Search for biomarkers and development of pharmacogenetic approaches


Search for biomarkers and development of pharmacogenetic approaches to personalized therapy of patients with schizophrenia. S. A. Ivanova, L. P. Smirnova, O. Yu. Fedorenko, A. V. Semke (Mental Health Research Institute, Tomsk) RUSSIAN CONFERENCE WITH INTERNATIONAL PARTICIPATION AND WORKSHOP FOR JUNIOR SCIENTISTS “BIOMARKERS IN PSYCHIATRY: IDENTIFICATION AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS”

– is a new breakthrough in development of molecular medicine which main objective consists in application of achievements of basic medico-biological sciences for search of effective methods of diagnostics and treatment (Archakov AI, 2012, Lieb W, 2012). In the field of translational psychiatry the main directions of research are connected with search for biomarkers which can be used for diagnosis of mental disorders, and in the long term be molecular targets for therapeutic influence and development of pharmacogenetic approaches to the personalized therapy. The translational medicine is based first of all on achievement of such directions of sciences as proteomics, genomics and metabolomics. According to prognosis of foreign researchers (Lakhan SE, 2011), progress in the area of neuroscience will be connected with proteomic studies. Translational medicine

I. BIOMARKERS II. PHARMACOGENETIC INVESTIGATION The main directions of research of schizophrenia in laboratory of molecular genetics and biochemistry
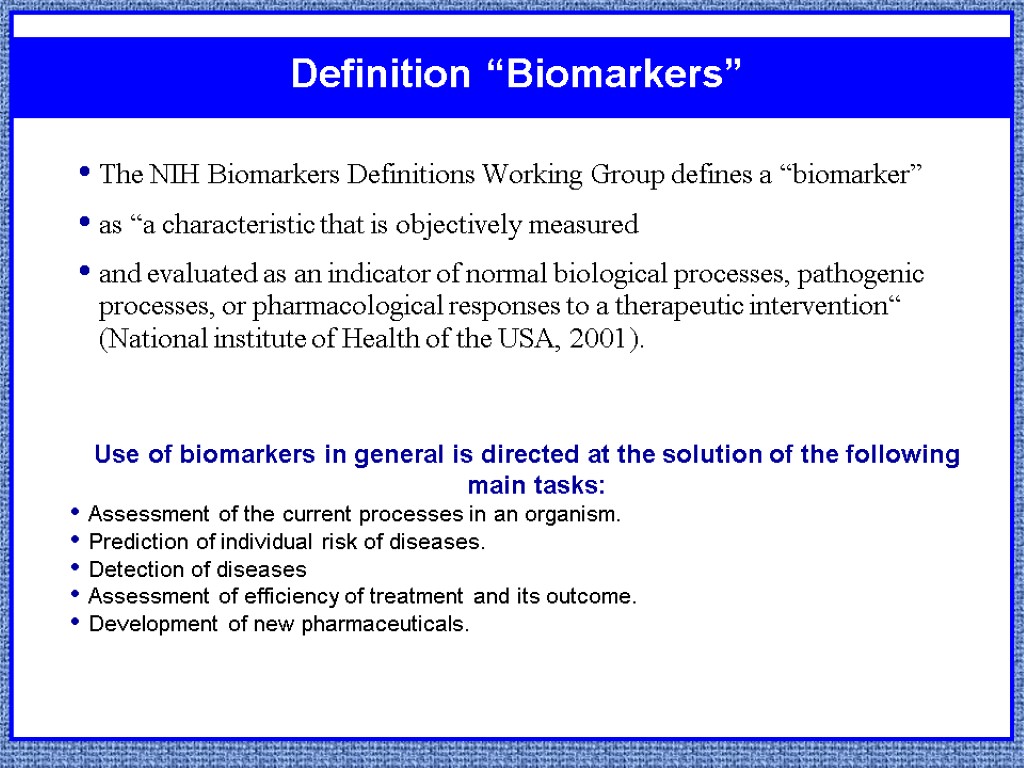
The NIH Biomarkers Definitions Working Group defines a “biomarker” as “a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacological responses to a therapeutic intervention“ (National institute of Health of the USA, 2001). Definition “Biomarkers” Use of biomarkers in general is directed at the solution of the following main tasks: Assessment of the current processes in an organism. Prediction of individual risk of diseases. Detection of diseases Assessment of efficiency of treatment and its outcome. Development of new pharmaceuticals.
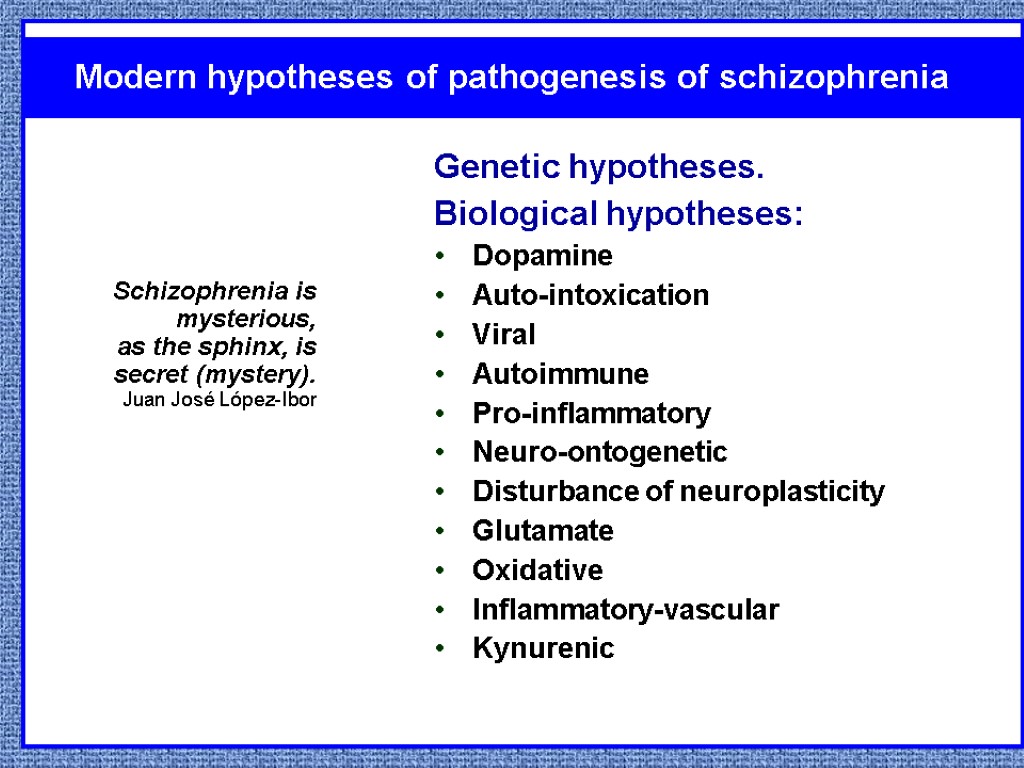
Genetic hypotheses. Biological hypotheses: Dopamine Auto-intoxication Viral Autoimmune Pro-inflammatory Neuro-ontogenetic Disturbance of neuroplasticity Glutamate Oxidative Inflammatory-vascular Kynurenic Modern hypotheses of pathogenesis of schizophrenia Schizophrenia is mysterious, as the sphinx, is secret (mystery). Juan José López-Ibor
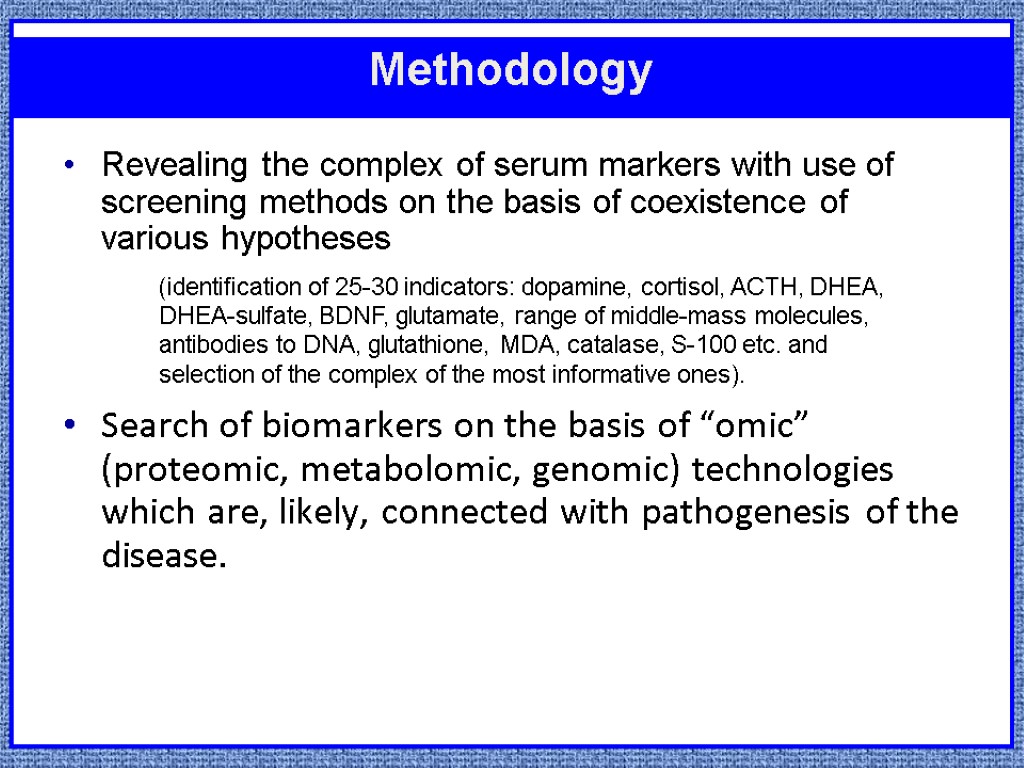
Methodology Revealing the complex of serum markers with use of screening methods on the basis of coexistence of various hypotheses Search of biomarkers on the basis of “omic” (proteomic, metabolomic, genomic) technologies which are, likely, connected with pathogenesis of the disease. (identification of 25-30 indicators: dopamine, cortisol, ACTH, DHEA, DHEA-sulfate, BDNF, glutamate, range of middle-mass molecules, antibodies to DNA, glutathione, MDA, catalase, S-100 etc. and selection of the complex of the most informative ones).
