b9c5ea377de4c8b3f0d253cb32beb488.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Search for Gravitational Wave Radiation Associated with the SGR 1806 -20 Hyper Flare LIGO-LHO RXTE / RHESSI Luca Matone, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Columbia University – GECo Group April 2007 APS Meeting LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
Search for Gravitational Wave Radiation Associated with the SGR 1806 -20 Hyper Flare LIGO-LHO RXTE / RHESSI Luca Matone, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Columbia University – GECo Group April 2007 APS Meeting LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
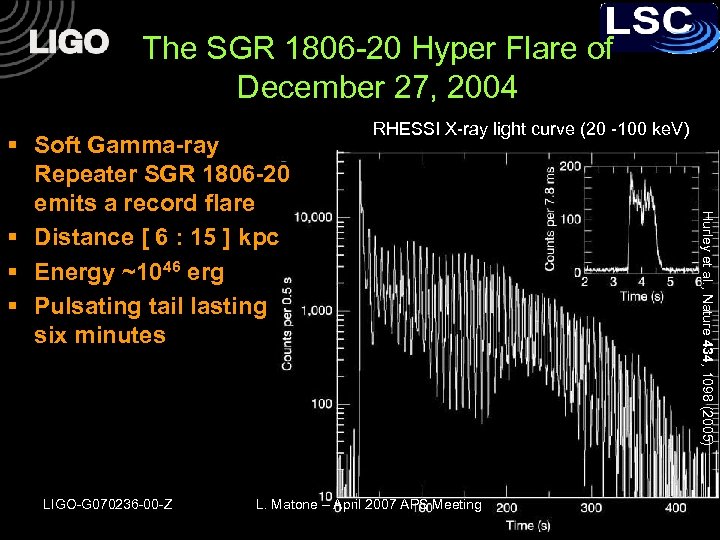 The SGR 1806 -20 Hyper Flare of December 27, 2004 LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting Hurley et al. , Nature 434, 1098 (2005) § Soft Gamma-ray Repeater SGR 1806 -20 emits a record flare § Distance [ 6 : 15 ] kpc § Energy ~1046 erg § Pulsating tail lasting six minutes RHESSI X-ray light curve (20 -100 ke. V)
The SGR 1806 -20 Hyper Flare of December 27, 2004 LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting Hurley et al. , Nature 434, 1098 (2005) § Soft Gamma-ray Repeater SGR 1806 -20 emits a record flare § Distance [ 6 : 15 ] kpc § Energy ~1046 erg § Pulsating tail lasting six minutes RHESSI X-ray light curve (20 -100 ke. V)
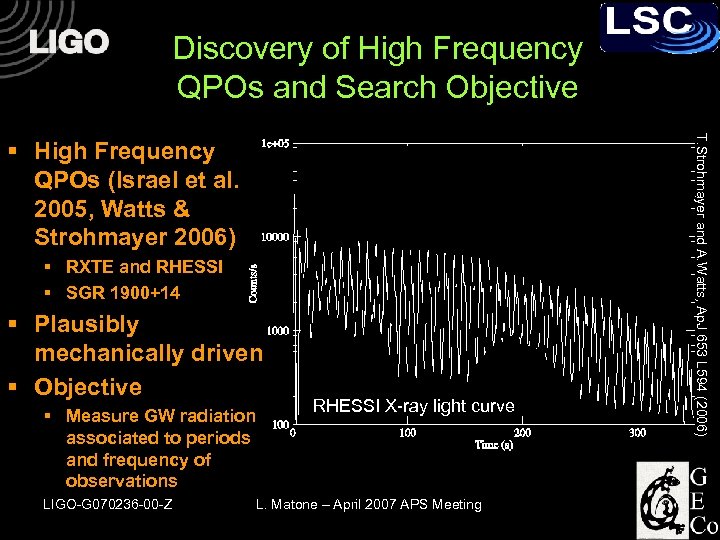 Discovery of High Frequency QPOs and Search Objective § RXTE and RHESSI § SGR 1900+14 § Plausibly mechanically driven § Objective § Measure GW radiation associated to periods and frequency of observations LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z RHESSI X-ray light curve L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting T. Strohmayer and A. Watts, Ap. J 653 L 594 (2006) § High Frequency QPOs (Israel et al. 2005, Watts & Strohmayer 2006)
