8d314d2f5a5401b9329af6f2098e1816.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 97
 Science as a process o Hypothesis o Theory o Measurement n Meter n Liter n gram
Science as a process o Hypothesis o Theory o Measurement n Meter n Liter n gram
 o Microscope diaphragm o Characteristics of life o Homeostasis
o Microscope diaphragm o Characteristics of life o Homeostasis
 Cells o o o o Nucleus Plasma membrane Ribosome Mitochondria Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi body Vesicle
Cells o o o o Nucleus Plasma membrane Ribosome Mitochondria Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi body Vesicle
 Biomolecules o o o Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic acids Water (a polar molecule) n Solvent dissolves a solute
Biomolecules o o o Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic acids Water (a polar molecule) n Solvent dissolves a solute
 Enzymes o Lock and Key hypothesis
Enzymes o Lock and Key hypothesis
 Energy in Cells o Photosynthesis (in chloroplasts) n Stores energy, makes sugar o Cell respiration (in mitochondria) n Releases energy, stores energy in ATP
Energy in Cells o Photosynthesis (in chloroplasts) n Stores energy, makes sugar o Cell respiration (in mitochondria) n Releases energy, stores energy in ATP
 Domains o Archaea o Bacteria o Eukarya
Domains o Archaea o Bacteria o Eukarya
 Diffusion and Osmosis o Active transport o Diffusion; Facilitated diffusion o Osmosis n Hypotonic, isotonic, hypertonic
Diffusion and Osmosis o Active transport o Diffusion; Facilitated diffusion o Osmosis n Hypotonic, isotonic, hypertonic
 Mitosis and Meiosis o 2 N means 2 members of each chromosome pair (diploid) o 2 N -- 2 N mitosis o 1 N means 1 member of each chromosome pair (haploid gametes) o 2 N --- 1 N meiosis