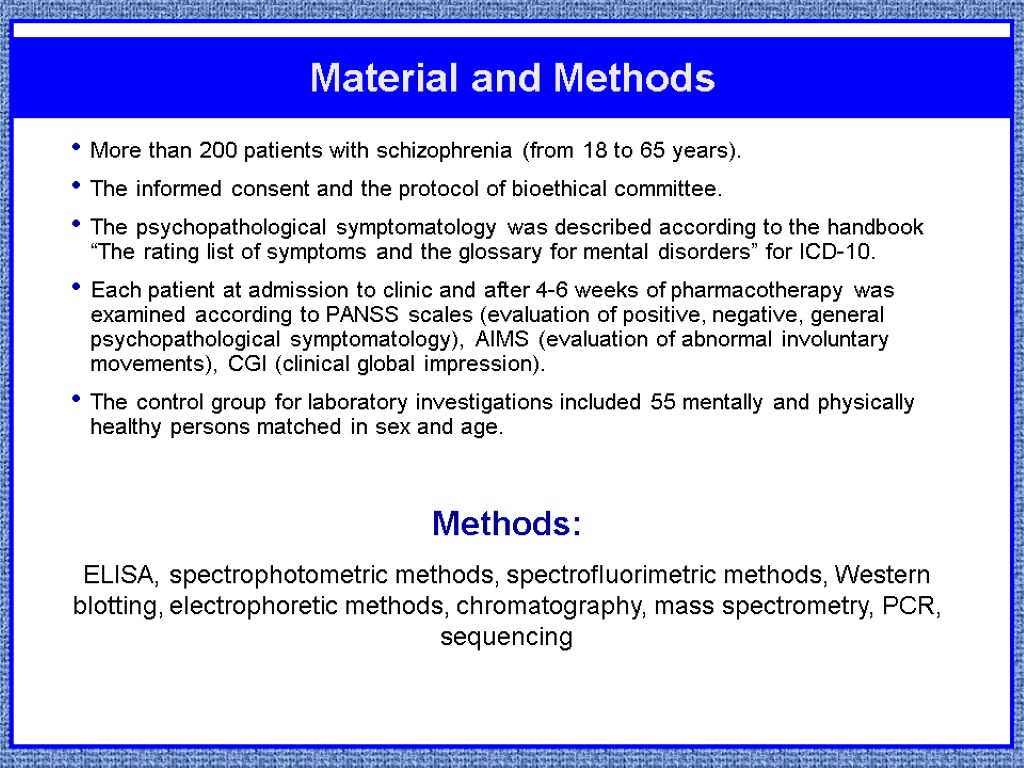
Материалы и методы More than 200 patients with schizophrenia (from 18 to 65 years). The informed consent and the protocol of bioethical committee. The psychopathological symptomatology was described according to the handbook “The rating list of symptoms and the glossary for mental disorders” for ICD-10. Each patient at admission to clinic and after 4-6 weeks of pharmacotherapy was examined according to PANSS scales (evaluation of positive, negative, general psychopathological symptomatology), AIMS (evaluation of abnormal involuntary movements), CGI (clinical global impression). The control group for laboratory investigations included 55 mentally and physically healthy persons matched in sex and age. Material and Methods Methods: ELISA, spectrophotometric methods, spectrofluorimetric methods, Western blotting, electrophoretic methods, chromatography, mass spectrometry, PCR, sequencing
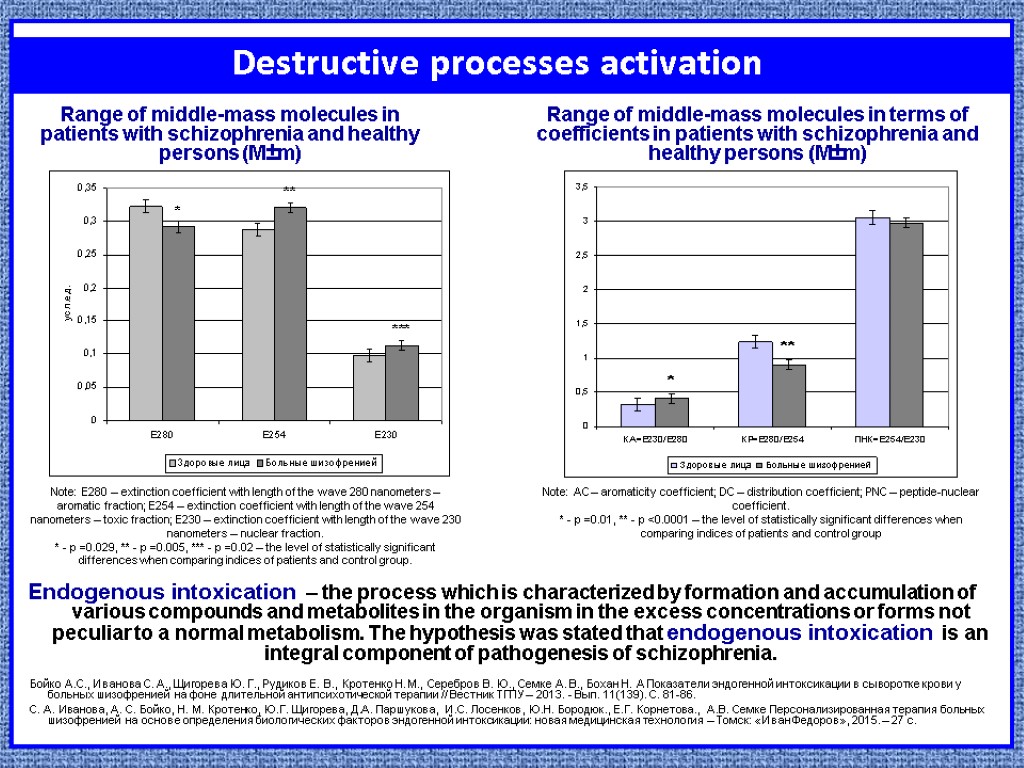
Destructive processes activation Endogenous intoxication – the process which is characterized by formation and accumulation of various compounds and metabolites in the organism in the excess concentrations or forms not peculiar to a normal metabolism. The hypothesis was stated that endogenous intoxication is an integral component of pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Note: E280 – extinction coefficient with length of the wave 280 nanometers – aromatic fraction; E254 – extinction coefficient with length of the wave 254 nanometers – toxic fraction; E230 – extinction coefficient with length of the wave 230 nanometers – nuclear fraction. * - p =0.029, ** - p =0.005, *** - p =0.02 – the level of statistically significant differences when comparing indices of patients and control group. Note: AC – aromaticity coefficient; DC – distribution coefficient; PNC – peptide-nuclear coefficient. * - p =0.01, ** - p <0.0001 – the level of statistically significant differences when comparing indices of patients and control group Бойко А.С., Иванова С. А., Щигорева Ю. Г., Рудиков Е. В., Кротенко Н. М., Серебров В. Ю., Семке А. В., Бохан Н. А Показатели эндогенной интоксикации в сыворотке крови у больных шизофренией на фоне длительной антипсихотической терапии // Вестник ТГПУ – 2013. - Вып. 11(139). С. 81-86. С. А. Иванова, А. С. Бойко, Н. М. Кротенко, Ю.Г. Щигорева, Д.А. Паршукова, И.С. Лосенков, Ю.Н. Бородюк., Е.Г. Корнетова., А.В. Семке Персонализированная терапия больных шизофренией на основе определения биологических факторов эндогенной интоксикации: новая медицинская технология – Томск: «Иван Федоров», 2015. – 27 с. Range of middle-mass molecules in patients with schizophrenia and healthy persons (М±m) Range of middle-mass molecules in terms of coefficients in patients with schizophrenia and healthy persons (М±m)
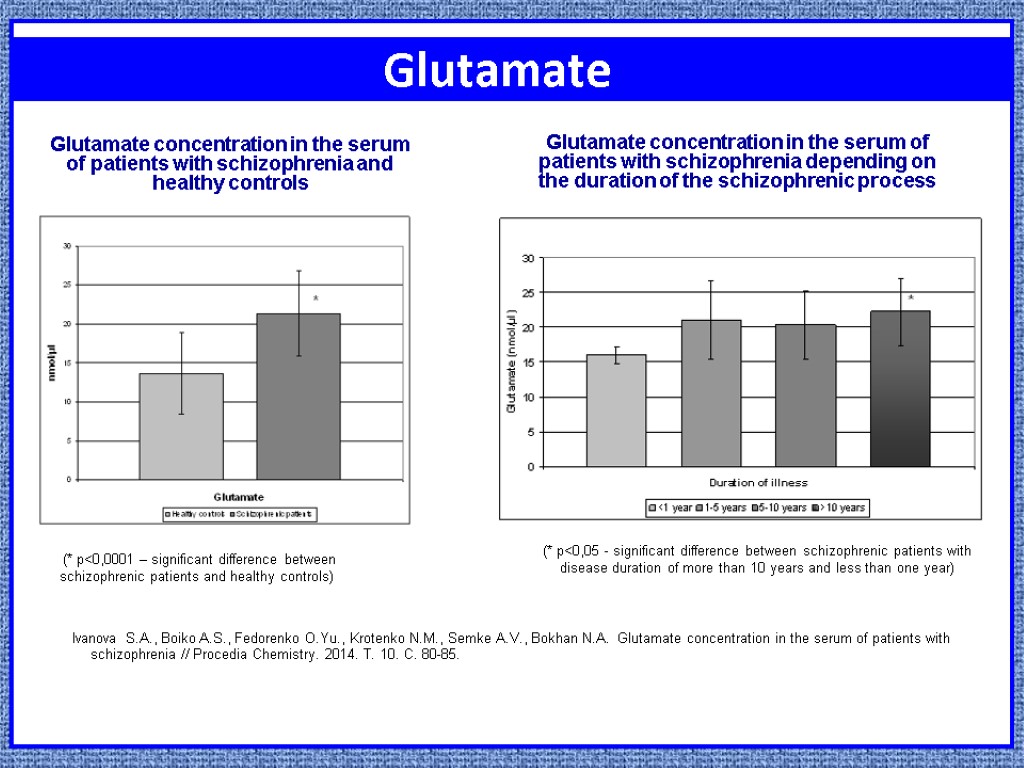
Glutamate Ivanova S.A., Boiko A.S., Fedorenko O.Yu., Krotenko N.M., Semke A.V., Bokhan N.A. Glutamate concentration in the serum of patients with schizophrenia // Procedia Chemistry. 2014. Т. 10. С. 80-85. (* p<0,0001 – significant difference between schizophrenic patients and healthy controls) Glutamate concentration in the serum of patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls Glutamate concentration in the serum of patients with schizophrenia depending on the duration of the schizophrenic process (* p<0,05 - significant difference between schizophrenic patients with disease duration of more than 10 years and less than one year)
