2aef1ef93dbf44bbb29b5dcaead1dd41.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 SCATTERED DATA VISUALIZATION Yingcai Xiao
SCATTERED DATA VISUALIZATION Yingcai Xiao
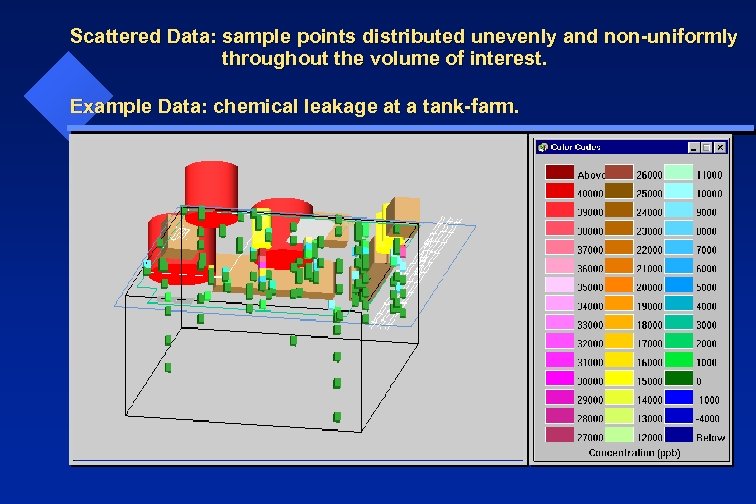 Scattered Data: sample points distributed unevenly and non-uniformly throughout the volume of interest. Example Data: chemical leakage at a tank-farm.
Scattered Data: sample points distributed unevenly and non-uniformly throughout the volume of interest. Example Data: chemical leakage at a tank-farm.
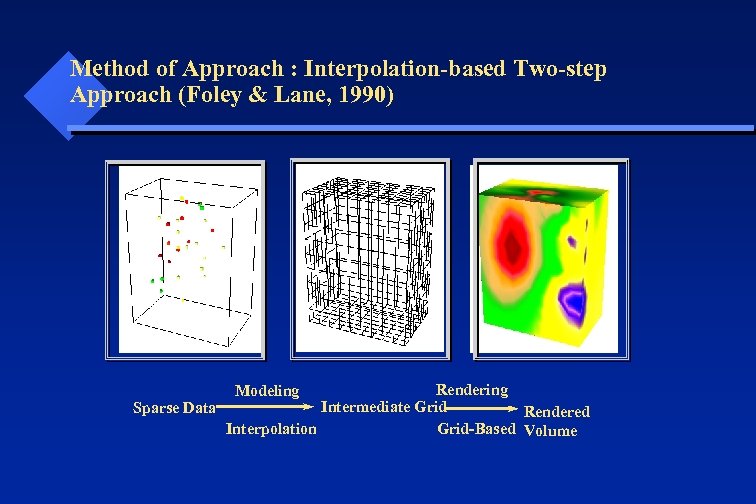 Method of Approach : Interpolation-based Two-step Approach (Foley & Lane, 1990) Rendering Intermediate Grid Sparse Data Rendered Interpolation Grid-Based Volume Modeling
Method of Approach : Interpolation-based Two-step Approach (Foley & Lane, 1990) Rendering Intermediate Grid Sparse Data Rendered Interpolation Grid-Based Volume Modeling
 Interpolation Methods (Nielson, 1993) Global: all sample points are used to interpolated a grid value. Local: only nearby sample points are used to interpolated a grid value. Exact: the interpolation function can exactly reproduce the data values on the sample points. Problems: Xiao etc. 1996
Interpolation Methods (Nielson, 1993) Global: all sample points are used to interpolated a grid value. Local: only nearby sample points are used to interpolated a grid value. Exact: the interpolation function can exactly reproduce the data values on the sample points. Problems: Xiao etc. 1996