Mitosis and Meiosis o 2 N means 2 members of each chromosome pair (diploid) o 2 N -- 2 N mitosis o 1 N means 1 member of each chromosome pair (haploid gametes) o 2 N --- 1 N meiosis
 Mendel o Discovered Dominance & Recessiveness o Principle of Segregation (pairs of genes always separate during meiosis) o Principle of Independent Assortment o Aa. Bb - AB, Ab, a. B, ab
Mendel o Discovered Dominance & Recessiveness o Principle of Segregation (pairs of genes always separate during meiosis) o Principle of Independent Assortment o Aa. Bb - AB, Ab, a. B, ab
 Mendel o Genotype o Phenotype
Mendel o Genotype o Phenotype
 Genetics o Monohybrid cross means Aa x Aa (ordinary Punnett square) o Sperm can have A or a o Dihybrid cross means Aa. Bb x Aa. Bb o Sperm can have o AB, Ab, a. B or ab
Genetics o Monohybrid cross means Aa x Aa (ordinary Punnett square) o Sperm can have A or a o Dihybrid cross means Aa. Bb x Aa. Bb o Sperm can have o AB, Ab, a. B or ab
 Multiple Alleles o ABO blood type
Multiple Alleles o ABO blood type
 Sex-linked o Gene found on “X” chromosome
Sex-linked o Gene found on “X” chromosome
 Mutations o Caused by energy and chemicals CHROMOSOME mutations nondisjunction translocation deletion GENE mutations (point mutations) deletion insertion substitution
Mutations o Caused by energy and chemicals CHROMOSOME mutations nondisjunction translocation deletion GENE mutations (point mutations) deletion insertion substitution
 Gene therapy o Replacing genes in a cell with new, healthy DNA o DNA Fingerprinting o GMO: Genetically modified organism
Gene therapy o Replacing genes in a cell with new, healthy DNA o DNA Fingerprinting o GMO: Genetically modified organism
 DNA o Deoxyribonucleic acid o. A+T G+C o Replication o Transcription o Translation
