2b049213935fa76410f7b84fb30e79a4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Search for Solar Axions with the CAST experiment J. Galán on behalf of the CAST Collaboration University of Zaragoza (Spain) 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy
Search for Solar Axions with the CAST experiment J. Galán on behalf of the CAST Collaboration University of Zaragoza (Spain) 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy
 The CAST Collaboration Canada Universiy of British Columbia, Department of Physics, Vancouver M. Hasinoff National Center for Scientific Research “Demokritos”, Athens T. Karageorgoplou, G. Fanourakis, T. Geralis, K. Kousouris Aristotle University of Thessaloniki C. Eleftheriadis, A. Liolios, I. Savvidis, T. Vafeiadis Croatia Rudjer Boskovic Institute, Zagreb Rudjer Boskovic, M. Krcmar, B. Lakic, A. Ljubicic Hellenic Open University, Patras C. Bourlis, S. Tzamarias France DAPNIA, CEA-Saclay, Gif-sur-Yvette S. Aune, E. Ferrer-Ribas, I. Giomataris, T. Papaevangelou Russian Academy of Science, Institute for Nuclear Research (INR), Moscow A. Belov, S. Gninenko Germany TU Darmstadt, Institut für Kernphysik D. H. H. Hoffmann, M. Kuster, A. Nordt Spain University of Zaragoza B. Beltrán, J. Carmona, S. Cebrián, T. Dafni, J. Galán, H. Gómez, I. G. Irastorza, G. Luzón, A. Morales, J. Morales, A. Ortiz, A. Rodríguez, J. Ruz, A. Tomás, J. Villar GSI Darmstadt D. H. H. Hoffman Universität Frankfurt, Institut für Angewandte Physik, Frankfurt J. Jacoby Universität Freiburg H. Fischer, J. Franz, F. H. Heinsus, D. Kang, K. Königsmann, J. Vogel MPE Garching H. Bräuninger, M. Kuster, A. Nordt WHI München R. Kotthaus, G. Lutz, G. Raffelt, P. Serpico Greece University of Patras A. Gardikiotis, Y. Semertzidis, M. Tsagri, K. Zioutas 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán Turkey Dogus University, Istambul E. Arik, S. Boydag, S. A. Cetin, O. B. Dogan, I. Hikmet, C. Yildiz USA Lawrence Livermore National laboratory, Livermore, CA M. Pivovaroff, R. Soufli, K. van Bibber University of Chicago, Enrico Fermi Institute and KICP J. Collar, D. Miller Switzerland European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), Genève D. Autiero, K. Barth, S. Borgui, M. Davenport, L. Di Lella, N. Elias, C. Lasseur, T. Ninikowski, A. Palacci, H. Riege, L. Stewart, L. Walkiers 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy
The CAST Collaboration Canada Universiy of British Columbia, Department of Physics, Vancouver M. Hasinoff National Center for Scientific Research “Demokritos”, Athens T. Karageorgoplou, G. Fanourakis, T. Geralis, K. Kousouris Aristotle University of Thessaloniki C. Eleftheriadis, A. Liolios, I. Savvidis, T. Vafeiadis Croatia Rudjer Boskovic Institute, Zagreb Rudjer Boskovic, M. Krcmar, B. Lakic, A. Ljubicic Hellenic Open University, Patras C. Bourlis, S. Tzamarias France DAPNIA, CEA-Saclay, Gif-sur-Yvette S. Aune, E. Ferrer-Ribas, I. Giomataris, T. Papaevangelou Russian Academy of Science, Institute for Nuclear Research (INR), Moscow A. Belov, S. Gninenko Germany TU Darmstadt, Institut für