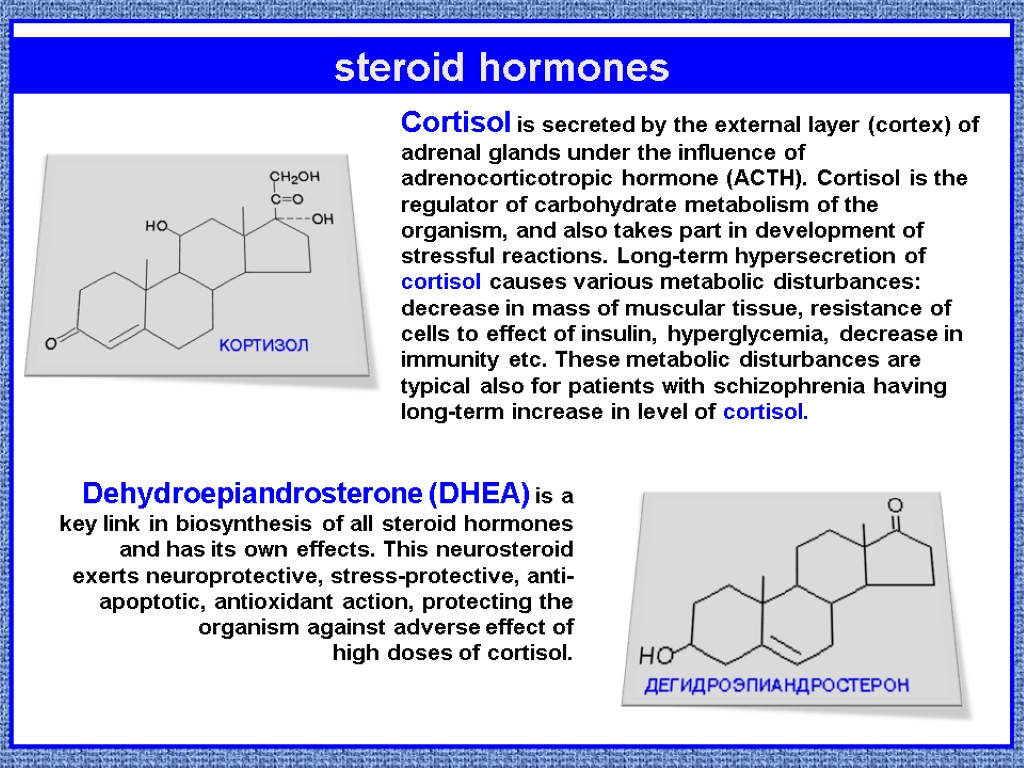
steroid hormones Cortisol is secreted by the external layer (cortex) of adrenal glands under the influence of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Cortisol is the regulator of carbohydrate metabolism of the organism, and also takes part in development of stressful reactions. Long-term hypersecretion of cortisol causes various metabolic disturbances: decrease in mass of muscular tissue, resistance of cells to effect of insulin, hyperglycemia, decrease in immunity etc. These metabolic disturbances are typical also for patients with schizophrenia having long-term increase in level of cortisol. Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is a key link in biosynthesis of all steroid hormones and has its own effects. This neurosteroid exerts neuroprotective, stress-protective, anti-apoptotic, antioxidant action, protecting the organism against adverse effect of high doses of cortisol.
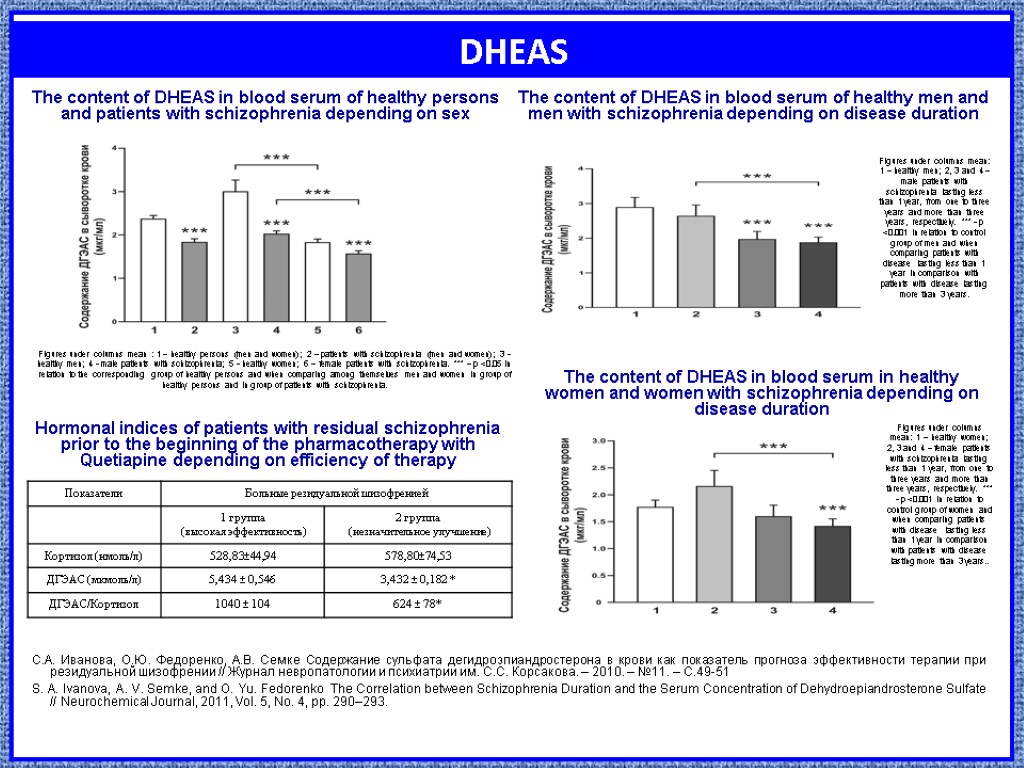
DHEAS С.А. Иванова, О.Ю. Федоренко, А.В. Семке Содержание сульфата дегидроэпиандростерона в крови как показатель прогноза эффективности терапии при резидуальной шизофрении // Журнал невропатологии и психиатрии им. С.С. Корсакова. – 2010. – №11. – С.49-51 S. A. Ivanova, A. V. Semke, and O. Yu. Fedorenko The Correlation between Schizophrenia Duration and the Serum Concentration of Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate // Neurochemical Journal, 2011, Vol. 5, No. 4, pp. 290–293. Figures under columns mean : 1 – healthy persons (men and women); 2 – patients with schizophrenia (men and women); 3 - healthy men; 4 - male patients with schizophrenia; 5 - healthy women; 6 – female patients with schizophrenia. *** – p <0.05 in relation to the corresponding group of healthy persons and when comparing among themselves men and women in group of healthy persons and in group of patients with schizophrenia. Figures under columns mean: 1 – healthy men; 2, 3 and 4 – male patients with schizophrenia lasting less than 1 year, from one to three years and more than three years, respectively. *** - p <0.001 in relation to control group of men and when comparing patients with disease lasting less than 1 year in comparison with patients with disease lasting more than 3 years. Figures under columns mean: 1 – healthy women; 2, 3 and 4 – female patients with schizophrenia lasting less than 1 year, from one to three years and more than three years, respectively. *** - p <0.001 in relation to control group of women and when comparing patients with disease lasting less than 1 year in comparison with patients with disease lasting more than 3 years.. Hormonal indices of patients with residual schizophrenia prior to the beginning of the pharmacotherapy with Quetiapine depending on efficiency of therapy The content of DHEAS in blood serum of healthy persons and patients with schizophrenia depending on sex The content of DHEAS in blood serum of healthy men and men with schizophrenia depending on disease duration The content of DHEAS in blood serum in healthy women and women with schizophrenia depending on disease duration
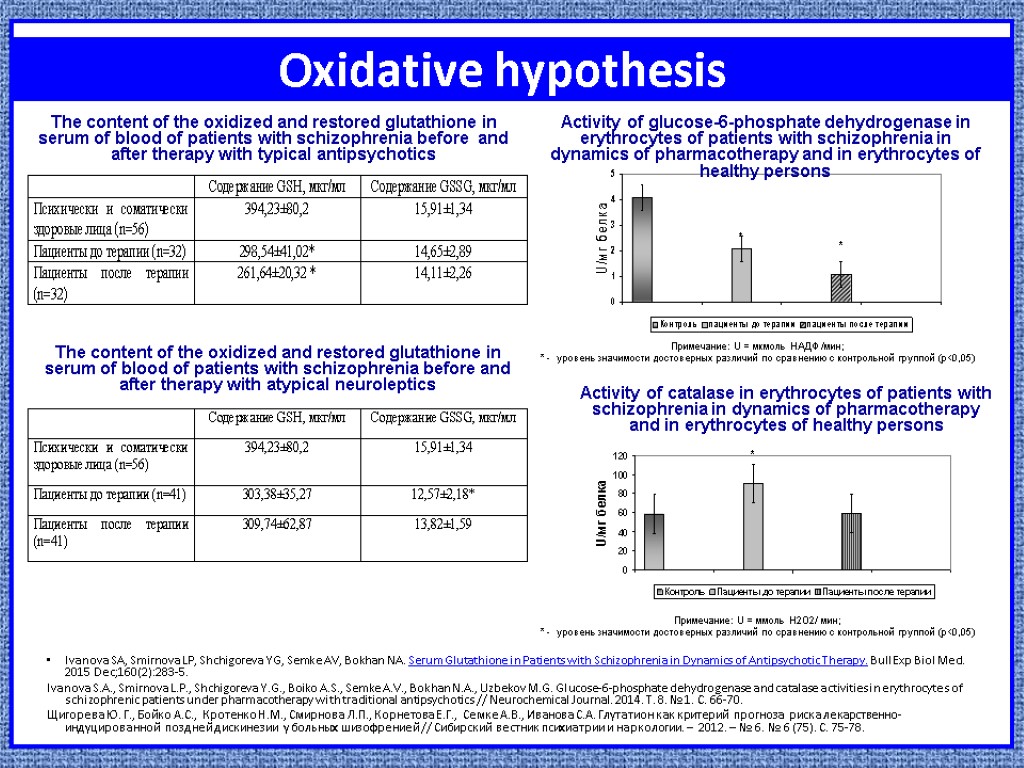
