34ff3895a5ad0a5b14fba34bd2fd728b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 Science Knowledge: Science 2: Life Processes and living things K 2. 4 Variation, Inheritance & Evolution • • • This document can be freely copied and amended if used for educational purposes. It must not be used for commercial gain. The author(s) and web source must be acknowledged whether used as it stands or whether adapted in any way. Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Authored by Liz Lakin and Keith Ross, University of Gloucestershire. accessed from http: //www. ase. org. uk/scitutors/ date created March 2006 June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 1
Science Knowledge: Science 2: Life Processes and living things K 2. 4 Variation, Inheritance & Evolution • • • This document can be freely copied and amended if used for educational purposes. It must not be used for commercial gain. The author(s) and web source must be acknowledged whether used as it stands or whether adapted in any way. Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Authored by Liz Lakin and Keith Ross, University of Gloucestershire. accessed from http: //www. ase. org. uk/scitutors/ date created March 2006 June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 1
 Variation, Inheritance & Evolution Learning Objectives • To explore the science • To identify the ‘big behind the headlines ideas’ in this field of biology and recognise • To establish a timeline how they are of events leading to interlinked our current scientific understanding • To discuss modern applications & their associated issues June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 2
Variation, Inheritance & Evolution Learning Objectives • To explore the science • To identify the ‘big behind the headlines ideas’ in this field of biology and recognise • To establish a timeline how they are of events leading to interlinked our current scientific understanding • To discuss modern applications & their associated issues June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 2
 http: //www. ncseweb. org/evc/Evs. C-cover_400. jpg June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 3
http: //www. ncseweb. org/evc/Evs. C-cover_400. jpg June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 3
 http: //users. hol. gr/~dilos/prehis/Darwcar. jpg June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 4
http: //users. hol. gr/~dilos/prehis/Darwcar. jpg June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 4
 Variation http: //www. healthcastle. com/images/vegetables. jpg & : www. picture-newsletter. com/ vegetables/index. htm June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 5
Variation http: //www. healthcastle. com/images/vegetables. jpg & : www. picture-newsletter. com/ vegetables/index. htm June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 5