Kernphysik D. H. H. Hoffmann, M. Kuster, A. Nordt Spain University of Zaragoza B. Beltrán, J. Carmona, S. Cebrián, T. Dafni, J. Galán, H. Gómez, I. G. Irastorza, G. Luzón, A. Morales, J. Morales, A. Ortiz, A. Rodríguez, J. Ruz, A. Tomás, J. Villar GSI Darmstadt D. H. H. Hoffman Universität Frankfurt, Institut für Angewandte Physik, Frankfurt J. Jacoby Universität Freiburg H. Fischer, J. Franz, F. H. Heinsus, D. Kang, K. Königsmann, J. Vogel MPE Garching H. Bräuninger, M. Kuster, A. Nordt WHI München R. Kotthaus, G. Lutz, G. Raffelt, P. Serpico Greece University of Patras A. Gardikiotis, Y. Semertzidis, M. Tsagri, K. Zioutas 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán Turkey Dogus University, Istambul E. Arik, S. Boydag, S. A. Cetin, O. B. Dogan, I. Hikmet, C. Yildiz USA Lawrence Livermore National laboratory, Livermore, CA M. Pivovaroff, R. Soufli, K. van Bibber University of Chicago, Enrico Fermi Institute and KICP J. Collar, D. Miller Switzerland European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), Genève D. Autiero, K. Barth, S. Borgui, M. Davenport, L. Di Lella, N. Elias, C. Lasseur, T. Ninikowski, A. Palacci, H. Riege, L. Stewart, L. Walkiers 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy
 Outline • Introducing the Axion and Solar Axion Model. • Review the Axion detection techniques. • The CAST Helioscope Description. • CAST Status (results from 4 He Phase and progress in 3 He Phase). • The new He 3 System and detector performances • Future of Helioscope Axion Searches. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy
Outline • Introducing the Axion and Solar Axion Model. • Review the Axion detection techniques. • The CAST Helioscope Description. • CAST Status (results from 4 He Phase and progress in 3 He Phase). • The new He 3 System and detector performances • Future of Helioscope Axion Searches. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy
 Why do we need Axions? QCD predicts violation of CP in strong interactions Bad agreement between theoretical and experimental values for the electric dipole moment of neutron All you need is Axions! Peccei-Quinn introduced the axion field to solve this problem 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 4
Why do we need Axions? QCD predicts violation of CP in strong interactions Bad agreement between theoretical and experimental values for the electric dipole moment of neutron All you need is Axions! Peccei-Quinn introduced the axion field to solve this problem 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 4
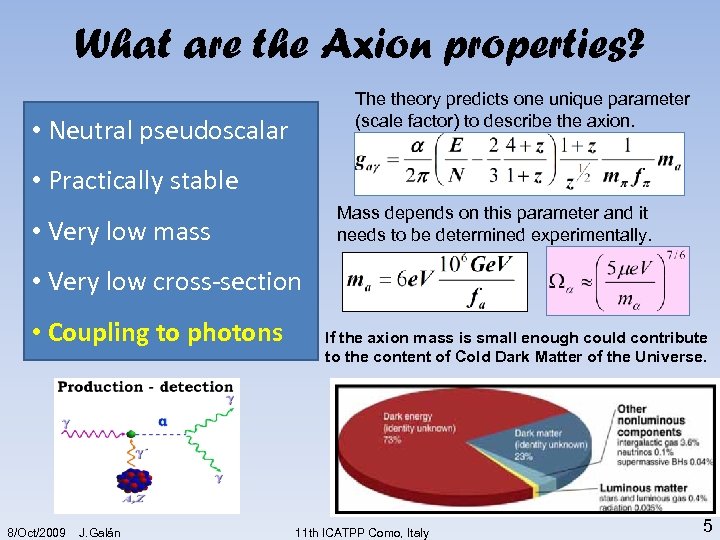 What are the Axion properties? The theory predicts one unique parameter (scale factor) to describe the axion. • Neutral pseudoscalar • Practically stable Mass depends on this parameter and it needs to be determined experimentally. • Very low mass • Very low cross-section • Coupling to photons 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán If the axion mass is small enough could contribute to the content of Cold Dark Matter of the Universe. 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 5