DNA o Deoxyribonucleic acid o. A+T G+C o Replication o Transcription o Translation
 RNA o Messenger RNA: o genetic code goes to ribosome, tells which amino acid to grab o Transfer RNA: o Carries amino acids to the ribosome
RNA o Messenger RNA: o genetic code goes to ribosome, tells which amino acid to grab o Transfer RNA: o Carries amino acids to the ribosome
 Growth Rate
Growth Rate
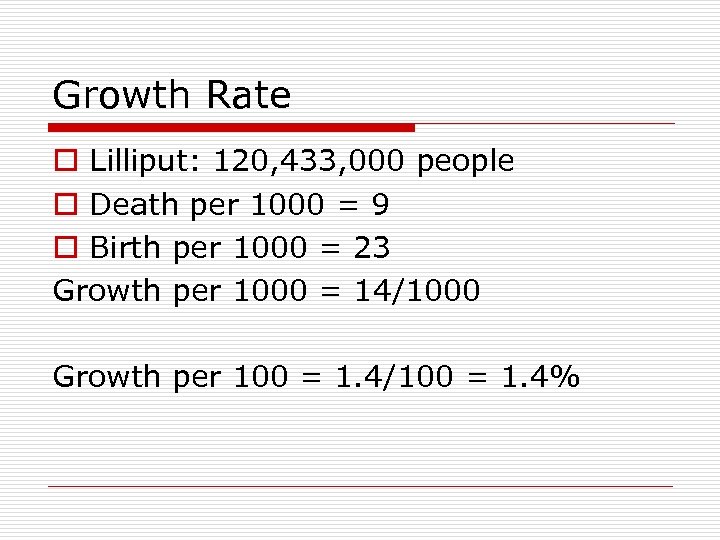 Growth Rate o Lilliput: 120, 433, 000 people o Death per 1000 = 9 o Birth per 1000 = 23 Growth per 1000 = 14/1000 Growth per 100 = 1. 4/100 = 1. 4%
Growth Rate o Lilliput: 120, 433, 000 people o Death per 1000 = 9 o Birth per 1000 = 23 Growth per 1000 = 14/1000 Growth per 100 = 1. 4/100 = 1. 4%
 Growth Rate o Lilliput: 120, 433, 000 people o Growth rate = 1. 4% o Multiply 120, 433, 000 o X 0. 014 o Added in one year = 1, 686, 062
Growth Rate o Lilliput: 120, 433, 000 people o Growth rate = 1. 4% o Multiply 120, 433, 000 o X 0. 014 o Added in one year = 1, 686, 062
 Growth Rate o Lilliput: 120, 433, 000 people o Added in one year = 1, 686, 062 o Total population next year: o 122, 119, 062
Growth Rate o Lilliput: 120, 433, 000 people o Added in one year = 1, 686, 062 o Total population next year: o 122, 119, 062
 Growth measurements 10 quadrat samples measured: Total number of poison ivy plants: 330/10 quadrats = 330/2. 5 square meters = 132/sq. meter
Growth measurements 10 quadrat samples measured: Total number of poison ivy plants: 330/10 quadrats = 330/2. 5 square meters = 132/sq. meter
 Growth measurements 132 plants/sq. meter X 10, 000 sq meters
Growth measurements 132 plants/sq. meter X 10, 000 sq meters
 1, 320, 000 plants in one hectare X 19 hectares= 250, 800, 000 plants in 19 hectare forest
1, 320, 000 plants in one hectare X 19 hectares= 250, 800, 000 plants in 19 hectare forest