 Defining a Global Exact Interpolant (Foley & Lane, 1990; Nielson, 1993) n sample points: (xi, yi, zi, vi) for i = 1, 2, . . n One interpolation function, e. g. , Thin-plate spline, di is the distance between sample point i and the point to be interpolated p(x, y, z). di = ((x-xi)2+(y-yi )2+(z-zi )2)1/2 bi, c 1, c 2, c 3, c 4 are n+4 constants to be solved by enforcing the following conditions: f (xi, yi, zi) = vi for i = 1, 2, . . n
Defining a Global Exact Interpolant (Foley & Lane, 1990; Nielson, 1993) n sample points: (xi, yi, zi, vi) for i = 1, 2, . . n One interpolation function, e. g. , Thin-plate spline, di is the distance between sample point i and the point to be interpolated p(x, y, z). di = ((x-xi)2+(y-yi )2+(z-zi )2)1/2 bi, c 1, c 2, c 3, c 4 are n+4 constants to be solved by enforcing the following conditions: f (xi, yi, zi) = vi for i = 1, 2, . . n
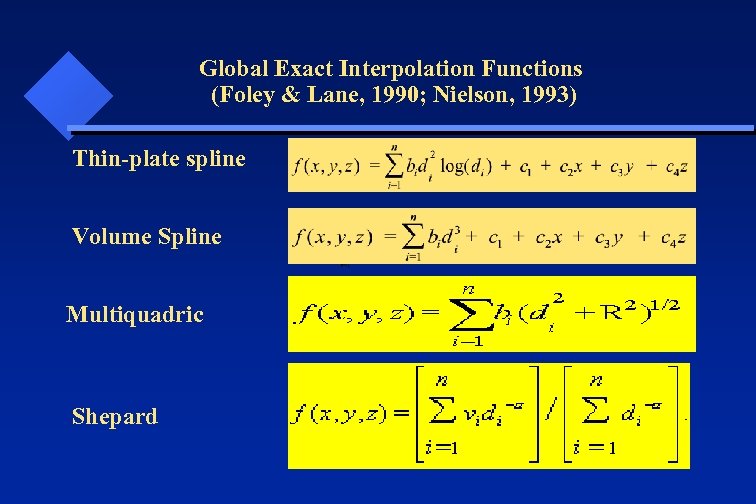 Global Exact Interpolation Functions (Foley & Lane, 1990; Nielson, 1993) Thin-plate spline Volume Spline Multiquadric Shepard
Global Exact Interpolation Functions (Foley & Lane, 1990; Nielson, 1993) Thin-plate spline Volume Spline Multiquadric Shepard
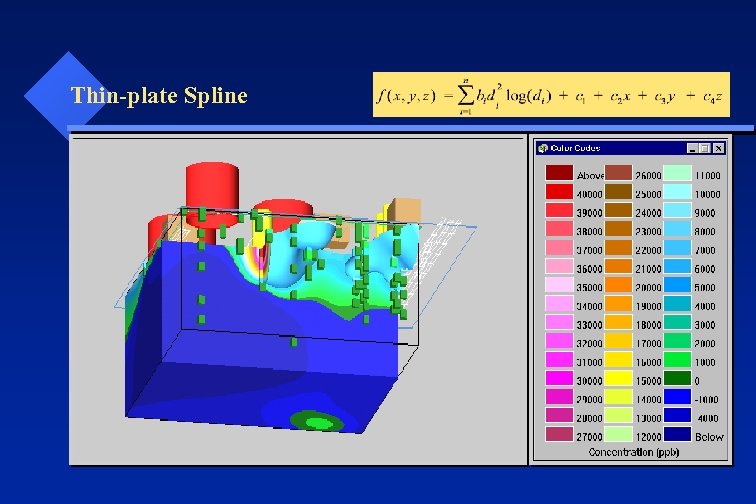 Thin-plate Spline
Thin-plate Spline
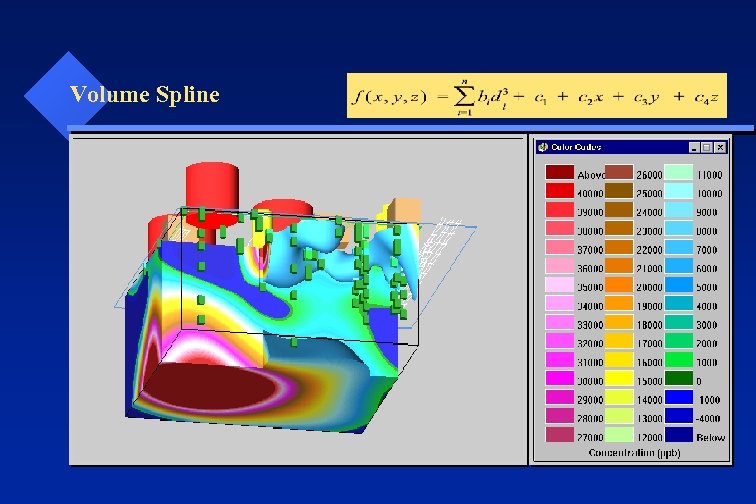 Volume Spline
Volume Spline
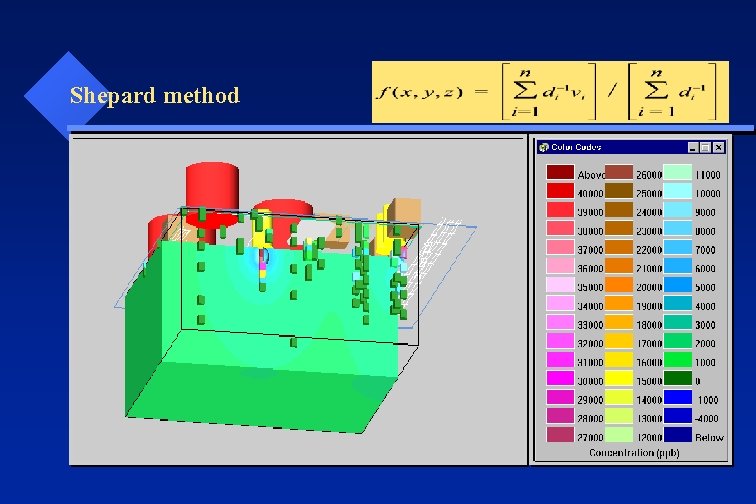 Shepard method
Shepard method
