Scrum in practice and the essentiel principles_eart.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 44
 SCRUM
SCRUM
 Scrum in Practice artefacts, ceremonies and roles Learning Goals What kind of business arguments promotes an agile development proces? Which methodes and techniques support an agile development proces How does Scrum works in practice How can scrum be adopted for a d-concept delvopment project
Scrum in Practice artefacts, ceremonies and roles Learning Goals What kind of business arguments promotes an agile development proces? Which methodes and techniques support an agile development proces How does Scrum works in practice How can scrum be adopted for a d-concept delvopment project
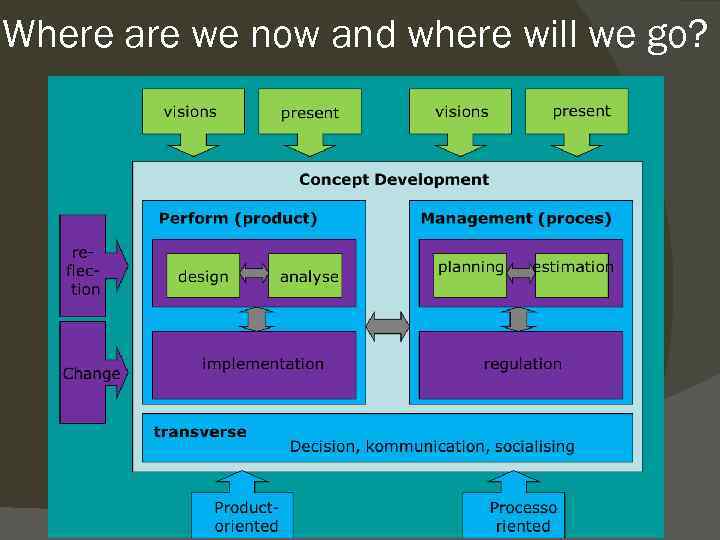 Where are we now and where will we go?
Where are we now and where will we go?
 Scrum overview - repetition Scrum is a framework for organizing and managing work Not following a standardized process as a series of sequential steps SCRUM is based upon a set of Values (FROCC) (which? ) Pricipels (what are the ideas in scrum) Practices (how to do) SCRUM provides the foundation (like the foundation of a building) to which you or your organization will add relevant professionel elements (remember the team house) The result will be a version of scrum that is uniquely yours
Scrum overview - repetition Scrum is a framework for organizing and managing work Not following a standardized process as a series of sequential steps SCRUM is based upon a set of Values (FROCC) (which? ) Pricipels (what are the ideas in scrum) Practices (how to do) SCRUM provides the foundation (like the foundation of a building) to which you or your organization will add relevant professionel elements (remember the team house) The result will be a version of scrum that is uniquely yours
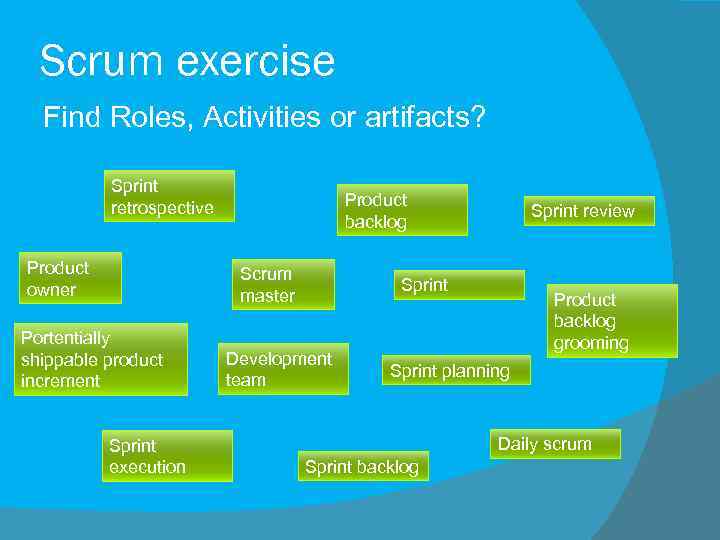 Scrum exercise Find Roles, Activities or artifacts? Sprint retrospective Product owner Product backlog Scrum master Portentially shippable product increment Sprint execution Sprint review Sprint Development team Product backlog grooming Sprint planning Daily scrum Sprint backlog
Scrum exercise Find Roles, Activities or artifacts? Sprint retrospective Product owner Product backlog Scrum master Portentially shippable product increment Sprint execution Sprint review Sprint Development team Product backlog grooming Sprint planning Daily scrum Sprint backlog
 Relevant links supporting this lesson www. agilenutshell. com/ intersting walk through http: //www. scrumwise. com/ good tool http: //www. scrumdesk. com/ scrum tool http: //www. scrumexpert. com/tools/usingcommercial-scrum-tools-for-free/ overview of a lot of scrum tools incl Kanban
Relevant links supporting this lesson www. agilenutshell. com/ intersting walk through http: //www. scrumwise. com/ good tool http: //www. scrumdesk. com/ scrum tool http: //www. scrumexpert. com/tools/usingcommercial-scrum-tools-for-free/ overview of a lot of scrum tools incl Kanban
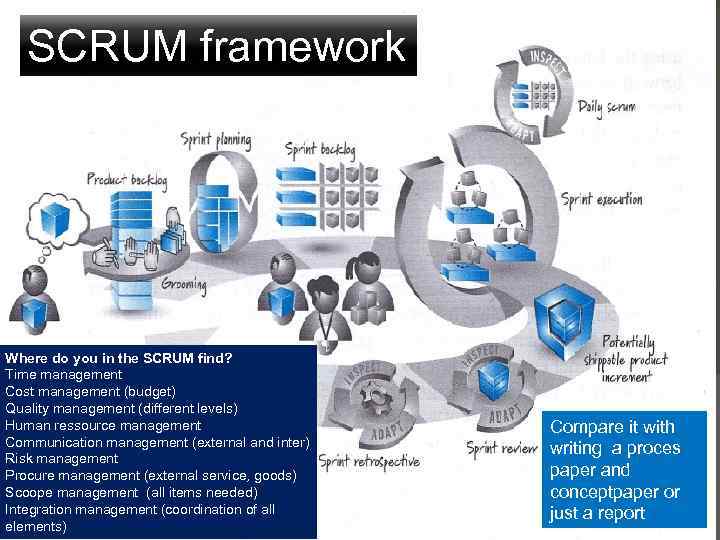 SCRUM framework Where do you in the SCRUM find? Time management Cost management (budget) Quality management (different levels) Human ressource management Communication management (external and inter) Risk management Procure management (external service, goods) Scoope management (all items needed) Integration management (coordination of all elements) Compare it with writing a proces paper and conceptpaper or just a report
SCRUM framework Where do you in the SCRUM find? Time management Cost management (budget) Quality management (different levels) Human ressource management Communication management (external and inter) Risk management Procure management (external service, goods) Scoope management (all items needed) Integration management (coordination of all elements) Compare it with writing a proces paper and conceptpaper or just a report
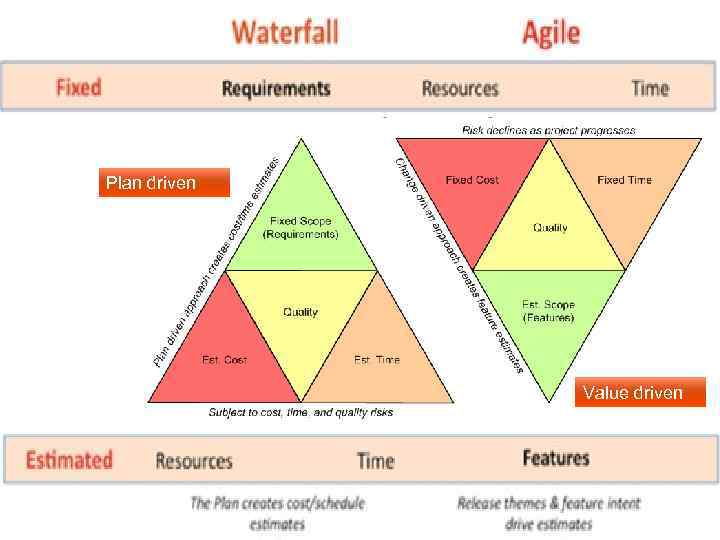 Plan driven Value driven
Plan driven Value driven
 Agile Principles organized in catagories Variablilty and uncertainty (changes, iterative, adaption, reduce risk) Prediction and adaption (wait, adapt, explore) Validated learning Work in Progress Performance
Agile Principles organized in catagories Variablilty and uncertainty (changes, iterative, adaption, reduce risk) Prediction and adaption (wait, adapt, explore) Validated learning Work in Progress Performance
