52ee0f4da4f69ca97f52132afdddf113.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Schedule Development Using Microsoft Project Jeff Oltmann President Synergy Professional Services www. spspro. com Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Schedule Development Using Microsoft Project Jeff Oltmann President Synergy Professional Services www. spspro. com Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Why Care About Schedule Development and Control? v A good schedule helps project planning. . . – Assess confidence in hitting key dates (or not) – Find clues to risks or potential problems – Determine project robustness v And execution – See early warning of upcoming trouble – Assess flexibility to fix problems v Good software helps – Easier to create and revise large schedules – Reduces errors (calculate a 100 node network by hand!) – Allows fast evaluation of many alternative scenarios – Provides a tracking framework Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Why Care About Schedule Development and Control? v A good schedule helps project planning. . . – Assess confidence in hitting key dates (or not) – Find clues to risks or potential problems – Determine project robustness v And execution – See early warning of upcoming trouble – Assess flexibility to fix problems v Good software helps – Easier to create and revise large schedules – Reduces errors (calculate a 100 node network by hand!) – Allows fast evaluation of many alternative scenarios – Provides a tracking framework Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Why Care. . . v But software in the wrong hands is a dangerous weapon. . . – “Many software programs that do exist suggest planning a project in ways that do not conform to proper project management methods - eg first make a list of tasks and then assign them to calendar dates and the project plan is finished. ” - Mulcahy, PMP Exam Prep p. 97, 2002 – Accelerates mistakes v YOU must control the software by understanding scheduling theory and processes Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Why Care. . . v But software in the wrong hands is a dangerous weapon. . . – “Many software programs that do exist suggest planning a project in ways that do not conform to proper project management methods - eg first make a list of tasks and then assign them to calendar dates and the project plan is finished. ” - Mulcahy, PMP Exam Prep p. 97, 2002 – Accelerates mistakes v YOU must control the software by understanding scheduling theory and processes Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Case Study Approach v Schedule development for Project Fuzzy. Wave – Fictional project to upgrade a microwave with fuzzy logic – Use Microsoft Project to apply theory to Fuzzy. Wave u But for safety we will remain in control at all times v Examples comply with PMBOK 2000 (IEEE std) v How rigorous should you be? Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Case Study Approach v Schedule development for Project Fuzzy. Wave – Fictional project to upgrade a microwave with fuzzy logic – Use Microsoft Project to apply theory to Fuzzy. Wave u But for safety we will remain in control at all times v Examples comply with PMBOK 2000 (IEEE std) v How rigorous should you be? Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Project Fuzzy. Wave Charter v Management objectives for Fuzzy. Wave – Update existing microwave with fuzzy logic controller and sensors – Imposed milestones: u Start no earlier than January 2, 2004 u Power on first prototype within 10 weeks of start u GA before July 1, 2004 – Resource Constraints: u 1 senior engineer and 2 junior engineers for duration u Up to 3 staff months from external electronics designer u Marketing and manufacturing each contribute 25% FTE – Must use company’s standard development lifecycle Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Project Fuzzy. Wave Charter v Management objectives for Fuzzy. Wave – Update existing microwave with fuzzy logic controller and sensors – Imposed milestones: u Start no earlier than January 2, 2004 u Power on first prototype within 10 weeks of start u GA before July 1, 2004 – Resource Constraints: u 1 senior engineer and 2 junior engineers for duration u Up to 3 staff months from external electronics designer u Marketing and manufacturing each contribute 25% FTE – Must use company’s standard development lifecycle Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
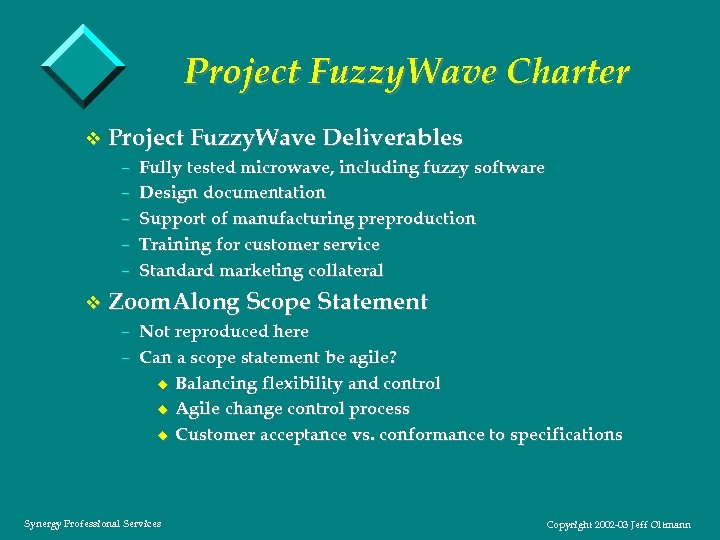 Project Fuzzy. Wave Charter v Project Fuzzy. Wave Deliverables – Fully tested microwave, including fuzzy software – Design documentation – Support of manufacturing preproduction – Training for customer service – Standard marketing collateral v Zoom. Along Scope Statement – Not reproduced here – Can a scope statement be agile? u Balancing flexibility and control u Agile change control process u Customer acceptance vs. conformance to specifications Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Project Fuzzy. Wave Charter v Project Fuzzy. Wave Deliverables – Fully tested microwave, including fuzzy software – Design documentation – Support of manufacturing preproduction – Training for customer service – Standard marketing collateral v Zoom. Along Scope Statement – Not reproduced here – Can a scope statement be agile? u Balancing flexibility and control u Agile change control process u Customer acceptance vs. conformance to specifications Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Congratulations - You Got the Job! v The boss wants to know the ship date already – Stop! Don’t write that task list yet! v Value of creating a work breakdown structure – Forces definition of “what’s in and what’s out” – Identifies redundancies and gaps – Promotes communication and buy in with team and stakeholders – Solid basis for time and cost estimation processes – Valuable in practice, though hard to do in class v A good WBS. . . – Is a hierarchical decomposition of the work, not a flat task list – Identifies ALL work to be performed by the project – Is created with the help of the team – Lowest level tasks have meaningful deliverables that can be estimated and tracked Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Congratulations - You Got the Job! v The boss wants to know the ship date already – Stop! Don’t write that task list yet! v Value of creating a work breakdown structure – Forces definition of “what’s in and what’s out” – Identifies redundancies and gaps – Promotes communication and buy in with team and stakeholders – Solid basis for time and cost estimation processes – Valuable in practice, though hard to do in class v A good WBS. . . – Is a hierarchical decomposition of the work, not a flat task list – Identifies ALL work to be performed by the project – Is created with the help of the team – Lowest level tasks have meaningful deliverables that can be estimated and tracked Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
