831a85b6a55b9584be5d2ff8af8c4421.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Scaling-up to MPA networks in the Coral Triangle: The Way Forward Stuart Green, Alan White, Stacey Kilarski, Anna Meneses, Patrick Christie, Giselle Samonte-Tan, Leah Karrer, Helen Fox, Stuart Campbell, John Claussen and Barbara Best
Scaling-up to MPA networks in the Coral Triangle: The Way Forward Stuart Green, Alan White, Stacey Kilarski, Anna Meneses, Patrick Christie, Giselle Samonte-Tan, Leah Karrer, Helen Fox, Stuart Campbell, John Claussen and Barbara Best
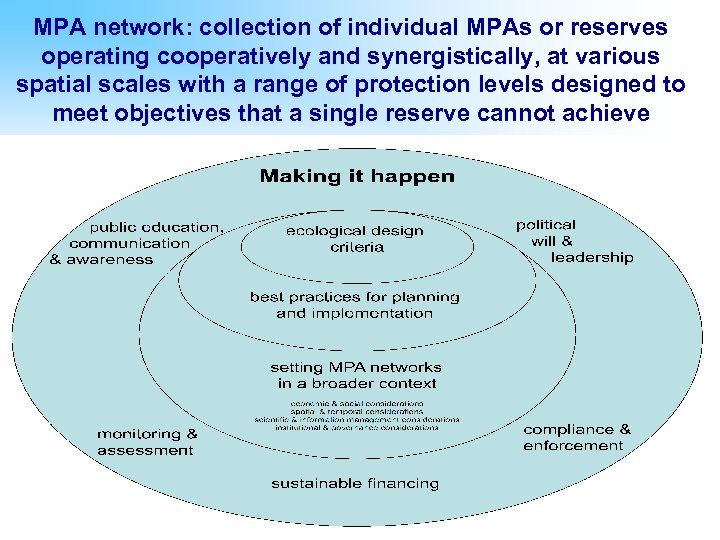 MPA network: collection of individual MPAs or reserves operating cooperatively and synergistically, at various spatial scales with a range of protection levels designed to meet objectives that a single reserve cannot achieve
MPA network: collection of individual MPAs or reserves operating cooperatively and synergistically, at various spatial scales with a range of protection levels designed to meet objectives that a single reserve cannot achieve
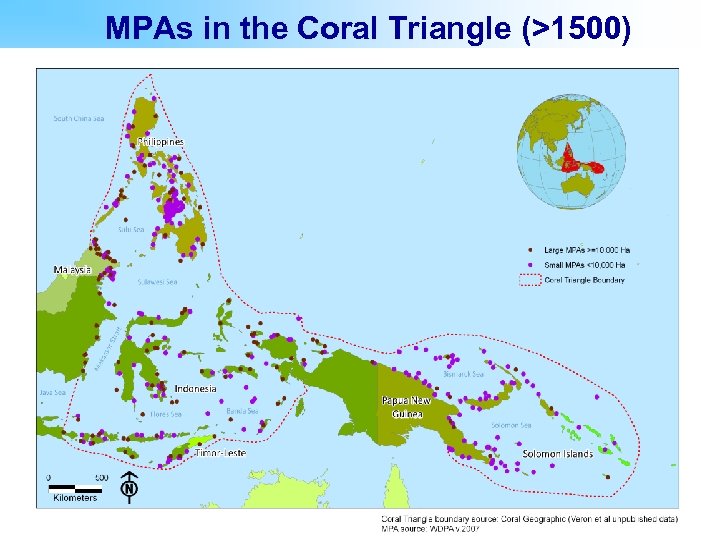 MPAs in the Coral Triangle (>1500)
MPAs in the Coral Triangle (>1500)
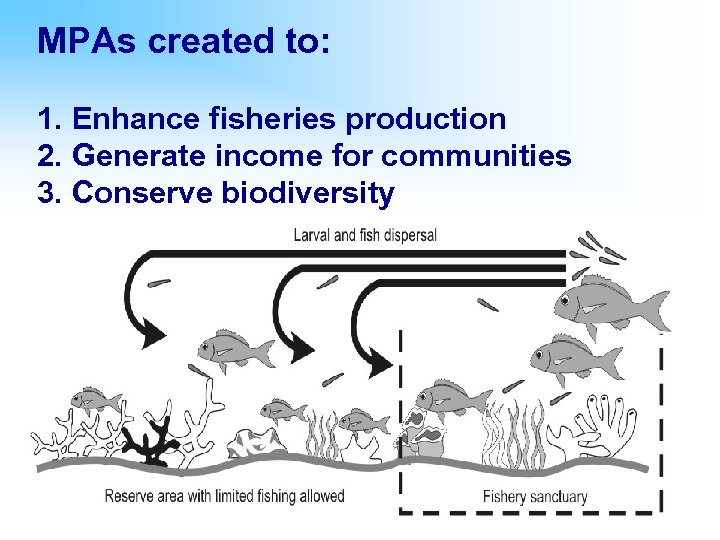 MPAs created to: 1. Enhance fisheries production 2. Generate income for communities 3. Conserve biodiversity
MPAs created to: 1. Enhance fisheries production 2. Generate income for communities 3. Conserve biodiversity
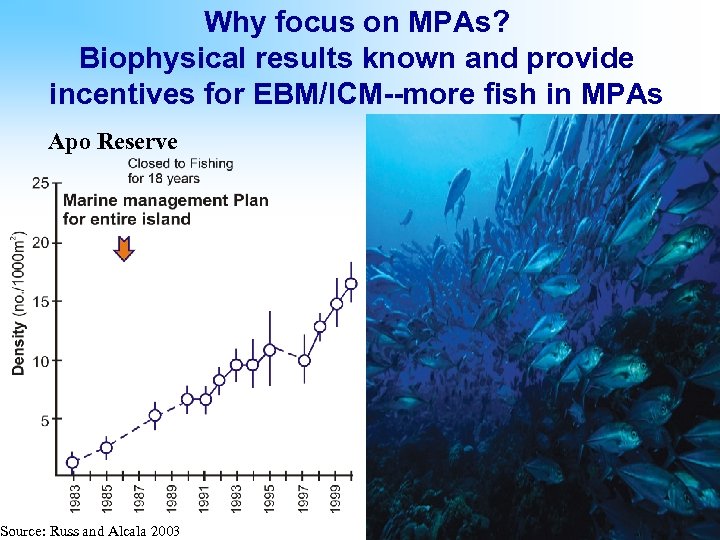 Why focus on MPAs? Biophysical results known and provide incentives for EBM/ICM--more fish in MPAs Apo Reserve Source: Russ and Alcala 2003
Why focus on MPAs? Biophysical results known and provide incentives for EBM/ICM--more fish in MPAs Apo Reserve Source: Russ and Alcala 2003

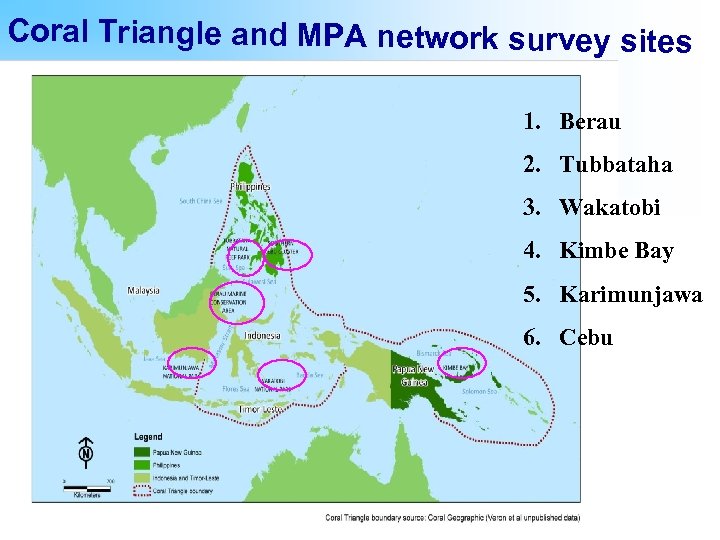 Coral Triangle and MPA network survey sites 1. Berau 2. Tubbataha 3. Wakatobi 4. Kimbe Bay 5. Karimunjawa 6. Cebu
Coral Triangle and MPA network survey sites 1. Berau 2. Tubbataha 3. Wakatobi 4. Kimbe Bay 5. Karimunjawa 6. Cebu
 Municipal jurisdictions with an evolving MPA network in Central Visayas
Municipal jurisdictions with an evolving MPA network in Central Visayas
 Coral triangle sites and meetings
Coral triangle sites and meetings
 Learning partnership among TNC, WWF, CI, WCS and USAID- started in 2004 with two overarching questions… 1. “How can we effectively design, implement, and manage representative and resilient MPA networks in tropical marine ecosystems? ” 2. “What ecological, socioeconomic, and institutional principles, if met, will ensure that MPA networks provide enduring and effective conservation for marine diversity? ”