What are the Axion properties? The theory predicts one unique parameter (scale factor) to describe the axion. • Neutral pseudoscalar • Practically stable Mass depends on this parameter and it needs to be determined experimentally. • Very low mass • Very low cross-section • Coupling to photons 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán If the axion mass is small enough could contribute to the content of Cold Dark Matter of the Universe. 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 5
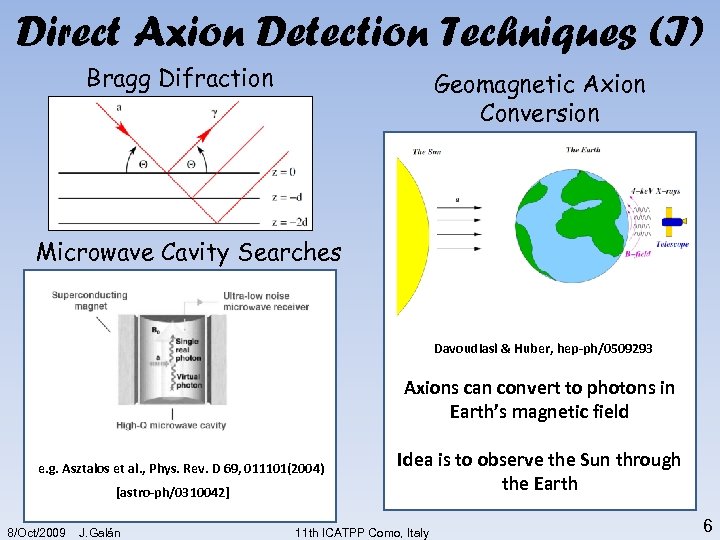 Direct Axion Detection Techniques (I) Bragg Difraction Geomagnetic Axion Conversion Microwave Cavity Searches Davoudiasl & Huber, hep-ph/0509293 Axions can convert to photons in Earth’s magnetic field e. g. Asztalos et al. , Phys. Rev. D 69, 011101(2004) [astro-ph/0310042] 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán Idea is to observe the Sun through the Earth 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 6
Direct Axion Detection Techniques (I) Bragg Difraction Geomagnetic Axion Conversion Microwave Cavity Searches Davoudiasl & Huber, hep-ph/0509293 Axions can convert to photons in Earth’s magnetic field e. g. Asztalos et al. , Phys. Rev. D 69, 011101(2004) [astro-ph/0310042] 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán Idea is to observe the Sun through the Earth 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 6
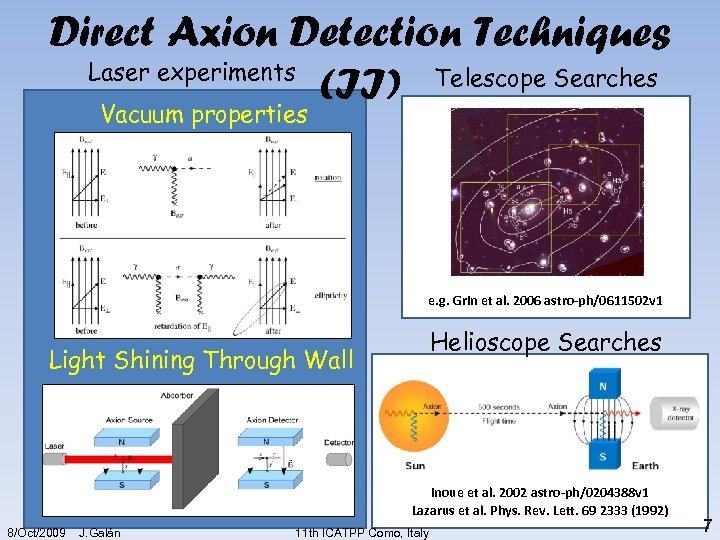 Direct Axion Detection Techniques Laser experiments (II) Telescope Searches Vacuum properties e. g. Grin et al. 2006 astro-ph/0611502 v 1 Helioscope Searches Light Shining Through Wall Inoue et al. 2002 astro-ph/0204388 v 1 Lazarus et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 2333 (1992) 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 7
Direct Axion Detection Techniques Laser experiments (II) Telescope Searches Vacuum properties e. g. Grin et al. 2006 astro-ph/0611502 v 1 Helioscope Searches Light Shining Through Wall Inoue et al. 2002 astro-ph/0204388 v 1 Lazarus et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 2333 (1992) 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 7
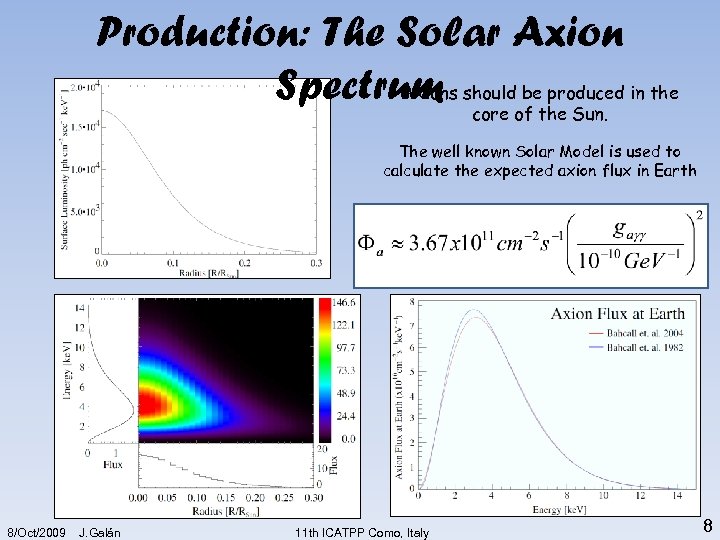 Production: The Solar Axions be produced Spectrum shouldof the Sun. in the core The well known Solar Model is used to calculate the expected axion flux in Earth 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 8
Production: The Solar Axions be produced Spectrum shouldof the Sun. in the core The well known Solar Model is used to calculate the expected axion flux in Earth 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 8
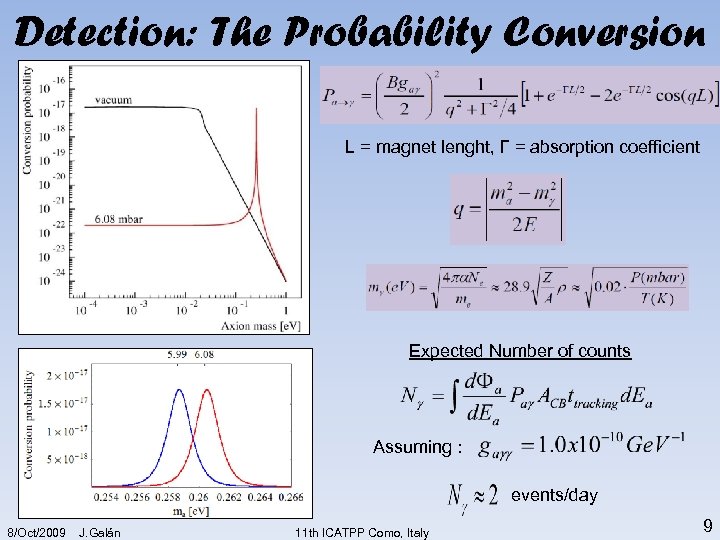 Detection: The Probability Conversion L = magnet lenght, Γ = absorption coefficient Expected Number of counts Assuming : events/day 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 9
Detection: The Probability Conversion L = magnet lenght, Γ = absorption coefficient Expected Number of counts Assuming : events/day 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 9