Oxidative hypothesis Ivanova SA, Smirnova LP, Shchigoreva YG, Semke AV, Bokhan NA. Serum Glutathione in Patients with Schizophrenia in Dynamics of Antipsychotic Therapy. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2015 Dec;160(2):283-5. Ivanova S.A., Smirnova L.P., Shchigoreva Y.G., Boiko A.S., Semke A.V., Bokhan N.A., Uzbekov M.G. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and catalase activities in erythrocytes of schizophrenic patients under pharmacotherapy with traditional antipsychotics // Neurochemical Journal. 2014. Т. 8. № 1. С. 66-70. Щигорева Ю. Г., Бойко А.С., Кротенко Н.М., Смирнова Л.П., Корнетова Е.Г., Семке А.В., Иванова С.А. Глутатион как критерий прогноза риска лекарственно-индуцированной поздней дискинезии у больных шизофренией // Сибирский вестник психиатрии и наркологии. – 2012. – № 6. № 6 (75). С. 75-78. The content of the oxidized and restored glutathione in serum of blood of patients with schizophrenia before and after therapy with atypical neuroleptics Примечание: U = мкмоль НАДФ /мин; * - уровень значимости достоверных различий по сравнению с контрольной группой (p<0,05) Примечание: U = ммоль Н2О2/ мин; * - уровень значимости достоверных различий по сравнению с контрольной группой (p<0,05) The content of the oxidized and restored glutathione in serum of blood of patients with schizophrenia before and after therapy with typical antipsychotics Activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in erythrocytes of patients with schizophrenia in dynamics of pharmacotherapy and in erythrocytes of healthy persons Activity of catalase in erythrocytes of patients with schizophrenia in dynamics of pharmacotherapy and in erythrocytes of healthy persons
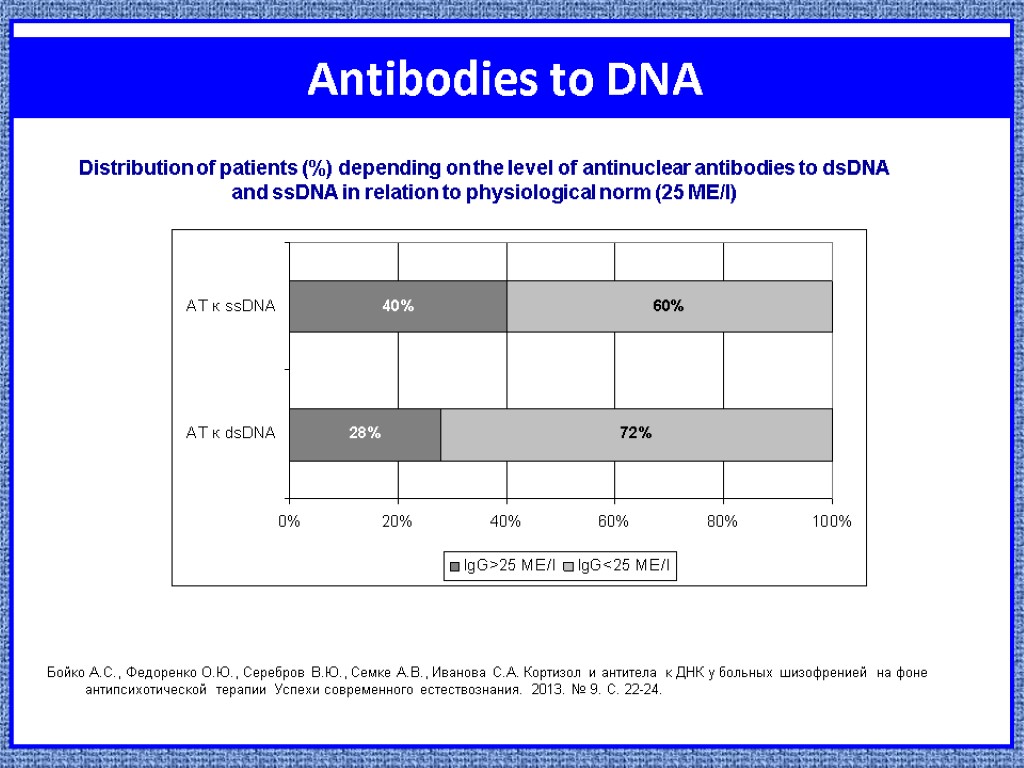
Antibodies to DNA Бойко А.С., Федоренко О.Ю., Серебров В.Ю., Семке А.В., Иванова С.А. Кортизол и антитела к ДНК у больных шизофренией на фоне антипсихотической терапии Успехи современного естествознания. 2013. № 9. С. 22-24. Distribution of patients (%) depending on the level of antinuclear antibodies to dsDNA and ssDNA in relation to physiological norm (25 ME/l)

ABZYMES Catalytically active AB – abzymes (АВZYME : AntiBody enZYME) The antibodies capable to catalyze biochemical reactions. Detection of catalytic activity of Ig changed standard ideas of their pathogenetic role. Ig possessing enzymatic properties are called abzymes. Such their properties as hydrolysis of DNA and proteolysis of proteins are known most of all. Studies of catalytic properties and specificity of Ig G of blood of patients with mental disorders and, in particular, schizophrenia were not carried out earlier. № фракции Proteolytic activity of IgG of schizophrenic patient к ОБМ in situ
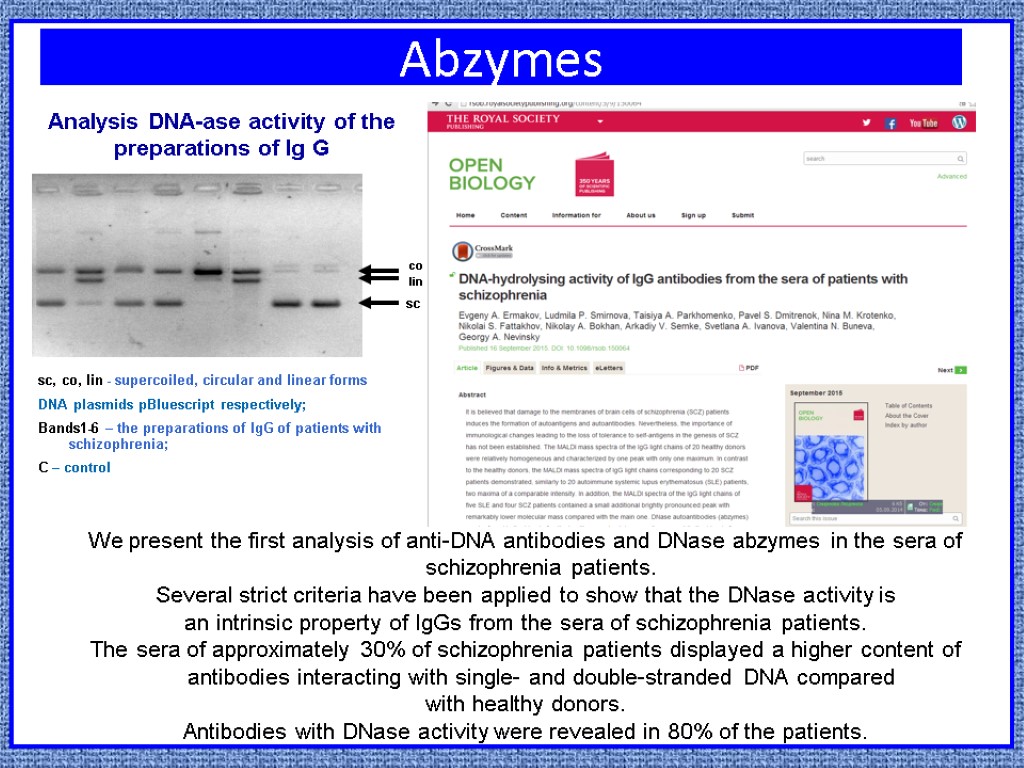
Abzymes sc, co, lin - supercoiled, circular and linear forms DNA plasmids pBluescript respectively; Bands1-6 – the preparations of IgG of patients with schizophrenia; C – control Analysis DNA-ase activity of the preparations of Ig G We present the first analysis of anti-DNA antibodies and DNase abzymes in the sera of schizophrenia patients. Several strict criteria have been applied to show that the DNase activity is an intrinsic property of IgGs from the sera of schizophrenia patients. The sera of approximately 30% of schizophrenia patients displayed a higher content of antibodies interacting with single- and double-stranded DNA compared with healthy donors. Antibodies with DNase activity were revealed in 80% of the patients.