Learning partnership among TNC, WWF, CI, WCS and USAID- started in 2004 with two overarching questions… 1. “How can we effectively design, implement, and manage representative and resilient MPA networks in tropical marine ecosystems? ” 2. “What ecological, socioeconomic, and institutional principles, if met, will ensure that MPA networks provide enduring and effective conservation for marine diversity? ”
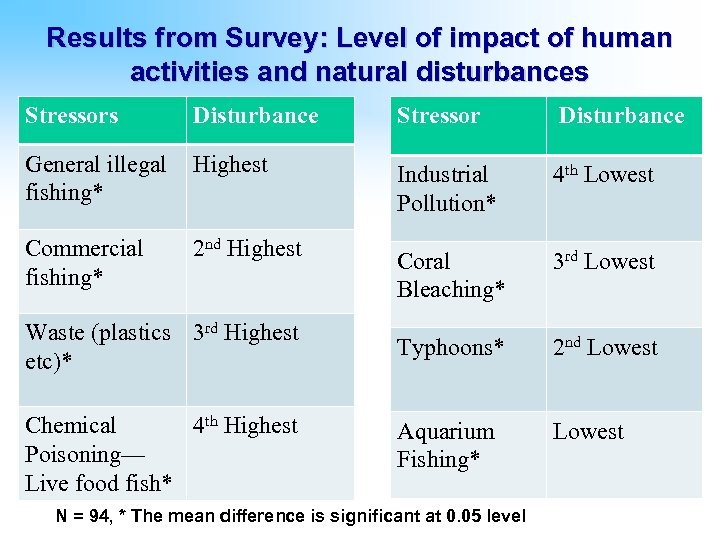 Results from Survey: Level of impact of human activities and natural disturbances Stressors Disturbance Stressor Disturbance General illegal fishing* Highest Industrial Pollution* 4 th Lowest Commercial fishing* 2 nd Highest Coral Bleaching* 3 rd Lowest Waste (plastics 3 rd Highest etc)* Typhoons* 2 nd Lowest Chemical 4 th Highest Poisoning— Live food fish* Aquarium Fishing* Lowest N = 94, * The mean difference is significant at 0. 05 level
Results from Survey: Level of impact of human activities and natural disturbances Stressors Disturbance Stressor Disturbance General illegal fishing* Highest Industrial Pollution* 4 th Lowest Commercial fishing* 2 nd Highest Coral Bleaching* 3 rd Lowest Waste (plastics 3 rd Highest etc)* Typhoons* 2 nd Lowest Chemical 4 th Highest Poisoning— Live food fish* Aquarium Fishing* Lowest N = 94, * The mean difference is significant at 0. 05 level
 Planning and Design Phase of MPA Development “It is quite difficult to put places under certain management regimes as you think best, when you need to consider social / economic considerations of people living in the area” - Main assisting NGO
Planning and Design Phase of MPA Development “It is quite difficult to put places under certain management regimes as you think best, when you need to consider social / economic considerations of people living in the area” - Main assisting NGO
 Dependent and independent variables (strongest predictors) Dependent variable Perceived increased fish catch Independent variables Correlation Coefficient (r) Sustainable financing for management 1 . 412(**) Clarity of MPA network rules . 382(**) Enforcement by community enforcers . 487(**) Local skills development . 375(**) Multi-stakeholder planning workshops . 333(**) Communication activities (e. g. , film showings, photo exhibits). 327(**) Involvement in management of traditional leaders / elders . 313(*) Involvement in management of local elected politicians . 310(*) Stakeholders’ participation in activities . 290(*) Involvement in management of police and law enforcement agencies . 284(*) Trainings in MPA management and leadership development . 282(*) Participatory biophysical assessments . 278(*) ** Correlation is significant at the. 01 level * Correlation is significant at the. 05 level 13