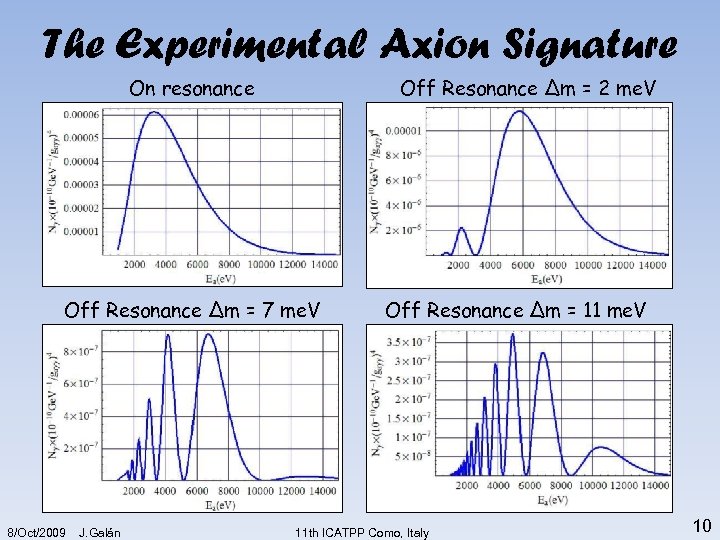 The Experimental Axion Signature On resonance Off Resonance ∆m = 2 me. V Off Resonance ∆m = 7 me. V 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán Off Resonance ∆m = 11 me. V 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 10
The Experimental Axion Signature On resonance Off Resonance ∆m = 2 me. V Off Resonance ∆m = 7 me. V 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán Off Resonance ∆m = 11 me. V 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 10
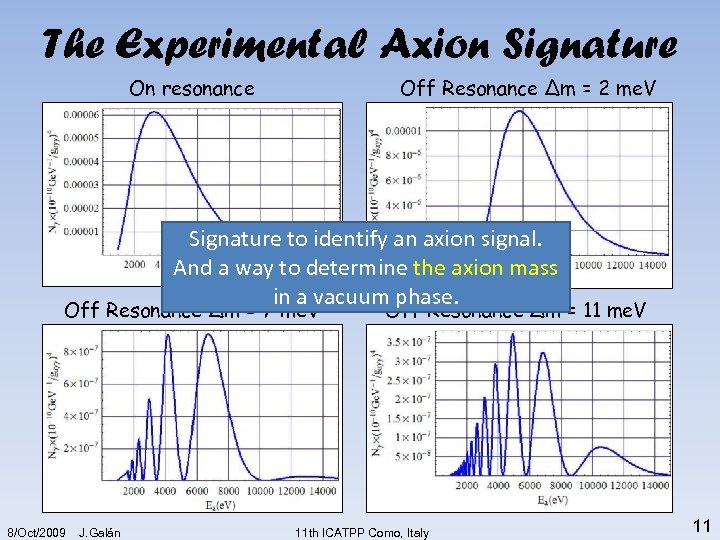 The Experimental Axion Signature On resonance Off Resonance ∆m = 2 me. V Signature to identify an axion signal. And a way to determine the axion mass in a vacuum phase. Off Resonance ∆m = 7 me. V 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán Off Resonance ∆m = 11 me. V 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 11
The Experimental Axion Signature On resonance Off Resonance ∆m = 2 me. V Signature to identify an axion signal. And a way to determine the axion mass in a vacuum phase. Off Resonance ∆m = 7 me. V 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán Off Resonance ∆m = 11 me. V 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 11
 CAST Location 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy
CAST Location 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy
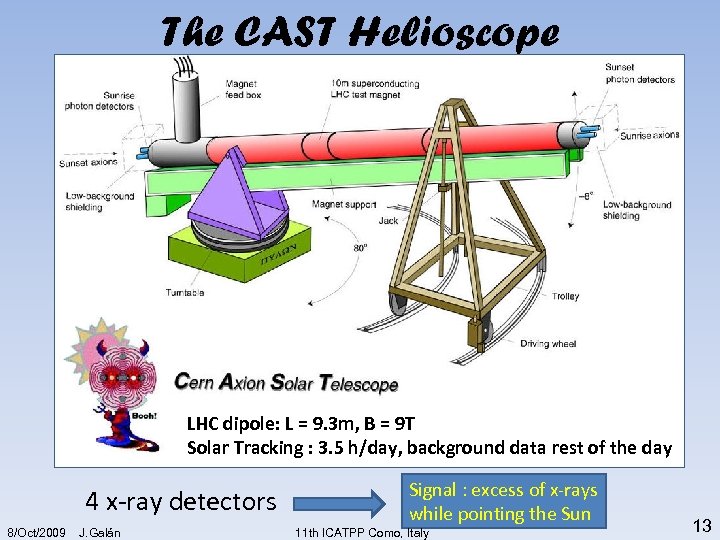 The CAST Helioscope LHC dipole: L = 9. 3 m, B = 9 T Solar Tracking : 3. 5 h/day, background data rest of the day 4 x-ray detectors 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán Signal : excess of x-rays while pointing the Sun 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 13
The CAST Helioscope LHC dipole: L = 9. 3 m, B = 9 T Solar Tracking : 3. 5 h/day, background data rest of the day 4 x-ray detectors 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán Signal : excess of x-rays while pointing the Sun 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 13
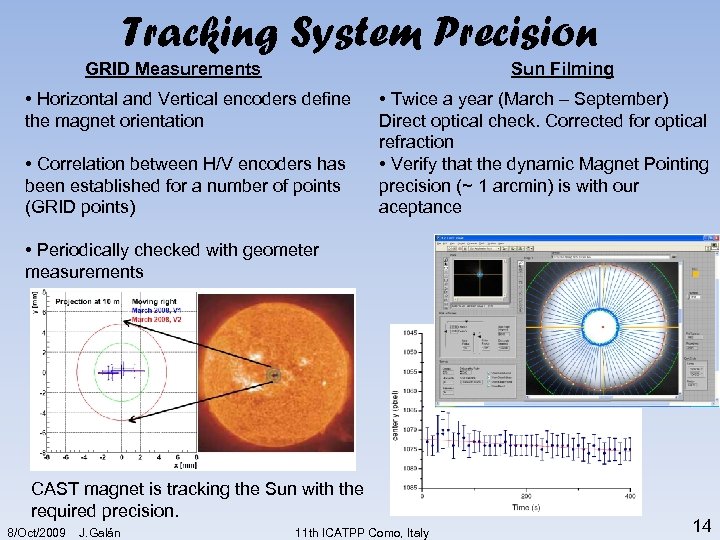 Tracking System Precision GRID Measurements Sun Filming • Horizontal and Vertical encoders define the magnet orientation • Correlation between H/V encoders has been established for a number of points (GRID points) • Twice a year (March – September) Direct optical check. Corrected for optical refraction • Verify that the dynamic Magnet Pointing precision (~ 1 arcmin) is with our aceptance • Periodically checked with geometer measurements CAST magnet is tracking the Sun with the required precision. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 14
Tracking System Precision GRID Measurements Sun Filming • Horizontal and Vertical encoders define the magnet orientation • Correlation between H/V encoders has been established for a number of points (GRID points) • Twice a year (March – September) Direct optical check. Corrected for optical refraction • Verify that the dynamic Magnet Pointing precision (~ 1 arcmin) is with our aceptance • Periodically checked with geometer measurements CAST magnet is tracking the Sun with the required precision. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 14