 Charles Darwin recognised the significance of variation in a range of organisms www. nmm. ac. uk/. . . / output. Register/lowhtml June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 6
Charles Darwin recognised the significance of variation in a range of organisms www. nmm. ac. uk/. . . / output. Register/lowhtml June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 6
 The Story of the Peppered Moth June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 7
The Story of the Peppered Moth June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 7
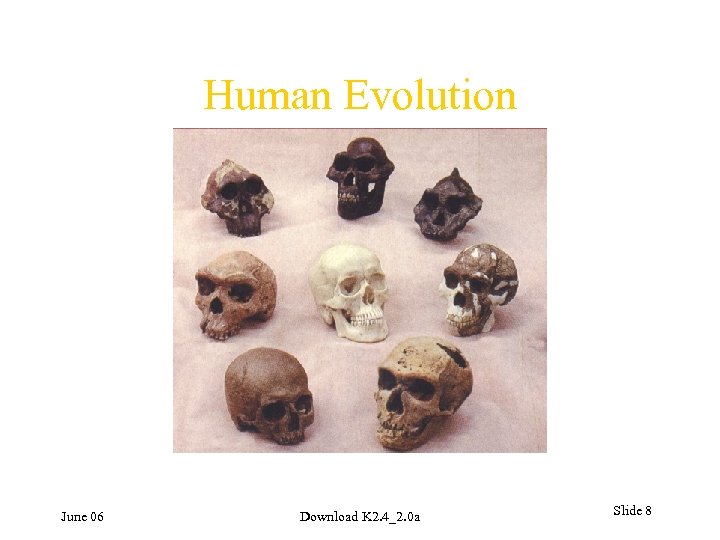 Human Evolution June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 8
Human Evolution June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 8
 Selection? • What we are is determined by our genes and our environment June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 9
Selection? • What we are is determined by our genes and our environment June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 9
 Father of Modern Genetics • Gregor Mendel • Austrian Monk (1850 s) • Identified the patterns of inheritance • Laws of Inheritance June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 10
Father of Modern Genetics • Gregor Mendel • Austrian Monk (1850 s) • Identified the patterns of inheritance • Laws of Inheritance June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 10
 Multiple choice questions The questions in the slides that follow are taken from a set of over 100 available from www. escalate. ac. uk/1141 Percentages quoted in the slides are for a group of 100 trainee primary teachers on entry to ITE, having obtained a ‘C’ or better at GCSE, usually two or three years previously. This gives secondary trainees an insight into the misconceptions that survive a GCSE course, and all trainees some comfort that they are not alone with their own misconceptions about how genetics and evolution works. June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 11
Multiple choice questions The questions in the slides that follow are taken from a set of over 100 available from www. escalate. ac. uk/1141 Percentages quoted in the slides are for a group of 100 trainee primary teachers on entry to ITE, having obtained a ‘C’ or better at GCSE, usually two or three years previously. This gives secondary trainees an insight into the misconceptions that survive a GCSE course, and all trainees some comfort that they are not alone with their own misconceptions about how genetics and evolution works. June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 11
 Recessive Genes If you and your partner both carry the disease for cystic fibrosis (but are not sufferers), what would be the probability that your children will then inherit the actual disease? a. 25% (1 in 4) 5% b. 33. 3% (1 in 3) 19% c. 50% (1 in 2) 35% d. 100% (1 in 1 - certainty) 39% (% are for a survey of post GCSE students – see notes)