Discovery of High Frequency QPOs and Search Objective § RXTE and RHESSI § SGR 1900+14 § Plausibly mechanically driven § Objective § Measure GW radiation associated to periods and frequency of observations LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z RHESSI X-ray light curve L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting T. Strohmayer and A. Watts, Ap. J 653 L 594 (2006) § High Frequency QPOs (Israel et al. 2005, Watts & Strohmayer 2006)
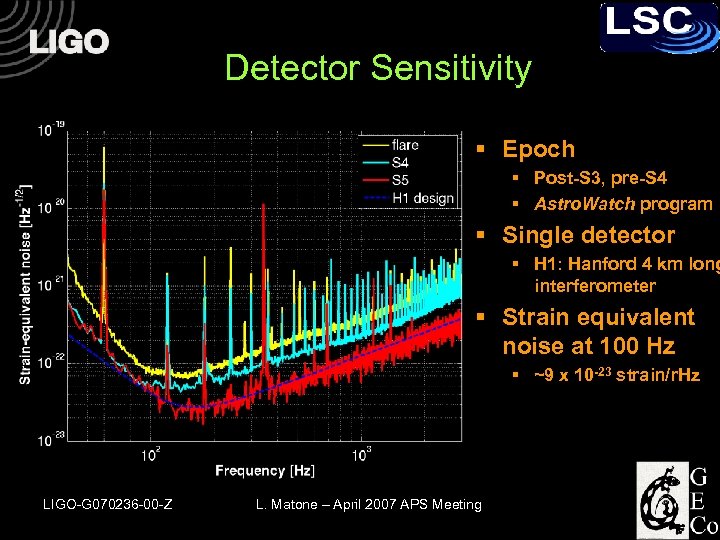 Detector Sensitivity § Epoch § Post-S 3, pre-S 4 § Astro. Watch program § Single detector § H 1: Hanford 4 km long interferometer § Strain equivalent noise at 100 Hz § ~9 x 10 -23 strain/r. Hz LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
Detector Sensitivity § Epoch § Post-S 3, pre-S 4 § Astro. Watch program § Single detector § H 1: Hanford 4 km long interferometer § Strain equivalent noise at 100 Hz § ~9 x 10 -23 strain/r. Hz LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
 Excess Energy Measure § Search for tens-of-seconds long signals § Narrow band § Veto data corresponding to short duration glitches § Unknown frequency content and evolution § QPO frequency and bandwidth is measured § Search algorithm § Provides a constant sensitivity over phase space LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
Excess Energy Measure § Search for tens-of-seconds long signals § Narrow band § Veto data corresponding to short duration glitches § Unknown frequency content and evolution § QPO frequency and bandwidth is measured § Search algorithm § Provides a constant sensitivity over phase space LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
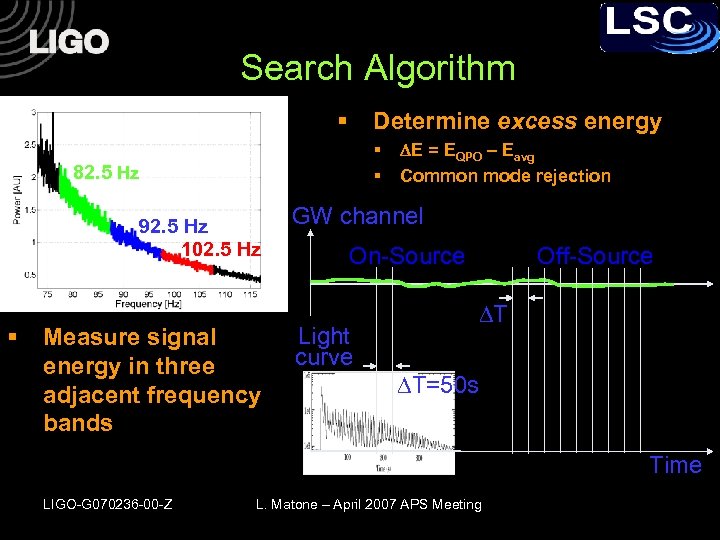 Search Algorithm § Determine excess energy § § 82. 5 Hz 92. 5 Hz 102. 5 Hz § Measure signal energy in three adjacent frequency bands DE = EQPO – Eavg Common mode rejection GW channel On-Source Light curve Off-Source T T=50 s Time LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
