9152a065be8c6ef299636e33f2b46a0c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 SE 470 Software Development Processes James Nowotarski 12 May 2003
SE 470 Software Development Processes James Nowotarski 12 May 2003
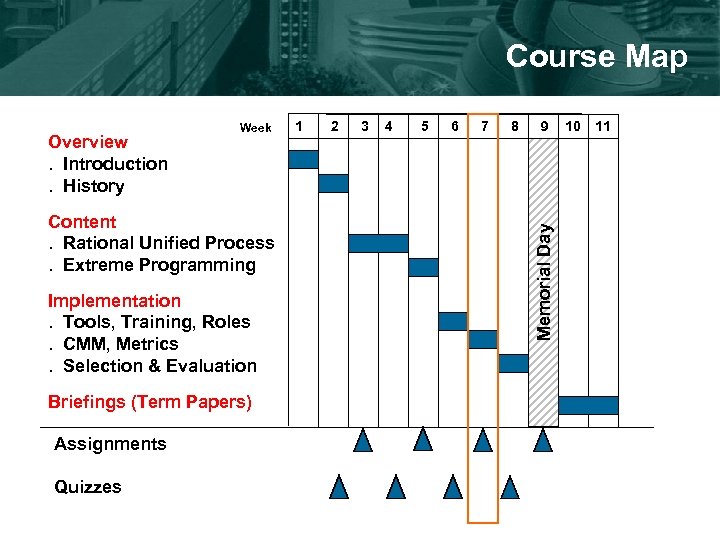 Course Map Content. Rational Unified Process. Extreme Programming Implementation. Tools, Training, Roles. CMM, Metrics. Selection & Evaluation Briefings (Term Papers) Assignments Quizzes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Memorial Day Overview. Introduction. History Week 10 11
Course Map Content. Rational Unified Process. Extreme Programming Implementation. Tools, Training, Roles. CMM, Metrics. Selection & Evaluation Briefings (Term Papers) Assignments Quizzes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Memorial Day Overview. Introduction. History Week 10 11
 Today’s Objectives • Understand the basics of the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) • Discuss term papers
Today’s Objectives • Understand the basics of the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) • Discuss term papers
 Today’s agenda Topic Duration • Housekeeping 15 minutes • CMM Overview 45 minutes • *** Break 10 minutes • CMM Activity 45 minutes • CMM Wrapup 45 minutes • Assignment 6 Reports • Term Paper Discussions 15 minutes 20 minutes
Today’s agenda Topic Duration • Housekeeping 15 minutes • CMM Overview 45 minutes • *** Break 10 minutes • CMM Activity 45 minutes • CMM Wrapup 45 minutes • Assignment 6 Reports • Term Paper Discussions 15 minutes 20 minutes
 Today’s agenda Topic Duration • Housekeeping 15 minutes • CMM Overview 45 minutes • *** Break 10 minutes • CMM Activity 45 minutes • CMM Wrapup 45 minutes • Assignment 6 Reports • Term Paper Discussions 15 minutes 20 minutes
Today’s agenda Topic Duration • Housekeeping 15 minutes • CMM Overview 45 minutes • *** Break 10 minutes • CMM Activity 45 minutes • CMM Wrapup 45 minutes • Assignment 6 Reports • Term Paper Discussions 15 minutes 20 minutes
 Today’s agenda Topic Duration • Housekeeping 15 minutes • CMM Overview 45 minutes • *** Break 10 minutes • CMM Activity 45 minutes • CMM Wrapup 45 minutes • Assignment 6 Reports • Term Paper Discussions 15 minutes 20 minutes
Today’s agenda Topic Duration • Housekeeping 15 minutes • CMM Overview 45 minutes • *** Break 10 minutes • CMM Activity 45 minutes • CMM Wrapup 45 minutes • Assignment 6 Reports • Term Paper Discussions 15 minutes 20 minutes
 What is CMM Overview • CMM = Capability Maturity Model • Developed in 1991 by Software Engineering Institute (SEI) to assess the software engineering capability of government contractors • A framework for software process improvement (SPI) that has gained wide acceptance in the industry • A roadmap of effective practices that build on one another in a logical progression – coherent – ordered set of incremental improvements