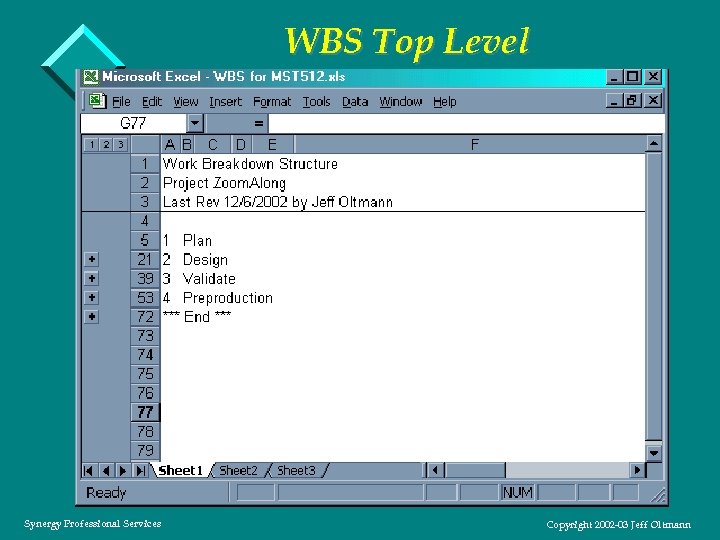 WBS Top Level Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
WBS Top Level Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
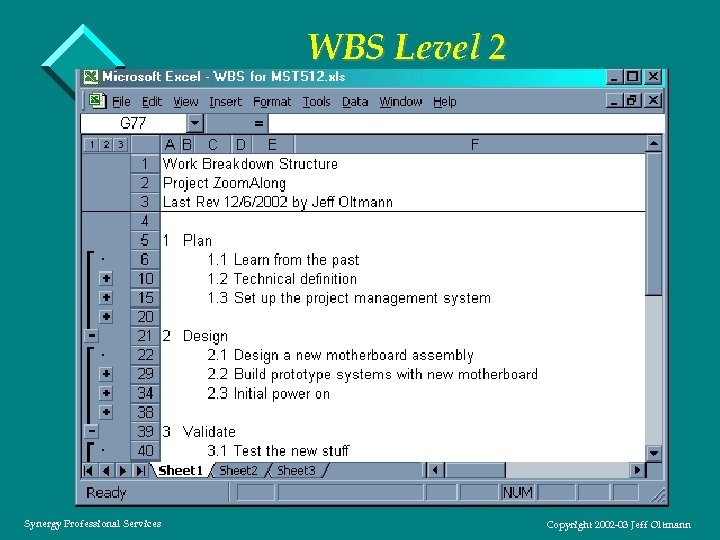 WBS Level 2 Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
WBS Level 2 Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
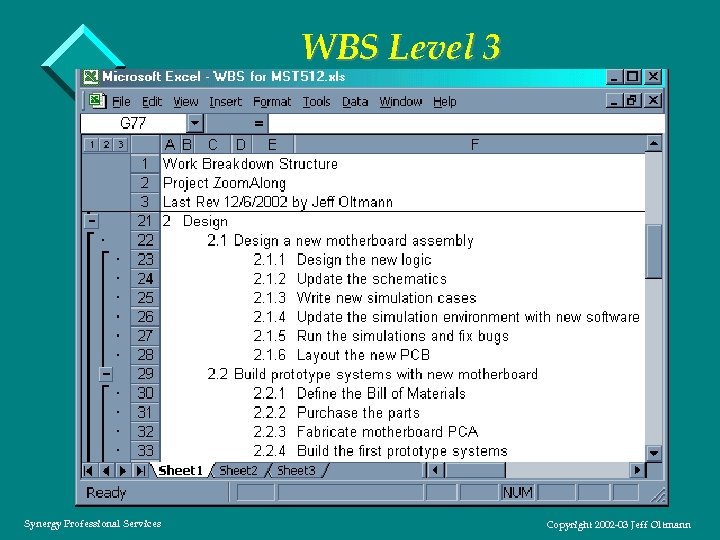 WBS Level 3 Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
WBS Level 3 Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Demo 1 WBS and Activity List v Demonstrate – Import of WBS – Example activity list u How to estimate roughly how many tasks should be on the list u Estimate durations u Note: task durations should be no more than 2 weeks Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Demo 1 WBS and Activity List v Demonstrate – Import of WBS – Example activity list u How to estimate roughly how many tasks should be on the list u Estimate durations u Note: task durations should be no more than 2 weeks Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Network (Precedence) Diagrams v Now can we assign dates and be done? v Activity on node (AON or PDM) diagrams – Nodes (boxes) represent activities – Arrows represent dependencies – Most common (used by Microsoft Project) v Activity on arrow (AOA) diagrams – Arrows represent activities – Nodes represent dependencies – Dummy arrows may be needed to show some relationships v Network tips – High path convergence indicates high risk – Don’t allow dangling tasks – Networks for real projects may have hundreds of activities Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Network (Precedence) Diagrams v Now can we assign dates and be done? v Activity on node (AON or PDM) diagrams – Nodes (boxes) represent activities – Arrows represent dependencies – Most common (used by Microsoft Project) v Activity on arrow (AOA) diagrams – Arrows represent activities – Nodes represent dependencies – Dummy arrows may be needed to show some relationships v Network tips – High path convergence indicates high risk – Don’t allow dangling tasks – Networks for real projects may have hundreds of activities Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Dependencies v Fast review - types of dependencies – Finish to start (FS) AON and AOA – Start to start (SS) AON only – Finish to finish (FF) AON only – Start to finish (SF) AON only – Lag is a delay imposed on a dependency (eg FF with 7 day lag) v Sources of dependencies – Hard: required by the nature of the work u eg. must build the foundation for a house before walls – Preferential: preferred but possible to change u eg. wiring goes faster if plumbing is completed first – External Tip: reduce confusion by avoiding SS, FF, SF and implicit lag Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Dependencies v Fast review - types of dependencies – Finish to start (FS) AON and AOA – Start to start (SS) AON only – Finish to finish (FF) AON only – Start to finish (SF) AON only – Lag is a delay imposed on a dependency (eg FF with 7 day lag) v Sources of dependencies – Hard: required by the nature of the work u eg. must build the foundation for a house before walls – Preferential: preferred but possible to change u eg. wiring goes faster if plumbing is completed first – External Tip: reduce confusion by avoiding SS, FF, SF and implicit lag Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Demo 2 Task Sequencing v Demonstrate – Adding a task to the network diagram – Sequencing several design tasks in the network diagram – Changing links in network view – Compare Network and GANTT views u advantages and disadvantages of each Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Demo 2 Task Sequencing v Demonstrate – Adding a task to the network diagram – Sequencing several design tasks in the network diagram – Changing links in network view – Compare Network and GANTT views u advantages and disadvantages of each Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Evaluation Methods v Critical Path Method (CPM): u Single duration estimate per task u Calculates path lengths by adding durations u Float shows which tasks have least scheduling flexibility u Easiest, most common, least accurate method v Program Eval and Review Technique (PERT) u Duration estimate is mean of triangular distribution where D = (P + 4 M + O) / 6 u Better than CPM at accounting for uncertainty in estimates v Simulation (eg Monte Carlo) u Simulates effects of many duration scenarios on network u Can account for path convergence Trivia: GERT Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Evaluation Methods v Critical Path Method (CPM): u Single duration estimate per task u Calculates path lengths by adding durations u Float shows which tasks have least scheduling flexibility u Easiest, most common, least accurate method v Program Eval and Review Technique (PERT) u Duration estimate is mean of triangular distribution where D = (P + 4 M + O) / 6 u Better than CPM at accounting for uncertainty in estimates v Simulation (eg Monte Carlo) u Simulates effects of many duration scenarios on network u Can account for path convergence Trivia: GERT Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Key Attributes for CPM v Critical path (CP) – Longest network path and shortest project duration – Shows where to focus attention – Multiple critical paths may indicate higher risk v Start and finish dates – ES and EF: earliest dates that a task can start and finish – LS and LF: latest start and finish dates that don’t delay end date – D = EF - ES + 1 = LF - LS + 1 v Slack (S) or float – Amount of time a task can be delayed without delaying the project finish date (total slack) – S = LF - EF = LS - ES Tip: Slack gives flexibility. Lack of slack indicates risky schedule. Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Key Attributes for CPM v Critical path (CP) – Longest network path and shortest project duration – Shows where to focus attention – Multiple critical paths may indicate higher risk v Start and finish dates – ES and EF: earliest dates that a task can start and finish – LS and LF: latest start and finish dates that don’t delay end date – D = EF - ES + 1 = LF - LS + 1 v Slack (S) or float – Amount of time a task can be delayed without delaying the project finish date (total slack) – S = LF - EF = LS - ES Tip: Slack gives flexibility. Lack of slack indicates risky schedule. Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