 Variability and uncertainty (1) Embrace helpful variablility (welcome change) ○ Difference between product manufacturing and ○ product development (creating a unique receipe used for manufactoring) Here variability is needed Employ iterative and inceremental development ○ Plan driven (waterfall) is based upon that all pieces developed will come together later ○ Iterative development (trial and error or poor before well done – creating a prototype – learning process). It is difficult to decide how many itrations ○ Incremental (build some of it before you build the rest which gives important information about changes before proceeding (maybe risk the big picture (see the trees but not the forest). Scrum is mostly incremental but also iterative. Waterscrum or scrummerfall (using scrum based upon waterfall plans)
Variability and uncertainty (1) Embrace helpful variablility (welcome change) ○ Difference between product manufacturing and ○ product development (creating a unique receipe used for manufactoring) Here variability is needed Employ iterative and inceremental development ○ Plan driven (waterfall) is based upon that all pieces developed will come together later ○ Iterative development (trial and error or poor before well done – creating a prototype – learning process). It is difficult to decide how many itrations ○ Incremental (build some of it before you build the rest which gives important information about changes before proceeding (maybe risk the big picture (see the trees but not the forest). Scrum is mostly incremental but also iterative. Waterscrum or scrummerfall (using scrum based upon waterfall plans)
 Variability and uncertainty (2) Leverage variability through inspection, adaptation and transparency ○ The right product is built and it is built right ○ Inspection (scrum inspect not only what we are producing, but also how we produce it) ○ Adaptation (after inspection we adapt and proceed with the good things) ○ Transparancy (makes inspection possible because all information for producing the product is available) ○ This make direct communication a keyword in scrum
Variability and uncertainty (2) Leverage variability through inspection, adaptation and transparency ○ The right product is built and it is built right ○ Inspection (scrum inspect not only what we are producing, but also how we produce it) ○ Adaptation (after inspection we adapt and proceed with the good things) ○ Transparancy (makes inspection possible because all information for producing the product is available) ○ This make direct communication a keyword in scrum
 Variability and uncertainty (3) Reduce all forms of uncertainty simultaneously ○ End uncertainty (what) - uncertainty surrounding the features of the final procduct (problem definition) ○ Means uncertainty (how) - uncertainty about process, technologies, theories etc. (problem solving) ○ Customer uncertainty (who) otherwise you can build brilliant products to the wrong market. Build a feature, show it to customer, test it in the market
Variability and uncertainty (3) Reduce all forms of uncertainty simultaneously ○ End uncertainty (what) - uncertainty surrounding the features of the final procduct (problem definition) ○ Means uncertainty (how) - uncertainty about process, technologies, theories etc. (problem solving) ○ Customer uncertainty (who) otherwise you can build brilliant products to the wrong market. Build a feature, show it to customer, test it in the market
 Prediction and adaptation (1) Keep options open ○ Strategy based upon last responsible moment – so delay decicions untill last responsibel moment. ○ That means when the cost of not making the decision becomes greater than the cost of making the decision (remember we learn a little every day so the decisions should be made upon the best knowledge) Accept that you can’t get it right up front ○ It is impossible to get all requirements from the beginning ○ Requirements can change during the development time
Prediction and adaptation (1) Keep options open ○ Strategy based upon last responsible moment – so delay decicions untill last responsibel moment. ○ That means when the cost of not making the decision becomes greater than the cost of making the decision (remember we learn a little every day so the decisions should be made upon the best knowledge) Accept that you can’t get it right up front ○ It is impossible to get all requirements from the beginning ○ Requirements can change during the development time