Recessive Genes If you and your partner both carry the disease for cystic fibrosis (but are not sufferers), what would be the probability that your children will then inherit the actual disease? a. 25% (1 in 4) 5% b. 33. 3% (1 in 3) 19% c. 50% (1 in 2) 35% d. 100% (1 in 1 - certainty) 39% (% are for a survey of post GCSE students – see notes)
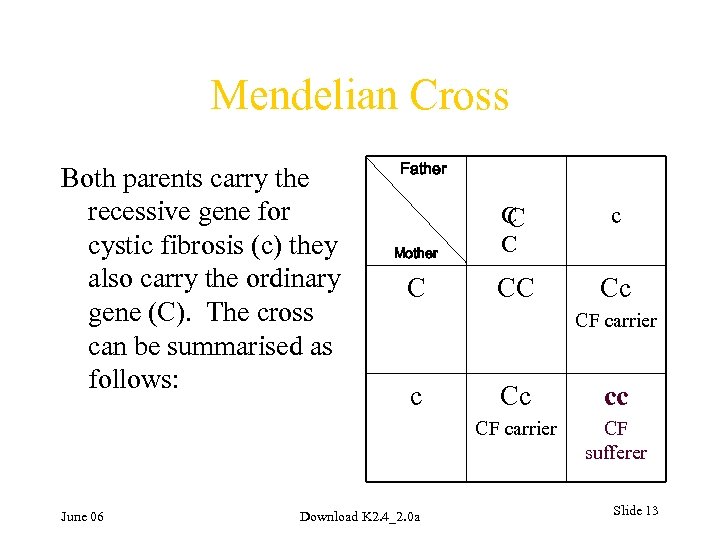 Mendelian Cross Both parents carry the recessive gene for cystic fibrosis (c) they also carry the ordinary gene (C). The cross can be summarised as follows: Father c Mother C C CC Cc CF carrier Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Cc cc CF carrier June 06 c CF sufferer Slide 13
Mendelian Cross Both parents carry the recessive gene for cystic fibrosis (c) they also carry the ordinary gene (C). The cross can be summarised as follows: Father c Mother C C CC Cc CF carrier Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Cc cc CF carrier June 06 c CF sufferer Slide 13
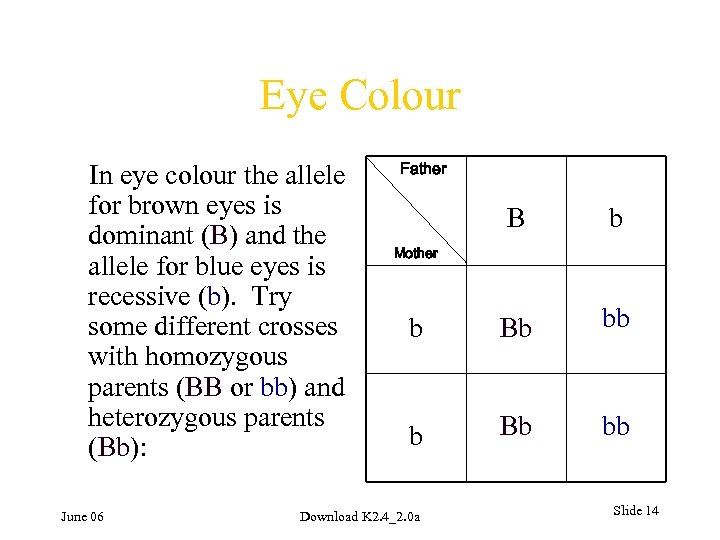 Eye Colour In eye colour the allele for brown eyes is dominant (B) and the allele for blue eyes is recessive (b). Try some different crosses with homozygous parents (BB or bb) and heterozygous parents (Bb): June 06 Father B b b Bb bb Mother Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 14
Eye Colour In eye colour the allele for brown eyes is dominant (B) and the allele for blue eyes is recessive (b). Try some different crosses with homozygous parents (BB or bb) and heterozygous parents (Bb): June 06 Father B b b Bb bb Mother Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 14
 So what are Genetics? • Look at the person next to you and identify Our common inheritance as humans as many external similarities between the two of you, as you can. • Now identify as many differences as The tiny amount of variation in our possible. genes We share half our genes with bananas and 99% with the chimpanzee June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 15
So what are Genetics? • Look at the person next to you and identify Our common inheritance as humans as many external similarities between the two of you, as you can. • Now identify as many differences as The tiny amount of variation in our possible. genes We share half our genes with bananas and 99% with the chimpanzee June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 15
 One fertilised cell to an organism! June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 16
One fertilised cell to an organism! June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 16
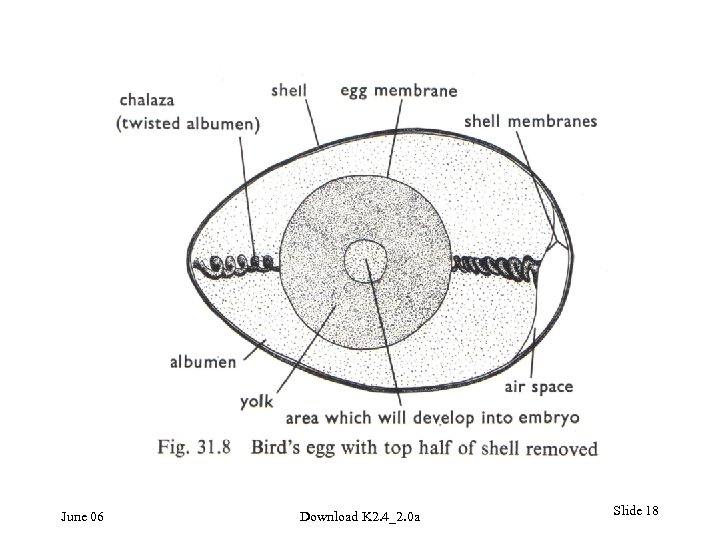
 Development of an egg What will happen to the weight of a fertilised bird's egg from time of laying to just before the chick hatches? • It gets lighter 6% • It gets heavier 54% • It stays much the same 35% (% are for a survey of post GCSE students – see notes) June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 17
