 Schedule April 22, 24: Particle tracking and Profile Models (PS 6). Work on Part III of Final Project. April 24: 30 min in-class, closed book quiz. April 28, May 1: Group presentations of final project. May 6, May 8: Grid design/parameter selection & final thoughts. PS 6 due on May 6.
Schedule April 22, 24: Particle tracking and Profile Models (PS 6). Work on Part III of Final Project. April 24: 30 min in-class, closed book quiz. April 28, May 1: Group presentations of final project. May 6, May 8: Grid design/parameter selection & final thoughts. PS 6 due on May 6.
 Sensitivity analysis is used: • In automated calibration (inverse modeling) (Sensitivity coefficients = sum of squared residuals/ parameter or h/ parameter) • As an uncertainty analysis after calibration
Sensitivity analysis is used: • In automated calibration (inverse modeling) (Sensitivity coefficients = sum of squared residuals/ parameter or h/ parameter) • As an uncertainty analysis after calibration
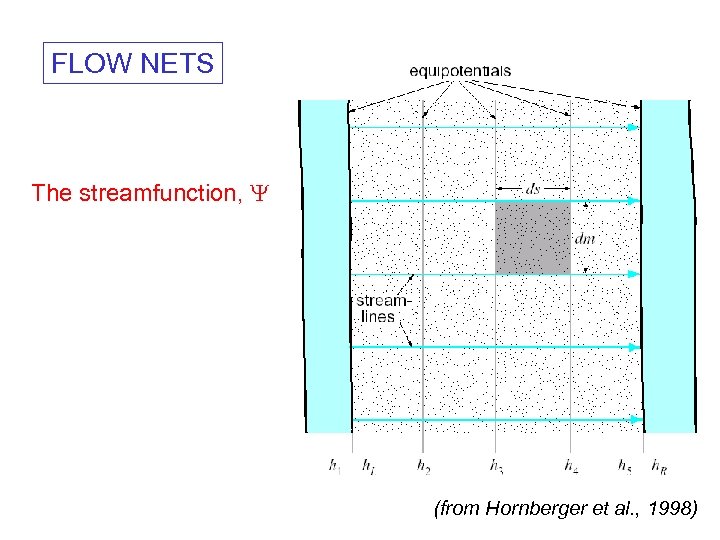 FLOW NETS The streamfunction, (from Hornberger et al. , 1998)
FLOW NETS The streamfunction, (from Hornberger et al. , 1998)
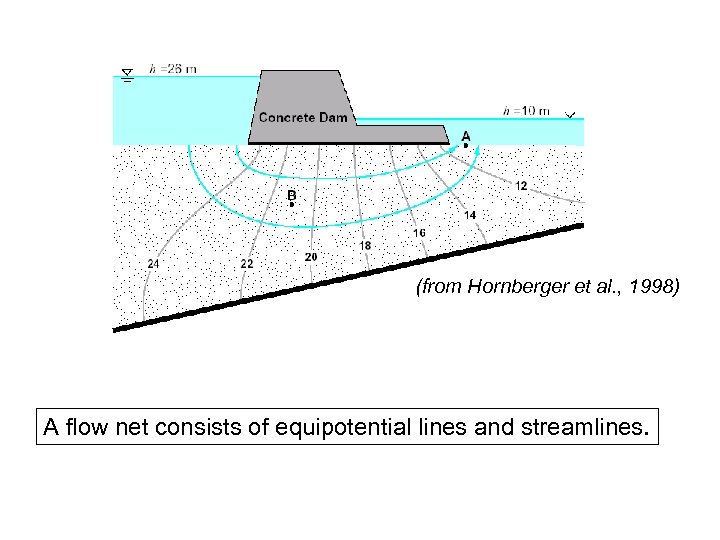 (from Hornberger et al. , 1998) A flow net consists of equipotential lines and streamlines.
(from Hornberger et al. , 1998) A flow net consists of equipotential lines and streamlines.