Search Algorithm § Determine excess energy § § 82. 5 Hz 92. 5 Hz 102. 5 Hz § Measure signal energy in three adjacent frequency bands DE = EQPO – Eavg Common mode rejection GW channel On-Source Light curve Off-Source T T=50 s Time LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
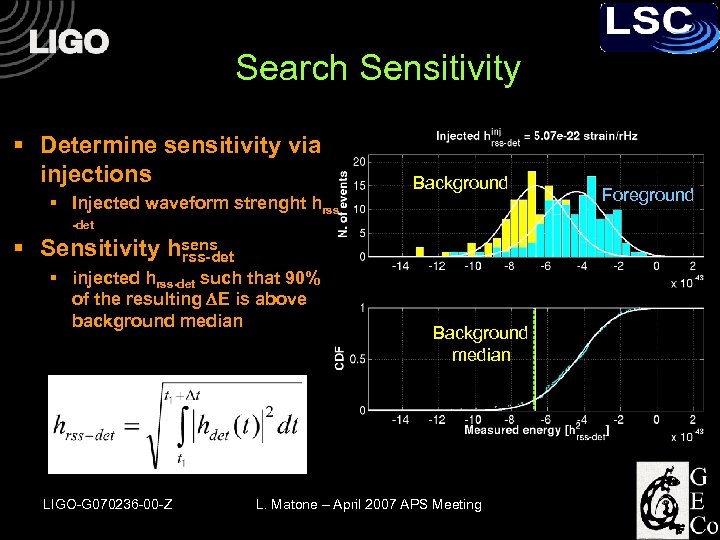 Search Sensitivity § Determine sensitivity via injections § Injected waveform strenght hrss Background -det § Sensitivity hsens rss-det § injected hrss-det such that 90% of the resulting DE is above background median LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z Background median L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting Foreground
Search Sensitivity § Determine sensitivity via injections § Injected waveform strenght hrss Background -det § Sensitivity hsens rss-det § injected hrss-det such that 90% of the resulting DE is above background median LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z Background median L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting Foreground
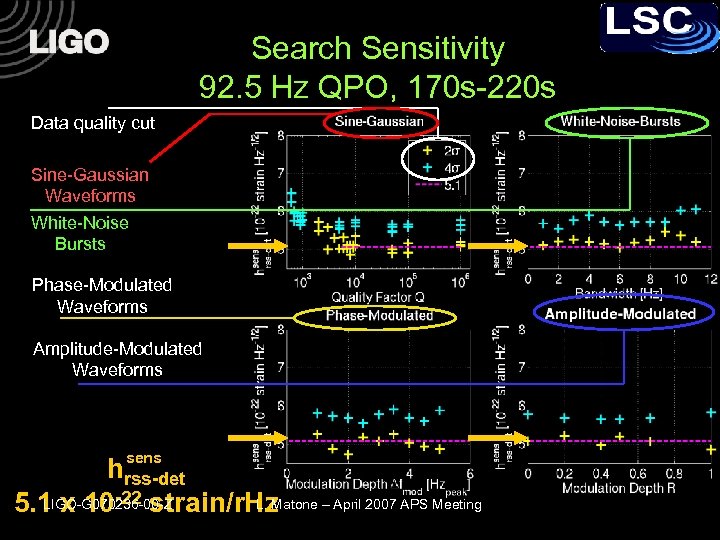 Search Sensitivity 92. 5 Hz QPO, 170 s-220 s Data quality cut Sine-Gaussian Waveforms White-Noise Bursts Phase-Modulated Waveforms Amplitude-Modulated Waveforms sens hrss-det LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting 5. 1 x 10 -22 strain/r. Hz
Search Sensitivity 92. 5 Hz QPO, 170 s-220 s Data quality cut Sine-Gaussian Waveforms White-Noise Bursts Phase-Modulated Waveforms Amplitude-Modulated Waveforms sens hrss-det LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting 5. 1 x 10 -22 strain/r. Hz