 Biotic o Living things: o Animals, plants, bacteria, fungi o (and their cells)
Biotic o Living things: o Animals, plants, bacteria, fungi o (and their cells)
 Abiotic o Non-living things: o Water, rocks, sand, air o Energy, sunlight
Abiotic o Non-living things: o Water, rocks, sand, air o Energy, sunlight
 Population
Population
 Community
Community
 Ecosystem
Ecosystem
 Biomes o o o Desert Taiga Tundra Tropical Rain Forest Temperate Forest
Biomes o o o Desert Taiga Tundra Tropical Rain Forest Temperate Forest
 SYMBIOSIS o Mutualism o Parasitism o Commensalism
SYMBIOSIS o Mutualism o Parasitism o Commensalism
 Food Pyramid o Producers are ALWAYS on the bottom, Consumers on top. o Producers ALWAYS have the most mass in any environment
Food Pyramid o Producers are ALWAYS on the bottom, Consumers on top. o Producers ALWAYS have the most mass in any environment
 Trophic Levels o o Producers (autotrophs) Primary consumers Secondary consumers Tertiary consumers
Trophic Levels o o Producers (autotrophs) Primary consumers Secondary consumers Tertiary consumers
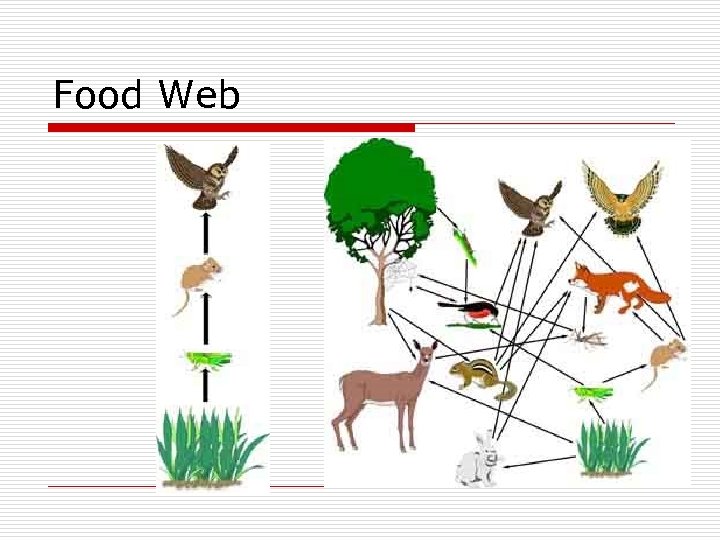 Food Web
Food Web
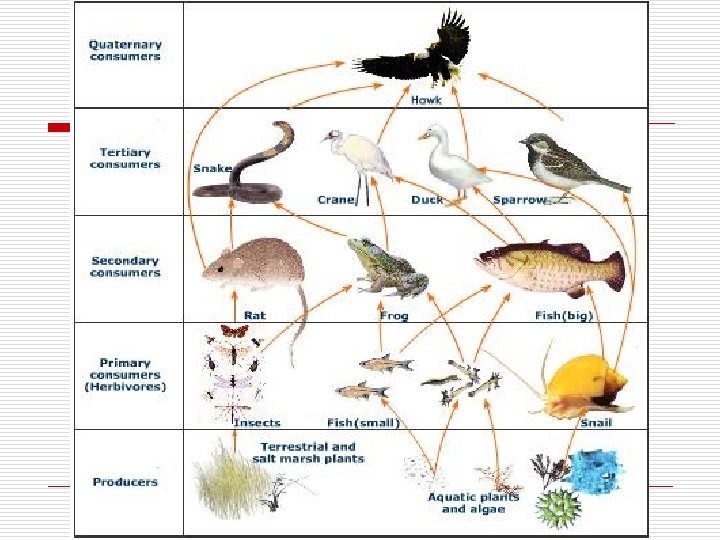
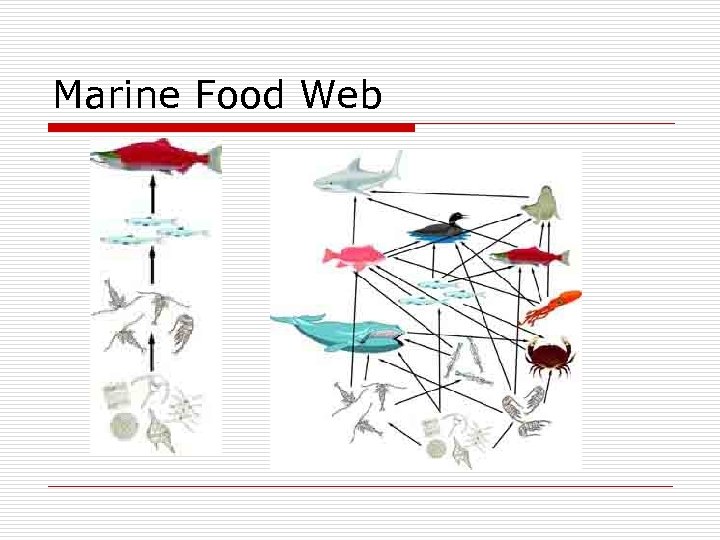 Marine Food Web
Marine Food Web
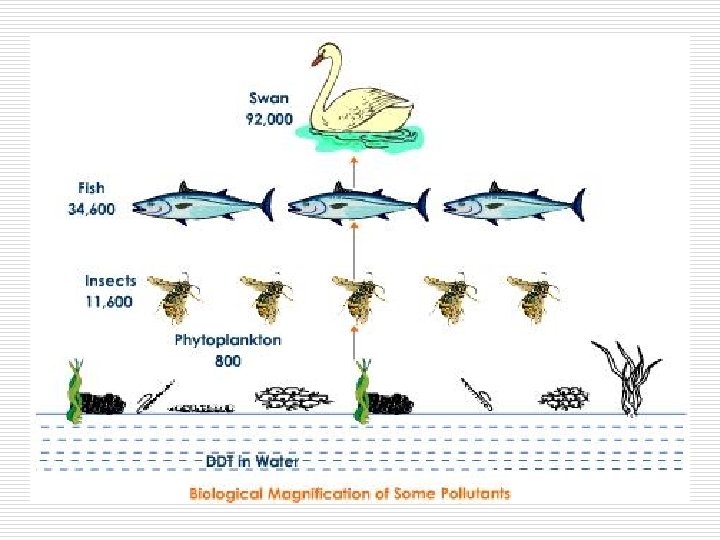
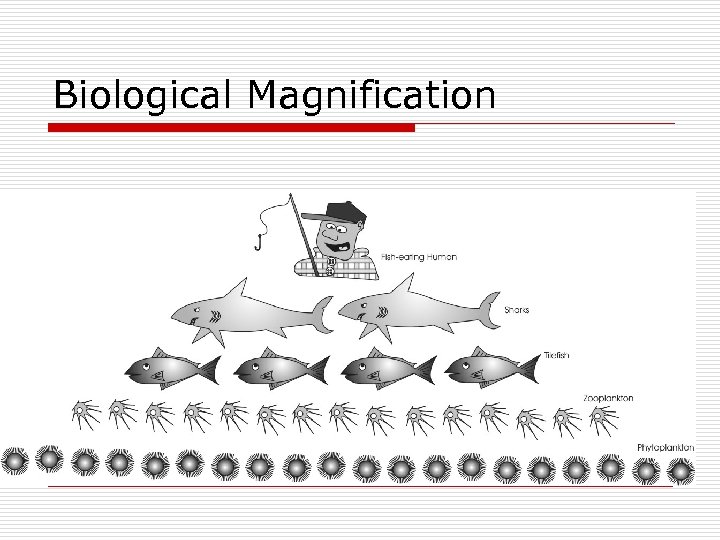 Biological Magnification
Biological Magnification
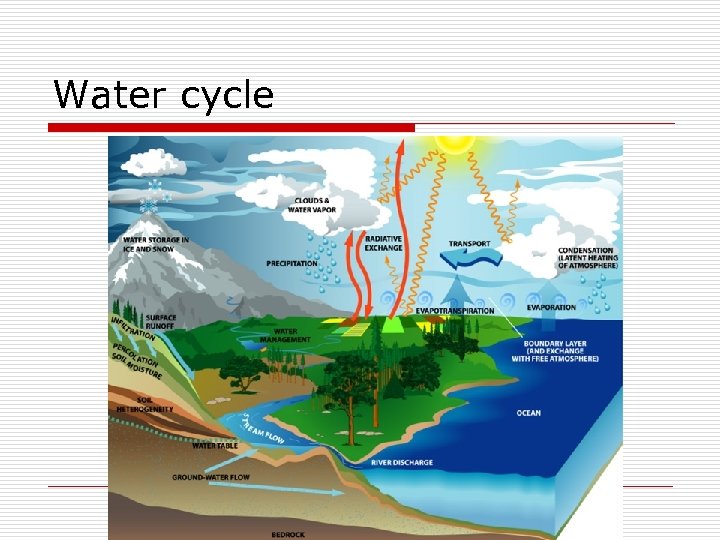 Water cycle
Water cycle
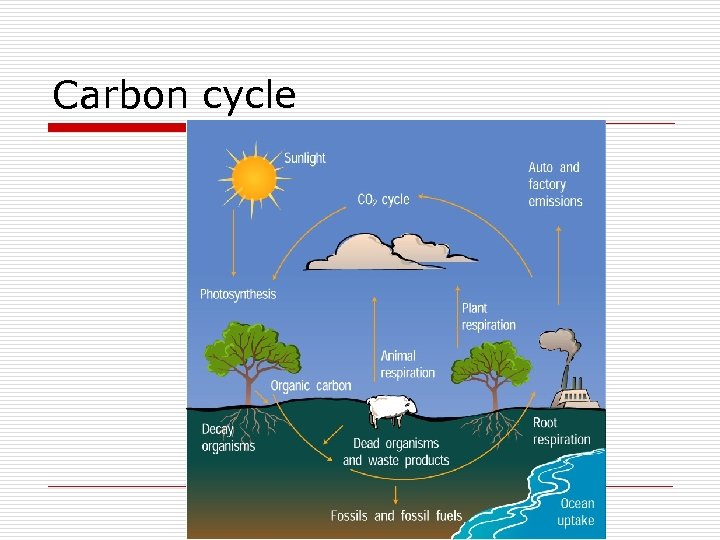 Carbon cycle
Carbon cycle
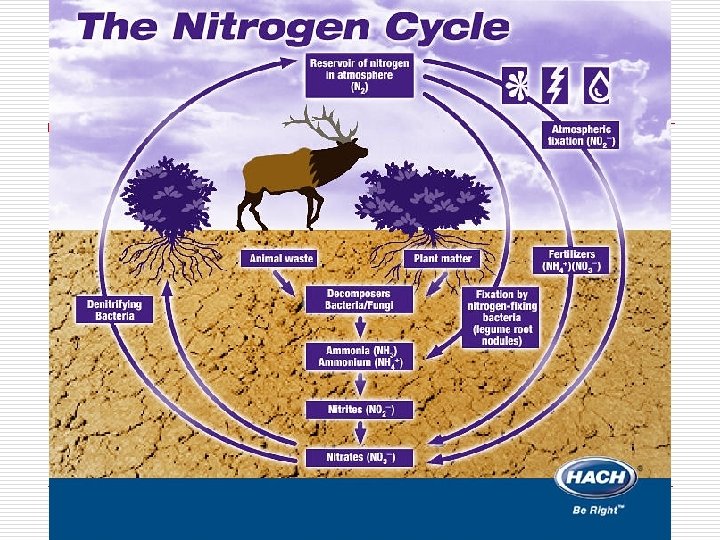 Nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen cycle
 Nitrogen cycle o Bacteria grab nitrogen from the air and convert it into nitrate. (Nitrogen fixation) o Plants use nitrate to make protein.