 Particle Tracking (used to trace flow lines) distance = velocity x time
Particle Tracking (used to trace flow lines) distance = velocity x time
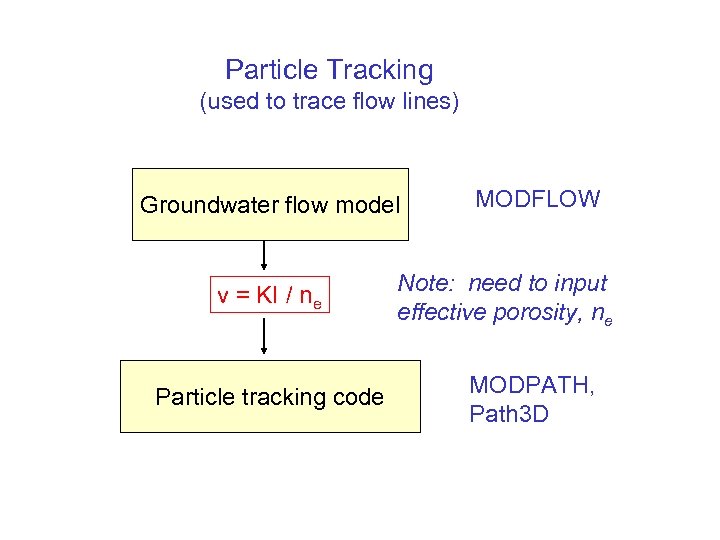 Particle Tracking (used to trace flow lines) Groundwater flow model v = KI / ne Particle tracking code MODFLOW Note: need to input effective porosity, ne MODPATH, Path 3 D
Particle Tracking (used to trace flow lines) Groundwater flow model v = KI / ne Particle tracking code MODFLOW Note: need to input effective porosity, ne MODPATH, Path 3 D
 Particle tracking simulates advection of contaminant “particles”. Transport models (e. g. , MT 3 D) simulate advection, dispersion and chemical reactions. Retardation caused by linear adsorption reactions can be simulated using particle tracking, since the velocity can be adjusted: vc = v/Rd Rd is the retardation coefficient.
Particle tracking simulates advection of contaminant “particles”. Transport models (e. g. , MT 3 D) simulate advection, dispersion and chemical reactions. Retardation caused by linear adsorption reactions can be simulated using particle tracking, since the velocity can be adjusted: vc = v/Rd Rd is the retardation coefficient.
 Steps in Particle Tracking 1. Need to interpolate velocities from nodal point values since particle tracking is done in a continuous coordinate system. 2. Need to track the movement of the particles in the computed velocity field.
Steps in Particle Tracking 1. Need to interpolate velocities from nodal point values since particle tracking is done in a continuous coordinate system. 2. Need to track the movement of the particles in the computed velocity field.
 Interpolation Schemes 1. Linear (MODPATH, Path 3 D) 2. Bilinear 3. Reverse distance (FLOWPATH)
Interpolation Schemes 1. Linear (MODPATH, Path 3 D) 2. Bilinear 3. Reverse distance (FLOWPATH)
 Tracking Schemes Semianalytical (MODPATH) Euler (FLOWPATH) Runge Kutta (Path 3 D) Taylor Series (WHPA)
Tracking Schemes Semianalytical (MODPATH) Euler (FLOWPATH) Runge Kutta (Path 3 D) Taylor Series (WHPA)
 Directions for using Version 3 of MODPATH in GWV 1. In the MODFLOW packages window, set all the unit numbers in the cell by cell flow unit number column to the same value (e. g, 51). 2. In Model>MODPATH>Packages, select Version 3.
Directions for using Version 3 of MODPATH in GWV 1. In the MODFLOW packages window, set all the unit numbers in the cell by cell flow unit number column to the same value (e. g, 51). 2. In Model>MODPATH>Packages, select Version 3.
 Hornberger et al. , 1998. Elements of Physical Hydrology, The Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, 302 p.
Hornberger et al. , 1998. Elements of Physical Hydrology, The Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, 302 p.