 Prediction and adaptation (2) Favor an adaptive exploratory approach ○ Instead of predicting, scrum favors a more adaptive trial and error approach based upon use of exploration. ○ Exploration can be done during prototyping, study or experimentation, desk research etc. Many tools exist today helping this proces Embrace change in an economically sensible way ○ Plan driven development try to avoid changes because they are expensive. Mistakes in analysis cost a lot during implentation. ○ Scrum welcomes changes as a part of the understanding. Artifacts are evaluated after a just in time priciple
Prediction and adaptation (2) Favor an adaptive exploratory approach ○ Instead of predicting, scrum favors a more adaptive trial and error approach based upon use of exploration. ○ Exploration can be done during prototyping, study or experimentation, desk research etc. Many tools exist today helping this proces Embrace change in an economically sensible way ○ Plan driven development try to avoid changes because they are expensive. Mistakes in analysis cost a lot during implentation. ○ Scrum welcomes changes as a part of the understanding. Artifacts are evaluated after a just in time priciple
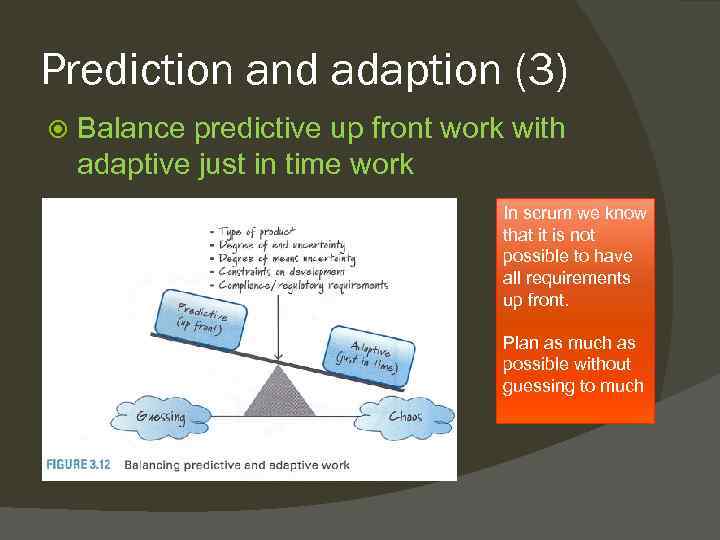 Prediction and adaption (3) Balance predictive up front work with adaptive just in time work In scrum we know that it is not possible to have all requirements up front. Plan as much as possible without guessing to much
Prediction and adaption (3) Balance predictive up front work with adaptive just in time work In scrum we know that it is not possible to have all requirements up front. Plan as much as possible without guessing to much
 Validated learning (1) Validate important assumptions fast ○ Assumptions represent a significant risk (validated late in plan driven approaches. These are minimized in scrum becuase they are continously evalutated together with low-cost exploration Leverage multiple concurrent learning loops ○ Real learning first arise when products are finished – that means that learning comes late in plan-driven approaches and often no time to benefit from it. ○ In scrum it is a parameter through the whole process. Both in proces- and product development ○ The same for feedback (sprint time slot)
Validated learning (1) Validate important assumptions fast ○ Assumptions represent a significant risk (validated late in plan driven approaches. These are minimized in scrum becuase they are continously evalutated together with low-cost exploration Leverage multiple concurrent learning loops ○ Real learning first arise when products are finished – that means that learning comes late in plan-driven approaches and often no time to benefit from it. ○ In scrum it is a parameter through the whole process. Both in proces- and product development ○ The same for feedback (sprint time slot)
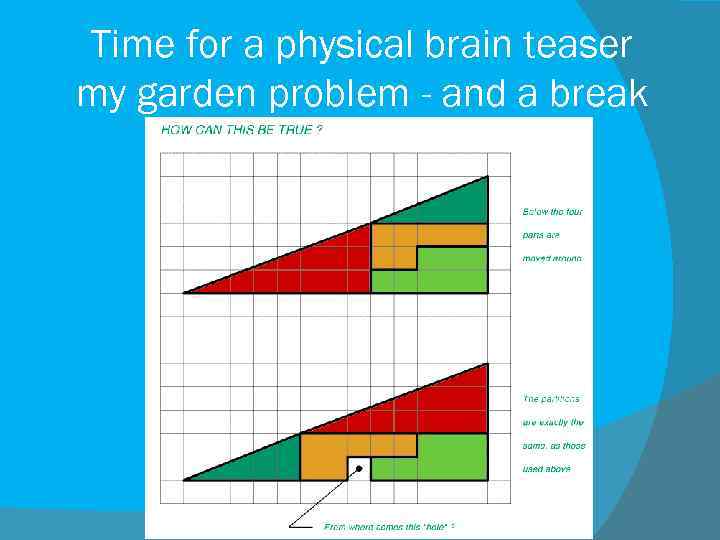 Time for a physical brain teaser my garden problem - and a break
Time for a physical brain teaser my garden problem - and a break
 Work in progress (work started but not yet finished) Use economically sensible batch size ○ Using economics of scale (plan driven) as bigger batch size as more efficient (manufactoring thinking). ○ Instead of use smaller batches (poker planning) Focus on idle work (work that cant be done now for some reason) instead of idle workers (team members who have capacity to do more work)
Work in progress (work started but not yet finished) Use economically sensible batch size ○ Using economics of scale (plan driven) as bigger batch size as more efficient (manufactoring thinking). ○ Instead of use smaller batches (poker planning) Focus on idle work (work that cant be done now for some reason) instead of idle workers (team members who have capacity to do more work)
 Progress Adapt real-time information and replan ○ In traditional project work the plan can be trusted when you have made it, ○ but in scrum you re-plan all the time according to your information and knowledge (the grooming process)
Progress Adapt real-time information and replan ○ In traditional project work the plan can be trusted when you have made it, ○ but in scrum you re-plan all the time according to your information and knowledge (the grooming process)
 Performance Go fast but never hurry ○ In scrum you have feedback very often ○ and know the status (how? ) Build-in quality ○ Tested after every sprint and gain new knowledge Employ minimally sufficient ceremony (documentation) ○ Only do what is necessary (meetings and documents) – not doing a special report just because of having time, but only if it has value for the work.