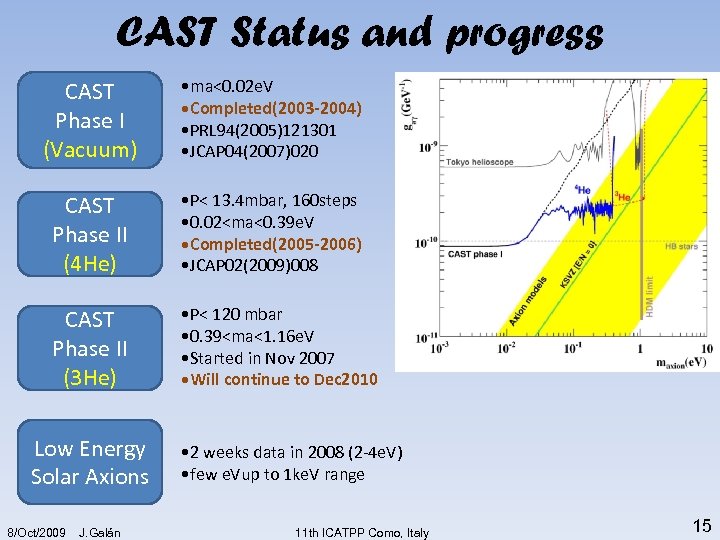 CAST Status and progress CAST Phase I (Vacuum) • ma<0. 02 e. V • Completed(2003 -2004) • PRL 94(2005)121301 • JCAP 04(2007)020 CAST Phase II (4 He) • P< 13. 4 mbar, 160 steps • 0. 02
CAST Status and progress CAST Phase I (Vacuum) • ma<0. 02 e. V • Completed(2003 -2004) • PRL 94(2005)121301 • JCAP 04(2007)020 CAST Phase II (4 He) • P< 13. 4 mbar, 160 steps • 0. 02
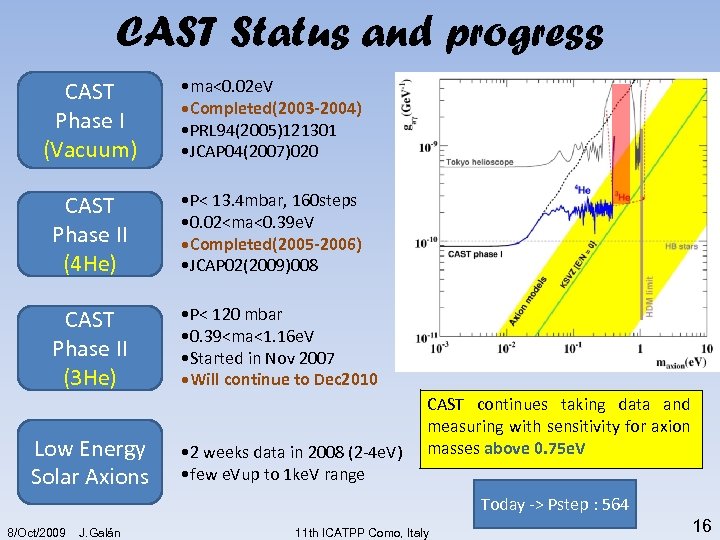 CAST Status and progress CAST Phase I (Vacuum) • ma<0. 02 e. V • Completed(2003 -2004) • PRL 94(2005)121301 • JCAP 04(2007)020 CAST Phase II (4 He) • P< 13. 4 mbar, 160 steps • 0. 02
CAST Status and progress CAST Phase I (Vacuum) • ma<0. 02 e. V • Completed(2003 -2004) • PRL 94(2005)121301 • JCAP 04(2007)020 CAST Phase II (4 He) • P< 13. 4 mbar, 160 steps • 0. 02
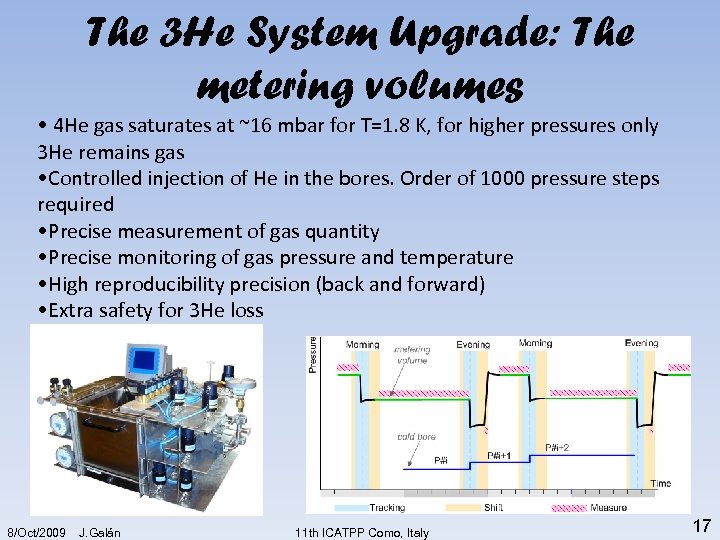 The 3 He System Upgrade: The metering volumes • 4 He gas saturates at ~16 mbar for T=1. 8 K, for higher pressures only 3 He remains gas • Controlled injection of He in the bores. Order of 1000 pressure steps required • Precise measurement of gas quantity • Precise monitoring of gas pressure and temperature • High reproducibility precision (back and forward) • Extra safety for 3 He loss 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 17
The 3 He System Upgrade: The metering volumes • 4 He gas saturates at ~16 mbar for T=1. 8 K, for higher pressures only 3 He remains gas • Controlled injection of He in the bores. Order of 1000 pressure steps required • Precise measurement of gas quantity • Precise monitoring of gas pressure and temperature • High reproducibility precision (back and forward) • Extra safety for 3 He loss 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 17
 The 3 He System : Expansion volume The new 3 He System is prepared to protect the thin Cold windows in case of Magnet Quench. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 18
The 3 He System : Expansion volume The new 3 He System is prepared to protect the thin Cold windows in case of Magnet Quench. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 18
 The 3 He System : Expansion volume The new 3 He System is prepared to protect the thin Cold windows in case of Magnet Quench. Refilling must be done as fast as posible to dont loss data taking efficiency. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 19
The 3 He System : Expansion volume The new 3 He System is prepared to protect the thin Cold windows in case of Magnet Quench. Refilling must be done as fast as posible to dont loss data taking efficiency. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 19
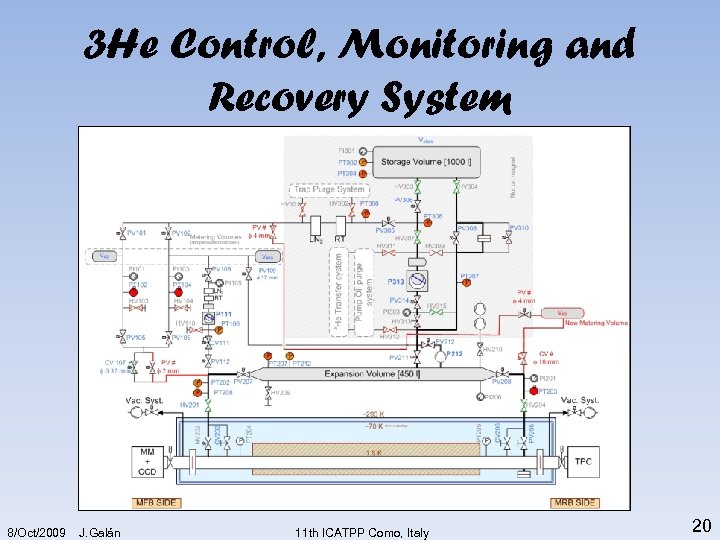 3 He Control, Monitoring and Recovery System 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 20
3 He Control, Monitoring and Recovery System 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 20
