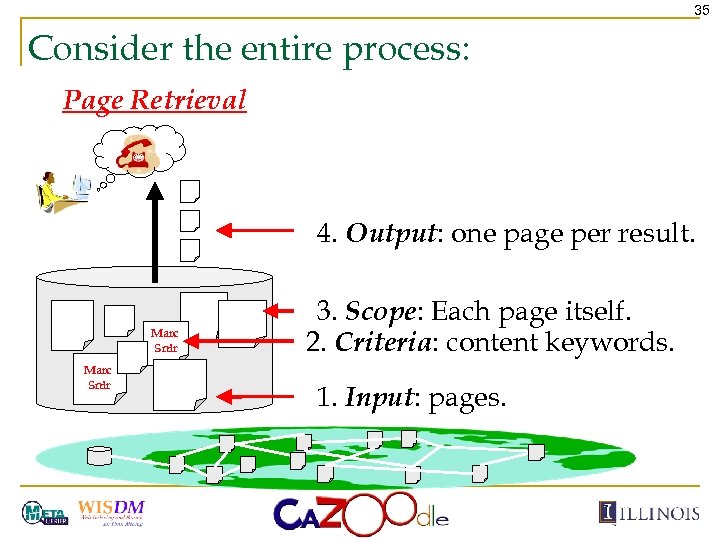 35 Consider the entire process: Page Retrieval 4. Output: one page per result. Marc Snir 3. Scope: Each page itself. 2. Criteria: content keywords. 1. Input: pages.
35 Consider the entire process: Page Retrieval 4. Output: one page per result. Marc Snir 3. Scope: Each page itself. 2. Criteria: content keywords. 1. Input: pages.
 36 First, in terms of input: Is this an entity? In contrast: You just don’t ask this for pages.
36 First, in terms of input: Is this an entity? In contrast: You just don’t ask this for pages.
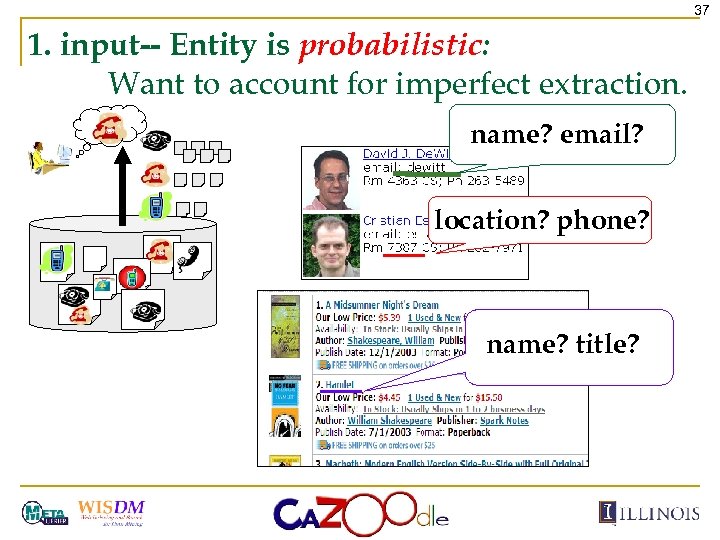 37 1. input-- Entity is probabilistic: Want to account for imperfect extraction. name? email? location? phone? name? title?
37 1. input-- Entity is probabilistic: Want to account for imperfect extraction. name? email? location? phone? name? title?
 38 Second, in terms of matching criteria: How to match an entity? In contrast: You match a page by content keywords.
38 Second, in terms of matching criteria: How to match an entity? In contrast: You match a page by content keywords.
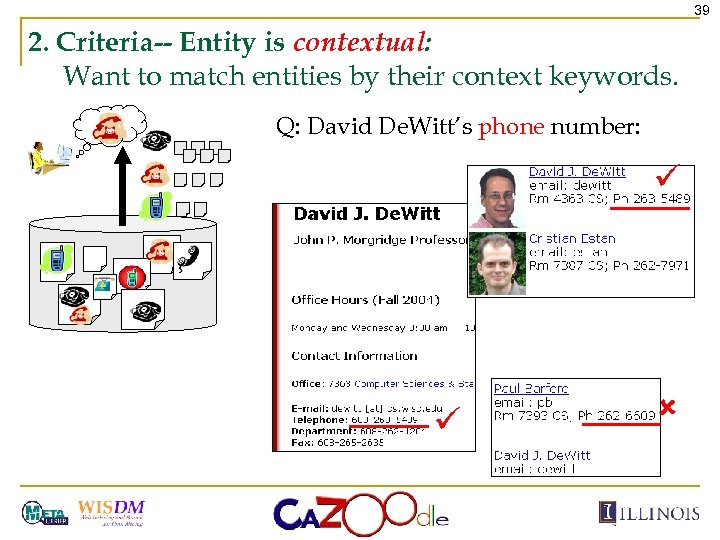 39 2. Criteria-- Entity is contextual: Want to match entities by their context keywords. Q: David De. Witt’s phone number: ü ü û
39 2. Criteria-- Entity is contextual: Want to match entities by their context keywords. Q: David De. Witt’s phone number: ü ü û