Nitrogen cycle o Bacteria grab nitrogen from the air and convert it into nitrate. (Nitrogen fixation) o Plants use nitrate to make protein.
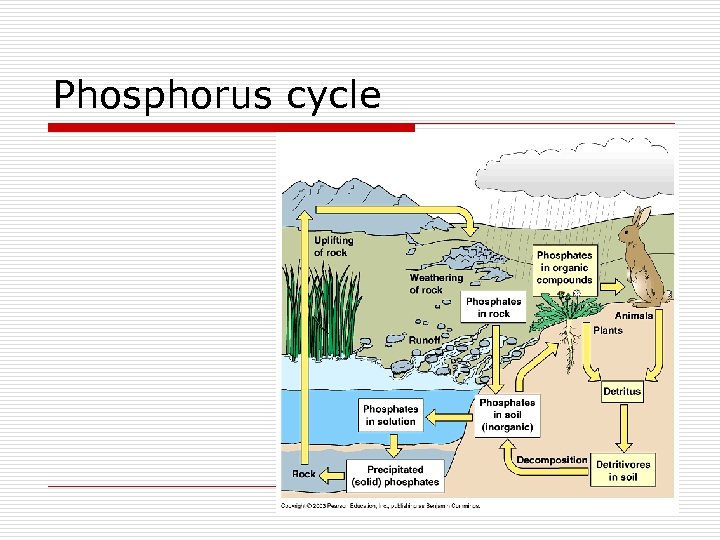 Phosphorus cycle
Phosphorus cycle
 Biodiversity o The number of species living in an area. o Biodiversity can change over time in a predictable way, called succession
Biodiversity o The number of species living in an area. o Biodiversity can change over time in a predictable way, called succession
 Succession o After a forest fire, volcanic eruption, new species move in. o “Pioneer species” (lichens) move in first. o PRIMARY succession= on bare rock o SECONDARY succession= on soil