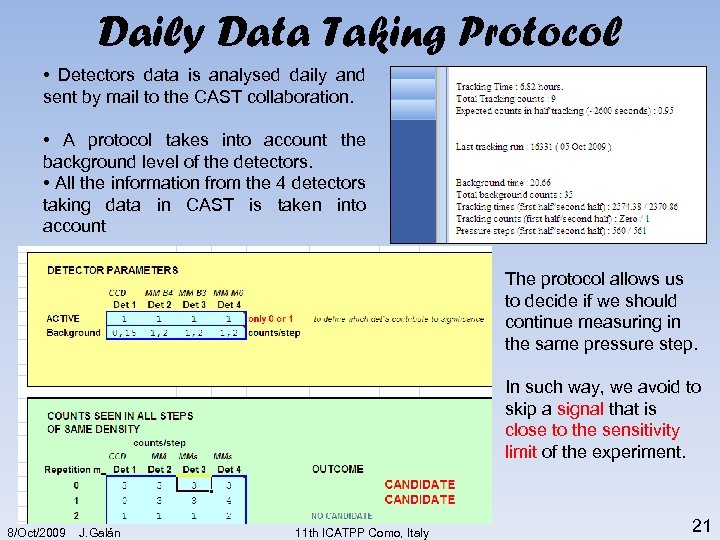 Daily Data Taking Protocol • Detectors data is analysed daily and sent by mail to the CAST collaboration. • A protocol takes into account the background level of the detectors. • All the information from the 4 detectors taking data in CAST is taken into account The protocol allows us to decide if we should continue measuring in the same pressure step. In such way, we avoid to skip a signal that is close to the sensitivity limit of the experiment. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 21
Daily Data Taking Protocol • Detectors data is analysed daily and sent by mail to the CAST collaboration. • A protocol takes into account the background level of the detectors. • All the information from the 4 detectors taking data in CAST is taken into account The protocol allows us to decide if we should continue measuring in the same pressure step. In such way, we avoid to skip a signal that is close to the sensitivity limit of the experiment. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 21
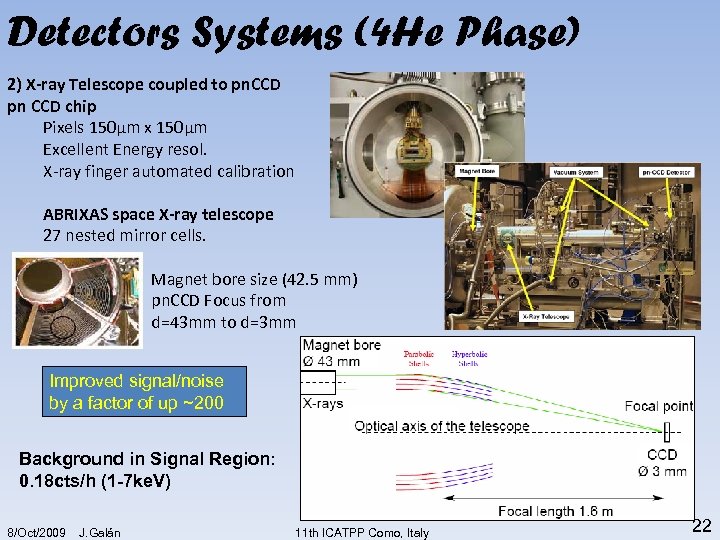 Detectors Systems (4 He Phase) 2) X-ray Telescope coupled to pn. CCD pn CCD chip Pixels 150μm x 150μm Excellent Energy resol. X-ray finger automated calibration ABRIXAS space X-ray telescope 27 nested mirror cells. Magnet bore size (42. 5 mm) pn. CCD Focus from d=43 mm to d=3 mm Improved signal/noise by a factor of up ~200 Background in Signal Region: 0. 18 cts/h (1 -7 ke. V) 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 22
Detectors Systems (4 He Phase) 2) X-ray Telescope coupled to pn. CCD pn CCD chip Pixels 150μm x 150μm Excellent Energy resol. X-ray finger automated calibration ABRIXAS space X-ray telescope 27 nested mirror cells. Magnet bore size (42. 5 mm) pn. CCD Focus from d=43 mm to d=3 mm Improved signal/noise by a factor of up ~200 Background in Signal Region: 0. 18 cts/h (1 -7 ke. V) 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 22
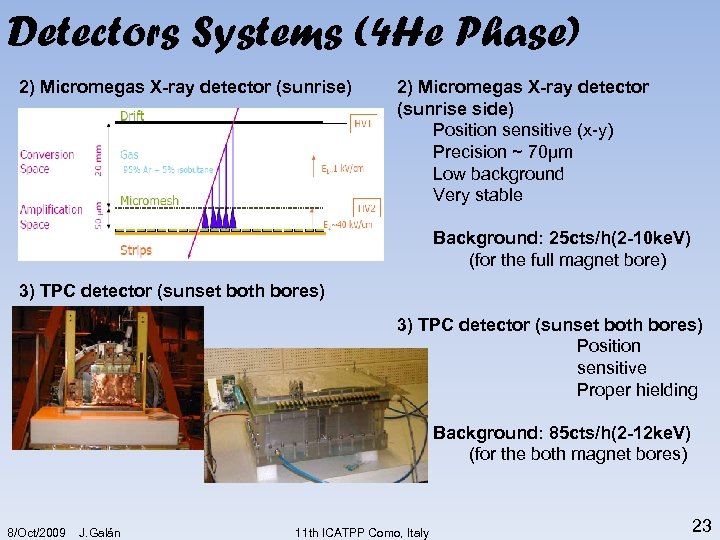 Detectors Systems (4 He Phase) 2) Micromegas X-ray detector (sunrise side) Position sensitive (x-y) Precision ~ 70μm Low background Very stable Background: 25 cts/h(2 -10 ke. V) (for the full magnet bore) 3) TPC detector (sunset both bores) Position sensitive Proper hielding Background: 85 cts/h(2 -12 ke. V) (for the both magnet bores) 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 23
Detectors Systems (4 He Phase) 2) Micromegas X-ray detector (sunrise side) Position sensitive (x-y) Precision ~ 70μm Low background Very stable Background: 25 cts/h(2 -10 ke. V) (for the full magnet bore) 3) TPC detector (sunset both bores) Position sensitive Proper hielding Background: 85 cts/h(2 -12 ke. V) (for the both magnet bores) 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 23
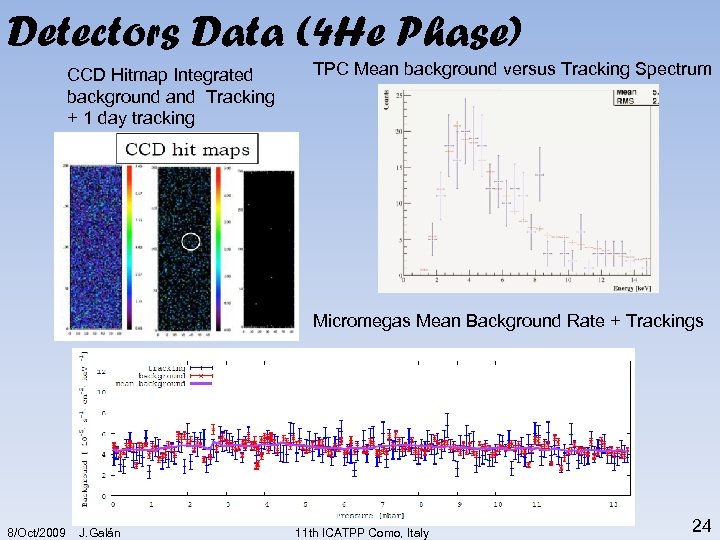 Detectors Data (4 He Phase) CCD Hitmap Integrated background and Tracking + 1 day tracking TPC Mean background versus Tracking Spectrum Micromegas Mean Background Rate + Trackings 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 24
Detectors Data (4 He Phase) CCD Hitmap Integrated background and Tracking + 1 day tracking TPC Mean background versus Tracking Spectrum Micromegas Mean Background Rate + Trackings 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 24