 40 Third, in terms of matching scope: Seen this entity somewhere else? In contrast: Every page is distinct, by itself.
40 Third, in terms of matching scope: Seen this entity somewhere else? In contrast: Every page is distinct, by itself.
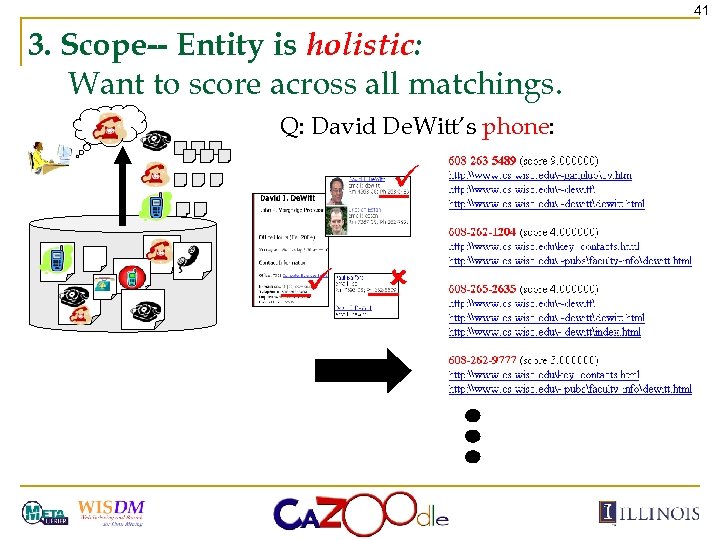 41 3. Scope-- Entity is holistic: Want to score across all matchings. Q: David De. Witt’s phone: ü ü û
41 3. Scope-- Entity is holistic: Want to score across all matchings. Q: David De. Witt’s phone: ü ü û
 42 Finally, in terms of output: What is the target of your search? In contrast: One page at a time.
42 Finally, in terms of output: What is the target of your search? In contrast: One page at a time.
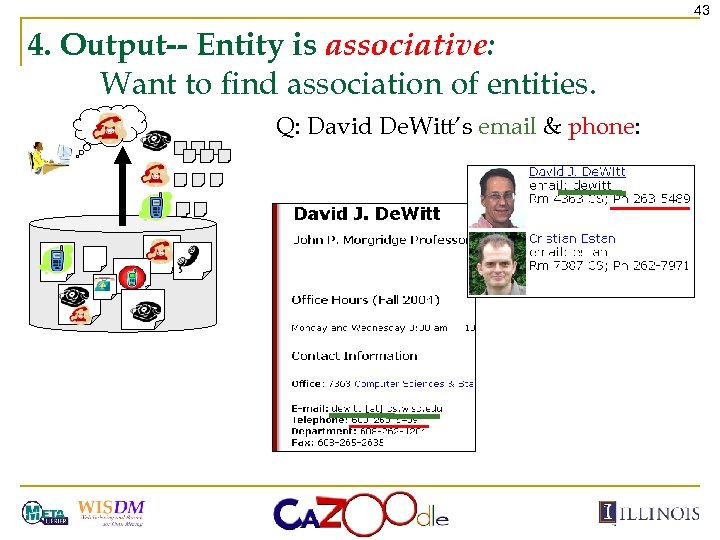 43 4. Output-- Entity is associative: Want to find association of entities. Q: David De. Witt’s email & phone:
43 4. Output-- Entity is associative: Want to find association of entities. Q: David De. Witt’s email & phone:
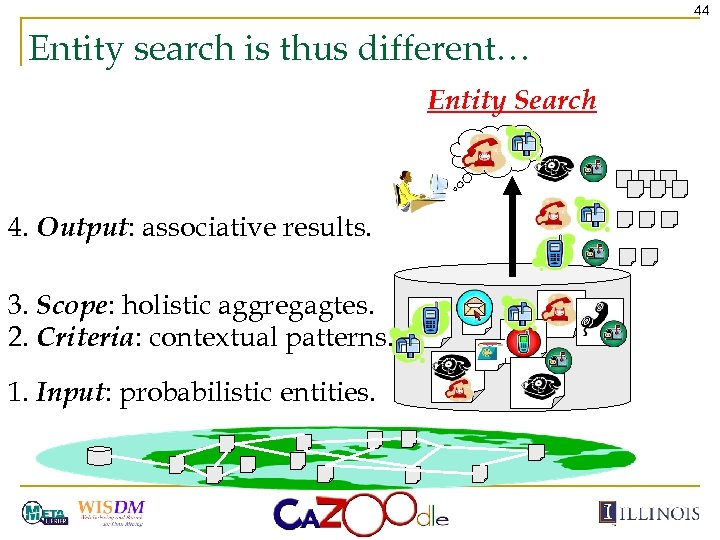 44 Entity search is thus different… Entity Search 4. Output: associative results. 3. Scope: holistic aggregagtes. 2. Criteria: contextual patterns. 1. Input: probabilistic entities.