Succession o After a forest fire, volcanic eruption, new species move in. o “Pioneer species” (lichens) move in first. o PRIMARY succession= on bare rock o SECONDARY succession= on soil
 Lichen
Lichen
 Lichen
Lichen
 Lichen
Lichen
 Secondary Succession
Secondary Succession
 Secondary Succession
Secondary Succession
 Secondary Succession
Secondary Succession
 Secondary Succession
Secondary Succession
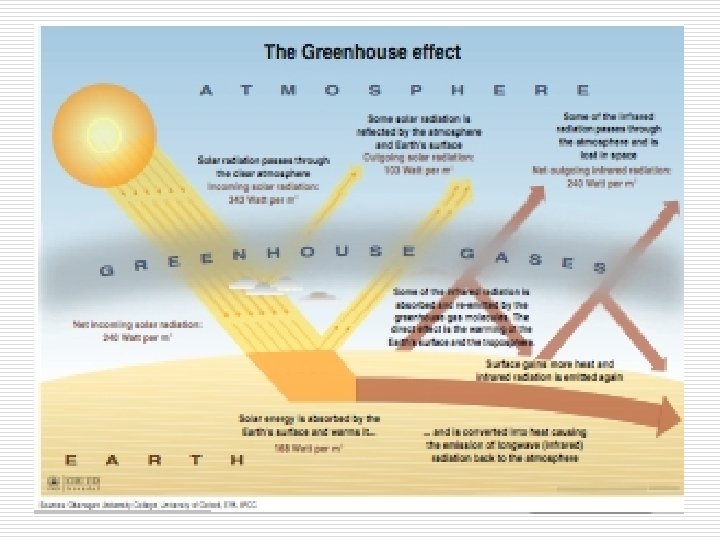
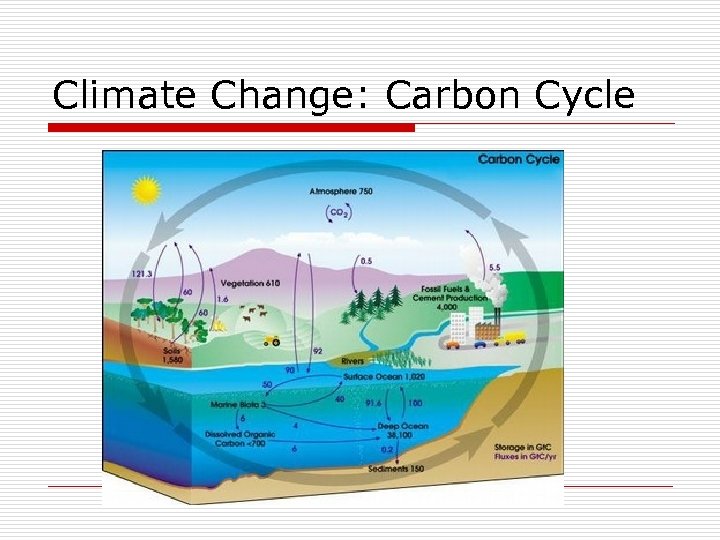 Climate Change: Carbon Cycle
Climate Change: Carbon Cycle
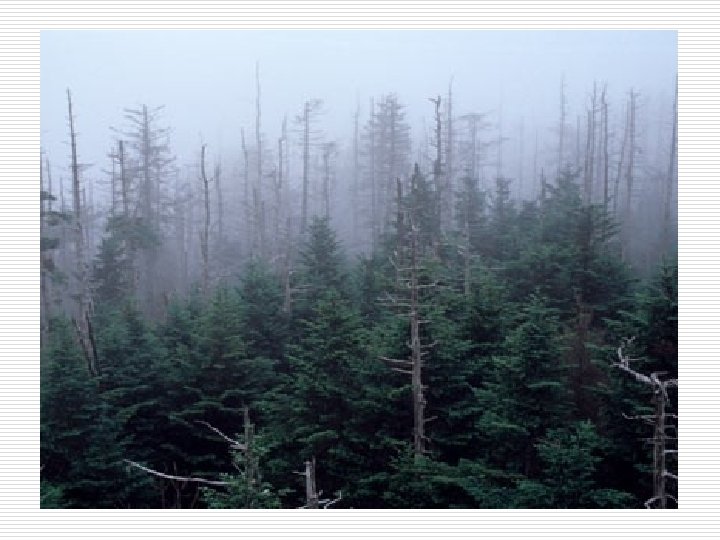
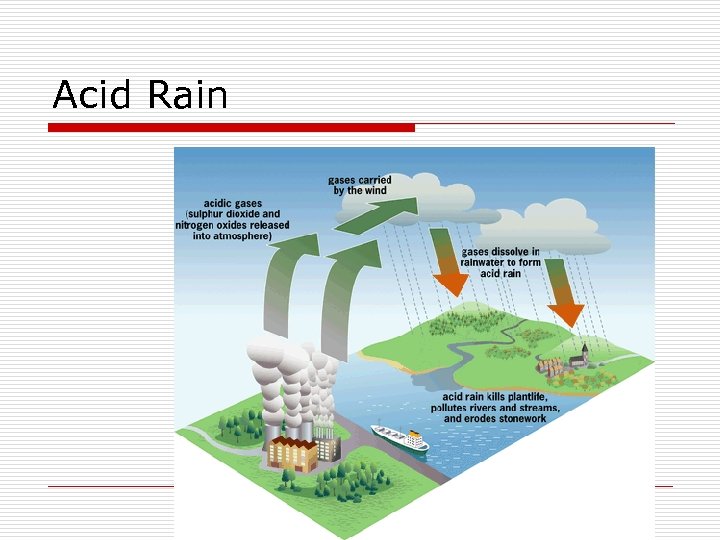 Acid Rain
Acid Rain