Dependent and independent variables (strongest predictors) Dependent variable Perceived increased fish catch Independent variables Correlation Coefficient (r) Sustainable financing for management 1 . 412(**) Clarity of MPA network rules . 382(**) Enforcement by community enforcers . 487(**) Local skills development . 375(**) Multi-stakeholder planning workshops . 333(**) Communication activities (e. g. , film showings, photo exhibits). 327(**) Involvement in management of traditional leaders / elders . 313(*) Involvement in management of local elected politicians . 310(*) Stakeholders’ participation in activities . 290(*) Involvement in management of police and law enforcement agencies . 284(*) Trainings in MPA management and leadership development . 282(*) Participatory biophysical assessments . 278(*) ** Correlation is significant at the. 01 level * Correlation is significant at the. 05 level 13
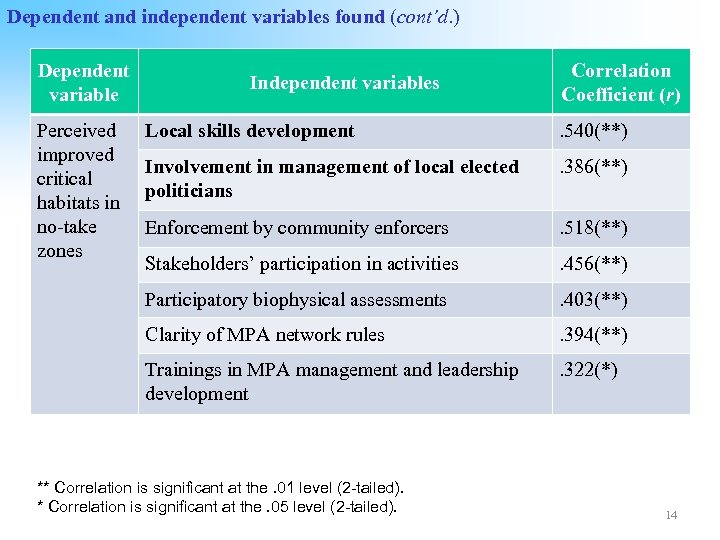 Dependent and independent variables found (cont’d. ) Dependent variable Perceived improved critical habitats in no-take zones Independent variables Correlation Coefficient (r) Local skills development . 540(**) Involvement in management of local elected politicians . 386(**) Enforcement by community enforcers . 518(**) Stakeholders’ participation in activities . 456(**) Participatory biophysical assessments . 403(**) Clarity of MPA network rules . 394(**) Trainings in MPA management and leadership development . 322(*) ** Correlation is significant at the. 01 level (2 -tailed). * Correlation is significant at the. 05 level (2 -tailed). 14
Dependent and independent variables found (cont’d. ) Dependent variable Perceived improved critical habitats in no-take zones Independent variables Correlation Coefficient (r) Local skills development . 540(**) Involvement in management of local elected politicians . 386(**) Enforcement by community enforcers . 518(**) Stakeholders’ participation in activities . 456(**) Participatory biophysical assessments . 403(**) Clarity of MPA network rules . 394(**) Trainings in MPA management and leadership development . 322(*) ** Correlation is significant at the. 01 level (2 -tailed). * Correlation is significant at the. 05 level (2 -tailed). 14
 Results from workshop for 6 sites on ideal vs reality of MPA network implementation--2008 1. Ecology: • How to easily design for resilience to climate change? • How to consider connectivity issues in MPA network design? • Evaluation of ecosystem services beyond fisheries • Lack of effective biophysical monitoring with data management