Performance Go fast but never hurry ○ In scrum you have feedback very often ○ and know the status (how? ) Build-in quality ○ Tested after every sprint and gain new knowledge Employ minimally sufficient ceremony (documentation) ○ Only do what is necessary (meetings and documents) – not doing a special report just because of having time, but only if it has value for the work.
 Role playing game! 1. Take three A 3 papers and on each of them write on of the 3 scrum roles 2. The team members divide the task tiles among each other so all have the same number task tiles as possible 3. Place appropriate tasks on different scrum roles in silence (no team discussion) Still no discussion and when the instructor say time then preceed 1. The whole team discuss and try to agree about the tile placement 2. When you are ready then swap boards with another team 3. Check anoter groups work and discuss some of the differences – what could be the reason for that solution? 4. Discuss in plenum why there are differences (different way of thinking in the roles, depneding on the organization, depending the type of project etc
Role playing game! 1. Take three A 3 papers and on each of them write on of the 3 scrum roles 2. The team members divide the task tiles among each other so all have the same number task tiles as possible 3. Place appropriate tasks on different scrum roles in silence (no team discussion) Still no discussion and when the instructor say time then preceed 1. The whole team discuss and try to agree about the tile placement 2. When you are ready then swap boards with another team 3. Check anoter groups work and discuss some of the differences – what could be the reason for that solution? 4. Discuss in plenum why there are differences (different way of thinking in the roles, depneding on the organization, depending the type of project etc
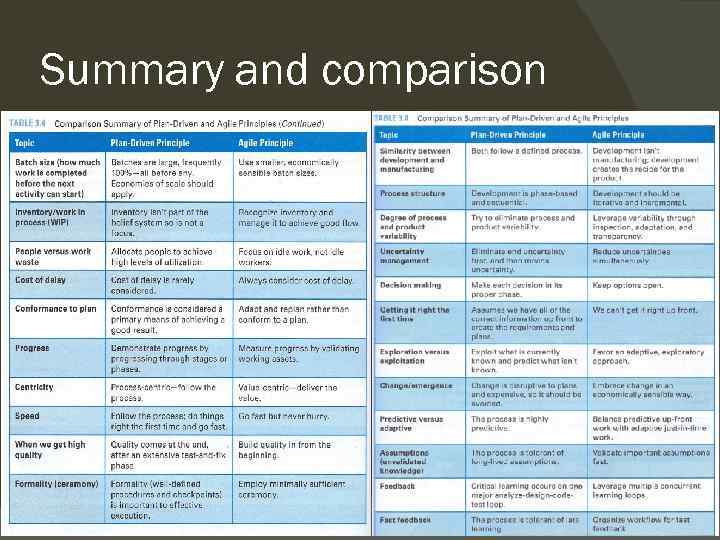 Summary and comparison
Summary and comparison
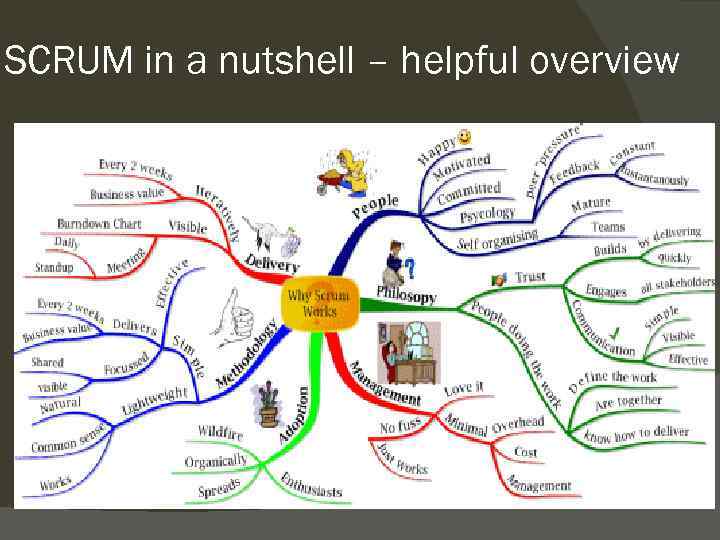 SCRUM in a nutshell – helpful overview
SCRUM in a nutshell – helpful overview
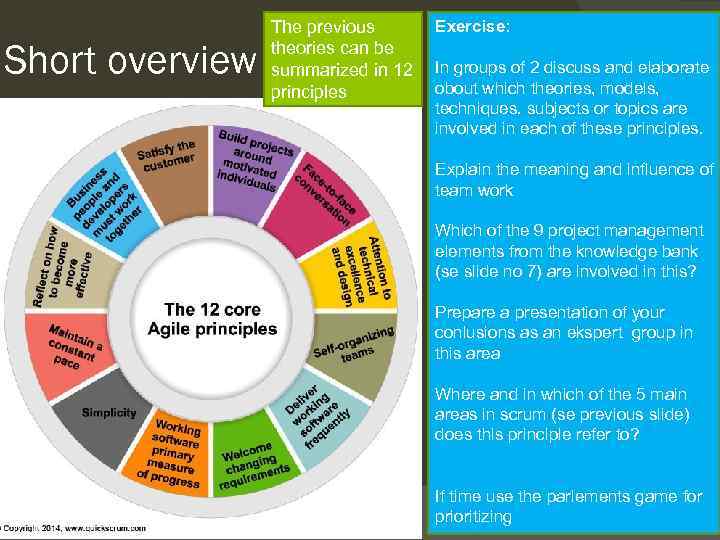 Short overview Exercise: The previous theories can be summarized in 12 In groups of 2 discuss and elaborate obout which theories, models, principles techniques. subjects or topics are involved in each of these principles. Explain the meaning and influence of team work Which of the 9 project management elements from the knowledge bank (se slide no 7) are involved in this? Prepare a presentation of your conlusions as an ekspert group in this area Where and in which of the 5 main areas in scrum (se previous slide) does this principle refer to? If time use the parlements game for prioritizing
Short overview Exercise: The previous theories can be summarized in 12 In groups of 2 discuss and elaborate obout which theories, models, principles techniques. subjects or topics are involved in each of these principles. Explain the meaning and influence of team work Which of the 9 project management elements from the knowledge bank (se slide no 7) are involved in this? Prepare a presentation of your conlusions as an ekspert group in this area Where and in which of the 5 main areas in scrum (se previous slide) does this principle refer to? If time use the parlements game for prioritizing
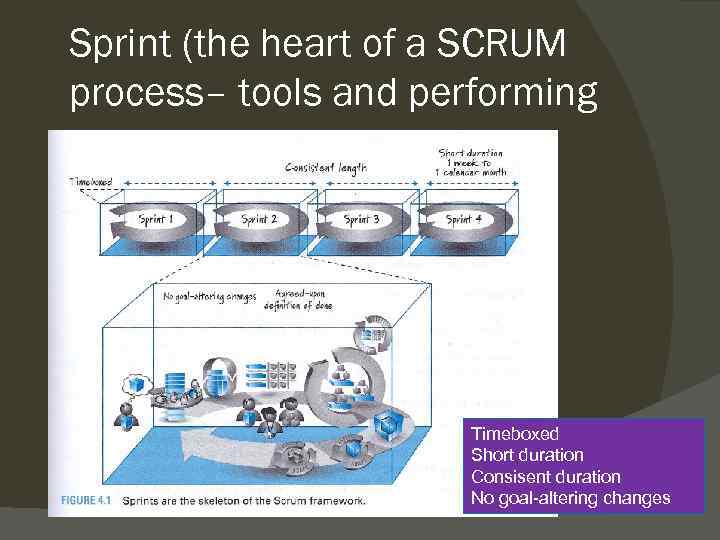 Sprint (the heart of a SCRUM process– tools and performing Timeboxed Short duration Consisent duration No goal-altering changes