 Deficiencies of the Interpolation-based Two-step Approach (Xiao et. Al. , 1996) l Misinterpretation (Negative Concentration) l Ambiguity in Selecting Interpolation Methods l Inconsistent Interpolations in Modeling and Rendering l Visualizing Secondary Data Instead of the Original Data l No Error Estimation l Unable to Add Known Information l Not Efficient
Deficiencies of the Interpolation-based Two-step Approach (Xiao et. Al. , 1996) l Misinterpretation (Negative Concentration) l Ambiguity in Selecting Interpolation Methods l Inconsistent Interpolations in Modeling and Rendering l Visualizing Secondary Data Instead of the Original Data l No Error Estimation l Unable to Add Known Information l Not Efficient
 Three Dilemmas and Three Constraints (Xiao & Woodbury, 1999) l Zero-value dilemma l Negative-value dilemma l Correctness dilemma l. Point Constraint l Value Constraint l Local Constraint
Three Dilemmas and Three Constraints (Xiao & Woodbury, 1999) l Zero-value dilemma l Negative-value dilemma l Correctness dilemma l. Point Constraint l Value Constraint l Local Constraint
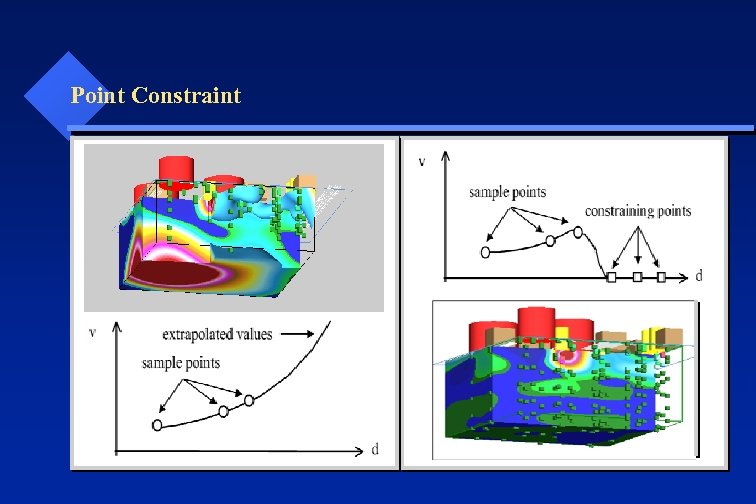 Point Constraint
Point Constraint
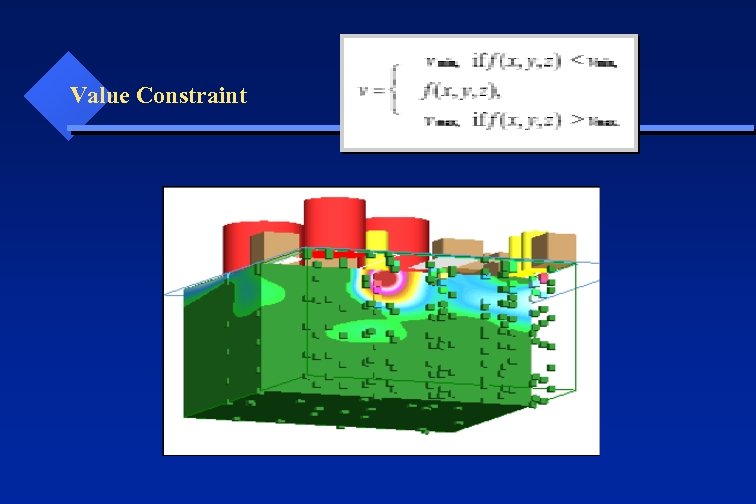 Value Constraint
Value Constraint
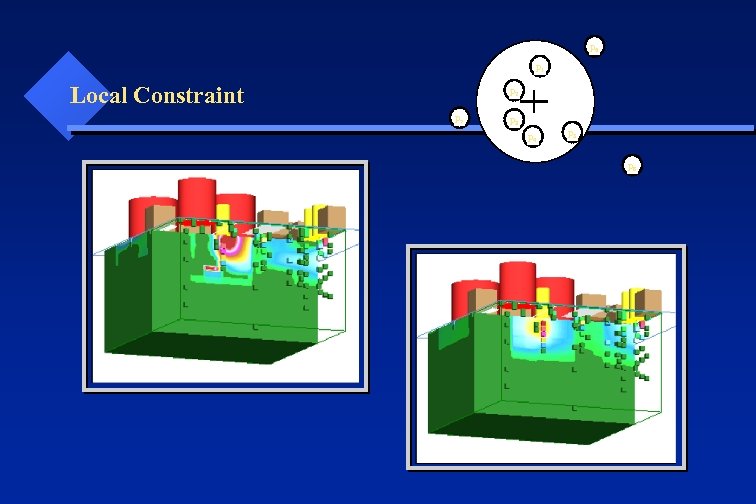 p 6 p 1 Local Constraint p 2 p 7 p 3 p 4 p 5 p 8
p 6 p 1 Local Constraint p 2 p 7 p 3 p 4 p 5 p 8
 Conclusions • Two-step approach faces three dilemmas. • Constrained interpolations can alleviate the dilemmas. • The problems are far from being solved. Data modeling is import to data visualization, just as geometry modeling is important to geometry visualization.