Results from workshop for 6 sites on ideal vs reality of MPA network implementation--2008 1. Ecology: • How to easily design for resilience to climate change? • How to consider connectivity issues in MPA network design? • Evaluation of ecosystem services beyond fisheries • Lack of effective biophysical monitoring with data management
 …points in MPA workshop 2. Social and Governance: • • Devolution from national to local--governance Need for holistic conflict resolution Increased community engagement and participation More education to raise awareness Simpler regulations better than complex (zoning) Support comprehensive management plans More and better social and learning networks
…points in MPA workshop 2. Social and Governance: • • Devolution from national to local--governance Need for holistic conflict resolution Increased community engagement and participation More education to raise awareness Simpler regulations better than complex (zoning) Support comprehensive management plans More and better social and learning networks
 …points: 3. Finance and economic returns • Value coastal resources and return on investment to support buy-in • Start sustainable financing early • Broad economic development strategies • Financial support for integrated plans • Generate revenues thru MPAs, tours, etc. • Integrate alternative livelihood within ICM
…points: 3. Finance and economic returns • Value coastal resources and return on investment to support buy-in • Start sustainable financing early • Broad economic development strategies • Financial support for integrated plans • Generate revenues thru MPAs, tours, etc. • Integrate alternative livelihood within ICM
 Recurring Themes in the Coral Triangle areas surveyed in 2008 • Opportunities for capacity building of MPA managers & supporting governments and NGOs • Lack of understanding of “network” among practitioners and scientists • Use of known and accepted biophysical and social science lacking in design and implementation across most sites • Need for basic planning and management within most to all MPAs before "networks" will be functional
Recurring Themes in the Coral Triangle areas surveyed in 2008 • Opportunities for capacity building of MPA managers & supporting governments and NGOs • Lack of understanding of “network” among practitioners and scientists • Use of known and accepted biophysical and social science lacking in design and implementation across most sites • Need for basic planning and management within most to all MPAs before "networks" will be functional