What is CMM Overview • CMM = Capability Maturity Model • Developed in 1991 by Software Engineering Institute (SEI) to assess the software engineering capability of government contractors • A framework for software process improvement (SPI) that has gained wide acceptance in the industry • A roadmap of effective practices that build on one another in a logical progression – coherent – ordered set of incremental improvements
 What is CMM Benefits • • • Practical Structured Proven Reputation Quantitative – productivity: 9 -67% – time to market: 15 -23% – post-release defects: 10 -94% – business value ratio: 4. 0 -8. 8: 1
What is CMM Benefits • • • Practical Structured Proven Reputation Quantitative – productivity: 9 -67% – time to market: 15 -23% – post-release defects: 10 -94% – business value ratio: 4. 0 -8. 8: 1
 What is CMM Overview • Different capability maturity models – Software CMM – People CMM – Systems Engineering CMM – Software Acquisition CMM – Integrated Product Development CMM – Team Software Process – Personal Software Process
What is CMM Overview • Different capability maturity models – Software CMM – People CMM – Systems Engineering CMM – Software Acquisition CMM – Integrated Product Development CMM – Team Software Process – Personal Software Process
 What is SEI Overview • SEI = Software Engineering Institute – – – Federally funded research & development center Sponsored by Department of Defense Affiliated with Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh Established in 1984 Research and publications oriented Mission is to improve the state of the practice of software engineering
What is SEI Overview • SEI = Software Engineering Institute – – – Federally funded research & development center Sponsored by Department of Defense Affiliated with Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh Established in 1984 Research and publications oriented Mission is to improve the state of the practice of software engineering
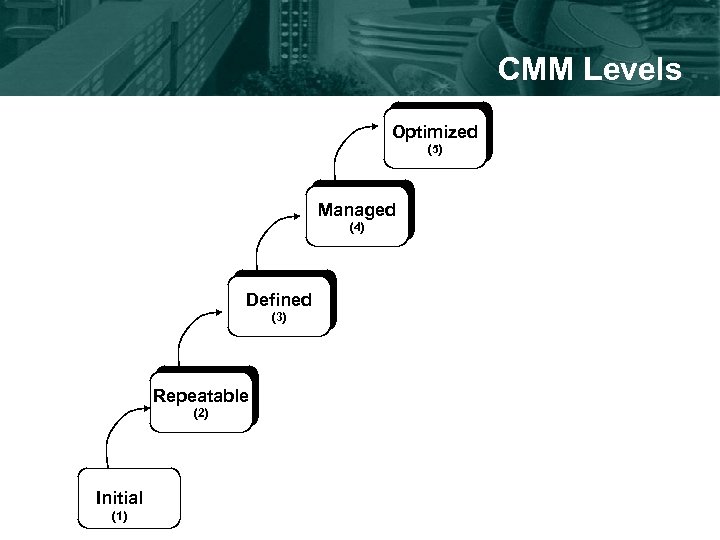 CMM Levels Optimized (5) Managed (4) Defined (3) Repeatable (2) Initial (1)
CMM Levels Optimized (5) Managed (4) Defined (3) Repeatable (2) Initial (1)
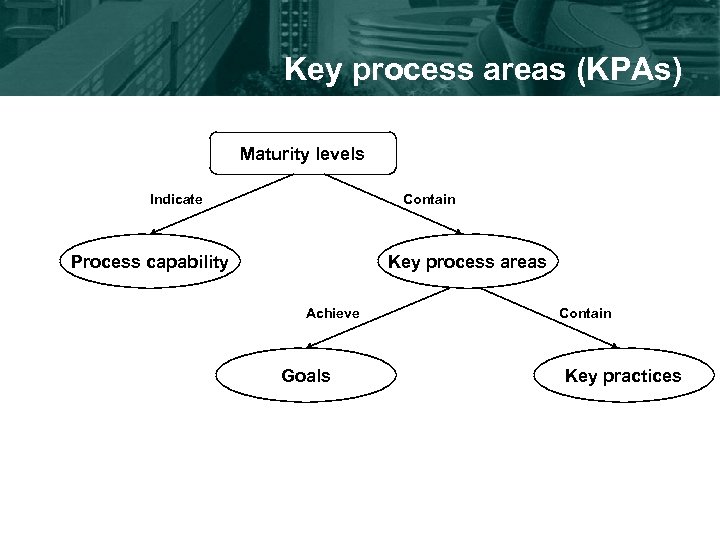 Key process areas (KPAs) Maturity levels Indicate Contain Process capability Key process areas Achieve Goals Contain Key practices
Key process areas (KPAs) Maturity levels Indicate Contain Process capability Key process areas Achieve Goals Contain Key practices
 Key Process Areas • Key Process Areas – Identify the issues that must be addressed to achieve a maturity level • Key Practice – Activities and infrastructure that contribute the most to the effective implementation of the KPA