Development of an egg What will happen to the weight of a fertilised bird's egg from time of laying to just before the chick hatches? • It gets lighter 6% • It gets heavier 54% • It stays much the same 35% (% are for a survey of post GCSE students – see notes) June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 17
 June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 18
June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 18
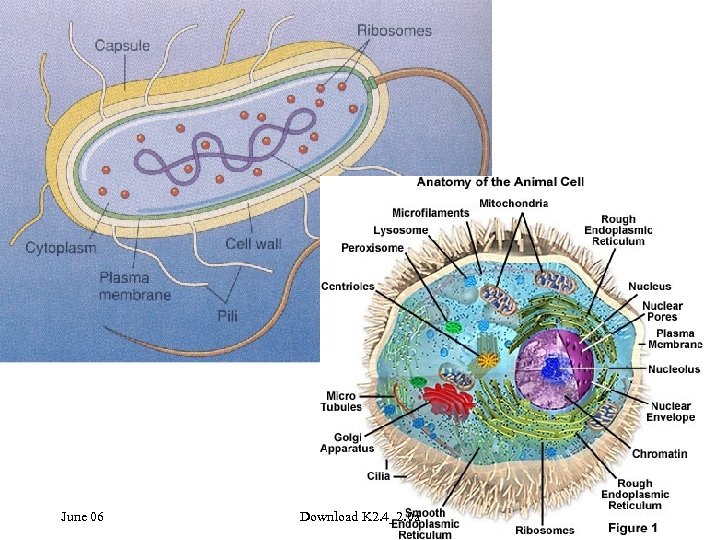 Genes • What are your genes? • Do bacteria have genes? • Is the genetic information in the sex cells the same as in other cells? June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 19
Genes • What are your genes? • Do bacteria have genes? • Is the genetic information in the sex cells the same as in other cells? June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 19
 Let’s look at cells … • Several types • 75 billion in a human being • Capable of carrying out many different functions e. g. … – Protection – Movement – Excretion June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 20
Let’s look at cells … • Several types • 75 billion in a human being • Capable of carrying out many different functions e. g. … – Protection – Movement – Excretion June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 20
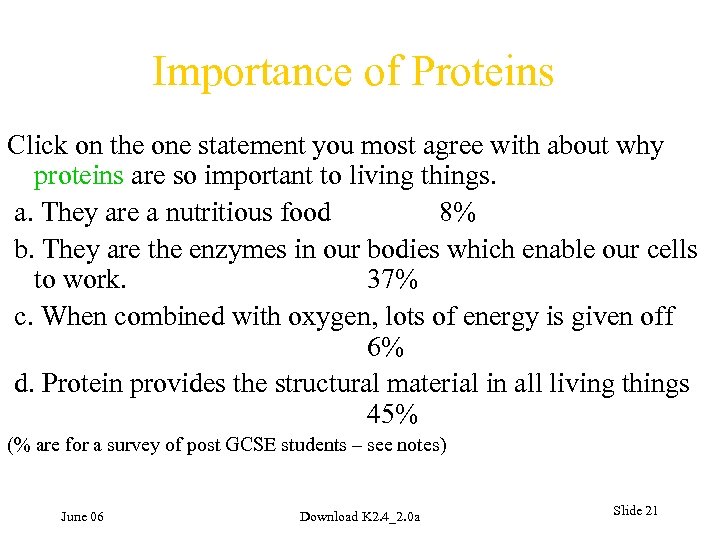 Importance of Proteins Click on the one statement you most agree with about why proteins are so important to living things. a. They are a nutritious food 8% b. They are the enzymes in our bodies which enable our cells to work. 37% c. When combined with oxygen, lots of energy is given off 6% d. Protein provides the structural material in all living things 45% (% are for a survey of post GCSE students – see notes) June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 21
Importance of Proteins Click on the one statement you most agree with about why proteins are so important to living things. a. They are a nutritious food 8% b. They are the enzymes in our bodies which enable our cells to work. 37% c. When combined with oxygen, lots of energy is given off 6% d. Protein provides the structural material in all living things 45% (% are for a survey of post GCSE students – see notes) June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 21
 Material of Inheritance … • What are the requirements of hereditary material? – Store information – Permanence – Ability to change (mutate) June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 22
Material of Inheritance … • What are the requirements of hereditary material? – Store information – Permanence – Ability to change (mutate) June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 22
 Unique function of DNA • Stores information for protein synthesis • Makes copies of itself ~ self replication • Able to change/vary/mutate June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 23