 Detector Systems (2008) New Sunrise Micromegas Detection Line • New vacuum detection line holding space for focussing device installed in 2007. • Implemented frontal calibration system. • Implemented new shielding (Cupper, Lead, Cadmium, Plexiglass and Polyethylene. • Improved control and monitoring of detector gas system and improved vacuum. • Clean Nitrogen flux surrounding the detector inside the inner shielding. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 25
Detector Systems (2008) New Sunrise Micromegas Detection Line • New vacuum detection line holding space for focussing device installed in 2007. • Implemented frontal calibration system. • Implemented new shielding (Cupper, Lead, Cadmium, Plexiglass and Polyethylene. • Improved control and monitoring of detector gas system and improved vacuum. • Clean Nitrogen flux surrounding the detector inside the inner shielding. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 25
 Detector Systems (2008) New Sunset Micromegas Detectors • 2 new Micromegas detectors installed in Sunset side replacing the previous TPC. • Background level reduced by more than a factor 20 due to discrimination capabilities from micromegas detectors versus TPC detector. • System redesigned and vacuum improvements achieved. • Calibration is taken daily from the detectors back. Some work already schedulled for implementing frontal calibrators. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 26
Detector Systems (2008) New Sunset Micromegas Detectors • 2 new Micromegas detectors installed in Sunset side replacing the previous TPC. • Background level reduced by more than a factor 20 due to discrimination capabilities from micromegas detectors versus TPC detector. • System redesigned and vacuum improvements achieved. • Calibration is taken daily from the detectors back. Some work already schedulled for implementing frontal calibrators. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 26
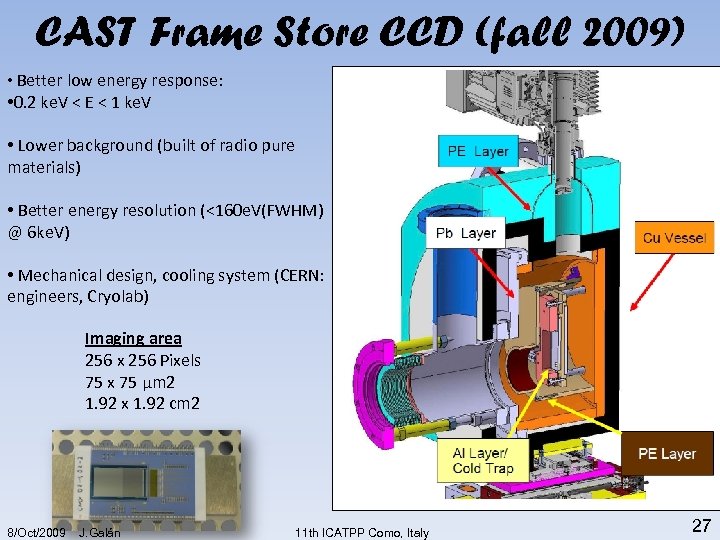 CAST Frame Store CCD (fall 2009) • Better low energy response: • 0. 2 ke. V < E < 1 ke. V • Lower background (built of radio pure materials) • Better energy resolution (<160 e. V(FWHM) @ 6 ke. V) • Mechanical design, cooling system (CERN: engineers, Cryolab) Imaging area 256 x 256 Pixels 75 x 75 μm 2 1. 92 x 1. 92 cm 2 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 27
CAST Frame Store CCD (fall 2009) • Better low energy response: • 0. 2 ke. V < E < 1 ke. V • Lower background (built of radio pure materials) • Better energy resolution (<160 e. V(FWHM) @ 6 ke. V) • Mechanical design, cooling system (CERN: engineers, Cryolab) Imaging area 256 x 256 Pixels 75 x 75 μm 2 1. 92 x 1. 92 cm 2 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 27
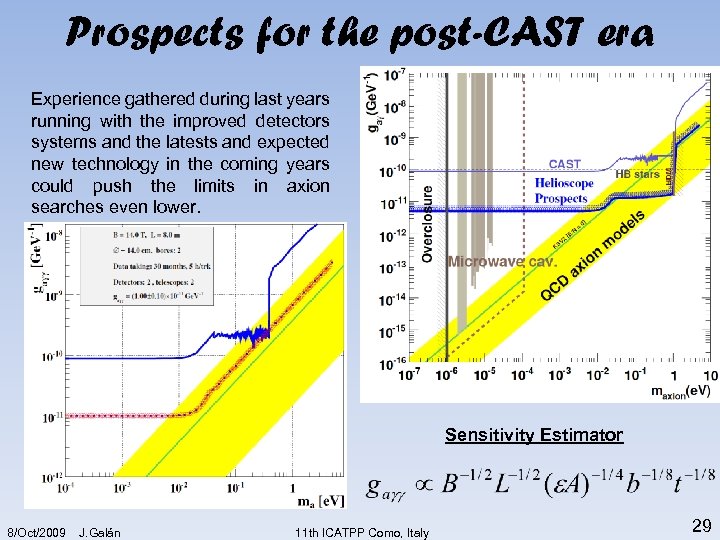 Prospects for the post-CAST era Experience gathered during last years running with the improved detectors systems and the latests and expected new technology in the coming years could push the limits in axion searches even lower. Sensitivity Estimator 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 29