Conclusions • Two-step approach faces three dilemmas. • Constrained interpolations can alleviate the dilemmas. • The problems are far from being solved. Data modeling is import to data visualization, just as geometry modeling is important to geometry visualization.
 Conclusions To visualize scattered data, we are challenged to find modeling techniques that l preserve input data values; l produce meaningful output values; l provide error estimations; l accept additional constraints; l reduce the requirement on the sampling intensity.
Conclusions To visualize scattered data, we are challenged to find modeling techniques that l preserve input data values; l produce meaningful output values; l provide error estimations; l accept additional constraints; l reduce the requirement on the sampling intensity.
 A FINITE ELEMENT BASED APPROACH XIAO & ZIEBARTH, 2000
A FINITE ELEMENT BASED APPROACH XIAO & ZIEBARTH, 2000
 The Finite Element Based Approach (1) Tessellation (2) Computation (3) Rendering
The Finite Element Based Approach (1) Tessellation (2) Computation (3) Rendering
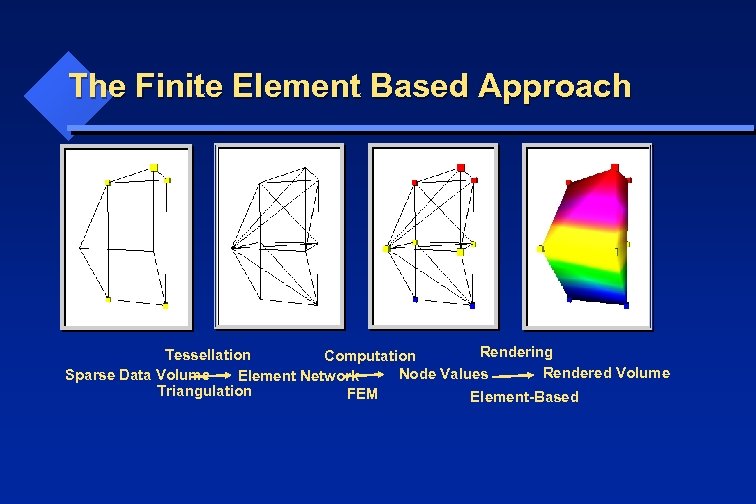 The Finite Element Based Approach Rendering Tessellation Computation Rendered Volume Node Values Sparse Data Volume Element Network Triangulation FEM Element-Based
The Finite Element Based Approach Rendering Tessellation Computation Rendered Volume Node Values Sparse Data Volume Element Network Triangulation FEM Element-Based