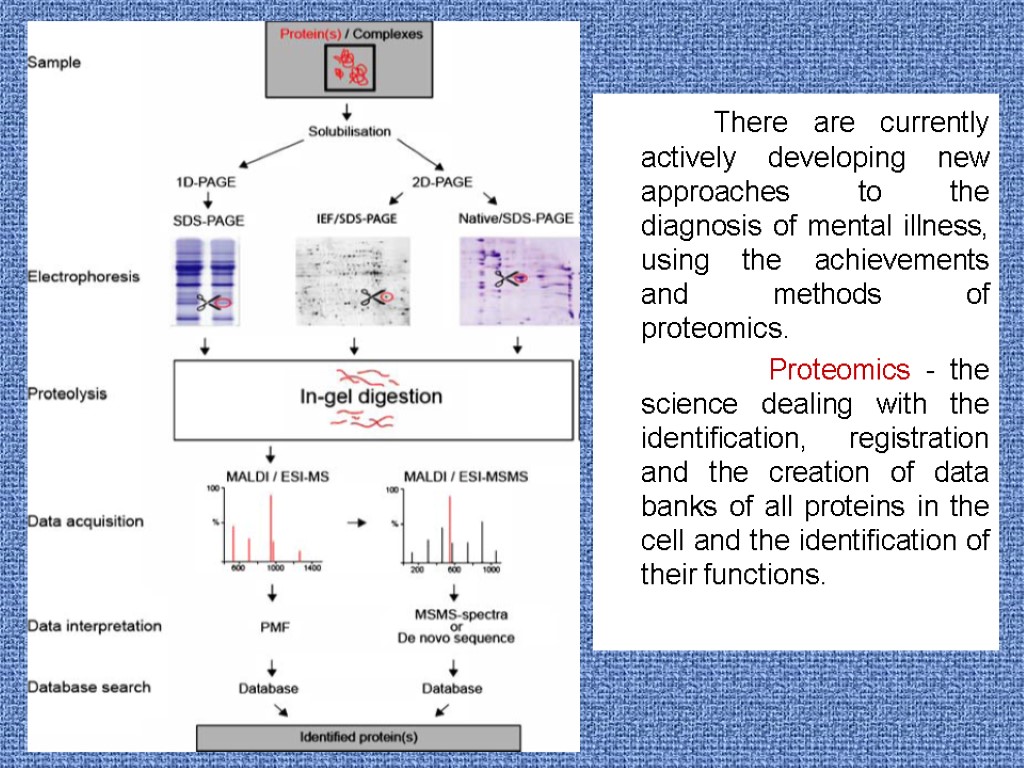
There are currently actively developing new approaches to the diagnosis of mental illness, using the achievements and methods of proteomics. Proteomics - the science dealing with the identification, registration and the creation of data banks of all proteins in the cell and the identification of their functions.

Work is carried out together with Institute of Chemical Biology and Basic Medicine of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Science (Novosibirsk) within the contract on scientific cooperation “Search of the key regulatory proteins participating in pathogenesis of schizophrenia”. Integration project of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Science and the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Science no. 5 “Medical proteomics: search of markers of socially significant mental disorders (2012-2014 )” Proteomic analysis of blood plasma proteins in patients with schizophrenia
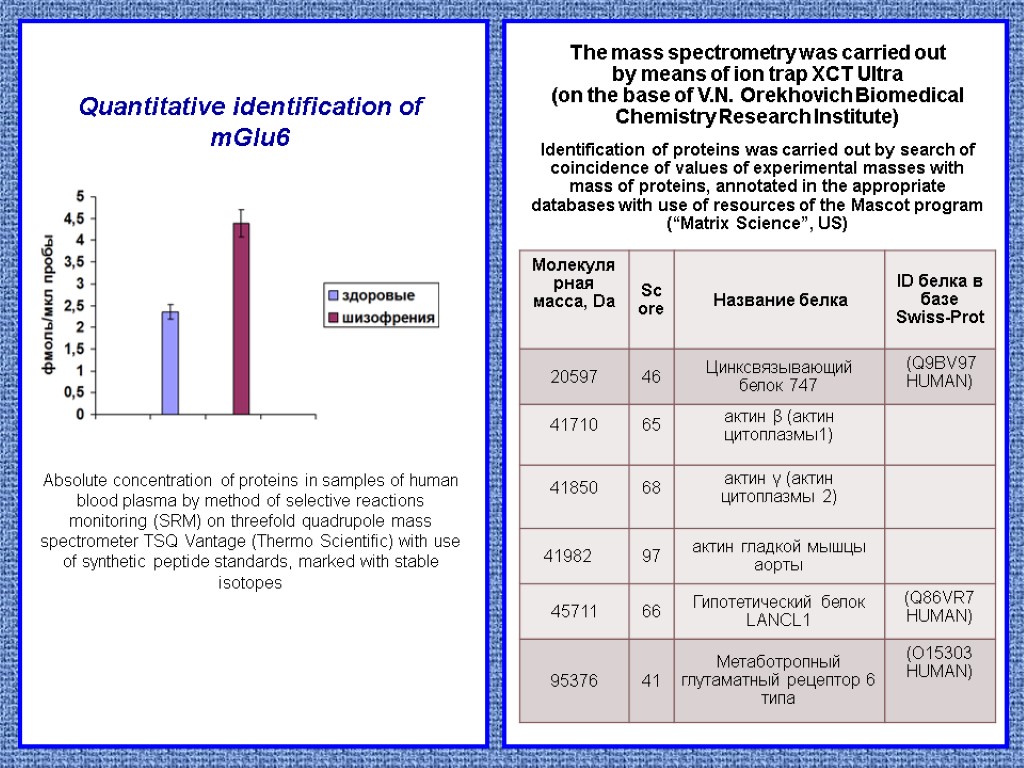
The mass spectrometry was carried out by means of ion trap XCT Ultra (on the base of V.N. Orekhovich Biomedical Chemistry Research Institute) Identification of proteins was carried out by search of coincidence of values of experimental masses with mass of proteins, annotated in the appropriate databases with use of resources of the Mascot program (“Matrix Science”, US) Quantitative identification of mGlu6 Absolute concentration of proteins in samples of human blood plasma by method of selective reactions monitoring (SRM) on threefold quadrupole mass spectrometer TSQ Vantage (Thermo Scientific) with use of synthetic peptide standards, marked with stable isotopes
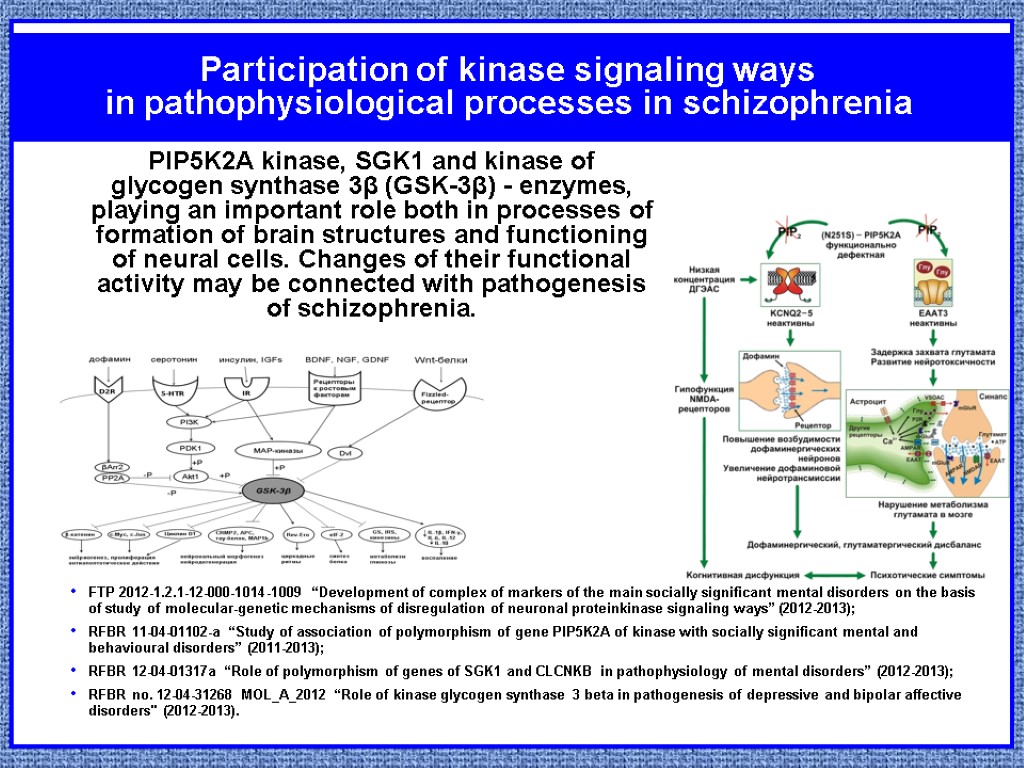
Participation of kinase signaling ways in pathophysiological processes in schizophrenia FTP 2012-1.2.1-12-000-1014-1009 “Development of complex of markers of the main socially significant mental disorders on the basis of study of molecular-genetic mechanisms of disregulation of neuronal proteinkinase signaling ways” (2012-2013); RFBR 11-04-01102-a “Study of association of polymorphism of gene PIP5K2A of kinase with socially significant mental and behavioural disorders” (2011-2013); RFBR 12-04-01317а “Role of polymorphism of genes of SGK1 and CLCNKB in pathophysiology of mental disorders” (2012-2013); RFBR no. 12-04-31268 MOL_A_2012 “Role of kinase glycogen synthase 3 beta in pathogenesis of depressive and bipolar affective disorders" (2012-2013). PIP5K2A kinase, SGK1 and kinase of glycogen synthase 3β (GSK-3β) - enzymes, playing an important role both in processes of formation of brain structures and functioning of neural cells. Changes of their functional activity may be connected with pathogenesis of schizophrenia.