Key Process Areas • Key Process Areas – Identify the issues that must be addressed to achieve a maturity level • Key Practice – Activities and infrastructure that contribute the most to the effective implementation of the KPA
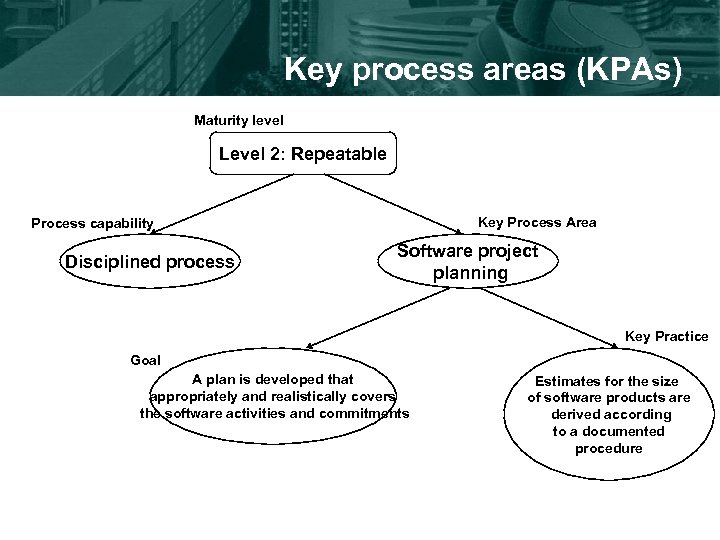 Key process areas (KPAs) Maturity level Level 2: Repeatable Key Process Area Process capability Disciplined process Software project planning Key Practice Goal A plan is developed that appropriately and realistically covers the software activities and commitments Estimates for the size of software products are derived according to a documented procedure
Key process areas (KPAs) Maturity level Level 2: Repeatable Key Process Area Process capability Disciplined process Software project planning Key Practice Goal A plan is developed that appropriately and realistically covers the software activities and commitments Estimates for the size of software products are derived according to a documented procedure
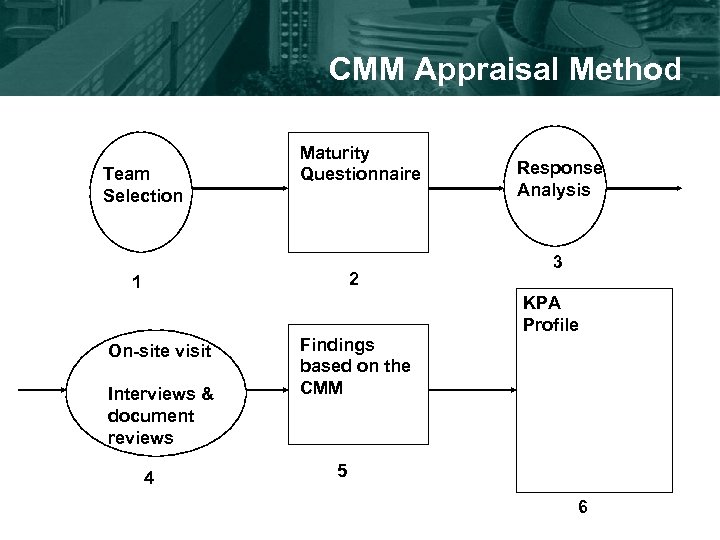 CMM Appraisal Method Team Selection Maturity Questionnaire 2 1 Response Analysis 3 KPA Profile On-site visit Interviews & document reviews 4 Findings based on the CMM 5 6
CMM Appraisal Method Team Selection Maturity Questionnaire 2 1 Response Analysis 3 KPA Profile On-site visit Interviews & document reviews 4 Findings based on the CMM 5 6
 Appraisal Methods • Software Process Assessments (SPA) – Performed in open, collaborative environment – Focuses on improving the organization’s software process – Now called CMM-Based Appraisal for Internal Process Improvement (CBA-IPI) • Software Capability Evaluations (SCE) – Performed in a more audit-oriented environment – Focuses on identifying risks associated with a contractor – Team’s recommendation will help select contractors or set fees
Appraisal Methods • Software Process Assessments (SPA) – Performed in open, collaborative environment – Focuses on improving the organization’s software process – Now called CMM-Based Appraisal for Internal Process Improvement (CBA-IPI) • Software Capability Evaluations (SCE) – Performed in a more audit-oriented environment – Focuses on identifying risks associated with a contractor – Team’s recommendation will help select contractors or set fees
 Level 1: Initial • • Instability Dependence on “heroes” Inability to meet targets Key process areas: – none
Level 1: Initial • • Instability Dependence on “heroes” Inability to meet targets Key process areas: – none
 Level 2: Repeatable • Track project results, which form basis for future project plans • Basic processes in place for: – requirements management – supplier management – standards • Key process areas – – – requirements management software project planning software project tracking and oversight software subcontract management software quality assurance software configuration management