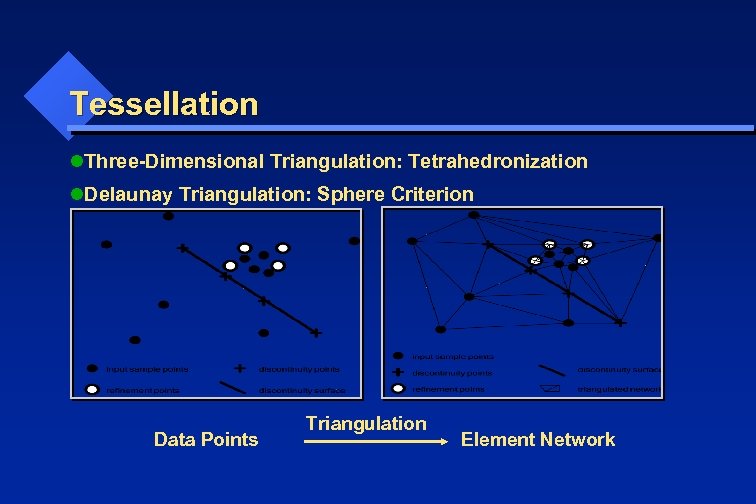 Tessellation l. Three-Dimensional Triangulation: Tetrahedronization l. Delaunay Triangulation: Sphere Criterion Data Points Triangulation Element Network
Tessellation l. Three-Dimensional Triangulation: Tetrahedronization l. Delaunay Triangulation: Sphere Criterion Data Points Triangulation Element Network
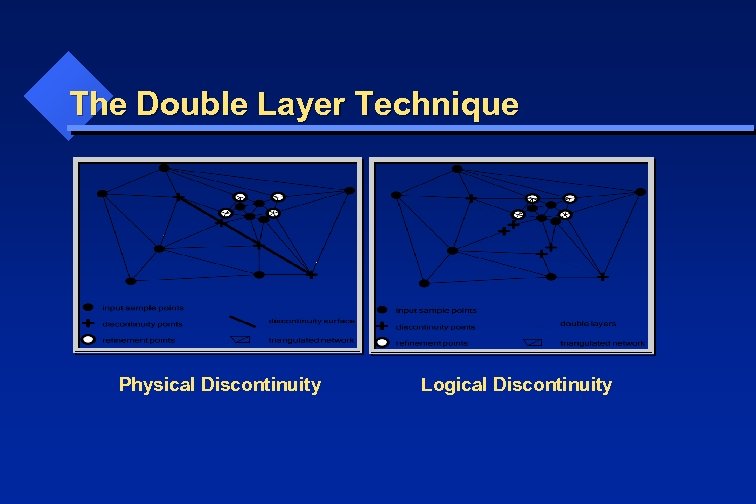 The Double Layer Technique Physical Discontinuity Logical Discontinuity
The Double Layer Technique Physical Discontinuity Logical Discontinuity
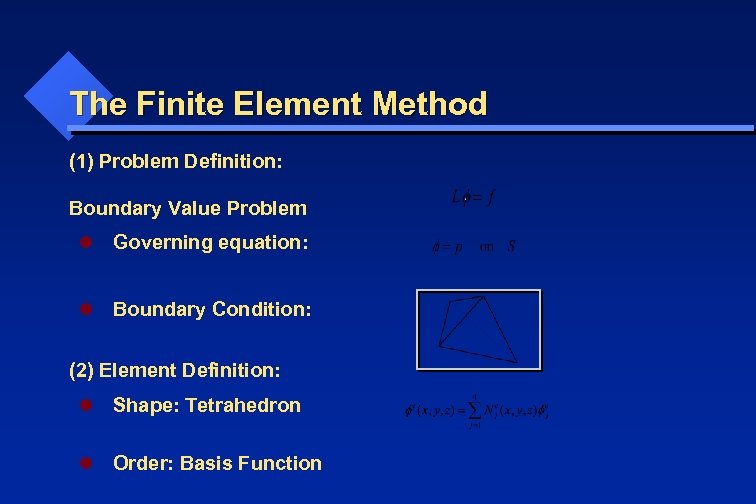 The Finite Element Method (1) Problem Definition: Boundary Value Problem l Governing equation: l Boundary Condition: (2) Element Definition: l Shape: Tetrahedron l Order: Basis Function
The Finite Element Method (1) Problem Definition: Boundary Value Problem l Governing equation: l Boundary Condition: (2) Element Definition: l Shape: Tetrahedron l Order: Basis Function
 The Finite Element Method (3) System Formulation l Ritz Method l Galerkin's method (4) Sparse Sample Data (5) System Solution l Gaussian Elimination l Householder's Method
The Finite Element Method (3) System Formulation l Ritz Method l Galerkin's method (4) Sparse Sample Data (5) System Solution l Gaussian Elimination l Householder's Method
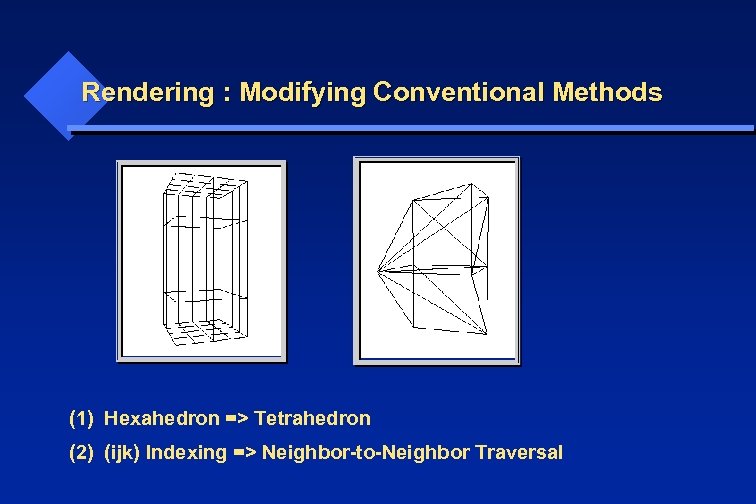 Rendering : Modifying Conventional Methods (1) Hexahedron => Tetrahedron (2) (ijk) Indexing => Neighbor-to-Neighbor Traversal