Sprint (the heart of a SCRUM process– tools and performing Timeboxed Short duration Consisent duration No goal-altering changes
 Timeboxing – another way of work Establishes a WIP limit ○ The development team have decided what is possible to do during this sprint Forces prioritization ○ Work with the most important first Demonstrate progress ○ Completing and validating important pieces all time. Avoid unnecessary perfectionism (and darlings) Motivate closure Improves predictability
Timeboxing – another way of work Establishes a WIP limit ○ The development team have decided what is possible to do during this sprint Forces prioritization ○ Work with the most important first Demonstrate progress ○ Completing and validating important pieces all time. Avoid unnecessary perfectionism (and darlings) Motivate closure Improves predictability
 Short duration Ease of planning Fast feed back ○ Short duration generate fast feedback Improve return of investment Bounded error ○ Errors are bounded to small periods Keep enthusiasm going Frequent checkpoints ○ Especially compared to plan-driven approach
Short duration Ease of planning Fast feed back ○ Short duration generate fast feedback Improve return of investment Bounded error ○ Errors are bounded to small periods Keep enthusiasm going Frequent checkpoints ○ Especially compared to plan-driven approach
 Consistent duration Cadence benefits ○ Always the same structure for meetings etc Simplifies planning and an ongoing process
Consistent duration Cadence benefits ○ Always the same structure for meetings etc Simplifies planning and an ongoing process
 No goal-altering changes during sprint Sprint goal Mutual commitment ○ Agreement between Product owner and development team Change versus clarification ○ Adding items to product backlog suddenly Being pragmatic Abnormal termination ○ Consequences for the next sprint length
No goal-altering changes during sprint Sprint goal Mutual commitment ○ Agreement between Product owner and development team Change versus clarification ○ Adding items to product backlog suddenly Being pragmatic Abnormal termination ○ Consequences for the next sprint length
 Definition of Done Potentially shippable products ”Done” needs to be defined (depends on type of product to be made ○ Finished by the person ○ Reviewed or tested ○ Uploaded to dropbox etc. ○ Spell controll etc. ○ Formated to report Definition of done can evolve over time Done versus done-done ○ Be carefull here
Definition of Done Potentially shippable products ”Done” needs to be defined (depends on type of product to be made ○ Finished by the person ○ Reviewed or tested ○ Uploaded to dropbox etc. ○ Spell controll etc. ○ Formated to report Definition of done can evolve over time Done versus done-done ○ Be carefull here
 Time for a another brain teaser The soldier problem about live or die Shown above are 4 men buried up to their necks in the ground. They cannot move so can only look forward. Between A and B is a brick wall which cannot be seen through. They all know that between them they are wearing 4 hats, 2 x black and 2 x white, but they do not know what colour they are wearing. In order to avoid being shot one of them must call out to the executioner the colour of their hat. If they get it wrong, everyone will be shot. They are not allowed to talk to each other and have 10 minutes to fathom it out. After 1 minute, one of them calls out. Question: Which one of them calls out? Question: Why is he 100% certain of the colour of his hat?