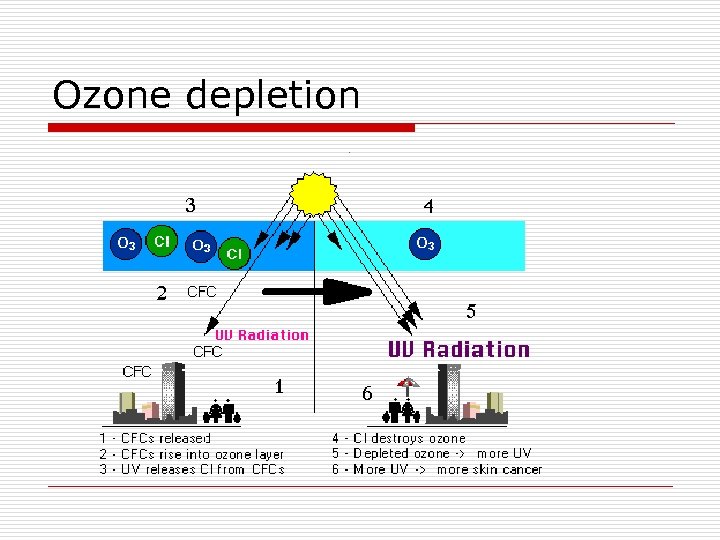 Ozone depletion
Ozone depletion
 Habitat fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation
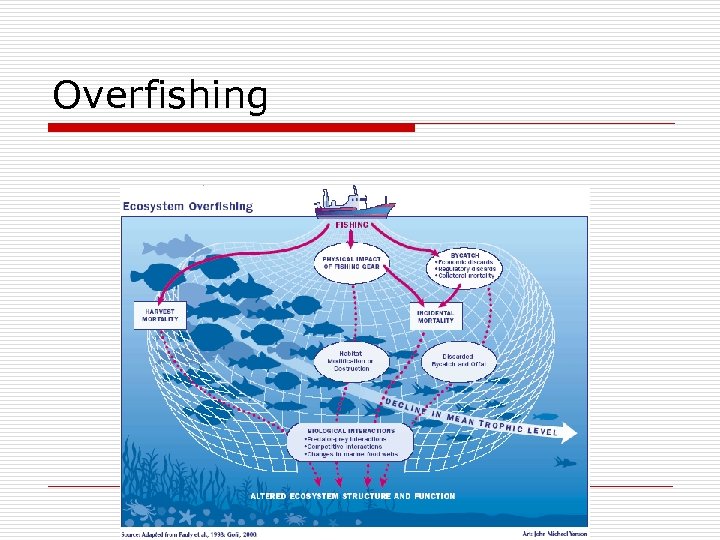 Overfishing
Overfishing
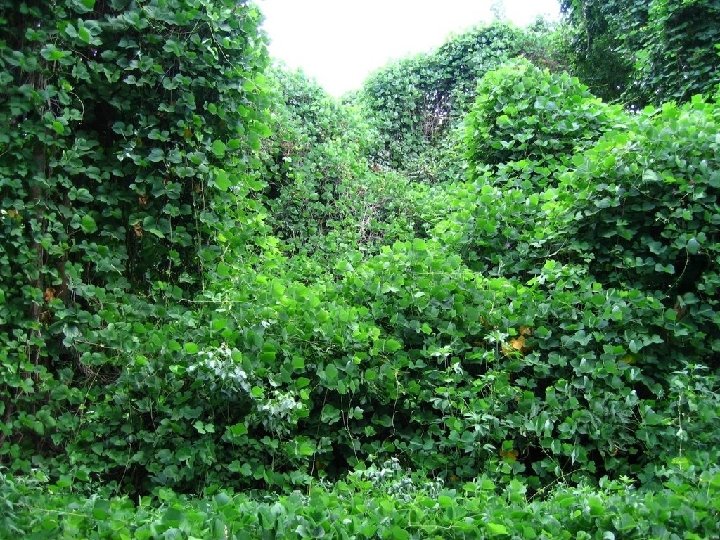 Invasive species
Invasive species
 Invasive species
Invasive species
 Cryptic coloration
Cryptic coloration

 Disruptive coloration
Disruptive coloration
 Mimicry
Mimicry
 Mimicry
Mimicry
 Mimicry
Mimicry
 Innate behavior o Reflexes o Instincts o (not learned)
Innate behavior o Reflexes o Instincts o (not learned)
 Biological Key of paired statements used to identify organisms.
Biological Key of paired statements used to identify organisms.