From the report of the academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences V. G. Kukes “The personalized medicine: prospects of introduction in practical healthcare” (2013) The personalized medicine – is the innovative and knowledge-intensive instrument of modernization of healthcare system: increase of efficiency and safety of pharmacotherapy on the basis of knowledge of specific genetic and functional features of the patient. II. PHARMACOGENETIC INVESTIGATION
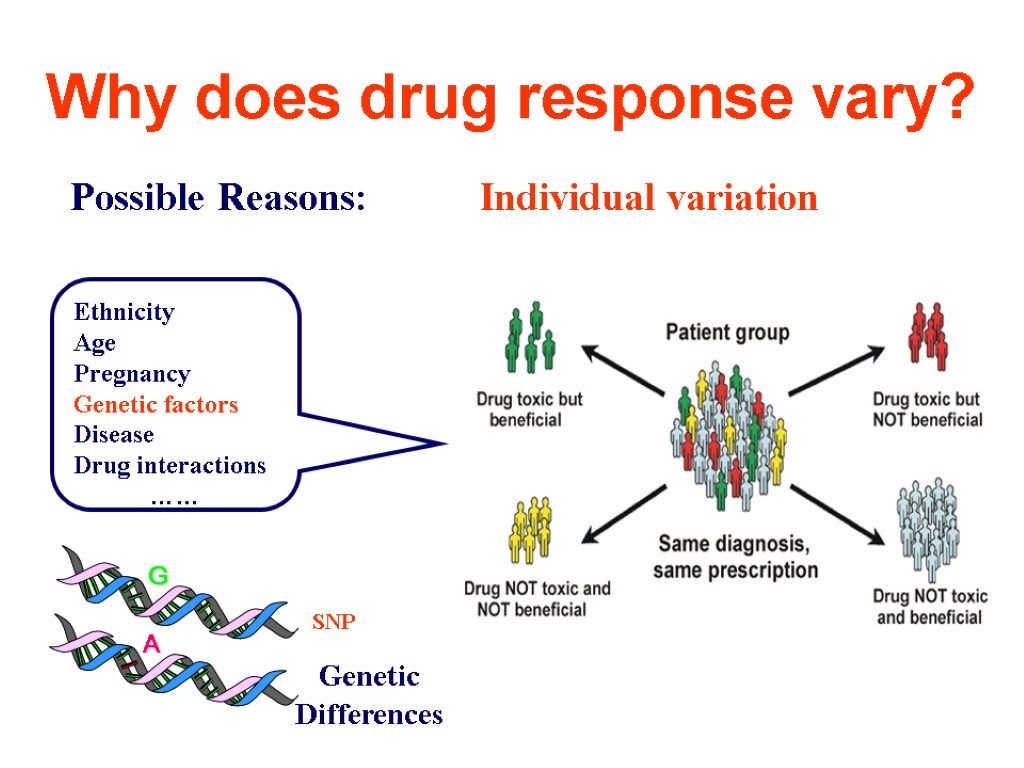
Why does drug response vary? Possible Reasons: Individual variation Ethnicity Age Pregnancy Genetic factors Disease Drug interactions …… Genetic Differences SNP

Why study pharmacogenetics of antipsychotics? Only 60-70% respond to antipsychotics Delayed diagnosis of ‘therapeutic failure’ is a common problem; antipsychotic action occurs after 4-12 weeks of therapy iii. In the meanwhile, patients may experience (severe) side-effects iv. Side-effects (EPS, weight gain, sexual dysfunction, etc.) occur frequently v. The exact pharmacology of antipsychotics is debated

Russian-Dutch project Pharmacogenetics of tardive dyskinesia Chronic psychiatric patients often show movement disorders that can at least partly be attributed to pretreatment with (classical) antipsychotic drugs. Tardive dyskinesia (TD) is a potentially irreversible antipsychotic-induced movement disorder with a prevalence of about 20-30% in psychiatric patients chronically exposed to antipsychotics
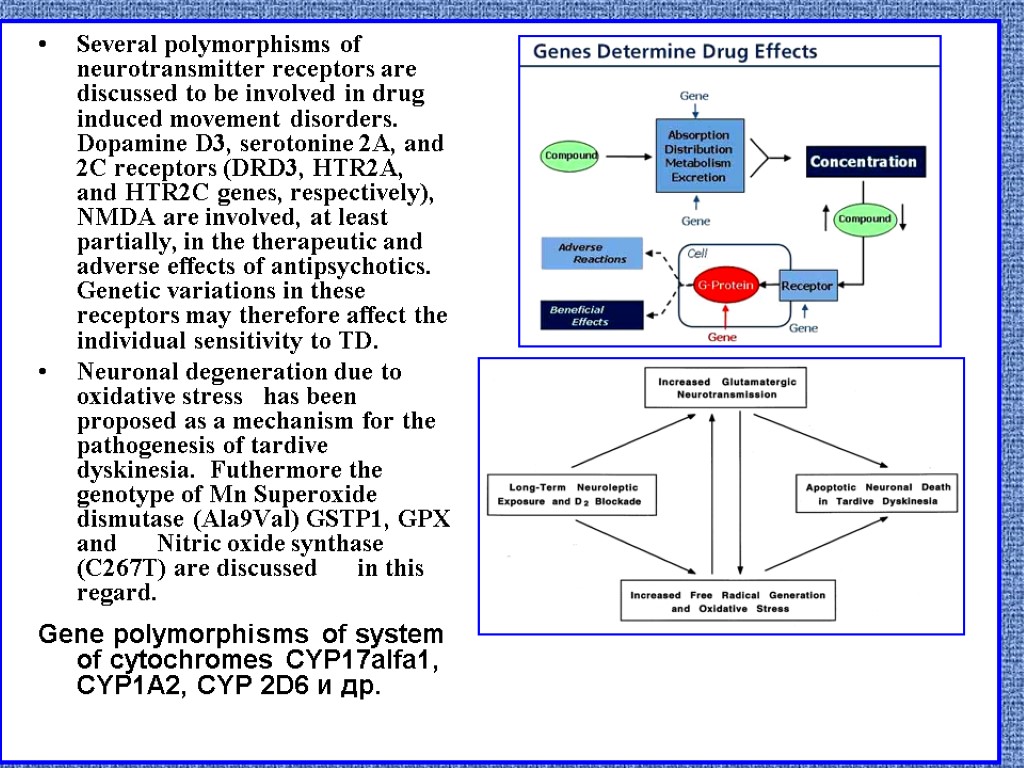
Several polymorphisms of neurotransmitter receptors are discussed to be involved in drug induced movement disorders. Dopamine D3, serotonine 2A, and 2C receptors (DRD3, HTR2A, and HTR2C genes, respectively), NMDA are involved, at least partially, in the therapeutic and adverse effects of antipsychotics. Genetic variations in these receptors may therefore affect the individual sensitivity to TD. Neuronal degeneration due to oxidative stress has been proposed as a mechanism for the pathogenesis of tardive dyskinesia. Futhermore the genotype of Mn Superoxide dismutase (Ala9Val) GSTP1, GPX and Nitric oxide synthase (C267T) are discussed in this regard. Gene polymorphisms of system of cytochromes CYP17alfa1, CYP1A2, CYP 2D6 и др.