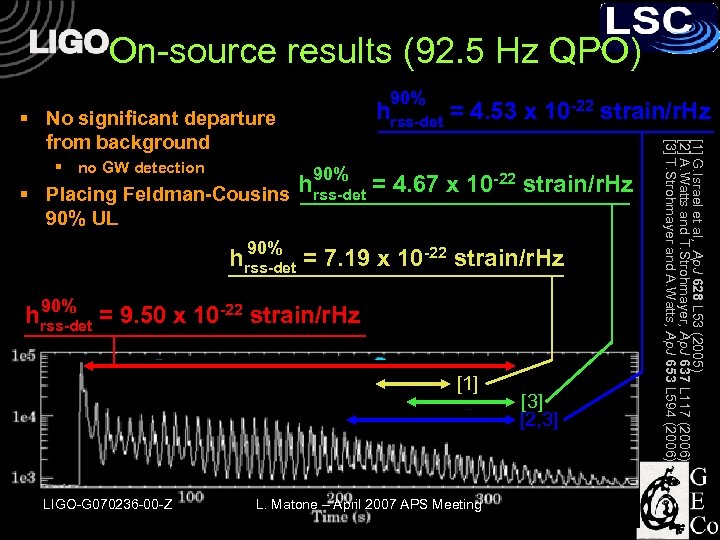 On-source results (92. 5 Hz QPO) 90% hrss-det = 4. 53 x 10 -22 strain/r. Hz § no GW detection 90% hrss-det = 4. 67 x 10 -22 strain/r. Hz § Placing Feldman-Cousins 90% UL 90% hrss-det = 7. 19 x 10 -22 strain/r. Hz 90% hrss-det = 9. 50 x 10 -22 strain/r. Hz [1] LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting [3] [2, 3] [1] G. Israel et al, Ap. J 628 L 53 (2005) [2] A. Watts and T. Strohmayer, Ap. J 637 L 117 (2006) [3] T. Strohmayer and A. Watts, Ap. J 653 L 594 (2006) § No significant departure from background
On-source results (92. 5 Hz QPO) 90% hrss-det = 4. 53 x 10 -22 strain/r. Hz § no GW detection 90% hrss-det = 4. 67 x 10 -22 strain/r. Hz § Placing Feldman-Cousins 90% UL 90% hrss-det = 7. 19 x 10 -22 strain/r. Hz 90% hrss-det = 9. 50 x 10 -22 strain/r. Hz [1] LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting [3] [2, 3] [1] G. Israel et al, Ap. J 628 L 53 (2005) [2] A. Watts and T. Strohmayer, Ap. J 637 L 117 (2006) [3] T. Strohmayer and A. Watts, Ap. J 653 L 594 (2006) § No significant departure from background
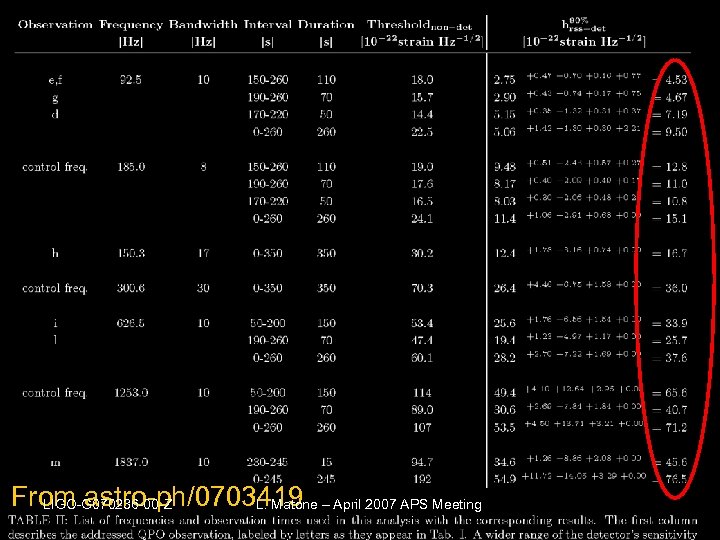 From astro-ph/0703419 – April 2007 APS Meeting LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone
From astro-ph/0703419 – April 2007 APS Meeting LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone
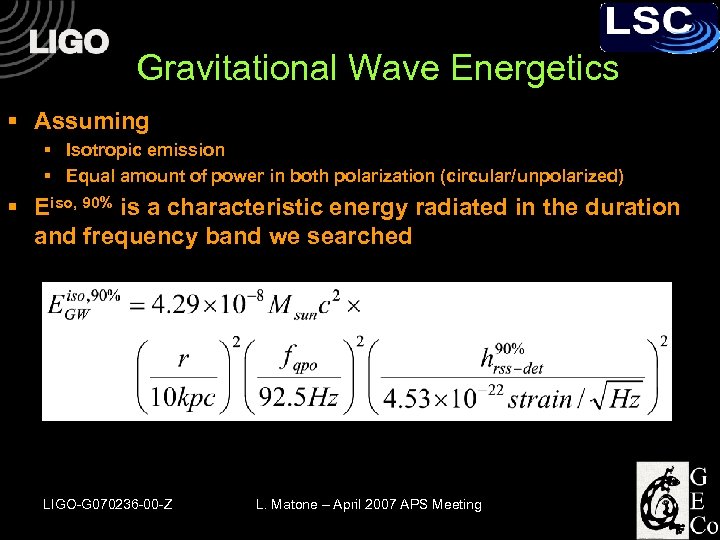 Gravitational Wave Energetics § Assuming § Isotropic emission § Equal amount of power in both polarization (circular/unpolarized) § Eiso, 90% is a characteristic energy radiated in the duration and frequency band we searched LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
Gravitational Wave Energetics § Assuming § Isotropic emission § Equal amount of power in both polarization (circular/unpolarized) § Eiso, 90% is a characteristic energy radiated in the duration and frequency band we searched LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
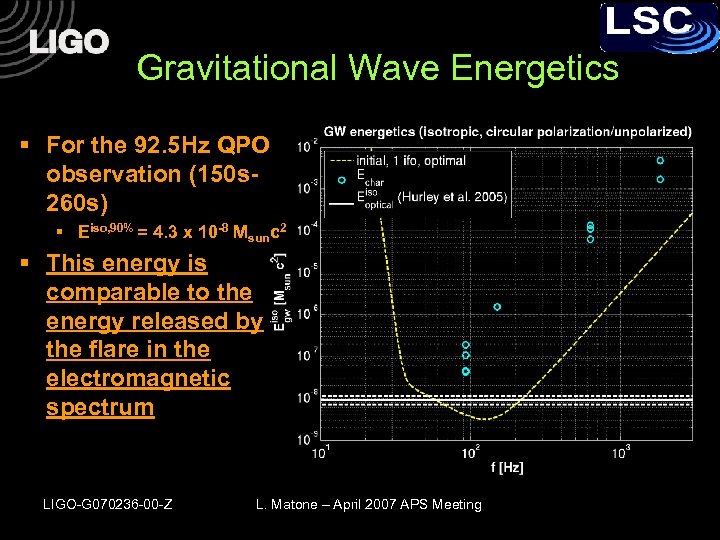 Gravitational Wave Energetics § For the 92. 5 Hz QPO observation (150 s 260 s) § Eiso, 90% = 4. 3 x 10 -8 Msunc 2 § This energy is comparable to the energy released by the flare in the electromagnetic spectrum LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