Time for a another brain teaser The soldier problem about live or die Shown above are 4 men buried up to their necks in the ground. They cannot move so can only look forward. Between A and B is a brick wall which cannot be seen through. They all know that between them they are wearing 4 hats, 2 x black and 2 x white, but they do not know what colour they are wearing. In order to avoid being shot one of them must call out to the executioner the colour of their hat. If they get it wrong, everyone will be shot. They are not allowed to talk to each other and have 10 minutes to fathom it out. After 1 minute, one of them calls out. Question: Which one of them calls out? Question: Why is he 100% certain of the colour of his hat?
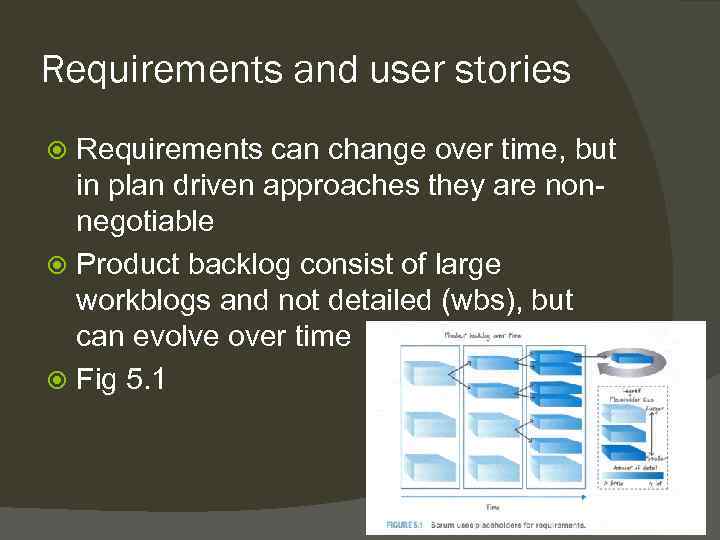 Requirements and user stories Requirements can change over time, but in plan driven approaches they are nonnegotiable Product backlog consist of large workblogs and not detailed (wbs), but can evolve over time Fig 5. 1
Requirements and user stories Requirements can change over time, but in plan driven approaches they are nonnegotiable Product backlog consist of large workblogs and not detailed (wbs), but can evolve over time Fig 5. 1
 User stories (product backlog items) Conversations about requirements instead of written requirements Userstories are used in product baglog and give an idea about what it is so both technical and business people understand it Using small cards like sticky notes. As a
User stories (product backlog items) Conversations about requirements instead of written requirements Userstories are used in product baglog and give an idea about what it is so both technical and business people understand it Using small cards like sticky notes. As a
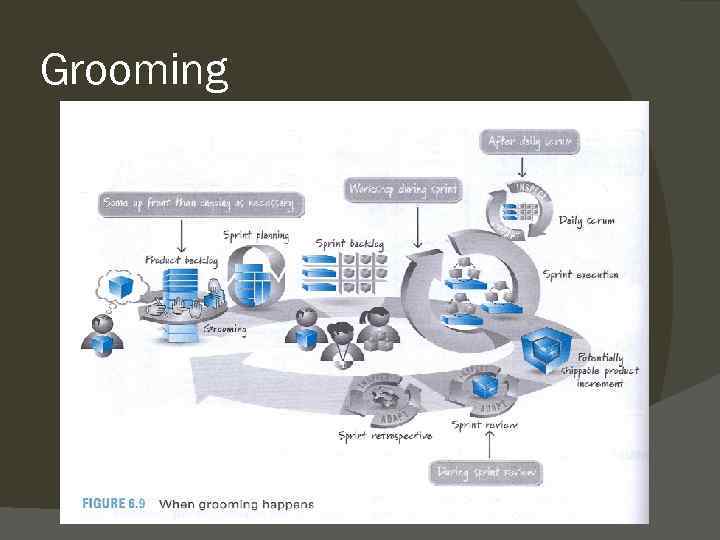
 Product backlog – Your next project Could be table of contents in a report Prioritized (more detailed in the top) Estimated ○ not detailed in the bottom (could be S, M, L etc. Or Must have, nice to have, want to have) Grooming (product owner and stakeholders, but olso scrum master and development team) is important. Used as a dialog tool Grooming is going on constantly
Product backlog – Your next project Could be table of contents in a report Prioritized (more detailed in the top) Estimated ○ not detailed in the bottom (could be S, M, L etc. Or Must have, nice to have, want to have) Grooming (product owner and stakeholders, but olso scrum master and development team) is important. Used as a dialog tool Grooming is going on constantly
 Grooming
Grooming
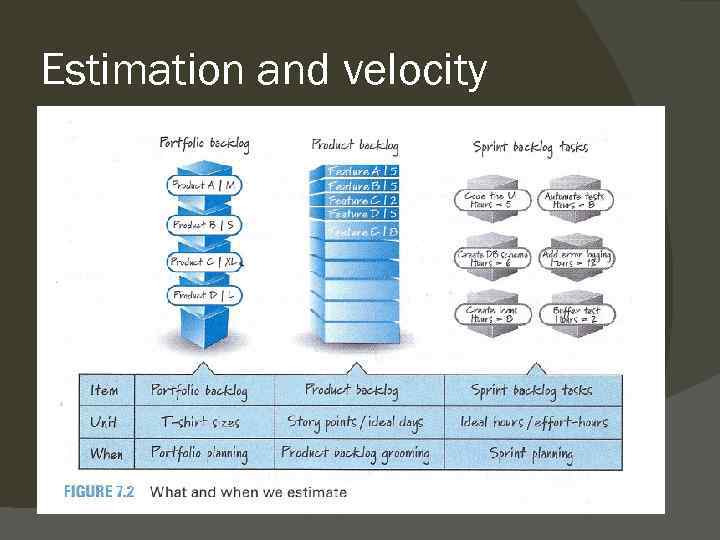 Estimation and velocity
Estimation and velocity
 Estimation Estimates are not commitments ○ It is the deveopment team who does this ○ Being correct. Ex from the exercise last tesson about the number of flights to make and then your bonus depends on exact estimate Accuracy versus Precision ○ Not calculating, but good enough – thats accuracy Relative size estimation (not absolute) ○ Glas of beer or distance in the room (dfistance or? ) ○ Using story points (relative sizes for each PBIs)) ○ Ideal days or real days
Estimation Estimates are not commitments ○ It is the deveopment team who does this ○ Being correct. Ex from the exercise last tesson about the number of flights to make and then your bonus depends on exact estimate Accuracy versus Precision ○ Not calculating, but good enough – thats accuracy Relative size estimation (not absolute) ○ Glas of beer or distance in the room (dfistance or? ) ○ Using story points (relative sizes for each PBIs)) ○ Ideal days or real days
 Planning Poker Consensus based Expert opinion Intense discussuion Relative sizing Accurate grouping ○ Same size items are grouped together (Fibonaccy sequence (sorting packages in bins) Leverage estimating history
Planning Poker Consensus based Expert opinion Intense discussuion Relative sizing Accurate grouping ○ Same size items are grouped together (Fibonaccy sequence (sorting packages in bins) Leverage estimating history
 Domino city – plan for the work Develop a prioritized product backlog using post-its. The product owner has specified the list on the next slide. Maybe you need to add some items Choose a scrum master who will be responcible for the scrum process. Remember it is more important to focus on understranding using scrum than finish the whole city (not a competion) You have 3 sprints – duration of 6 min Sprint review with product owner – only show what you hav finished Retrospective and grooming Ressources: a box with domino bricks in different colours and a Lego box for sharing – you can only take one brigs at a time and must be build in the common area. Hint: Could be maybe be relevant to have a ressouce team member There will be an extern Product owner who will particpate and approve the tasks you declare finished Quality, use of ressources, test etc)