We examined 431 patients from three psychiatric hospitals in Siberia (patients were suffering from schizophrenia or schizotypical disorder and were on long-term treatment with antipsychotic drugs) : Mental Health Research Institute Kemerovo Clinical Psychiatric Hospital Chita State Medical Academy. 143 patients of the neurology department of the Siberian State Medical University of Tomsk who had spontaneous extrapyramidal disorders (101 had PD). Pharmacogenotypes and drug-induced movement disorders
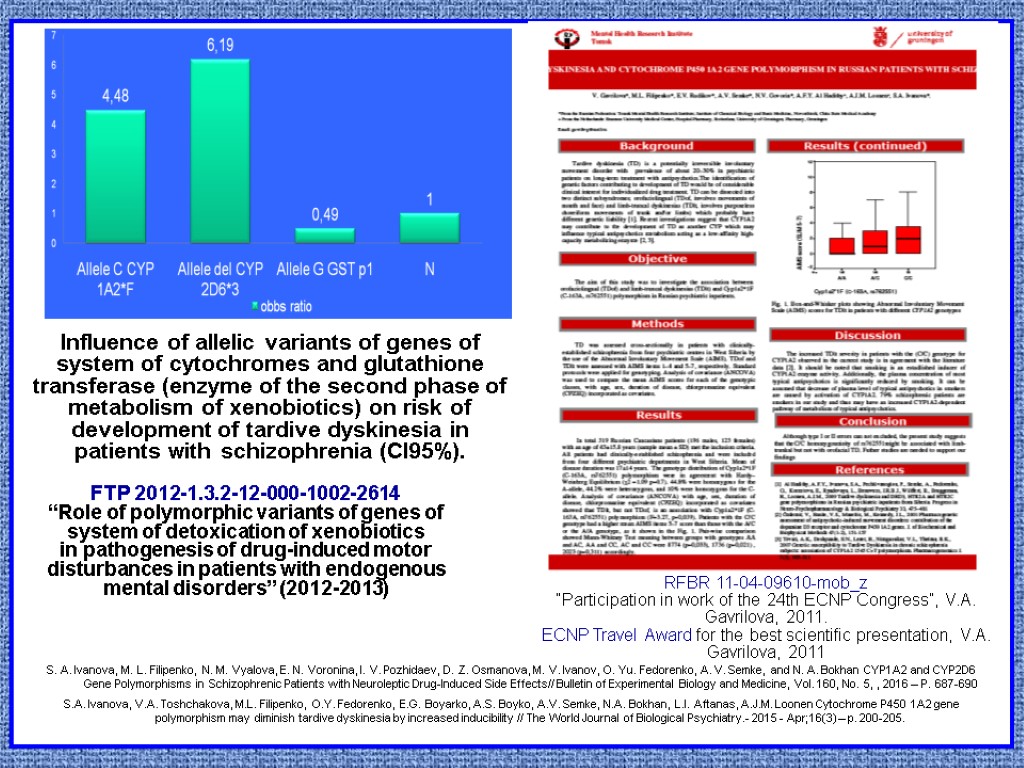
Influence of allelic variants of genes of system of cytochromes and glutathione transferase (enzyme of the second phase of metabolism of xenobiotics) on risk of development of tardive dyskinesia in patients with schizophrenia (CI95%). RFBR 11-04-09610-mob_z “Participation in work of the 24th ECNP Congress”, V.A. Gavrilova, 2011. ECNP Travel Award for the best scientific presentation, V.A. Gavrilova, 2011 FTP 2012-1.3.2-12-000-1002-2614 “Role of polymorphic variants of genes of system of detoxication of xenobiotics in pathogenesis of drug-induced motor disturbances in patients with endogenous mental disorders” (2012-2013) S. A. Ivanova, M. L. Filipenko, N. M. Vyalova, E. N. Voronina, I. V. Pozhidaev, D. Z. Osmanova, M. V. Ivanov, O. Yu. Fedorenko, A. V. Semke, and N. A. Bokhan CYP1A2 and CYP2D6 Gene Polymorphisms in Schizophrenic Patients with Neuroleptic Drug-Induced Side Effects// Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, Vol. 160, No. 5, , 2016 – P. 687-690 S.A. Ivanova, V.A. Toshchakova, M.L. Filipenko, O.Y. Fedorenko, E.G. Boyarko, A.S. Boyko, A.V. Semke, N.A. Bokhan, L.I. Aftanas, A.J.M. Loonen Cytochrome P450 1A2 gene polymorphism may diminish tardive dyskinesia by increased inducibility // The World Journal of Biological Psychiatry.- 2015 - Apr;16(3) – p. 200-205.
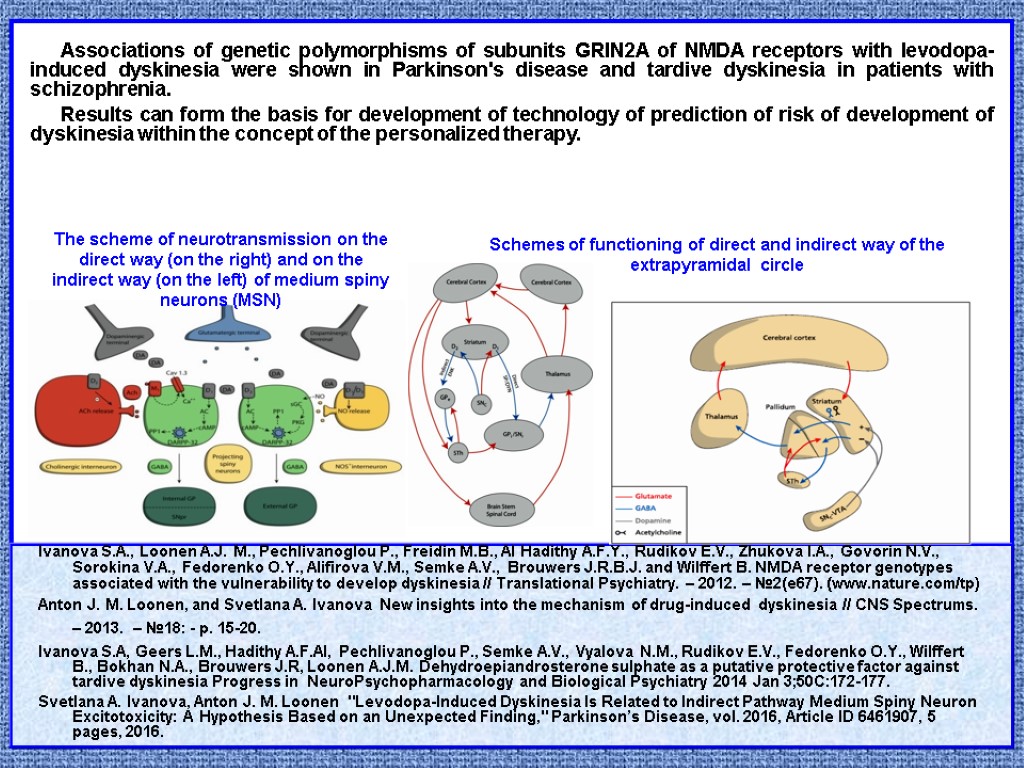
Associations of genetic polymorphisms of subunits GRIN2A of NMDA receptors with levodopa-induced dyskinesia were shown in Parkinson's disease and tardive dyskinesia in patients with schizophrenia. Results can form the basis for development of technology of prediction of risk of development of dyskinesia within the concept of the personalized therapy. Ivanova S.A., Loonen A.J. M., Pechlivanoglou P., Freidin M.B., Al Hadithy A.F.Y., Rudikov E.V., Zhukova I.A., Govorin N.V., Sorokina V.A., Fedorenko O.Y., Alifirova V.M., Semke A.V., Brouwers J.R.B.J. and Wilffert B. NMDA receptor genotypes associated with the vulnerability to develop dyskinesia // Translational Psychiatry. – 2012. – №2(e67). (www.nature.com/tp) Anton J. M. Loonen, and Svetlana A. Ivanova New insights into the mechanism of drug-induced dyskinesia // CNS Spectrums. – 2013. – №18: - p. 15-20. Ivanova S.A, Geers L.M., Hadithy A.F.Al, Pechlivanoglou P., Semke A.V., Vyalova N.M., Rudikov E.V., Fedorenko O.Y., Wilffert B., Bokhan N.A., Brouwers J.R, Loonen A.J.M. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate as a putative protective factor against tardive dyskinesia Progress in NeuroPsychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 2014 Jan 3;50C:172-177. Svetlana A. Ivanova, Anton J. M. Loonen "Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia Is Related to Indirect Pathway Medium Spiny Neuron Excitotoxicity: A Hypothesis Based on an Unexpected Finding," Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 2016, Article ID 6461907, 5 pages, 2016. The scheme of neurotransmission on the direct way (on the right) and on the indirect way (on the left) of medium spiny neurons (MSN) Schemes of functioning of direct and indirect way of the extrapyramidal circle
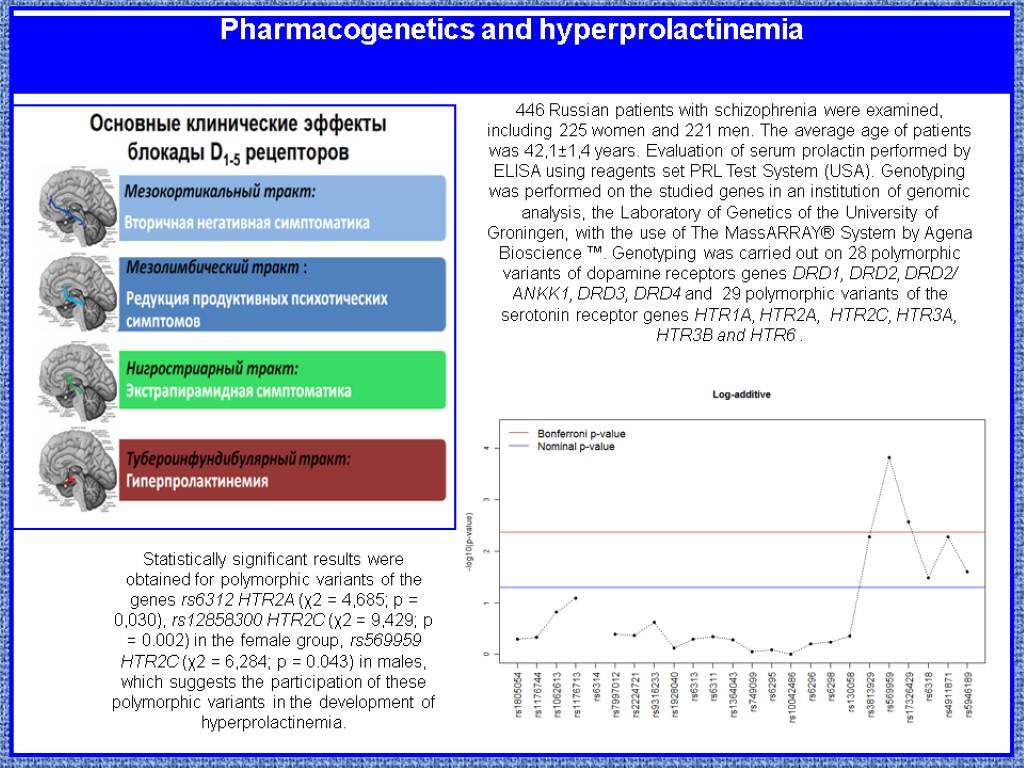
Pharmacogenetics and hyperprolactinemia 446 Russian patients with schizophrenia were examined, including 225 women and 221 men. The average age of patients was 42,1±1,4 years. Evaluation of serum prolactin performed by ELISA using reagents set PRL Test System (USA). Genotyping was performed on the studied genes in an institution of genomic analysis, the Laboratory of Genetics of the University of Groningen, with the use of The MassARRAY® System by Agena Bioscience ™. Genotyping was carried out on 28 polymorphic variants of dopamine receptors genes DRD1, DRD2, DRD2/ ANKK1, DRD3, DRD4 and 29 polymorphic variants of the serotonin receptor genes HTR1A, HTR2A, HTR2C, HTR3A, HTR3B and HTR6 . Statistically significant results were obtained for polymorphic variants of the genes rs6312 HTR2A (χ2 = 4,685; p = 0,030), rs12858300 HTR2C (χ2 = 9,429; p = 0.002) in the female group, rs569959 HTR2C (χ2 = 6,284; p = 0.043) in males, which suggests the participation of these polymorphic variants in the development of hyperprolactinemia.