Rendering : Modifying Conventional Methods (1) Hexahedron => Tetrahedron (2) (ijk) Indexing => Neighbor-to-Neighbor Traversal
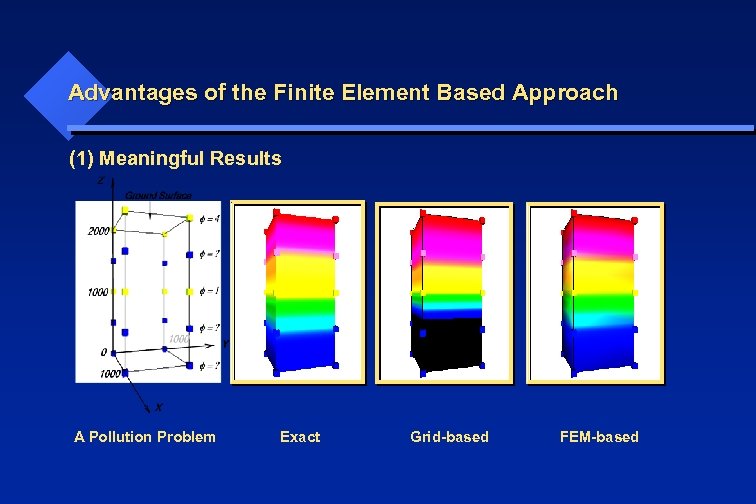 Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (1) Meaningful Results A Pollution Problem Exact Grid-based FEM-based
Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (1) Meaningful Results A Pollution Problem Exact Grid-based FEM-based
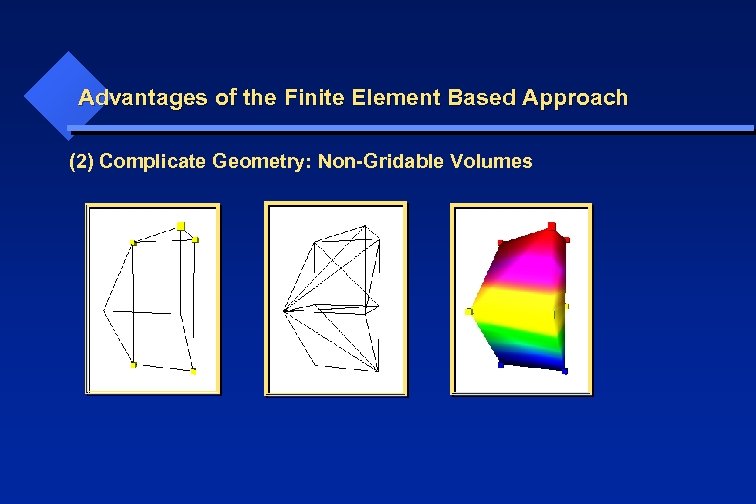 Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (2) Complicate Geometry: Non-Gridable Volumes
Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (2) Complicate Geometry: Non-Gridable Volumes
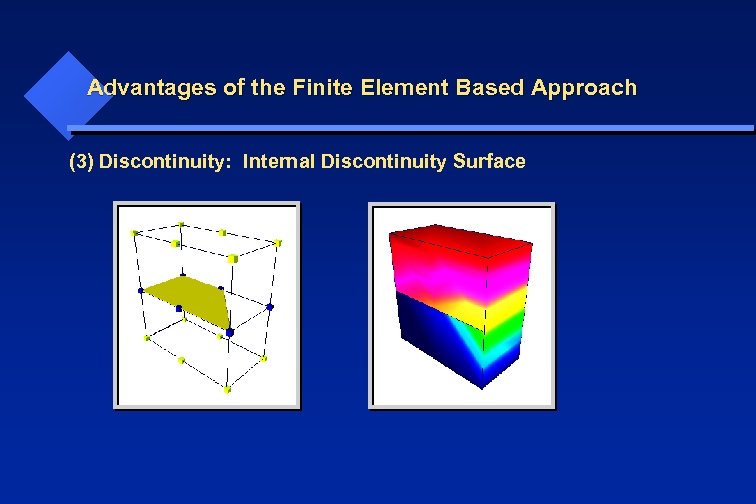 Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (3) Discontinuity: Internal Discontinuity Surface
Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (3) Discontinuity: Internal Discontinuity Surface
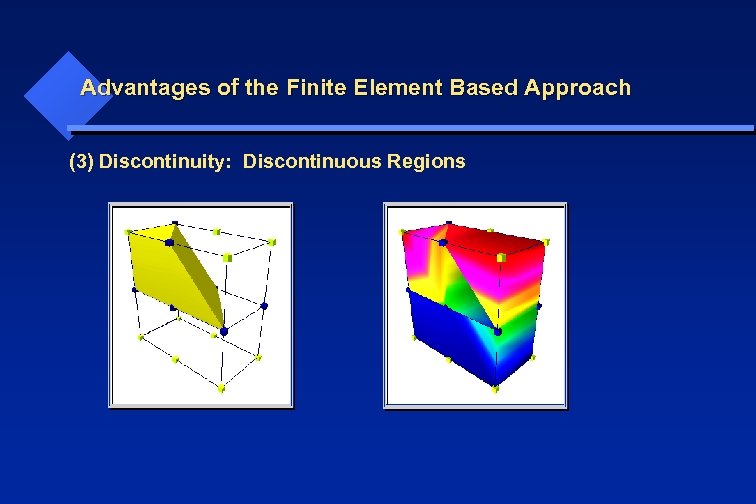 Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (3) Discontinuity: Discontinuous Regions
Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (3) Discontinuity: Discontinuous Regions
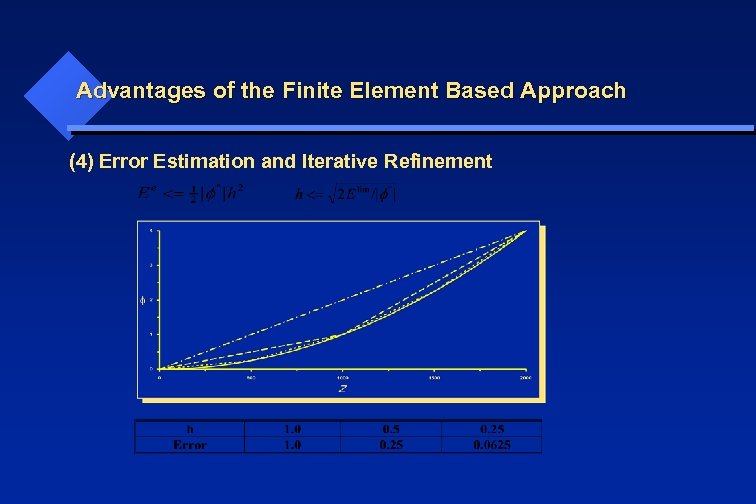 Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (4) Error Estimation and Iterative Refinement
Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (4) Error Estimation and Iterative Refinement