 Linneaus o Genus & species names o Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus and species
Linneaus o Genus & species names o Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus and species
 Virus reproduce o A virus is made of only DNA and protein o Protein sticks to a cell, DNA enters the cell. o DNA tells the cell to make new viruses o Cell lyses (bursts)
Virus reproduce o A virus is made of only DNA and protein o Protein sticks to a cell, DNA enters the cell. o DNA tells the cell to make new viruses o Cell lyses (bursts)
 Bacteria o Decomposers o PROKARYOTIC o Cell wall made of peptidoglycan
Bacteria o Decomposers o PROKARYOTIC o Cell wall made of peptidoglycan
 FUNGI o Decomposer o Eukaryotic o Cell wall made of chitin
FUNGI o Decomposer o Eukaryotic o Cell wall made of chitin
 PLANT o Eukaryotic o Multicellular autotroph o Cell walls made of cellulose
PLANT o Eukaryotic o Multicellular autotroph o Cell walls made of cellulose
 Plants o o o Photosynthesis in leaf and stem Transpiration (water loss) Phototropism Gravitropism Thigmotropism
Plants o o o Photosynthesis in leaf and stem Transpiration (water loss) Phototropism Gravitropism Thigmotropism
 Plants o o Can be vascular or nonvascular Reproduce with spore or seed Seeds in cone or flower Flowers monocot or dicot
Plants o o Can be vascular or nonvascular Reproduce with spore or seed Seeds in cone or flower Flowers monocot or dicot
 Animals o Multicellular heterotroph o NO cell walls
Animals o Multicellular heterotroph o NO cell walls
 Exponential growth o o o o o 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 512
Exponential growth o o o o o 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 512
 Evolution Change in allele frequency in a population
Evolution Change in allele frequency in a population
 Lamarck: WRONG! o o Animals face a need to change Animal changes Passes change to offspring “Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics”
Lamarck: WRONG! o o Animals face a need to change Animal changes Passes change to offspring “Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics”
 Hardy-Weinberg o o o Five ways populations can change: Migration (gene flow) Mutation/meiosis/crossing over Mate selection (non-random) Natural selection Genetic drift
Hardy-Weinberg o o o Five ways populations can change: Migration (gene flow) Mutation/meiosis/crossing over Mate selection (non-random) Natural selection Genetic drift
 Genetic equilibrium o NO change in allele frequency over time.
Genetic equilibrium o NO change in allele frequency over time.
 Types of Natural selection o Stabilizing Selection
Types of Natural selection o Stabilizing Selection
 Types of Natural selection o Directional Selection
Types of Natural selection o Directional Selection
 Types of Natural selection o Disruptive (Divergent) Selection
Types of Natural selection o Disruptive (Divergent) Selection
 How do new species form? o Step 1: Variation exists in a population o Step 2: Part of the population is ISOLATED o Step 3: The two groups do not likely have the same mutations over time o Step 4: Put the two groups together and they can no longer interbreed.
How do new species form? o Step 1: Variation exists in a population o Step 2: Part of the population is ISOLATED o Step 3: The two groups do not likely have the same mutations over time o Step 4: Put the two groups together and they can no longer interbreed.
 Define species o A group of critters that look alike and can interbreed in nature to produce fertile offspring.
Define species o A group of critters that look alike and can interbreed in nature to produce fertile offspring.
 Methods of Reproductive Isolation o Geographic (Allopatric) o Behavioral (Sympatric)
Methods of Reproductive Isolation o Geographic (Allopatric) o Behavioral (Sympatric)
 Adaptive Radiation o LOTS of new species forming if lots of isolating environments are found.
Adaptive Radiation o LOTS of new species forming if lots of isolating environments are found.
 Homologous structures o Similar structures indicate genetic relationships
Homologous structures o Similar structures indicate genetic relationships
 Coevolution o Evolution of two species that live together
Coevolution o Evolution of two species that live together
 Convergent Evolution o Unrelated organisms look alike. Why? o Example: Shark and Dolphin
Convergent Evolution o Unrelated organisms look alike. Why? o Example: Shark and Dolphin
 Gradualism and Punctuated Equilibrium o Sometimes evolution seems to proceed slowly (gradualism) o Sometimes evolution proceeds in fast jumps (punctuated equilibrium)
Gradualism and Punctuated Equilibrium o Sometimes evolution seems to proceed slowly (gradualism) o Sometimes evolution proceeds in fast jumps (punctuated equilibrium)
 Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance o How do bacteria become resistant to penicillin?
Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance o How do bacteria become resistant to penicillin?
 Mitochondria and Bacteria o Mutualism o Make ATP
Mitochondria and Bacteria o Mutualism o Make ATP