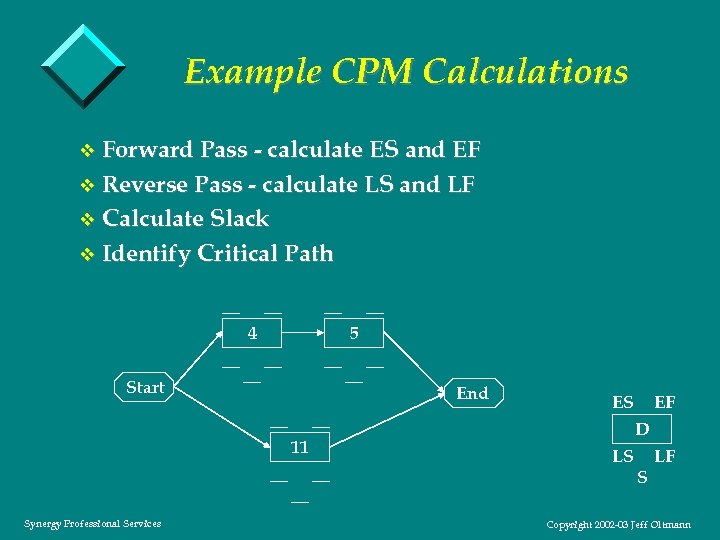 Example CPM Calculations v Forward Pass - calculate ES and EF v Reverse Pass - calculate LS and LF v Calculate Slack v Identify Critical Path __ __ __ 4 __ Start __ 5 __ __ 11 __ Synergy Professional Services __ __ __ End ES EF D LS S LF Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Example CPM Calculations v Forward Pass - calculate ES and EF v Reverse Pass - calculate LS and LF v Calculate Slack v Identify Critical Path __ __ __ 4 __ Start __ 5 __ __ 11 __ Synergy Professional Services __ __ __ End ES EF D LS S LF Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
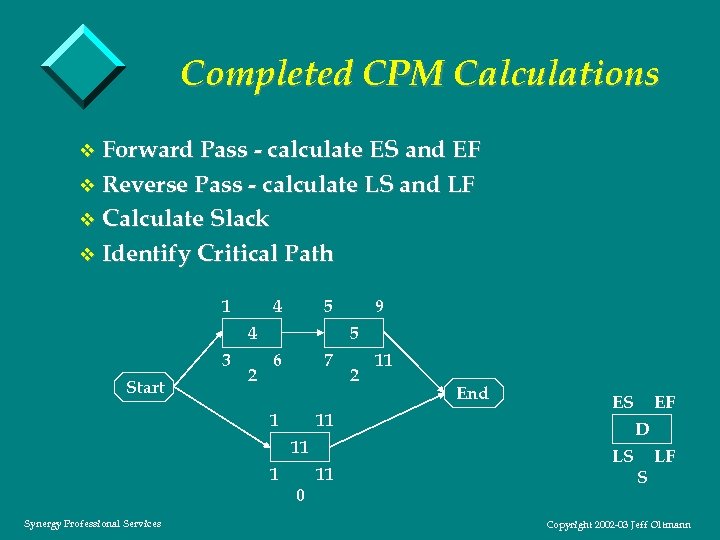 Completed CPM Calculations v Forward Pass - calculate ES and EF v Reverse Pass - calculate LS and LF v Calculate Slack v Identify Critical Path 1 4 5 4 3 Start 2 5 6 7 1 11 11 1 Synergy Professional Services 9 0 11 2 11 End ES EF D LS S LF Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Completed CPM Calculations v Forward Pass - calculate ES and EF v Reverse Pass - calculate LS and LF v Calculate Slack v Identify Critical Path 1 4 5 4 3 Start 2 5 6 7 1 11 11 1 Synergy Professional Services 9 0 11 2 11 End ES EF D LS S LF Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Demo 3 Network Calculation v Demonstrate – Task list with duration and resource assignments – Calculated network diagram u Point out critical path and CPM attributes – GANTT view – Resource histogram u Did we meet resource limits from the charter? Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Demo 3 Network Calculation v Demonstrate – Task list with duration and resource assignments – Calculated network diagram u Point out critical path and CPM attributes – GANTT view – Resource histogram u Did we meet resource limits from the charter? Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Fixing a Schedule Problem v End date does not meet charter requirement v Fast tracking parallelizes CP tasks – Usually increases risk – Can increase cost v Crashing adds resources to CP tasks – Identify lowest cost places to add resources – Shift resources from tasks that have slack or use outside resources v Must have network diagram – Critical path – Locations of slack time – Dependencies Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Fixing a Schedule Problem v End date does not meet charter requirement v Fast tracking parallelizes CP tasks – Usually increases risk – Can increase cost v Crashing adds resources to CP tasks – Identify lowest cost places to add resources – Shift resources from tasks that have slack or use outside resources v Must have network diagram – Critical path – Locations of slack time – Dependencies Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Demo 4 Schedule Pull In v Demonstrate – Shorten critical path by fast tracking – Shorten critical path by crashing Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Demo 4 Schedule Pull In v Demonstrate – Shorten critical path by fast tracking – Shorten critical path by crashing Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Schedule Tracking and Control v Don’t let your schedule get dusty! v Regularly gather status and compare to baseline – 50/50 method – Enforce regular team reporting habits v Look for warning signs – Watch critical path AND areas with little slack – Beware of tasks with long durations – Watch for overdue starts and finishes – Check on work that should be starting or finishing soon v Take corrective action – Use the network diagram to explore options – Monitor effectiveness of corrective action – Update baseline, including Microsoft Project files v Communicate! Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Schedule Tracking and Control v Don’t let your schedule get dusty! v Regularly gather status and compare to baseline – 50/50 method – Enforce regular team reporting habits v Look for warning signs – Watch critical path AND areas with little slack – Beware of tasks with long durations – Watch for overdue starts and finishes – Check on work that should be starting or finishing soon v Take corrective action – Use the network diagram to explore options – Monitor effectiveness of corrective action – Update baseline, including Microsoft Project files v Communicate! Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Demo 5 Reports v Fast forward to 1/20/03 v Demonstrate – Marking items partly and fully complete in network view – Tracking GANTT for team – Milestone report for management (Reports / Overview / Milestone) – Critical tasks (Reports / Overview / Critical) – Should have started (Reports / Current / Should / 1 -20 -03) Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Demo 5 Reports v Fast forward to 1/20/03 v Demonstrate – Marking items partly and fully complete in network view – Tracking GANTT for team – Milestone report for management (Reports / Overview / Milestone) – Critical tasks (Reports / Overview / Critical) – Should have started (Reports / Current / Should / 1 -20 -03) Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Advanced Aspects v Handling multiple projects – shared resources in MS Project Server – tradeoffs vs multiple Project files v Tracking earned value v Completion buffer (Goldratt’s Theory of Constraints) v Groupware and integration – – – email integration with other programs (databases, Excel) plug ins v Comparison to other scheduling programs Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Advanced Aspects v Handling multiple projects – shared resources in MS Project Server – tradeoffs vs multiple Project files v Tracking earned value v Completion buffer (Goldratt’s Theory of Constraints) v Groupware and integration – – – email integration with other programs (databases, Excel) plug ins v Comparison to other scheduling programs Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Conclusion v Good scheduling skills are a crucial tool in your project management toolbox v Software will amplify your schedule development capabilities for better or worse v Call me with your questions or thoughts Jeff Oltmann Synergy Professional Services (503) 644 -6433 jeff@spspro. com Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Conclusion v Good scheduling skills are a crucial tool in your project management toolbox v Software will amplify your schedule development capabilities for better or worse v Call me with your questions or thoughts Jeff Oltmann Synergy Professional Services (503) 644 -6433 jeff@spspro. com Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
 Questions and Answers Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann
Questions and Answers Synergy Professional Services Copyright 2002 -03 Jeff Oltmann