Domino city – plan for the work Develop a prioritized product backlog using post-its. The product owner has specified the list on the next slide. Maybe you need to add some items Choose a scrum master who will be responcible for the scrum process. Remember it is more important to focus on understranding using scrum than finish the whole city (not a competion) You have 3 sprints – duration of 6 min Sprint review with product owner – only show what you hav finished Retrospective and grooming Ressources: a box with domino bricks in different colours and a Lego box for sharing – you can only take one brigs at a time and must be build in the common area. Hint: Could be maybe be relevant to have a ressouce team member There will be an extern Product owner who will particpate and approve the tasks you declare finished Quality, use of ressources, test etc)
 Domino city with domino streets Build a road consisting of 30 domino brigs (part 1) Build 3 small similar low budget bridges of Lego brigs where domino road can pass under Build a bridge at least 10 cm long of lego brigs where a domino road can pass over Build a small tree of lego brigs (see illustration on the lego box) Build an europlane of brigs (see illustration) Find the missing card in the card deck – put the answer on a post it Find the 2 missing card in red card deck – put the answer on a post it Build a dog of lego brigs Part 4 must pass over a mountain – use the wood stairs from the domino bricks box Build a cat of lego brigs Build part 2 – at least 50 cm for the part connection the 2 green roads Build part 3 Build part 5 Build part 4 Make a short part of the river using post-it to simulate (at least 30 cm) The city is build upon an old legend about aliens who traveled through time. At the mayors office was found an old map baed upon the legend about an entrance and exit time port. The city must be renamed after the place where the legend says the exit are located. The name must be placed covered in the city and revealed during the final review. airport In the airport you need the numbers from 1 to 500 written visible on 5 A 5 papers Which drink is made by 2 cl Finsbury gin and 2 cl Rose’s lime? If the instuctor add this then you also need to sort all the scrum-tiles into the 3 roles scrum roles on an A 3 paper. Start writing the scrum rules and then places the tiles where they belongs
Domino city with domino streets Build a road consisting of 30 domino brigs (part 1) Build 3 small similar low budget bridges of Lego brigs where domino road can pass under Build a bridge at least 10 cm long of lego brigs where a domino road can pass over Build a small tree of lego brigs (see illustration on the lego box) Build an europlane of brigs (see illustration) Find the missing card in the card deck – put the answer on a post it Find the 2 missing card in red card deck – put the answer on a post it Build a dog of lego brigs Part 4 must pass over a mountain – use the wood stairs from the domino bricks box Build a cat of lego brigs Build part 2 – at least 50 cm for the part connection the 2 green roads Build part 3 Build part 5 Build part 4 Make a short part of the river using post-it to simulate (at least 30 cm) The city is build upon an old legend about aliens who traveled through time. At the mayors office was found an old map baed upon the legend about an entrance and exit time port. The city must be renamed after the place where the legend says the exit are located. The name must be placed covered in the city and revealed during the final review. airport In the airport you need the numbers from 1 to 500 written visible on 5 A 5 papers Which drink is made by 2 cl Finsbury gin and 2 cl Rose’s lime? If the instuctor add this then you also need to sort all the scrum-tiles into the 3 roles scrum roles on an A 3 paper. Start writing the scrum rules and then places the tiles where they belongs
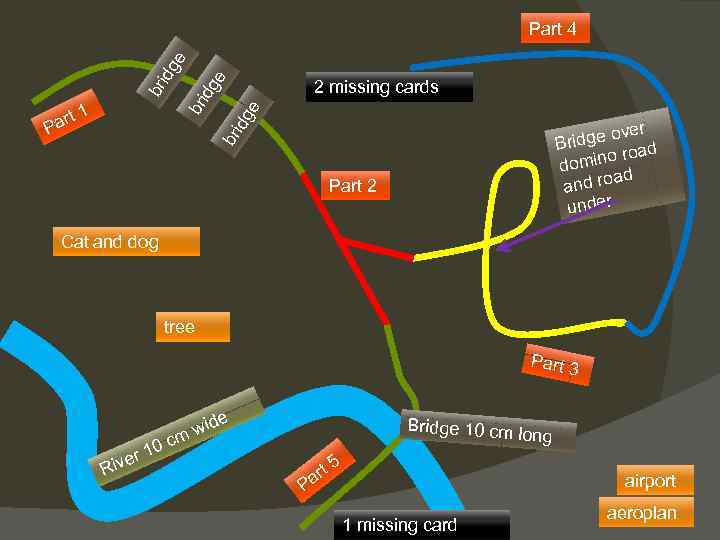 idg ver idge o d Br o roa domin ad and ro under br rt Pa 2 missing cards e br 1 idg e br idg e Part 4 Part 2 Cat and dog tree Part 3 e id m w 0 c Bridge 10 cm l on g r 1 e Riv 5 rt a airport P 1 missing card aeroplan
idg ver idge o d Br o roa domin ad and ro under br rt Pa 2 missing cards e br 1 idg e br idg e Part 4 Part 2 Cat and dog tree Part 3 e id m w 0 c Bridge 10 cm l on g r 1 e Riv 5 rt a airport P 1 missing card aeroplan