Prospects for the post-CAST era Experience gathered during last years running with the improved detectors systems and the latests and expected new technology in the coming years could push the limits in axion searches even lower. Sensitivity Estimator 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 29
![Conclusions • CAST has published (JCAP 02(2009)008, ar. Xiv: 0810. 4482 v 2 [hep-ex])the Conclusions • CAST has published (JCAP 02(2009)008, ar. Xiv: 0810. 4482 v 2 [hep-ex])the](https://present5.com/presentation/2b049213935fa76410f7b84fb30e79a4/image-29.jpg) Conclusions • CAST has published (JCAP 02(2009)008, ar. Xiv: 0810. 4482 v 2 [hep-ex])the best laboratory limit for the mass range 0. 02 e. V-0. 39 e. V, with 4 He as buffer gas inside the magnet bores. • Since 2008 CAST has been collecting data with 3 He in the magnet bores. • 2010: CAST should be able to fulfil its program • In parallel, we are developing the low energy (visible) axion program • High sensitivity detectors may lead to great improvements in mass region up to 0. 02 e. V (Vaccuum) 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 30
Conclusions • CAST has published (JCAP 02(2009)008, ar. Xiv: 0810. 4482 v 2 [hep-ex])the best laboratory limit for the mass range 0. 02 e. V-0. 39 e. V, with 4 He as buffer gas inside the magnet bores. • Since 2008 CAST has been collecting data with 3 He in the magnet bores. • 2010: CAST should be able to fulfil its program • In parallel, we are developing the low energy (visible) axion program • High sensitivity detectors may lead to great improvements in mass region up to 0. 02 e. V (Vaccuum) 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 30
 Backup Slides
Backup Slides
 MICROMEGAS Ultralow Background Periods Observed periods of very low background in micromegas detectors. Several improvements: • New designed shielding. • New micromegas detectors made of low radiactivity materials. • More sofisticated statistical analysis. Still not well understood nature background could be dominated by: • Radon • Compton scattering (not signal like in 85 -90% of the cases) • Ectons ( explosive electron emission ) Work in progress for understanding the low background nature. • Full simulation process chain. • Underground Laboratory controlled measurements. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 28
MICROMEGAS Ultralow Background Periods Observed periods of very low background in micromegas detectors. Several improvements: • New designed shielding. • New micromegas detectors made of low radiactivity materials. • More sofisticated statistical analysis. Still not well understood nature background could be dominated by: • Radon • Compton scattering (not signal like in 85 -90% of the cases) • Ectons ( explosive electron emission ) Work in progress for understanding the low background nature. • Full simulation process chain. • Underground Laboratory controlled measurements. 8/Oct/2009 J. Galán 11 th ICATPP Como, Italy 28