 Prerequisites to form MPA networks • Need baseline information in sufficient detail (size, locations, habitat parameters, hydrology) • Must have institution that operates at scale of potential network OR • Institutions must be networked and coordinated • Social networks must be formed • Monitoring capability and data management system capability within institution at scale of management
Prerequisites to form MPA networks • Need baseline information in sufficient detail (size, locations, habitat parameters, hydrology) • Must have institution that operates at scale of potential network OR • Institutions must be networked and coordinated • Social networks must be formed • Monitoring capability and data management system capability within institution at scale of management
 Prerequisites to form MPA networks… • Clarification on benefits of MPA networks for whom? • MPA networks are beneficial in the eyes of scientists and those well versed in marine conservation, but… • Must get local stakeholders on board with knowledge and motivation to support and implement
Prerequisites to form MPA networks… • Clarification on benefits of MPA networks for whom? • MPA networks are beneficial in the eyes of scientists and those well versed in marine conservation, but… • Must get local stakeholders on board with knowledge and motivation to support and implement
 Although large investments exist in MPAs/networks—management effectiveness is poor and apparent results from large areas under legal protection are not indicative of the actual level of management and conservation being achieved 1970 s 1980 s Command control 1990 s 2000’s Co-management Environmental Governance
Although large investments exist in MPAs/networks—management effectiveness is poor and apparent results from large areas under legal protection are not indicative of the actual level of management and conservation being achieved 1970 s 1980 s Command control 1990 s 2000’s Co-management Environmental Governance
 MPAs cannot succeed as islands in a complex coastal environment—they must be part of integrated management systems with interventions tailored to local needs and conditions
MPAs cannot succeed as islands in a complex coastal environment—they must be part of integrated management systems with interventions tailored to local needs and conditions

 More on lessons from MPAs and MPA networks to build coastal and biodiversity resilience in the Coral Triangle… www. oneocean. org www. tnc. org www. wwf. org www. ci. org www. wcs. org
More on lessons from MPAs and MPA networks to build coastal and biodiversity resilience in the Coral Triangle… www. oneocean. org www. tnc. org www. wwf. org www. ci. org www. wcs. org