44 Entity search is thus different… Entity Search 4. Output: associative results. 3. Scope: holistic aggregagtes. 2. Criteria: contextual patterns. 1. Input: probabilistic entities.
![45 Query language: Entity-search goes beyond keyword queries. n n #a-b( <#entity(type)[restriction] | keyword>+ 45 Query language: Entity-search goes beyond keyword queries. n n #a-b( <#entity(type)[restriction] | keyword>+](https://present5.com/presentation/c217f9b8ccdd715ecc93a51e57a89d6f/image-45.jpg) 45 Query language: Entity-search goes beyond keyword queries. n n #a-b( <#entity(type)[restriction] | keyword>+ ) To qualify: b -- Boolean instantiation of instances. q n To quantify: a -- Fuzzy scoring function. q n e. g. , uw 100, ow 50, nnow 100 e. g. , pr, tf, dtf, mi Examples: q q #tf-nnow 50(#entity(professor De. Witt) fax #entity(phone)) #pr-od 20(#entity(title Romeo and Juliet) #entity(author))
45 Query language: Entity-search goes beyond keyword queries. n n #a-b( <#entity(type)[restriction] | keyword>+ ) To qualify: b -- Boolean instantiation of instances. q n To quantify: a -- Fuzzy scoring function. q n e. g. , uw 100, ow 50, nnow 100 e. g. , pr, tf, dtf, mi Examples: q q #tf-nnow 50(#entity(professor De. Witt) fax #entity(phone)) #pr-od 20(#entity(title Romeo and Juliet) #entity(author))
 46 What are technical challenges? Or, how to write (reviewer-friendly) papers?
46 What are technical challenges? Or, how to write (reviewer-friendly) papers?
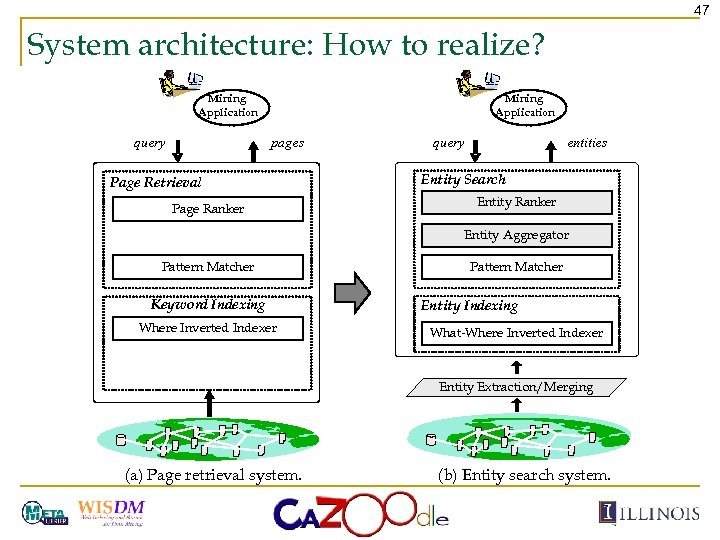 47 System architecture: How to realize? Mining Application query pages Page Retrieval Page Ranker query entities Entity Search Entity Ranker Entity Aggregator Pattern Matcher Keyword Indexing Where Inverted Indexer Pattern Matcher Entity Indexing What-Where Inverted Indexer Entity Extraction/Merging (a) Page retrieval system. (b) Entity search system.