Unique function of DNA • Stores information for protein synthesis • Makes copies of itself ~ self replication • Able to change/vary/mutate June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 23
 DNA • Deoxyribonucleic Acid • Molecular language ~ 4 different letters • Codon – three letter word – most code for an amino acid • GENE ~ sentence of many words (amino acids) which enables it to build PROTEINS • Proteins are enzymes that enable reactions to take place in cells June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 24
DNA • Deoxyribonucleic Acid • Molecular language ~ 4 different letters • Codon – three letter word – most code for an amino acid • GENE ~ sentence of many words (amino acids) which enables it to build PROTEINS • Proteins are enzymes that enable reactions to take place in cells June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 24
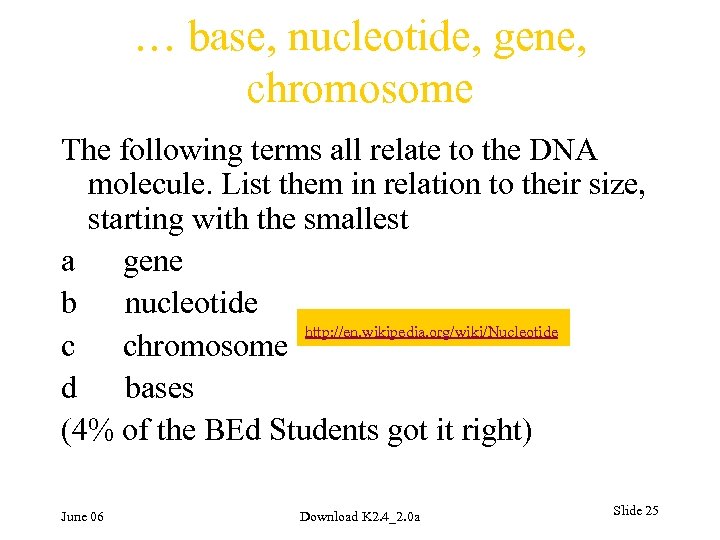 … base, nucleotide, gene, chromosome The following terms all relate to the DNA molecule. List them in relation to their size, starting with the smallest a gene b nucleotide http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Nucleotide c chromosome d bases (4% of the BEd Students got it right) June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 25
… base, nucleotide, gene, chromosome The following terms all relate to the DNA molecule. List them in relation to their size, starting with the smallest a gene b nucleotide http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Nucleotide c chromosome d bases (4% of the BEd Students got it right) June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 25
 DNA Click on the four sentences about human DNA that are true. a. It carries the code to make proteins. 50% b. It can pass from one generation to the next. 83% c. It can make copies of itself. 68% d. It is a single stranded molecule. 26% e. It is made of protein. 51% f. It is identical in almost every cell of our body. 66% (% are for a survey of post GCSE students – see notes)
DNA Click on the four sentences about human DNA that are true. a. It carries the code to make proteins. 50% b. It can pass from one generation to the next. 83% c. It can make copies of itself. 68% d. It is a single stranded molecule. 26% e. It is made of protein. 51% f. It is identical in almost every cell of our body. 66% (% are for a survey of post GCSE students – see notes)
 Protein Synthesis • A simulation … June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 27
Protein Synthesis • A simulation … June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 27
 Link to HOME Quiz June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 28
Link to HOME Quiz June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 28