Level 2: Repeatable • Track project results, which form basis for future project plans • Basic processes in place for: – requirements management – supplier management – standards • Key process areas – – – requirements management software project planning software project tracking and oversight software subcontract management software quality assurance software configuration management
 Level 3: Defined • Software engineering and management processes are defined • Software engineering process group (SEPG) exists • Organization-wide training • Key process areas: – – – – organizational process focus organizational process definition training program integrated software management (i. e. , tailoring) software product engineering intergroup coordination peer reviews
Level 3: Defined • Software engineering and management processes are defined • Software engineering process group (SEPG) exists • Organization-wide training • Key process areas: – – – – organizational process focus organizational process definition training program integrated software management (i. e. , tailoring) software product engineering intergroup coordination peer reviews
 Level 4: Managed • Stable and measured processes • Measurements are captured across the organization – productivity – quality • Processes are predictable • Key process areas: – quantitative process management – software quality management
Level 4: Managed • Stable and measured processes • Measurements are captured across the organization – productivity – quality • Processes are predictable • Key process areas: – quantitative process management – software quality management
 Level 5: Optimizing • Continuous process improvement • Defect prevention – productivity – quality • Processes are predictable • Key process areas: – process change management – technology change management – defect prevention
Level 5: Optimizing • Continuous process improvement • Defect prevention – productivity – quality • Processes are predictable • Key process areas: – process change management – technology change management – defect prevention
 As maturity increases • Less prone to miss targets • Less variation around the target goals • Better, faster, cheaper development
As maturity increases • Less prone to miss targets • Less variation around the target goals • Better, faster, cheaper development
 Today’s agenda Topic Duration • Housekeeping 15 minutes • CMM Overview 45 minutes • *** Break 10 minutes • CMM Activity 45 minutes • CMM Wrapup 45 minutes • Assignment 6 Reports • Term Paper Discussions 15 minutes 20 minutes