The new “Pharmacogenetic Laboratory of of Mental and Neurodegenerative Disorders” was established with participation of Department of Cytology and Genetics of National Research Tomsk State University and Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery of Siberian State Medical University. Gene PGP (ABCB1, P-GLYCOPROTEIN/MDR1) in tardive dyskinesia and hyperprolactinemia Genes of muscarine receptors (CHRM1, CHRM2, CHRM4) and tardive dyskinesia. Genes of transporters and enzymes of metabolism of neuromediators (COMT, MAO, TPH1, TPH2, SLC18A2, SLC6A2 etc.) Pharmacogenetic investigations of metabolic side effects of antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia. Prospects of further studies at “Mental Health Research Institute” in the field of pharmacogenetics

Ivanova S.A., Toshchakova V.A., Filipenko M.L., Fedorenko O.Y., Boyarko E.G., Boiko A.S., Semke A.V., Bokhan N.A., Aftanas L.I., Loonen A.J. Cytochrome P450 1A2 co-determines neuroleptic load and may diminish tardive dyskinesia by increased inducibility. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Apr;16(3):200-5. doi: 10.3109/15622975.2014.995222. (IF 4.183) Ermakov E.А., Smirnova L.P., Parkhomenko T.A., Dmitrenok P.S., Krotenko N.M., Fattakhov N.S., Bokhan N.A., Semke A.V., Ivanova S.A., Buneva V.N. and Nevinsky G.A. DNA-hydrolysing activity of IgG antibodies from the sera of patients with schizophrenia. Open Biolоgy. - 2015. – Vol. 5: 150064. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rsob.150064 (IF 5.783) Svetlana A. Ivanova, Anton J. M. Loonen "Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia Is Related to Indirect Pathway Medium Spiny Neuron Excitotoxicity: A Hypothesis Based on an Unexpected Finding," Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 2016, doi:10.1155/2016/6461907. (IF 2,01). Fedorenko O.Y, Loonen A.J.M., Lang F., Toshchakova V.A., Boyarko E.G., Semke A.V., Bokhan N.A., Govorin N.V., Aftanas L.I., Ivanova S.A.Association study indicates a protective role of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate-5-kinase against tardive dyskinesia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015. 18 (6) p.1-6: DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyu098 (IF 4.009) Ivanova S.A., Geers L.M., Al Hadithy A.F., Pechlivanoglou P., Semke A.V., Vyalova N.M., Rudikov E.V., Fedorenko O.Y., Wilffert B., Bokhan N.A., Brouwers J.R., Loonen A.J. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate as a putative protective factor against tardive dyskinesia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014. N. 50. P. 172—177. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp. (IF 3.552) Anton J. M. Loonen, Svetlana A. Ivanova New insights into the mechanism of drug induced dyskinesia. CNS Spectrums 2013 Volume 18 Issue 01 pp 15-20 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23593652 (IF: 2.71) Ivanova S.A., Al Hadithy A.F., Brazovskaya N., Semke A., Wilffert B., Fedorenko O., Brouwers J.R., Loonen A.J. No involvement of the adenosine A2A receptor in tardive dyskinesia in Russian psychiatric inpatients from Siberia. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2012. V. 27. N. 3. P. 334—337. doi: 10.1002/hup.2226. (IF 2.097). Ivanova S. A., Loonen A. J. M., Pechlivanoglou P., Freidin M. B., Al Hadithy A. F. Y, Rudikov E. V., Zhukova I. A., Govorin N. V., Sorokina V. A., Fedorenko O., Alifirova V. M., Semke A. V., Brouwers J. R. B. J., Wilffert B. NMDA receptor genotypes associated with the vulnerability to develop dyskinesia. Translational Psychiatry. 2012. V. 2. N. 1.: e67; doi:10.1038/tp.2011.66 (www.nature.com/tp) (IF 5.62) Al Hadithy A. F. Y., Ivanova S. A., Pechlivanoglou P., Semke A., Fedorenko O., Kornetova E., Ryadovaya L., Brouwers J. R. B. J., Loonen A. J. M. Missense polymorphisms in three oxidative-stress enzymes (GSTP1, SOD2, and GPX1) and dyskinesias in Russian psychiatric inpatients from Siberia. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. ExP. 2010. V. 25. N. 1. P. 84—91. doi: 10.1002/hup.1087.(IF 2.192). Al Hadithy A. F. Y., Ivanova S. A., Pechlivanoglou P., Semke A., Fedorenko O., Kornetova E., Ryadovaya L., Brouwers J. R. B. J., Wilffert B., Bruggeman R., Loonen A. J. M. Tardive dyskinesia and DRD3, HTR2A and HTR2C gene polymorphisms in Russian psychiatric inpatients from Siberia. Progress in NeuroPsychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry. 2009. N. 33. P. 475—481 doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2009.01.010. ( IF 3.552). Research indicators (publications in journals indexed in Web of Science, IF> 2)

Grant of RSF 14-15-00480 Search of key biomarkers of pathogenesis of socially significant endogenous mental disorders. BIOMARKERS Laboratory of Molecular Genetics and Biochemistry of MHRI: O.Yu. Fedorenko, M.D. L.P. Smirnova, Ph.D. A.S. Boiko, junior researcher D.G. Parshukova, junior researcher E.M. Dmitriyeva, junior researcher A.A. Seregin, junior researcher N.M. Krotenko, Ph.D. in Biology Yu.G. Shchigoreva, Ph.D. L.V. Loginova, postgraduate student Endogenous Disorders Department of MHRI: A.V. Semke, Prof. E.G. Kornetova, Ph.D. Yu. Borodyuk, junior researcher F.F. Mikelev, Ph.D. E.G. Dmitriyeva, junior researcher Institute of Chemical Biology and Basic Medicine, Novosibirsk O.S. Fedorova, Prof. G.A. Nevinsky, Prof. V.N. Buneva, Sc.D. V.V. Koval, Ph.D. in Biology A.A. Chernonosov, Ph.D. in Biology I.V. Alekseeva, junior researcher E.A. Ermakov, postgraduate student V.N. Orekhovich Biomedical Chemistry Research Institute, Moscow V.G. Zgoda, Sc.D.

II. PHARMACOGENETIC INVESTIGATION Russian Science Foundation, Grant 14-35-00023 Pharmacogenetics of psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders Mental Health Research Institute (Tomsk): S. Ivanova, A. Semke, O Fedorenko, E. Kornetova, A.Boiko, E.Boyarko, A. Agarkov, Y.Borodyk, Siberian State Medical University (Tomsk): I.A. Zhukova, V.M. Alifirova, N.V. Zhukova., M. Titova, Yu.Mironova. Research Institute for Medical Genetics (Tomsk): Maxim Freidin Chita State Medical Academy, (Chita): Nikolay Govorin Kemerovo Regional Clinical Psychiatric Hospital (Kemerovo): Veronika Sorokina, Tomsk Clinical Psychiatric Hospital (Tomsk): S.M. Andreev, D.E. Abramov Institute of Chemical Biology and Basic Medicine (Novosibirsk): M.L. Filipenko National Research Tomsk State University: V.M. Stegny, D.Z. Osmanova, I.V. Pozhidayev The Netherlands : AJM Loonen. AFY Al Hadithy, P Pechlivanoglou, JRBJ Brouwers, B. Wilffert, R Bruggeman, Dr. P. van der Vlies, - Pharmacotherapy and Pharmaceutical Care, GUIDE, University of Groningen, Groningen. - Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology, Zorggroep Noorderbreedte and De Tjongerschans, Leeuwarden. - Department of Clinical Pharmacology, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen,. - Department of Psychiatry, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen. - Groningen Research Institute of Pharmacy (GRIP), University of Groningen, Groningen. Genome Analysis Facility, dept. Genetics, University Medical Centre Groningen (UMCG)

THANK YOU FOR ATTENTION!
search_for_biomarkers_and_development_of_pharmacogenetic_approaches_to_personalized_therapy_of_patients_with_schizophrenia.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