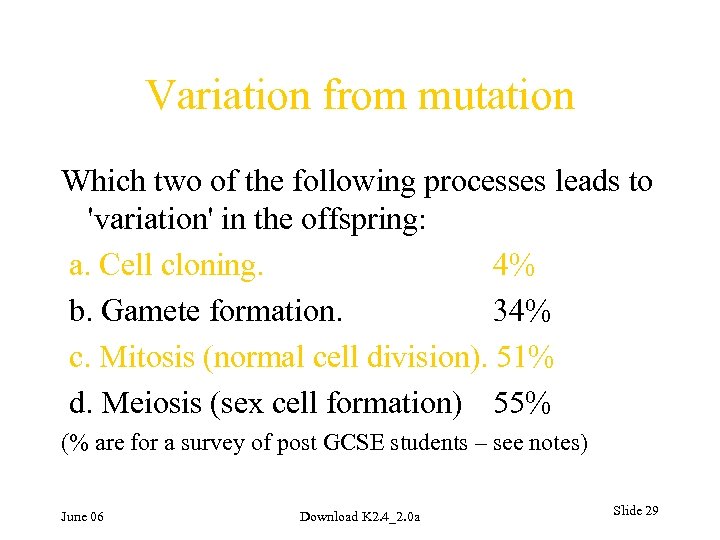 Variation from mutation Which two of the following processes leads to 'variation' in the offspring: a. Cell cloning. 4% b. Gamete formation. 34% c. Mitosis (normal cell division). 51% d. Meiosis (sex cell formation) 55% (% are for a survey of post GCSE students – see notes) June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 29
Variation from mutation Which two of the following processes leads to 'variation' in the offspring: a. Cell cloning. 4% b. Gamete formation. 34% c. Mitosis (normal cell division). 51% d. Meiosis (sex cell formation) 55% (% are for a survey of post GCSE students – see notes) June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 29
 Tracing your ancestry A mutation of which of the following could be inherited from both your parents? a. Messenger RNA 20 b. Nuclear DNA 29 c. Ribosomal RNA 13 d. Mitochondrial DNA 35 (% are for a survey of post GCSE students – see notes) June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 30
Tracing your ancestry A mutation of which of the following could be inherited from both your parents? a. Messenger RNA 20 b. Nuclear DNA 29 c. Ribosomal RNA 13 d. Mitochondrial DNA 35 (% are for a survey of post GCSE students – see notes) June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 30
 Artificial Selection June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 31
Artificial Selection June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 31
 Manipulation of genes … • Genotype • Phenotype & selective breeding • Manipulation of genes • Biotechnology June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 32
Manipulation of genes … • Genotype • Phenotype & selective breeding • Manipulation of genes • Biotechnology June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 32
 How genes work … • Inheritance • Mutations • Stem cells June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 33
How genes work … • Inheritance • Mutations • Stem cells June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 33
 Genetic Engineering June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 34
Genetic Engineering June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 34
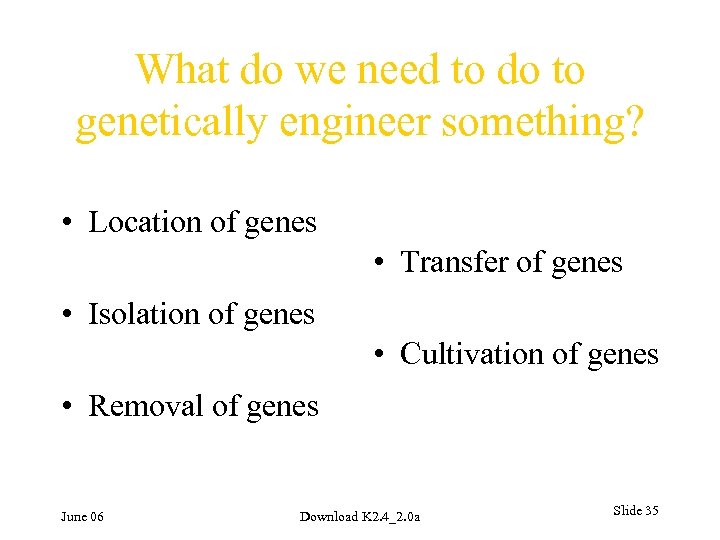 What do we need to do to genetically engineer something? • Location of genes • Transfer of genes • Isolation of genes • Cultivation of genes • Removal of genes June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 35
What do we need to do to genetically engineer something? • Location of genes • Transfer of genes • Isolation of genes • Cultivation of genes • Removal of genes June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 35
 Where do we go from here …? • Dolly ~ cloned from a mature cell by nuclear transfer • Polly ~ cloned from an embryo cell, but contains a human gene which produces the human protein in the sheep’s milk • Why are they scientifically significant? June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 36