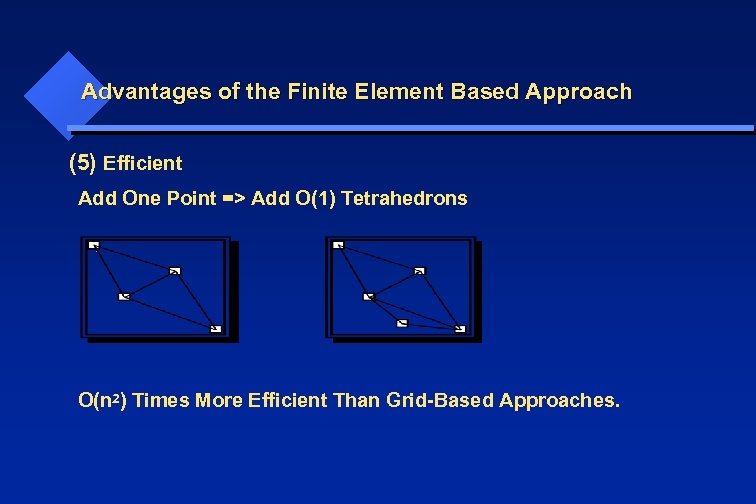 Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (5) Efficient Add One Point => Add O(1) Tetrahedrons O(n 2) Times More Efficient Than Grid-Based Approaches.
Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (5) Efficient Add One Point => Add O(1) Tetrahedrons O(n 2) Times More Efficient Than Grid-Based Approaches.
 Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (6) No Whittaker-Shannon Sampling Rate Interpolation Problem ==> Boundary Value Problem (7) No Ambiguity in Selecting Modeling Methods
Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (6) No Whittaker-Shannon Sampling Rate Interpolation Problem ==> Boundary Value Problem (7) No Ambiguity in Selecting Modeling Methods
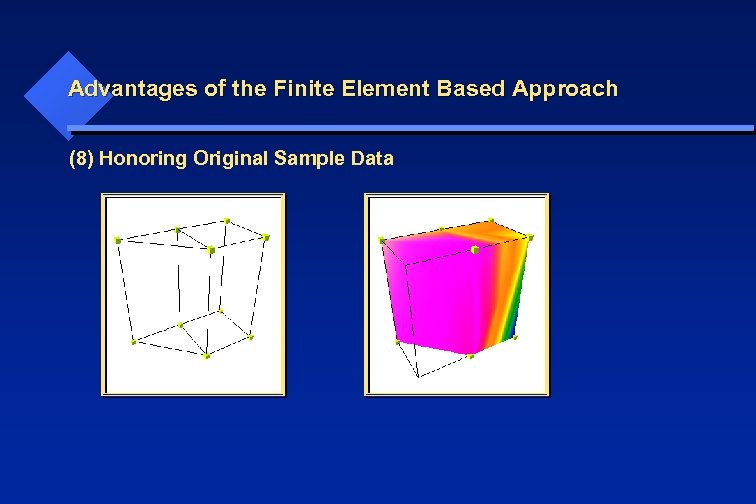 Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (8) Honoring Original Sample Data
Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (8) Honoring Original Sample Data
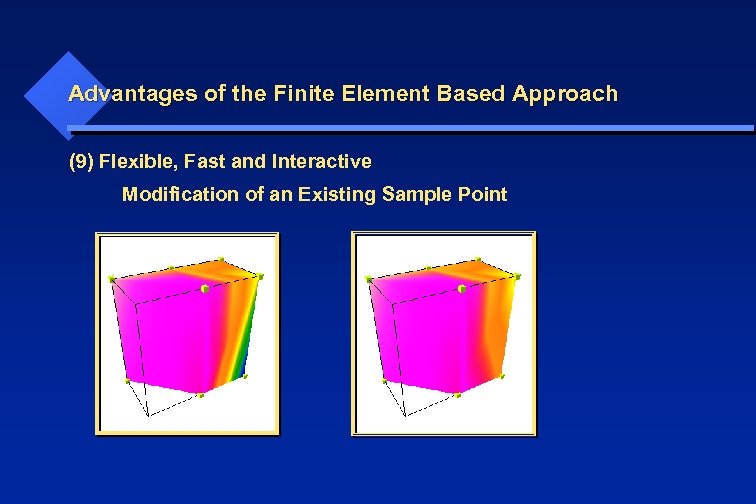 Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (9) Flexible, Fast and Interactive Modification of an Existing Sample Point
Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (9) Flexible, Fast and Interactive Modification of an Existing Sample Point
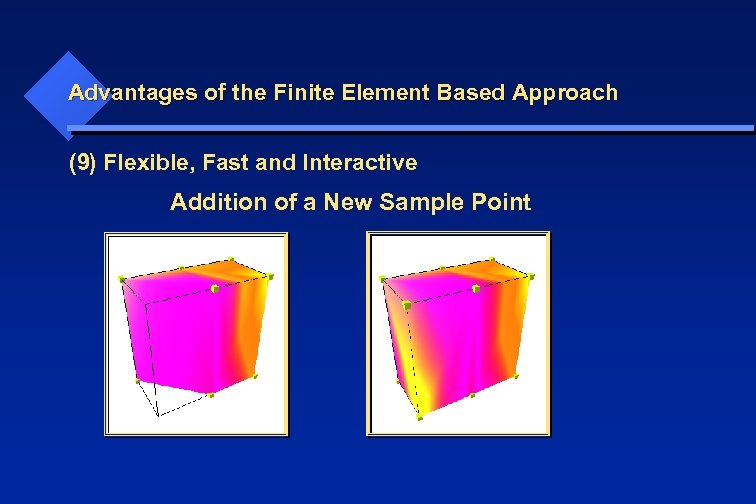 Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (9) Flexible, Fast and Interactive Addition of a New Sample Point
Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (9) Flexible, Fast and Interactive Addition of a New Sample Point