 comments Remark that maybe not all the tasks in product backlog are well described Product owner can change his mind during the whole project Bridges should be build cheep (limited ressources used) The cat, dog, tree airoplane must be similar to the figures on the bulk Some task items should maybe incorporate explorative development (acquire knowledge about how domino-roads work best) – find a good distance between the bricks What about some safety during the building process like removing some elements of the roads What about quality management What about cost management Focus on the scrum process (it takes more time for plan the sprint and evalute because of the very short sprint The product backlog could be comprimised in userstories like holding relevant things together in bigger parts so there is something to break up in smaller parts Use user story point to estimate the backlog items Ohh how to get to the airport ? – I need a road to the airport You have limited ressources in lego- and domino brigs In the end it must work as a domino city Product owner prioritize the central part of the city very high. Next to that the road over the river to the city It takes about 90 minutes for a small team and 4 sprints. Less time and less sprint for a bigger team Remember to break the bigger parts in to smaller items Knowing this exercise spend more time on planning than execution Use game planning and burn down chart if you have 4 sprint The 3 bridges must be aboslutely at low cost Complain if the 3 bridges are not the same What about risk management, qual Ity management, tests, safety roads, ressource management
comments Remark that maybe not all the tasks in product backlog are well described Product owner can change his mind during the whole project Bridges should be build cheep (limited ressources used) The cat, dog, tree airoplane must be similar to the figures on the bulk Some task items should maybe incorporate explorative development (acquire knowledge about how domino-roads work best) – find a good distance between the bricks What about some safety during the building process like removing some elements of the roads What about quality management What about cost management Focus on the scrum process (it takes more time for plan the sprint and evalute because of the very short sprint The product backlog could be comprimised in userstories like holding relevant things together in bigger parts so there is something to break up in smaller parts Use user story point to estimate the backlog items Ohh how to get to the airport ? – I need a road to the airport You have limited ressources in lego- and domino brigs In the end it must work as a domino city Product owner prioritize the central part of the city very high. Next to that the road over the river to the city It takes about 90 minutes for a small team and 4 sprints. Less time and less sprint for a bigger team Remember to break the bigger parts in to smaller items Knowing this exercise spend more time on planning than execution Use game planning and burn down chart if you have 4 sprint The 3 bridges must be aboslutely at low cost Complain if the 3 bridges are not the same What about risk management, qual Ity management, tests, safety roads, ressource management
 Scrum in a busienss perspective Scrum is an agile Process that allows us to focus on delivering the highest business value in the shortest time. (Mike Cohn, Mountain Goat Software) Scrum is an iterative, incremental framework for project management and agile software development. (Wikipedia). Scrum is a Framework that let us create concepts focused in both business needs and business changes in the shortest period of time
Scrum in a busienss perspective Scrum is an agile Process that allows us to focus on delivering the highest business value in the shortest time. (Mike Cohn, Mountain Goat Software) Scrum is an iterative, incremental framework for project management and agile software development. (Wikipedia). Scrum is a Framework that let us create concepts focused in both business needs and business changes in the shortest period of time
 Learning goals Welcome change Our project is constantly changing Optimize the project around that environment Working software is the primary measure of progress Nothing is complete until we have working software “Just Enough” Process and Artifacts Sufficient to achieve iteration goals and readily maintain the results Self-Organizing Teams The team actively participates in managing the iteration Teams develop low level plans to achieve iteration goals Knowledge transfer via conversation. . . Is the most effective communication method, written words / Models leave too much open to interpretation (hmm!) What kind of business arguments promotes an agile development proces?
Learning goals Welcome change Our project is constantly changing Optimize the project around that environment Working software is the primary measure of progress Nothing is complete until we have working software “Just Enough” Process and Artifacts Sufficient to achieve iteration goals and readily maintain the results Self-Organizing Teams The team actively participates in managing the iteration Teams develop low level plans to achieve iteration goals Knowledge transfer via conversation. . . Is the most effective communication method, written words / Models leave too much open to interpretation (hmm!) What kind of business arguments promotes an agile development proces?