Where do we go from here …? • Dolly ~ cloned from a mature cell by nuclear transfer • Polly ~ cloned from an embryo cell, but contains a human gene which produces the human protein in the sheep’s milk • Why are they scientifically significant? June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 36
 June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 37
June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 37
 What are the issues … ? • Monsanto monopoly • 1998 Government moratorium on the growth of GM crops • Media hype and scare mongering • Human cloning & designer babies June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 38
What are the issues … ? • Monsanto monopoly • 1998 Government moratorium on the growth of GM crops • Media hype and scare mongering • Human cloning & designer babies June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 38
 So what do you think? June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 39
So what do you think? June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 39
 So what do you really think? • Should scientist be • Should scientists be allowed to alter animal genes: Human genes: – For medical reasons? – For healthier or – For commercial more efficient reasons? food production? – For commercial reasons? Slide 40 June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a
So what do you really think? • Should scientist be • Should scientists be allowed to alter animal genes: Human genes: – For medical reasons? – For healthier or – For commercial more efficient reasons? food production? – For commercial reasons? Slide 40 June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a
 Recap … • What do genes do? • Where do we find genes? • What makes DNA so good as hereditary material? • What information does DNA store? • How does it store it? • What happens next … June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 41
Recap … • What do genes do? • Where do we find genes? • What makes DNA so good as hereditary material? • What information does DNA store? • How does it store it? • What happens next … June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 41
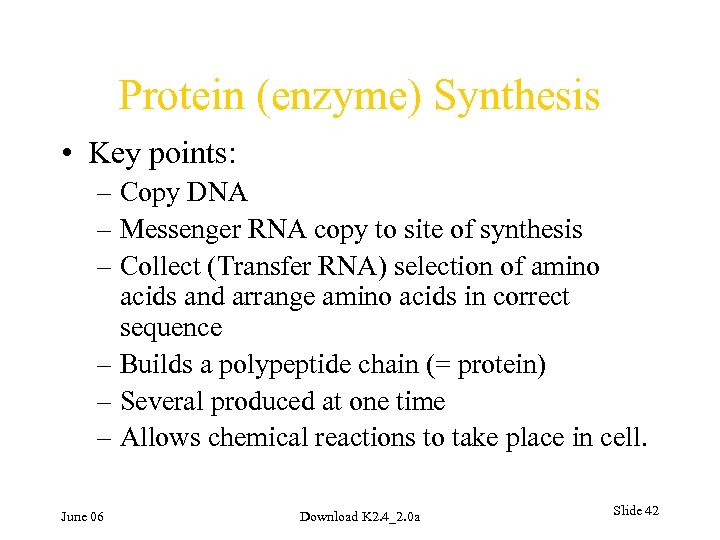 Protein (enzyme) Synthesis • Key points: – Copy DNA – Messenger RNA copy to site of synthesis – Collect (Transfer RNA) selection of amino acids and arrange amino acids in correct sequence – Builds a polypeptide chain (= protein) – Several produced at one time – Allows chemical reactions to take place in cell. June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 42
Protein (enzyme) Synthesis • Key points: – Copy DNA – Messenger RNA copy to site of synthesis – Collect (Transfer RNA) selection of amino acids and arrange amino acids in correct sequence – Builds a polypeptide chain (= protein) – Several produced at one time – Allows chemical reactions to take place in cell. June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 42