Today’s agenda Topic Duration • Housekeeping 15 minutes • CMM Overview 45 minutes • *** Break 10 minutes • CMM Activity 45 minutes • CMM Wrapup 45 minutes • Assignment 6 Reports • Term Paper Discussions 15 minutes 20 minutes
 Class Activity • Summarize and explain to the rest of the class: – Maturity levels 2 -5 – The 18 key process areas
Class Activity • Summarize and explain to the rest of the class: – Maturity levels 2 -5 – The 18 key process areas
 Today’s agenda Topic Duration • Housekeeping 15 minutes • CMM Overview 45 minutes • *** Break 10 minutes • CMM Activity 45 minutes • CMM Wrapup 45 minutes • Assignment 6 Reports • Term Paper Discussions 15 minutes 20 minutes
Today’s agenda Topic Duration • Housekeeping 15 minutes • CMM Overview 45 minutes • *** Break 10 minutes • CMM Activity 45 minutes • CMM Wrapup 45 minutes • Assignment 6 Reports • Term Paper Discussions 15 minutes 20 minutes
 CMM and ISO 9001 • Both share a common concern with quality and process management • Some issues in ISO 9001 are not covered in the CMM and vice-versa • While the CMM focuses on continuous improvement, ISO 9001 addresses the minimum criteria for an acceptable quality system • Roughly speaking, an organization at CMM Level 2 should satisfy ISO 9001
CMM and ISO 9001 • Both share a common concern with quality and process management • Some issues in ISO 9001 are not covered in the CMM and vice-versa • While the CMM focuses on continuous improvement, ISO 9001 addresses the minimum criteria for an acceptable quality system • Roughly speaking, an organization at CMM Level 2 should satisfy ISO 9001
 CMM Issues in the Real-World • “Level envy” • Areas not addressed – Business strategy and linkage to IT – Operations, help desk, support – Management of the IT human resource – Application portfolio – Tools • Many question whether it is worth the effort to pursue levels 4 and 5
CMM Issues in the Real-World • “Level envy” • Areas not addressed – Business strategy and linkage to IT – Operations, help desk, support – Management of the IT human resource – Application portfolio – Tools • Many question whether it is worth the effort to pursue levels 4 and 5
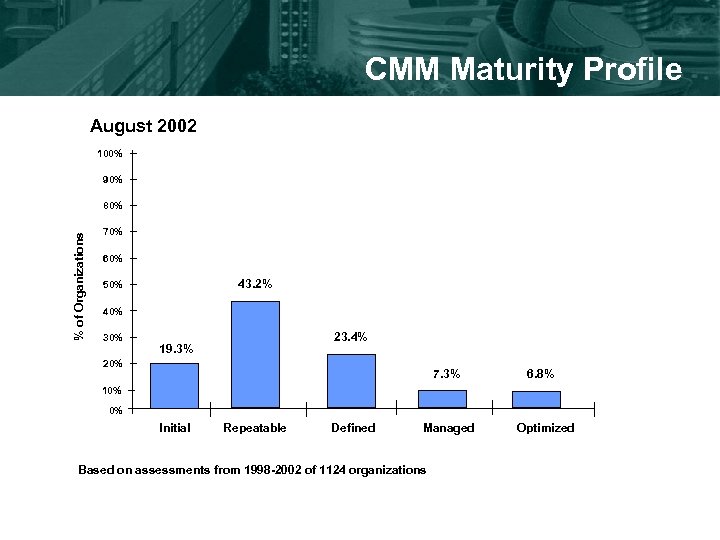 CMM Maturity Profile August 2002 100% 90% % of Organizations 80% 70% 60% 43. 2% 50% 40% 30% 23. 4% 19. 3% 20% 7. 3% 6. 8% 10% 0% Initial Repeatable Defined Managed Based on assessments from 1998 -2002 of 1124 organizations Optimized
CMM Maturity Profile August 2002 100% 90% % of Organizations 80% 70% 60% 43. 2% 50% 40% 30% 23. 4% 19. 3% 20% 7. 3% 6. 8% 10% 0% Initial Repeatable Defined Managed Based on assessments from 1998 -2002 of 1124 organizations Optimized