47 System architecture: How to realize? Mining Application query pages Page Retrieval Page Ranker query entities Entity Search Entity Ranker Entity Aggregator Pattern Matcher Keyword Indexing Where Inverted Indexer Pattern Matcher Entity Indexing What-Where Inverted Indexer Entity Extraction/Merging (a) Page retrieval system. (b) Entity search system.
 48 Ranking Functions: How to score results? Say, Jiawei Han with #email, #phone, #researcharea n Entity matters q n Context matters: q n How often is Jiawei Han – “data mining”? Associativity matters: q q n Order, distance Frequency matters: q n Is “jhan@” an email? Is “ 2 -3457” a phone? “webmaster@cs. uiuc. edu” “algorithm” Source matters: q Where did you get this info from?
48 Ranking Functions: How to score results? Say, Jiawei Han with #email, #phone, #researcharea n Entity matters q n Context matters: q n How often is Jiawei Han – “data mining”? Associativity matters: q q n Order, distance Frequency matters: q n Is “jhan@” an email? Is “ 2 -3457” a phone? “webmaster@cs. uiuc. edu” “algorithm” Source matters: q Where did you get this info from?
![49 Query Processing: How to optimize? Q: #tf-nnow 50(#entity(professor[David De. Witt]) fax #entity(phone)) tf 49 Query Processing: How to optimize? Q: #tf-nnow 50(#entity(professor[David De. Witt]) fax #entity(phone)) tf](https://present5.com/presentation/c217f9b8ccdd715ecc93a51e57a89d6f/image-49.jpg) 49 Query Processing: How to optimize? Q: #tf-nnow 50(#entity(professor[David De. Witt]) fax #entity(phone)) tf gphone w v nnow 50 sprof=“…” #entity(professor) “fax”-#entity(phone) (pre-materialized context index)
49 Query Processing: How to optimize? Q: #tf-nnow 50(#entity(professor[David De. Witt]) fax #entity(phone)) tf gphone w v nnow 50 sprof=“…” #entity(professor) “fax”-#entity(phone) (pre-materialized context index)
 50 Sample issues– Indexing, Optimization n Index configuration: q q n What “pre-join” into context index? Tradeoff: space cost vs. time efficiency Query optimization: q q Multiple ways to answer-- What plan to use? Plan generation and cost estimation
50 Sample issues– Indexing, Optimization n Index configuration: q q n What “pre-join” into context index? Tradeoff: space cost vs. time efficiency Query optimization: q q Multiple ways to answer-- What plan to use? Plan generation and cost estimation
 51 More issues… n Tagging/merging of basic entities? q q n Powerful pattern language q n Linguistic; visual Advanced statistical analysis q n Application-driven tagging Web’s redundancy will alleviate accuracy demand. correlation; sampling Scalable query processing q new components scale?
51 More issues… n Tagging/merging of basic entities? q q n Powerful pattern language q n Linguistic; visual Advanced statistical analysis q n Application-driven tagging Web’s redundancy will alleviate accuracy demand. correlation; sampling Scalable query processing q new components scale?
 52 Promises of the Concepts n From page at a time to entity-tuple at a time q n From IR to a mining engine q n enable large scale ad-hoc mining over the web From Web to controlled corpus q n not only page retrieval but also construction From offline to online Web mining and integration q n getting directly to target info and evidences enhance not only efficiency but also effectiveness From passive to active application-driven indexing q enable mining applications
52 Promises of the Concepts n From page at a time to entity-tuple at a time q n From IR to a mining engine q n enable large scale ad-hoc mining over the web From Web to controlled corpus q n not only page retrieval but also construction From offline to online Web mining and integration q n getting directly to target info and evidences enhance not only efficiency but also effectiveness From passive to active application-driven indexing q enable mining applications
 53 Conclusion: Mining in just the middle! F Dual Challenges: Getting access to the deep Web. q Getting structure from the surface Web. F Central Techniques: q Holistic mining for both search and integration. q Search Mining Integration
53 Conclusion: Mining in just the middle! F Dual Challenges: Getting access to the deep Web. q Getting structure from the surface Web. F Central Techniques: q Holistic mining for both search and integration. q Search Mining Integration
 54 Implications: Open up mining over the Web. Search Mining Engines: n Mining as primary functions n Mining for end users Mining Integration
54 Implications: Open up mining over the Web. Search Mining Engines: n Mining as primary functions n Mining for end users Mining Integration
 55 Search Mining What will such a Mining Engine be? Integration You tell me! Students’ imagination knows no bounds.
55 Search Mining What will such a Mining Engine be? Integration You tell me! Students’ imagination knows no bounds.