 Gene Expression • Switching genes on and off … • Stem cells and mature differentiated cells • Growth = cell division and cell differentiation June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 43
Gene Expression • Switching genes on and off … • Stem cells and mature differentiated cells • Growth = cell division and cell differentiation June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 43
 Gene Therapy • Treatment of diseases by the introduction of powders containing working copies of the defective gene ~ saturation approach • Cystic Fibrosis • Problems: – Disease is rare in the population – Expensive to treat – Research pressure into common ailments June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 44
Gene Therapy • Treatment of diseases by the introduction of powders containing working copies of the defective gene ~ saturation approach • Cystic Fibrosis • Problems: – Disease is rare in the population – Expensive to treat – Research pressure into common ailments June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 44
 Genetic Engineering • Transfer of genes from one species to another. • How is it done? • Gene Splicing • Limitations ~ can only add genes June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 45
Genetic Engineering • Transfer of genes from one species to another. • How is it done? • Gene Splicing • Limitations ~ can only add genes June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 45
 • http: //www. food. gov. uk/gmdebate/aboutgm/? view=GM%20 Microsite June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 46 Countries which are already growing some GM crops
• http: //www. food. gov. uk/gmdebate/aboutgm/? view=GM%20 Microsite June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 46 Countries which are already growing some GM crops
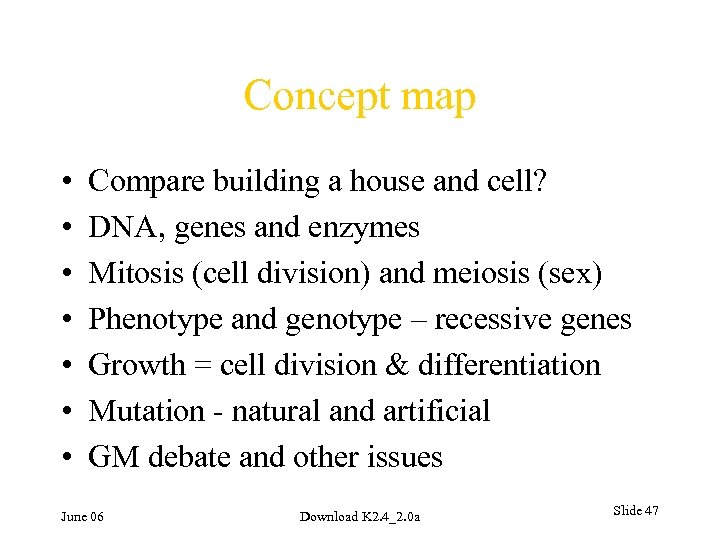 Concept map • • Compare building a house and cell? DNA, genes and enzymes Mitosis (cell division) and meiosis (sex) Phenotype and genotype – recessive genes Growth = cell division & differentiation Mutation - natural and artificial GM debate and other issues June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 47
Concept map • • Compare building a house and cell? DNA, genes and enzymes Mitosis (cell division) and meiosis (sex) Phenotype and genotype – recessive genes Growth = cell division & differentiation Mutation - natural and artificial GM debate and other issues June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 47
 Learning log • Look at the questions – where were your conceptual misunderstandings? June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 48
Learning log • Look at the questions – where were your conceptual misunderstandings? June 06 Download K 2. 4_2. 0 a Slide 48