Gravitational Wave Energetics § For the 92. 5 Hz QPO observation (150 s 260 s) § Eiso, 90% = 4. 3 x 10 -8 Msunc 2 § This energy is comparable to the energy released by the flare in the electromagnetic spectrum LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
 Conclusions § Excess energy algorithm § Designed to search for tens of seconds long narrow band signals § Estimated the search sensitivity using software injections § Upper bounds on the GW strength associated to the observed QPOs § Best case for the 92. 5 Hz QPO (150 s - 260 s) 90% § hrss-det = 4. 5 x 10 -22 strain/r. Hz § Characteristic energy (isotropic, equal power in both polarization states) § E iso, 90% = 4. 3 x 10 -8 M sun c 2 § comparable to the emitted energy in the electromagnetic spectrum § Next step: § address flares from SGR 1806 -20 and SGR 1900+14 during the fifth science run (S 5) § strain equivalent noise improvement (~3 x at 150 Hz) § exploiting multiple data streams (cross-correlation) LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting
Conclusions § Excess energy algorithm § Designed to search for tens of seconds long narrow band signals § Estimated the search sensitivity using software injections § Upper bounds on the GW strength associated to the observed QPOs § Best case for the 92. 5 Hz QPO (150 s - 260 s) 90% § hrss-det = 4. 5 x 10 -22 strain/r. Hz § Characteristic energy (isotropic, equal power in both polarization states) § E iso, 90% = 4. 3 x 10 -8 M sun c 2 § comparable to the emitted energy in the electromagnetic spectrum § Next step: § address flares from SGR 1806 -20 and SGR 1900+14 during the fifth science run (S 5) § strain equivalent noise improvement (~3 x at 150 Hz) § exploiting multiple data streams (cross-correlation) LIGO-G 070236 -00 -Z L. Matone – April 2007 APS Meeting