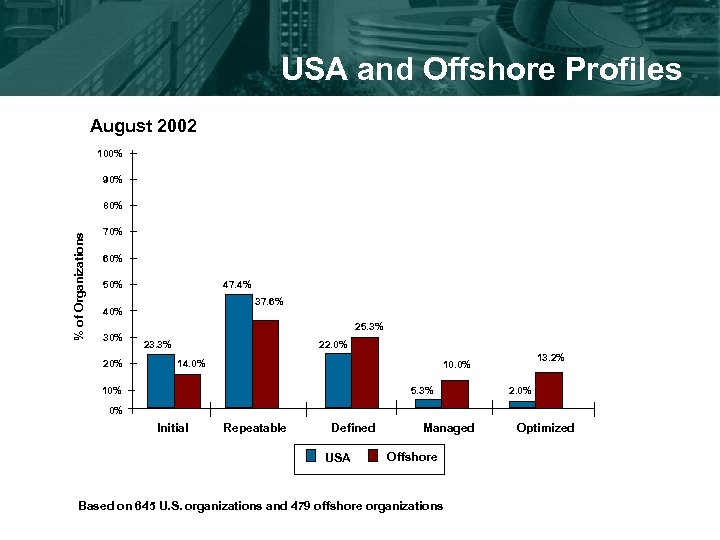 USA and Offshore Profiles August 2002 100% 90% % of Organizations 80% 70% 60% 50% 47. 4% 37. 6% 40% 30% 25. 3% 23. 3% 22. 0% 14. 0% 13. 2% 10. 0% 10% 5. 3% 2. 0% 0% Initial Repeatable Defined USA Managed Offshore Based on 645 U. S. organizations and 479 offshore organizations Optimized
USA and Offshore Profiles August 2002 100% 90% % of Organizations 80% 70% 60% 50% 47. 4% 37. 6% 40% 30% 25. 3% 23. 3% 22. 0% 14. 0% 13. 2% 10. 0% 10% 5. 3% 2. 0% 0% Initial Repeatable Defined USA Managed Offshore Based on 645 U. S. organizations and 479 offshore organizations Optimized
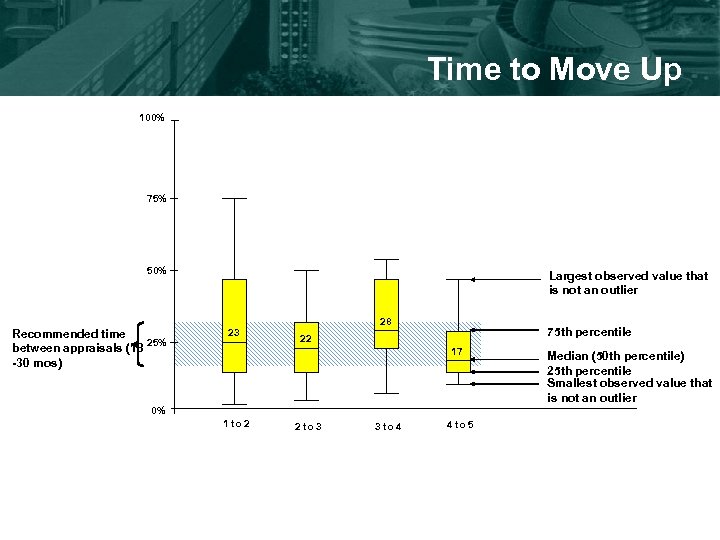 Time to Move Up 100% 75% 50% Recommended time 25% between appraisals (18 -30 mos) Largest observed value that is not an outlier 23 28 75 th percentile 22 17 0% 1 to 2 2 to 3 3 to 4 4 to 5 Median (50 th percentile) 25 th percentile Smallest observed value that is not an outlier
Time to Move Up 100% 75% 50% Recommended time 25% between appraisals (18 -30 mos) Largest observed value that is not an outlier 23 28 75 th percentile 22 17 0% 1 to 2 2 to 3 3 to 4 4 to 5 Median (50 th percentile) 25 th percentile Smallest observed value that is not an outlier
 References • For CMM articles and publications, see http: //www. sei. cmu. edu/cmm. articles. html
References • For CMM articles and publications, see http: //www. sei. cmu. edu/cmm. articles. html
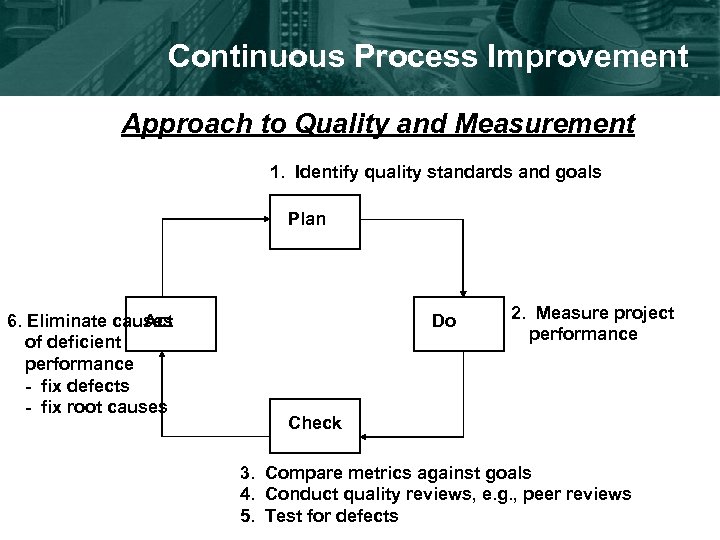 Continuous Process Improvement Approach to Quality and Measurement 1. Identify quality standards and goals Plan 6. Eliminate causes Act of deficient performance - fix defects - fix root causes Do 2. Measure project performance Check 3. Compare metrics against goals 4. Conduct quality reviews, e. g. , peer reviews 5. Test for defects
Continuous Process Improvement Approach to Quality and Measurement 1. Identify quality standards and goals Plan 6. Eliminate causes Act of deficient performance - fix defects - fix root causes Do 2. Measure project performance Check 3. Compare metrics against goals 4. Conduct quality reviews, e. g. , peer reviews 5. Test for defects
 Metrics First Principles • “You can’t control what you can’t measure” (Tom Demarco) • “Anything that can’t be measured doesn’t exist” -- Locke, Berkeley, Hume (Beck, p. 45) • Metrics - “Lines of code is a useless measurement in the face of code that shrinks when we learn better ways of programming” (Beck, p. 42)
Metrics First Principles • “You can’t control what you can’t measure” (Tom Demarco) • “Anything that can’t be measured doesn’t exist” -- Locke, Berkeley, Hume (Beck, p. 45) • Metrics - “Lines of code is a useless measurement in the face of code that shrinks when we learn better ways of programming” (Beck, p. 42)
 Quiz for May 19 • CMM
Quiz for May 19 • CMM
 Extra Slides
Extra Slides