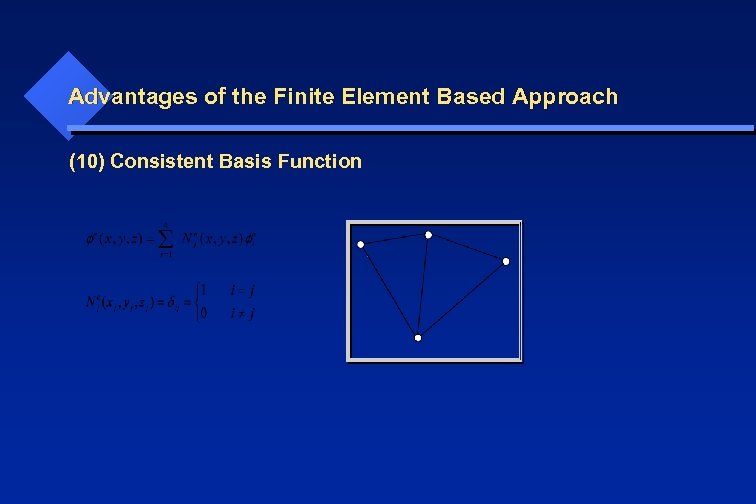 Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (10) Consistent Basis Function
Advantages of the Finite Element Based Approach (10) Consistent Basis Function
 Future Work (1) Other Types of Problems: Initial Value Problems (2) Other Types of Elements: Polyhedrons (3) Higher-Order Elements: P-Version (4) Automated Tessellation: Densification (5) Thinning (6) Curved Discontinuity Surfaces (7) Delaunay Triangulation near Discontinuity Surfaces (8) Higher-Order Rendering Method
Future Work (1) Other Types of Problems: Initial Value Problems (2) Other Types of Elements: Polyhedrons (3) Higher-Order Elements: P-Version (4) Automated Tessellation: Densification (5) Thinning (6) Curved Discontinuity Surfaces (7) Delaunay Triangulation near Discontinuity Surfaces (8) Higher-Order Rendering Method
 Summary The finite element based approach is a new framework for scattered data visualization. Many challenging problems can be solved easily within this framework. This approach revealed a promising direction and brought many interesting research topics into the field of sparse data volume visualization.
Summary The finite element based approach is a new framework for scattered data visualization. Many challenging problems can be solved easily within this framework. This approach revealed a promising direction and brought many interesting research topics into the field of sparse data volume visualization.


